TS Forest Ecology i
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Autecology (population)
Study of the influence of the environmental on a single tree or species
Synecology
Study of relationships/interactions between groups of different species
Theory of island biogeography
Basically, the larger the forest the more biodiversity, the farther the island is from the core forest the less biodiversity
Edge effects
Changes in pops that occur on the boundaries of habitat types due to changes in environment
How much is the forest edge
First 100-300m
Corridors
Improve connection so facilitate gene flow, increase amount of habitat, negatively impacted by edge effects
Fields of forest ecology
Environment, ecosystem, silvics, history
Forest environment
Living and non living things occurring naturally
Forest ecosystem
Interdependency of environmental elements
Silvics
Growth and reproduction requirements of trees
Forest history
Developmental patterns over time (succession)
Factors that influence tree distribution
Climate, soil, topography, biotic factors
Climate factors that influence distribution in major terrestrial ecosystems
Standing biomass, primary production, nitrogen uptake, evapotranspiration
Stages of forest succession
Stand initiation, stem exclusion, understory reinitiation, old growth
Forest stand
Big area of trees that’s the same composition/age/etc
Forest structure
Vertical and horizontal layering, creates microclimates/niches
Structural components
Tree age/size distribution, vertical foliage distribution, horizontal canopy distribution, dead wood
Vertical forest structure
Vertical layering of different species occupying different levels within the overall canopy
Vertical forest layers
Dominant, co-dominant, intermediate, suppressed, shrubs/regeneration, forbs/grasses, soil layers
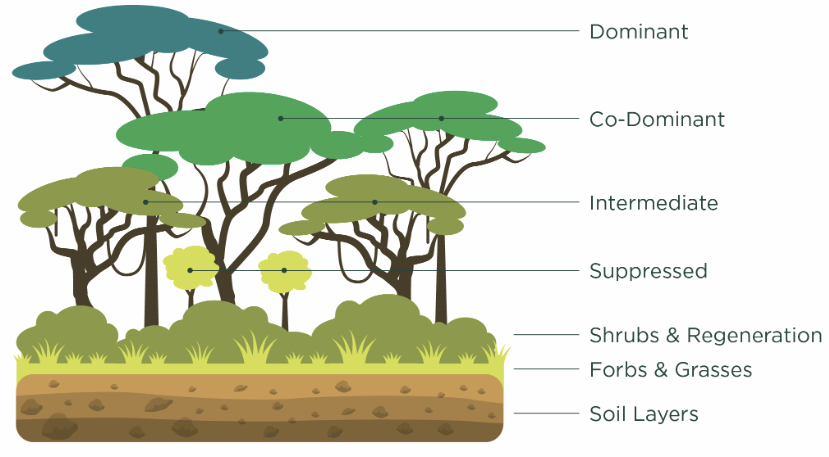
Significance of vertical structure
Influences bird species, influences insects/things that eat the fruits/nuts
Canopy closure
Portion of sky obscured by canopy from a single point