ingestive behaviors
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
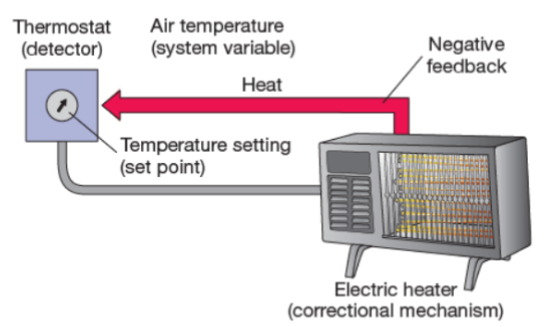
system variable
the physiological property that is being controlled by the regulatory mechanism (air temp)
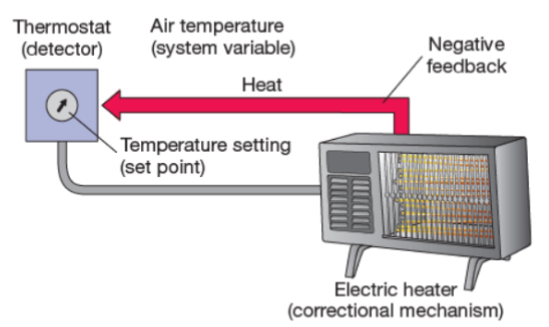
set point
the optimal value for the system variable (temp setting)
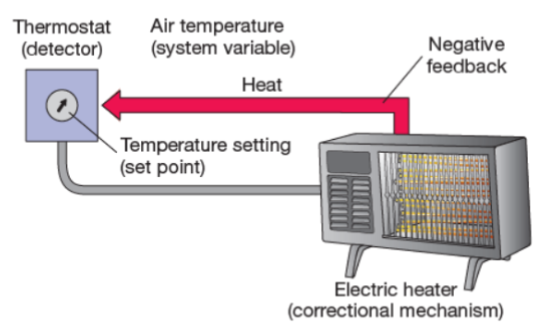
detector
a sensor to measure changes in the set point (thermostat)
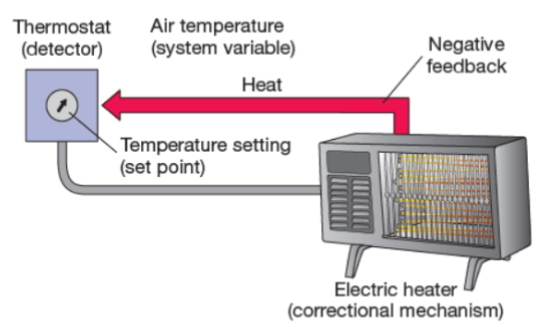
correctional mechanism
a mechanism for changing the system variable in order to restore it to the set point (electric heater)
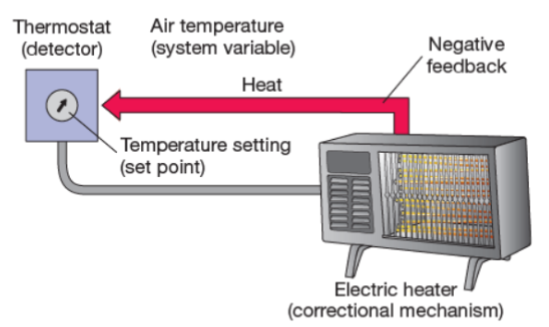
negative feedback
a mechanism that works to shut down the action of the correctional mechanism (heat)
satiety mechanism
brain mechanism that causes the cessation of hunger or thirst signals when the body has adequate nutrients from food or replenishment of water
intracellular fluid
detects fluid inside our cells and helps to maintain the balance of salts and fluids around our cells
intravascular fluid
we can detect the volume of intravascular fluid in order to maintain the functions of the heart and circulatory system
osmoreceptor
stretch sensitive neuron
signal for osmometric thirst
changes in cell volume causes in the membrane
volumetric thirst
detects a decrease in blood plasma levels; multiple things can cause these changes: evaporation of water through skin, loss of blood, vomiting, diarrhea
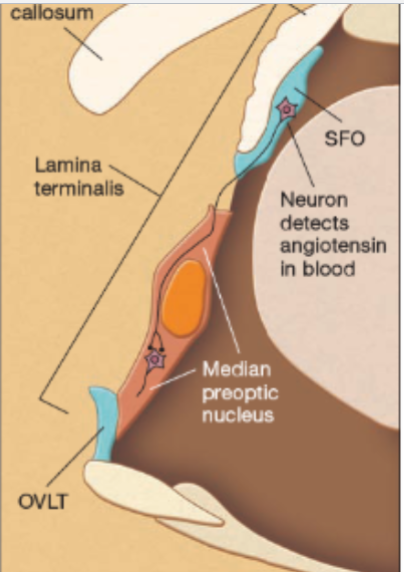
angiotensin
triggers drinking and induces a salt appetite; also causes kidneys to increase blood pressure and conserve intravascular fluid in order to protect the body
baroreceptors
in the heart rate stretch sensitive and also detect changes in blood volume
ovlt and sfo
two structures that monitor osmotic thirst; located outside of the blood brain barrier
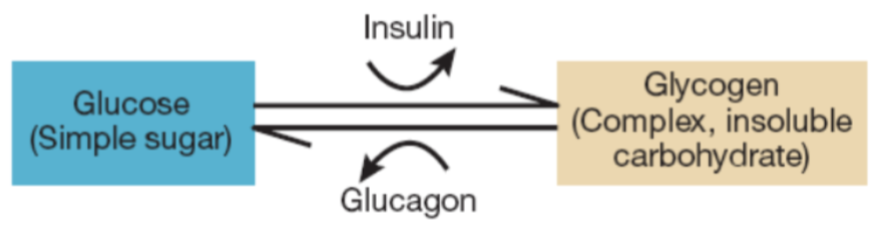
glycogen
main fuel; complex carbohydrate
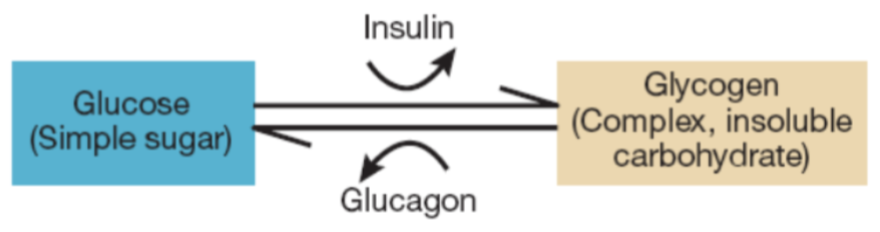
insulin
in the liver triggers the conversion of glucose to glycogen for storage
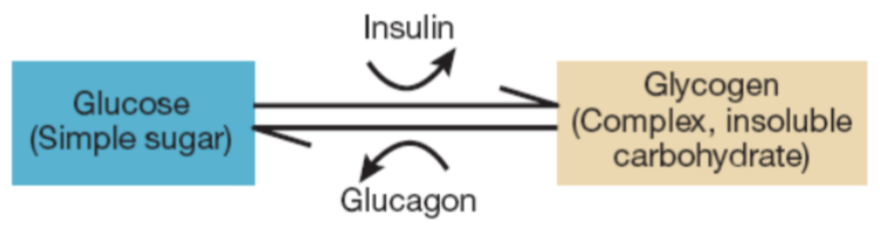
glucagon
can then convert glycogen to glucose when needed to stabilize blood sugar
adipose
fat tissue that contains cells that concert nutrients from the blood into triglycerides or back into fuel for the body when needed
triglycerides
a type of fat in the body that are essential for energy but can be harmful in excess; most common type of fat in the body and come from food, especially butter, oils, and other fats
empty digestive
the pancreas stops secreting insulin and starts secreting glucagon; glucose become reserved for the brain; we begin drawing from short and long term reserves; proteins will eventually be converted for fuel
available digestive
glucose levels rise, causing the pancreas to stop secreting glucagon and start making insulin; this allows the cells in the body to use glucose as fuel (and for the projection of glycogen); amino acids are used to build proteins or stored as fat; fat from food is stored for later
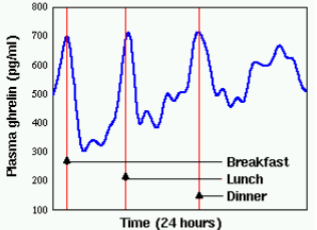
ghrelin
hormone that also acts as a neuropeptide (neurotransmitter for signaling neurons); released by the stomach and other parts of the gastrointestinal system when they are empty; binds to the hypothalamus to help initiate feeding or food-seeking; ghrelin increases before each meal; injections stimulate thoughts of eating
satiation
occurs when we are full after a mean or beyond the point of full/satisfied
satiety signals
the signals for satiation
medulla
receives taste info from the togue, input from the intestines and stomach and contains detectors for glucose to help signal the brains need for glucose when levels fall, active in hungry rats and can signal the need to pull nutrients from adipose tissue
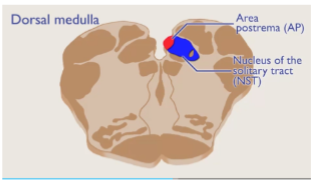
dorsal
Relating to the back or posterior of a structure
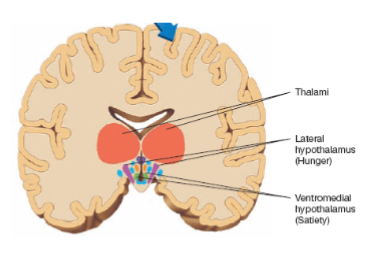
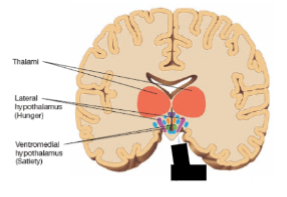
lateral hypothalamus
lesions stops eating or drinking, while electrical stimulation causes voracious eating and drinking
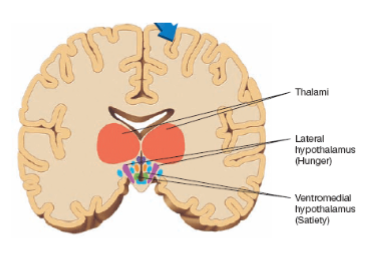
ventromedial hypothalamus
lesions produce overeating and electrical stimulation suppress feeding
mch and orexin
neurons in the lateral hypothalamus stimulate hunger
neuropeptide y (npy)
neurons that release this are found in the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus; increased when animals are food deprived and decrease following a meal; infusion into the hypothalamus drives eating; thought to be affected by signals from ghrelin (released from stomach)
bariatric surgeries
reduce the amount of food that can be taken in at one time; gastric band; gastric bypass