AP MICRO section 9 test
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
Inverse
what relation does price and quantity demanded have
substitution effect
consumers substitute good that becomes relatively cheaper for good that had more expensive
willingness
lower priced items
more effective than other effect that goes hand in hand with the demand curve
Income effect
the quantity demanded results from a change in the consumer’s purchasing power when the price of the goods changes
ability
for higher priced items
reinforces another effect
normal goods
change in demand directed related to a change in income
income and substitution effect move in the same direction
lowers
when price increases what happens to purchasing power?
inferior goods
change in demand inverse related to change in income
income adn substitution effect move in opposite directions
giffen good
demand curve is upward slopping
lower priced goods (generally)
income effect outweighs substitution effect
inferior good
necessity
few substitutes
price elasticity of demand
refelects how sensitive consumers are to a change in price
absolute value
elastic demand
ped>1
inelastic demand
ped<1
unitary elastic demand
ped=1
perfectly inelastic demand
price change will have no impact on consumer
quantity demand is unchanged
ped=0
vertical
Perfectly elastic demand
price change will create an infinite quantity demand when price lowers, quantity demand will go to 0 when price goes up
quantity demand=0
horizontal
ped=infinity
higher prices
demand is elastic at
lower prices
demand is inelastic at
total revenue
total value of sales of a good or service
inelastic demand
price increases and total revenue increases
price decreases and total revenue decreases
elastic demand
price decreases and total revenue increases
price increases and total revenue decreases
unitary demand
price changes and total revenue is the same
marginal revenue is 0
at what quantity is total revenue maximized?
marginal revenue is positive; negative
On a graph, where is demand elastic? in elastic?
price effect
after a price increase each unit sold sells at a higher price which tends to raise revenue
quantity effect
after a price increase, fewer units are sold which tends to lower revenue
elastic demand
quantity effect> price effect
total revenue decreases
inelastic demand
price effect> quantity effect
total revenue increases
close substitutes
the more _____ the more elastic demand will be; ped increases
inelastic
Necessity or luxury: necessity will have more __ demand
T
The smaller portion of your income, the more inelastic demand will become; the higher share income you are going to spend the more elastic demand will become (luxury goods)
time
demands becomes elastic when consumers have more ___ to adjust to the price change
cross price elasticity of demand
measures the effect of the change in one good’s price on the quantity demanded of the other good (substitutes or complements)
no absolute value
substitutes
Exy=+
(same direction)
Complements
Exy= -
(opposite direction)
no relationship
Exy=0
Income elasticity
measures the percent change in quantity demanded when income changes (normal good or inferior good)
no absolute value
normal good
ie=+
inferior good
ie= -
luxury good, income elastic
ie>1
necessity; income inelastic
ie<1
Necessity; perfect income elastic
ie=0
price elasticity of supply
measures the responsiveness of the quantity supplied to the price of the good
elastic supply
Es>1
inelastic supply
Es<1
unitary elastic supply
Es=1
Factors impacting elasticity of supply
availability of inputs (readily available at lower cost= e; high cost= I)
Time (more time to adj=more e)
ability to store (deteriorate?—I durable?)
Mobility (more mobility=more elastic)
Technology Advances
Consumer surplus
difference between the consumers’ willingness to pay for. a good and the actual price paid by them
represents how much consumers benefit by participating in the market
willingness to pay
-height of DC=value to buyer
net gain
willing pay amount-available price
producer surplus
difference between the producers cost to sell a good and the actual price paid to them
represents how much produces benefit by participating in the market
sellers cost
-height of supply curve=cost to seller
sellers cost
lowerst price willing to sell the good
cost to seller
height of supply curve
value to the buyer
height of the demand curve
lower price
consumer surplus increases: increase in surplus for original buyers and increases surplus gained with new buyers entering the market
-producer supply decreases
higher price
producer surplus increases: increase in surplus for original sellers and increase surplus gained with new sellers entering the market
-consumer surplus decreases
welfare
how people benefit by participating in the market
at equilibrium
welfare and total surplus is maximized at…
decrease total surplus
Reallocation of Consumption Among Consumers
reallocation of sales among sellers
change in Quantity traded
efficient markets
allocates consumption of the good to potential buyers who most value it= higher will to pay
allocates sales to potential sellers who most value the right to sell- lowest cost
ensures every consumer who makes a purchase values the good more than every sell who makes a sale=beneficial transaction
ensures that every potential buyer who doesn’t make a purchase values the good less than every potential seller who doesn’t make a sale=no mutual beneficial transactions are missed
caveats of efficient markets
not necessarily fair or equity
markets can fail to deliver efficiency
equilibrium does not ensure best outcome for each consumer and producer
Trade off
equity and efficiency are a ____
regressive tax
tax that has increased income taxpayers pay a small percent of income than low income tax payers
-rise less than in proportion to income
proportional tax
tax that all taxpayers pay the same percent of their income
-rises in proportion to income
progressive tax
tax that increased income taxpayers pay a large percent of income than low income taxpayers
-rises more than in proportion to income
excise tax
tax charged on a specific good
-sin taxes
-inelastic demand
effects of excise tax
shift up supply curve
drives a wedge
creates missed opportunities—discourage, distort incentive
demand shifts left, decreases
Tax incidence
demonstrates who is paying the larger burden of the tax
Consumers
when Demand is price inelastic and supply is elastic burden falls on the____.
demand, Left
which curve shifts when the burden falls on the consumers? and where?
Producers
when demand is price elastic and the supply is price inelastic, the burden of the excise tax falls on…
supply, left
when there is tax placed on producers which curve shifts and in which direction?
Deadweight Loss
loss of total surplus in the market
Lump sum tax
tax of a fixed amount paid by all tax payers
-does not affect price or quantity, does not create DWL
administrative costs
resources used by the government to collect the tax and by taxpayers to pay or evade it, over and above the amount collected
-could be doing other stuff
utility
a measurement of a personal satisfaction received from consuming a good
-offers a way to study choices in a rational way
Utils
unit used that measure your satisfaction
Marginal utility
change in total utility when consuming an additional unit
negative slope
what slope does marginal utility have?
diminishing marginal utility
as you consume more good, marginal utility decreases
consumer equilibrium
allows consumers to obtain most possible satisfaction from their income
-reached when consumers purchases assortment of goods that best meet the satisfaction requirements within financial constraints
budget constraint
limits the cost of a consumer bundle to no more than consumer income
consumption possibilites
set all consumer bundles that are affordable to income and prevailing prices
budget line
shows all the consumer bundles available to consumer who spends all of his or her income
-always consume
affects of budget line
change in income (increases, shift right)
change in price (decrease in price, rotate line out)
optimal consumption bundle
consumption bundles maximizes the consumer total utility given budget constraint=highest total income considering the trade offs
Marginal utility per dollar
additional utility from spending one more dollar on that good or service
-used to compare what should be bought first and more of
optimal consumption rule
when a consumer maximum utility in teh face of a budget constraint the marginal utility per dollar spent on each good or service in consumption bundle is the same
Q0 to Q1
what is the loss of economic activity?
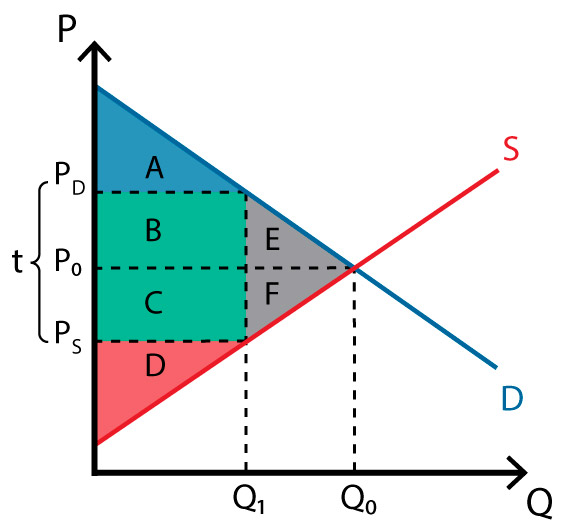
line of Q1
what is the wedge in the market?
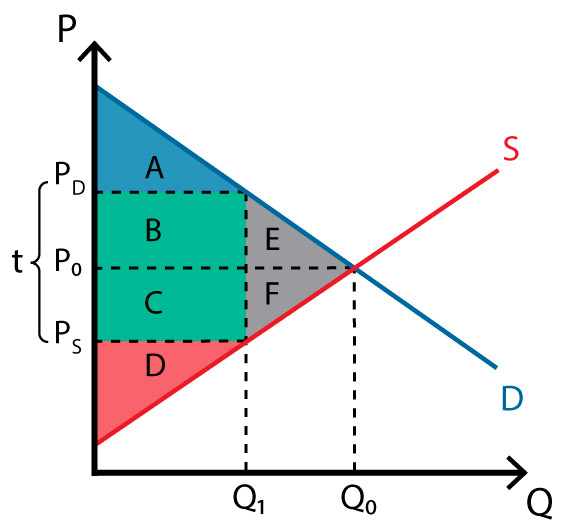
BC
what is the government revenue
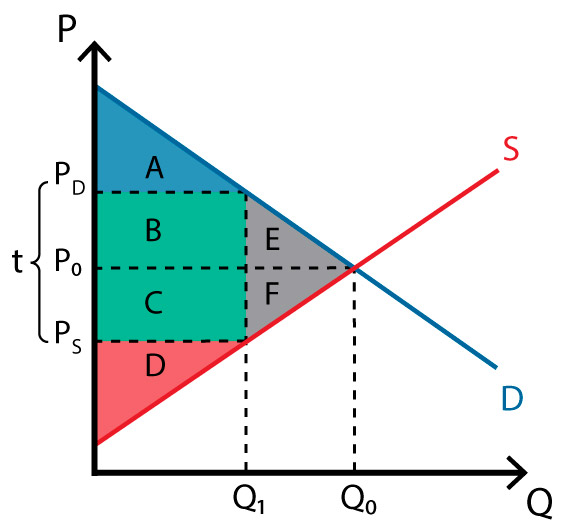
ABE; A
what is consumer surplus before tax? after tax?
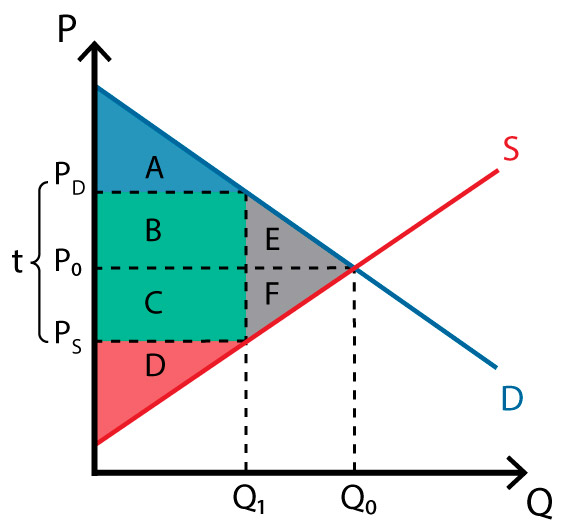
CDF; D
Producer surplus before tax? after tax?
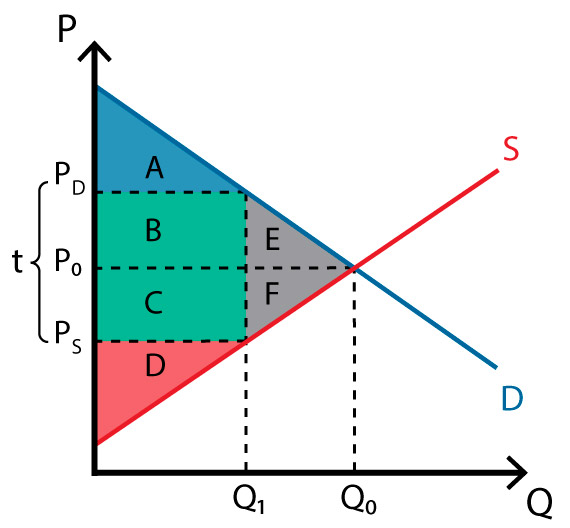
ABCDEF;ABCD
Total surplus before tax? After tax?
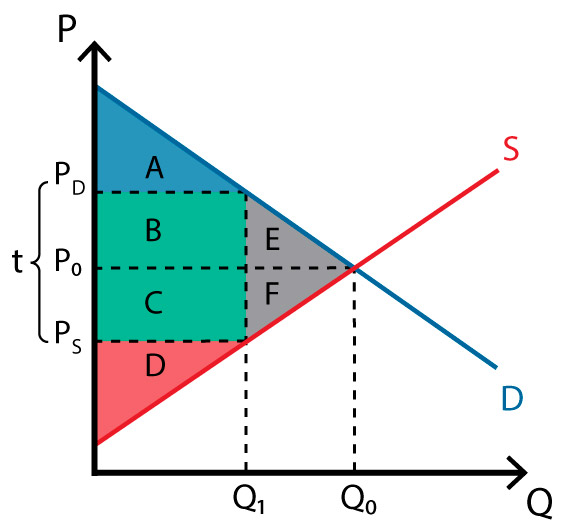
EF
what is the deadweight loss?
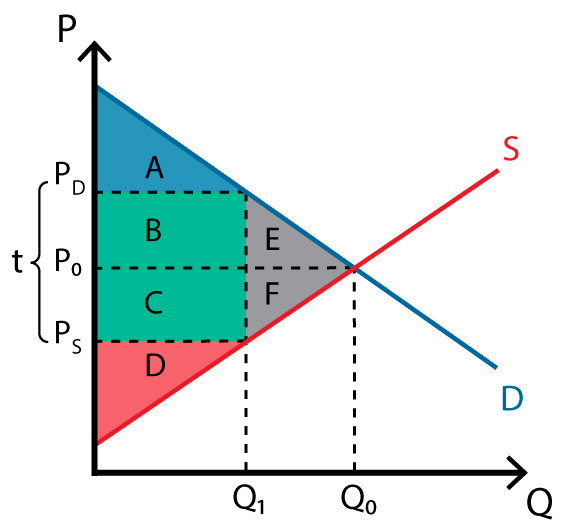
affects of tax
loss of economic activity
wedge in market
shared burden
government revenue
loss of consumer surplus and producer surplus
dead weight loss
Increasing, Max, Decreasing
when marginal utility is positive, the total utility is___, when it is 0 it is ___, when it is negative it is___.
Marginal Rate of Substitution
Rate at which a consumer will exchange one good for another while maintaining the same level of satisfaction
-indifference curve
Diminishing MRS
as a person substitutes one good for another, they require more of the substituted good to maintain utility
-reflects diminishing marginal utility
Indifference curve
combination of two good that yield equal satisfaction. In other words, the consumer would be indifferent to these different combinations.
Tangent
to maximize utility, a consumer chooses a combination of two goods at which the indifference curve is ___ to the budget line