Polymer Physics Final
1/330
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
331 Terms
number average, weight average, viscosity average, z-average
four ways to calculate the average molecular weight of a polymer
different lengths and numbers of side branches
reasons that polymers have a distribution of molecular weights instead of one value
number average
in the general molecular weight formula was does k = 0 mean
weight average
in the general molecular weight formula was does k = 1 mean
z-average
in the general molecular weight formula was does k = 2 mean
viscosity average
which molecular weight average cannot be found using the general formula
Mk = (sum(NiMi^(k+1))/sum(NiMi^k)
general molecular weight form
number average molecular weight
the total weight of polymer divided by the total number of molecules
end group analysis, osmometry, ebullioscopy (boiling point evaluation)
three ways that number average molecular weight can be determined directly
weight average molecular weight
depends on the weight of the weight of the molecules as well as the number molecular weight
light scattering measurements
way that weight average molecular weight can be determined experimentally
polydispersity index (PDI)
measure of the distribution of molecular weights within a sample
>= 1
values of PDI
PDI = Mw/Mn
equation for PDI
the weights of all the molecules are the same
what does it mean if PDI = 1
combination of diffusion and sedimentary measurements
how can the z-average molecular weight be determined experimentally
the presence of high molecular weight chains
what is the z-average molecular weight sensitive to
dilute solution viscosity measurements
how is the viscosity average molecular weight determined experimentally
Mv = [sum(NiMi^(1+alpha)/sum(NiMi)]^(1/alpha)
equation for the viscosity average molecular weight
the shape of the molecule in the the solution
what does alpha represent in the viscosity average molecular weight equation
Mw=Mv
what happens when alpha = 1 in viscosity average molecular weight
Mz>Mm>Mv>Mn
for a typical polymer with alpha<1, rank the average molecular weights from largest to smallest
absolute, equivalent, relative
three characterizations for methods used to determine molecular weight in polymers.
measurement is directly related to molecular weight without assumptions
what makes a mw determining type absolute
the chemical structure of the polymer must be known to obtain molecular weight
what makes a mw determining method equivalent
a calibration curve relating measurement to molecular weight must be known
what makes a mw determining method relative
membrane osmometry, ebullioscopy, cryoscopy, analytical ultracentrifugation, static light scattering
five absolute mw determiners
end group analysis
equivalent mw determiner
solution viscosity, gel permeation chromotrography
relative mw determiners
10^4-10^6, Mn
membrane osmometry molecular weight values and mean value measured
<10^4, Mn
ebullioscopy molecular weight values and mean value measured
<10^4, Mn
cryoscopy molecular weight values and mean value measured
<10^5, Mn
end group analysis molecular weight values and mean value measured
10³-10^8, Mw, Mz
analytical ultracentrifugation molecular weight values and mean value measured
10²-10^8, Mw
static light scattering molecular weight values and mean value measured
10²-10^8, Mv
solution viscosity molecular weight values and mean value measured
10²-10^7, different values
gel permeation chromatography molecular weight values and mean value measured
colligative properties
properties of solutions that depend on the ratio of the number of solute molecules (polymer molecules) to the number of solvent molecules in a solution
freezing point depression, boiling point elevation, vapor pressure lowering, osmatic pressure
four types of colligative properties
lower
compared to pure solvent, freezing point is
higher
compared to pure solvents, boiling point is
lower
compared to pure solvent, vapor pressure is
reduced
compared to pure solvent, chemical potential is
molality of solute
freezing point depression and boiling point elevation are directly proportional to
mole fraction
vapor pressuring lower is directly proportional to
cryoscopy
freezing point lowering can also be called
(deltaTc/C)(C to zero) = (RTf^2)/rhodeltaHfMn + A2C
equation for freezing point depression
latent heat of fusion, density of the solvent, freezing point depression, freezing point of solvent
in the equation for freezing point depression what is deltaHf and rho and deltaTf and Tf
number of solute molecules dissolved per unit volume
what does freezing point depression depend on
ebulliometry
also called boiling point elevation
deltaTb, Tb, and deltaHv
what are the differences from the freezing point depression equation to boiling point elevation equation
latent heat of vapor
what is deltaHv in boiling point elevation equation
20000
for boiling point elevation the limitation of Mn is below
low observed temp differences for low concentrations of a polymer in molecular weight range of greater or equal to 20000 and lack of development of equipment
why are ebulliometric and cryoscopic measurements unattractive and less useful
4×10^-3 mmHg pressure
for polystyrene dissolved in benzene what is the vapor pressure depression
1.3×10^-3 deg C temp difference
for polystyrene dissolved in benzene what is the boiling point elevation
2.5×10^-3 deg C temp difference
for polystyrene dissolved in benzene what is the freezing point depression
1.5 cm height difference
for polystyrene dissolved in benzene what is the osmotic pressure
pi/c = RT(1/Mn + A2c + … )
what is the equation for real solutions for osmometer
gravity, difference in heights, solvent density, osmotic pressure
what is g, deltah, rho, and pi in the osmometer equation
second virial coefficient
what is A2
good solvent
what kind of solvent what A2 > 0
theta solvent
what kind of solvent when A2 = 0
poor solvent
what kind of solvent when A2 < 0
RT/Mn
what is the intercept
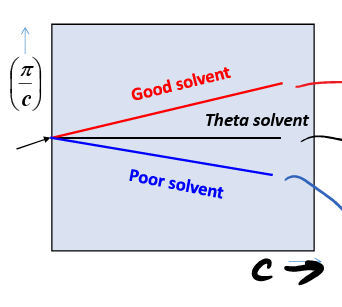
remains coiled and minimizes mixing
what happens when a poor solvent is used
maximizes mixing
what happens when a good solvent is used
polymers prepared by step polymerization since they have characteristic end groups
what kind of polymers is end group analysis suitable for
-OH and -COOH
what kind of end groups do polyesters have
-NH2 and -COOH
what kind of end groups do polyamides
ultracentrifugation
heavy and large particles settle at the bottom of the solution by process of sedimentation
frictional drag, buoyant force, gravitational force
what are the forces acting on a particle in ultracentrifugation
Ff = fu, frictional coefficient, velocity of particle
what is the equation for frictional drag and what are the variables in ultracentrifugation
Fs = m(omega^2r), mass, angular velocity, distance from the axis of rotation
what is the equation for gravitational/sedimentary force in ultracentrifugation
Fb = m0vbarr, mass of fluid displaced, specific volume, distance from axis of rotation
what is the equation and variables for buoyant force in ultracentrifugation
s = u/(omega^2r)
what is the equation for the sedimentation coefficient
the velocity of the particle per unit gravitational acceleration
what is the sedimentation coefficient
rate of spreading
what do you need to measure in ultracentrifugation to determine the diffusion coefficient
Mw = s/D(RT/(1-vbarrho))
what is the equation for weight average molecular weight from ultracentrifugation aka the svedberg equation
sedimentation coefficient and diffusion coefficient
what are the two coefficients that you need for molecular weight with ultracentrifugation
D = RT/Nf
what is the equation for diffusion coefficient ultracentrifugation
gel permeation chromatography, size exclusion chromatography, gel filtration chromatography
what are the types of chromatography used
molecular weight distribution
what is gel permeation chromatography (GPC) the only technique for characterizing
the strength and toughness of the polymer
as Mw/Mn decreases what increases
it becomes more difficult to process
as Mw/Mn decreases what happens negatively
pump, injector, columns, detector, data collection
what are the five stages of GPC
GPC
what is this the calibration for
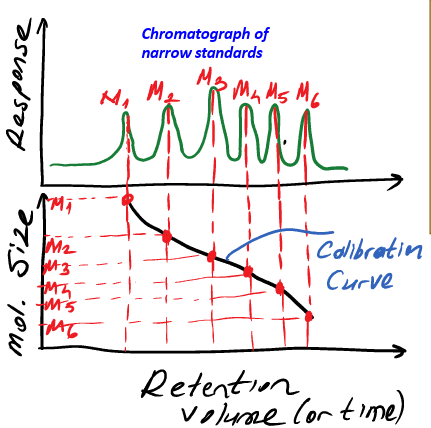
the column set used
the calibration curve in GPC is characteristic to what
it separates on the basis of molecular size not molecular weight
what is the main limitation of GPC
identical molecular weights dissolved in suitable solvent
in GPC what is this illustrating
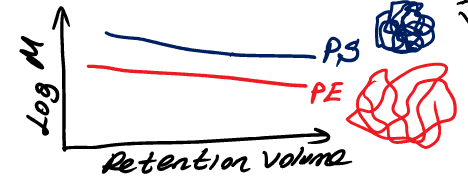
use both a viscometer detector along with a concentration detector
how do you avoid the convention GPC problem that it can only be used for a specific polymer that was used to find the calibration curve
property of isolated polymer coil solution as concentration tends to zero
intrinsic viscosity is
molecular density
intrinsic viscosity is inversely proportional to
eta = limctozero(etasp/c)
what is the huggins equation for intrinsic viscosity
eta = limctozero(lnetarel/c)
what is the kramer equation for intrinsic viscosity
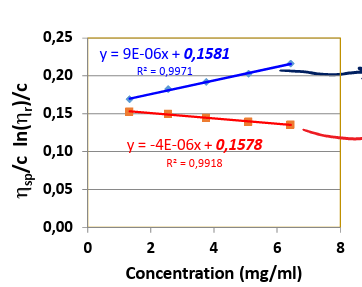
huggins
which equation is used for the top line
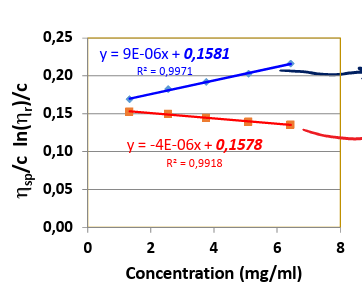
kramer
which equation is used for the bottom line
volume/mass
intrinsic viscosity is proportional to
lower IV is a more compact structure therefore higher density
how does branching affect IV and why
density decreases so IV increases
how does increasing length affect IV