Cell Theory, Types, and Organelles: Biology Basics for Students
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
Cell Theory
A scientific theory that describes the properties of cells.
Matthias Schleiden
A botanist who observed cells under a microscope in 1838 and noted that they contained a nucleus.
Robert Hooke
The scientist who discovered cells in 1665 while observing a slice of cork under a microscope.
Micrographia
The journal in which Robert Hooke published his observations of cells.
Theodor Schwann
A scientist who studied different types of animal tissues and noted that they were made up of cells and contained a nucleus.
Rudolf Virchow
The scientist who concluded that all cells come from preexisting cells.
First part of Cell Theory
All living things are composed of cells.
Second part of Cell Theory
Cells are the basic unit of structure AND function of life.
Third part of Cell Theory
All cells come from preexisting cells.
Eukaryotic Cells
Cells that are newer, larger, and more complex, which can be unicellular or multicellular and contain organelles.
Prokaryotic Cells
Older, smaller, and simpler cells that are unicellular organisms.
Eubacteria
A type of prokaryotic cell, examples include E. Coli and Streptococcus.
Archaebacteria
A type of prokaryotic cell, examples include methanogens and halophiles.
Common Cell Features
All cells have five features in common.
Ribosomes
Structures within the cytoplasm of all cells that provide a site to make proteins coded by DNA.
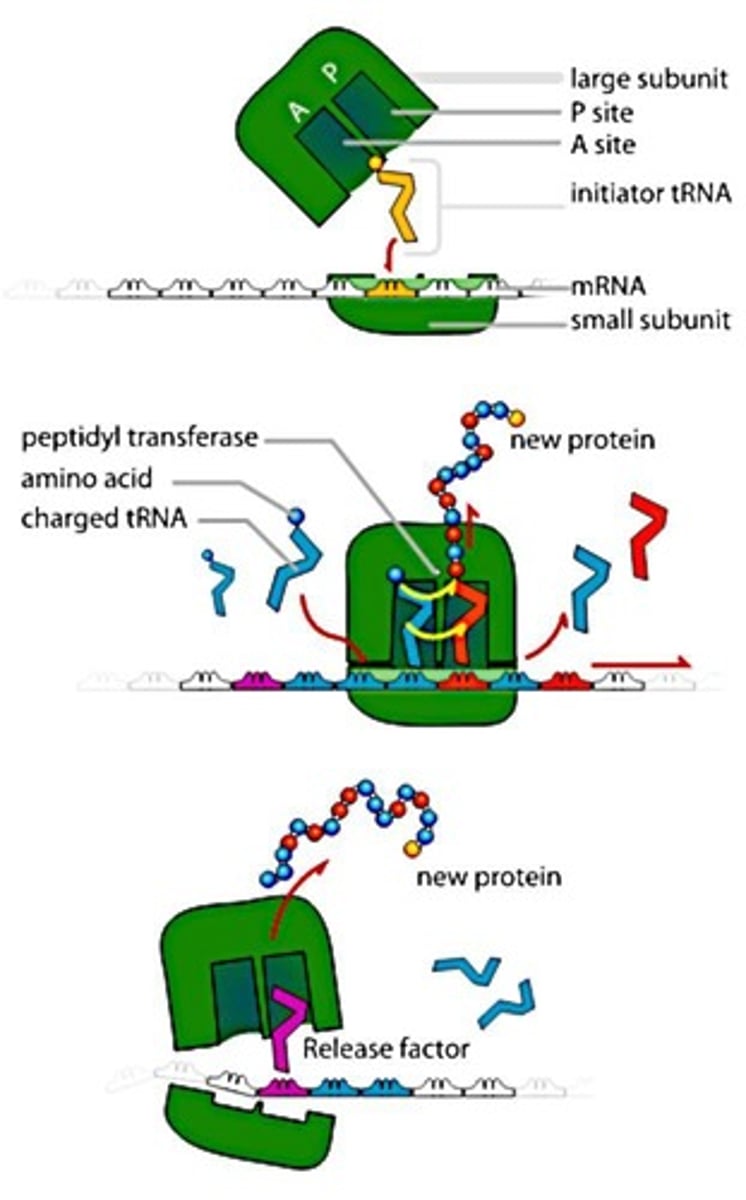
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid, which contains genetic information required to make proteins.
Nucleus
The structure in eukaryotic cells where chromosomes are housed.
Unicellular Organisms
Organisms made up of a single cell, characteristic of prokaryotes.
Multicellular Organisms
Organisms made up of multiple cells, characteristic of eukaryotes.
Cell Structures
Components that make up cells, including ribosomes and the nucleus.
Cell Division
The process by which cells arise from preexisting cells.
Antoni van Leeuwenhoek
The scientist whose findings inspired Hooke to experiment with microscopes.
Prokaryotes
Organisms made up of prokaryotic cells, which do not have a nucleus.
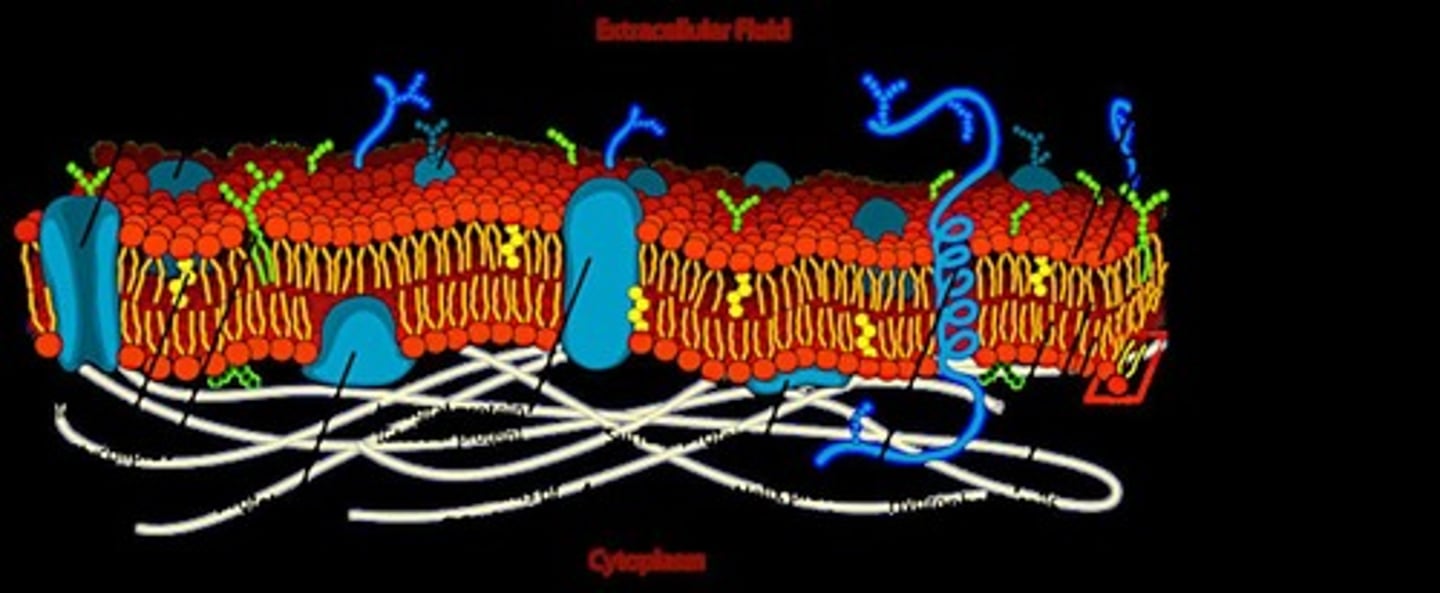
Cell Membrane
An outer boundary that separates the interior of the cell from the exterior and regulates what enters and leaves the cell.
Cytoplasm
The interior of the cell that consists of everything inside the cell except the nucleus, with the fluid portion called cytosol.
Cytoskeleton
A network of microscopic fibers within the cell that contributes to cell shape and helps movement within the cell.
Nucleoid
A clump of circular DNA found in prokaryotic cells instead of a nucleus.
Tuberculosis Mycobacteria
A highly evolved pathogenic bacteria that infects the lungs of mammals.
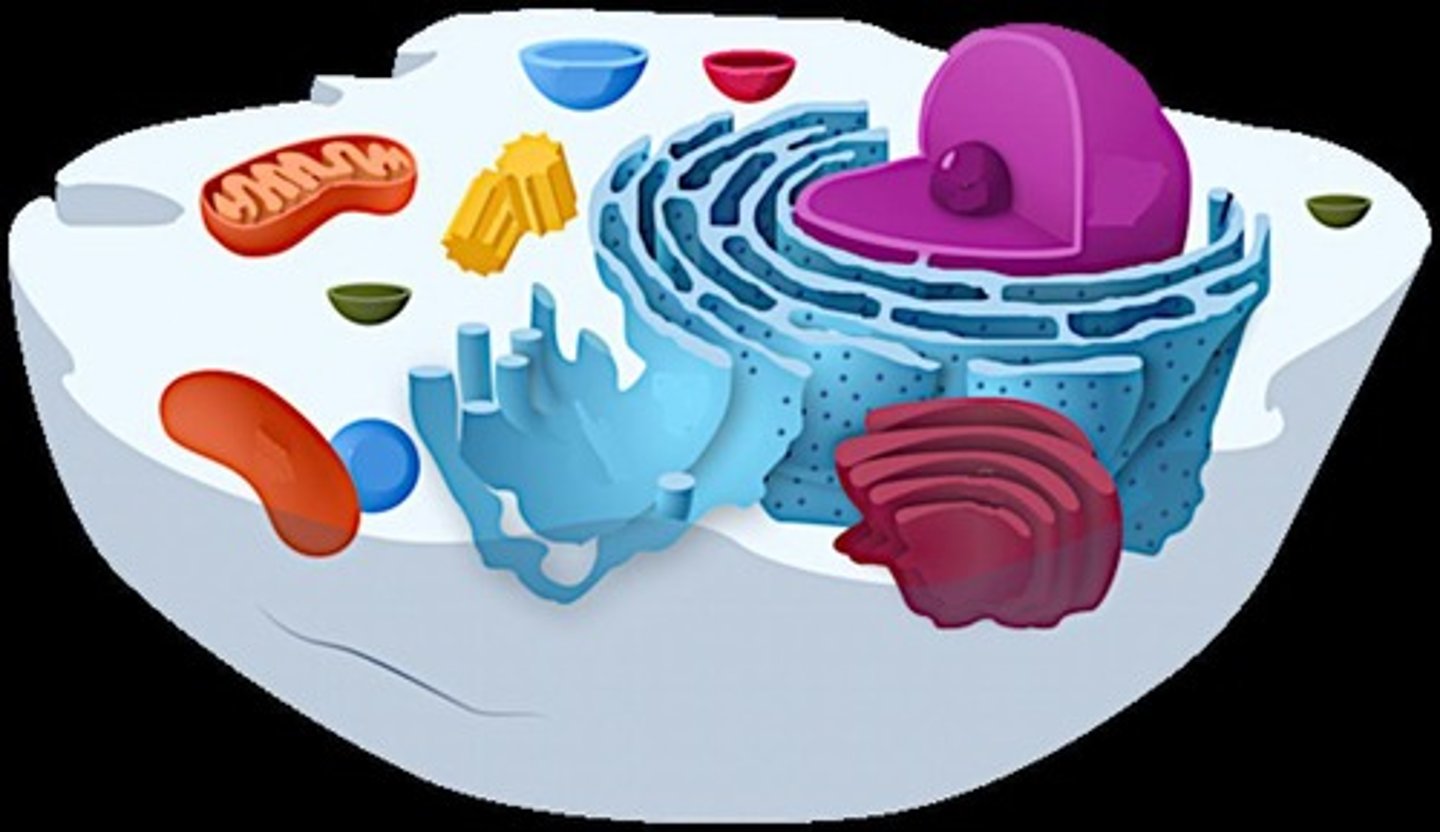
Organelles
Specialized internal compartments within eukaryotic cells.
Cell Size Comparison
Prokaryotic cells are about 5 μm, while eukaryotic cells are about 10 μm.
Evolution of Prokaryotic Cells
Prokaryotic cells evolved approximately 3.5 billion years ago.
Evolution of Eukaryotic Cells
Eukaryotic cells evolved approximately 2 billion years ago.
Cytosol
The fluid portion of the cytoplasm.
Eukaryotes
Organisms that are made up of eukaryotic cells.
Multicellular organism
An organism that consists of many cells that act as one.
Unicellular organism
An organism that consists of only one cell.
Volvox
A species of algae that lives in colonies.
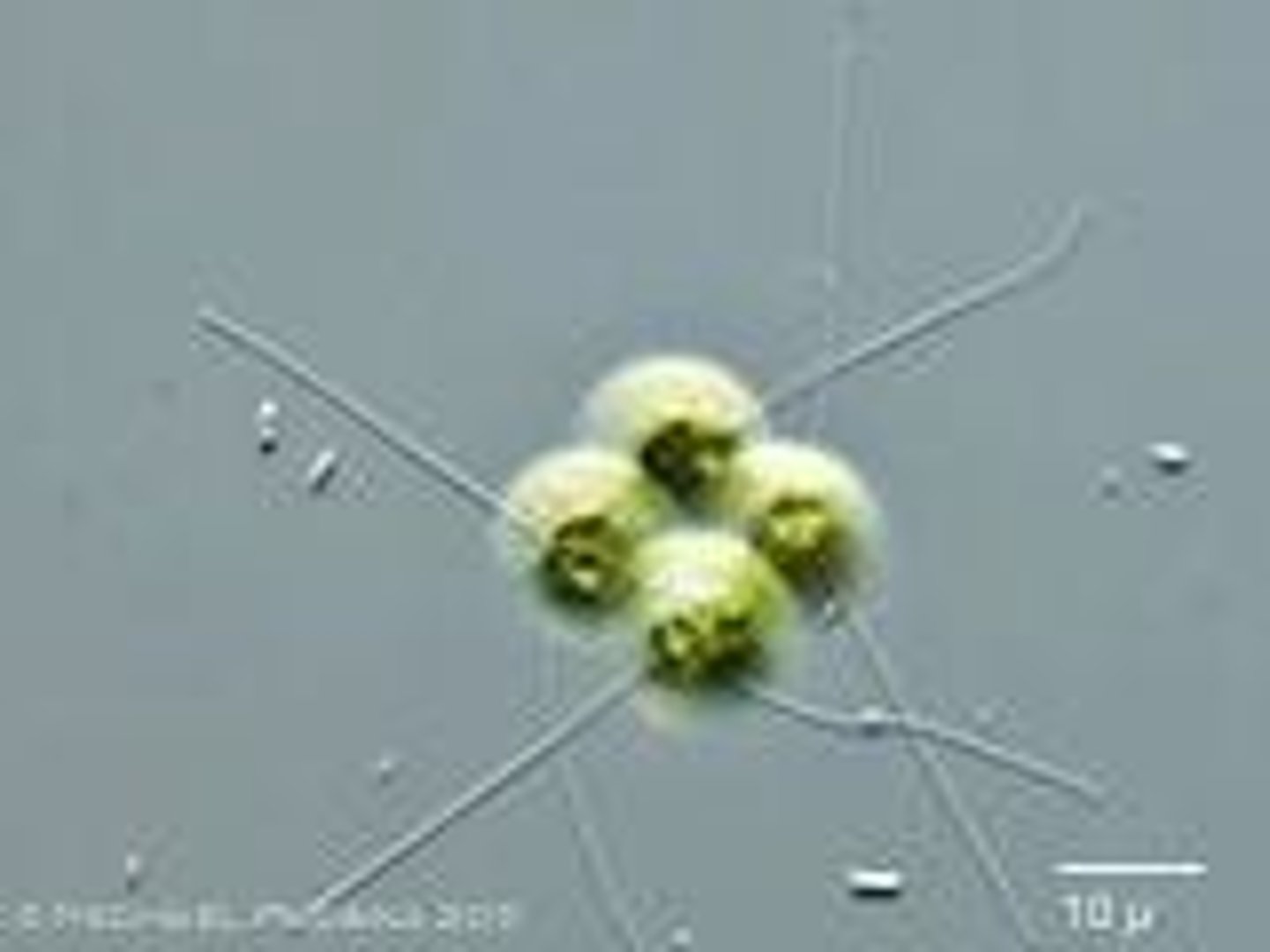

Colony
A group of many unicellular organisms that act and live as one.
Levels of Organization
The multiple levels of organization in multicellular organisms, which are: 1. Organelles 2. Cells 3. Tissues 4. Organs 5. Organ Systems 6. Organism.
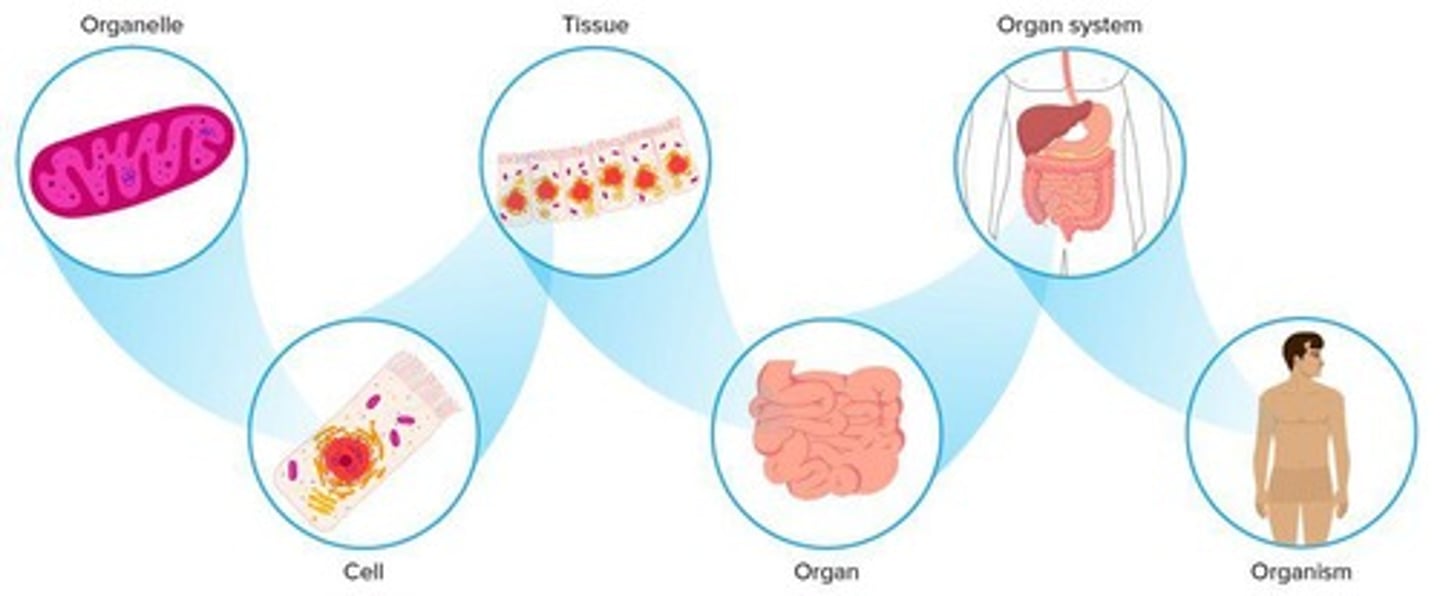
Cells
The basic building blocks of tissues and organs, made up of many different molecules which are all made of atoms.
Nucleolus
A prominent structure within the nucleus whose primary function in eukaryotic cells is to make ribosomes.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
A hollow network of tiny tubes involved in the transport and synthesis of proteins and other substances.
Smooth ER
A type of endoplasmic reticulum that is free of ribosomes and makes enzymes for specialized tasks such as calcium regulation and detoxification.
Rough ER
A type of endoplasmic reticulum that contains ribosomes and serves as a roadway for proteins to travel to different parts of the cell.
Vesicles
Membrane-bound 'containers' used to transport various substances within the cell.
Golgi body
A stack of flattened membranes that receives proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum and modifies them before sending them to other parts of the cell.
Camillo Golgi
The doctor who discovered the Golgi body in 1898.
Nuclear envelope
The membrane that surrounds the nucleus, containing tiny pores.
Nuclear pores
Tiny holes in the nuclear envelope that allow substances to enter and exit the nucleus.
Protein modification
The process by which proteins are altered after synthesis, often occurring in the Golgi body.
Animal cells
Eukaryotic cells that are typically larger than prokaryotic cells and contain a nucleus.
Plant cells
Eukaryotic cells that contain a nucleus and have a rigid cell wall.
Tissues
Groups of similar cells that work together to perform a specific function.
Organs
Structures composed of different types of tissues that work together to perform a specific function.
Golgi vesicles
These are specific vesicles involved in the transport and modification of proteins and lipids.
Mitochondria
Organelles surrounded by a double membrane that store energy as ATP.

Mitochondrion
The singular form for mitochondria.
Cellular respiration
The process by which mitochondria use glucose to create ATP.
Mitochondrial DNA
DNA inherited from the mother, also known as 'Eve's DNA'.
Vacuoles
Small membrane-bound organelles that store waste and assist in transporting substances in and out of the cell.
Lysosomes
Specialized vesicles that contain powerful enzymes to help digest old cell parts and foreign particles.
Plasma membrane
Also known as the cell membrane, it is made up of a selectively permeable phospholipid bilayer.
Selectively permeable
A property of the plasma membrane that lets only certain things in and out.
Phospholipid bilayer
A double layer of phospholipids that makes up the plasma membrane.
Water-loving head
The part of phospholipids that faces the cytoplasm and extracellular matrix, which contain water-based fluids.
Water-fearing tail
The part of phospholipids that does not interact with water.
Chloroplasts
Chloroplasts are membrane-bound organelles that contain light-absorbing pigments, such as chlorophyll.
Photosynthesis
Chloroplasts perform life's most important reaction: photosynthesis. They are able to harvest energy from the sun and use it to create sugar.
Chlorophyll
The green pigment chlorophyll is found inside the chloroplast in the cells of the leaves. It is what gives leaves their green color.
Central Vacuole
The central vacuole is a large water storing organelle found in plant cells.
Turgor Pressure
The central vacuole contributes to a plant's turgor pressure, which keeps it rigid.
Cell Wall
The cell wall is a rigid structure made of cellulose and proteins, which surrounds the cell membrane and gives the plant cell its shape.
Prokaryotic Cell Wall
Prokaryotes also have a cell wall, but it is made up of different molecules known as peptidoglycan.
Apoptosis
Some cells, such as white blood cells, only live 5 days and die by cell suicide known as apoptosis.
Stem Cells
Stem cells are immature cells that have the potential to become a number of different cells, such as a bone cell, red blood cell, skin cell or muscle cell.
Cancer
Cancer can be the result of cell life cycles that have gone out of control, causing them to multiply much faster than they should.
Largest Human Cell
The largest cell among humans is the female egg, it is about 30x larger than a sperm cell (about as thick as a strand of hair).
Number of Cells
Though we are made up of about 30 trillion cells, there are nearly 100 trillion cells in our body.