Electrode potential & fuel cells
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
What is this?
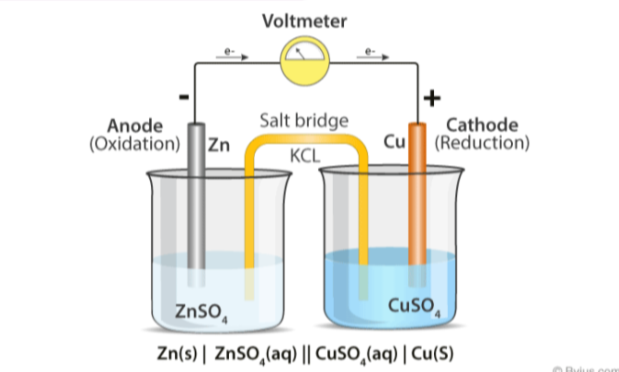
Electrochemical cell
What do electrochemical cells involve:
two different metals dipped in salt solutions of their own ions (2 half cells), connected by a wire and salt bridge
What is a salt bridge?
made from filter paper soaked in ionic substance such as KNO3 and allows ions to flow through and balance our charges in order to complete circuit
How do you determine which metal is oxidised?
The metal that has the most NEGATIVE electrode potential as it will lose electrons more easily and donate them to the hydrogen half-cell (MORE REACTIVE METAL)
What does a positive electrode potential mean?
The metal accepts electrons from the hydrogen half cell so is more likely to be reduced
What causes a large voltage to be produced?
Large difference in reactivity
What is the direction of the flow of electrons?
electrons flow through the wire from the MORE reactive metal to the LESS reactive metal
What is the name of the voltage between the 2 half cells?
cell potential (Ecell or emf - electromotorforce)
If a reaction is reversible what determines the direction of the reaction?
depends on how easily metal loses electron
What is the standard electrode potential of a half cell?
emf of a half cell compared with a standard hydrogen half cell measured at 298K with solution concentrations of 1 mol dm-3 and gas pressures of 100KPa
Why must standard conditions be used?
Equilibium is reversible so is altered by concentration, temperature, and pressure so therefore needs to remain the same
What is the standard electrode potential of a hydrogen cell?
0V
What is this?
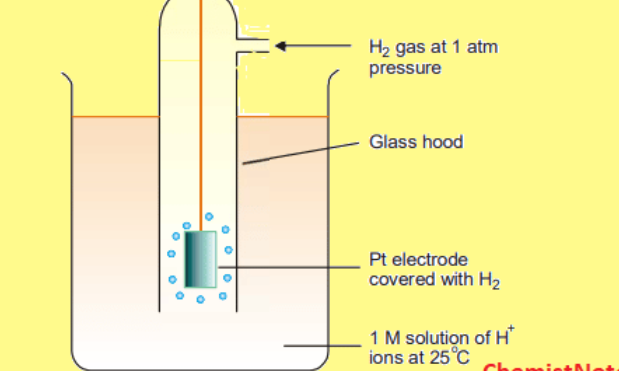
Standard hydrogen electrode
What does a standard hydrogen electrode consist of?
Concentrated HCl (1 mol dm-3 which is the source of H+ ions
H2 gas at 100KPa and 298K bubbled through H+ solution
Platinum electrode which is inert but allows electrons to pass into or out of the half cell by a connecting wire
What is a standard hydrogen half cell used for?
Used as a reference to measure all other half cells to find their standard electrode potentials
What do you do if half cell contains aqueous ions of the SAME element with diff oxidation numbers?
Include a solid platinum electrode to allow electrons to pass in and out and solution needs to be EQUIMOLAR (same conc of ions in solution)
What is the overall cell potential dependant on?
Dependant on the electrode potentials of the half cells involved
What is this?
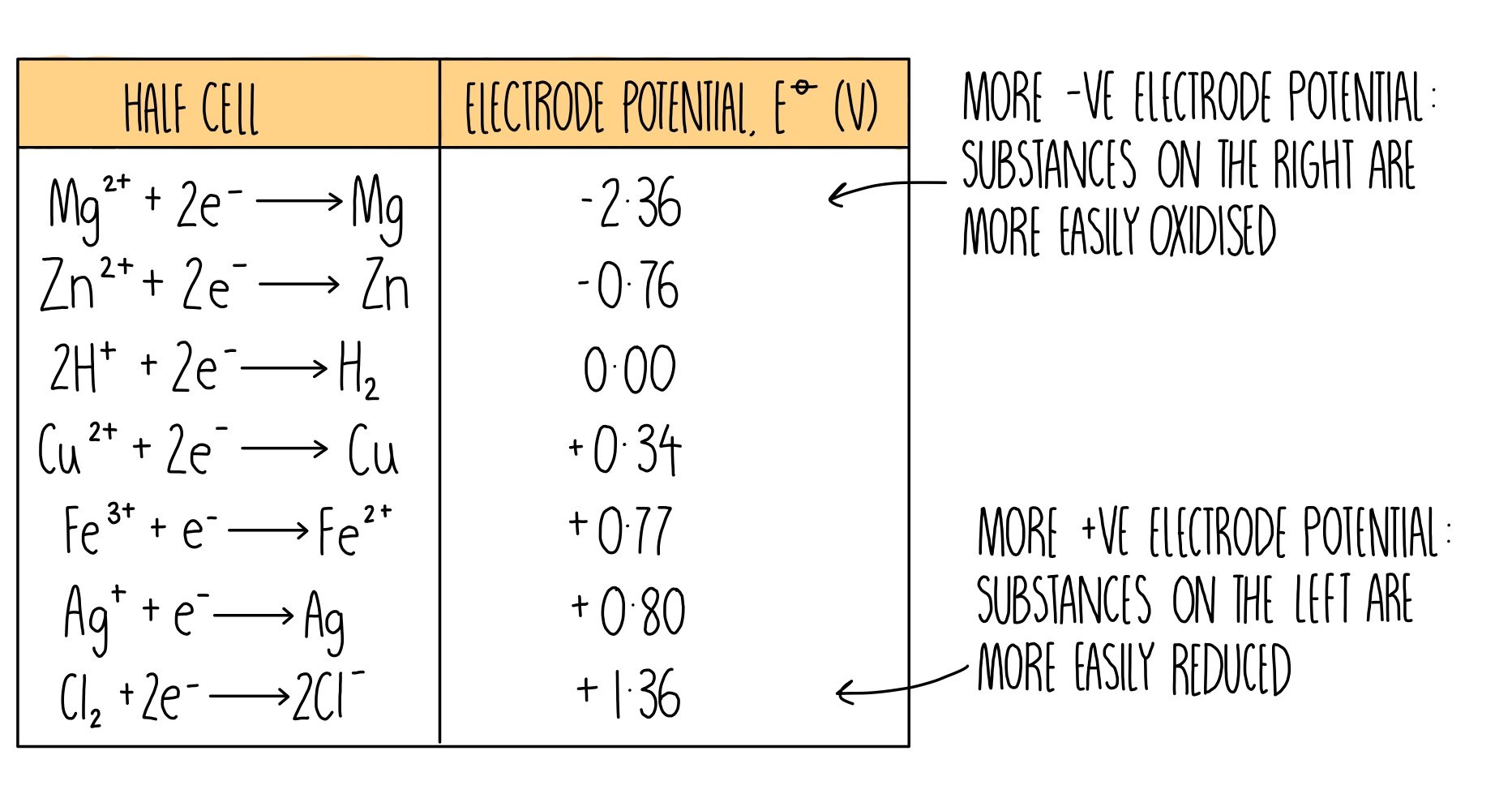
Electrochemical series
What does the electrochemical series show?
a species will react with the species below it, this species is oxidised so favours the backwards reaction
What does a more reactive metal have?
More NEGATIVE electrode potential as it wants to lose electrons so is negative to favour oxidation and donate electrons to the hydrogen half cell
What does a more reactive non-metal have?
more POSITIVE electrode potential as it wants to gain electrons to is positive to favour reduction and accept electrons from the hydrogen half cell
What is the equation for electrode potential?
REDUCED electrode potential - OXIDISED electrode potential
What does a positive overall electrode potential mean?
The reaction can happen
What do non-rechargeable cells do?
provide electrical energy until chemicals have reacted so much the voltage falls and the cell is flat so is discarded
What happens in rechargable cells?
chemicals react to provide electrical energy and the direction of the reaction is reversed when charging so chemicals in cell are regenerated and can be used again
What do fuel cells do?
use energy from the reaction of a fuel with oxygen to create a voltage
Give an example of a fuel cell:
Hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell
Describethe features of a fuel cell:
reactants flow in and products flow out while electrolyte stays in, don’t need to be recharged, can be operated continuously as long as the fuel and oxygen continue to flow in
Redox equilibrium for hydrogen fuel cell:
2OH-(aq) + H2(g) ⇌ 2H2O (l) + 2e-
½ O2(g) + H2O + 2e- ⇌ 2OH-
What are the two limitations for predicting reactions?
non-standard conditions and unfavourable kinetics
How does non standard conditions limit prediction of reactions?
an increase in concentration of reactants will shift the equilibrium right so increases ease of losing / gaining electrons so the electrode potential of cell will be decreased / increased
How do unfavourable kinetics limit prediction of reactions?
Very slow rate of reaction due to high activation energy will affect the overall reaction
How is unfavourable kinetics determined?
If the electrode potential difference is less than 0.4V the reaction is unlikely