The Money Market
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What is money?
Any commodity that is generally accepted as a form of payment
What are the 3 roles of money?
Medium of exchange
Unit of account i.e. a measure of worth
A store of value for future purchases
What is fiat money?
Money which has no intrinsic value but is acceptable by law
How do banks make money?`
By charging a higher interest rate to borrowers than sellers
How are a bank’s reserves calculated?
Reserves = Cash in the bank’s vault + bank’s deposits at the Central Bank
R = xD; where R=Cash held as reserves; x=reserve ratio; D=Fraction of total deposits
What is a bank’s main objective?
To maximise net worth (shareholder value) by creating as much profit as possible
What is Money Supply (MS)?
Currency + Bank/Building Society Deposits (C+D)
What is MS determined by?
Central Bank, which sets the monetary base (MB=C+R)
Currency (C) = cD; where c = ration of currency to deposits; D = deposits
Commercial Banks and Building Societies create deposits by making loans
What is the money multiplier (MM) equation?
MM = ∆MS/∆MB
Explain how the money multiplier is found
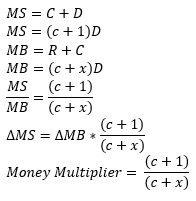
What are the 3 reasons why people hold money?
Transactions Demand
Money needed for purchases
Rises with income and nominal prices
Precautionary Demand
For emergencies
Speculative Demand
AKA Asset Demand
Falls as r rises
Increases with wealth
M/P = L(r,Y)
What does the quantity of money people plan to hold on to depend on?
Price level
Interest Rate
Real GDP
Financial Innovation
(Note: Price level only affects nominal demand, whilst the others all affect real demand)
What is an interest rate?
The opportunity cost of holding wealth in the form of money, rather than an interest-bearing asset
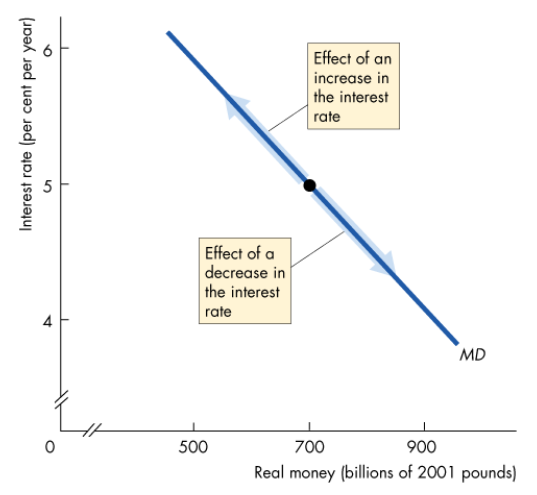
How do interest rates change when there’s a change in the quantity of money demanded?
An increase in r brings a decrease in QD
A decrease in r brings an increase in QD
How does a change in GDP affect the demand for money?
An increase in real GDP increases the volume of expenditure, which increases the quantity of real money people plan to hold, shifting the money demand curve right
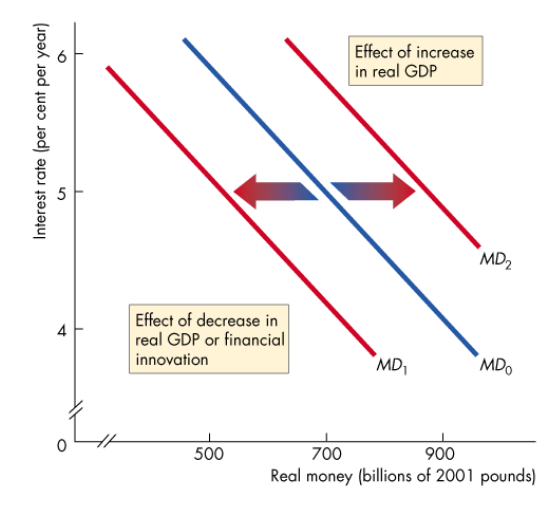
How does financial innovation affect the demand for money?
A financial innovation that lowers the cost of switching between money and interest-bearing assets decreases the quantity of money that people plan to hold, shifting the money demand curve leftwards.
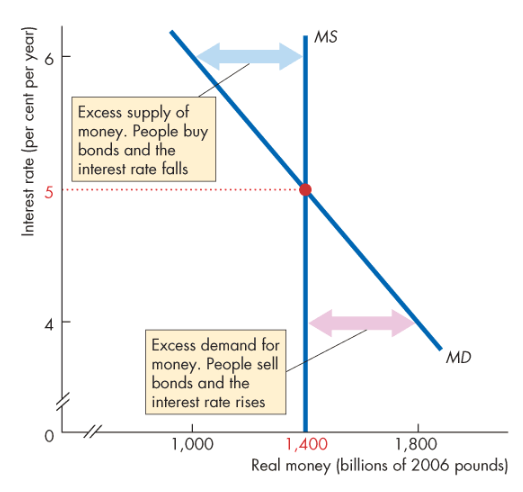
What happens if the interest rate is above the equilibrium interest rate?
There’s a surplus of money so people try to get rid of it by buying financial assets, which lowers r
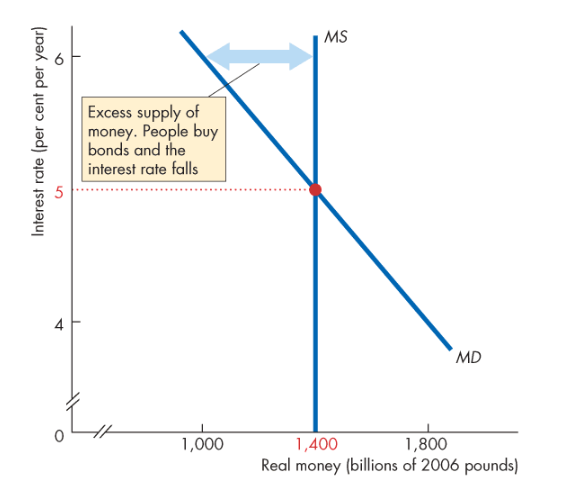
What happens if the interest rate is below the equilibrium interest rate?
There’s a shortage of money, so in order for people to get more money, they try to sell financial assets such as bonds, which increases r