Cells
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Describe the structure of the nucleus. (4 marks)
Nuclear envelope
Nuclear pores
Chromosomes/chromatin
Nucleolus
What are the functions of the nucleus? (2 marks)
Codes genetic information to code for polypeptides
Site of DNA replication
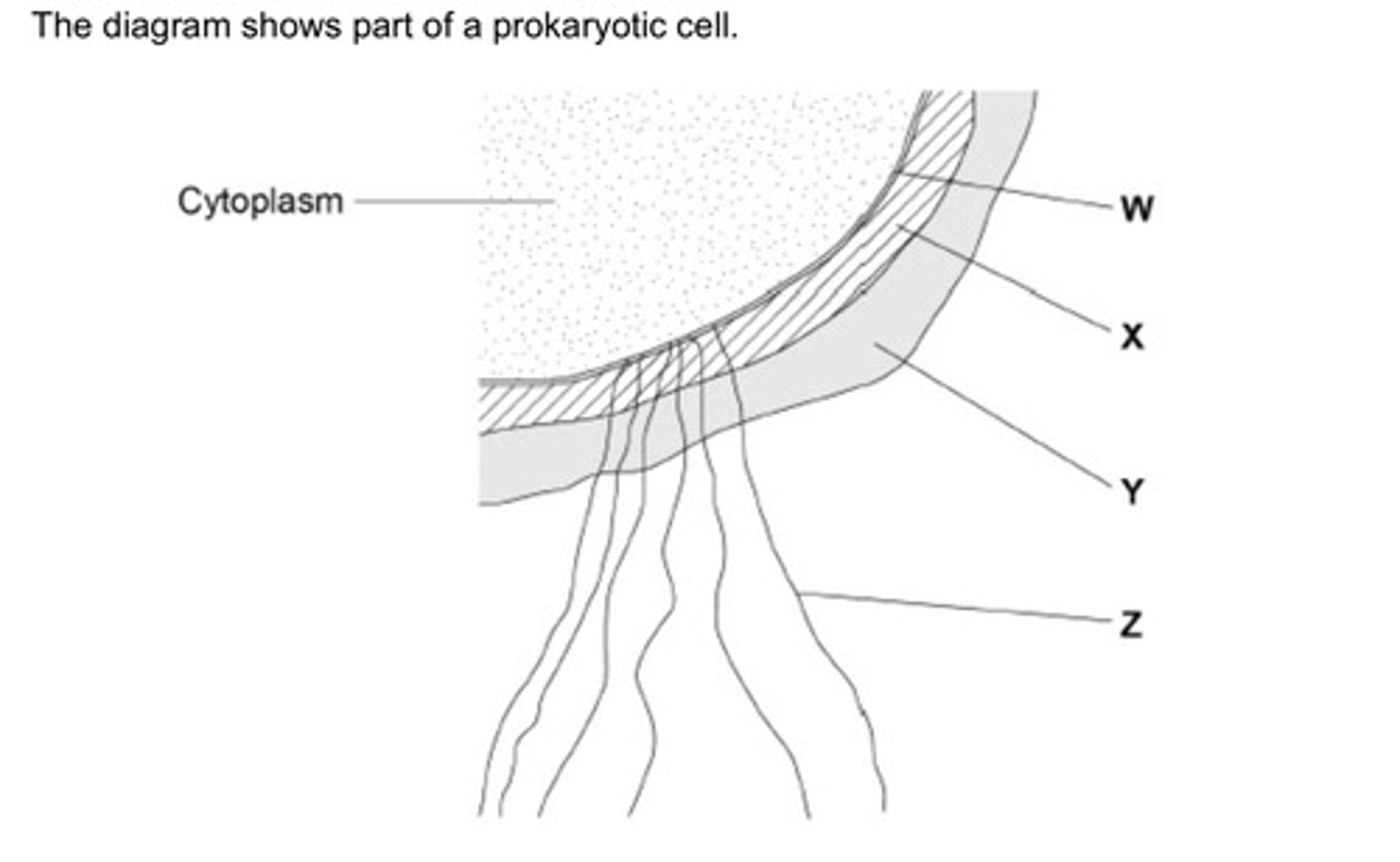
Name the structures labelled W to Z in the diagram (2 marks)
W - (cell surface) membrane
X - cell wall
Y - capsule
Z - flagellum
Contrast how an optical microscope and a transmission electron microscope work and contrast the limitations of their use when studying cells. (6 marks)
TEM use electrons and optical use light
TEM allows a greater resolution
So with TEM smaller organelles can be observed OR greater detail in organelles can be observed
TEM can view only dead specimens and optical can view live specimens
TEM does not show colour and optical does
TEM requires thinner specimens
TEM requires a more complex/time consuming preparation
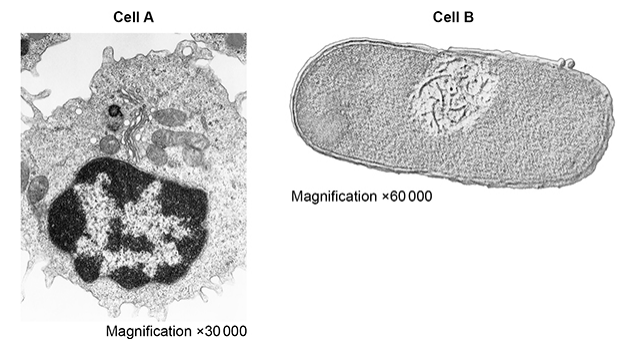
The figure shows transmission electron micrographs of two cells, one animal cell and one prokaryotic cell.
Contrast the structure of the two cells visible in the electron micrographs shown in the figure above. (5 marks)
Magnification (figures) show A is bigger than B
A has a nucleus whereas B has free DNA
A has Golgi body whereas B does not
A has no cell wall whereas B has a murein/glycoprotein cell wall
A has larger ribosomes
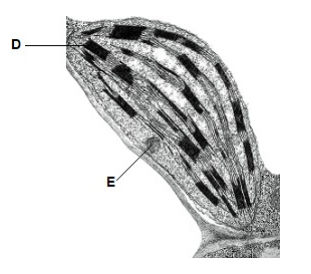
Identify structures labelled D and E. (2 marks)
D - Thylakoid
E - Starch grain
U. marinum cells ingest bacteria and digest them in the cytoplasm.
Describe the role of one named organelle in digesting these bacteria. (3 marks)
Lysosomes
Fuse with vesicle
Releases hydrolytic enzymes
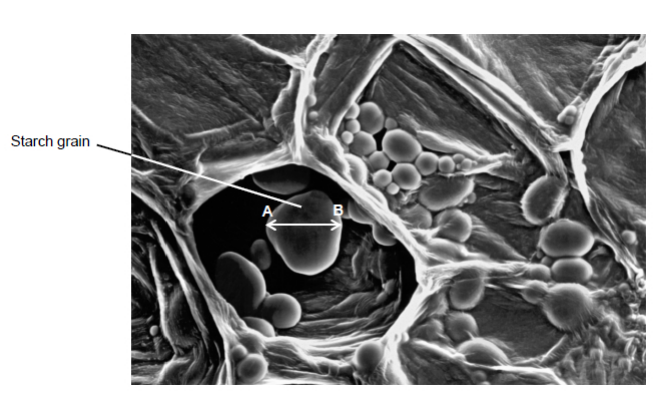
What type of microscope was used to obtain the image shown in the diagram?
Give one piece of evidence to support your answer. (2 marks)
Scanning electron microscope
3D image
Outline the sequence of events following the production of extracellular proteins that leads to their release from the cell. (3 marks)
Proteins move to Golgi apparatus where they are processed or modified
Packaged into vesicles
Vesicles moved to CSM where they fuse in a process called exocytosis
The epithelial cells of the small intestine have large numbers of mitochondria. Explain how this is an adaption for the function of these cells. (3 marks)
Mitochondria is site of ATP production
High respiration rate if there are lots of them for active transport.
Energy released needed for the absorption of digested foods
Describe how to make a temporary mount of a piece of plant tissue to observe the number of chloroplasts in the cells when using an optical microscope. (4 marks)
Add a drop of water to the glass slide
Obtain a thin section of plant tissue and place on slide
Stain with iodine in potassium iodide
Lower cover slip using a mounted needle
Describe and explain how cell fractionation and ultracentrifugation can be used to isolate mitochondria from a suspension of animal cells. (5 marks)
Use isotonic solution to prevent damage to organelles
Keep cold to prevent damage by enzymes/use buffer to prevent protein denaturation
Cell homogenisation to break open cells
Filter to remove large debris and whole cells
Centrifuge (at lower speed) to separate nuclei/heavy organelles
Re-spin supernatant at higher speed to get mitochondria in pellet
Explain why the solution the biologist used was ice-cold, buffered and the same water potential as the liver tissue. (3 marks)
Ice-cold - reduces enzyme activity to prevent digestion of organelles
Buffered - Maintains pH so that proteins are not denatured
Same water potential - Prevents osmosis so no bursting / shrinking of organelles
Before the cell was examined using the electron microscope, it was stained. This stain caused parts of the structure of the cell-surface membrane to appear as two dark lines.
Suggest an explanation for the appearance of the cell-surface membrane as two dark lines. (3 marks)
Membrane has phospholipid bilayer
Stain binds to phosphate
On inside and outside of membrane
Describe binary fission in bacteria. (3 marks)
Replication of circular DNA
Replication of plasmids
Division of cytoplasm to produce daughter cells
Give two processes which occur during interphase and which are necessary for nuclear division to take place. (2 marks)
Replication of DNA
ATP production
Suggest and explain how two environmental variables could be changed to increase the growth rate of these cells. (4 marks)
Increased concentration of glucose
Increased respiration
Increased temperature
Increased enzyme activity
The student carried out several repeats at each ____________ . Explain why the repeats are important. (2 marks)
Allows anomalies to be identified, which can then be ignored
Makes the average more reliable
Endocytosis and exocytosis are processes that move large molecules into and out of cells.
Describe the similarities and differences between endocytosis and exocytosis. (3 marks)
Both processes form vesicles
Both processes require energy from ATP
Endocytosis involves substances entering cell while exocytosis involve substances leaving cell
Suggest one explanation for the faster rate of plasmid replication in cells growing in a culture with a high amino acid concentration. (2 marks)
Amino acids used in protein synthesis
So more enzymes for DNA replication
Read the following passage.
In laboratory tests, scientists investigated the effects of a new drug called ABZ on stomach tumour cells. They found ABZ stopped mitosis by preventing the formation of spindle fibres. They also found that ABZ affected some healthy cells.
Suggest why preventing the formation of spindle fibres stopped the cell cycle. (2 marks)
Chromatids cannot separate (on spindle)
So no anaphase
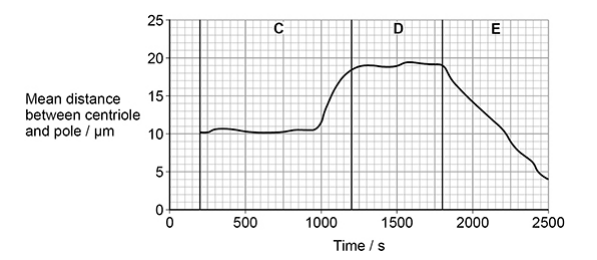
Name the three phases of mitosis shown by C, D and E on the figure above. Describe the role of the spindle fibres and the behaviour of the chromosomes during each of these phases. (5 marks)
C = prophase and D = metaphase and E = anaphase
In prophase, chromosomes condense
In metaphase, chromosomes at equator/centre of cell
In anaphase, chromatids (from each pair) pulled to (opposite) poles/ends of cell
In anaphase, spindle fibres shorten

The image shows one cell the student saw in the onion tissue. The student concluded that the cell in the image above was in the anaphase stage of mitosis.
Was she correct? Give two reasons for your answer. (2 marks)
Yes - Chromatids are in separate poles of spindle
V-shape shows that sister chromatids have been pulled apart at their centromeres
The dark stain used on the chromosomes binds more to some areas of the chromosomes than others, giving the chromosomes a striped appearance.
Suggest one way the structure of the chromosome could differ along its length to result in the stain binding more in some areas. (1 mark)
Differences in base sequences
Describe the appearance and behaviour of chromosomes during mitosis. (5 marks)
During prophase
Chromosomes condense
During metaphase
Chromosomes line up on the equator / centre of the cell
Chromosomes attached to spindle fibres
During anaphase
The centromere divides
Sister chromatids are pulled to opposite poles of the cell
During telophase
Chromatids uncoil
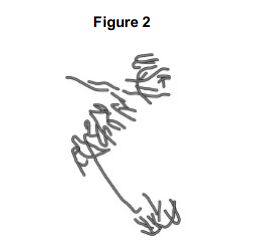
A scientist treated growing tips of onion roots with a chemical that stops roots growing. After 24 hours, he prepared a stained squash of these root tips.
Figure 2 is a drawing showing the chromosomes in a single cell observed in the squash of one of these root tips in anaphase. This cell was typical of other cells in anaphase in these root tips.
Use all of this information to suggest how the chemical stops the growth of roots.
Stops anaphase
Stopping spindle fibres forming
Preventing separation of sister chromatids
So no new cells added to root tip
Describe the method the student would have used to obtain the results in the graph. Start after all of the cubes of potato have been cut. Also consider variables he should have controlled. (3 marks)
Method to ensure all cut surfaces of the eight cubes are exposed to the sucrose solution
Method of controlling temperature
Method of drying cubes before measuring
Measure mass of cubes at stated time intervals
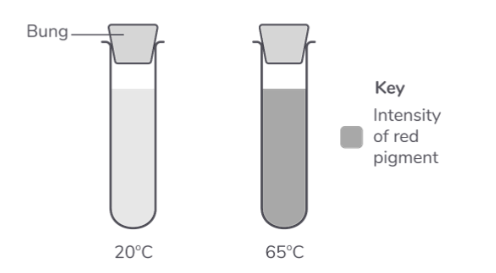
The diagram shows one of the test tubes from the 20°C water bath and one from the 65°C water bath.
What conclusion can be made about the effect of temperature on the damage to beetroot cells? Provide an explanation for your conclusion. (4 marks)
water at 20°C caused no damage
to the cell-surface membrane
65°C caused damage to the membrane
65°C denatured membrane proteins
The movement of substances across cell membranes is affected by membrane structure. Describe how. (5 marks)
Phospholipid bilayer allows movement of nonpolar/lipid-soluble substances
Membrane proteins allow polar/charged substances to cross the membrane/bilayer
Carrier proteins allow active transport
Channel/carrier proteins allow facilitated diffusion/co-transport
Cholesterol affects permeability
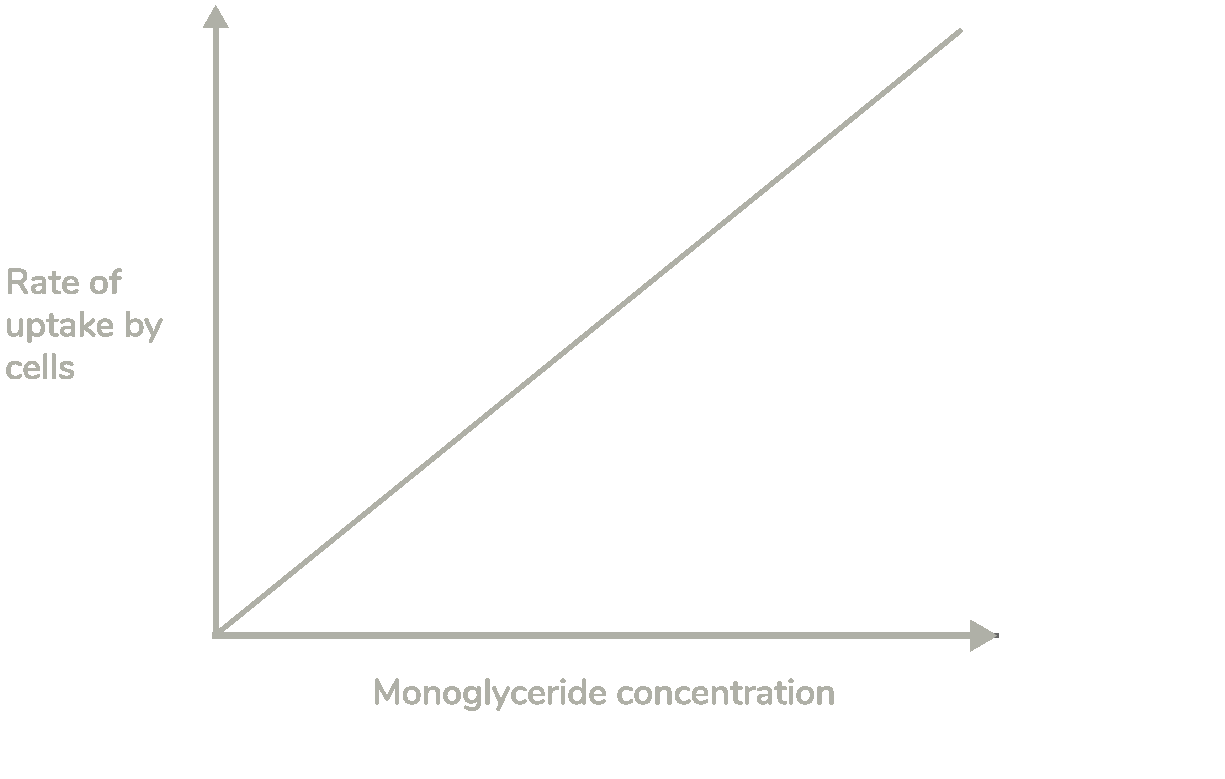
Use the graph to explain how this monoglyceride is transported into cells within the digestive system. (3 marks)
Rate of uptake is proportional to concentration
This means that monoglycerides move by simple diffusion
Because they are lipid soluble
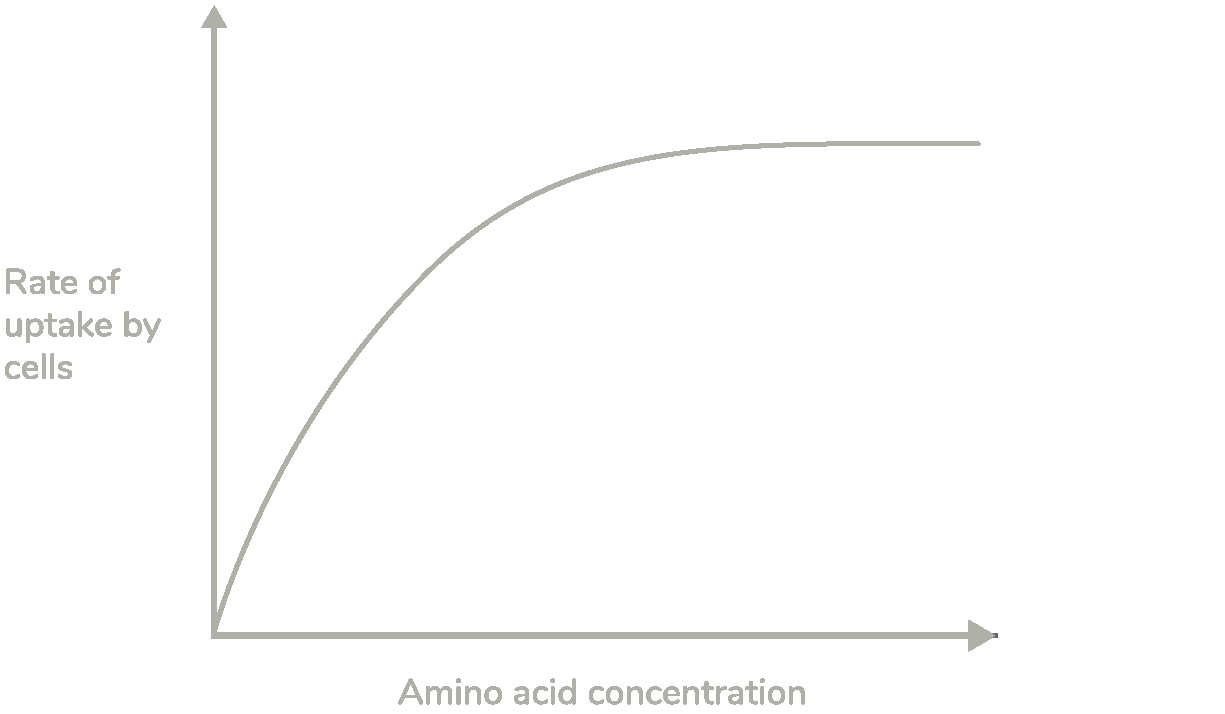
A scientist investigated the rate of absorption at different amino acid concentrations by cells lining the small intestine.
Use your knowledge of membrane transport to describe and explain the shape of the curve shown above. (4 marks)
As the amino acid concentration increases, the rate of uptake increases
Because as amino acid concentration increases, more amino acids move through carrier proteins
The rate of uptake levels off at higher amino acid concentrations
Because all carrier proteins are saturated
The sports drink contains sodium chloride. Sodium chloride increases uptake of glucose in the small intestine. Explain how. (4 marks)
Sodium ions and glucose absorbed by co-transport
Sodium ions removed by active transport into blood
Sodium ions enter epithelial cells by facilitated diffusion taking glucose with them
Glucose moved by facilitated diffusion into blood
Individuals that suffer with lactose intolerance cannot break down lactose and so it remains in the lumen of the intestine.
The presence of lactose decreases the volume of water that is absorbed into the blood, causing diarrhoea.
Explain why undigested lactose in the intestine causes diarrhoea. (3 marks)
Lactose lowers the water potential (in the lumen of the intestine)
This reduces the water potential gradient (between the intestine and blood)
Less water is reabsorbed into the blood by osmosis so more water is present in faeces
Applying salt to a wound can help prevent bacterial infection.
Using your understanding of water potential, propose how the application of salt to a wound could eliminate bacteria. (3 marks)
Salt lowers the water potential of the solution surrounding the bacteria
The bacterial cytoplasm contains a higher water potential than its surroundings
Water moves out the bacterial cells by osmosis
Loss of water from bacterial cells causes dehydration and death of bacteria
Explain the differences between facilitated diffusion and active transport. (3 marks)
Facilitated diffusion involves channel or carrier proteins while active transport only involves carrier proteins
Facilitated diffusion is passive while active transport is not passive
Facilitated diffusion takes place down a concentration gradient while active transport can occur against a concentration gradient
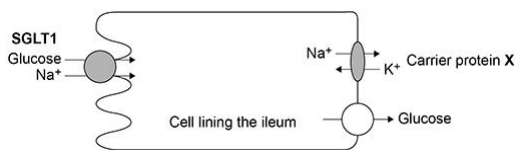
The action of the carrier protein X in Figure 1 is linked to a membrane-bound ATP hydrolase enzyme.
Explain the function of this ATP hydrolase. (2 marks)
ATP to ADP + Pi releases energy
Energy allows ions to be moved against a concentration gradient
Sodium ions from salt (sodium chloride) are absorbed by cells lining the gut. Some of these cells have membranes with a carrier protein called NHE3. NHE3 actively transports one sodium ion into the cell in exchange for one proton (hydrogen ion) out of the cell.
Use your knowledge of transport across cell membranes to suggest how NHE3 does this. (3 marks)
Co-transport
Uses (hydrolysis of) ATP
Sodium ion and proton bind to the protein
Protein changes shape (to move sodium ion and proton across the membrane)
Suggest and explain two ways the cell-surface membranes of the cells lining the uterus may be adapted to allow rapid transport of nutrients. (2 marks)
Microvilli to increase surface area
Large number of carrier proteins for facilitated diffusion;
Describe how phagocytosis of a virus leads to presentation of its antigens. (3 marks)
Phagocyte engulfs pathogen and forms phagosome vesicle
Lysosomes release lysozymes which hydrolyse the pathogen
Antigen is presented on cell surface membrane
Suggest one reason why it was necessary to give two doses of the vaccine. (1 mark)
Antibodies go down over time
An antigen in a vaccine leads to the production of antibodies. Describe the part played by B lymphocytes in the process. (4 marks)
Macrophages present antigens to B lymphocytes
Antigen binds to receptors on lymphocyte
B lymphocytes reproduce by mitosis
Plasma cells secrete antibodies
Although this vaccine is made from antigens from malarial parasites, it does not cause malaria. Explain why this vaccine does not cause malaria. (2 marks)
Antigens only part of the parasite
They do not cause the disease
Changes to the protein coat of the influenza virus cause antigenic variability. Explain how antigenic variability has caused some people to become infected more than once with influenza viruses. (2 marks)
Antibodies previously produced are not effective
As shape not complementary to the new antigen
Describe how antibodies are produced in the body following a viral infection. (6 marks)
Virus contains antigen
Virus engulfed by phagocyte
Presents antigen to B-cell;
B-cell becomes activated
Divides to form clones by mitosis
Plasma cells produce antibodies specific to antigen
Explain the role of B-lymphocytes and T-lymphocytes in the defence of the body against a virus infection. (6 marks)
B lymphocytes produce antibodies involved in humoral response
T lymphocytes involved in cell-mediated immunity
B lymphocytes bind to antigen which increase in numbers by mitosis
Produce plasma cells, secrete antibodies which bind to and agglutinate virus
Tc cells kill virus-infected cells
Antibiotics are not used to treat viral infections, such as HIV. Explain why. (2 marks)
Antibiotics stop metabolism, and viruses don’t have metabolism
Viruses hide in cells where antibiotics cannot reach them
Some antibiotics work against ribosomes, which viruses don’t have
So far, these types of vaccine have not been considered safe to use in a mass vaccination programme.
Suggest why they have not been considered safe. (3 marks)
Inactive virus may become active
Attenuated virus may become harmful
Non-pathogenic virus may mutate and harm cells
Describe how HIV is replicated after it has entered a human cell. (4 marks)
Reverse transcriptase enzyme uses HIV RNA to make DNA copy
Used to make HIV capsid proteins
New virus particles assembled
Budding off from membrane
Describe how the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is replicated once inside helper T cells (TH cells). (4 marks)
RNA converted into DNA using reverse transcriptase
DNA incorporated into helper T cell DNA
DNA transcribed into HIV mRNA
HIV mRNA translated into new HIV/viral proteins for assembly into viral particles
Describe the role of antibodies in producing a positive result in an ELISA test. (4 marks)
First antibody binds to antigen
Second antibody with enzyme attached is added
Second antibody attaches to antigen
Substrate/solution added and colour changes
Bacterial meningitis is a potentially fatal disease affecting the membranes around the brain. Neisseria meningitidis (Nm) is a leading cause of bacterial meningitis.
In the UK, children are vaccinated against this disease. Describe how vaccination can lead to protection against bacterial meningitis. (6 marks)
Antigen on surface of bacterium binds to surface receptor on a B cell
Activated B cell divides by mitosis
Division stimulated by cytokines
B cells / plasma cells release antibodies
Some B cells become memory cells
Memory cells produce antibodies faster