AP Bio Unit 7
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
UNIT 7
Natural Selection
What is evolution?
change in allele frequencies in a population over time
What is a population?
One species living together
What are the five microevolutionary forces?
1. Mutation
2. Natural selection
3. Sexual selection
4. Gene flow
5. Genetic drift
What observations did Darwin make about the Galapagos?
1. Overproduction: more babies than the environment can support
2. Limited resources: habitat, food, and mates are not infinit
3. Variation: no two individuals are the same
4. Conclusion: individuals best suited for the environment live longer and have more babies
What is fitness?
ability to survive and reproduce to pass genes on
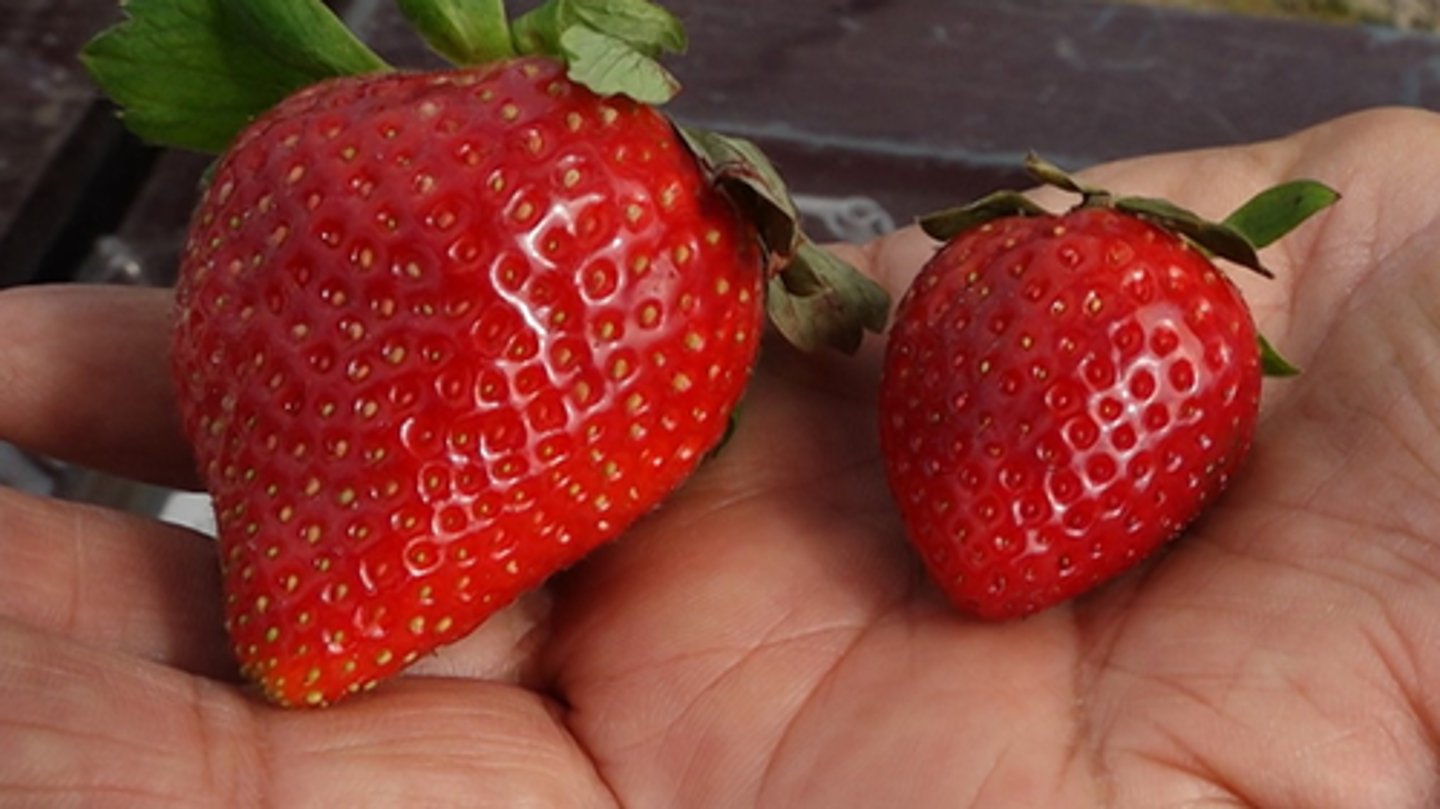
What is artificial selection?
Selective breeding by humans
Ex: Strawberries have been selectively bred to be really big

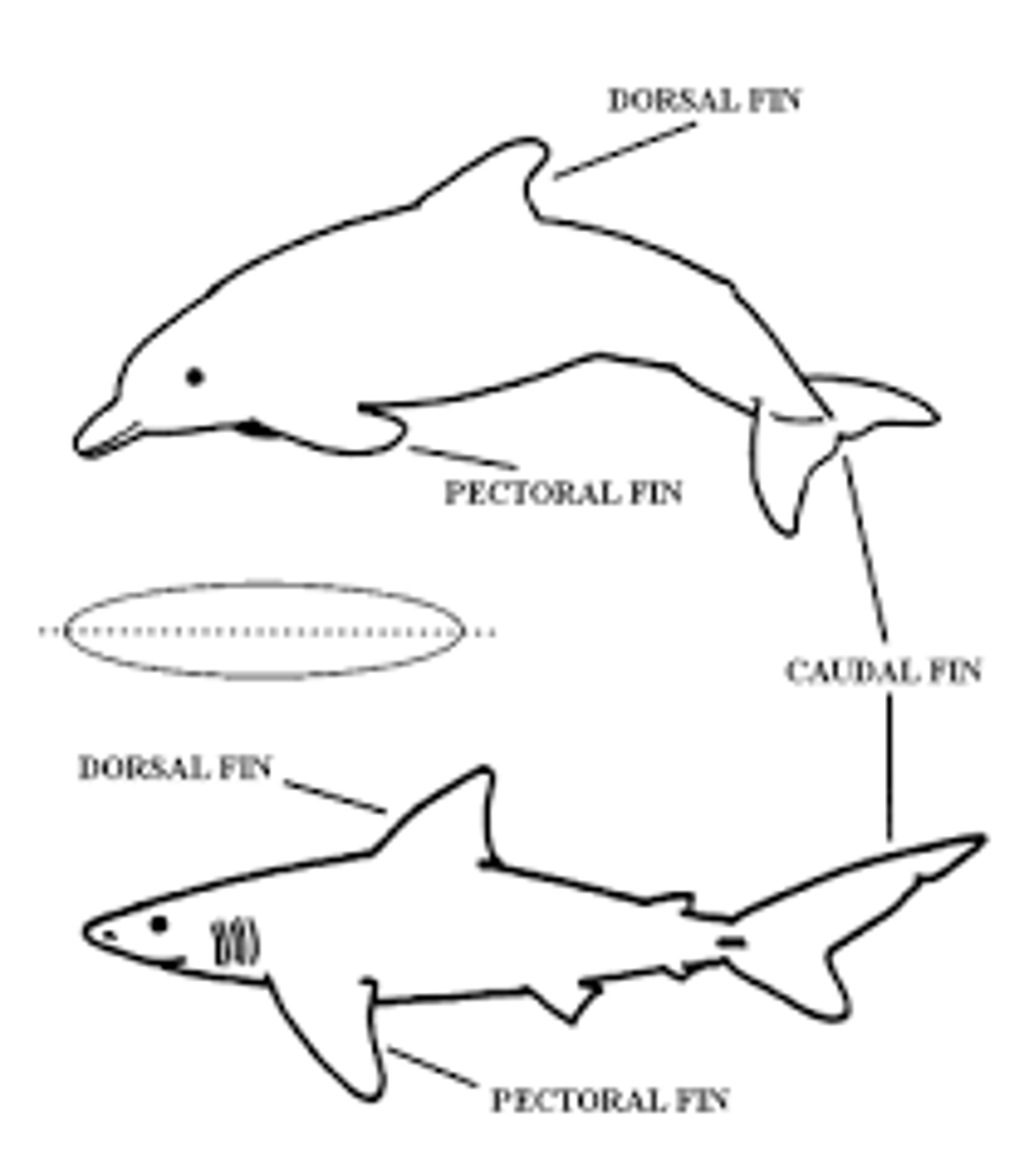
What is convergent evolution?
Similar environments lead to similar phenotypes.
Ex: dolphins look like sharks, not closely related though
What is sexual selection?
Sexiest animals have the most babies
Ex: in humans, breast size, hip size, head size, and smell can all be indicators on if someone would be better to have kids with
What is genetic drift?
When random events drive evolution.
This is more common in small populations because an individual in a small population dying has a greater effect than an individual dying in a large species
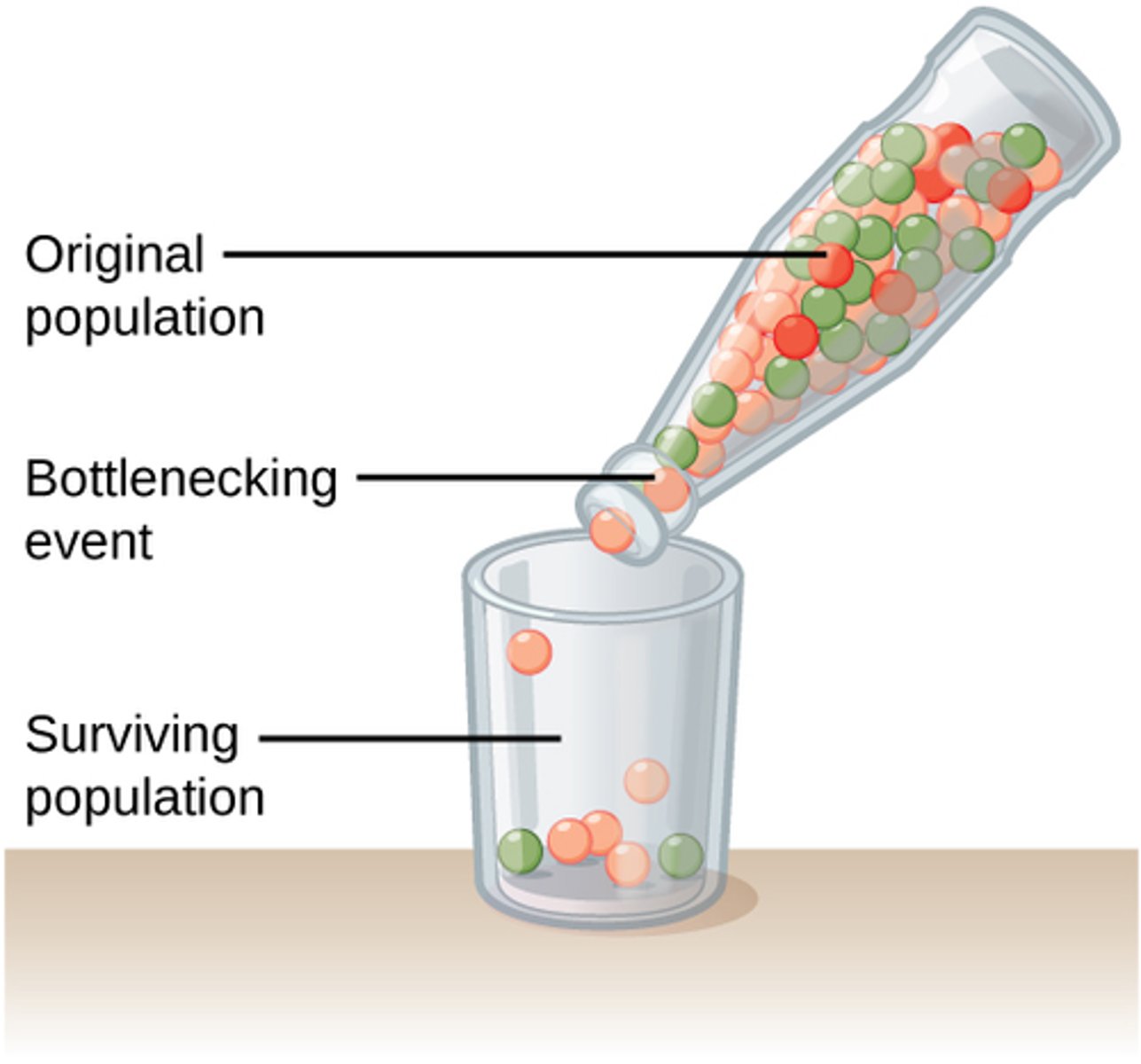
What is the bottleneck effect?
When a large population mostly dies off
this leads to leads diversity, which makes the population less likely to adapt to changes well.
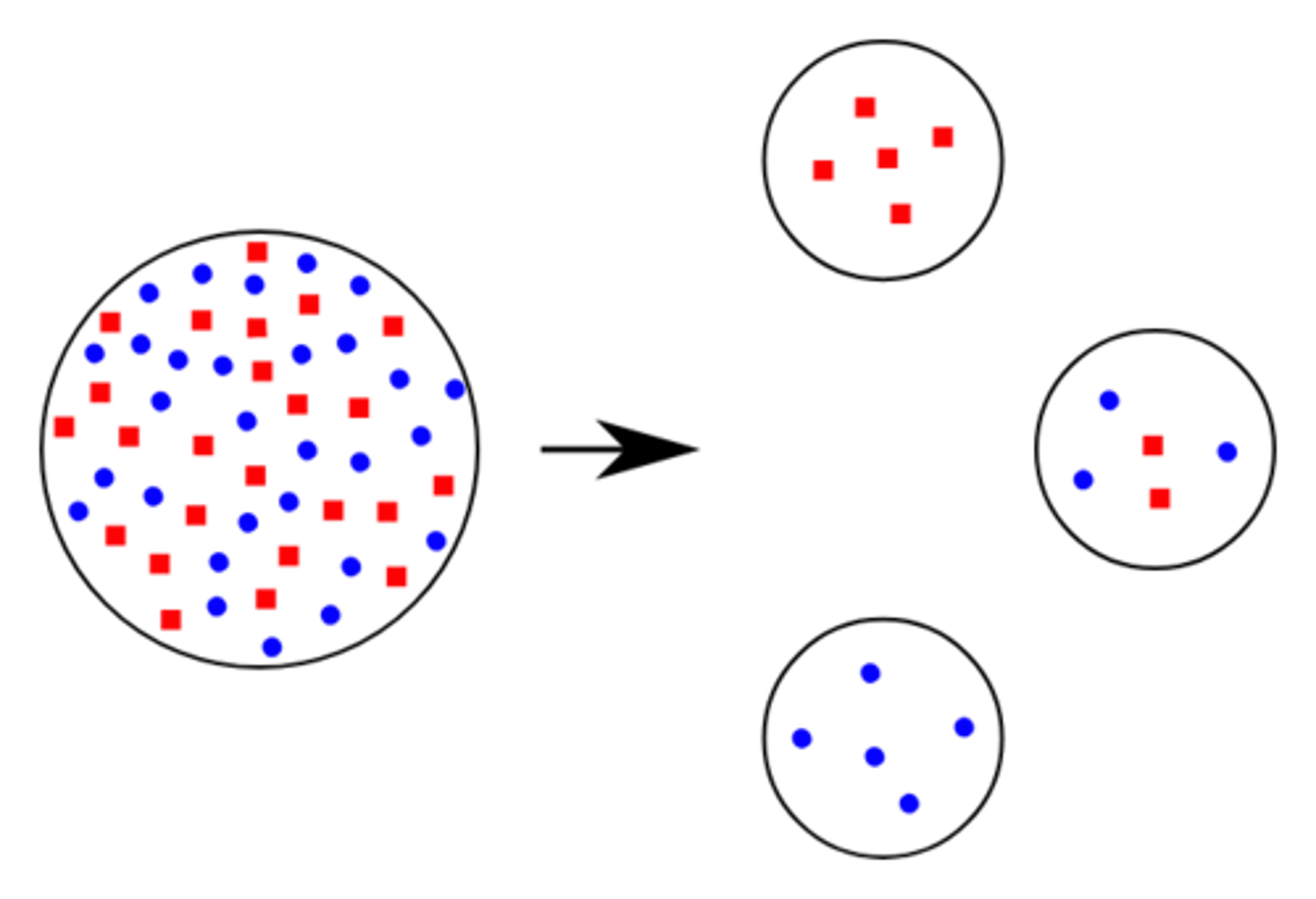
What is the founder effect?
When a small part of a population is found in a new area like an island
This leads to less diversity in the new population
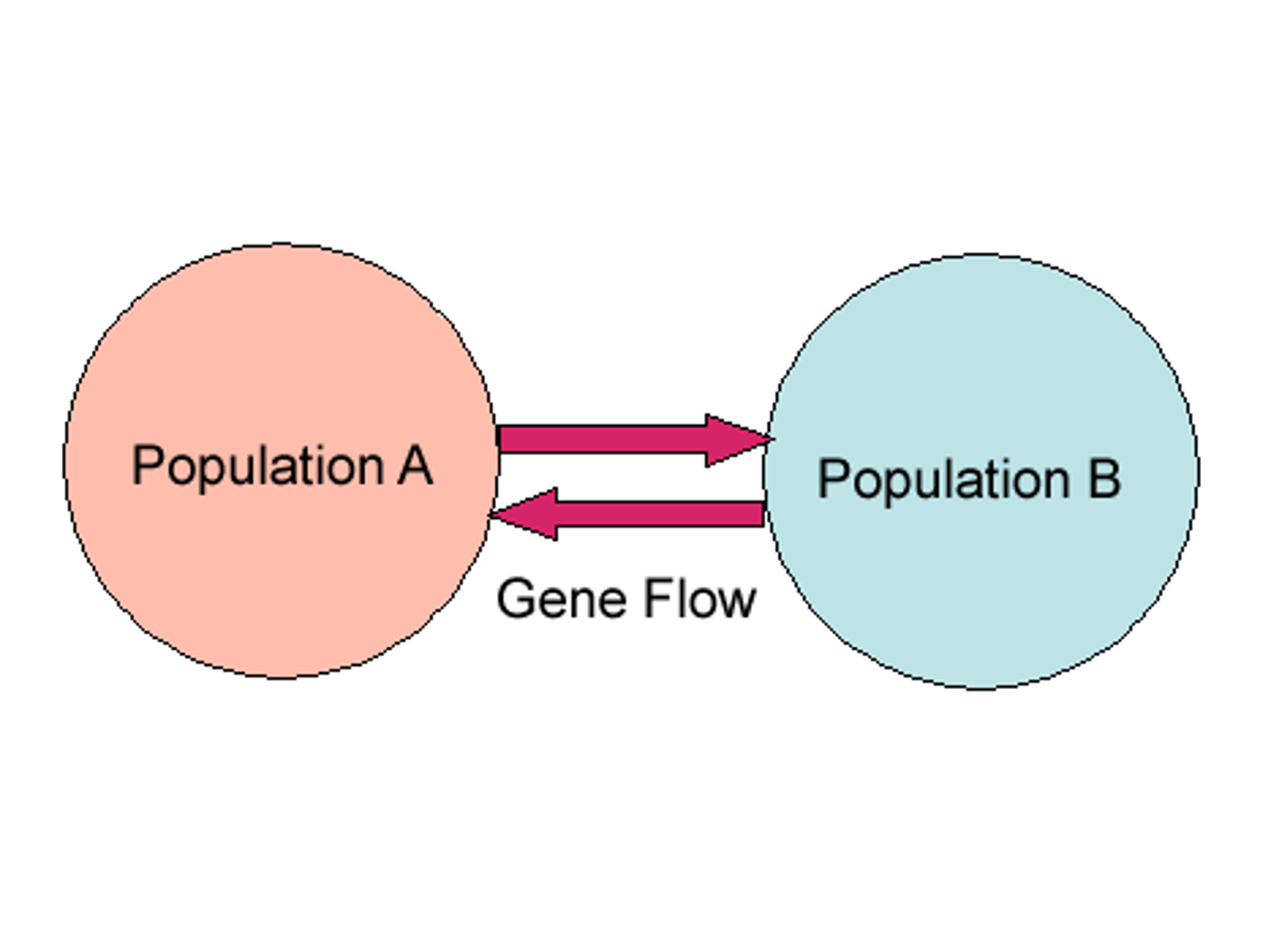
How does migration and gene flow drive evolution
1. If two populations of the same species are separated by mountains, rivers, etc. they will evolve differently
2. If a species from one of these populations migrates to the other population, diversity will increase
What happens with increased variation vs. decreased variation?
1. Decreased variation: the population will be worse at adapting and extinction is more likely
2. Increased variation: better at adapting so extinction is less likely
What are the characteristics of a non evolving population?
1. No mutations
2. No migration
3. No natural selection
4. Random mating (no sexual selection)
5. Large population (no genetic drift)
How is a non evolving population described?
The population is at Hardy Weinberg Equilibrium
What are the Hardy Weinberg equations for predicting allele frequencies in a non evolving population?
p^2 + 2pq + p^2 = 1
p + q = 1
p = A, q = a, p^2 = AA, q^2 = aa, pq = Aa
So, if you are given that the frequency of a recessive trait is .16, sub .16 in for q^2 because that would be aa
What evidence suggests that eukaryotes have common ancestry?
1. They all have genes containing introns
2. They all have linear chromosomes
3. they all have membrane bound organelles
What is phylogeny?
Evolutionary relationships among organisms
How is a phylogenetic tree interpreted?
if you have a more recent common ancestor, you are more related.
An easy example of this is that you are more related to your sister than your cousin
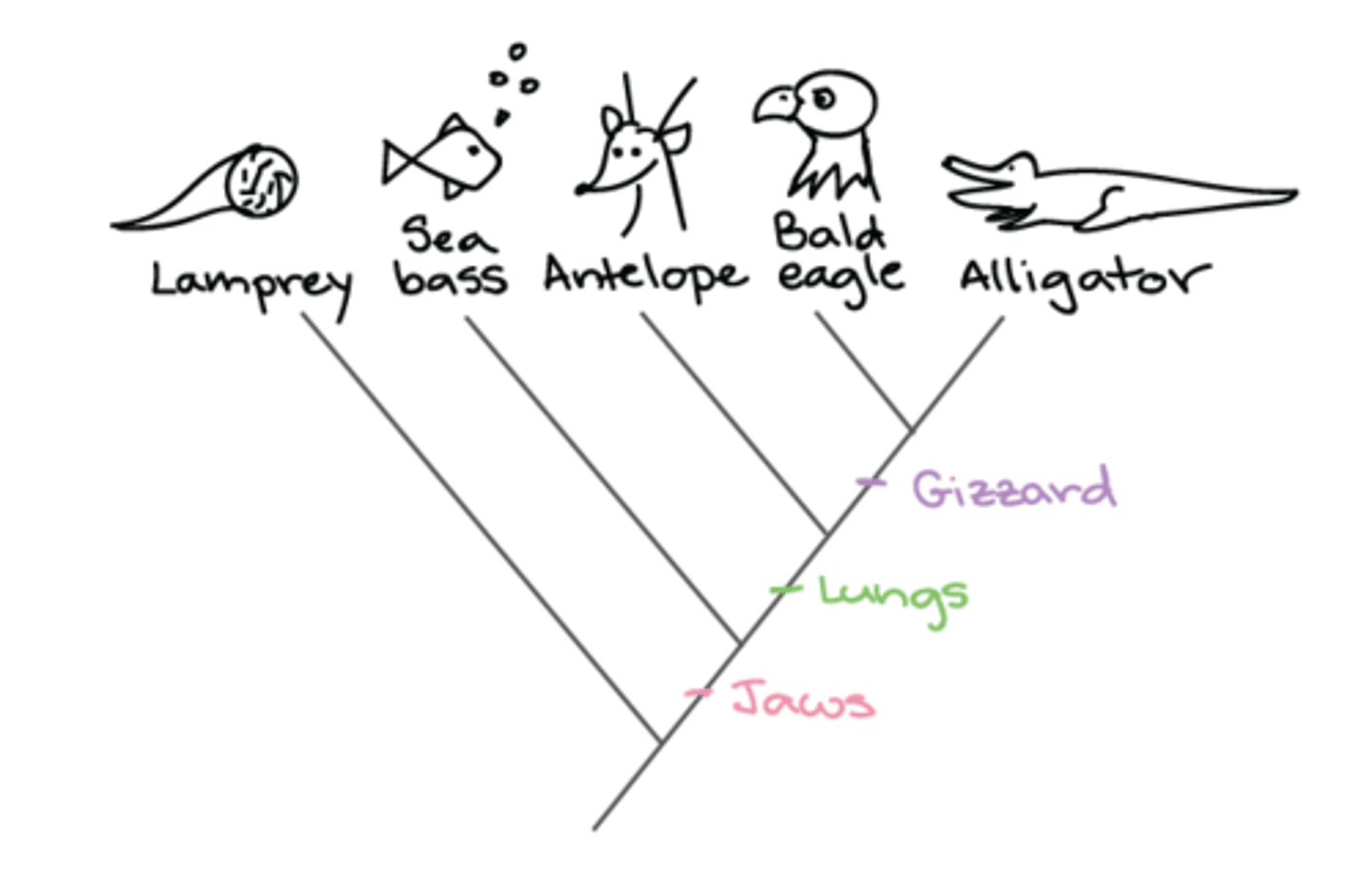
What is a sister group on a phylogenetic tree?
Two species with the most recent common ancestor
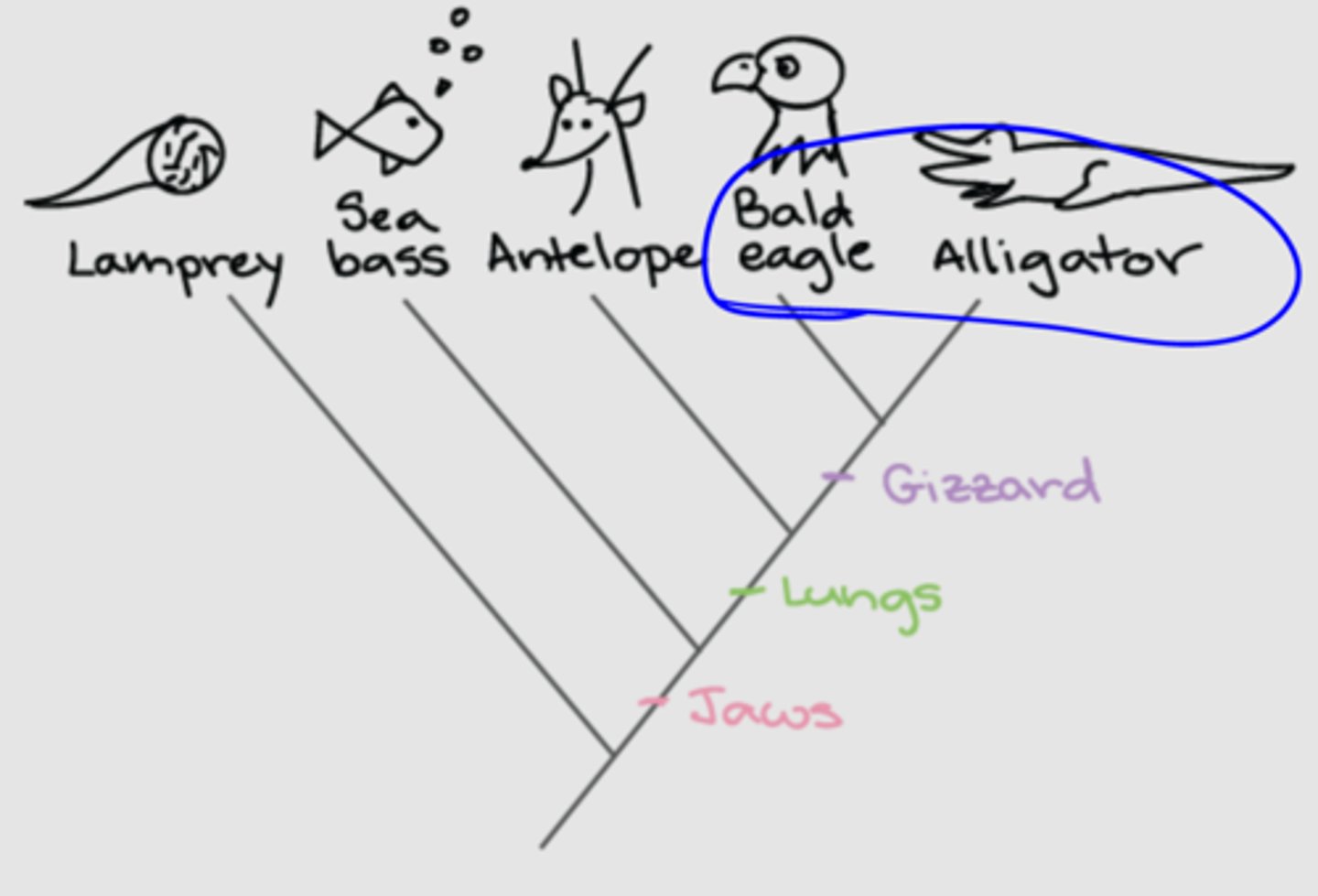
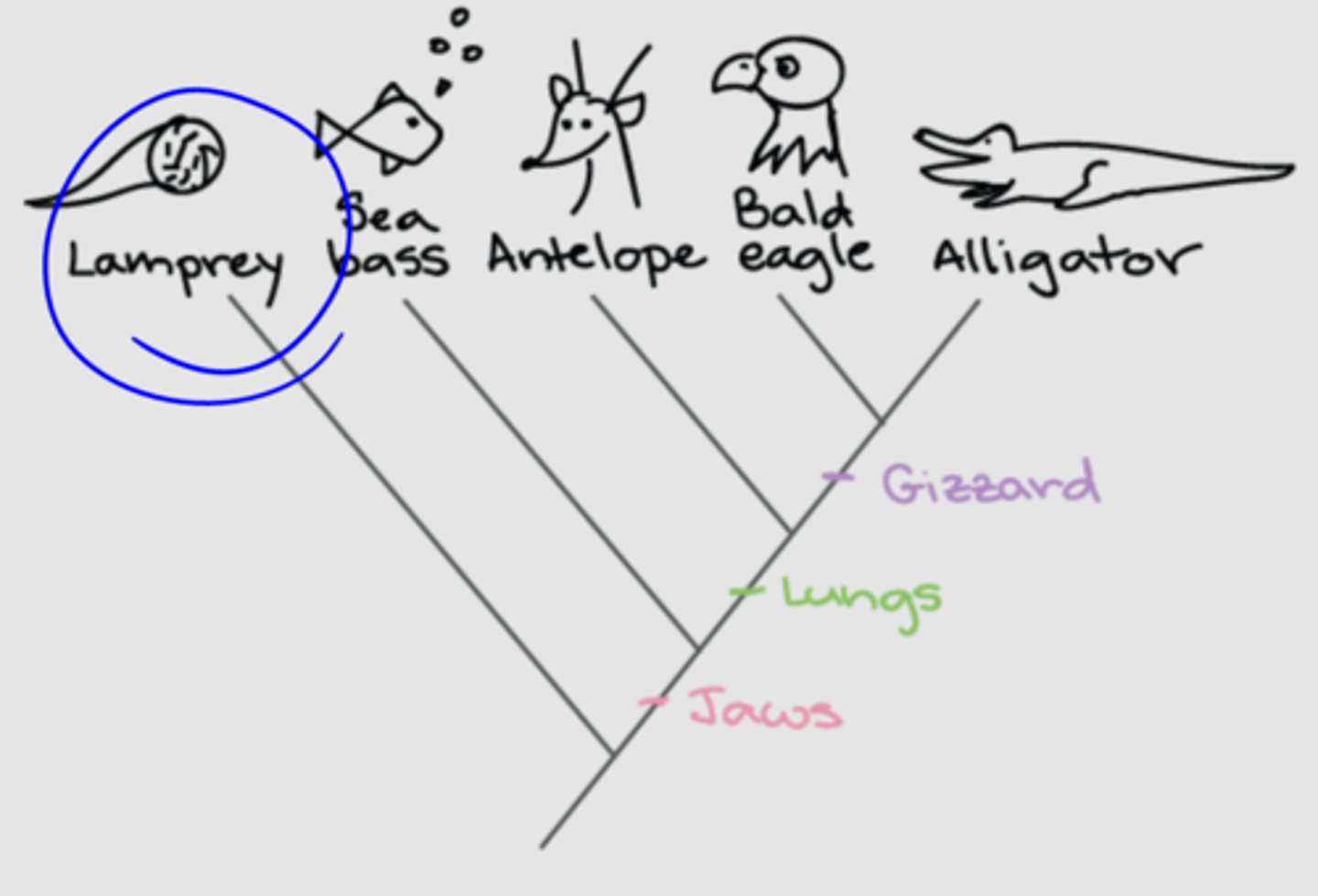
What is the out group on a phylogenetic tree?
The most distant relative on the tree
What conditions can indicate that organisms are different species?
1. Reproductive isolation: Can't reproduce together
2. Geographic: won't live together
3. Physiological: different cellular mechanisms
4. Behavioral: don't recognize each other (will not mate)
5. Genetic: chromosome differences
What ultimately determines if organisms are the same species?
If they can breed in nature and produce fertile offspring
appearance doesn't matter!
What are the two ways a species can diverge?
1. Punctuated equilibrium: rapid speciation, usually after mass extinction
2. Gradualism: a species gradually diverges from two groups accumulating differences
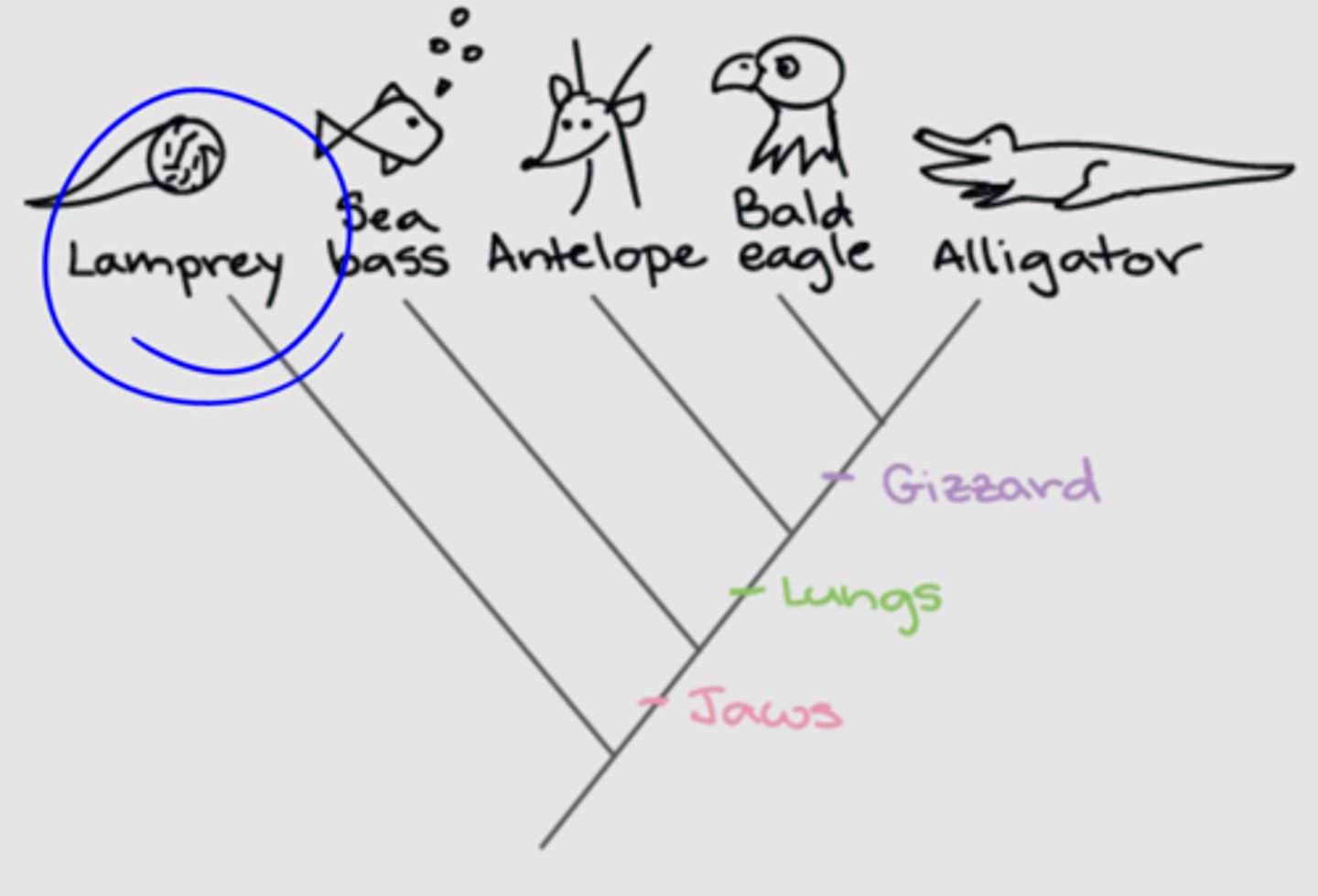
What is divergent evolution?
Two groups from a common ancestor accumulate differences
Ex: dolphins and tigers have a more recent common ancestor than dolphins and sharks. Tigers have just accumulated many differences
What is a mass extinction and why do they happen?
1. Definition: at least half of everything dies in a short period of time
2. Happens because of Environmental changes
What are two theories about the origin of life?
1. Organic material came from a meteor
2. Primitive earth had free energy and no O2, allowing life to form
What evidence is there that life formed on its own?
Humans have been able to make biological molecules such as carbohydrates and DNA by simulating primitive earth. However, no onw has every made a cell.
What is the RNA world hypothesis?
RNA came first
life on earth began with a simple RNA molecule that could copy itself
What are the classifications of organisms? What are humans in each of these classifications?
1. Kingdom: Animalia
2. phylum: chordata
3. class: mammalia
4. Order: primate
5. family: hominidae
6. genus: homo
7. species: sapiens