Visualizing Human Bio Ch 21
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Inheritance, genetics, molecular bilogy
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
What are genes responsible for?
Genes determine traits, appearances, and some aspects of intellect.
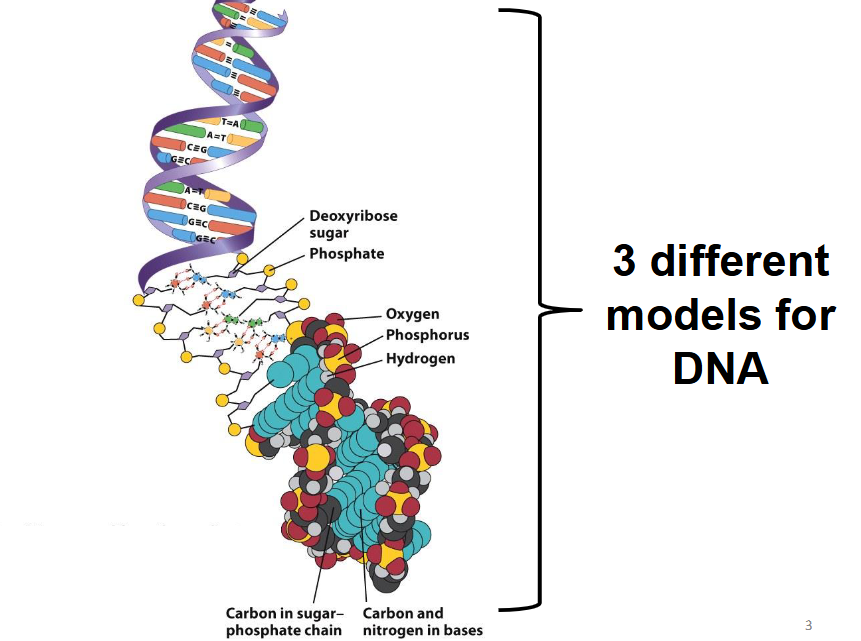
What is the primary component of genes?
Genes are made of DNA strings.
Where are genes and DNA located in the body?
In the nucleus of every cell.
How many estimated genes are in the human body?
About 20,500.
What do genes contain the information to make?
Proteins needed by the body.
What percentage of genetic material do humans share?
More than 99%.
What is the total number of chromosomes in humans?
46 individual units (23 pairs).
Who is Gregor Mendel?
A monk who studied the inheritance of traits in plants, particularly garden peas.
What did Mendel control in his experiments?
The process of fertilization to understand inheritance.
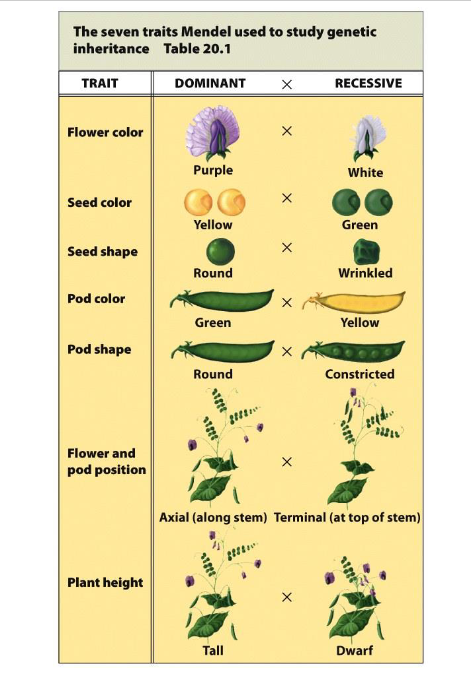
What terms did Mendel introduce through his experiments?
Dominant and recessive.
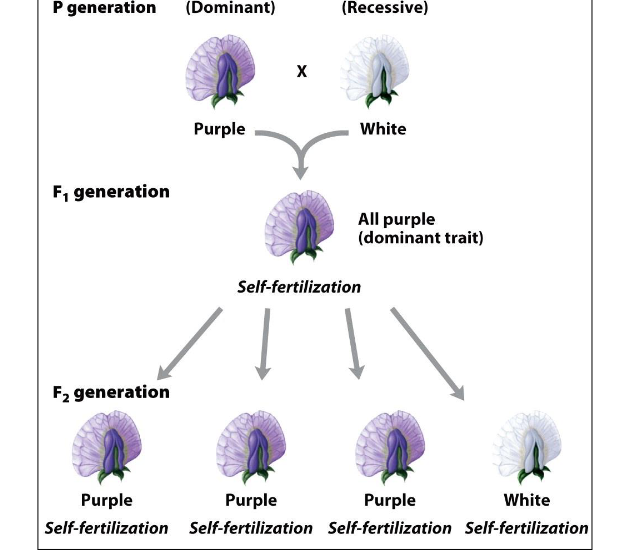
What is Mendel's Law of Segregation?
The random separation of parental 'heritable units' during gamete formation.
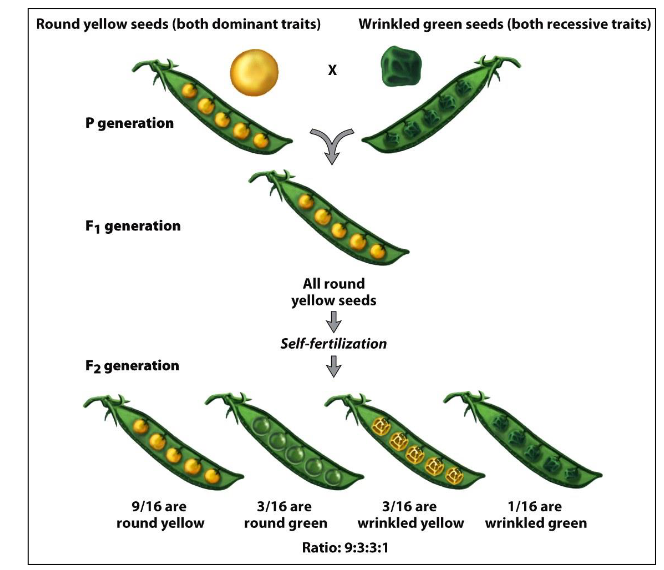
What is the Law of Independent Assortment?
Each trait is carried in gametes as a separate entity, unaffected by other traits.
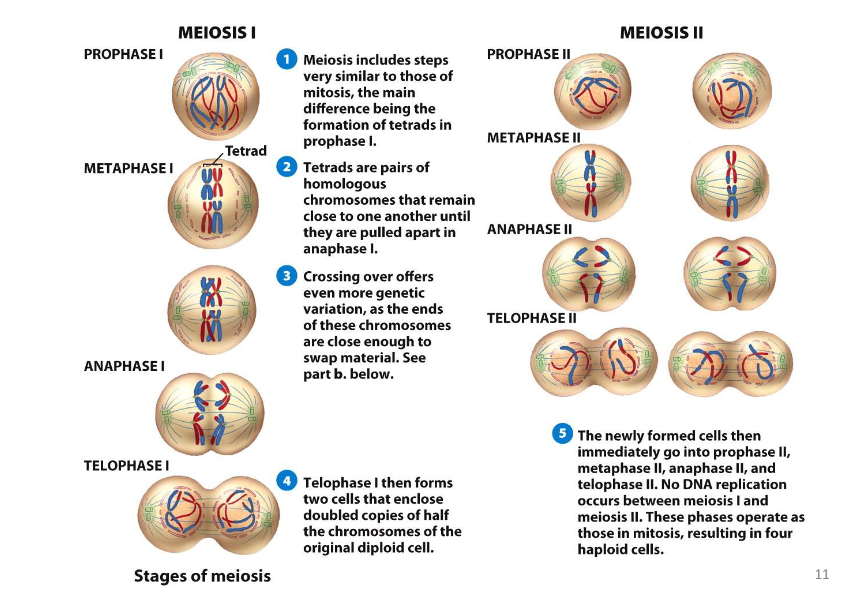
What is the significance of meiotic cell division?
It ensures each gamete has a predictable and reliable half of the chromosomes.
What is a genotype?
The complete set of genes that determines an individual's traits.
What is a phenotype?
All observable traits or characteristics of an individual.

What are alleles?
Alternative forms of a gene that can be identical or slightly different.
What does it mean if an individual is homozygous?
They have two identical alleles for a trait.
What is the difference between homozygous dominant and homozygous recessive?
Homozygous dominant has two dominant alleles (AA), while homozygous recessive has two recessive alleles (aa).
What is a heterozygous genotype?
A genotype with one dominant and one recessive allele (Aa).
How do small differences in alleles affect proteins?
They can lead to the production of different proteins from genes.
What is the role of environmental factors in determining phenotype?
They interact with the genotype to shape observable traits.
What is the significance of Mendel's work in genetics?
It laid the foundation for the science of genetics, although its importance was not recognized for decades.
What phenotype is expressed by homozygous recessive individuals?
A recessive phenotype
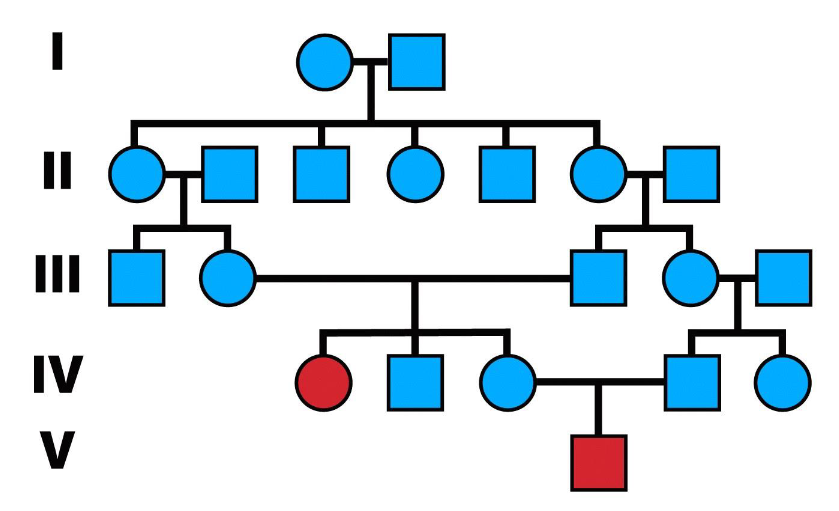
What do pedigree charts represent?
The genetic transmission of phenotypic traits through families
What does it indicate if a heritable disease appears in a child of two asymptomatic parents?
The disease is probably autosomal recessive, and both parents are heterozygous carriers.
What is incomplete dominance?
A genetic scenario where the phenotype is intermediate, such as wavy hair from straight and curly parents.
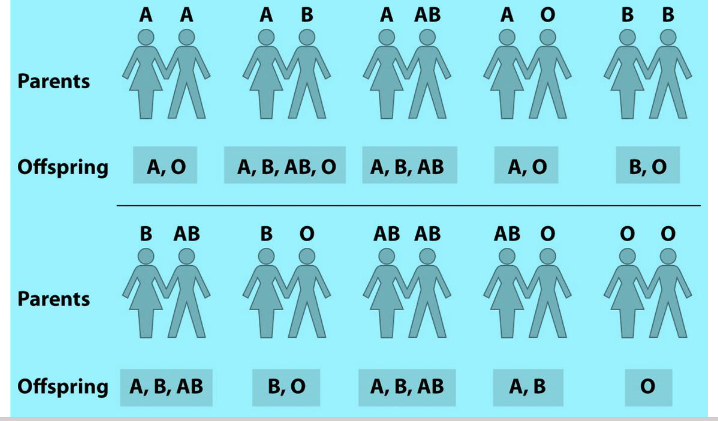
What is codominance?
A situation where both alleles are expressed in the phenotype, such as in blood type inheritance.
What are sex chromosomes?
Chromosomes that determine gender, including the X and Y chromosomes.
How does the presence of a Y chromosome affect fetal development?
If a Y chromosome is present (XY), the fetus develops as male; if absent (XX), it develops as female.
What are autosomes?
Any chromosomes other than the sex chromosomes.
What complicates the inheritance pattern of sex-linked traits?
The X and Y chromosomes carry different traits and have different numbers of alleles.
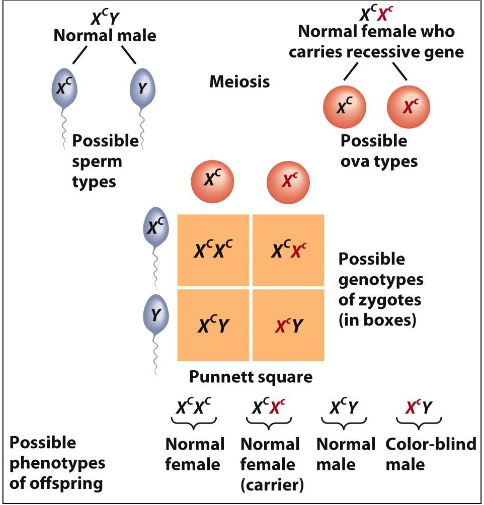
What is a Punnett square used for?
To determine the probability of genotypic combinations in offspring and predict phenotypic ratios.
What is the role of genes in protein formation?
Genes direct the formation of proteins through the processes of transcription and translation.
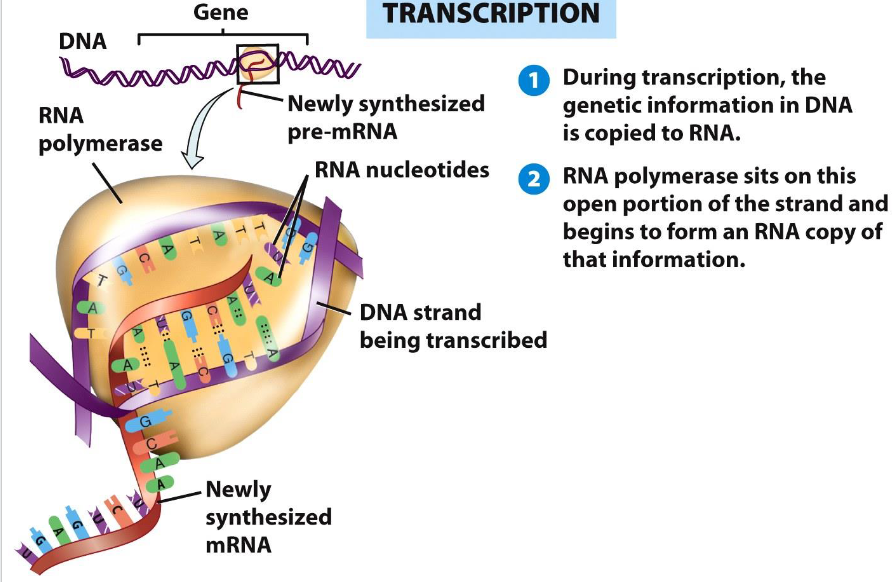
What happens during transcription?
A sequence of nucleotide bases in DNA is copied to messenger RNA (mRNA).
What is translation in the context of protein synthesis?
The process of converting mRNA information from nucleic acid language to amino acid language.
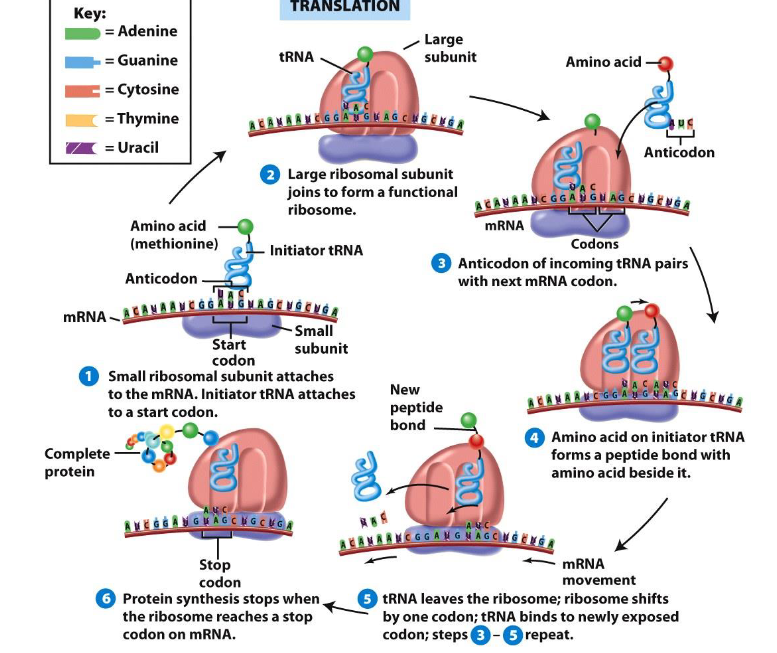
What are codons?
Three bases on mRNA that indicate one of the 20 amino acids.
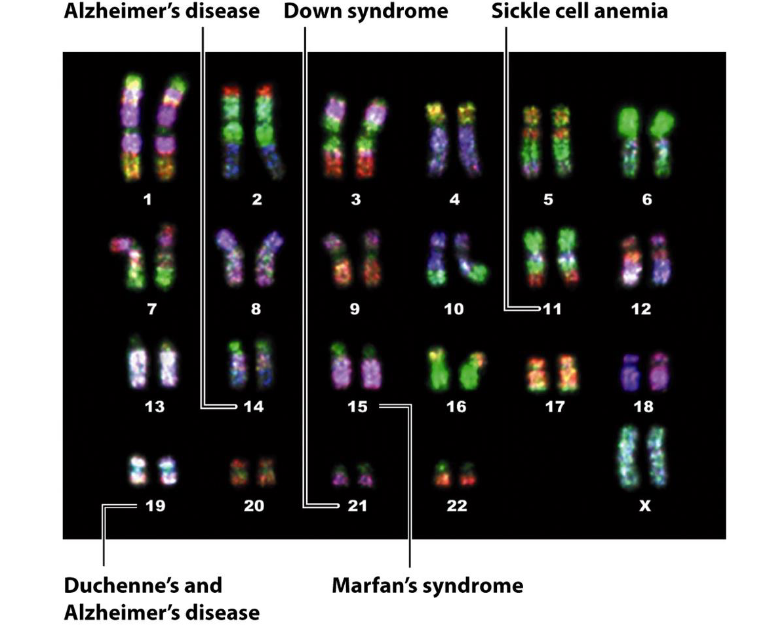
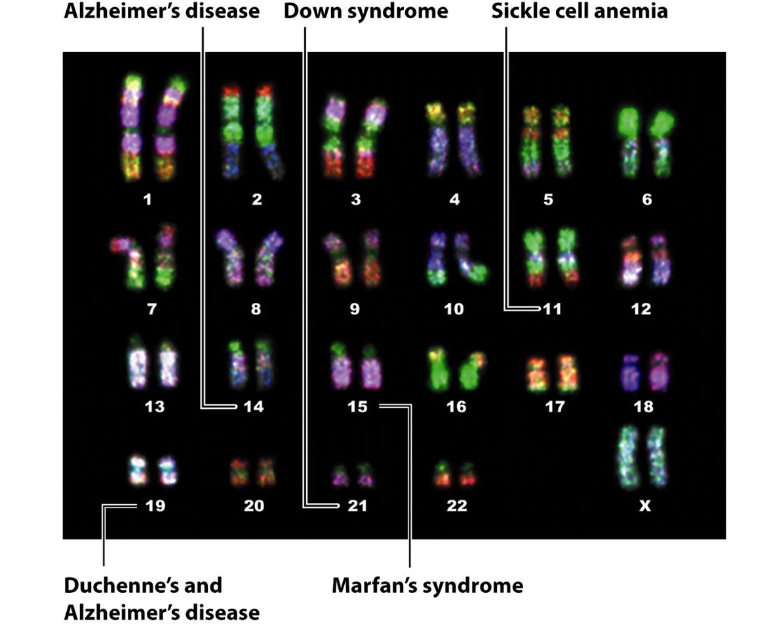
What are chromosomal disorders?
Genetic variations due to mutations affecting chromosome structure or number.
What is genetic counseling?
The practice of predicting potential allele combinations from two individuals.
What can genetic counseling help with?
It can help couples understand the probability of having a child with a genetic anomaly.
What is an example of a multifactorial trait?
Traits like body type, muscular development, fat deposition, and height.
What is the significance of the X chromosome in sex-linked traits?
It carries many more functional genes than the Y chromosome, affecting traits like color blindness.
What is the outcome for a female carrier of a color blindness allele?
She will not express color blindness but can pass the allele to her sons, who may be color-blind.
What are multifactorial traits?
Polygenic traits influenced by environmental factors.
What is the role of transfer RNA (tRNA) in translation?
tRNA matches amino acids with mRNA bases during protein synthesis.
What is the relationship between DNA and mRNA?
mRNA is synthesized from DNA during transcription and carries genetic information to ribosomes.
What are the two steps of protein formation?
Transcription and translation.
What is an example of a chromosomal disorder?
Down syndrome.
What does it mean if a trait shows incomplete dominance?
The phenotype is a blend of both alleles, rather than one being completely dominant.
What is the effect of a recessive allele in a heterozygous individual?
The dominant allele masks the expression of the recessive allele.