chapter 42 - immunity
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
immune system
protection against pathogens
comprised of multiple organs and cells, each having a different role
pathogens
harmful organisms or viruses that cause disease
two major types of defense systems
innate/non-specific
adaptive/specific
innate/non-specific
always up and running/functioning, tries to protect against everything
adaptive/specific
needs to be activated, tries to protect against specific pathogens
has memory - activates quicker and stronger upon subsequent encounter with particular pathogen
innate/non-specific defense system
surface barriers
internal defenses
surface barriers
skin, mucous membranes
multilayered skin - normal flora “good bacteria” and secretions (salty, acidic, help suppress bacterial growth)
mucous membranes - mucus, lysozyme (breaks down bacterial cell wall & protects against gram positive bacteria), HCl (stomach)
mucous membranes
line digestive tract/passageways
line respiratory tract/passageways
line urogenital tract/passageways
ALL allow for access to outside world
internal defenses
phagocytes, NK cells, antimicrobial proteins, inflammation, fever
phagocytes
cells that engulf and digest foreign substances
ex: macrophages and neutrophils (carry out phagocytosis)
initial binding step is key
natural killer cells (NK)
contact and check cells
induce apoptosis in cancer or virus-infected (not 100% effective)
eosinophils
white blood cell
gathers around parasites
releases killing chemicals
inflammation
signaling molecule - leaky caps (increase blood flow) and recruit WBCs
4 cardinal signs
heat
swelling
redness
pain
fever
temporary increase in body temperature
increases speed of biochemical rxns
liver and spleen sequester iron and zinc
specific
looking for a particular pathogen
systemic
components are not localized to one place in the body
memory
if re-encounter the same antigen, then it can react quicker and stronger
HAS to be ACTIVATED
white blood cells
phagocytes
NK cells
eosinophils
neutrophils
two arms of specific immune system response
humoral and cellular
humoral
mediated by B lymphocytes/cells
produce an antibody based response or defense
cellular
mediated by T lymphocytes/cells
involves of a cell to cell response
generation of immune system cells
APC (antigen-presenting cell)
phagocytoses foreign invader - digests - displays fragments
stem cells
in red bone marrow
undergo cell division
differentiate or maintain line
progenitor lymphocytes
not fully mature
proliferate and differentiate to either B cells or T cells
B cells
plasma membrane: produce antibodies (ABs)
memory: B cells that will remain in the body long-term
these cells can activate more quickly; if re-exposed to the antigen
live about 3-5 days and then die
T Cells
Cytotoxic (Tc)
Helper (TH)
Suppressor T cells
Memory cells
Cytotoxic (Tc)
do the cell-to-cell killing
Helper (TH)
do communication among lymphocytes
Suppressor T cells
regulatory cells, tore down immune response toward end of infection
Memory T cells
these cells can activate more quickly; if re-exposed to the antigen
antigen
molecule that provokes immune response; usually foreign protein
could be sugar or lipid
could be protein from virus or pathogen
antigen challenge
bind SPECIFICALLY to the antigen
this neutralizes the antigen
non-active and active receptors proliferate
then differentiate into plasma cells and memory B cells
which create antibodies
antibody structure
immunoglobulins (Ig’s)
basic structure: 2 heavy chains (polypeptide, connected by disulfide bonds), 2 light chains
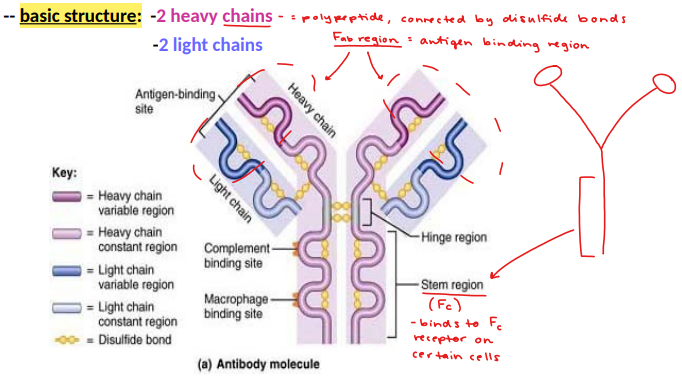
Fab region
antigen binding region
Fc (stem region)
binds to Fc receptor on certain cells
neutralization
antibody binds and masks dangerous parts of antigen
precipitation
antibodies crosslink antigens, take out of solution and enhances their phagocytosis
opsinization
antibodies serve as handles on antigens and pathogens
ENHANCES the initial binding phagocytosis
complement fixation
complement = family of proteins
pre-existing separately in blood plasma
enhances the insertion of MAC (membrane attack protein)
forms a pore
primary response
1st time response for this antigen
secondary immune response
stronger (higher antibody level)
faster (no lag)
longer-lasting (levels elevated longer)
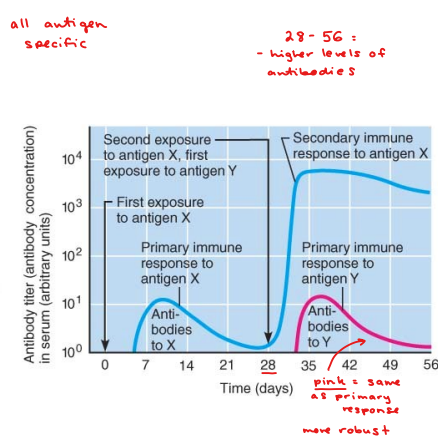
basis for vaccines
weakened form of antigen (e.g. attenuated virus)
primary response - memory cells
maybe give booster
self-antigens
Major Histocompatibility Complex Proteins (MHC Proteins, exist on surface of all cells - i.d badge) & HLA (Human Leukocyte Antigen)
group of glycoproteins on surface of an individual’s cells
unique to each individual, identify cells as “self”
usually not reactive with self immune sys, but strongly reactive to foreign immune sys
two classes of self-antigens
class I MHC
class II MHC
class I MHC
found on surface of nearly all body cells
usually display peptides from breakdown & recycling of body’s own cellular proteins
class II MHC
found on surface of certain cells of immune sys
APCs = antigen-presenting cells (dendritic cells, macrophages, B cells)
if dendritic cell…
exception: can have non-self antigen MHC I
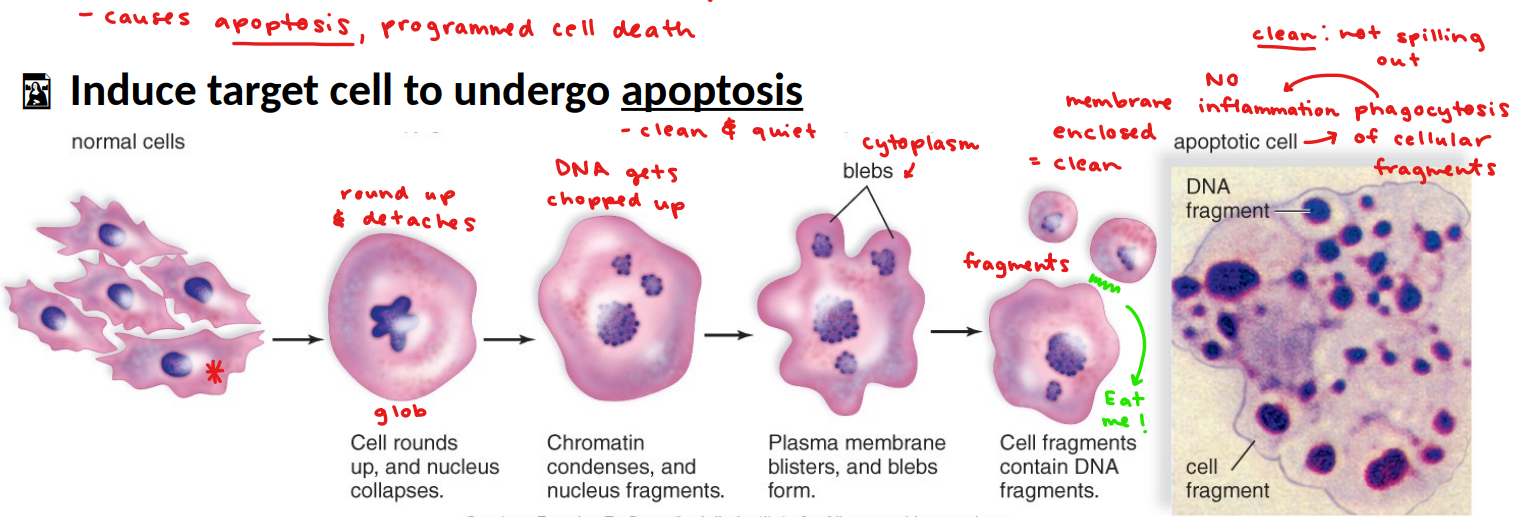
why undergo apoptosis?
cancerous cell: proteins are mutated
autoimmune disease: can’t distinguish self for non-self
failure of positive or negative
viruses: viral protein fragments, abnormal cell
perforin
protein released by Tc
inserts into membrane of target cells and makes pores
granzyme
enzyme that breaks down proteins in target cell
causes apoptosis
induce target cells to undergo apoptosis
central role of TH cells
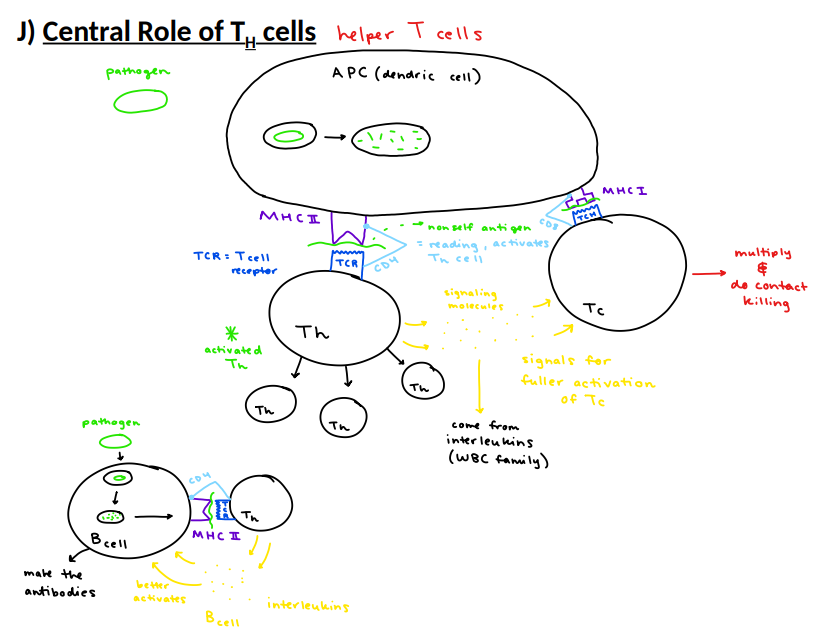
autoimmune disease
when fails to distinguish from self v non-self
over 100 of them
immune systems attacks own cells
type I diabetes
insulin dependent, autoimmune disease
immune system attacks and wipes out bet cells in pancreas
insulin released, peptide hormone
rheumatoid arthritis
autoimmune disease
infection and one agent have peptide sequence
immune system attacks joints
multiple sclerosis
autoimmune disease
immune systems attacks myelin sheath in neurons
myelin sheath
helps with insulation
no insulation = slows down signals, base axons have short circuiting
prednisone
fat and water retention, loss of bone mass
dexamethasone
stimulates suppressor T cells
allergies
not autoimmune
allergens = antigens that provoke an allergic immune system response
MADGE (different classes of antibodies)
IgM
IgA
IgD
IgG
IgE
histamine
causes leaky capillaries
increase mucous, trying to flush out
smooth muscle constriction
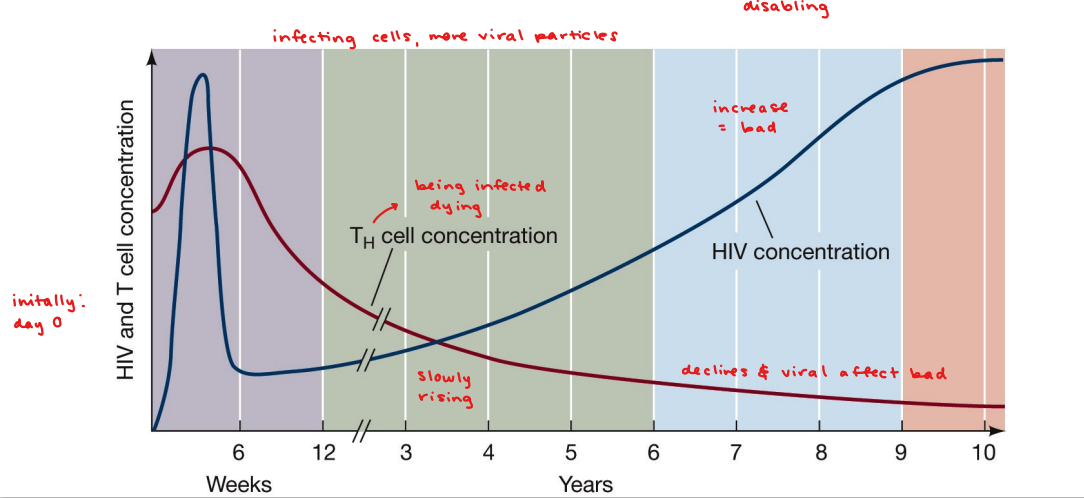
HIV
human immunodeficiency virus
causes AIDS
infect macrophages (integrates viral DNA into host DNA)
production, assembly, exit - doesn’t hurt macrophages
eventual mutation of HIV coat protein (gp120)
makes virus able to infect TH cells - exiting kills TH cell