Surgery Lecture 23
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Orthopedic Surgery I: Bone Structure, Biomechanics, and Fracture Healing
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
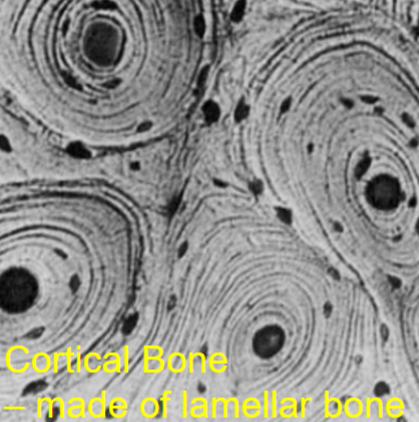
What is cortical bone
Compact bone found in the shaft of long bones, made of lamellar bone
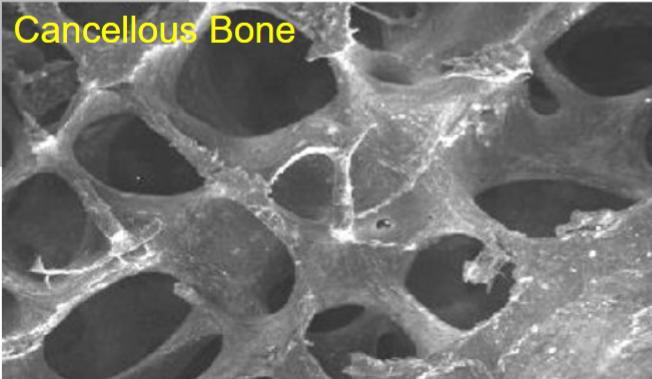
What is cancellous bone?
Trabecular bone found in the center and ends of long bones and flat bones, made of lamellar bone
Lamellar Bone
Major portion of cortical and cancellous bone, deposited layer upon layer (slow rate of formation; remodelling)
How much lamellar bone do osteoblasts form per day?
2 um
Woven Bone
Bone that occurs during rapid growth, rapid bone repair, and at insertions of tendons/ligaments; mechanically inferior to lamellar bone
Periosteum
Outer fibrous layer covering bones (except where covered by cartilage), containing an inner osteogenic layer
Haversian Canals
Channels within bone that contain blood vessels
Volkmann's Canals
Connect Haversian Canals
Bone Cells
Osteocytes, osteoblasts, and osteoclasts
Hydroxyapatite
Inorganic part of bone matrix (71% of wet weight), composed of calcium and phosphorus
Osteoid
Organic matrix of bone (21% of wet weight), mostly Type I collagen; made by osteoblasts
Membranous Bone Formation
Ossification by direct mineral deposition into the organic matrix of mesenchymal connective tissue
Used for skull, mandible, and appositional growth
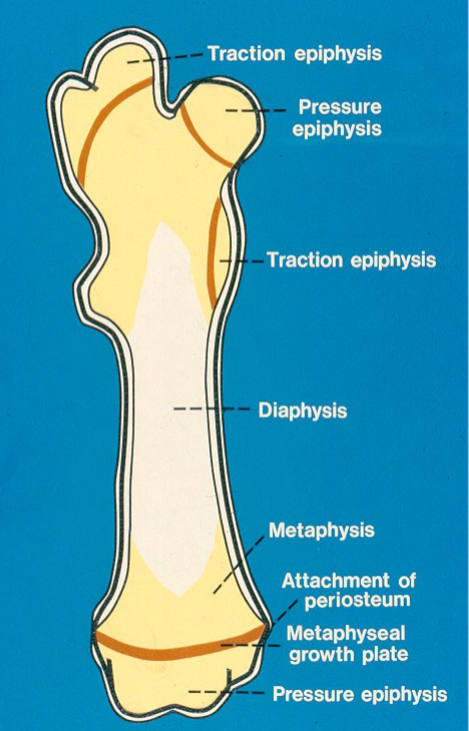
Endochondral Bone Formation
Cartilaginous template formed first, then transformed via calcification and replacement by bone
Used for longitudinal growth of long bones.
What are the 3 growth cartilage types?
Discoid growth plate → longitudinal growth
Sperical growth plate → centrifugal growth
Apophysis → traction epiphysis
What are the different zones of growth cartilage?
Resting / Reserve zone
Proliferative zone
Hypertrophic zone
Calcification zone
Ossification zone (primary spongiosa of bone)
Wolff's Law
Bone adapts to the loads placed on it, increasing mass where needed and decreasing where not needed
What curves are used to demonstrate biomechanisms of bone?
Load deformation curve
Stress-strain curve
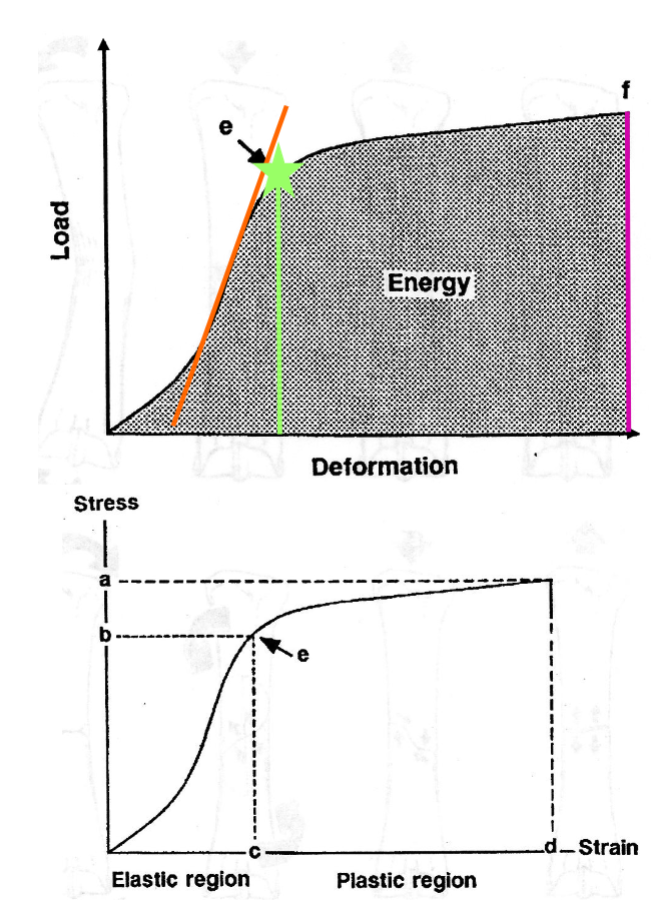
What are the loading modes of bone?
Bending, torsion, shear, tension, and compression
Failure configurations in bone
Transverse
Oblique
Butterfly fragment
Spiral
Causes of Bone Fractures
Single ultimate failure load
Repeated cyclic loading
Fracture Classifications
Complete vs. incomplete
Displaced vs. non-displaced
Open vs. closed
What are the 3 open fracture classifications?
Type 1: small skin laceration without bone exposure, no gross contamination
Type 2: skin laceration with little tissue loss, inimally exposed bone, minimal gross contamination
Type 3: extensive laceration, significant tissue loss, extensive gross contamination
What are different fracture configurations?
Fissure/hairline/greenstick
Transverse
Oblique
Spiral
Comminuted/compound
Avulsion
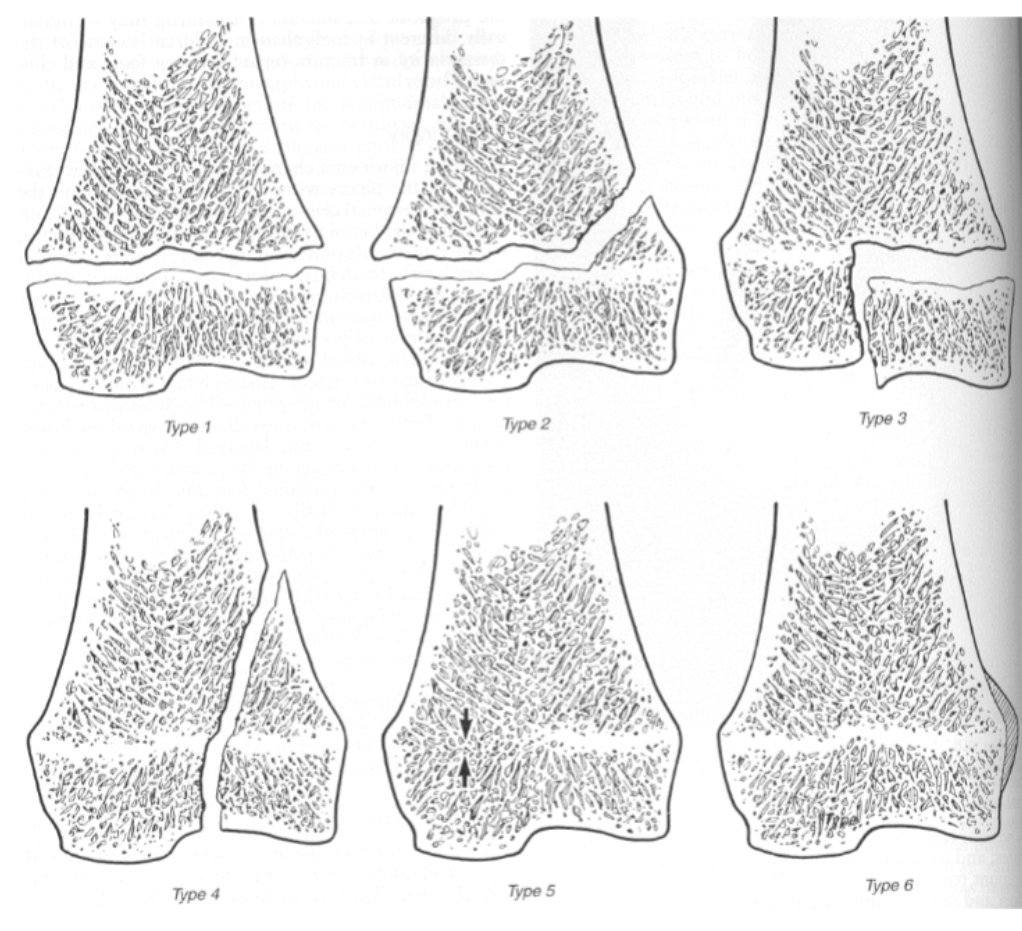
Salter-Harris Classifications (all)
Type 1: Complete separation of the physis
Type 2: Physeal Fx breaks out in metaphysis
Type 3: Intra-articular Fx, through epiphysis and physis
Type 4: Intra-articular Fx through epiphysis, physis, and metaphysis
Type 5: Crushing injury leading to closure of physis in limited area
Type 6: Periosteal bridge between metaphysis and epiphysis slows growth on affected side
What are the 2 types of bone healing?
Primary / direct Fx healing
Secondary / indirect Fx healing
Primary/Direct Fracture Healing
Rigid internal fixation, adequate reduction, and sufficient blood supply leading to fracture ends uniting via Haversian remodeling
Secondary/Indirect Fracture Healing
Small movement in fracture gaps
Healing via periosteal, intercortical, and endosteal callus formation
Describe sequence of bone healing
Hematoma → granulation tissue → fibrous tissue→ fibrocartilage → mineralized → woven bone → lamellar bone
Describe the elongation interfragmentary strain tolerance on granulation tissue, cartilage, and bone
Granulation tissue - 100%
Cartilage - 10-15%
Bone - 2%
Describe the bending interfragmentary strain tolerance on granulation tissue, cartilage, and bone
Granulation tissue - 40 degrees
Cartilage - 5 degrees
Bone - 0.5 degrees
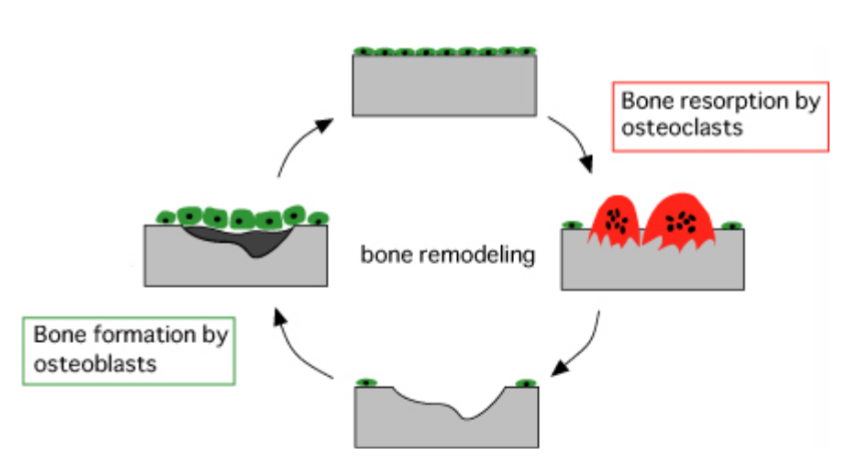
Phases of Bone Healing
Inflammatory
Reparative
Remodeling
Describe inflammatory phase of bone healing
Vasodilation, leukocyte migration, chemotaxis
Mesenchymal cell proliferation, angiogenesis
2-3 weeks post injury
Describe reparative phase of bone healing
Overlaps with inflammatory phase
2-12 months duration
Repair tissue highly vulnerable to interfragmentary motion
Periosteal and endosteal callus formation by endochondral and membranous ossification
Describe remodeling phase of bone healing
Overlaps with reparative phase
Ostional remodeling
fracture gap(s) widen ___-___ weeks post injury
2-3
Size of callus reflects degree of _______ motion but may not predict degree of Fx ________
interfragmentary;
stability
Ultimate Goals of Bone Healing
Reconstruction of original cortices
Early return to total limb function
Rapid bone union
Prevention of fracture disease
What are examples of fracture diseases?
Soft tissue contracture
Loss of muscle
Osteopenia
Loss of joint function - prevent OA
Contralateral limb disease - breakdown or laminitis
Malunion / nonunion
Most Desirable Type of Bone Healing
Primary fracture healing by Haversian remodeling rather than callus formation, achieved by rigid fixation, adequate reduction, and preservation of blood supply
Advantages & disadvantages of Plating
Advantage
Direct bone union if fracture compression
Stress protection
Rigid fixation
Adequate reduction
Disadvantage
Disrupt periosteum and Fx hematoma to apply
Biologic Osteosynthesis
Closed reduction + external fixator
Encouraging early callus growth
Emphasizes preservation of blood supply over anatomic reconstruction
Provide for early dynamization to stimulate callus growth
Difficult in horses-large biomechanical stress often dictates fixation technique
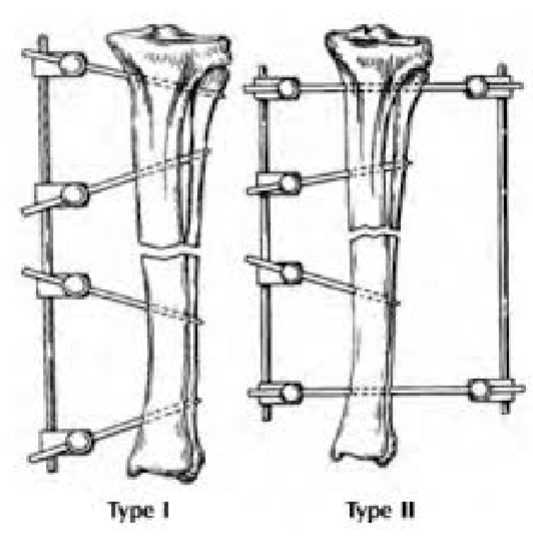
Dynamization
Strategic reduction in rigidity of fixation to allow micromotion of fracture ends, ONLY in smaller animals
Main Functions of Bone Grafts
[OOO]
Osteogenesis → by fresh osteoblasts
Osteoinduction → growth factors, cytokines
Osteoconduction → matrix scaffold
Types of Bone Grafts and Replacements
Autogenous fresh cancellous bone grafts
Cortical bone
Bone replacements (hydroxyapatite, tricalcium phosphate, etc.)
Growth factors (BMP-2)