Muscular Histology
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Year 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
3 types of muscle fibre
skeletal, cardiac, smooth
fascicle
a bundle of muscle fibres surrounded by a layer of connective tissue called the perimysium
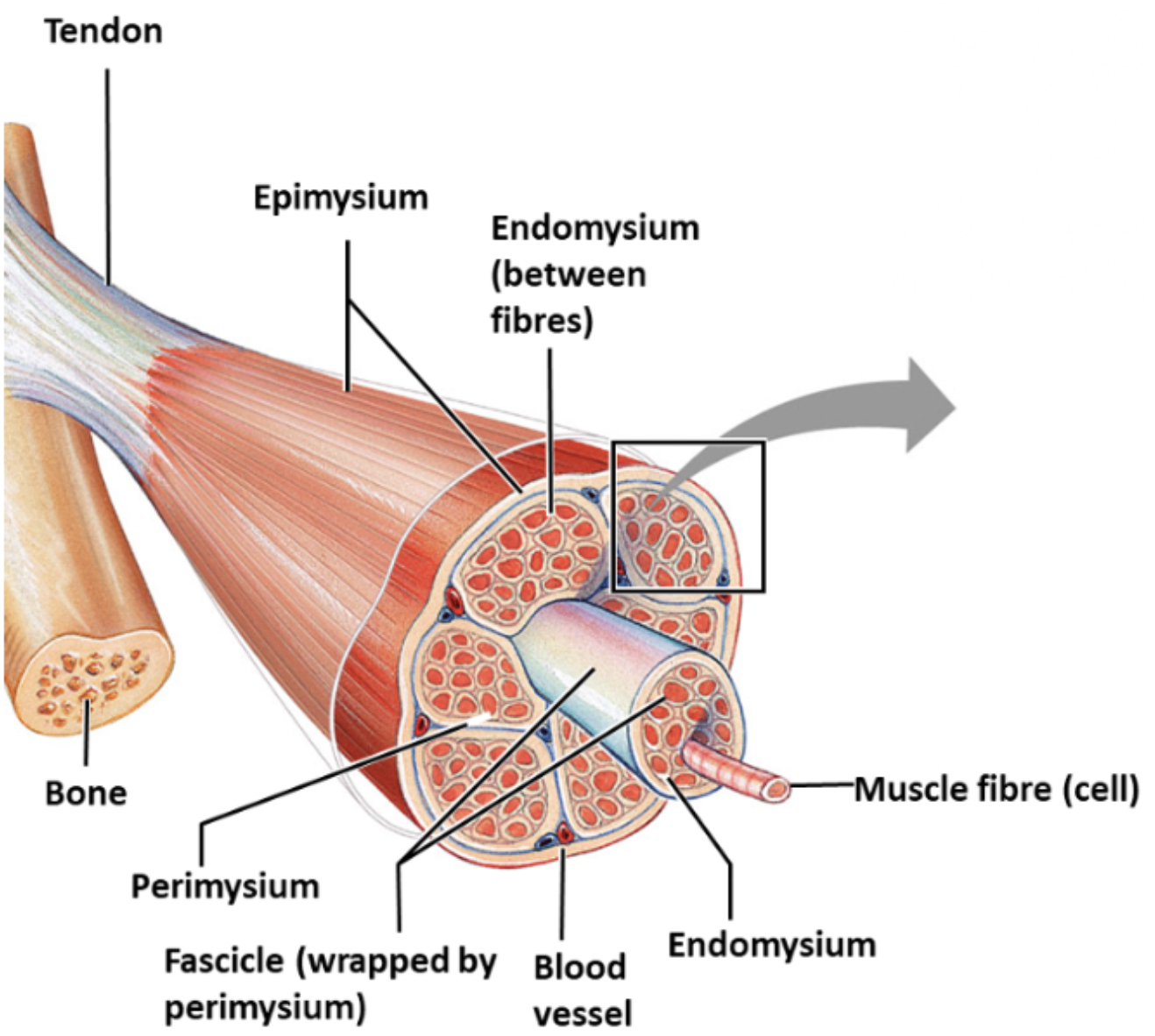
perimysium
protective connective tissue surrounding fascicles found in muscle tissue, carries blood vessels and nerves
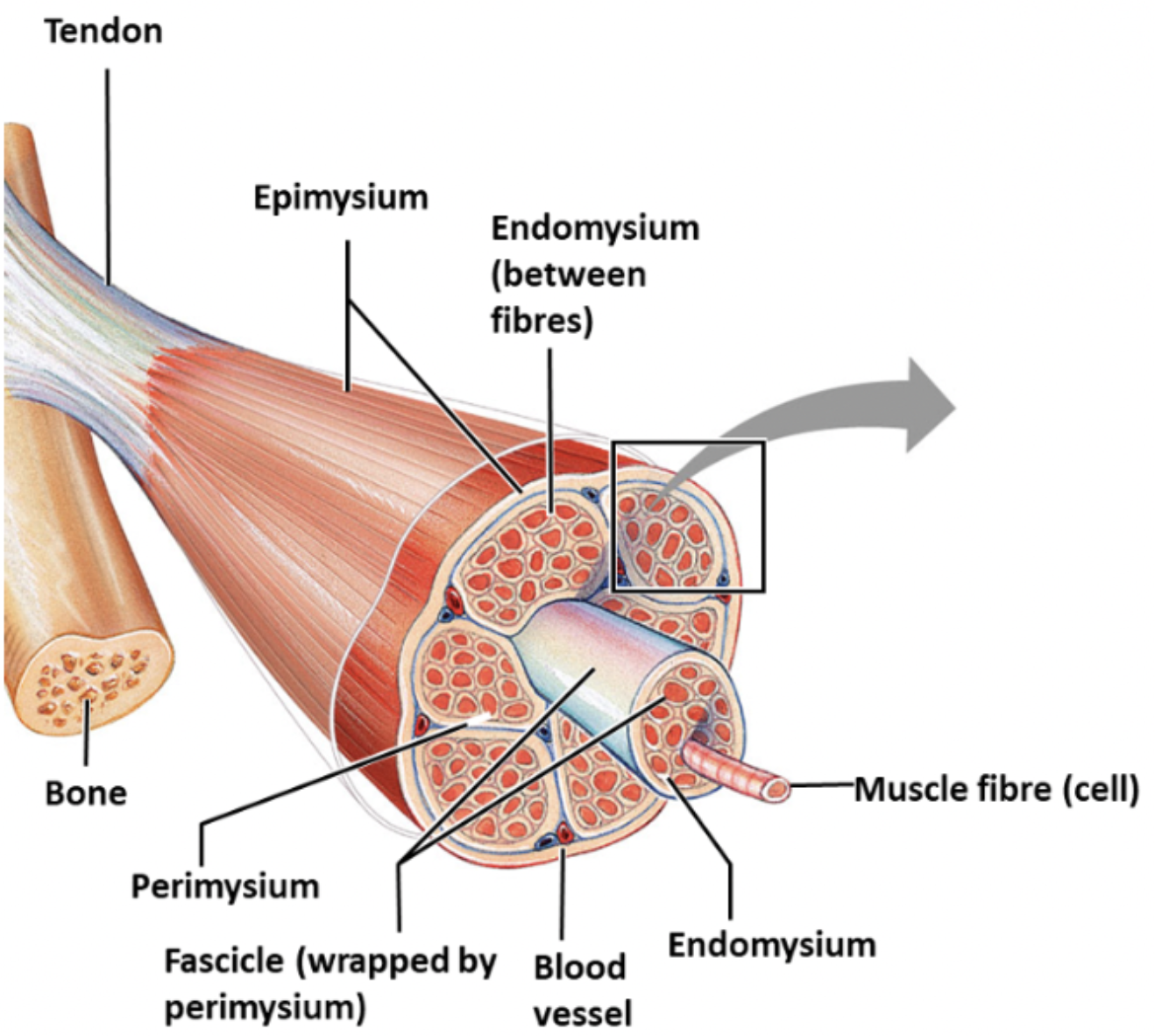
epimysium
dense, irregular connective tissue surrounding the entire muscle
features to look at when observing muscle under the microscope
striated?
single cell or multinucleate syncytium?
peripheral or central nucleus?
special types of cell junction?
voluntary or involuntary?
features of skeletal muscle
voluntary, striated, multiple peripheral nuclei, long cylindrical fibres, no intercalated discs, attached to bones, limited regeneration, rapid forceful contractions, fatigue possible
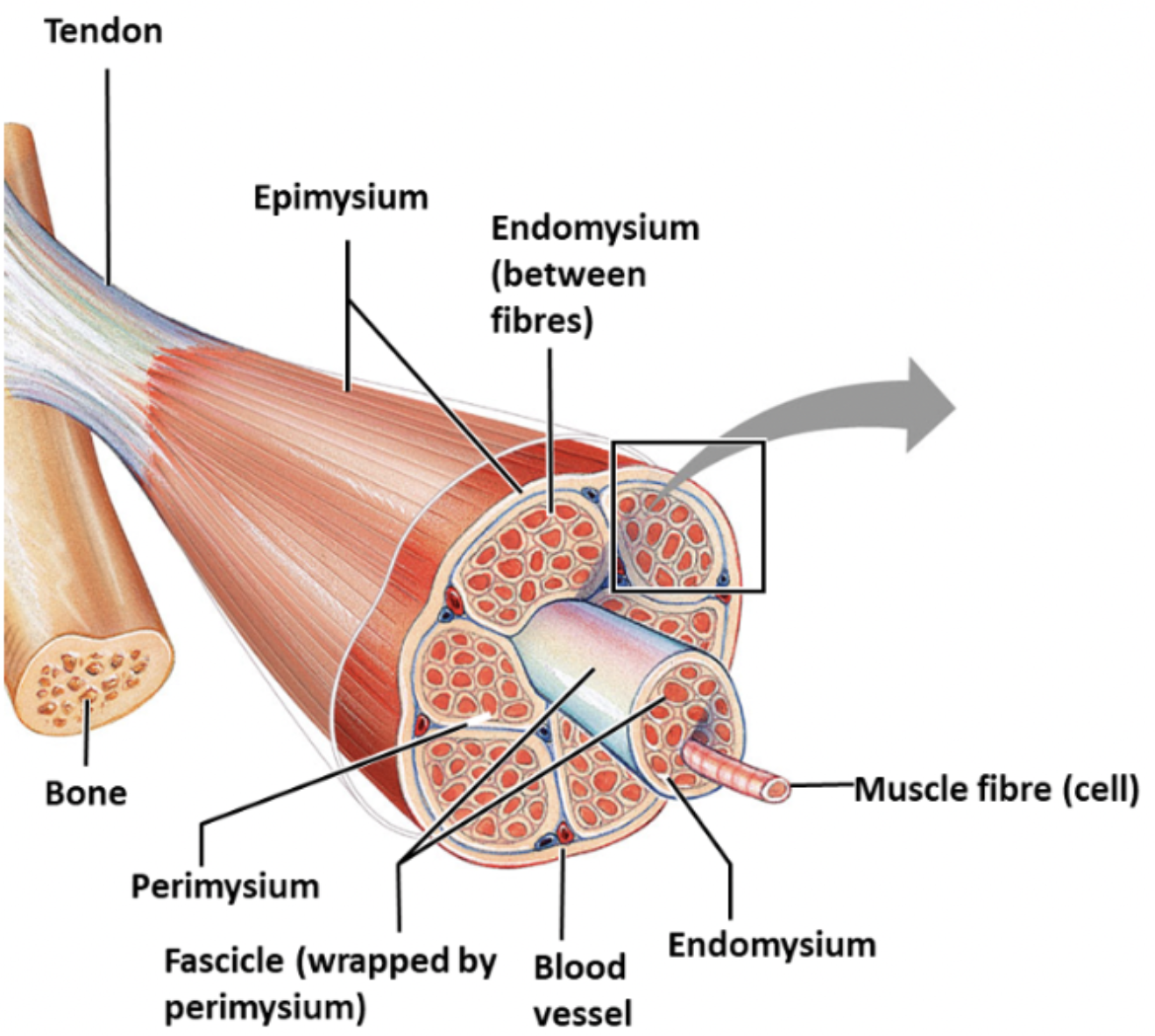
endomysium
thin connective tissue around individual muscle fibres which tonains capillaries and nerve endings

function of connective tissue in muscle
provides structural support, allows force transmission from muscle fibres to tendons, provides pathways for nerves and blood vessels
features of cardiac muscle
involuntary, striated, one or two central nuclei, branched fibres, intercalated discs, found in the heart, very limited regeneration, more mitochondria than skeletal
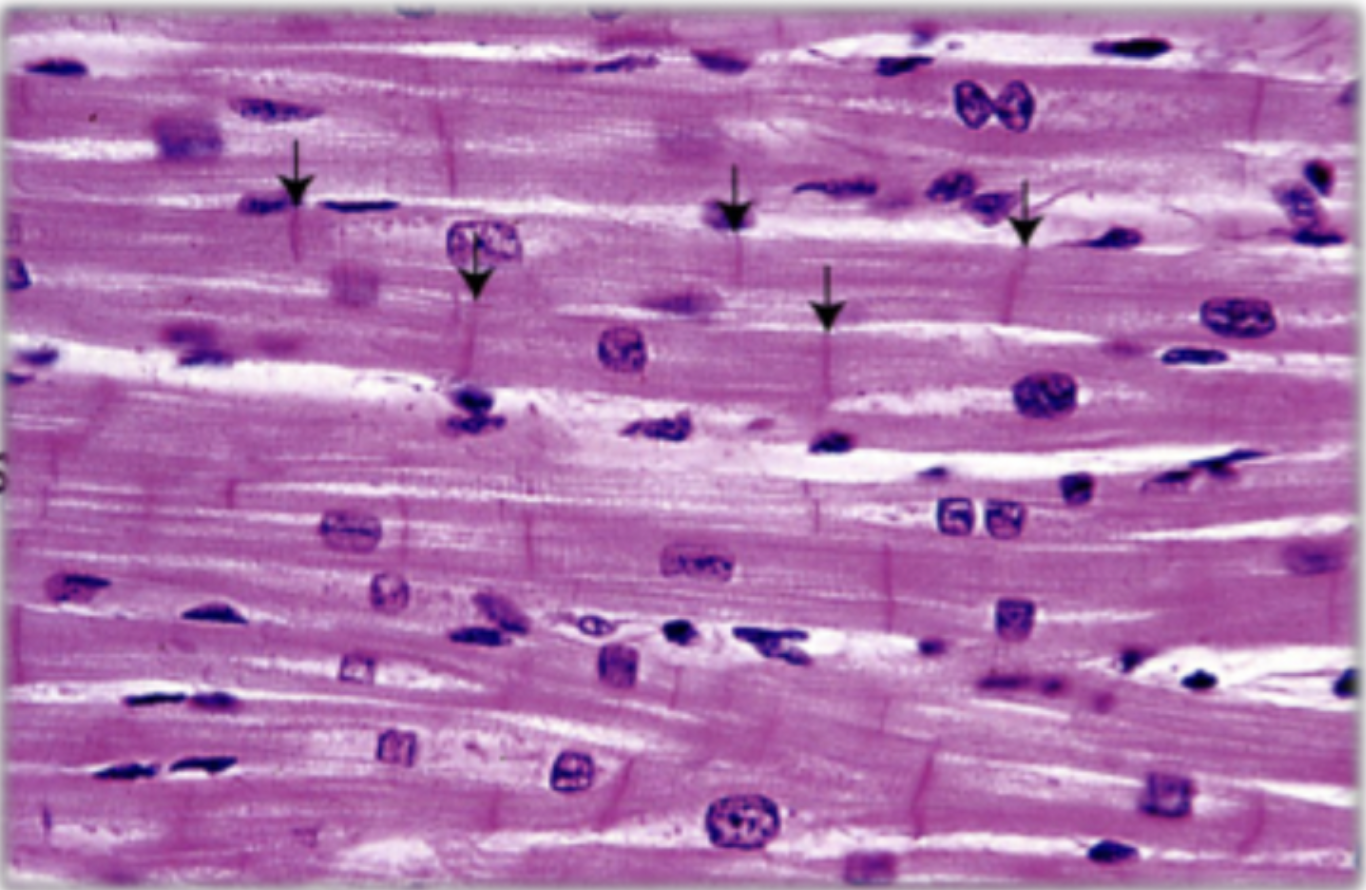
features of smooth muscle
involuntary, un-striated, single central nuclei, spindle-shaped cells, no intercalated discs, found in walls of hollow organs, good regeneration

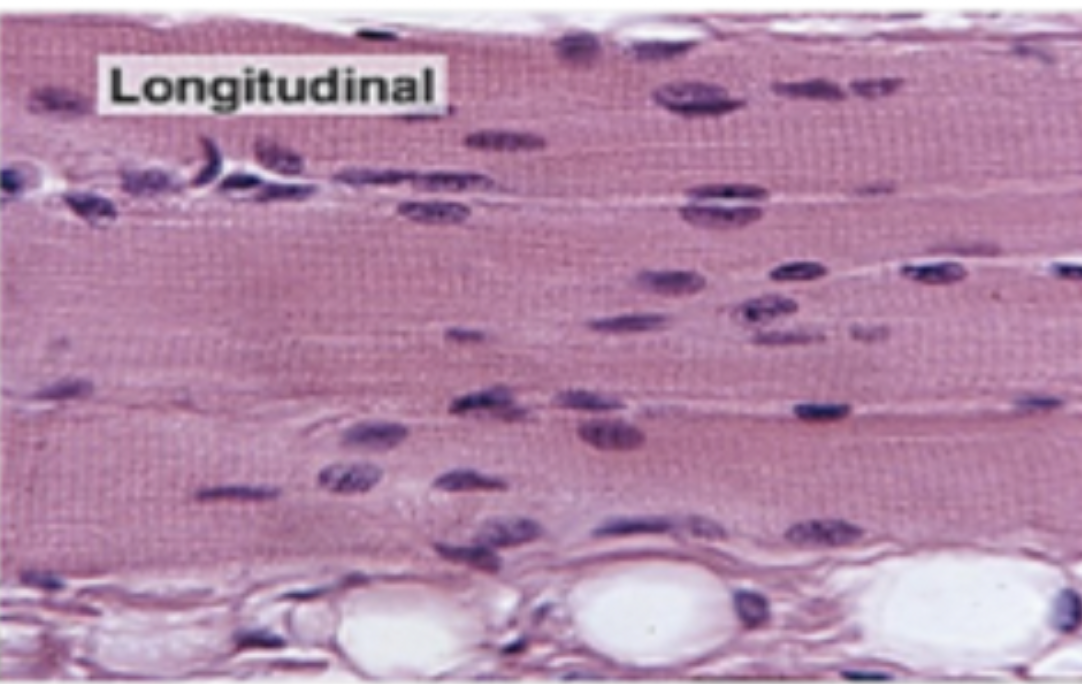
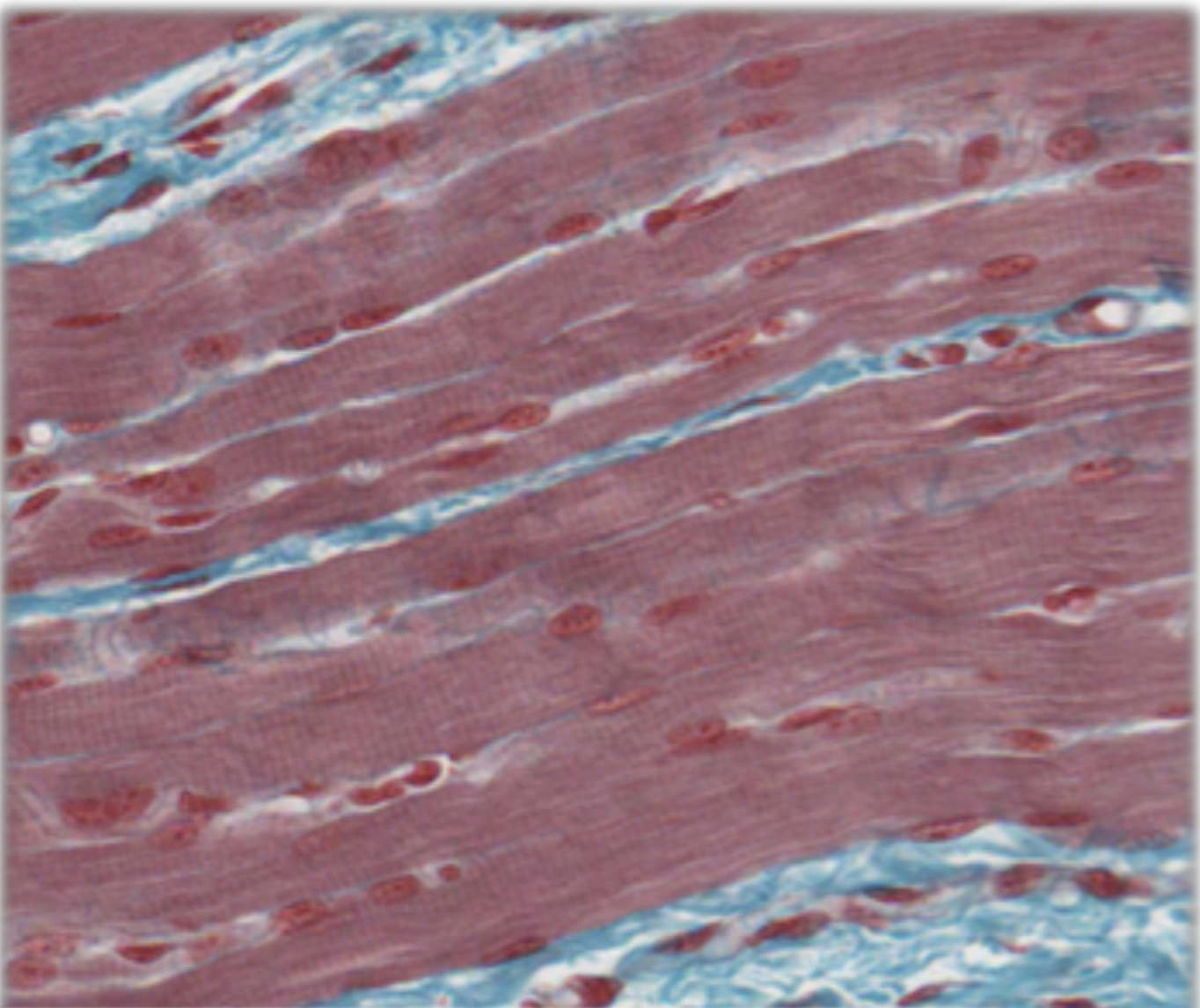
histological appearance of longitudinal skeletal muscle
parallel arrangement of unbranched muscle fibres, visible striations, thin layer of connective tissue between muscle fibres, multiple nuclei at boundary
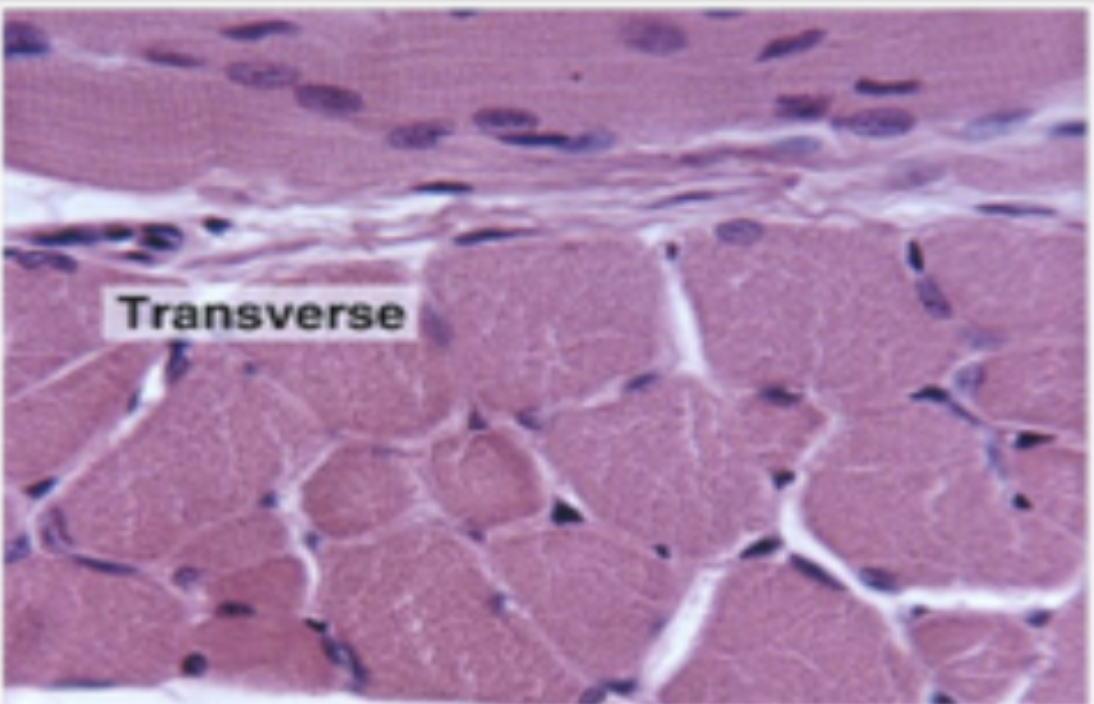
histological appearance of transverse skeletal muscle
peripheral nuclei, sarcoplasm and myofibrils visible, separate fascicles separated by connective tissue visible
sarcomere
a contractile unit of muscle fibre
histological appearance of longitudinal cardiac muscle
looser arrangement of fibres, branching pattern, central nucleus, visible striations, lots of blood vessels associated with endomysium, intercalated discs

intercalated discs in muscle fibres
specialised junctional complexes between muscle fibres which allow adhesion and communication
histological appearance of transverse cardiac muscle
cross sections of comparable size, centrally placed nucleus, endomysium is more abundant
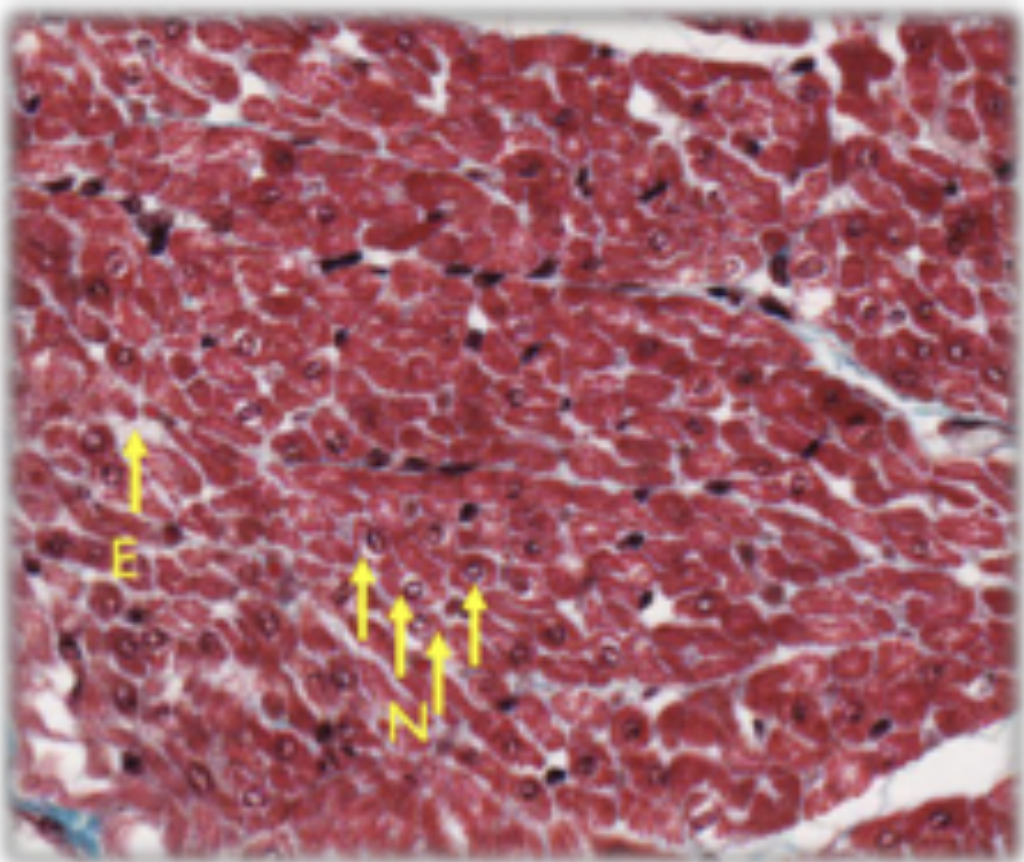
function of T-tubules and sarcoplasmic reticulum in cardiac muscle cells
to ensure simultaneous contraction of myofibrils in each cell
function of intercalated discs in muscle cells
ensure mechanical continuity, ensure spread of excitation between cell gap junctions, allow rapid spread of wave of contraction, act like functional syncytium
features of Purkinje fibres
spontaneous contraction, found in cardiac muscle, pale staining, high glycogen contents, fewer myofibrils than cardiac myocytes
histological appearance of smooth muscle fibres
interlinking of tapered cells, various amounts of connective tissue between fibres, cell boundaries difficult to see, nucleus within elongated cells, no striations
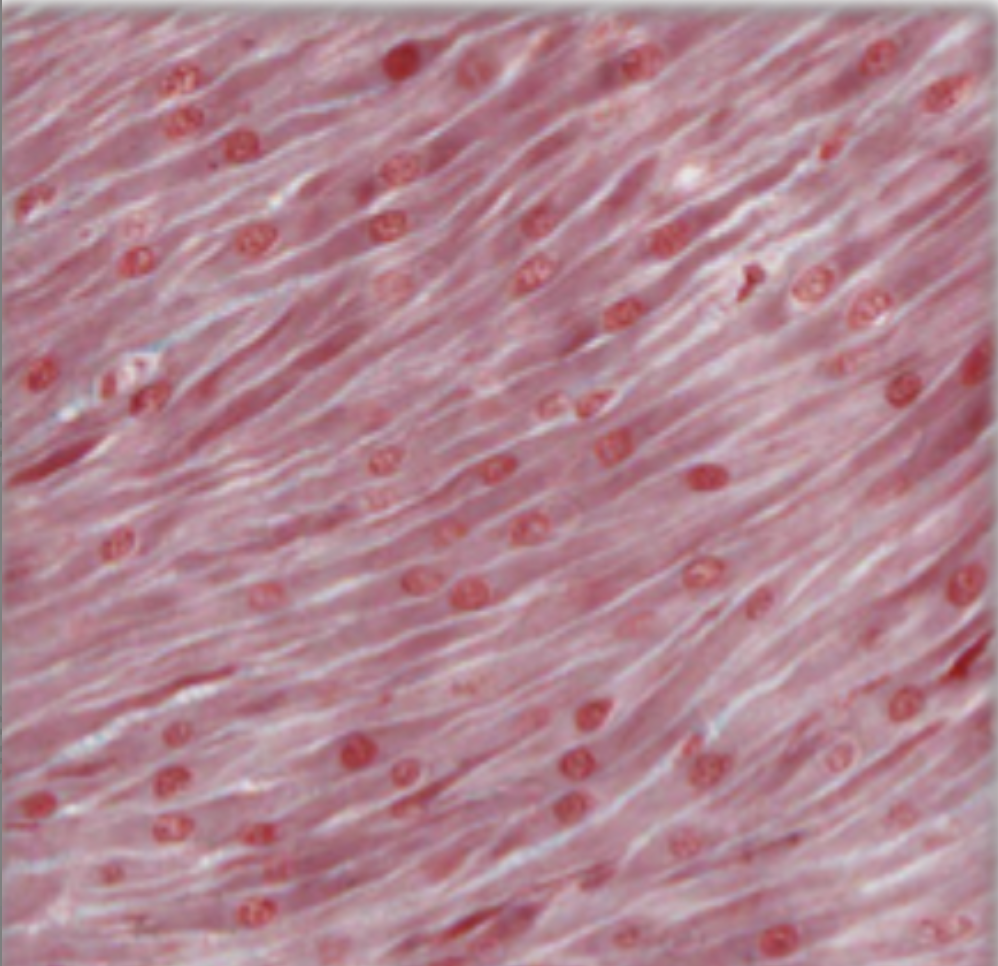
where are intercalated discs found?
in cardiac muscle only