SS 104 Modules 5-10
1/145
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
146 Terms
Abdication
renouncing monarchial authority
Blockade
a naval blockade against Germany, aiming to restrict supplies of food, resources, and war materials, ultimately contributing to widespread shortages and economic hardship within Germany
Convoy system
a method of organizing and protecting groups of vehicles or ships traveling together, typically with a military escort or other protective measures
Multinational empire
political aggregation of distinct peoples generally broken down along ethnic and religious lines
“No Man’s Land”
strip of land separating the two armies and their trenches
Ultimatum
The Austro-Hungarian ultimatum to Serbia on July 23, 1914 was a key event leading to the outbreak of war. The ultimatum, presented after the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand, demanded Serbia accept a series of harsh conditions within 48 hours. While Serbia conceded to most demands, it rejected Austro-Hungarian participation in a judicial inquiry, which Austria-Hungary used as a pretext to declare war.
Command economies
increased government control over production, distribution, and prices. While initially aimed at efficiency, these measures often led to shortages, inflation, and black markets
Economic depression
occurred due to structural weakness in the US economy, careless speculation, crash of the American stock market, insolvency of domestic banks and financial institutions
Economic nationalism
nations prioritizing their own economic interests and independence, often at the expense of international cooperation. This approach involved protectionist measures like tariffs, state control, and efforts towards self-sufficiency, which ultimately contributed to the tensions that fueled the conflict
Inflation
increased government spending, reduced production, and disruptions to supply chains. While not all countries experienced hyperinflation during the war, some, particularly Austria and Germany, faced extreme price increases and currency devaluation after the war
Isolationism
the United States' initial reluctance to engage in European conflicts and its preference for avoiding permanent alliances and international political involvement
Mandates
established by the League of Nations to oversee territories formerly controlled by the defeated Ottoman Empire and Germany. These territories were not annexed by the victorious Allied powers, but rather placed under their administration with the goal of eventually leading them to self-governance
Protectionism
gained traction as nations sought to bolster their domestic economies and address the economic disruptions caused by the war. This involved increased tariffs, import quotas, and other trade barriers aimed at protecting domestic industries from foreign competition. While intended to foster national economic strength, these measures contributed to trade wars and exacerbated economic instability, ultimately playing a role in the lead-up to the Great Depression
Reparations
payments demanded from Germany and its allies by the Allied powers after the war, primarily under the Treaty of Versailles. These payments were intended to cover the costs of damage and losses incurred by the Allies during the war.
Self-determination
promoted by U.S. President Woodrow Wilson, advocating for the right of nations to govern themselves. This principle became a key aspect of the post-war peace negotiations, particularly regarding the redrawing of borders in Eastern Europe. The concept aimed to create a more stable and just world by allowing peoples with shared cultural or ethnic identities to form their own independent states.
Tariffs
many nations implemented tariffs to protect domestic industries and raise revenue, also due to increased protectionism
Corporatism
an economic and political system where businesses and the government collaborate, saw increased development and influence in participant states. This collaboration was driven by the need to mobilize resources, maintain labor peace, and ensure economic stability for the war effort
Eugenic science
a willingness to weed out the weak and racially impure that rejected moral values, Aryan physical and mental superiority
Fascism
a far-right, authoritarian ultranationalist political ideology and movement. It was characterized by a dictatorial leader, a single-party state, militarism, suppression of opposition, and a belief in national unity and strength above individual rights.
Martial law
replacement of civilian government by military rule and the suspension of civilian legal processes for military powers
Statism
the ideology that emphasizes the power and authority of the state, often to the extent of subordinating individual or group interests to the perceived needs of the nation or government.
Totalitarianism
a political system where the state holds absolute control over all aspects of public and private life
Volksgemeinschaft
propaganda concept used to unify the German population under a shared racial identity and ideology, excluding those deemed racially or otherwise undesirable
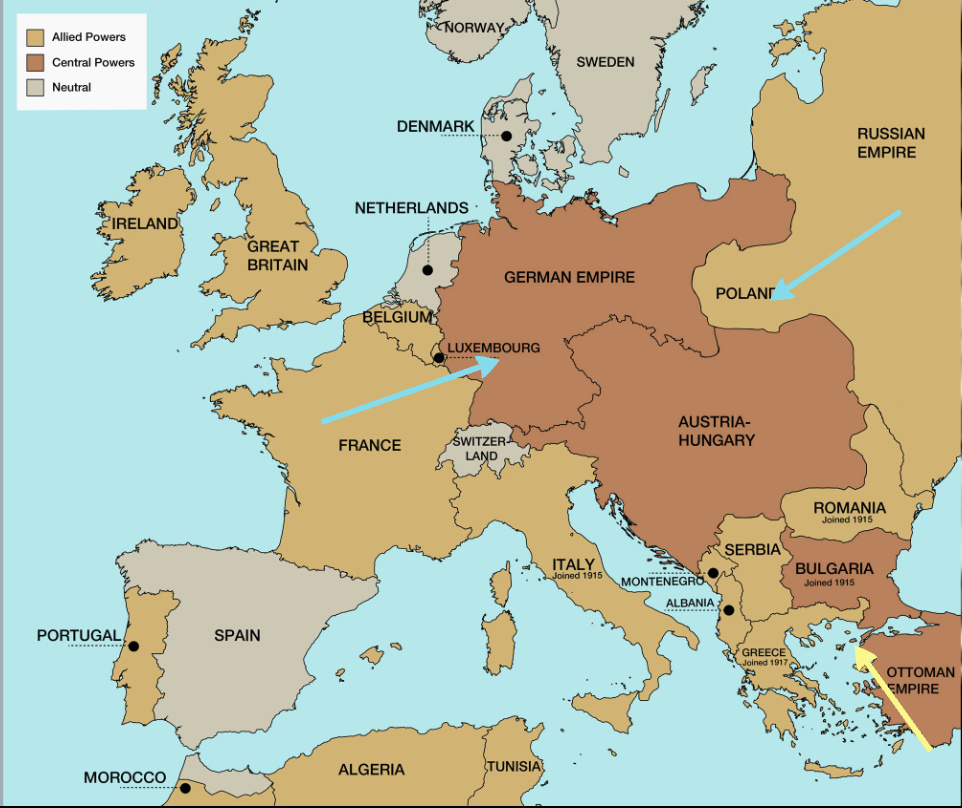
Causes of WWI
Assassination of Archduke Ferdinand, Nationalism and imperialism, alliance systems, multi-ethnic empires (decline because of the rise of nationalism), arms race → navies, poor leadership and lack of diplomacy → Kaiser transfer of power and lack of training, rhetoric, propaganda AND
Industrialization, Tanks, Steel from the second industrial revolution, Planes, Poisonous gases, Machine guns, Electricity, Social Changes
MCMXIV
Excited energy
Oval (cricket ground)
Villa park (football)
Lark: carefree adventure
Shops are shut due to the bank holiday
Old money: farthings and sovereigns
Children have more formal names to show that they are English
Range of ages
Domesday: shows ancient connection to place, heritage
Pastoral area vs upper class combined with working class
Suburbian: garden = backyard
Men go to war and die, ending marriages
The Lost Generation: university educated men die
Testament of youth: what our youth was
Phase I
Germans invade France but were stopped at the Battle of the Marne (September 1914)
British Expeditionary Force (BEF) helped to stop the Germans at the Battle of Mons (23 August 1914)
Russians invade Germany but destroyed at Battle of Tannenburg (August 1914)
Phase II
September to November 1914
The Race to the Sea
Both sides dig 400 mile line of trenches from Switzerland to English channel
Soldiers have to deal with being wet, rats, illness
Phase III
Stalemate
Attacks on German trenches lead to huge casualities
Britain’s attempt to open up a second front at Gallipoli in Turkey was a failure
Winston Churchill → invade from down through Ottoman empire, Gallipoli Dardanelles
Picking people off from up on the hills (Anzac Day)
Lusitania (1915)
US president stays neutral until Germans bomb it, Americans get pissed because passengers are American, draws America into conflict through German submarine warfare in 1917
Phase IV
The War of Attrition: person that stays the longest has won
Total War: a type of warfare where all resources of a nation, including its civilian population and infrastructure, are mobilized and considered legitimate targets in the pursuit of complete victory
Thousands die or are wounded, new weapons, poison gas, tanks, aeroplanes fail to make much effect
Bad conditions in trenches, casualties from machine gun and artillery fire
British blockade German ports to try and starve Germans into surrender
October 1918: revolution in Germany, German U-Boats try to starve British by sinking merchant ships but this angered Americans
German Zeppelins and Gotha planes bomb London
Dulce et Decorum Est
uses it ironically in his poem to highlight the contrast between the romanticized idea of dying for one's nation and the brutal experience of soldiers in war. The poem, through vivid imagery and powerful language, depicts the physical and psychological trauma of trench warfare, ultimately concluding that the idea of a glorious death in battle is a "lie"
Apollinaire: The Stunned Dove and the Water Jet
Gardens → burial grounds
Detrimental
Friends have turned to ashes
Shaped poem
Phase V
US enters war in 1917
2 March 1918 Germans launch Operation Michael: last-ditch attack
8 August 1918 “Black Day” where Germany army was defeated, allies and America push back Germans
11 November 1918 Allies and Germany sign ceasefire (armistice)
Treaty of Versailles
France angry because of major losses, war guilt clause enacted and Germany has to accept responsibility for causing the whole war
Punishment of Germany
Lost 13% of territory, no military, 132 billion gold marks, surrender of all colonies
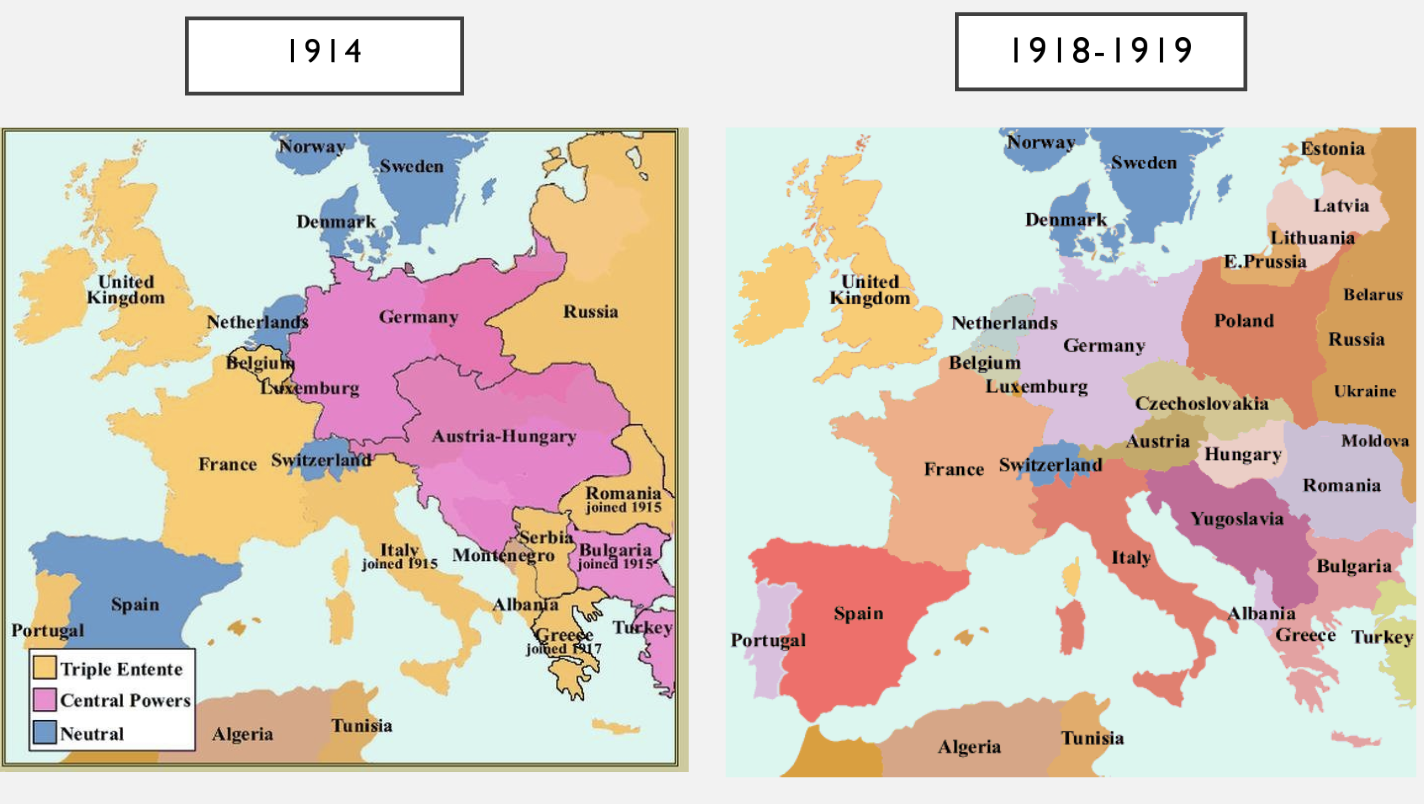
German War Reparations and Government Loans
Germany receives loans from the US to pay UK and France
Reparations used to rebuild France and Belgium and pay UK/US war debts
France occupies the Ruhr
France and Belgium intervene to take control of the Ruhr valley as Germany defaulted on reparations payments
Black Friday, The Crash, The Great Depression
International markets depend on America, when market bursts the whole system goes down
Fascism
Ultranationalism
Charismatic leadership (Mussolini)
Dictatorship (Do what I say)
Racism
Need outgroup to take out their anger on
For Nazi Germany, Jews
A single party
Everyone wants to be part of that party, Nazism
Paramilitism (Wield latent or external force)
Violence, actual or threatened (Outgroup fear of ingroup, Burning, notes, etc., Breaking windows of Jewish shops for Nazi Germany)
Corporatism
A totalitarian ideology
Anti-socialism/communism
Anti-liberalism
Anti-parliamentarianism
Anti-constitutionalism
Germany fascism
based on extreme racialism, outgroup Jews, Germanic speaking peoples have a spirit and behave in a certain way, so they do not fit into this, ultra-nationalistic, emphasizes state over individual, citizen’s loyalty to state and Fuhrer, war not peace is natural state of affairs
Nazi political program
unification of all Germans, Abrogation of the Versailles Treaty, only a member of the German race and German blood can be a citizen, Jews cannot be citizens, demand land and territory for our surplus population
Adolf Hitler
bitter over war’s end, Mein Kampf calls for creation of Lebensraum for German people in Eastern Europe, reworks Volksgeist to suit, chancellor of Germany 1933-1945, fall of Weimar and Rise of the Third Reich
Racial darwinism/eugenics in Nazi Germany
Forced sterilization
Nuremburg laws: marriages between Jews and citizens of German or kindred blood forbidden, Jews cannot employ female citizens under age of 45, forbidden to display the Reich and national flag or the national colors
Anschluss
the annexation of Austria by Nazi Germany in March 1938. The term, meaning "connection" or "joining" in German, was used to describe the political union of Austria with Germany.
Appeasement
the policy adopted by Britain and France in the 1930s, primarily led by British Prime Minister Neville Chamberlain, of making concessions to Adolf Hitler's Nazi Germany in an attempt to avoid war
Neville Chamberlain
British Prime Minister from 1937 to 1940, during the initial stages of World War II. He is most remembered for his policy of appeasement towards Nazi Germany, particularly the Munich Agreement of 1938, which aimed to avoid war by conceding to Hitler's territorial demands in Czechoslovakia
Phoney War
the period in World War II from late 1939 to early 1940 when there was a lack of major military action on the Western Front, despite Britain and France declaring war on Germany after its invasion of Poland
Kindertransport + Evacuations
pre-war rescue operation, primarily focused on Jewish children from Nazi-controlled territories, who were brought to the UK and other countries for safety
Blitzkrieg
a military tactic employed by Nazi Germany during World War II, characterized by swift, concentrated attacks using combined arms, primarily tanks and air power, to overwhelm and quickly defeat an enemy
Battle of Britain
first major defeat of Germany’s military forces, the Royal Air Force and the Fleet Air Arm of the Royal Navy defended the United Kingdom against large-scale attacks by Nazi Germany's air force, the Luftwaffe.
Winston Churchill
erved as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom during the majority of World War II, from 1940 to 1945, and again from 1951 to 1955. He is widely celebrated for his leadership during the war, particularly his inspiring speeches that rallied the British people and his role in shaping Allied strategy.
Petain and Vichy France
a collaborationist French government established after the fall of France to Nazi Germany in 1940. Vichy France governed the southern zone of France while the northern zone was under direct German occupation.
Lend-Lease Agreement
formally rendered the Neutrality Acts of the 1930s obsolete and provided Britain and its Allies with armaments, food and raw materials to continue fighting the war
Operation Barbarossa
invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and serveral of its European Axis allies during WWII
Rationing
implemented to manage scarce resources and ensure fair distribution of essential goods. It wasn't just food; clothing, fuel, and other items were also rationed. Rationing aimed to prevent shortages and inflation, and fostered a sense of community as everyone faced similar restrictions, families encouraged to grow their own food
Anderson shelters
air raid shelters used in the UK during World War II. They were designed to provide basic protection to civilians during air raids by being half-buried in the garden and covered with earth.
D-Day
Germany driven back into Western Europe by British, Americans, and their allies
VJ-Day + Hiroshima
marks the end of World War II following Japan's surrender on August 15, 1945. While the surrender is often associated with the dropping of atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki, VJ Day specifically refers to the announcement of Japan's surrender and the subsequent celebrations
Cold War
an ongoing political rivalry between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies that developed after World War II
Kristallnacht
German Nazis attack Jewish persons and property
Wanssee Conference (1942)
meeting of Nazi officials on January 20, 1942, in the Berlin suburb of Wannsee to plan the “final solution” (Endlösung) to the so-called “Jewish question” (Judenfrage)
Timeline for WWII
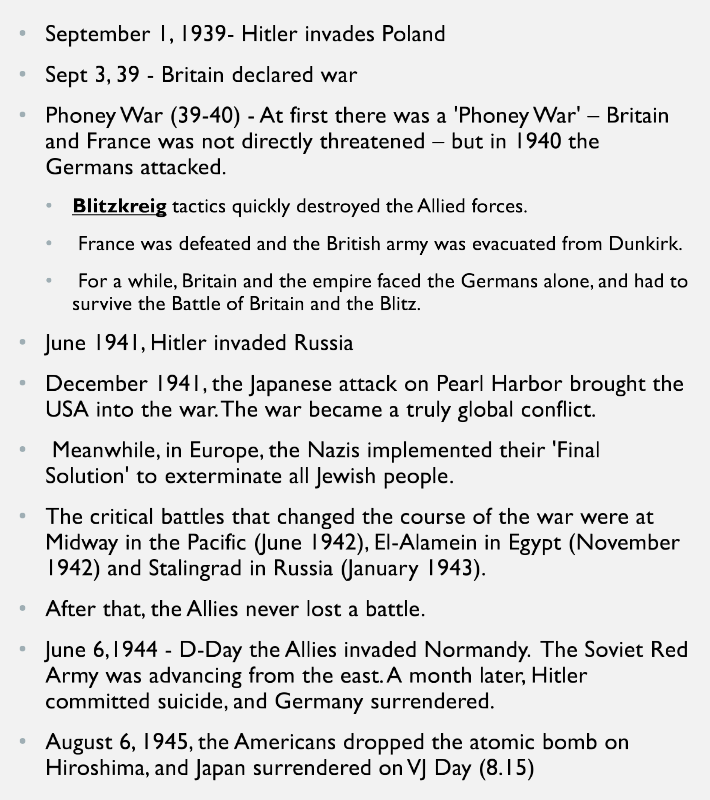
Phase I of WWII
Hitler conquers Poland, Germany, Britain, France begin to issue propaganda, Britain drops propaganda leaflets over Germany, all countries developing military bases and new technologies, people frustrated because there was no point in staying in the countryside when there were no bombs being dropped
Phase II of WWII
Nazis consquer Denmark, Norway, Holland, Belgium, France, Churchill becomes PM May 1940, delivers famous speech to House of Commons in Westminster, Petain (French president) sued for peace with Hitler, agreed to cede 3/5s of French territory to the Germans
Phase III of WWII
Britain withstood airforce in Battle of Britain, but Britain was alone and in danger of losing the war, bombed consistently for 76 nights, driven out of Greece and most of North Africa, ran out of $$$ and had to sign Lend-Lease agreements with America
Phase IV of WWII
Operation Barbarossa, German invasion of Russia brings them back into the war against Germany, Japanese bomb Pearl Harbor December 1941 and America is brought into the war, Allie gradually begin to win the war.
June 1942 Americans defeat the Japanese at Battle of Midway, November 1942 British win Battle of El-Alamein in Egypt, January 1943 Russians defeat Nazis at Battle of Stalingrad.
Phase V of WWII
Germany driven back into western Europe, Americans and British continue to bomb Germany, Russians advanced in Eastern Europe and reached Berlin, Hitler commits suicide and Germany surrenders. War continues in Japan for another three months, where Americans drop the atomic bomb on Hiroshima and Nagasaki in August 1945
Consequences of the war in Britain
50 million people (6 million Jews die)
Old empires of France and Britain end
Almost all old colonies of the British empire gain independence (wind of change)
America and Russia new superpowers (Cold War)
League of Nations —> United Nations
Welfare state
Dismantling of British Empire
Rationing remained until 1950s
Right over evil
Persecution
Kristallnacht, Jews herded into ghettos, Nazis begin to murder Jewish people in “einsatzgruppen,” Wannsee conference enacts Auschwitz camps
Genocide
1940: ghettoization
1941: wearing the star, 1 million murdered
1942: Wannsee conference, camps built
Roma, LGBTQ, mentally ill and disabled people, Slavic people
Post-memory and trauma
Marianne Hirsch
Explains trauma handed down generationally, reference and processes feelings of children and survivors of the Holocaust
Understanding popular culture in post war, post imperial Britain
Gap between high and popular culture is lessened
Barriers between arts and entertainment begin to diminish
Teenager sub cultures begin in post-war world
Links with mass culture
Working class culture depicted in arts: popular and high
Significance of football, popular music, fashion increase in national consciousness
British forms of popular music and film reemerge
Connection to older forms, especially music hall
Historical Context: 1950s
50s Rationing, money put into researching nuclear weapons, end of empire and fall from power, affluence and austerity, youth have disposable income and no fear of war, invention of the teenager, London overtakes Paris as cultural epicenter, American and Italian influence
Working class culture
Town and Planning Act, slum clearances, affluence, cheap homes, economic opportunities, Education Act 1944, “Angry Young Men” and Kitchen Sink Realism 1959, John Osborne, Look Back in Anger 1956, 1966 World Cup and George Best, Beatles/Yardbirds/The Who, Mary Quant and John Stephen
New Wave Films
drew attention to the realities of working class life, challenged social convention, pseudo-documentary style, shot on location, often with non-professional or new actors, usually set outside London but some may involve plots to relocate to London
Mary Quant and John Stephen
practical, fashion forward clothes for real life wear, cheap disposable fashion, menswear, traditional fabrics in non-traditional cuts, Carnaby St., model for current styles
Swinging Sixties
signifies a period of social and cultural change, characterized by a focus on modernity, hedonism, and a rejection of traditional norms
Teddy Boys
1950s
Ted (Edward)
Harkening back to the Edwardians 1901-1914
Longer frot coat
American bolo ties, swiffy hairdoes like Elvis Presley
Riot races Notting Hill 1958
“Hanging about,” dancing, fight at the dance?, uh…, groupthink
Rockers
Jeans, frot coat, quiff, leather coats, more metal, driving motorcycles
Nortons, triumphs
Caffs (cafe) → cheap place to go for brekkie
American influence
Hate mods
Mods
A different way of being working class
Preppy
Barracuda jackets
Vespa scooters, Italian influence
Coffeehouses, intellectual
Lots of mirrors for flare
Brighton:
Drugs, amphetamines
Rocker shows up, but as soon as I’m part of this group then I don't think I can be friends with you bc you are my enemy
Beatniks
Birth of Ska
Change into hippies by 1968
On the Road?
Mod jazz not regular jazz
Smoke pot, mushrooms soon
“Intellectuals of their generation”
Bob Dylan
Working class
May 1968
Students in Revolt, France
Esp in Europe
Post War Paris, Charles Dugall president
Very traditional, Catholic church
1965, women can get jobs without asking their husbands
Want to learn new things
Rise of identity politics: politics based on a particular identity, such as ethnicity, race, nationality, religion, denomination, gender, sexual orientation, social background, political affiliation, caste, age, education, disability, opinion, intelligence, and social class.
Workers connect with them to work in the street
Protests against Vietnam
Women’s Liberation
Contraception
Equal Rights
The Feminine Mystique
The Second Sex
1945: French women get the vote
1971: Swiss women
Thatcher in 80s: not many other women in politics until 90s
Domestic stuff comes back at the end of the war
Combahee River Collective Statement
1974: American women who are queer, Asian, Black, etc. finally hear from them
Wellesley, put together statement called Combahee river collective, confronts corporate powers as important material forces of oppression: “We realize that the liberation of all oppressed peoples necessitates the destruction of the political- economic systems of capital- ism and imperialism as well as patriarchy.”
Barbara Smith
Margo Okazawa-Rey
Devita Frazier
1919-1924 Decolonization
Propertied women get the right to vote, working class women still without the franchise, have won the war “never before, never since",” 1924: Height of empire and the Pax Britannica, 1924: Celebrated in the Wembley exhibition
Wembley
meant to stimulate trade and strengthen bonds that bind Mother Country to her Sister States and Daughters,
Woolf
When you have an empire and you have decided to invocate everyone with how you do things, generationally you want the people in the colonies countries to be like you
But once they do they are starting to think like you and they wonder why they do not have the same rights as you (letting the light in)
Africans in London
Come to London to change their home countries
Forming communities and making connections
Pan-Africa movement
Power of connections that change positions of Africans when they come back
Commonwealth
1926 Balfour Declaration: Canada, Australia, New Zealand, South Africa, freely associated as members of the British commonwealth of nations
Post WWII Empire and Decolonization
Britain is doing bad, barely surviving
Commonwealth Nationality Act: 1948, welcoming people into Britain, British citizenship
Home rule: government by its own citizens (IRELAND)
Ireland ruled by Parliament in Britain
Identity politics: people of same background form political alliances
Self-determination: a people’s right to form its own political entity
Civil rights: the rights that each person has in a society, whatever their race, sex, or religion, lawful element to that
See what is going on in the US regarding segregation and want better for themselves
France has most colonies because of Germans
Colossus of Rhodes: Cecil Rhodes
Many in 1960, 1956
The late ones: Portugal
Salazar refuses to let go because small country already
People flee because they did not want to fight the war in Africa
Phases of Decolonization in Africa
Economics
Europeans do not have money to support, sucked everything we can, taken people and trafficked them
Cannot sell manufactured goods because you are too poor to afford them
African efforts
Push to represent themselves
Self rule
Helped during WWII
African protest for self rule
Educated people come home to show how wrong everything is
Mau Mau Rebellion
Agricultural, pastoral place
Kikuyu tribe: pushed off lands because white farmers arrive and take land, forced into Nairobi which becomes overcrowded
Pissed because generational land
Tensions high for many years
Mau Mau want home rule
Others believe that Brits need to be here because otherwise they will lose job
All Kikuyu are all black
Meant to create sense of fear in the video, why would you bite the hand that feeds you?
White people in positions of power, Kikuyu working under them to get paid
Paint as uncivilized
Kwame Nkrumah
First prime minister of Ghana
Educated in London and America
Force behind Pan-Africa movement
Pictured with MLK and the Queen to emphasize his peacefulness and appeal to certain audiences
And wears cultural wear to appeal to the people of his culture
Becomes a dictator
The Struggle for Independence and Decolonization
Suez crisis: Israel, France, Britain, make secret deal to fuck Egypt over with the canal
Britain no longer world power, it is USA because they make decisions in the west and need to ask America first
1956 conclusion of British power
The Winds of Change Speech: free colonies from Africa by Africans
Republic of Ireland
Trying to get rule since 1550
Protestant Ascendency
Catholics subjected to penal laws
Rebellion
Ireland is controlled by Britain, takes away Parliament because Catholic
Civil war happens in Ireland because of partitioning, Catholics in northern Ireland upset, Protestant north and Catholic south
April 1949 ends British authority, 1948 act repeals external relations act and took Eire out of the Commonwealth
Partition of India
Gandhi tries in early 1900s
Hind Swaraj written
Muslims take part in movement
Al jinnah: Muslim leader
INC: Indian national congress to get rid of British rule
Muslims live in Pakistan
West and East Pakistan: forced migration forced by the British
East Pakistan becomes Bangladesh
End up immigrating around the old commonwealth
Diaspora big, Britain main locus
Indian shops established despite acculturation
Brick Lane 1978
Committed against Bangladesh community, 7,000 Bengalis marched from Brick Lane to 10 Downing Street, delivering a petition which called for police protection and an end to racial violence. It was led by young people, and was part of a fightback that helped turn the tide against far-right politics in the UK.
Altab Ali: murdered by three white east enders
Windrush
refers to the arrival of the ship HMT Empire Windrush at Tilbury Docks in June 1948, carrying over 800 passengers from the Caribbean to the UK. This event is symbolic of the wider Windrush generation, the Caribbean migrants who came to Britain between 1948 and 1971, many of whom were invited to help rebuild the country after World War II and fill labor shortages.
Enoch Powell
Rivers of Blood Speech, speaks out against continued immigration
Facism, generate fear against the outgroup
Brixton 1981
“Sus”pect laws
Walking around being black was enough to be stopped and searched
1973-79: Ongoing crisis
1973: EEC, European Economic Community (EU)
Founded 1957, France major figure
Meant to be an economic opening of borders between European countries
Britain joins later because Charles Dugall hates Britain because they did not do enough to help France
Britain gains better connections with Europe despite poor economic conditions
Oil Crisis
Yom Kippur War
War between Israel, Britain, France, America, Arab countries OPEC
Put embargo on them (stop shipment on oil)
Now Britain has no petrol and there is real pressure on how to get things going, depend on horses, nuclear energy, coal energy
The coal strike in 1973
Ban in November because government tried to manage the coal
All coal miners
Trade unions have so much power that the government tries to step in
Raise taken away from the coal miners again
3 day week
Response to coal strike
Less energy and electricity going around
Limited to three consecutive days a week of commercial usage
Stagflation
Both inflation and unemployment were high simultaneously. This was largely due to the oil price shocks and increased wage demands, which led to a contraction in supply and demand.
Higher rates of violence and sexual violence among youth because adults taking their jobs
IMF Loan
The Labour government sought a loan from the International Monetary Fund to meet deteriorating economic conditions.
The Fund demanded large cuts in public spending. After a bitter Cabinet battle, the Cabinet agreed, so ending plans to expand the economy and improve the social services.
Many believed that 1976 was also a crisis for democratic socialism, a philosophy which had sought social improvement through economic growth. That philosophy now appeared irrelevant during a period of austerity.
78-79 Winter of discontent
A period of widespread industrial action in the United Kingdom between late 1978 and early 1979, marked by strikes across various sectors, including public services, affecting essential services like refuse collection, healthcare, and even burials.
These strikes were primarily driven by workers seeking higher wages and a better standard of living, particularly amidst rising inflation and government wage controls
Sex Pistols God Save the Queen
Punk is born out of this movement
Queen’s Jubilee in this era, special anniversary, God Save the Queen
Serve as the anti-celebration, everything sucks!
Queen is very removed
Treats her subjects like shit, dehumanized
Moron because she is not educated, no opinion, cannot go out in the world, just a figurehead
Youth have no future because of the state of the world
Flowers in the dustbin: lack of support for the youth, growing in this shithole
Hear no evil see no evil: flag