t30 - bone and degenerative disorders
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
osteoarthritis
-aka degenerative joint disease
-most common arthritis world wide
-leading cause of disability in older adults
-affects knees, hips, hands (DIP, PIP, CMC) and spine
osteoarthritis patho
-progressive degradation of articular cartilage with attempted repairs mechanism > imbalance between cartilage breakdown and synthesis by chondrocytes > mechanical stress and biochemical changes create cycle of joint destruction
-subchondral bone changes
-synovial inflammation
-joint space narrowing as cartilage is lost
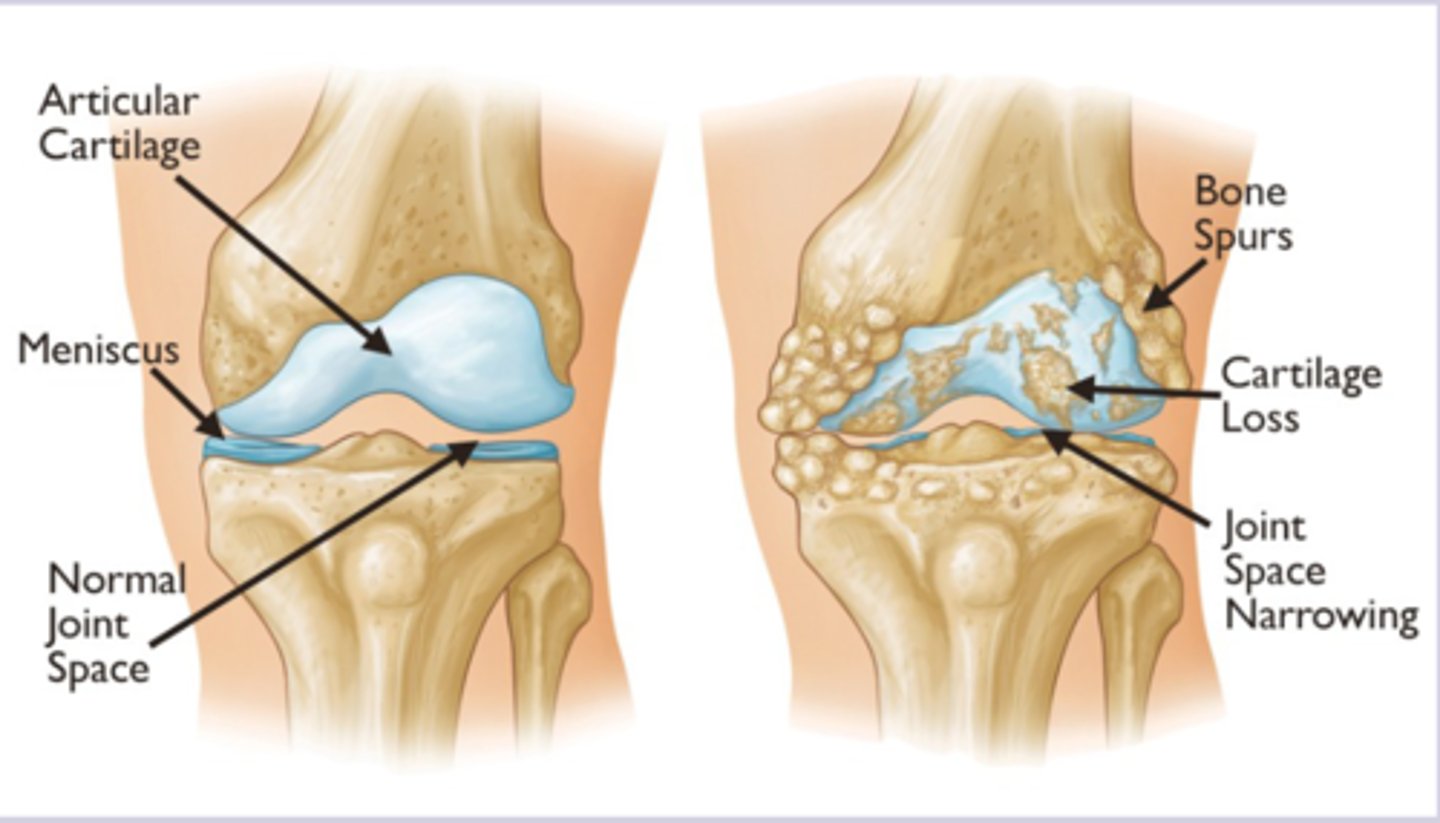
osteoarthritis etiology
Primary
-idiopathic
-biomechanical factors can contribute to disease
Secondary
-previous injury
-previous septic arthritis
-hemochromatosis
-acromegaly
-gout
osteoarthritis RF
-increasing age
-females
-postmenopausal
-african americans
-obesity
-mechanical stress
osteoarthritis sx
-joint pain: gradual onset, worse with activity, improve with rest
-morning stiffness lasting less than 30 min
-joint stiffness goes away after activity slowly
-may lock or give away
-NO systemic sx
-tenderness to palpation along joint lines
-effusion, muscle atrophy, crepitus
-Heberden node (DIP), Bouchard node (PIP), square hand deformity
-varus or valgus deformity in knees
-limited internal rotation, pain with flexion
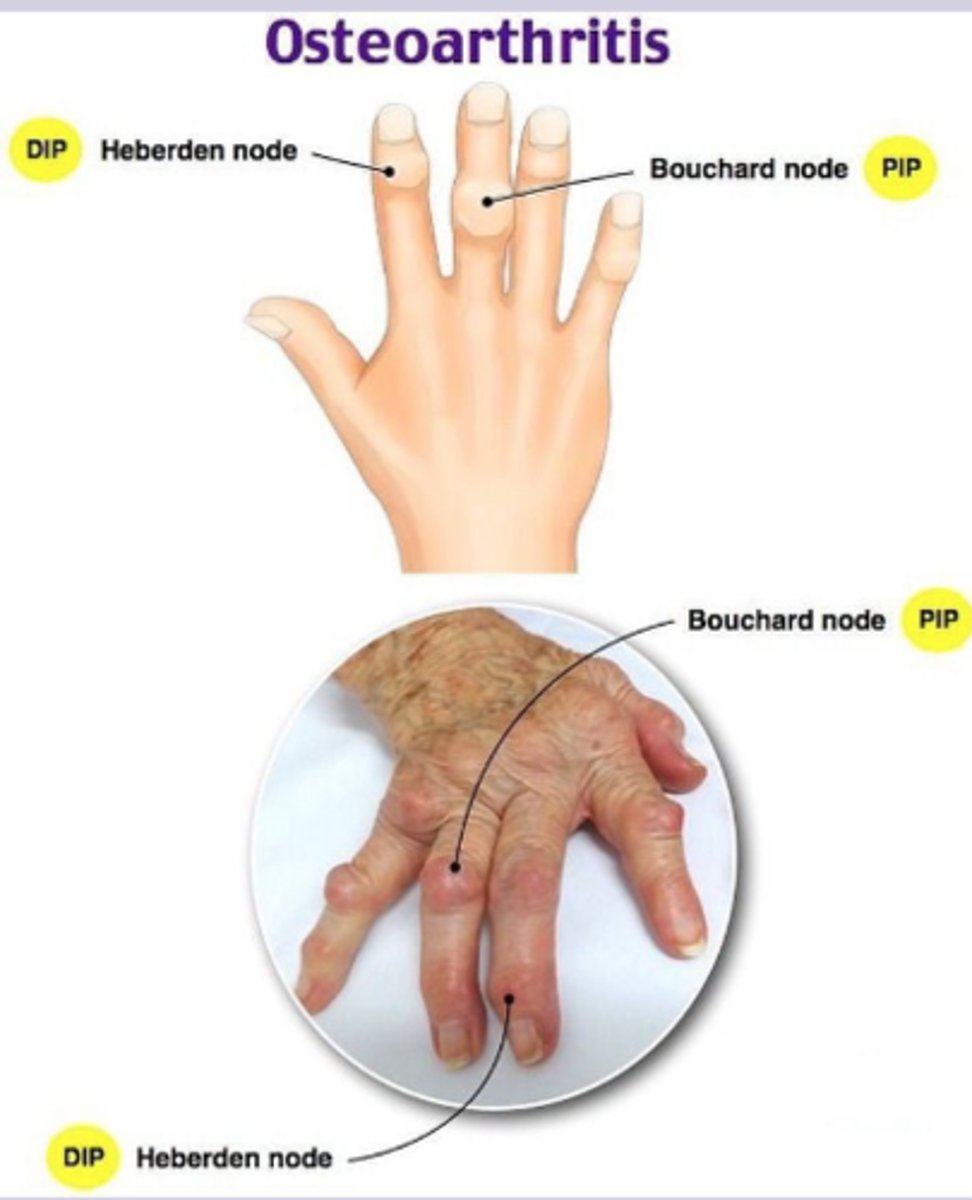
osteoarthritis dx
-clinical
Imaging
-Xray weight bearing: Asymmetric joint space narrowing
-subchondral sclerosis, osteophytes, subchondral cysts
If effusion present
-synovial fluid analysis: noninflammatory (<2000), clear/yellow, high viscosity
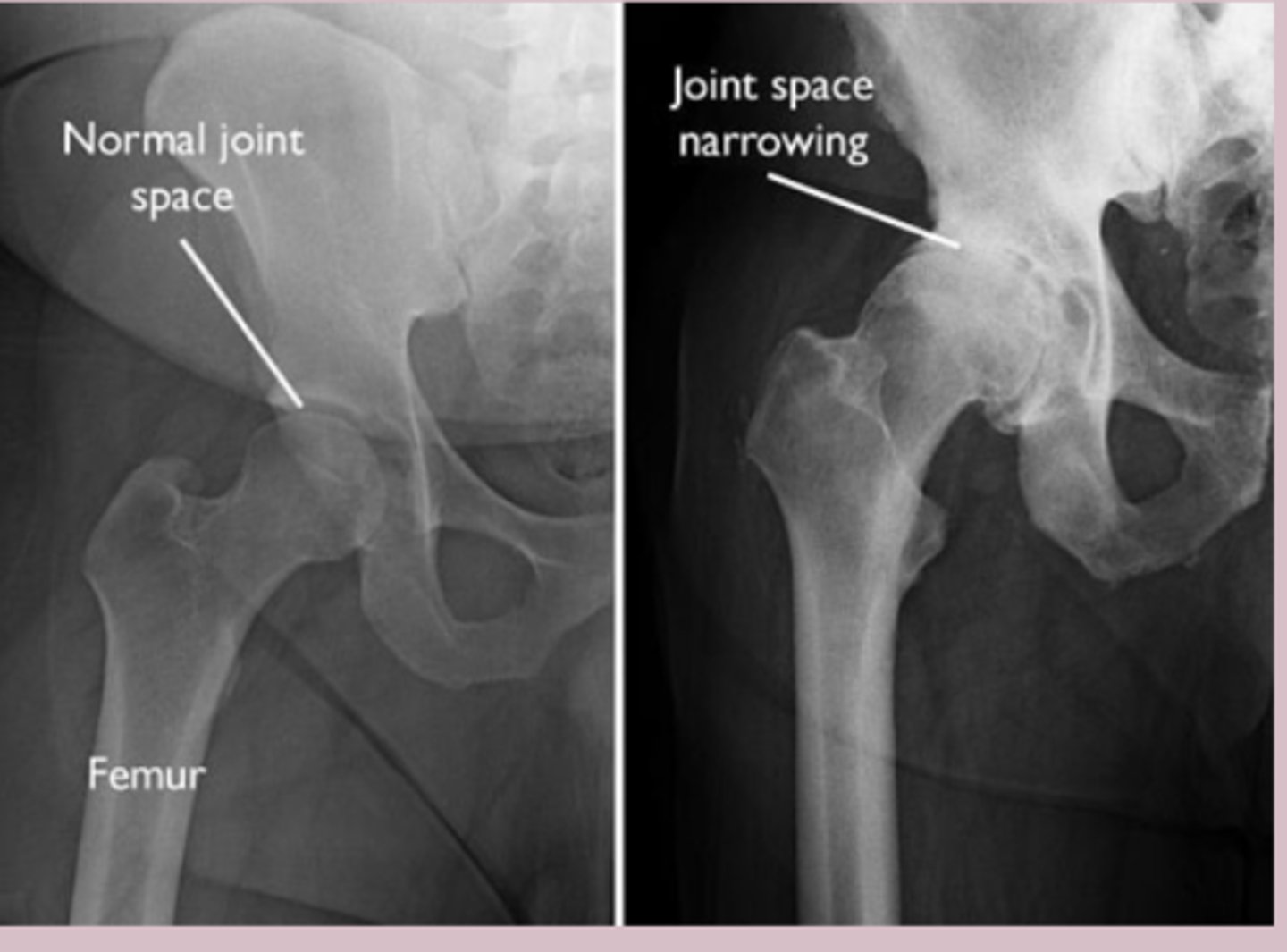
osteoarthritis tx
Nonpharm
-weight loss
-Refer all patients to PT
Pharm
-first line: acetaminophen
-topical diclofenac gel for hands and knees
-NSAIDs: test for GI bleed risk
-duloxetine: SNRI for chronic pain
-tramadol: if NSAID contraindicated
Surgery
-document failed conservative first
-intraarticular corticosteroid injection
-arthroscopy, osteotomy, joint replacement
osteoporosis
-skeletal disease characterized by low bone mass and microarchitectural deterioration
-caucasian and asian
-women postmenopausal
-affects hip, vertebral body, distal radius
osteoporosis patho
-bone resorption exceeds bone formation > decreased bone mass and deterioration of bone microarchitecture > increased bone fragility and fracture risk
-trabecular bone affects more severely
osteoporosis types
-postmenopausal osteoporosis: estrogen deficiency leads to increased osteoclast activity
-age related osteoporosis: decreased osteoblast function, decreased calcium absorption
-secondary osteoporosis: underlying disease or medication causing bone loss
osteoporosis etiology
Primary
-postmenopausal (type I)
-age related (type II)
Secondary
-hyperthyroidism, hyperparathyroidism, Cushings, hypogonadism, DM
-glucocorticoids, heparin, PPI, SSRI
-celiac disease, IBD
-CKD
osteoporosis RF
-advanced age
-female
-small body stature
-early menopause
-sedentary lifestyle
-cigarette smoking
-eating disorder
osteoporosis sx
-asymptomatic until fracture
-fragility fracture = fracture from fall from standing height
-loss of height
-kyphosis
-decreased rib to pelvis ratio
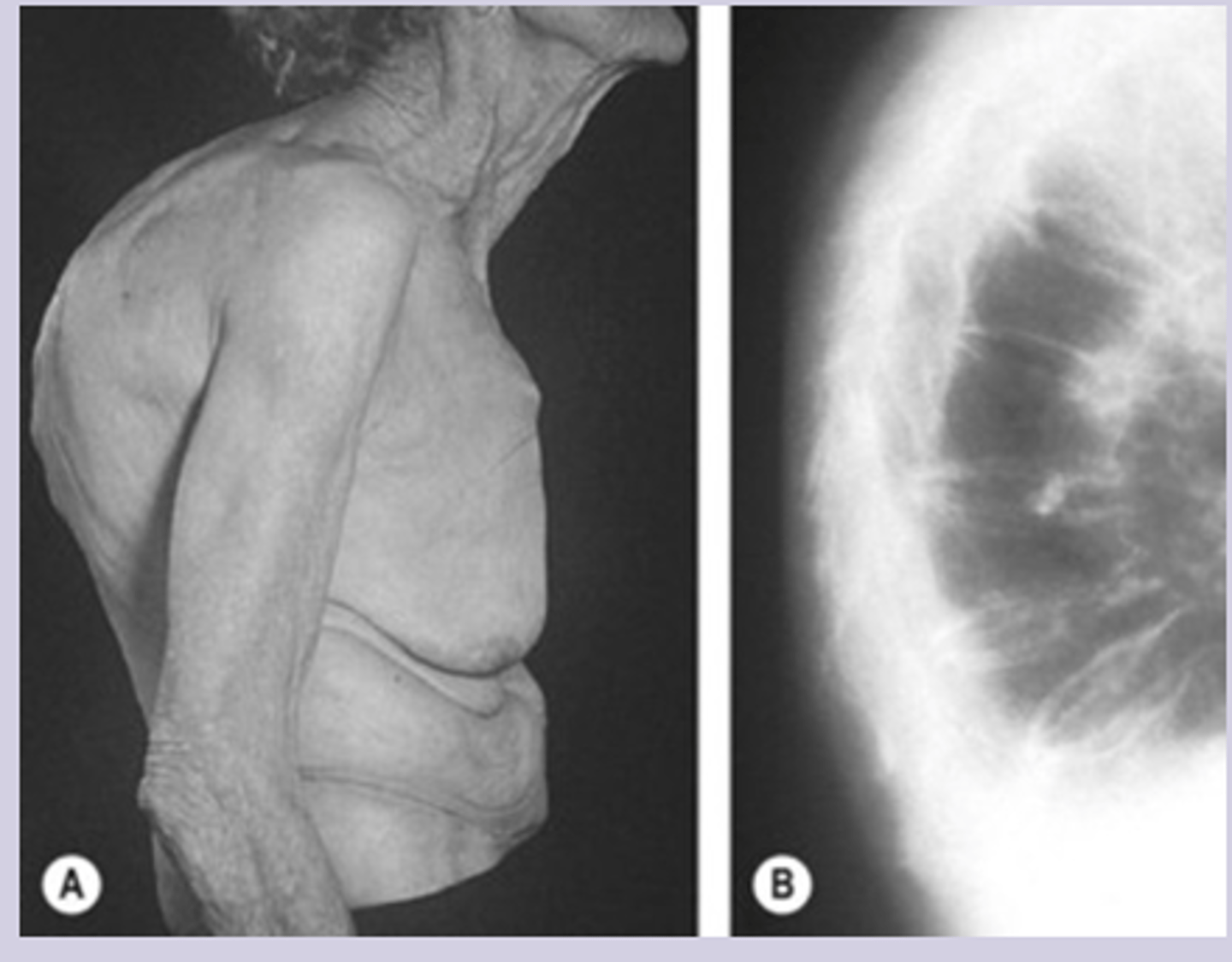
osteoporosis dx
Gold standard = DEXA scan
T score
-normal: >-1
-osteopenia: -1.0 to -2.5
-osteoporosis: <-2.5
Labs
-BMP: calcium, creatinine
-Vit D levels
FRAX score
-estimate 10 year probability of major fracture
-should be calculated for all osteoporotic pts
Imaging
-used to identify fractures
Screening Q1-2 years
-all women >65, postmenopausal women <65 with RF
-men >70 or younger with RF
osteoporosis tx
Nonpharm
-calcium intake 1000-2000 mg QD
-Vit D 800-1000 IU QD, goal >30
-exercise, fall prevention
Pharm
-indications: T score <-2.5, hx of fragility fracture, T score -1 to -.25 + FRAX score >20%
-first line: alendronate or risedronate
-denosumab SQ if bisphosphonates not tolerated
-anabolic agents reserved for high risk
-hormone replacement therapy
osteogenesis imperfecta
-genetic disorder of collagen synthesis causing bone fragility
-autosomal dominant or recessive
-due to COL1A1 or COL1A2 gene
-type 1: mildest and most common
osteogenesis imperfecta patho
-genetic mutations affect quantity or structure of type I collagen > leads to decreased bone mass and abnormal bone architecture > bone are fragile and prone to fractures with minimal trauma
osteogenesis imperfecta etiology
-primarily genetic disorder with autosomal dominant or recessive
-90% are due to COL1A1 or COL1A2 mutation
osteogenesis imperfecta sx
-multiple fractures throughout life with minimal or no trauma
-bone pain
-short stature and growth delay
-easy bruiding, excessive sweating
-dental problems
-blue or gray sclera
-bone deformities, hearing loss, triangular facies
-type 1: normal stature, blue sclera, hearing loss
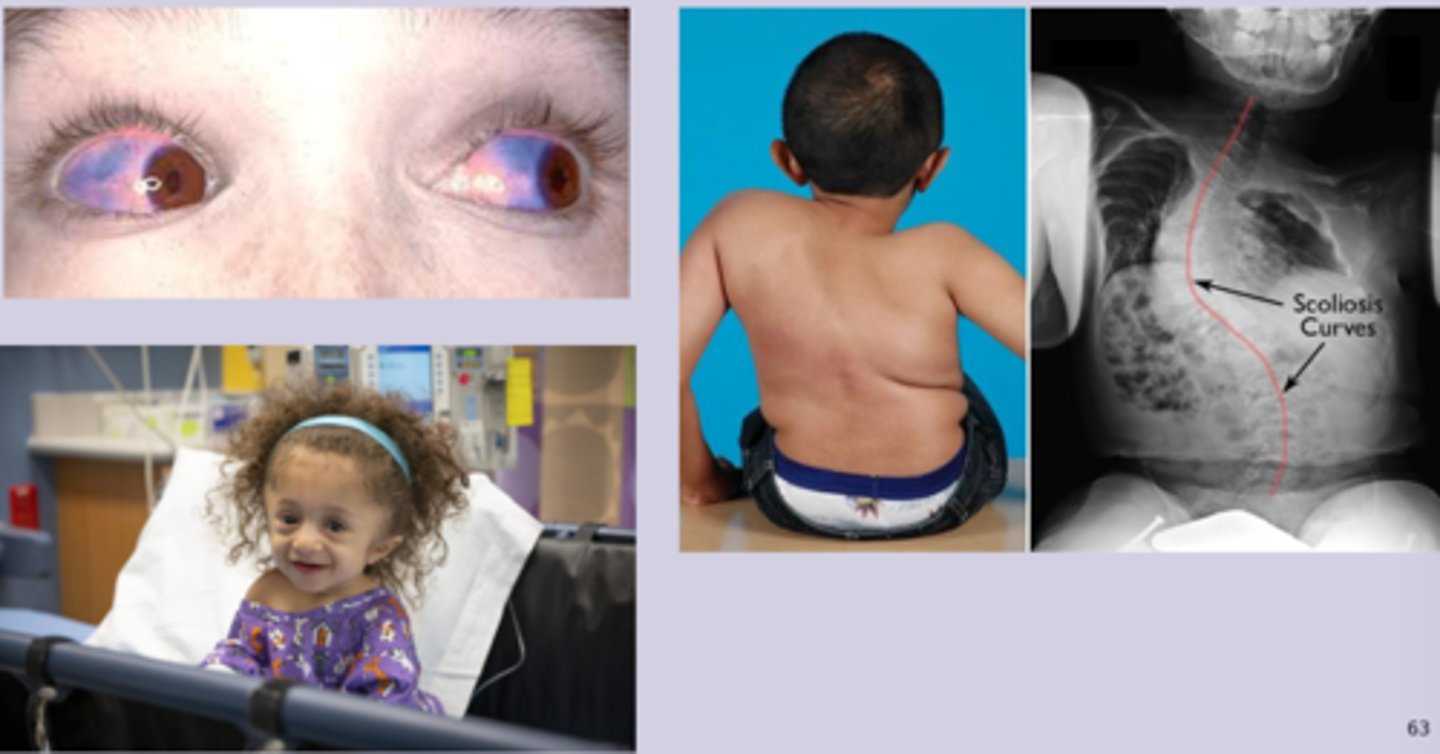
osteogenesis imperfecta dx
-clinical
Labs
-usually normal
-genetic testing = confirmatory
Imaging
-Xray: generalized osteopenia, multiple fractures, thin cortices, bowing deformities, codfish vertebrae
-DEXA scan: show decreased BMD
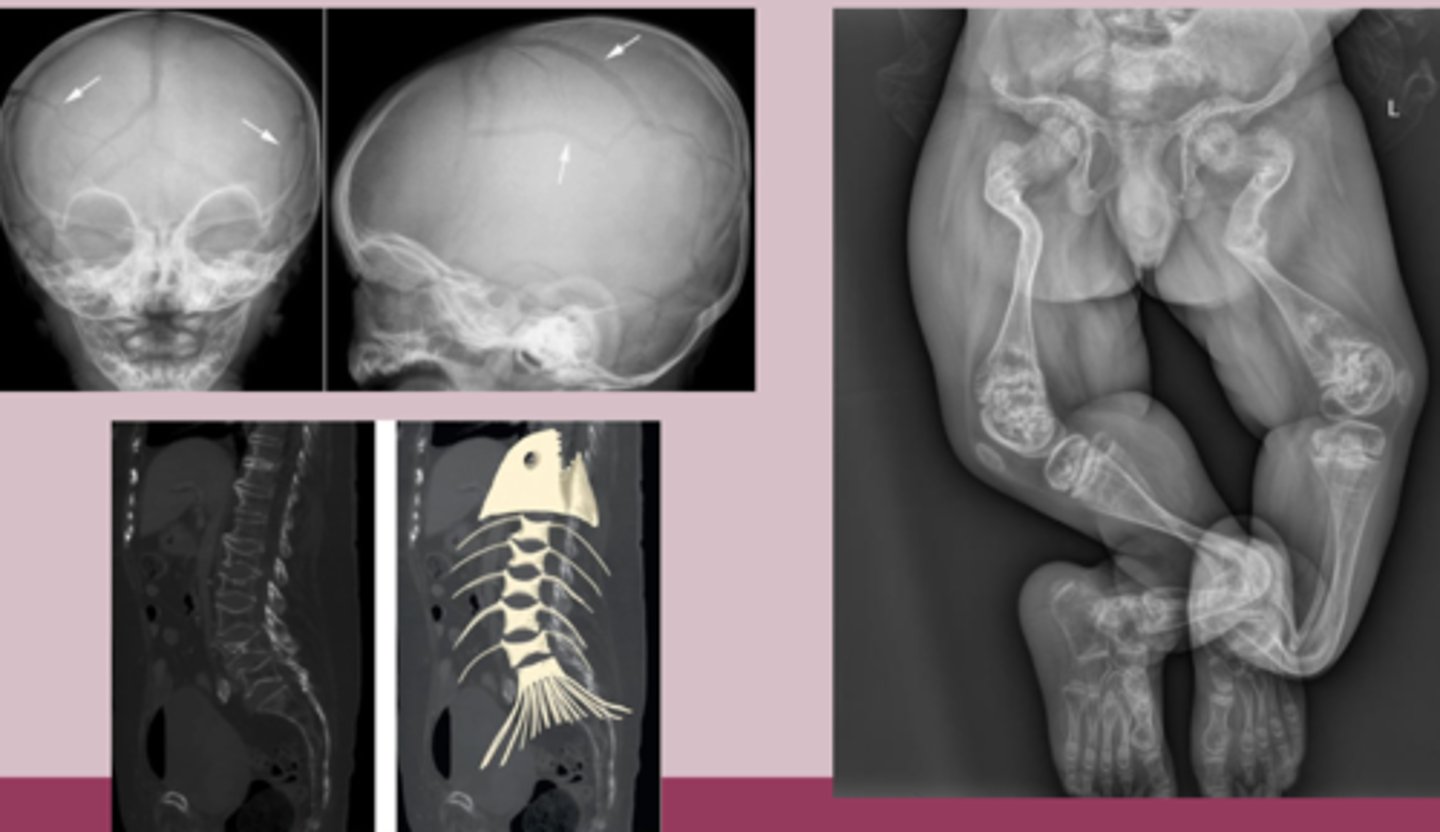
osteogenesis imperfecta tx
Nonpharm
-fracture prevention, PT, OT
-adequate calcium and vit D
Pharm
-bisphosphonates: pamidronate IV or zoledronic acid IV
osteomalacia and rickets
Osteomalacia: defective bone mineralization in adults
Rickets: defective bone mineralization in children
-MCC = vit D deficiency
osteomalacia and rickets patho
Inadequate mineralization of bone matrix due to vitamin D
-Osteomalacia: new bone formed during remodeling remains unmineralized > fracture, bone pain
-Rickets: growth plate cartilage fails to mineralize properly > widening, irregular growth plates
osteomalacia and rickets etiology
-MCC = vitamin D deficiency
-phenytoin or phenobarbital
-phosphate deficiency
-genetic defects
osteomalacia and rickets RF
-limited sun exposure
-darker skin
-elderly age
-exclusive breastfeeding
-strict vegetarian diet
-CKD
osteomalacia and rickets sx
Osteomalacia
-diffuse bone pain in hip, pelvis, lower back
-muscle weakness, waddling gait
-fragility with minimal trauma
-tenderness over bones
Rickets
-delayed motor milestones
-bone pain in legs and spine
-growth delay, dental problems
-seizures, tetany
-craniofacial deformities, rachitic rosary, harrison groove, widening wrist
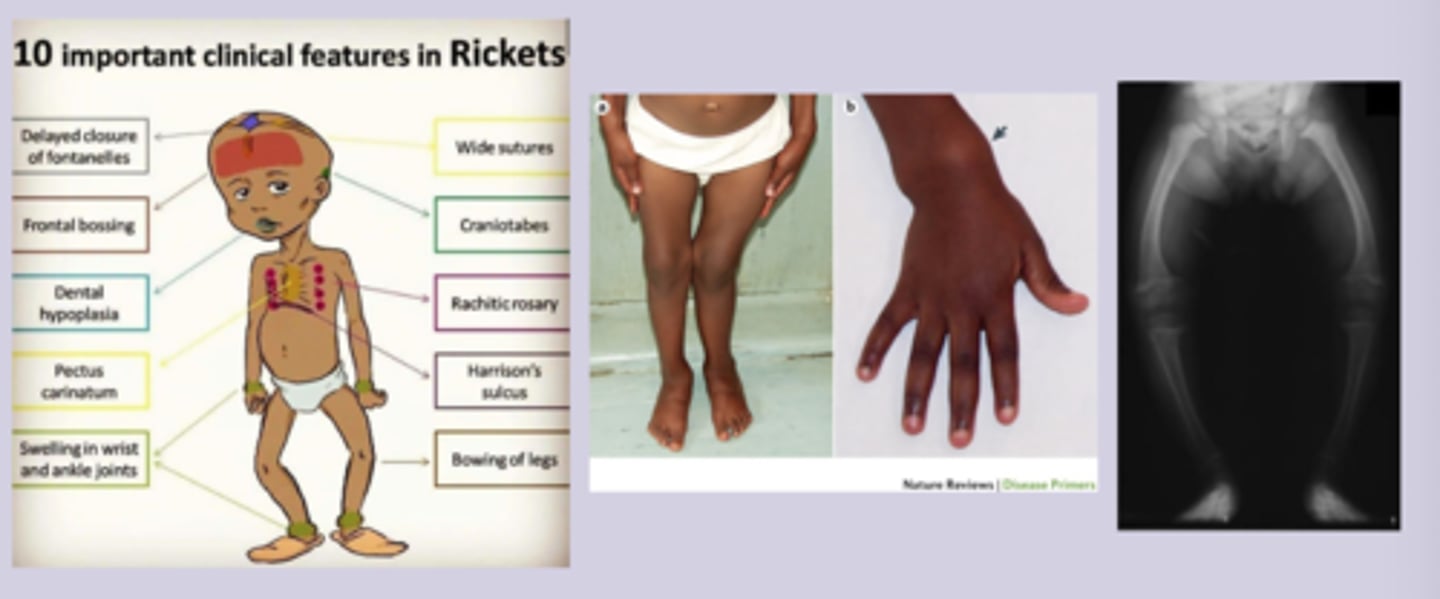
osteomalacia and rickets dx
-clinical
Labs
-25-hydroxyvitamin D level = low <20
-calcium and phosphate = low
-alkaline and PTH = elevated
-renal function test, LFT
Imaging
-Rickets Xray: widening, irregular, frayed growth plates, bowing deformity
-Osteomalacia Xray: looser zone, generalized osteopenia, fractures
-bone biopsy = gold standard
osteomalacia and rickets tx
Mainstay = vitamin D and calcium supplementation
-ergocalciferol or cholecalciferol 2000-6000 IU QD
-monitor levels after 3 months
-goal >30
Prevention
-exclusively breastfed infants should receive 400 IU QD
paget's disease
-chronic localized disorder of bone remodeling
-localized to specific bones, does not spread to other bones
-second most common bone disorder
-men
-70-80 yo
paget's disease patho
Excessive, disorganized bone remodeling at focal sites
Lytic phase: excessive osteoclastic bone resorption
Mixed phase: compensatory osteoblastic bone formation
Sclerotic phase: sclerosis formation
paget's disease etiology
-unknown
-genetics
-mutation in SQSTM1 gene
paget's disease RF
-advanced age
-family hx of paget's
-anglo-saxon
-male
paget's disease sx
-asymptomatic
-deep, aching, worse at night bone pain
-enlarged skull, bowing of legs, kyposis
-warmth over affected bone
-bone tenderness to palpation
paget's disease dx
Labs
-alkaline phosphatase = elevated
-calcium, phosphate, PTH = normal
Imaging
-often incidental finding
-Xray: lytic lesions, slcerotic lesions, bone enlargement and deformity
-bone scan: increased uptake in affected bone
-bone biopsy: mosaic pattern
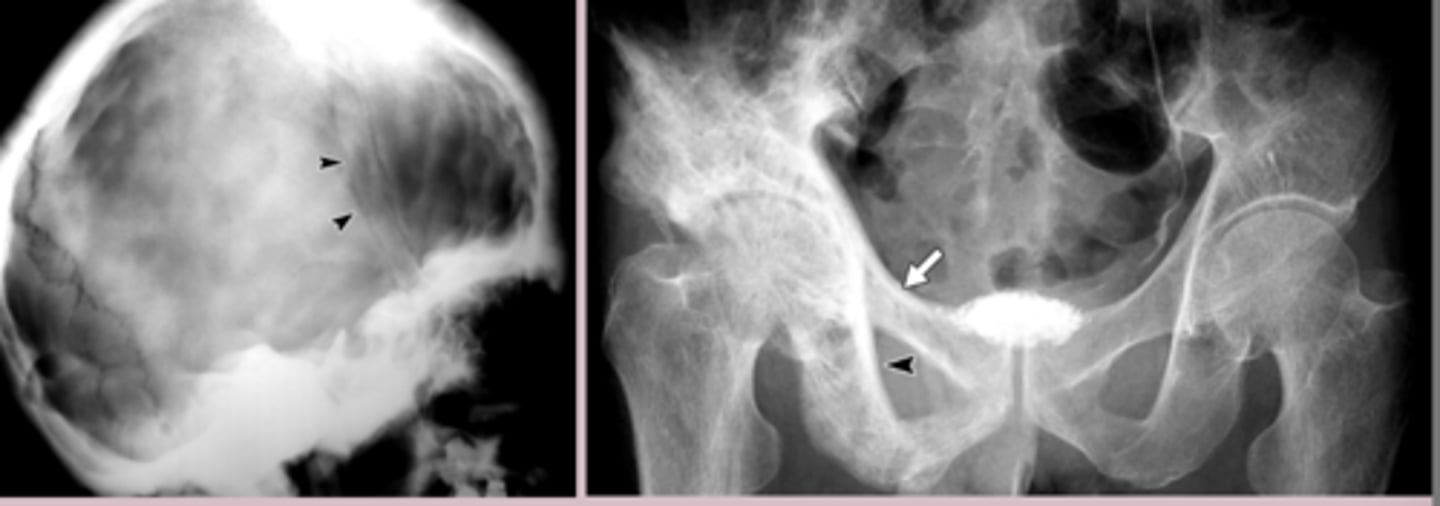
paget's disease tx
Nonpharm
-observation of asymptomatic
-pain management
-adequate calcium intake
Pharm
-first line: zoledronic acid 5mg IV once
-calcitonin