1. Nervous tissue histology
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Excitable plasma membrane
Specialization for fast conduction (myelination/nodes of Ranvier)
Specializations for immune production (BBB)
CT for insulation
Blood and nerve supply for large nerves
Characteristics of peripheral nervous tissue
Nerve cells (neurons)
Supporting cells
Schwann cells
Satellite cells
Fibroblasts
Perineural sheath (blood-nerve barrier)
Cells of PNS
Neurons composed of:
Nerve cell body aka soma, perikaryon
Cytoplasmic processes:
Afferent (dendrites)
Efferent (axons aka nerve fibers)
Dendrite afferent or efferent?
Afferent
Axons/nerve fibers afferent or efferent?
Efferent
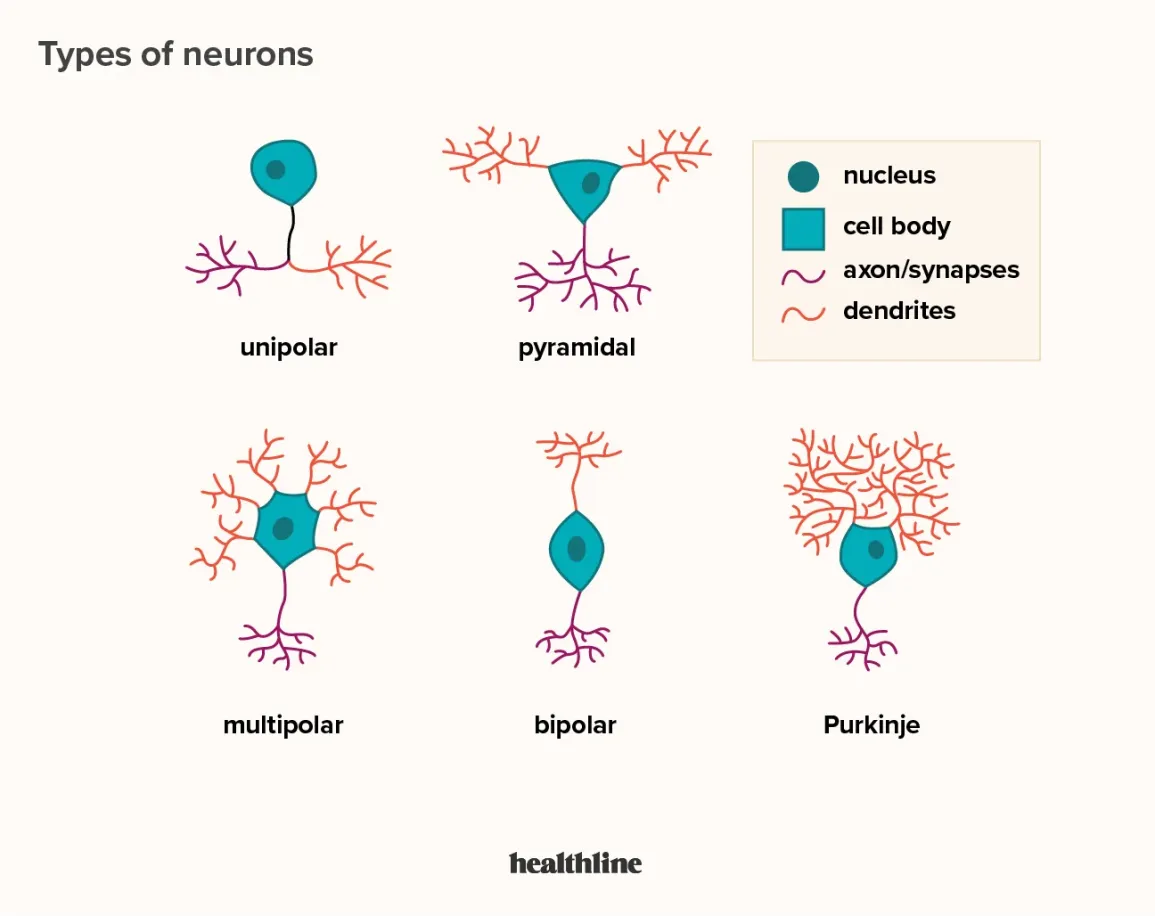
the three nerve cell types:
pseudounipolar
bipolar
multipolar
neuron cell process
extensions of a neuron cell, primarily the dendrites which receive signals from other neurons, and the axon which transmits the electrical signal away from the cell body to other neurons
the dendrites "listen" to incoming signals while the axon "speaks" by sending signals out.
cytoplasmic processes (neuron cell processes)
axons (1/neuron)
ensheathed by Schwann cells
may be myelinated
dendrites (many per motor neuron)
major characteristic of axon?
no Nissl bodies
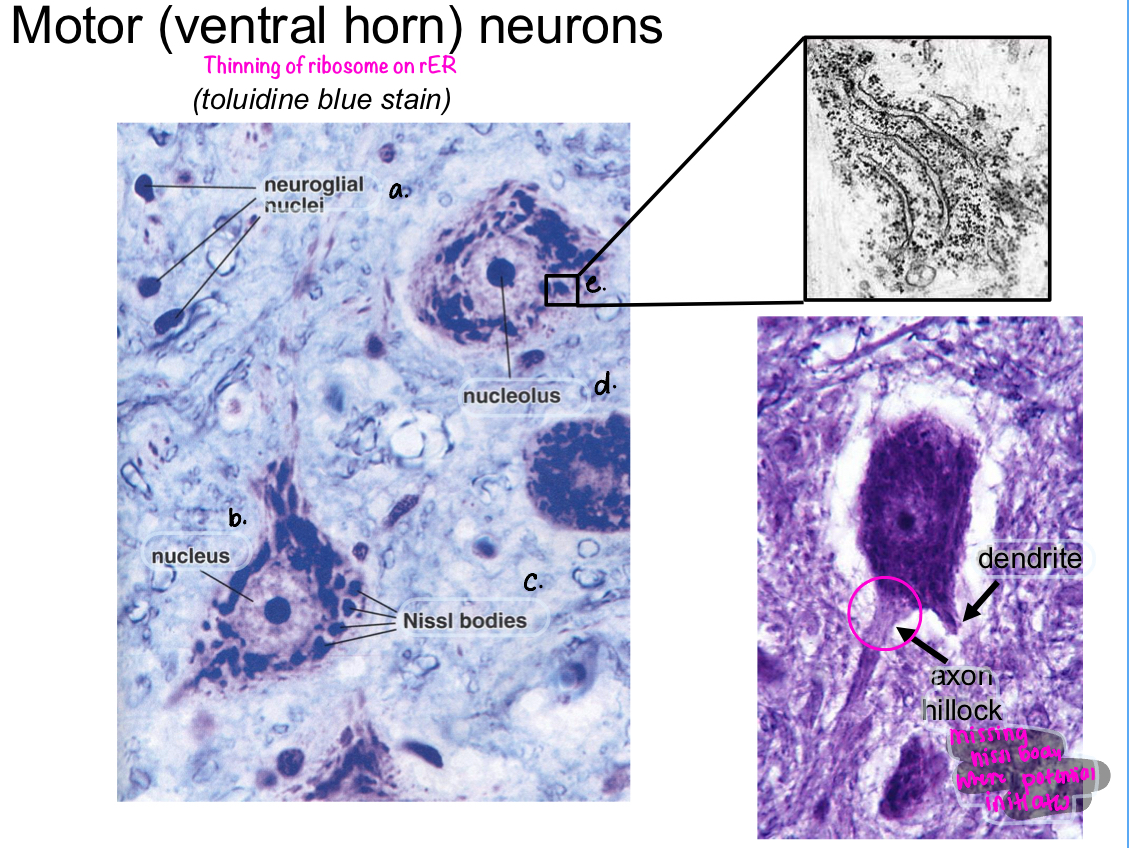
what is an axon hillock?
a cone-shaped part of a neuron that controls when an electrical impulse is sent. It's located where the axon connects to the cell body.
Receives signals from other neurons and the environment
Determines if the neuron should send an action potential
Generates action potentials
nerve cell for sensory
one cell process that extends from the cell body (soma)
one axon that splits into two branches
no dendrites
pseudounipolar
nerve cell for sensory and sensory organs (e.g. olfactory epithelium)
two cell processes (axon and dendrite) extend from soma
bipolar
nerve cell for somatic motor and visceral motor
many cell processes
typically one axon and many dendrites
multipolar
PNS neuron cell bodies are clustered in
nuclei (CNS), multipolar neurons
ganglia
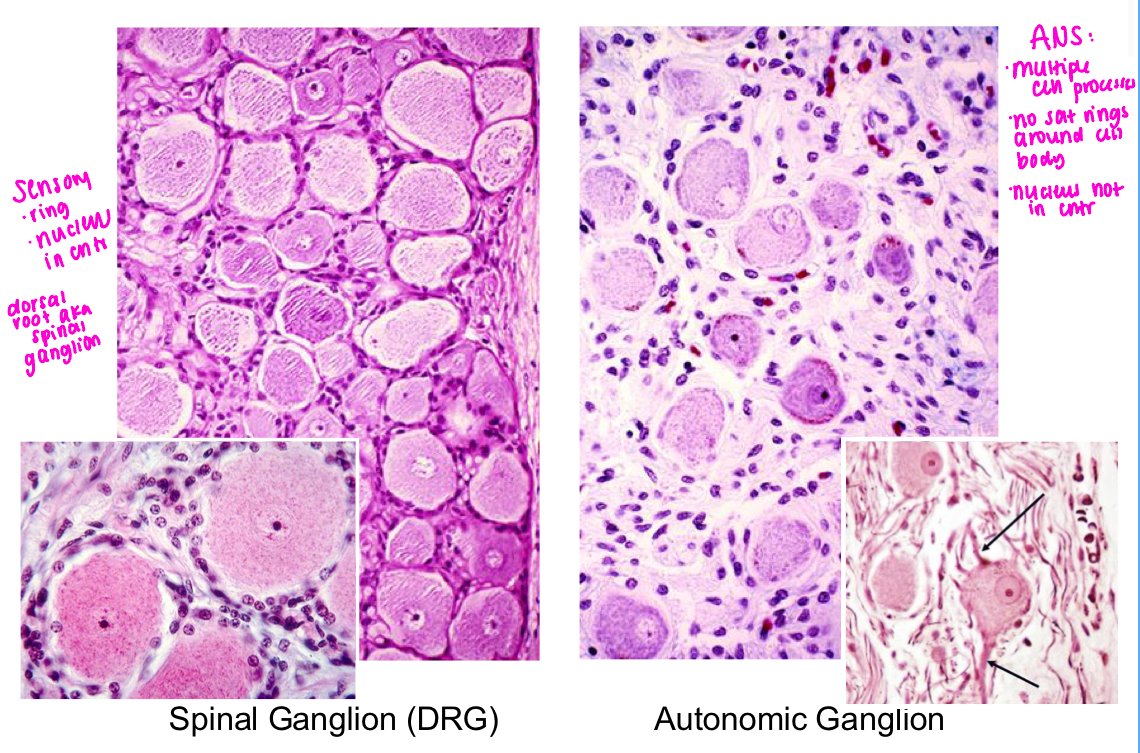
dorsal root: cranial sensory nerve ganglia (sensory)
autonomic ganglia: visceral motor (parasympathetic, sympathetic, enteric)
ganglia
collection of neuron cell bodies located outside the central nervous system, within the PNS
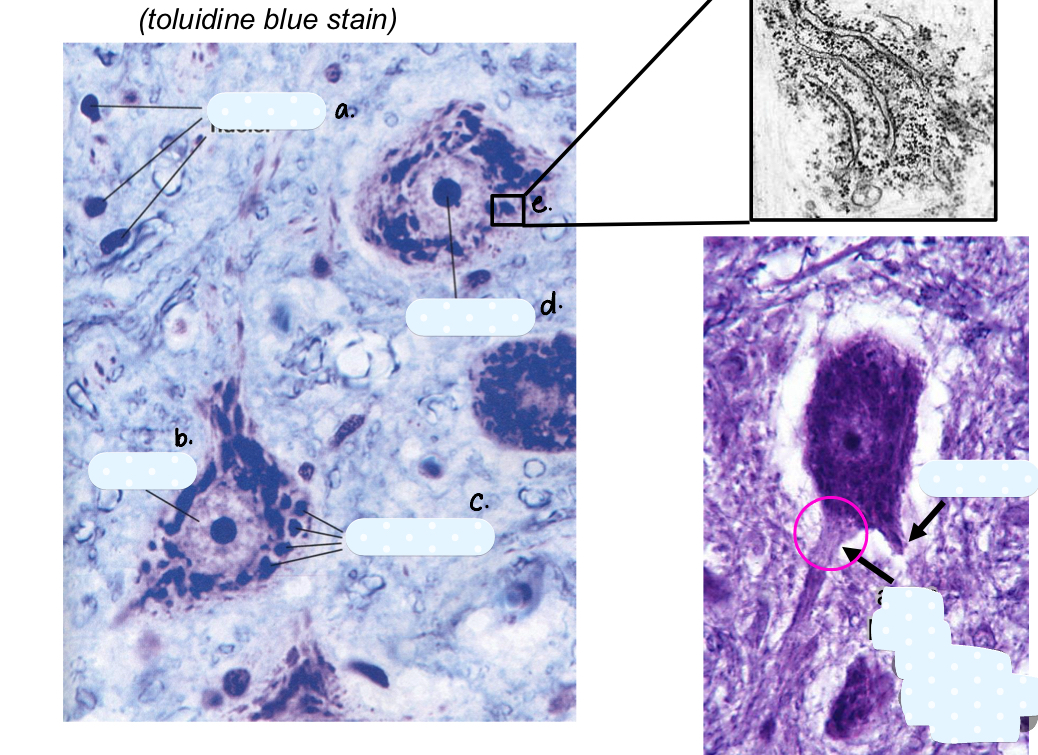
characteristics of soma
large euchromatic nucleus
prominent nucleolus (w/in nucleus where ribosomes are assembled)
Nissl substance (rER cluster for protein synthesis)
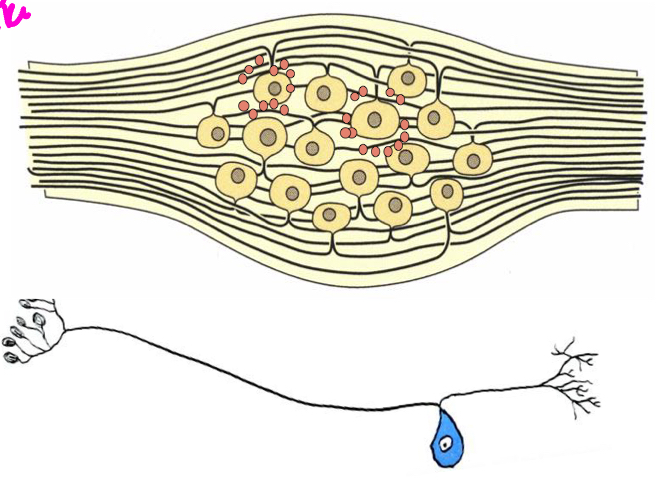
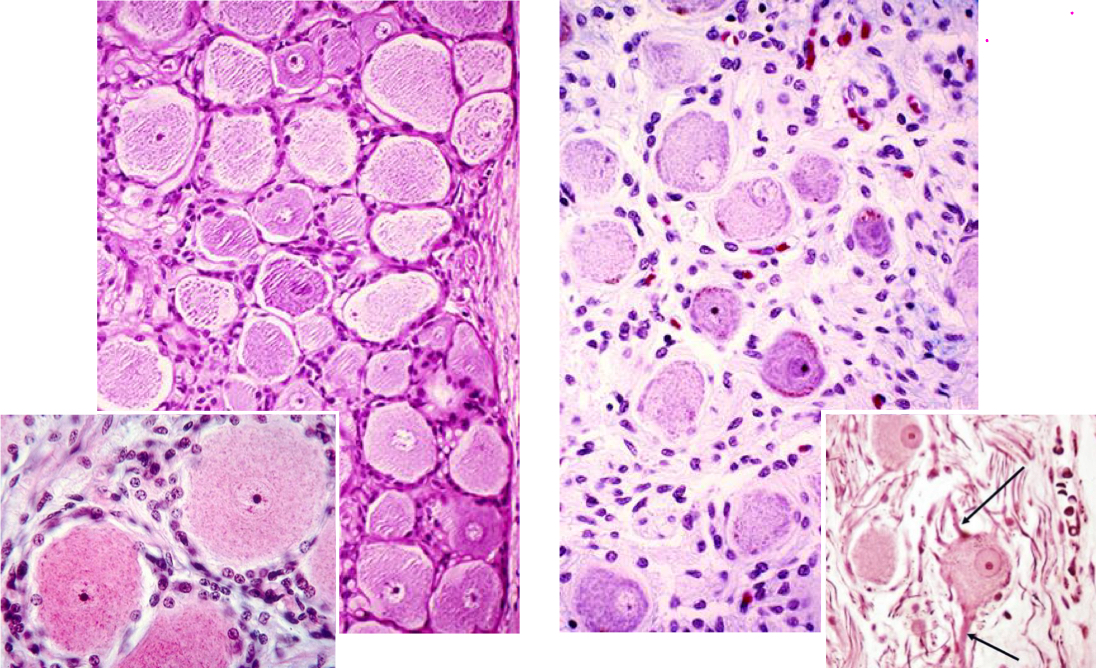
ex: dorsal rot ganglion, cranial sensory nerve ganglion
pseudounipolar neurons
morphology: central nucleus, ring of satellite cells
synapses: none
sensory neurons
sensory neurons
ex: sympathetic, parasympathetic, enteric
multipolar neurons
morphology: eccentric nucleus, dispersed satellite cells
synapses: abundant
autonomic neurons
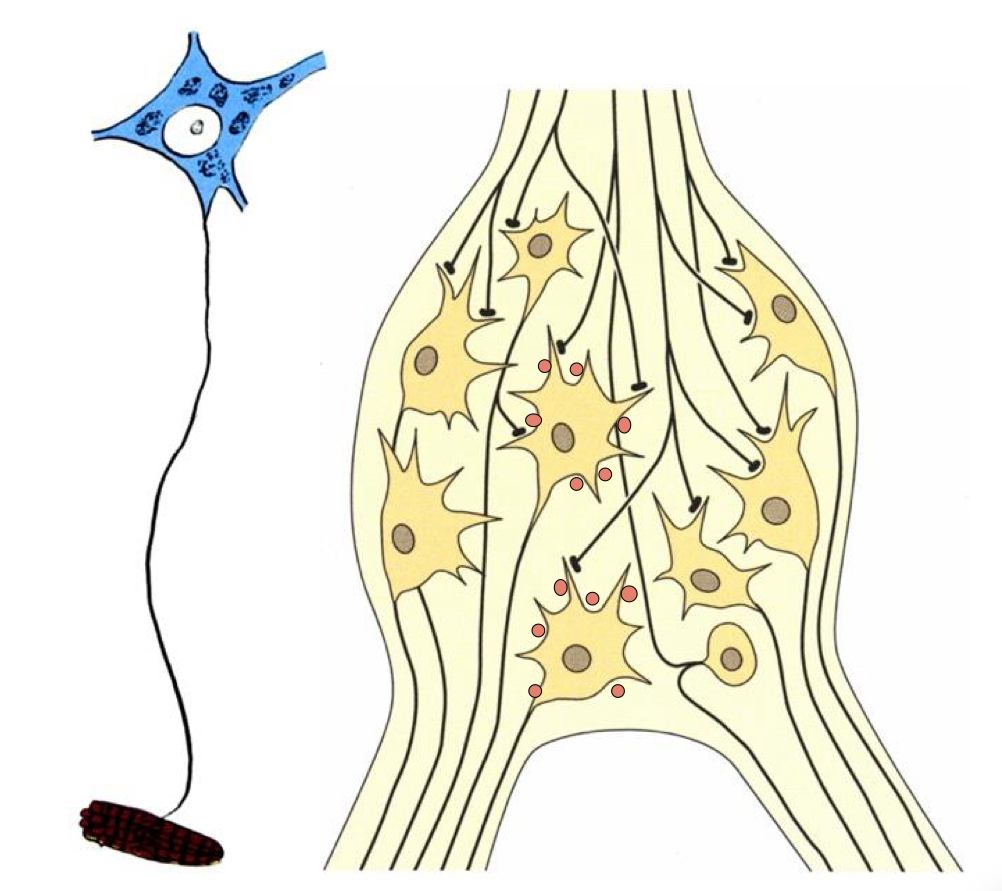
autonomic neurons (visceral)
describe organization of a peripheral nerve
ex: median nerve is comprised of outer connective tissue called epineurium surrounding many individual nerve bundles each wrapped by perineurium. The nerve bundles are comprised of many somatic sensory, somatic motor, and/or autonomic unmyelinated neurons. Inbetween the different nerve fibers is insulating tissue endometrium. there are also blood vessels in nerves
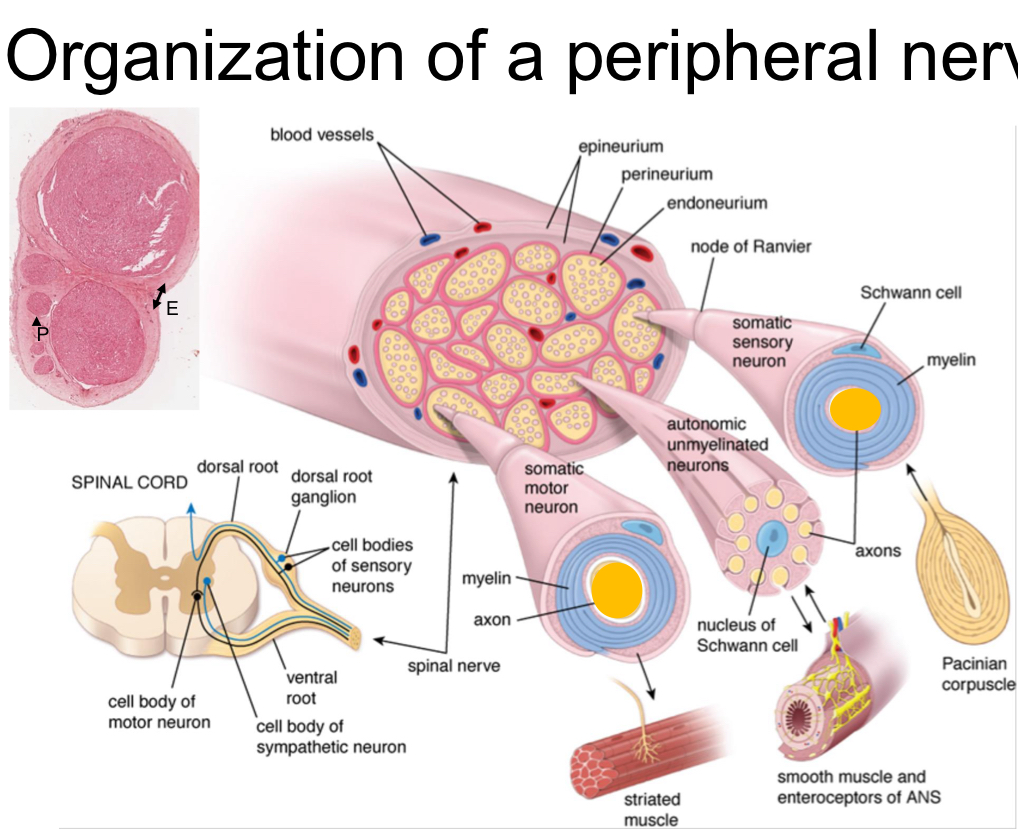
cell bodies of motor neurons originate in?
ventral root
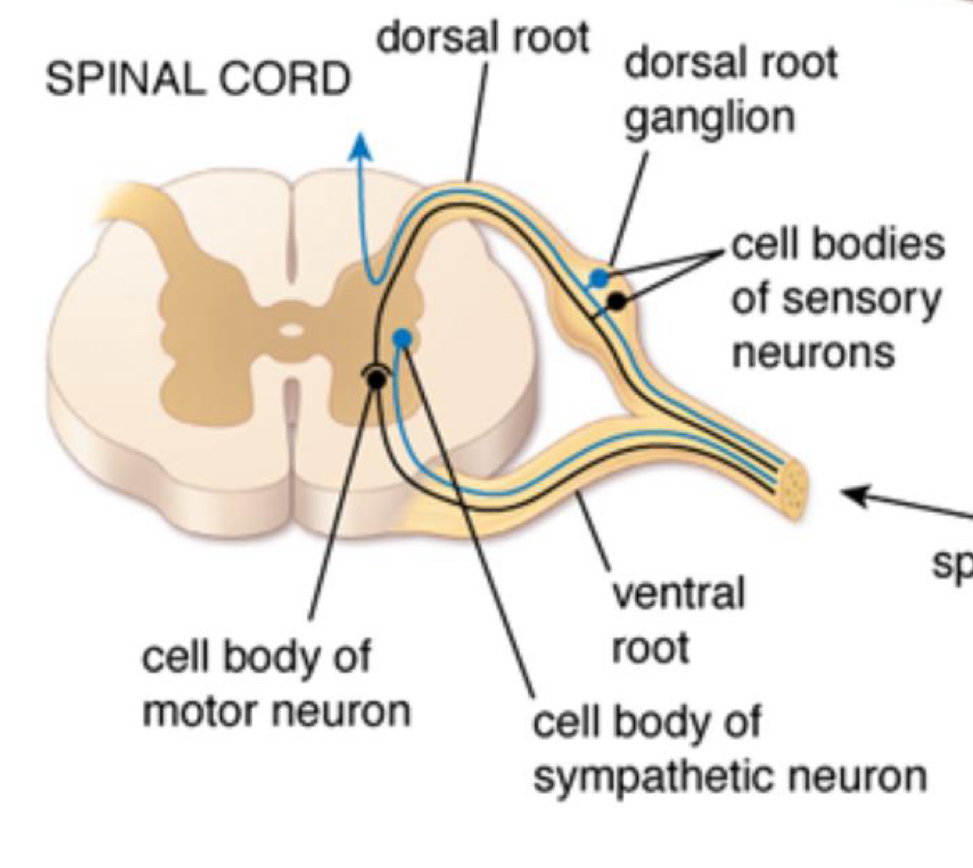
cell bodies of sensory neurons originate in?
dorsal root ganglion
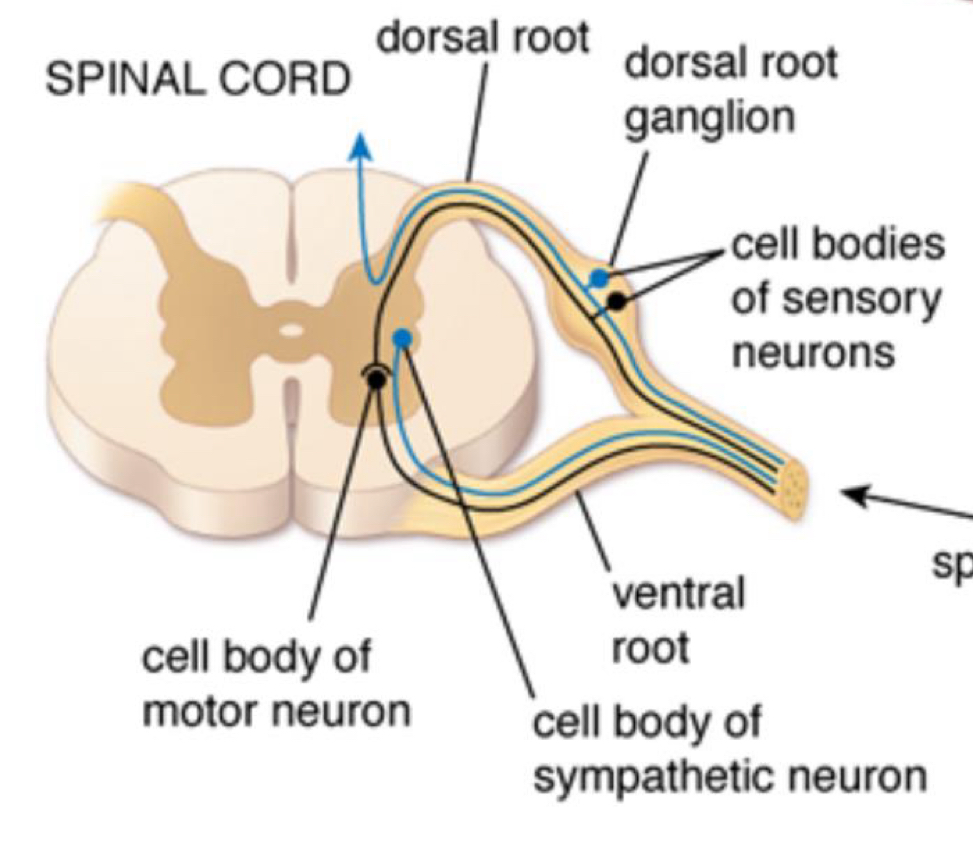
cell bodies of sympathetic neuron originate in?
ventral root
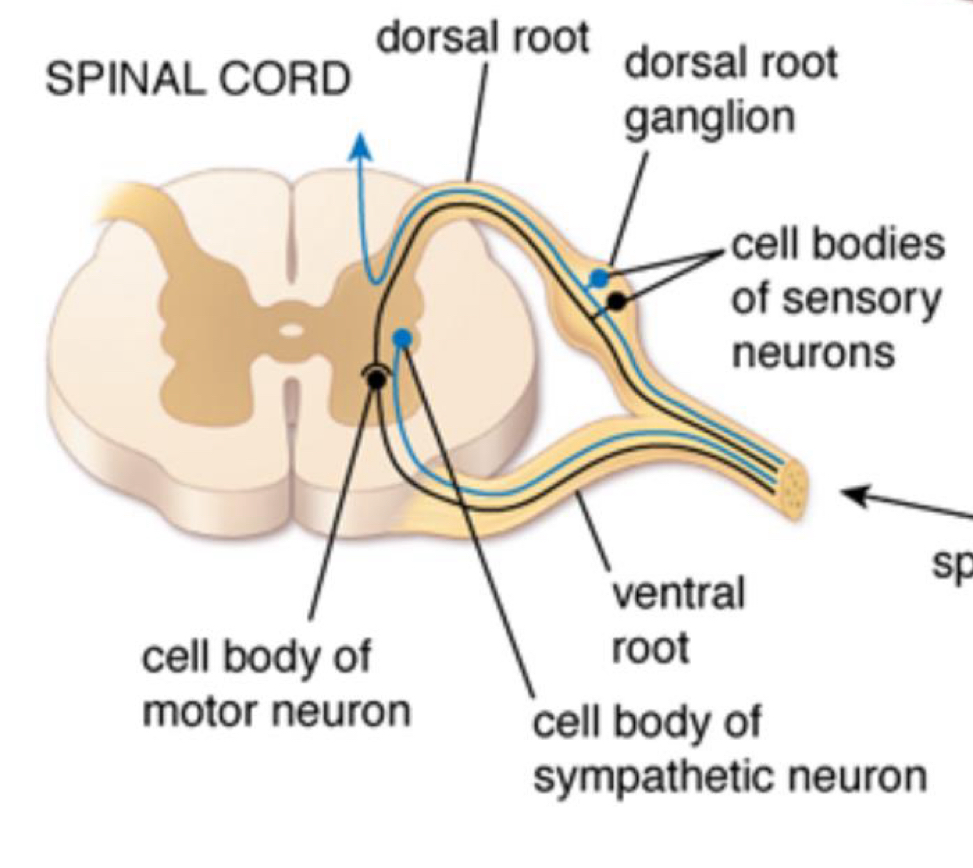
what happens when dorsal and ventral roots come together?
it is now called a spinal nerve
somatic motor neurons
striated muscle
autonomic unmyelinated neurons
smooth muscle and enterorecptors of ANS
somatic sensory neurons
pacinian corpuscle
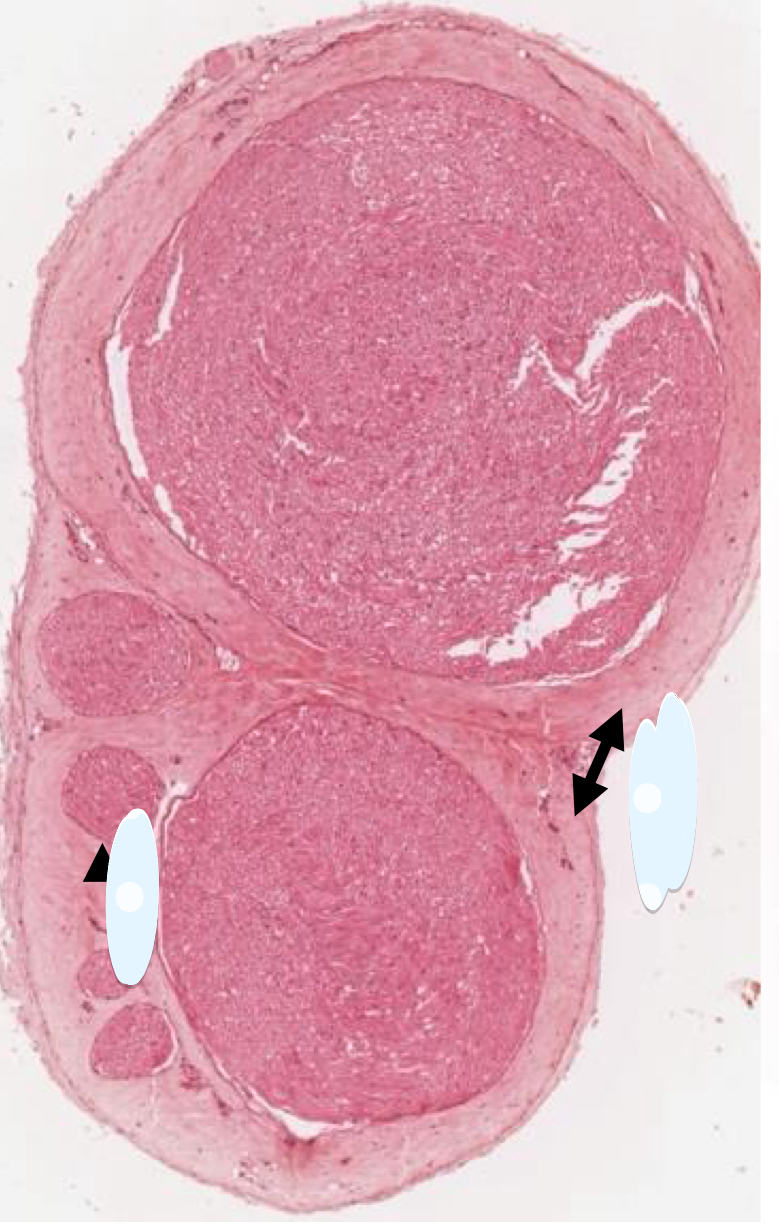
6 nerve bindles in this cross section of a nerve
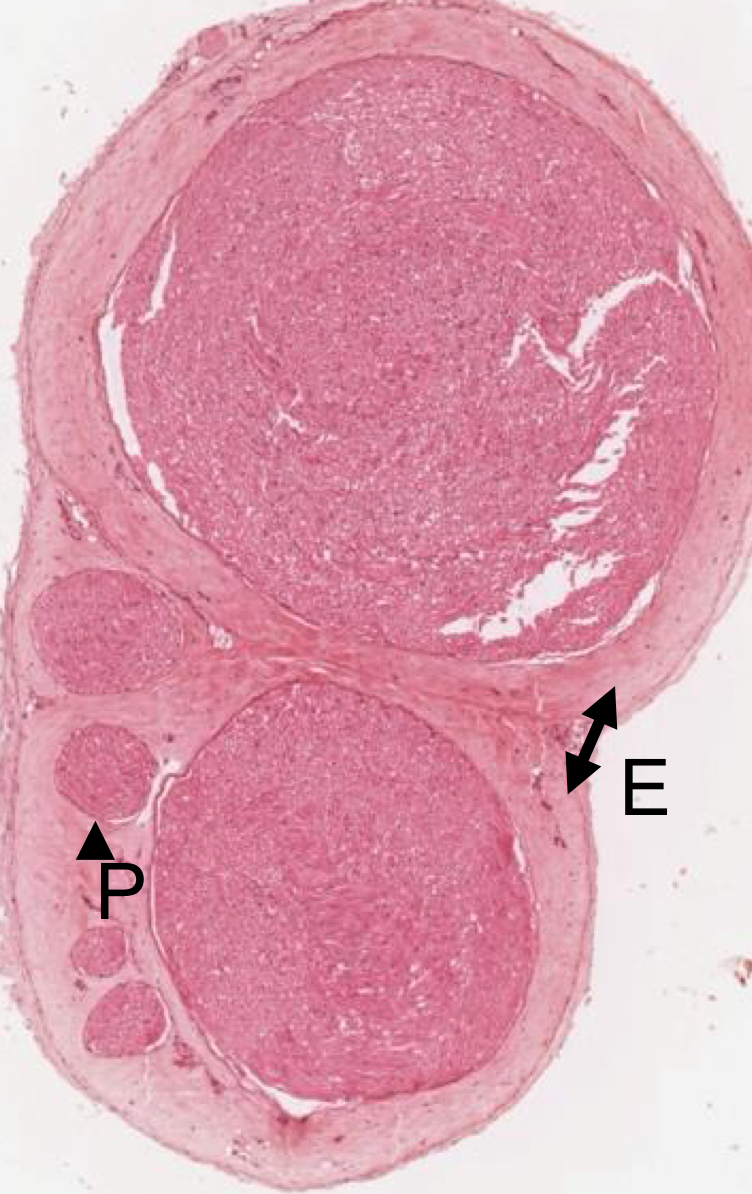
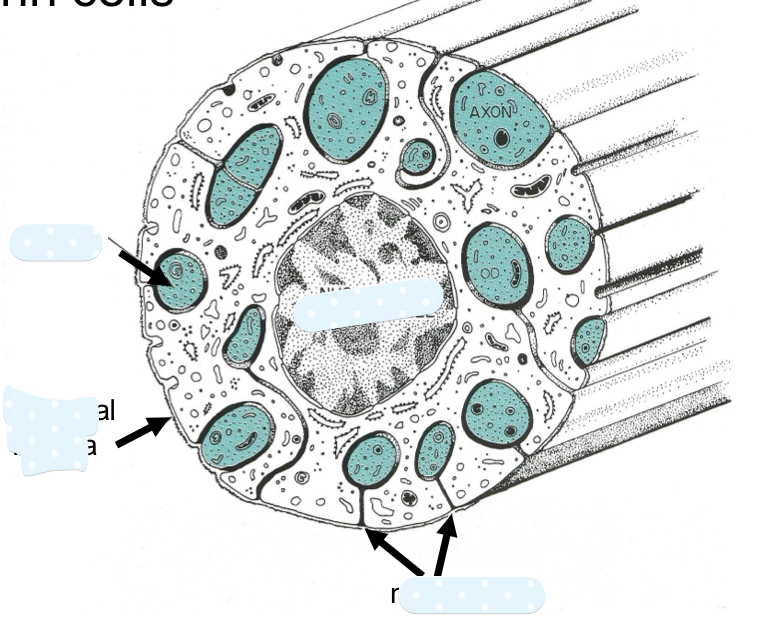
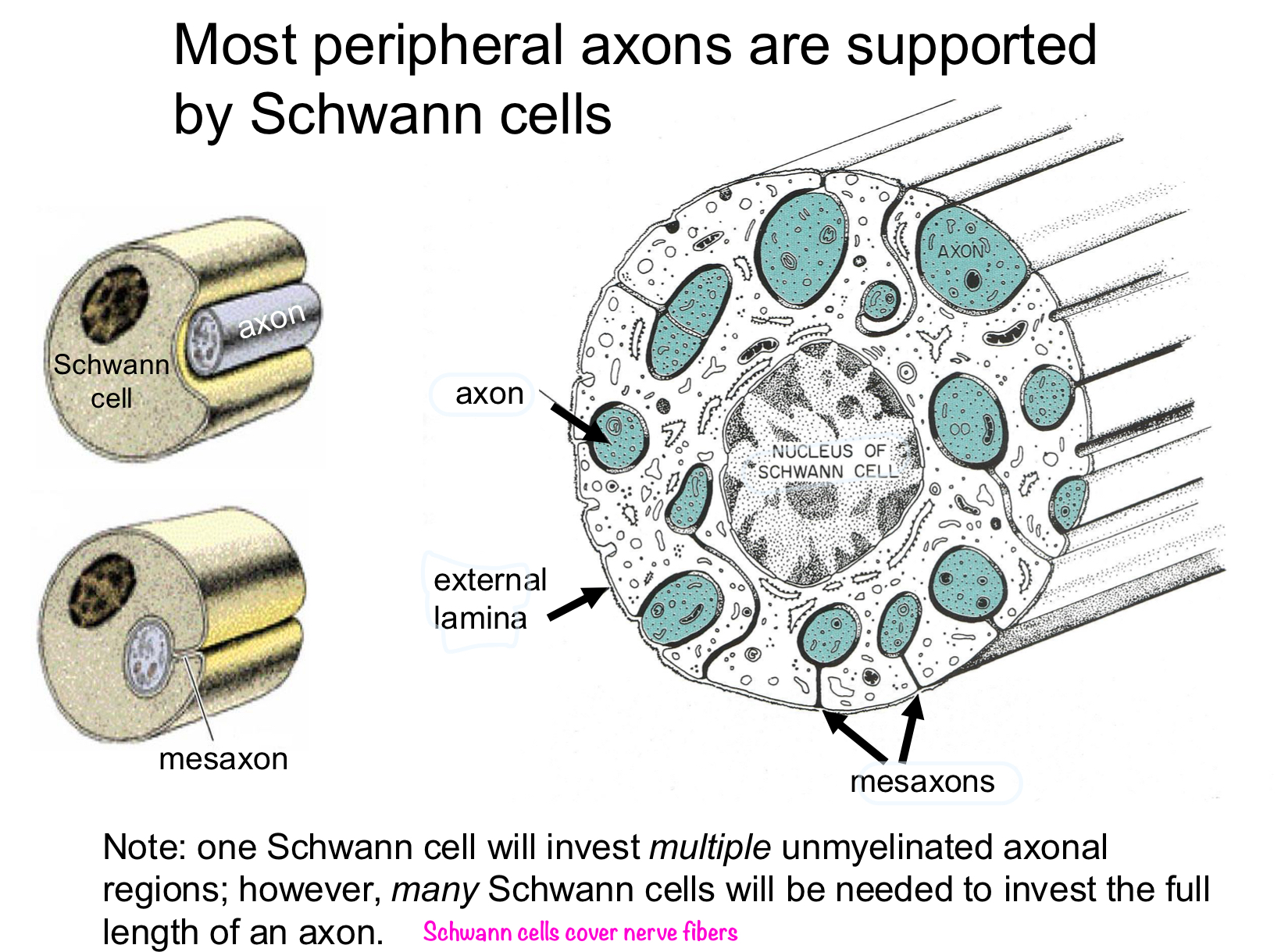
explain Schwann cells myelinated vs unmyelinated
Schwann cell can only surround one myelinated axon because it takes a lot of energy; sheath
for unmyelinated one Schwann cell can surround many unmyelinated axons
*actually one Schwann cell will myelinate a single axonal region and it takes many into invest in full length of an axon. its the sheath that makes it thicl
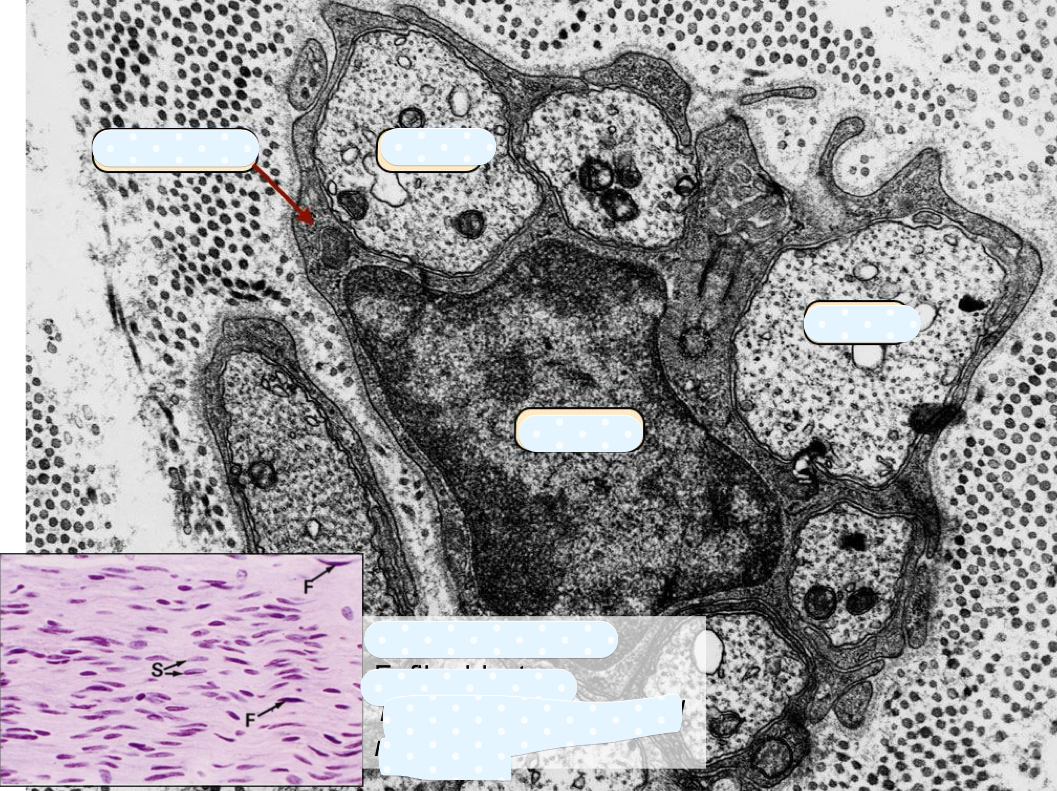
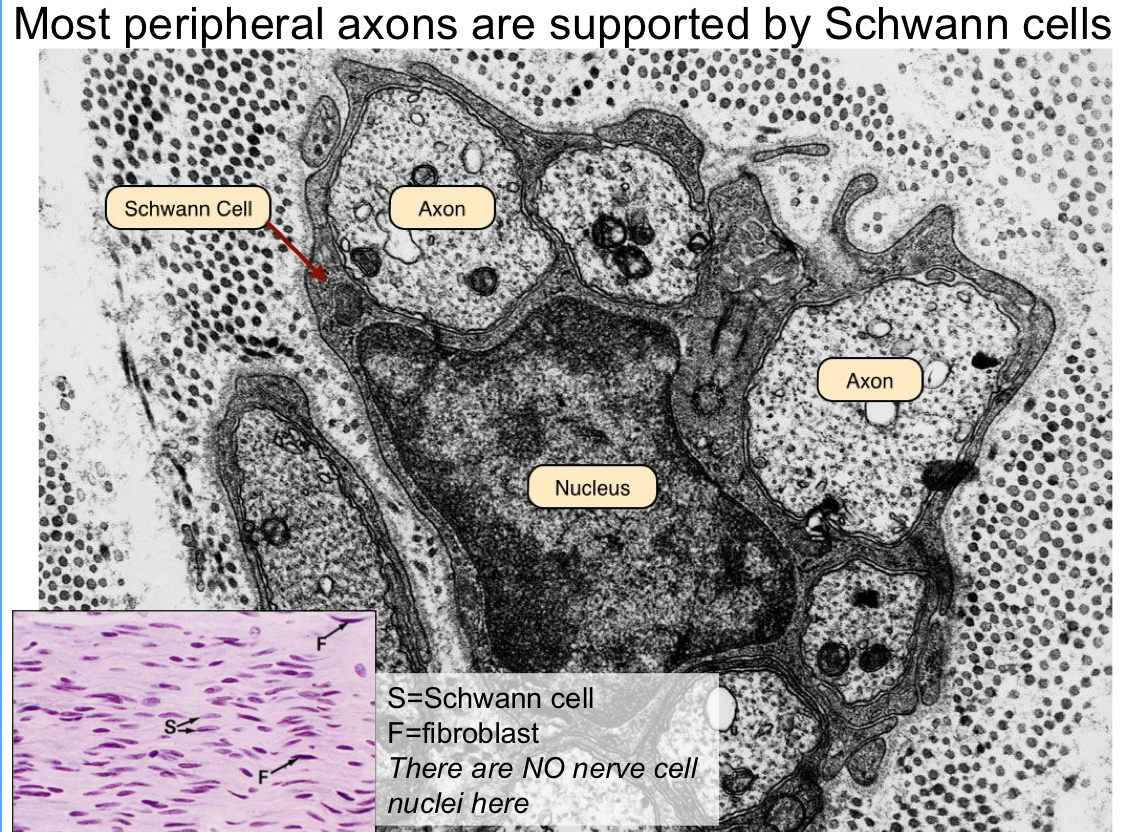
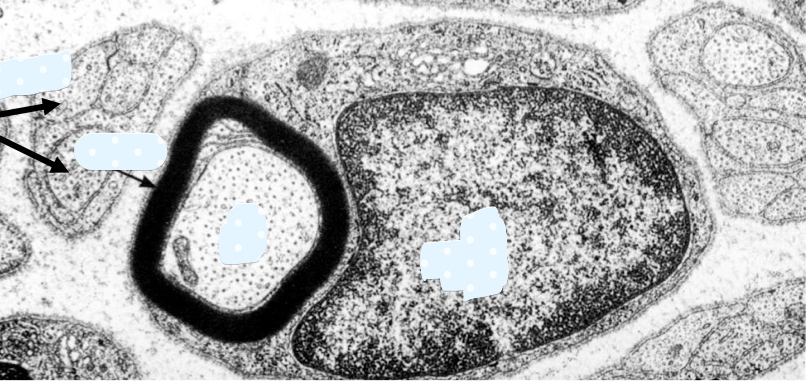
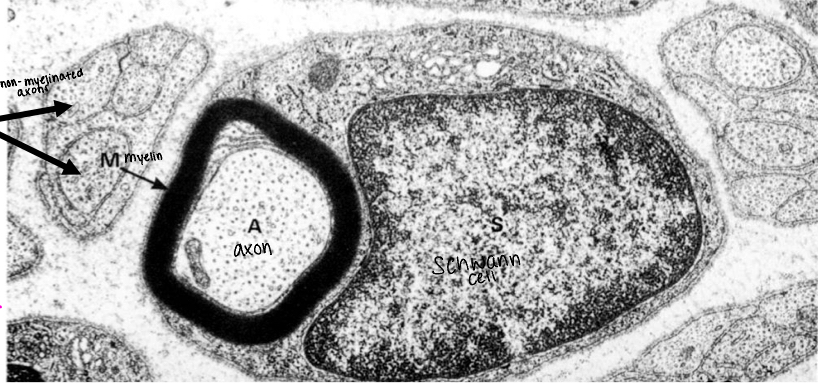
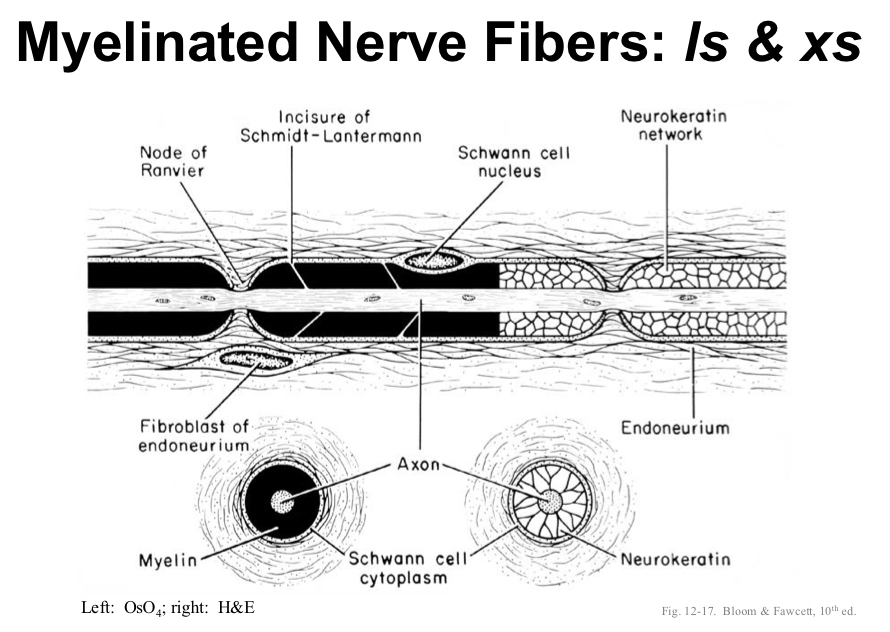
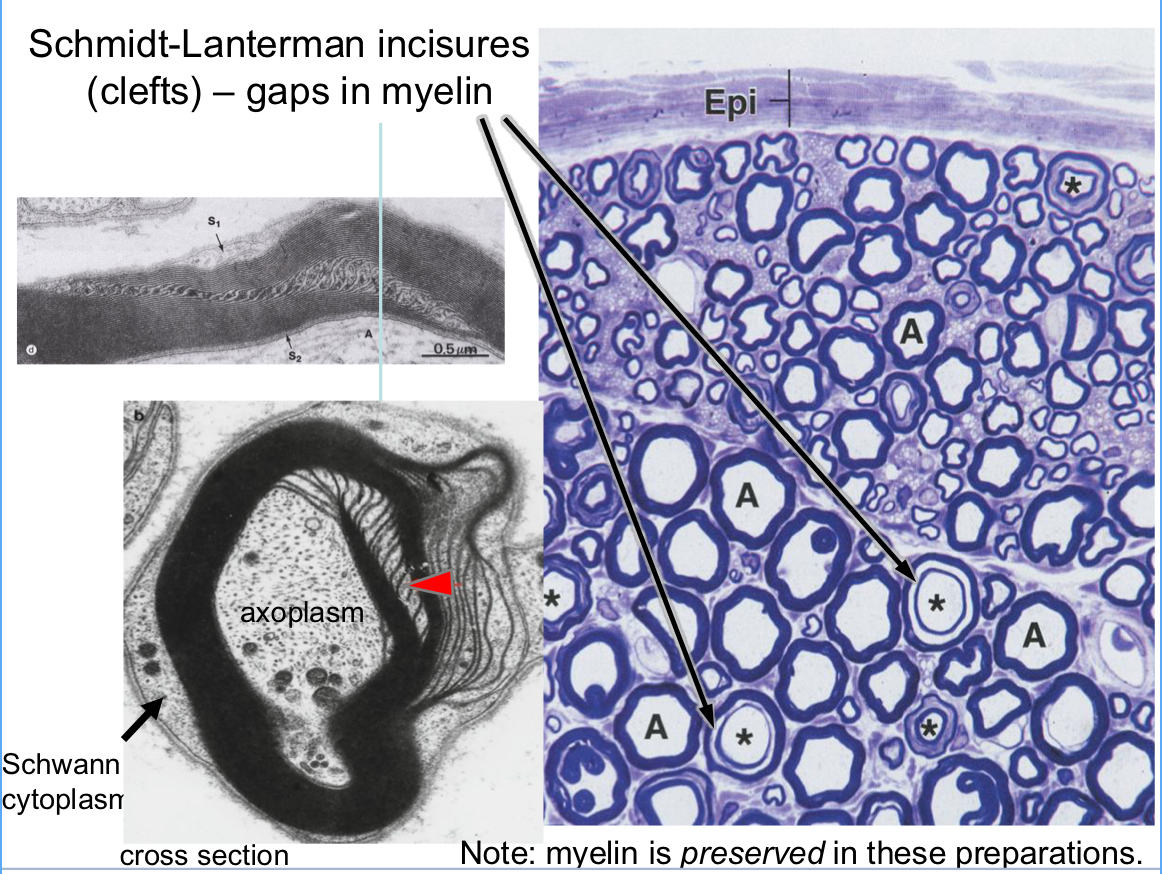
what is not well-preserved in most preparations?
myelin which is lipid rich
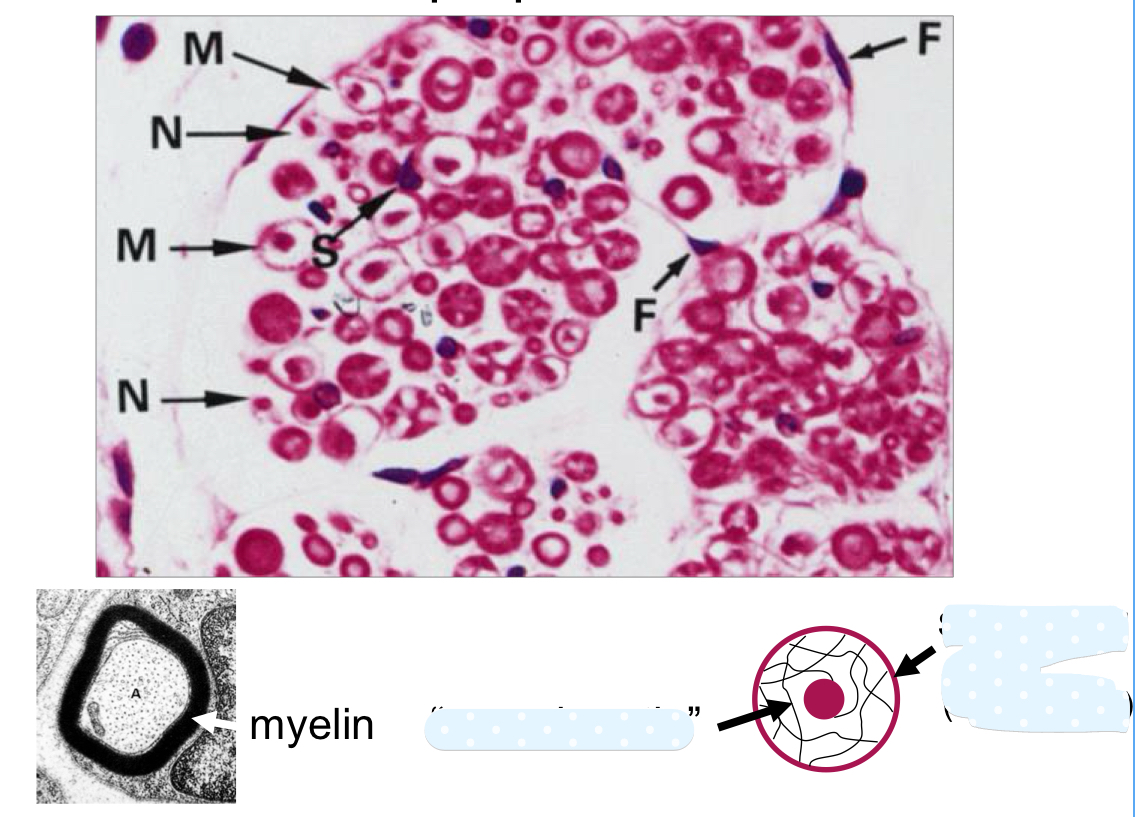
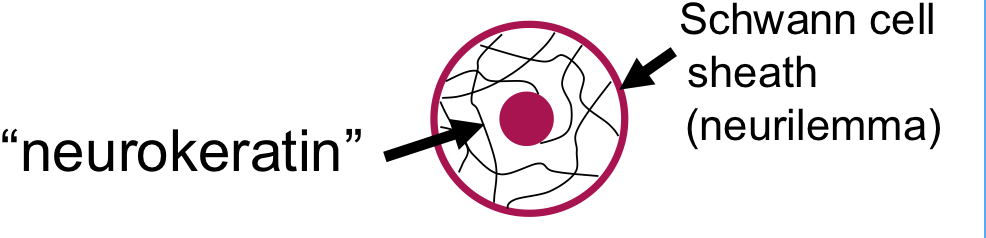
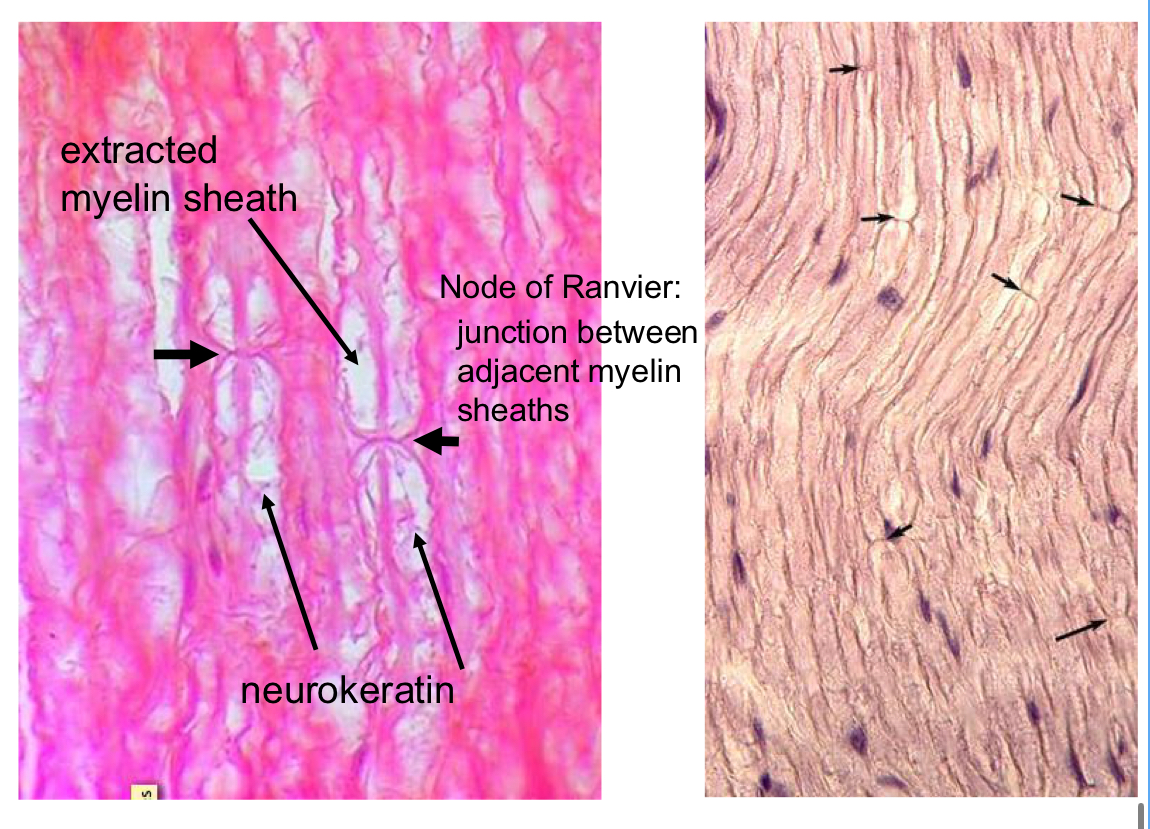
define neurokeratin
where is neurokeratin found?
protein in myelin sheath of axon; protein residue after lipids extracted during tissue process
found in myelinated nerves only (Schwann cells can be around non-myelinated)
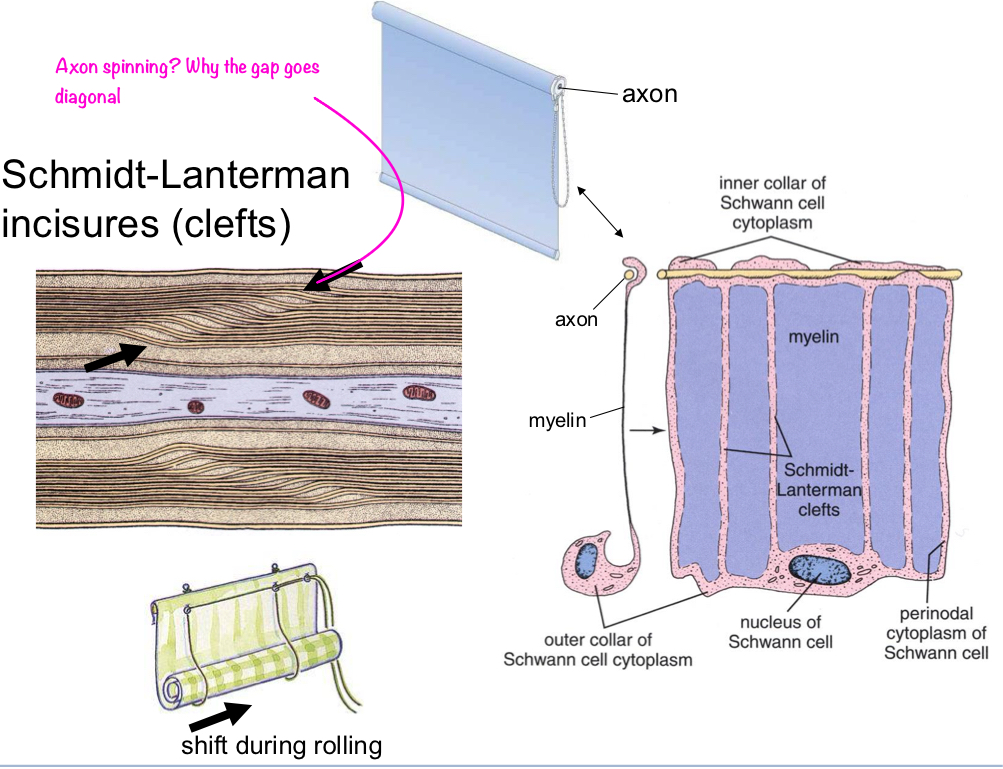
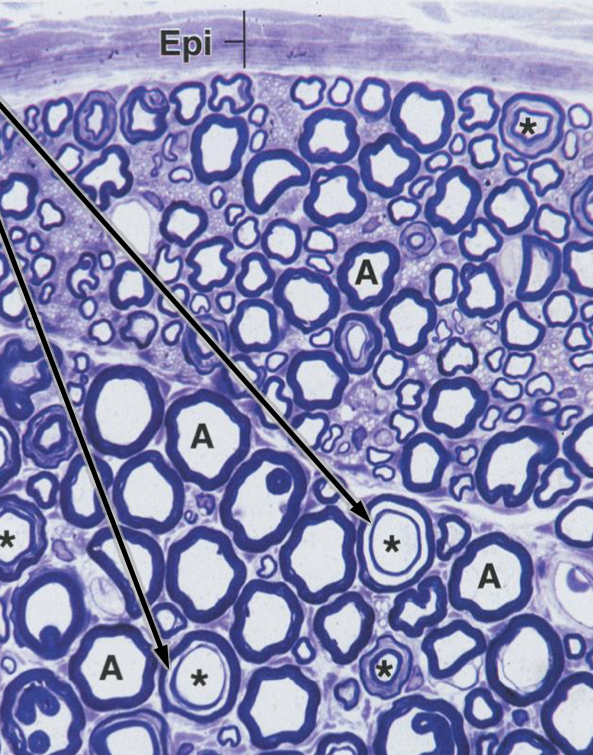
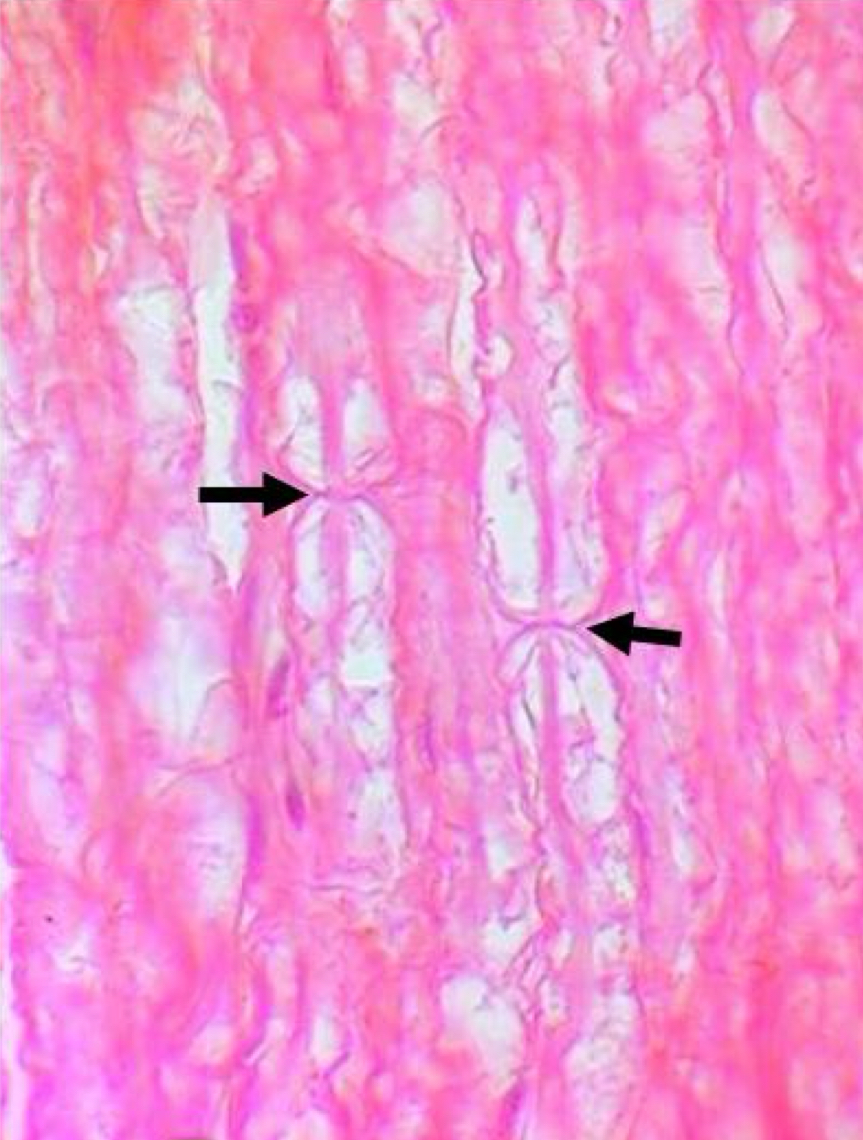
what are the two types of myelin interruptions?
Schmidt Lanterman incisures (clefts)
Schmidt-Lanterman incisures (clefts)
small gaps when myelin sheaths shift during rolling/formation
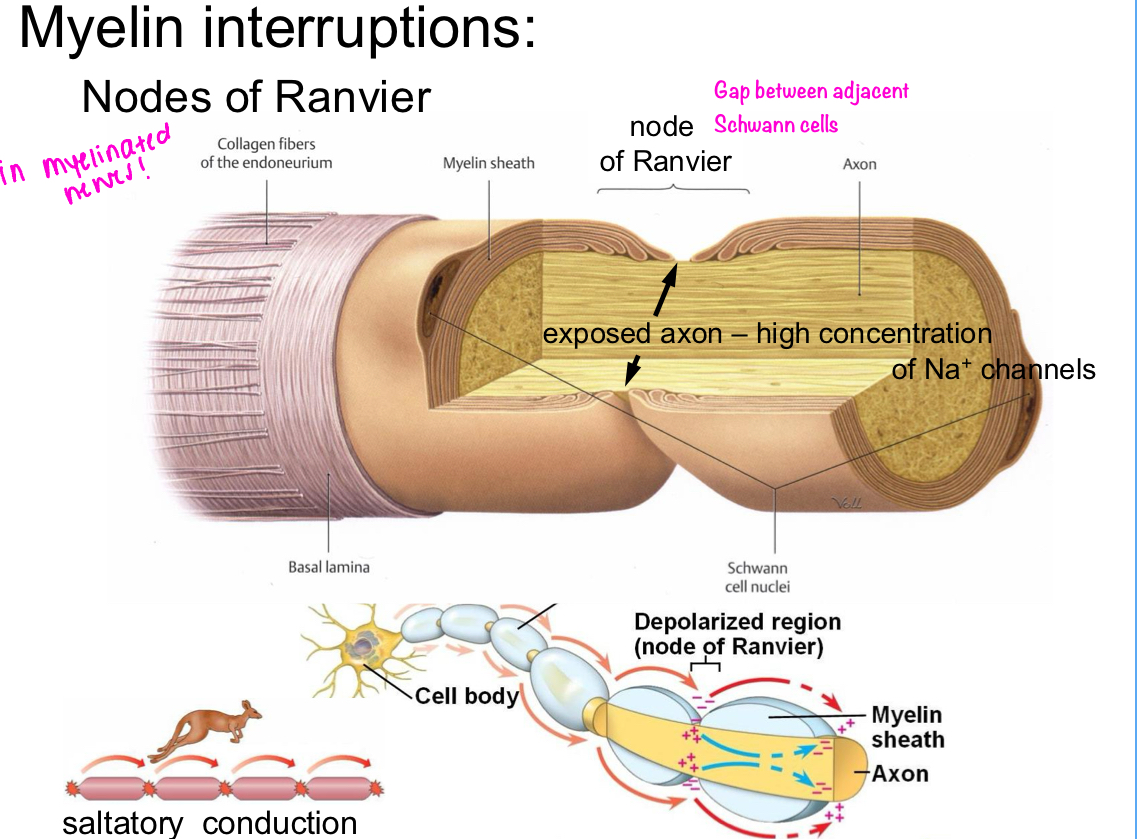
Nodes of Ranvier
T or F: most of the autonomic pathway is myelinated
FALSE
which CT layer has:
tight junctions
gap junctions
restrict cell entry (no lymphocytes and plasma cells; dye placed in blood vessel? won’t stain nerve)
control transport
are contractile
perineurium
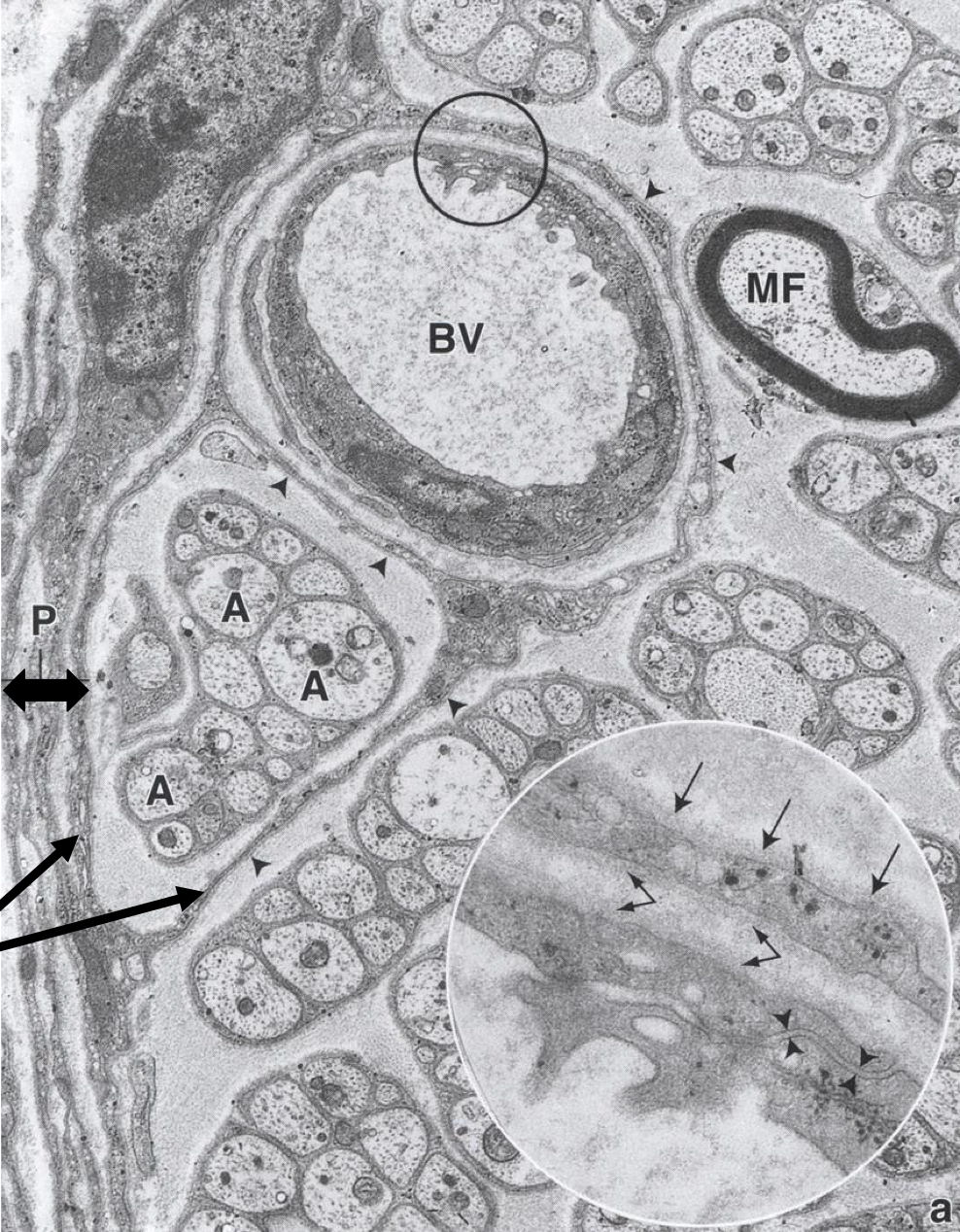
do myelinated fibers have Schwann cells? blood-nerve barrier? neuorkeratin? is their main represented group autonomic fibers?
Schwann cells: yes
blood-nerve barrier: yes
neurokeratin: no
autonomic fibers: they are the majority
many axon to 1 Schwann cell relationship
define Guillain-barre syndrome
life threatening PNS disease caused by T cell mediated immune response against myelin (leads to exposed fiber and damaged myelin)
which neuron types have myelin sheaths?
somatic sensory and somatic motor; so Guillain-barre syndrome would damage these