Bootcamp.com - Skeletal System
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
113 Terms
the _____ provides structure, support, rigidity, and protection to organs
skeletal system
_____ skeletons belong to organisms without bones, especially backbones
invertebrate
insects tend to have _____, which are skeletons on the outside of the organism
exoskeletons

_____ skeletons belong to organisms that have a backbone
vertebrate
vertebrates have _____, which are skeletons on the inside of the organism
endoskeletons
what are the two parts of human endoskeletons?
axial; appendicular skeletons
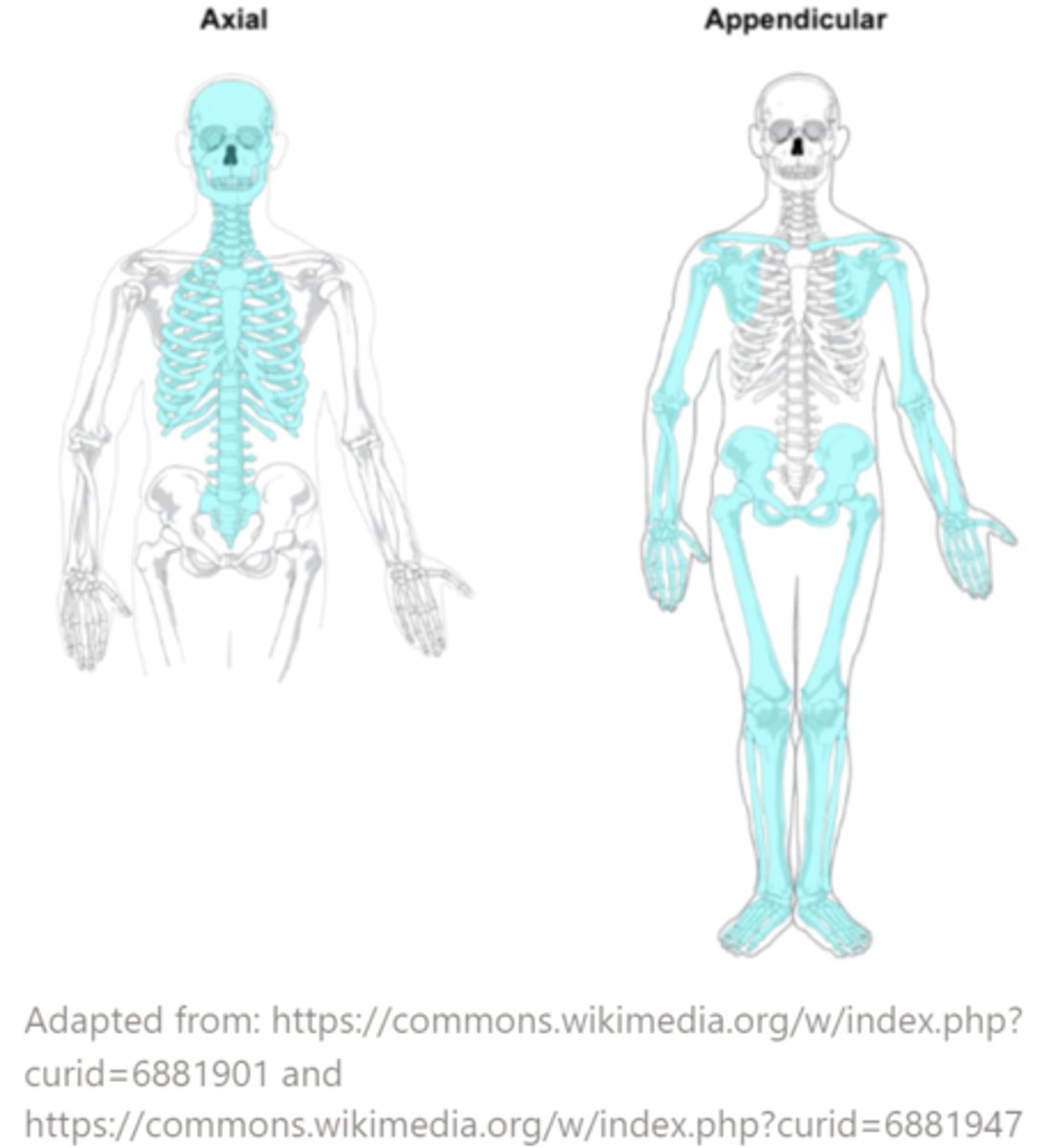
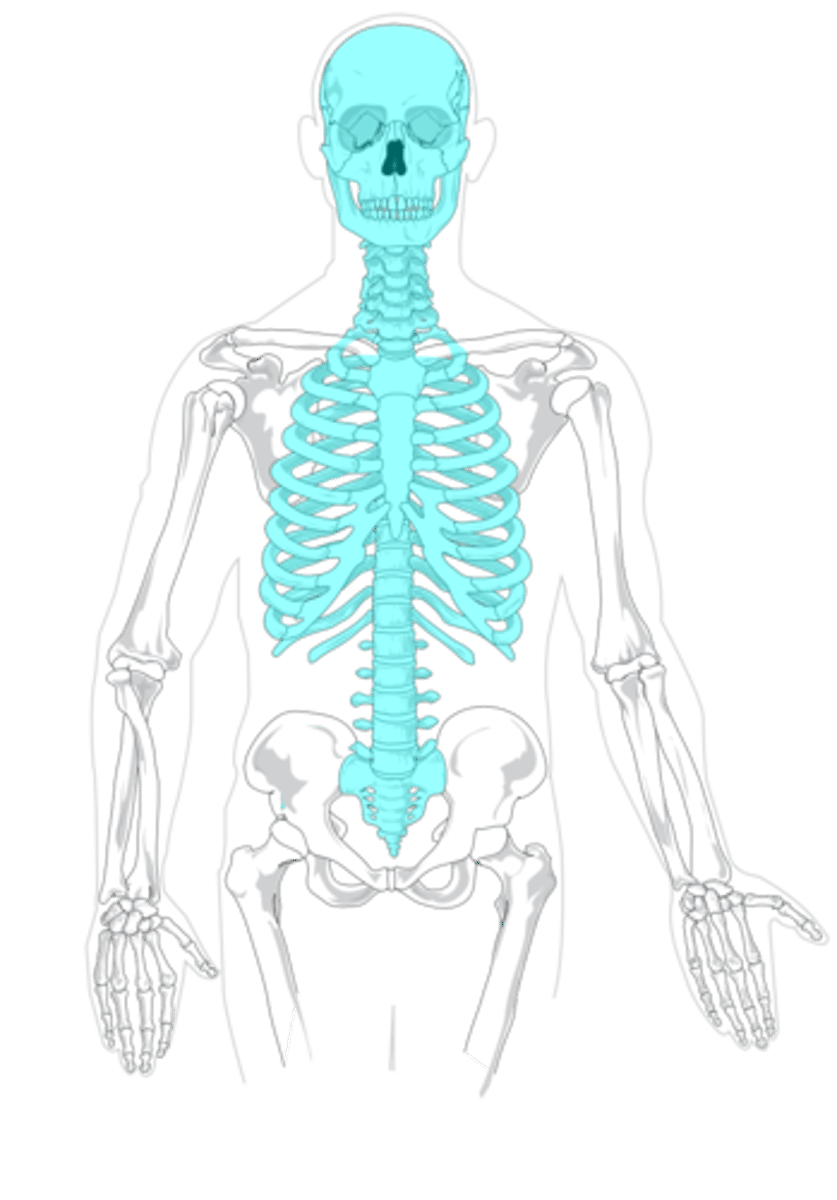
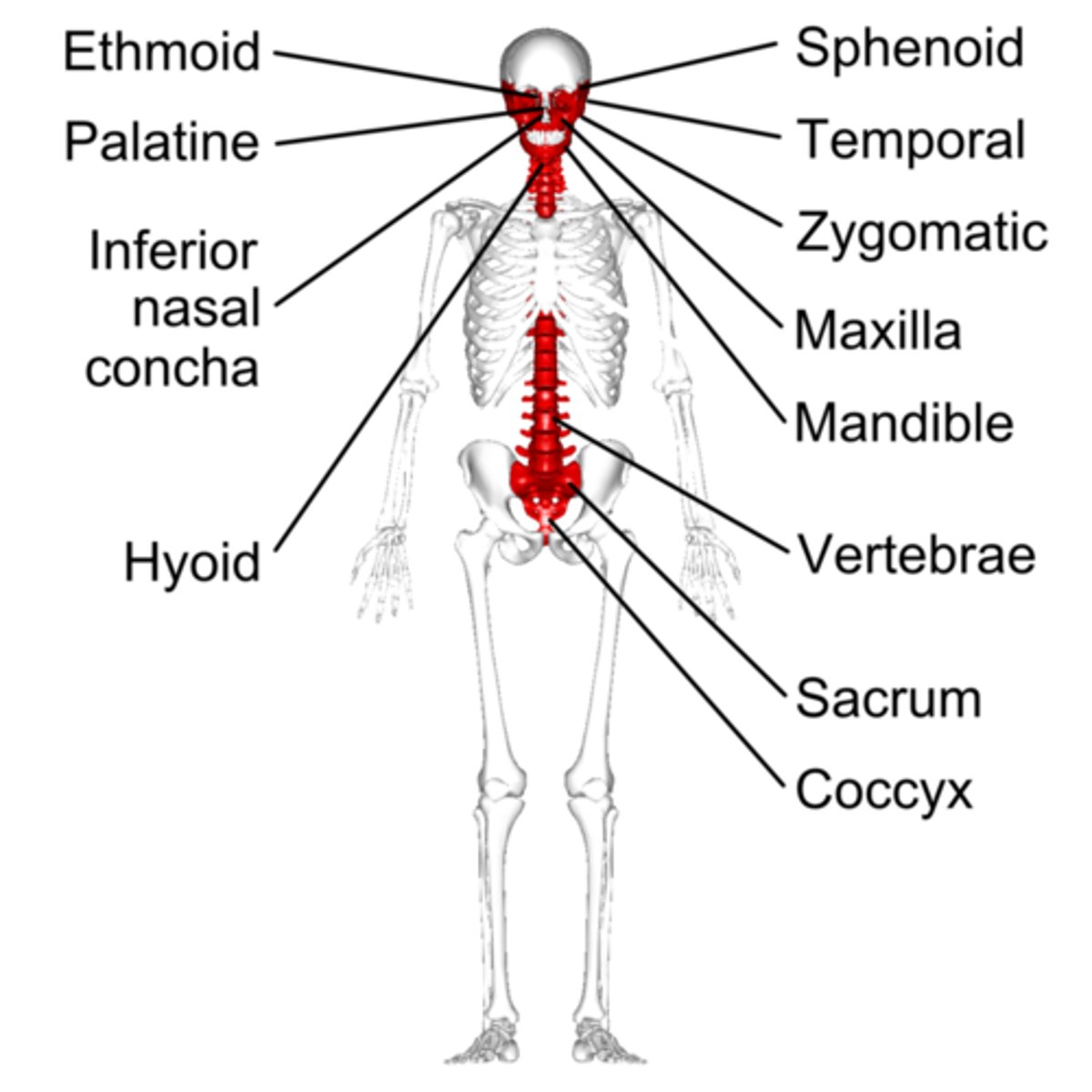
which bones are included in the axial skeleton?
bones at the core of the endoskeleton like the skull, vertebral column, and rib cage
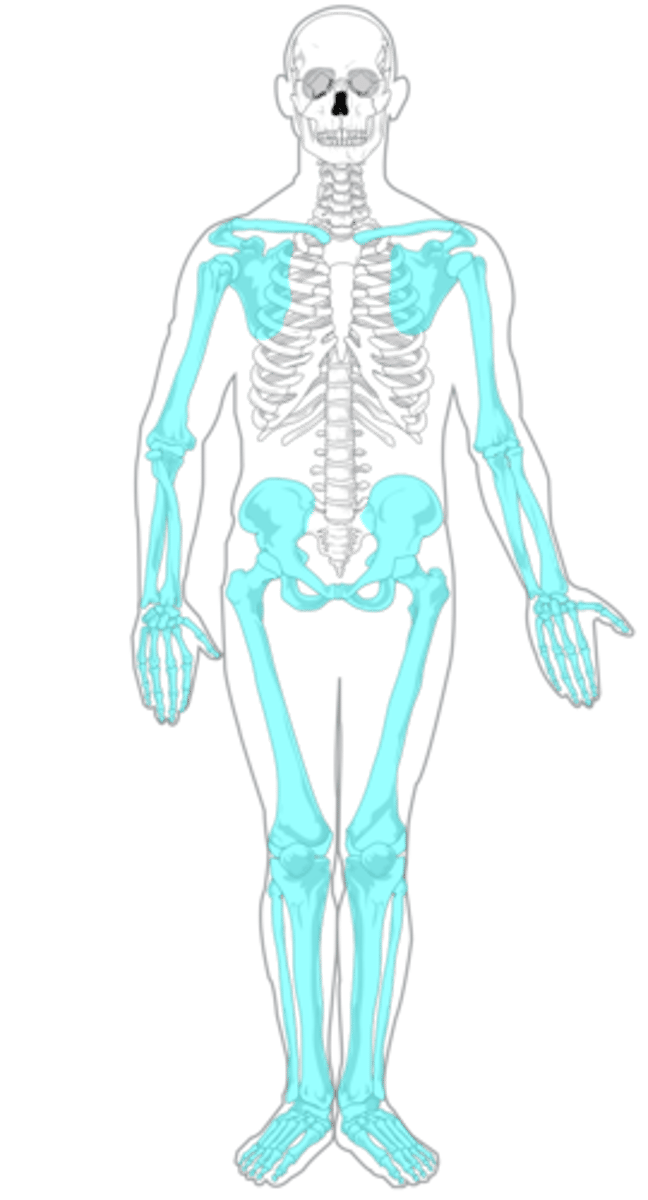
which bones are included in the appendicular skeleton?
bones of the appendages as well as the pectoral and pelvic girdle
what are the types of bones?
long; short; flat; sesamoid; irregular
of which bone types are long bones composed?
cortical and cancellous
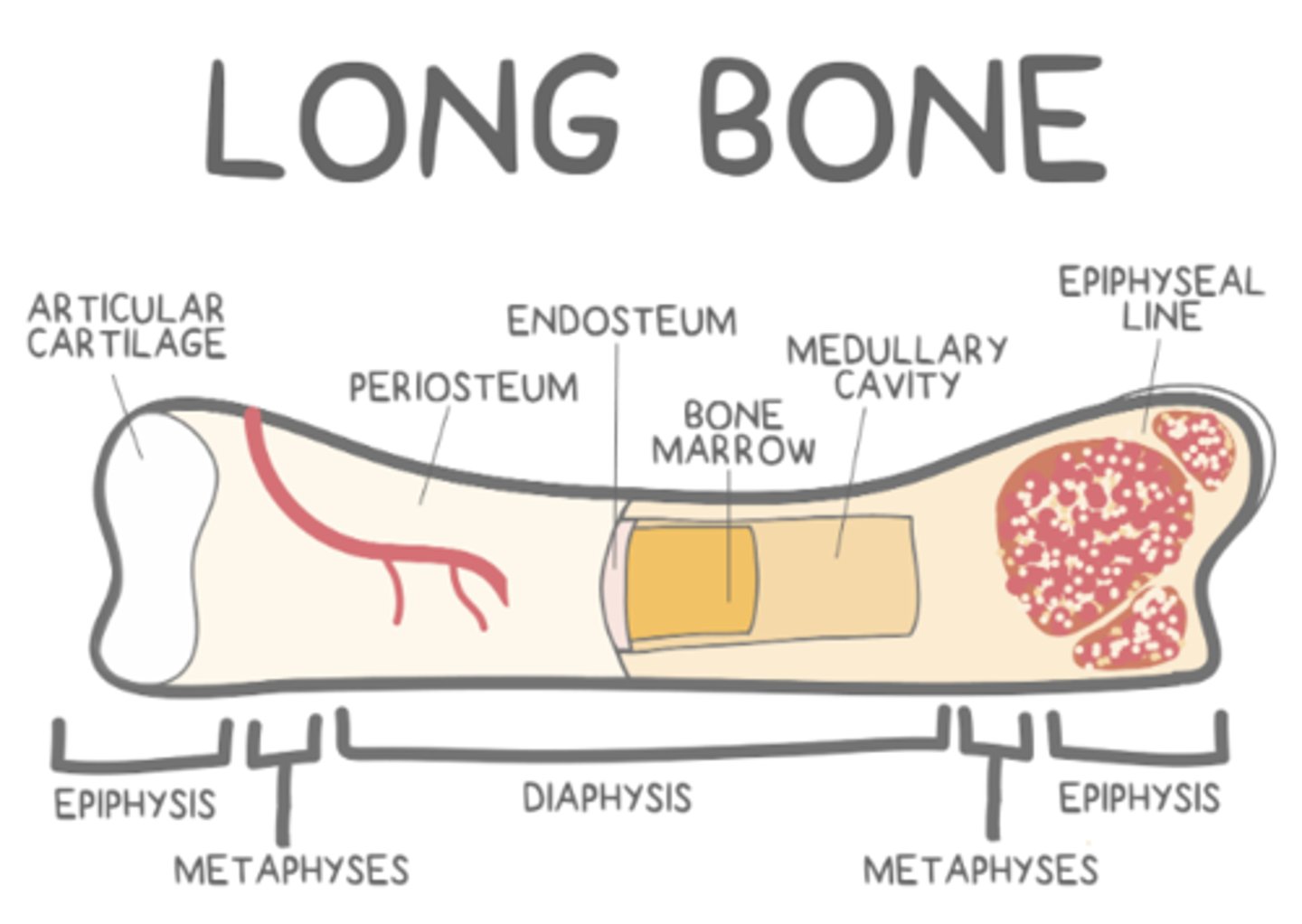
what are some examples of long bones?
femur; radius; ulna
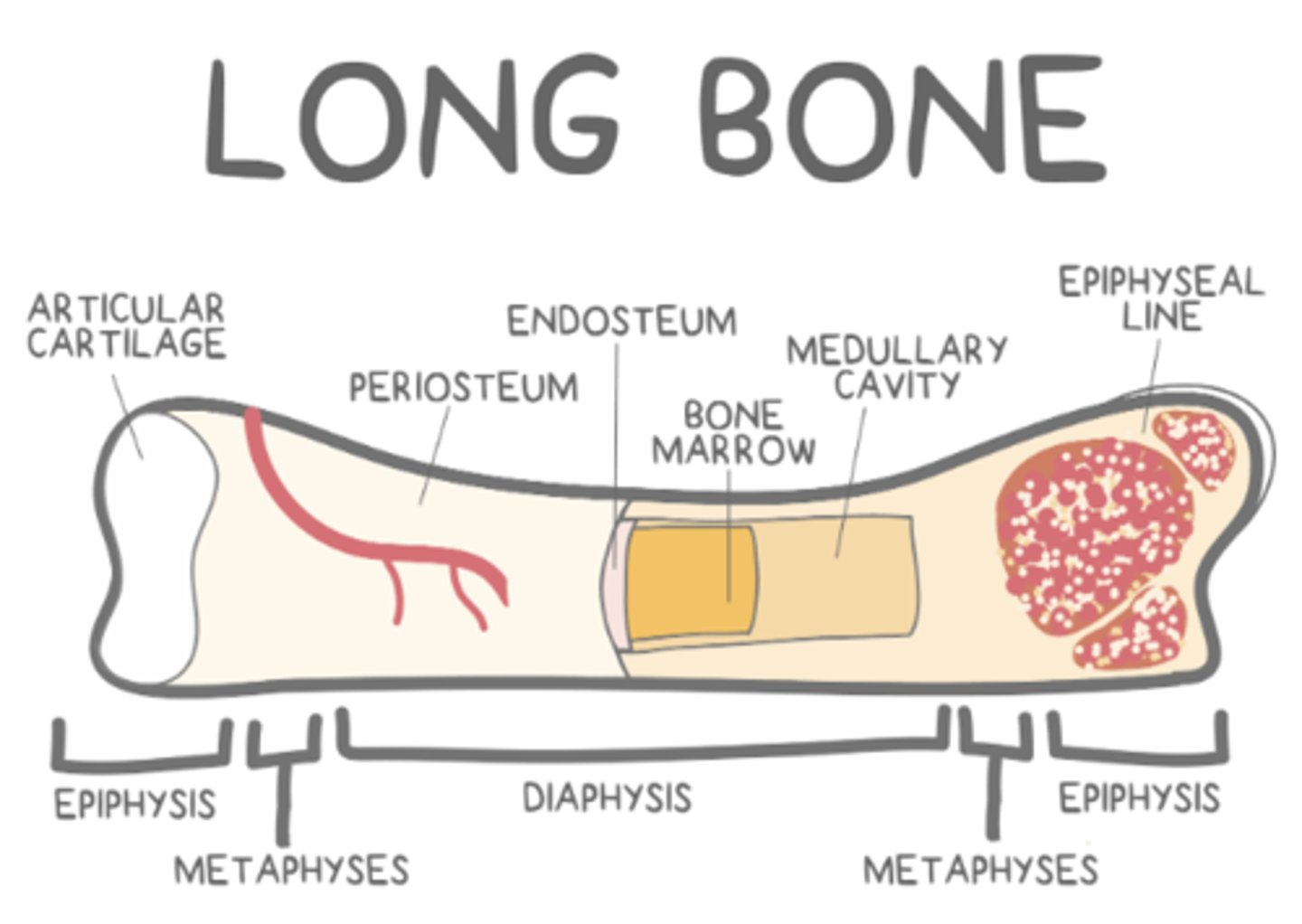
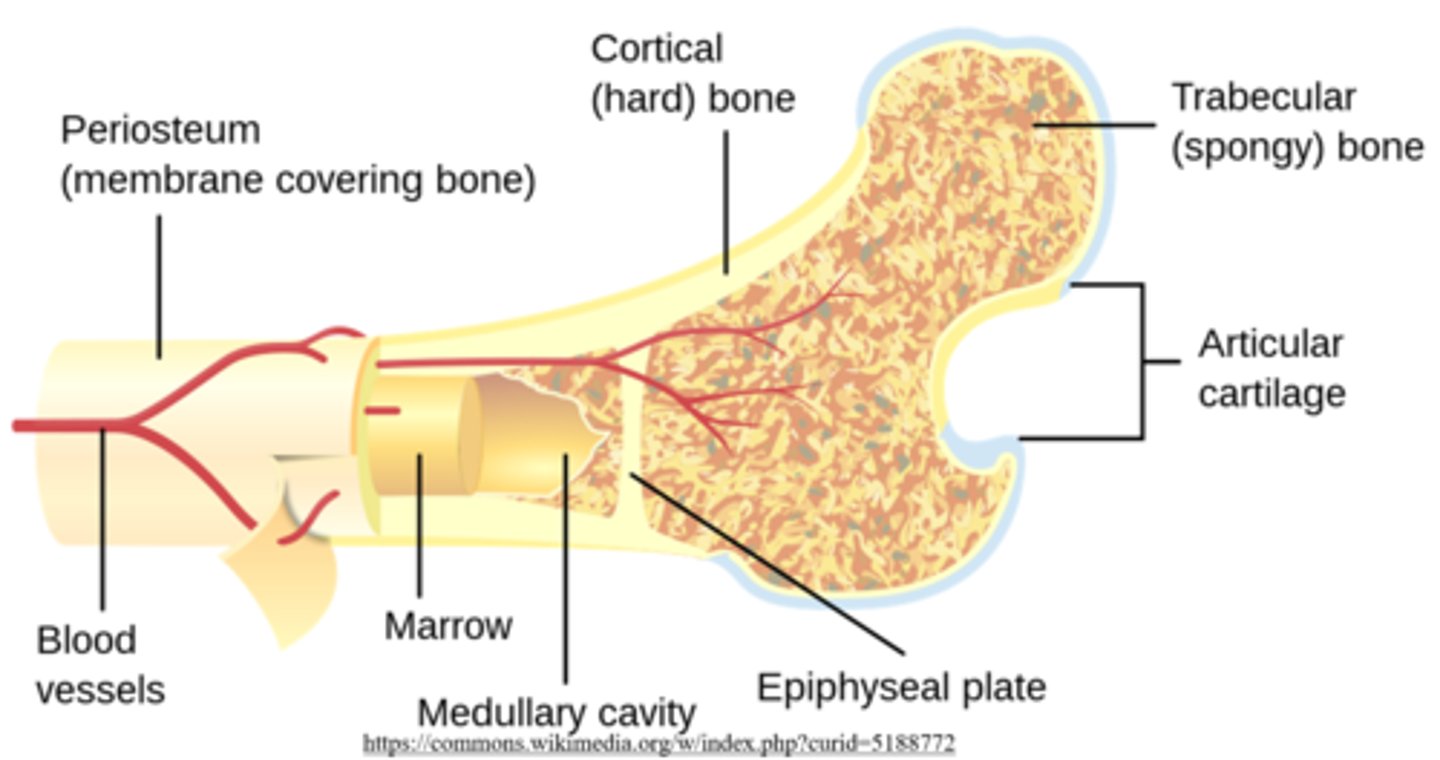
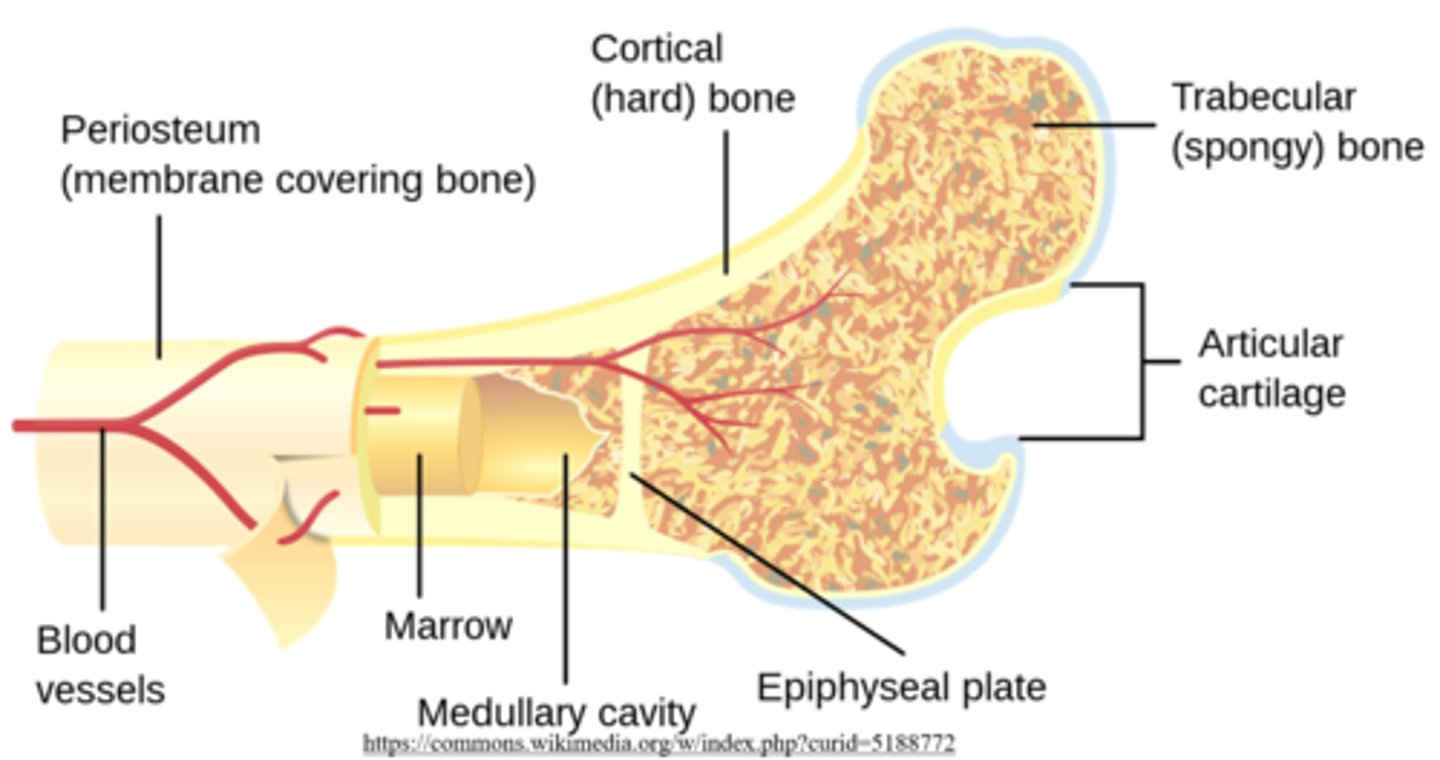
what are some of the predominant structural features of long bones?
epiphyses; diaphysis; a medullary cavity; metaphyses; epiphyseal growth plates
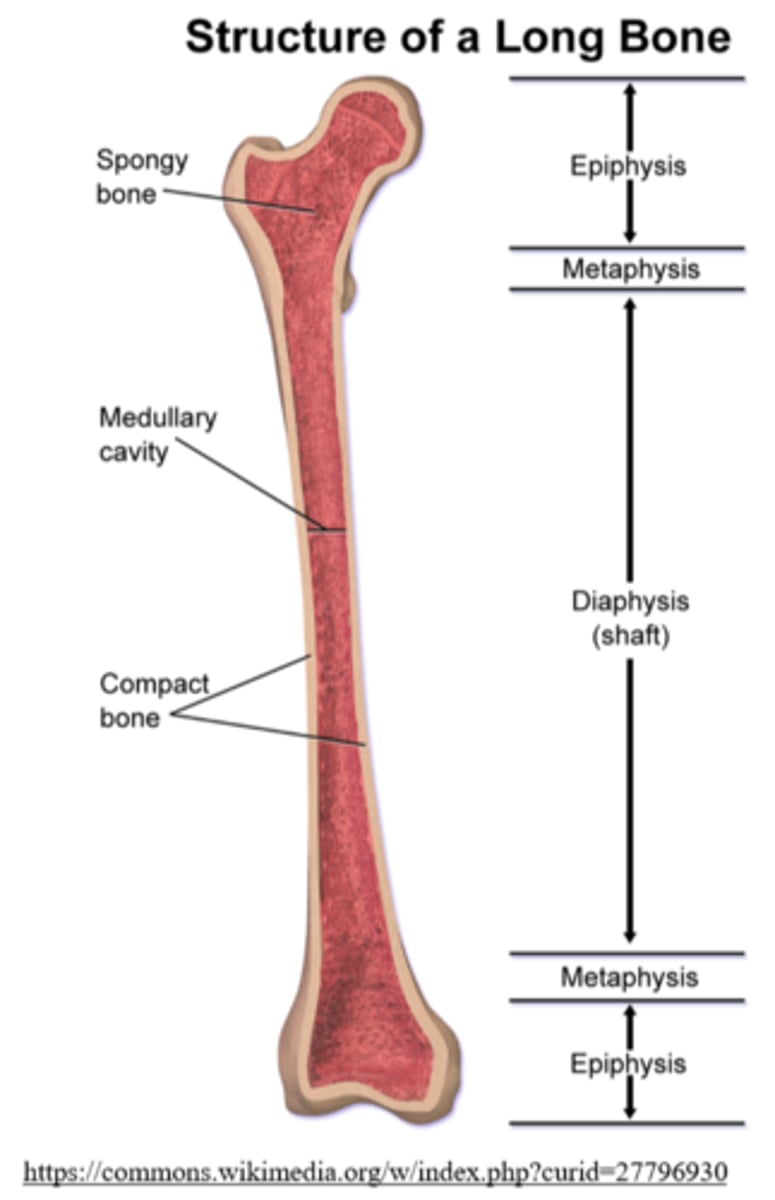
_____ are the bumpy parts at the ends of long bones
epiphyses
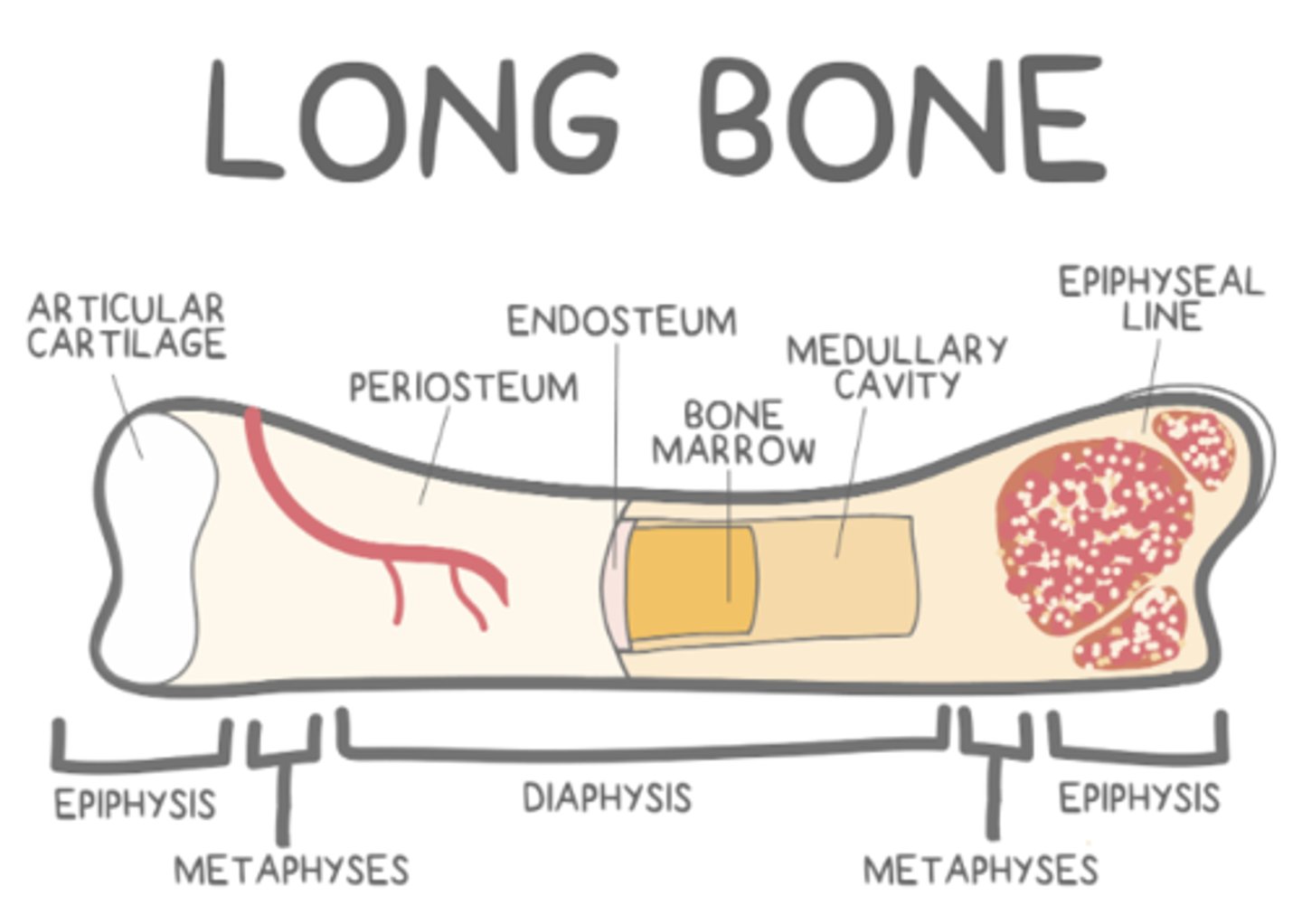
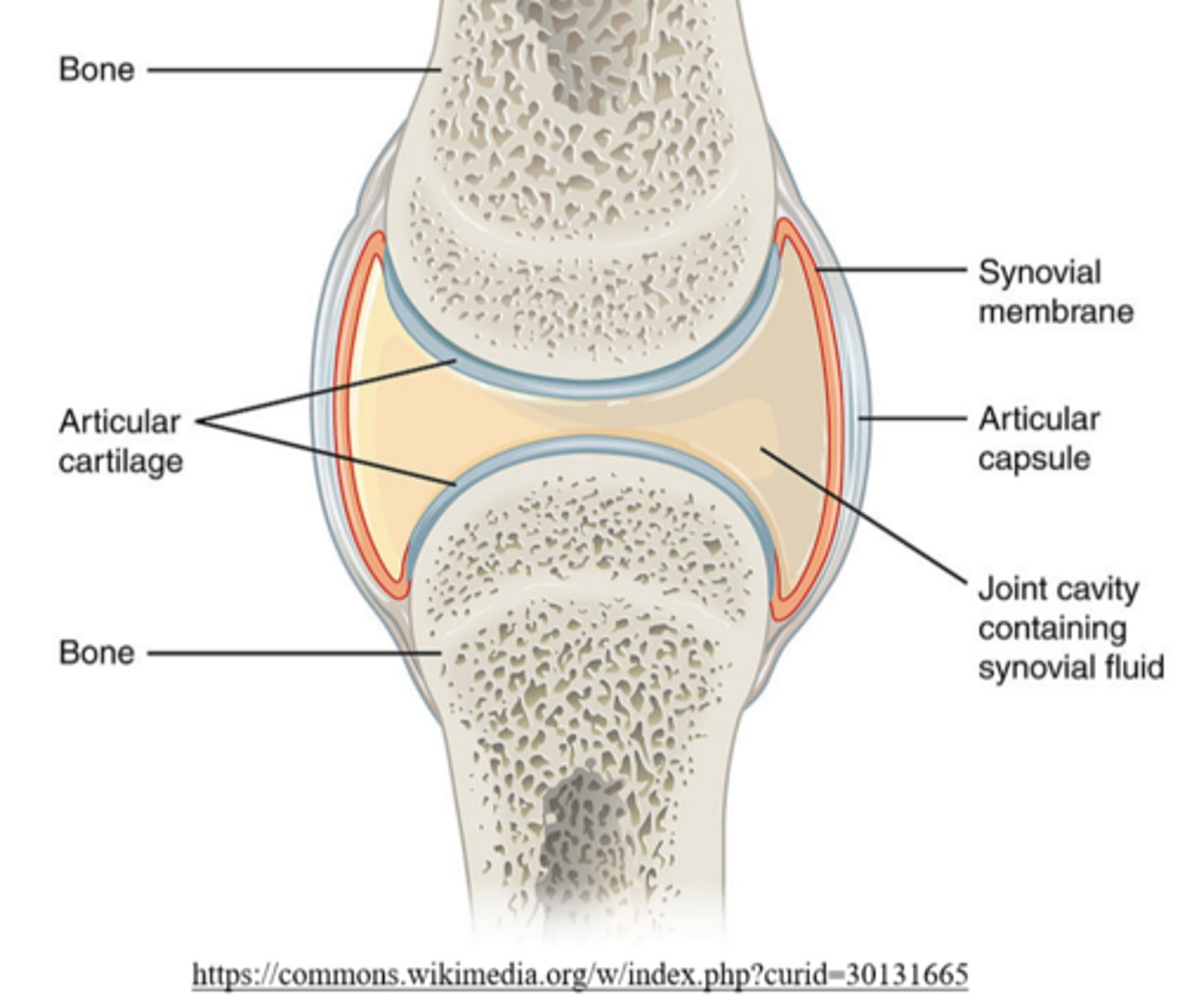
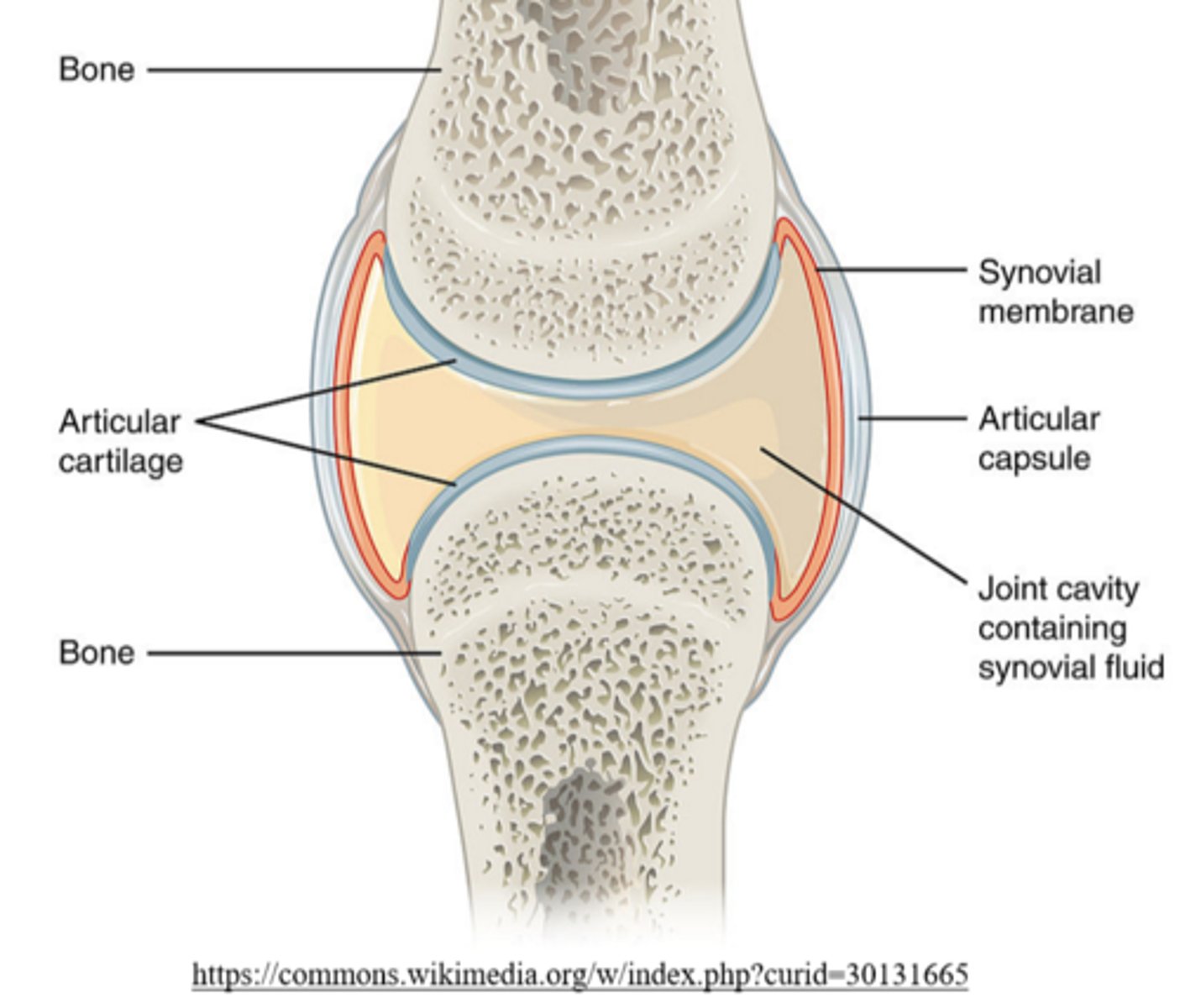
_____ covers epiphyseal compact bone in synovial joints
articular cartilage
articular cartilage covers epiphyseal compact bone in _____ joints
synovial
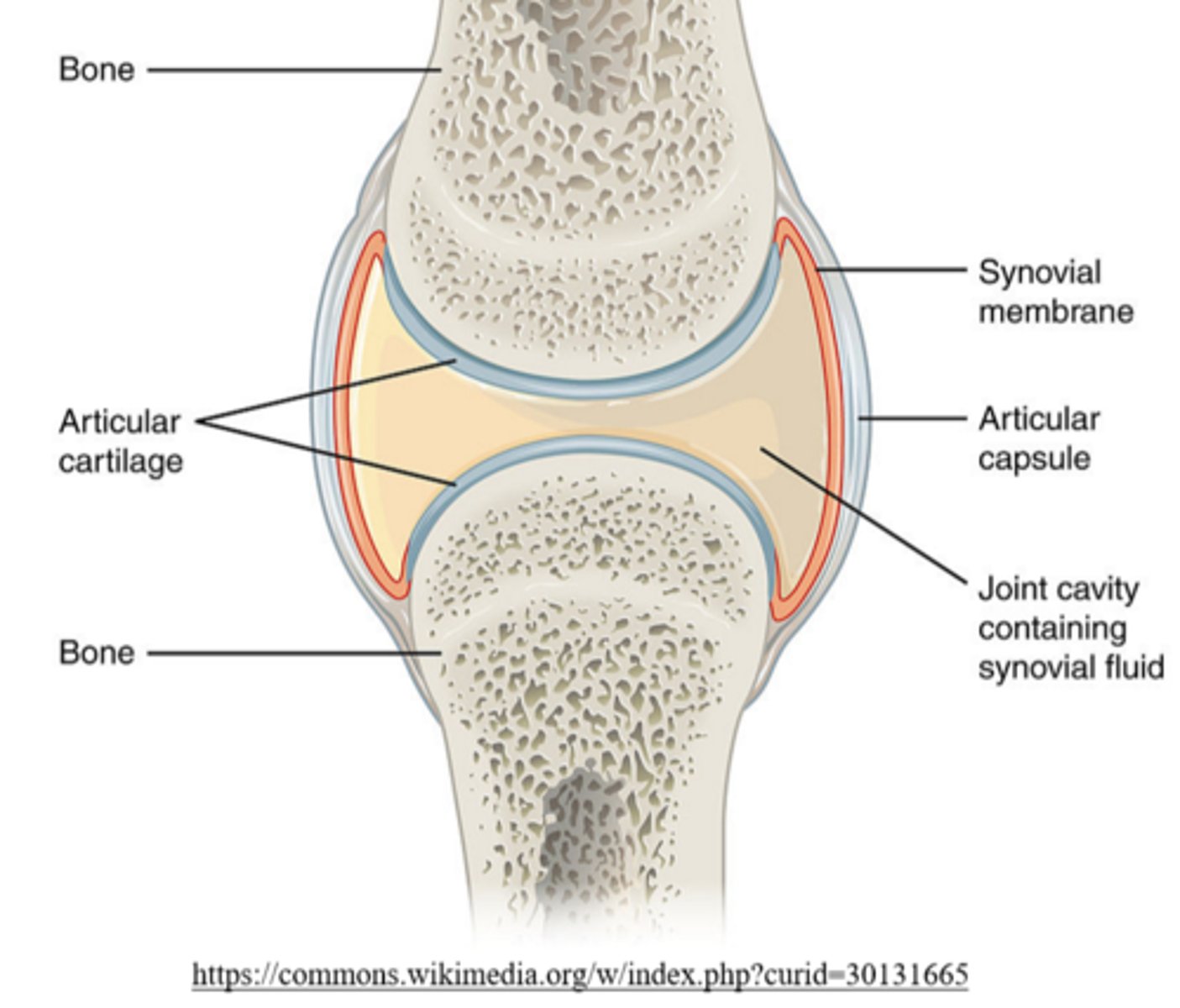
what type of joint is formed between long bones?
synovial joints
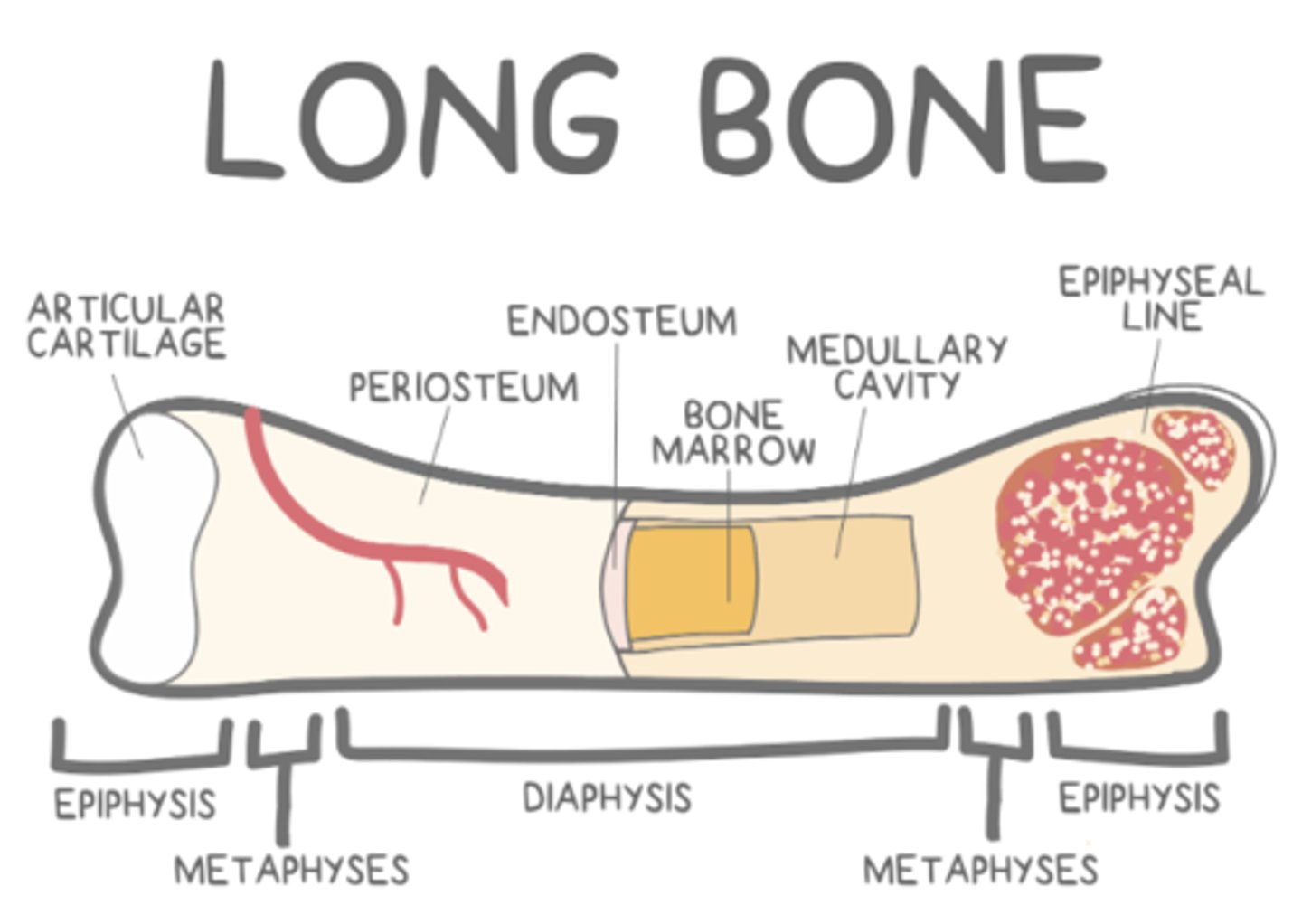
_____ bone marrow is located in spongy trabecular bone of adults
red
hematopoiesis occurs in the _____ bone marrow of _____ bone
red; spongy trabecular
the _____ of a long bone is the shaft between the ends
diaphysis
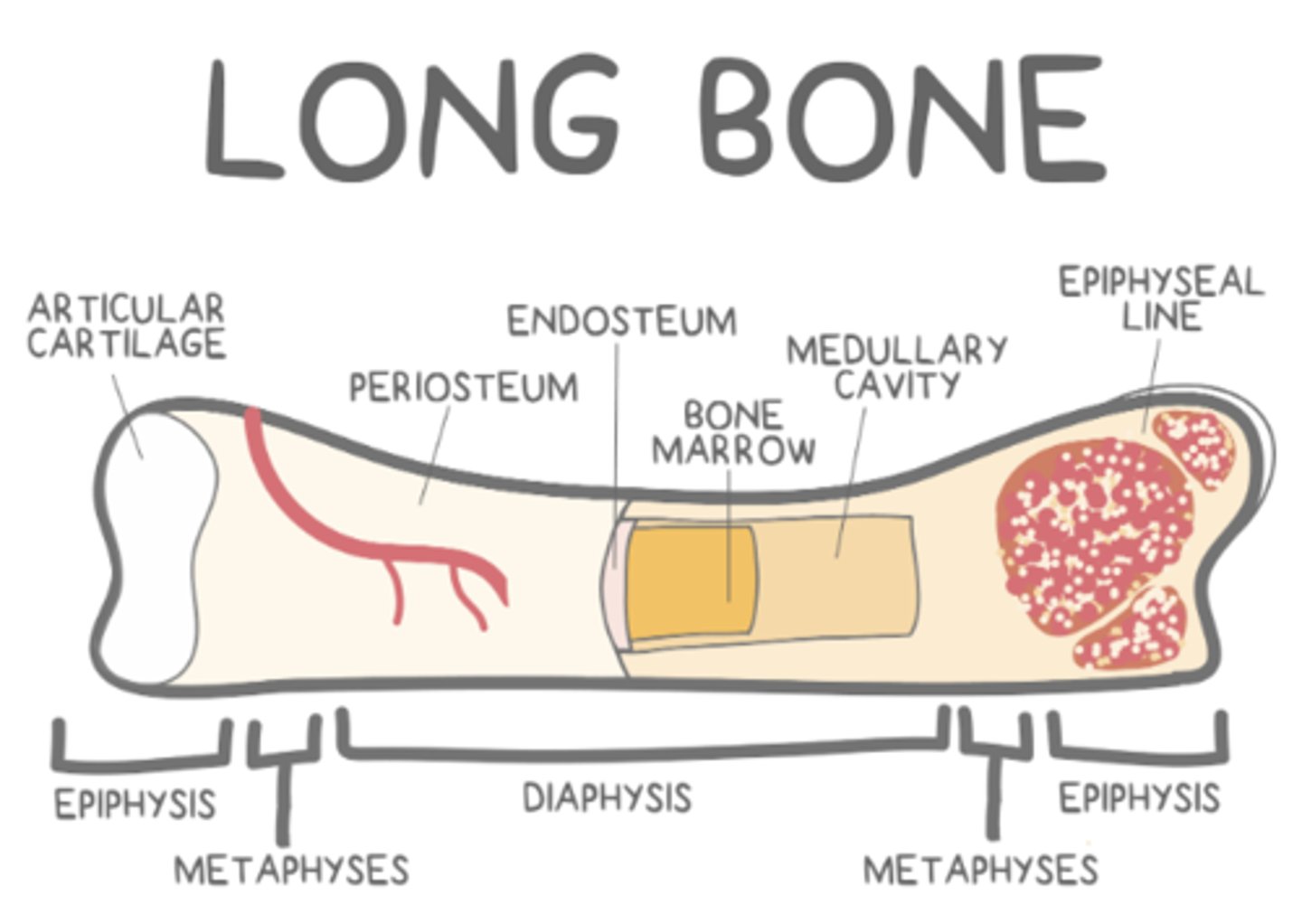
the _____ is the "hollow" part of the diaphysis, which contains _____ bone marrow in adulthood
medullary cavity; yellow
_____ are found between the medullary cavity and epiphyseal plates of a long bone
metaphyses
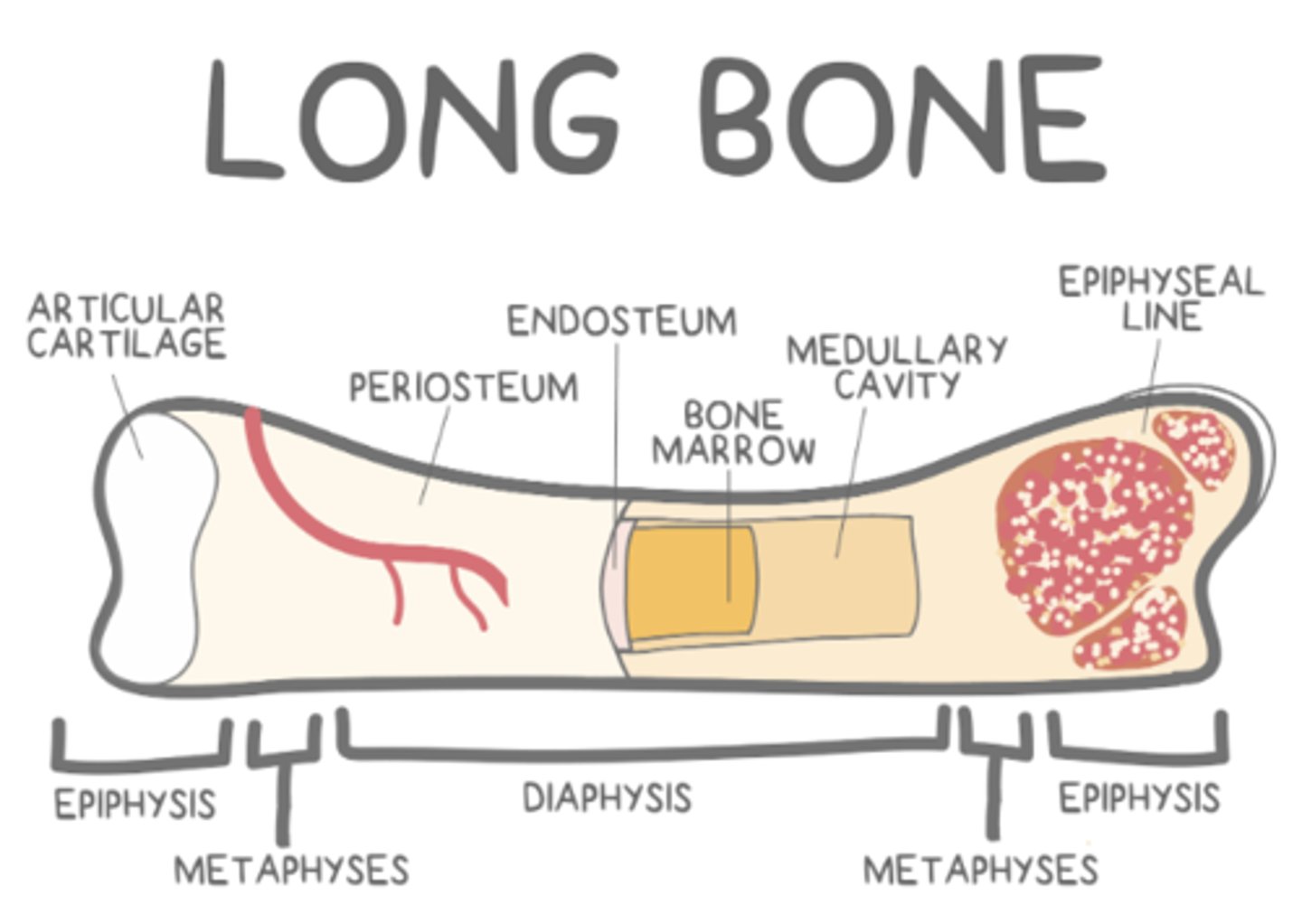
metaphyses have a similar structure to the _____ of a long bone
epiphyses
(structure is spongy trabecular bone)
which type of cartilage are epiphyseal plates composed of during adolescence?
hyaline cartilage
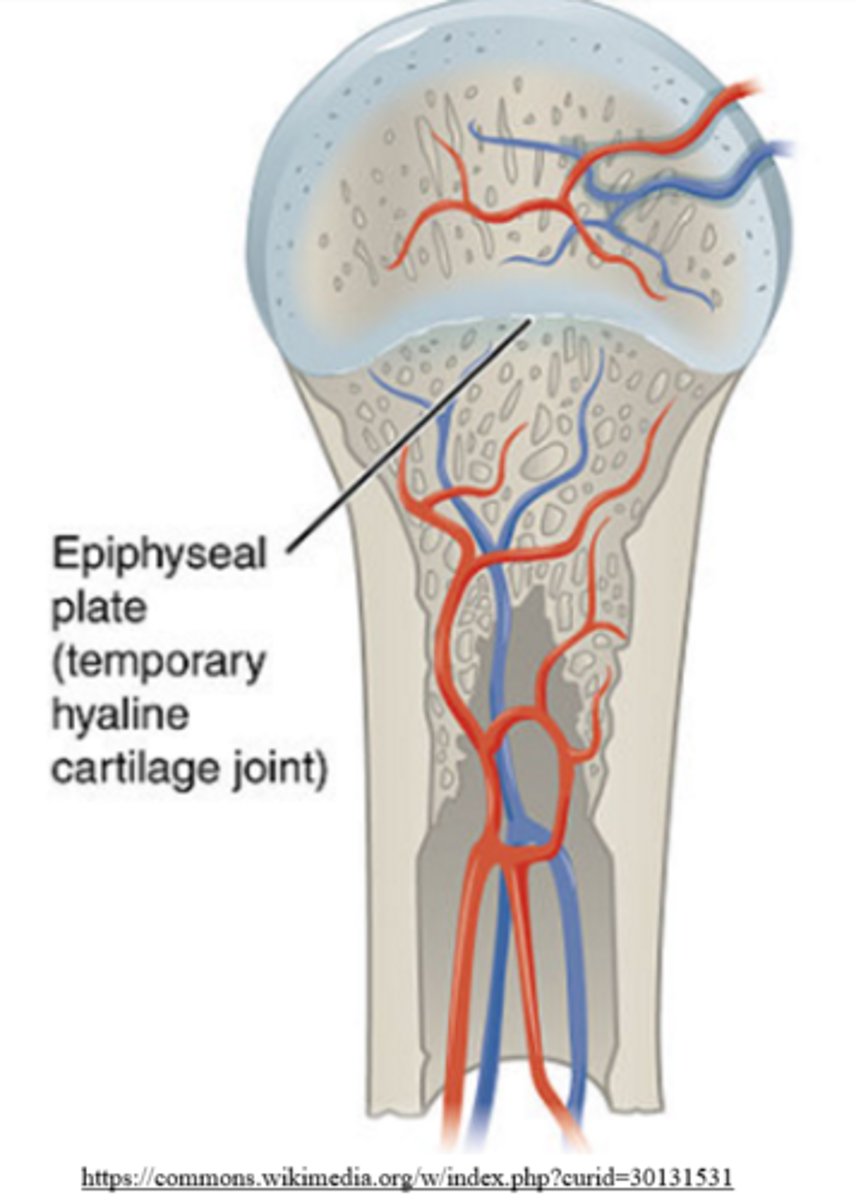
during puberty, epiphyseal plates form an epiphyseal line via _____
ossification
epiphyseal plates grow before ossification to promote _____
bone lengthening
epiphyseal plates grow toward the _____ to lengthen the _____ of a long bone
metaphyses; diaphysis
epiphyseal lines are found between long bone _____ and _____ in adults
epiphyses; metaphyses
(same holds true for epiphyseal plates in adolescents)
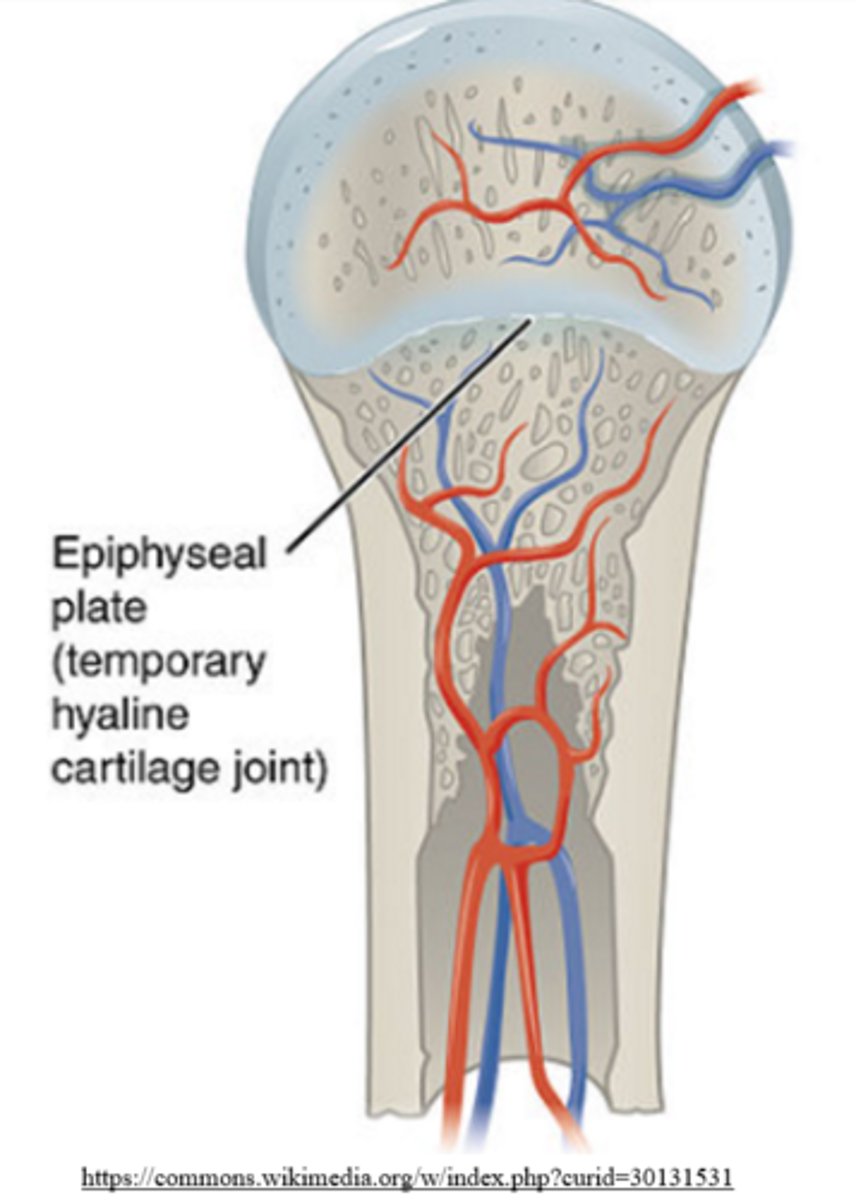
cartilage is _____, which makes it difficult to heal
avascular
breaking a bone at the epiphyseal plate can stunt growth because epiphyseal plates are made of _____, which is avascular and difficult to heal
hyaline cartilage
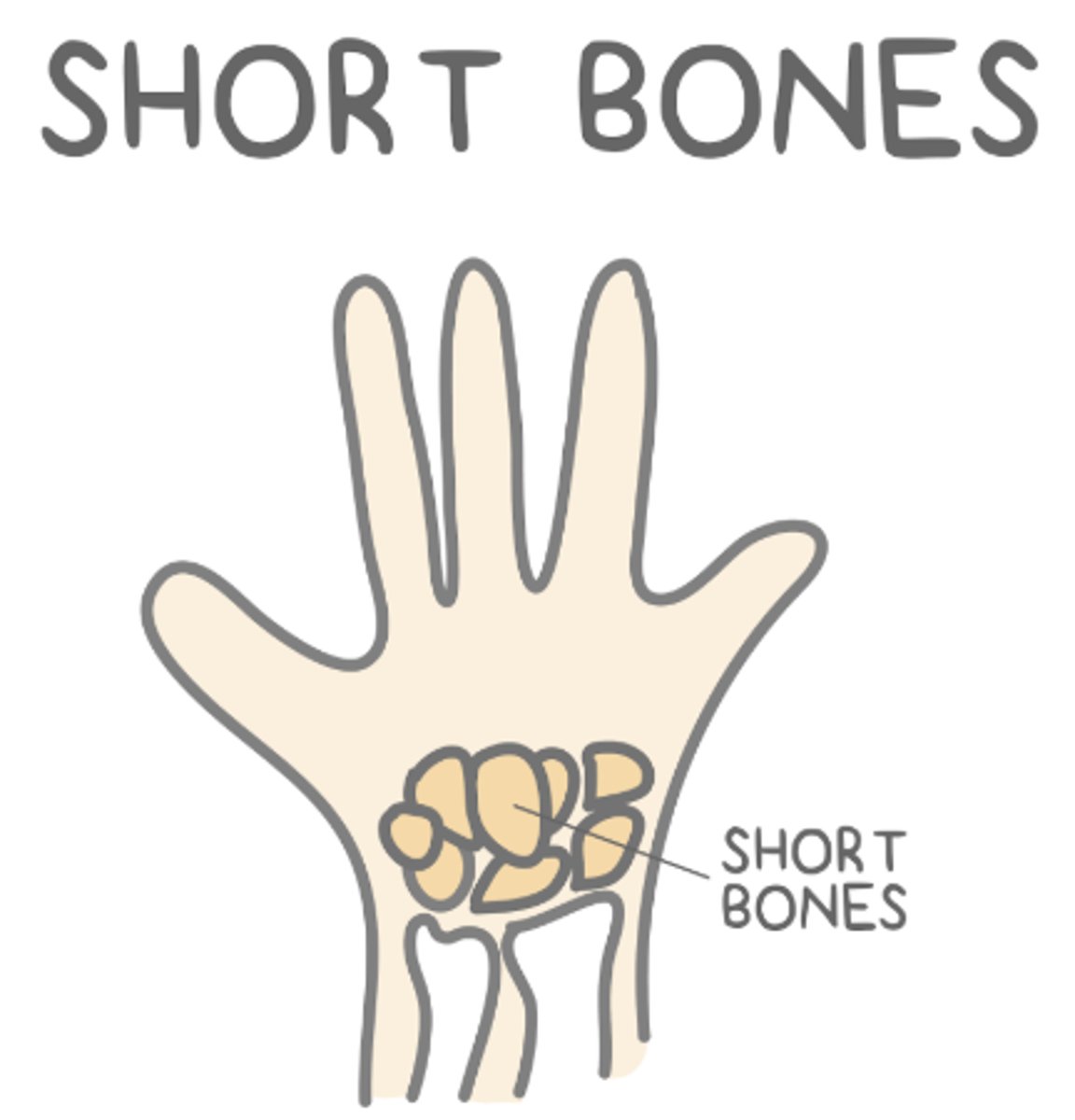
_____ bones are cuboidal and provide support with little movement
short
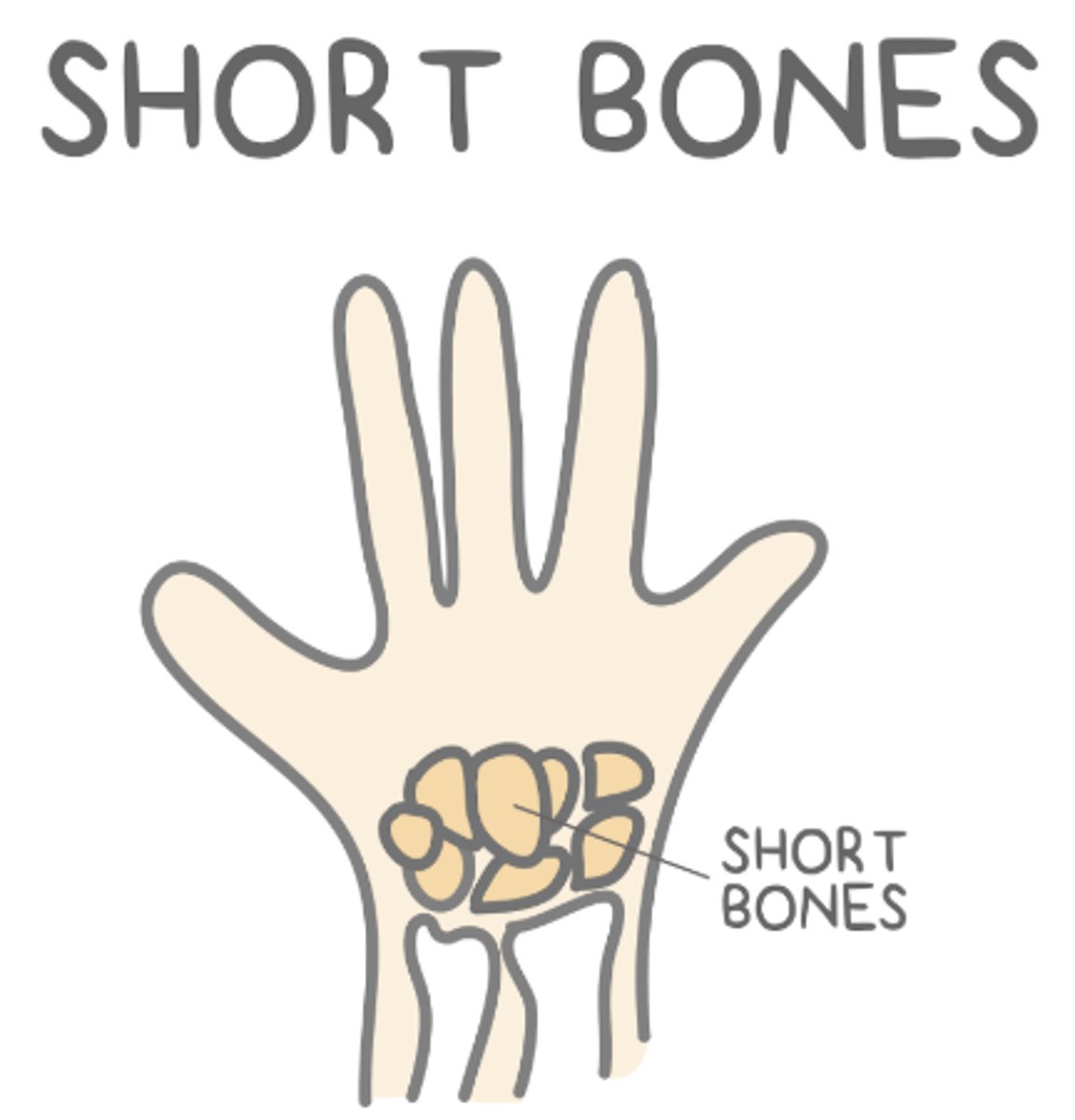
short bones are primarily _____ bone covered by a thin layer of _____ bone
cancellous (spongy trabecular); cortical (dense)
what are some examples of short bones?
carpals of the wrist or tarsals of the ankle
_____ bones are thin, with outer layers of cortical bone surrounding spongy, cancellous interiors
flat
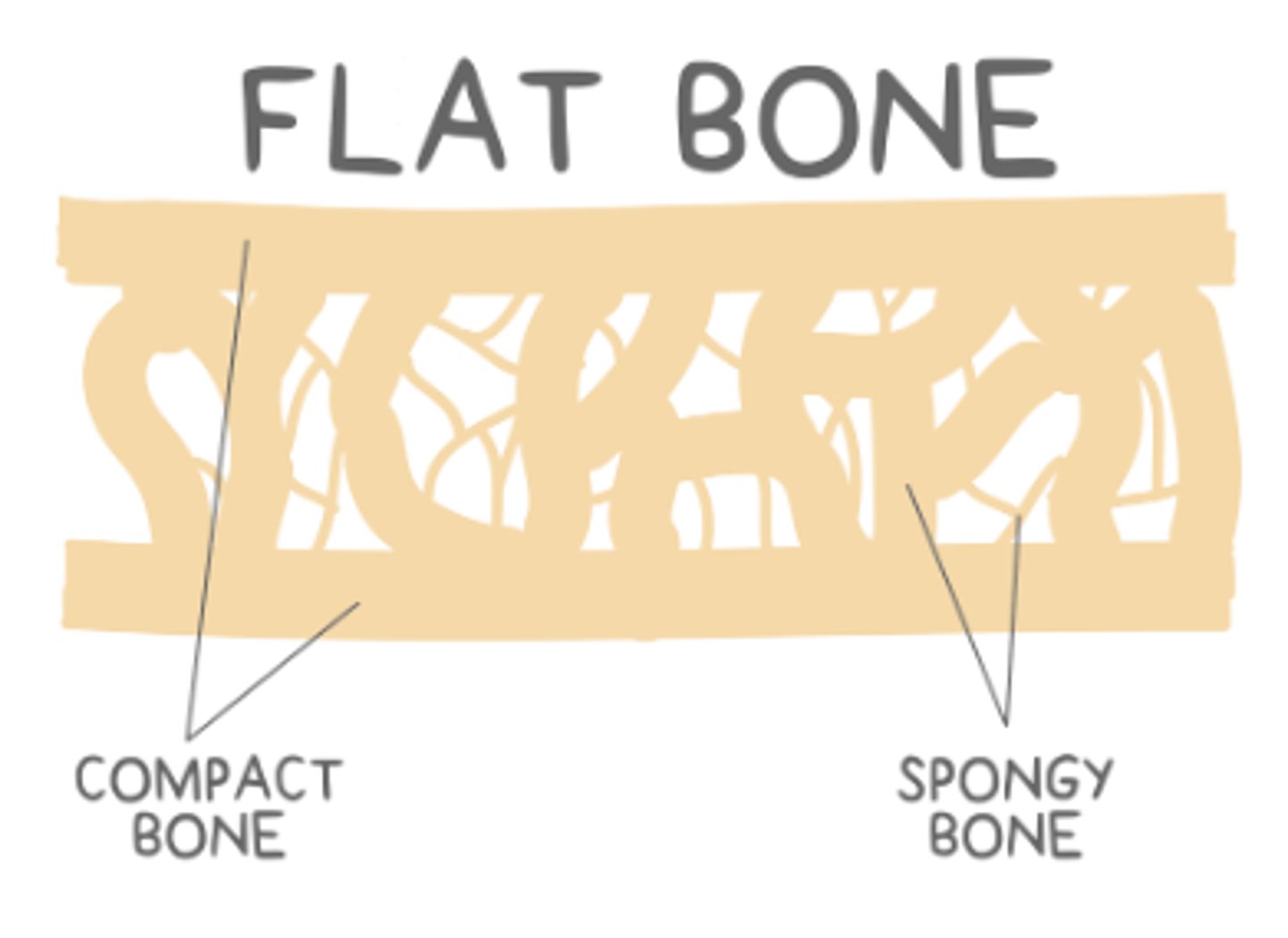
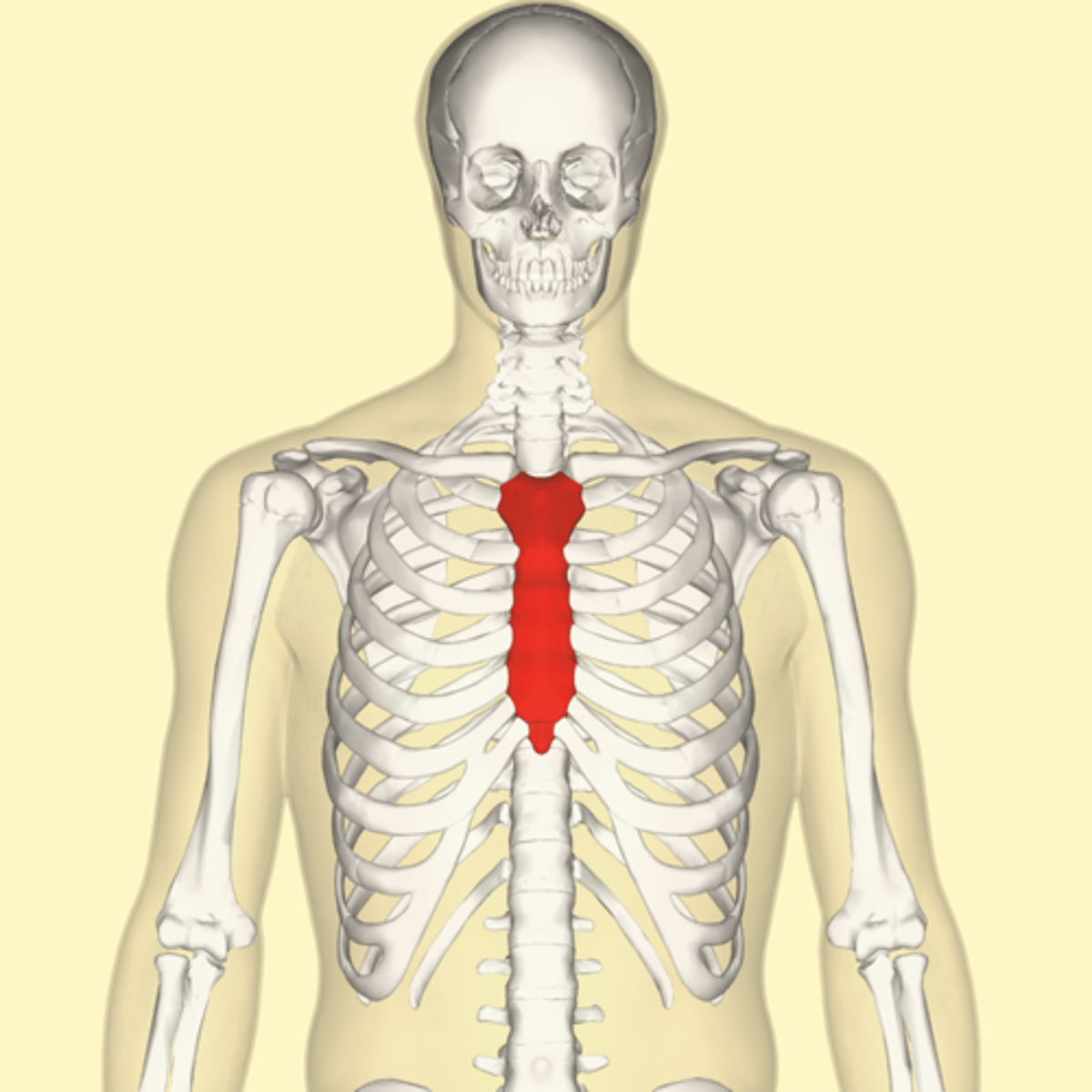
what are some examples of flat bones?
sternum and the bones forming the skull
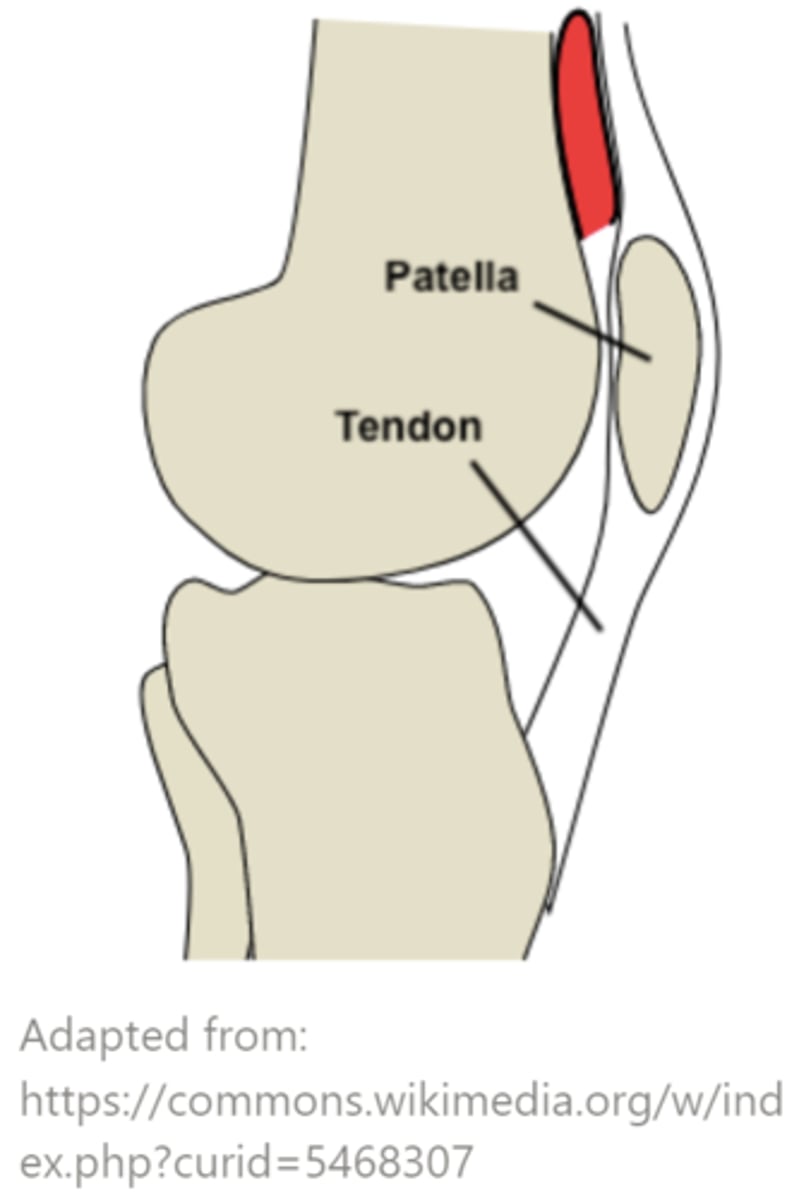
sesamoid bones are found in _____, and they act to increase muscle power - what is an example of a sesamoid bone?
tendons; patella
irregular bones have _____ layers surrounding _____ interiors; however, their shapes do not fit any other bone class
dense, cortical; spongy, cancellous
what are some examples of irregular bones?
vertebrae; sacrum; pelvis
_____ bone is the outer layer of bones
cortical
what allows bones to support weight?
cortical bone density
what are the microstructures in cortical bone?
osteons; Haversian canals; lamella; lacunae; canaliculi; Volkmann's canals
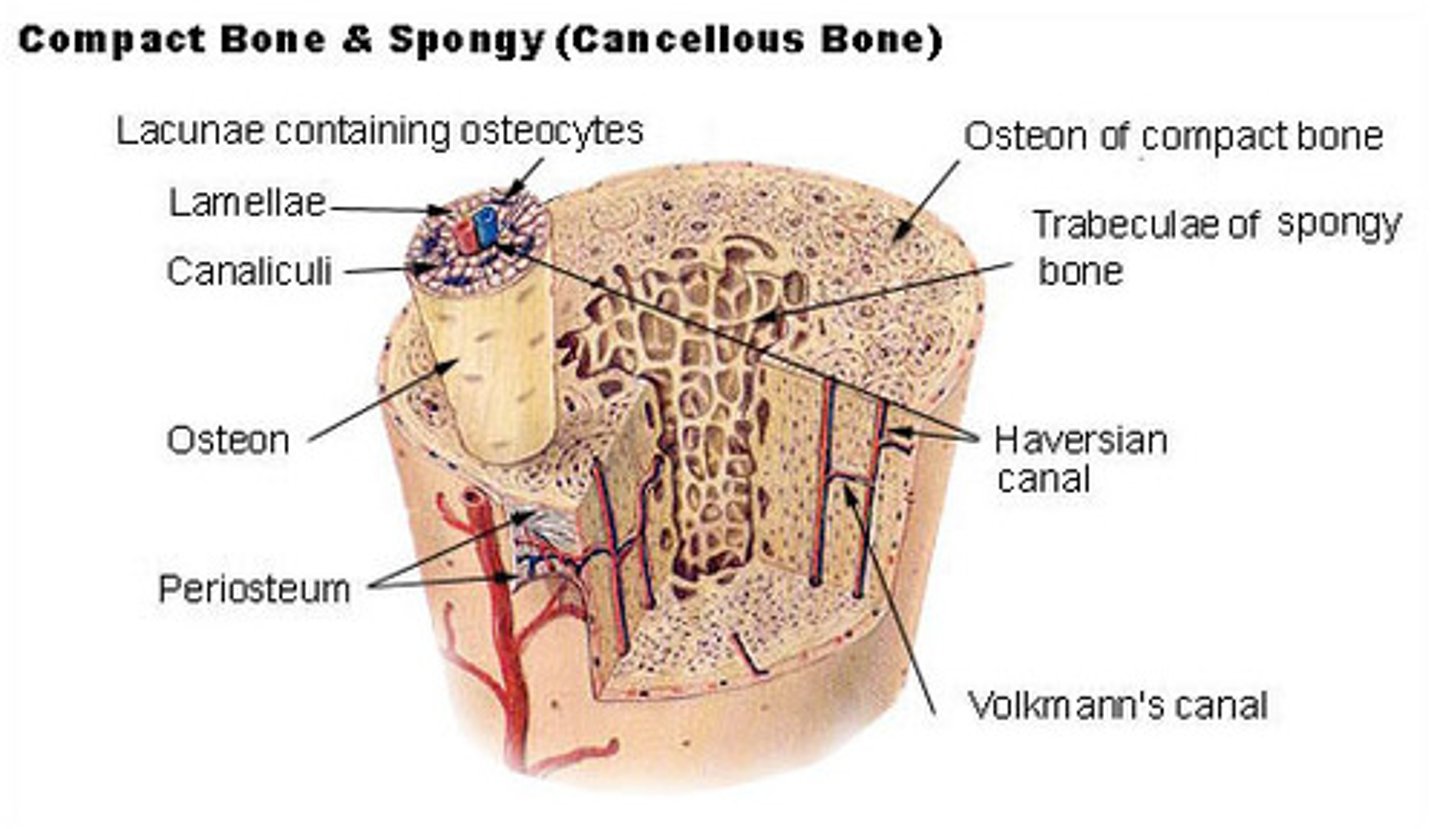
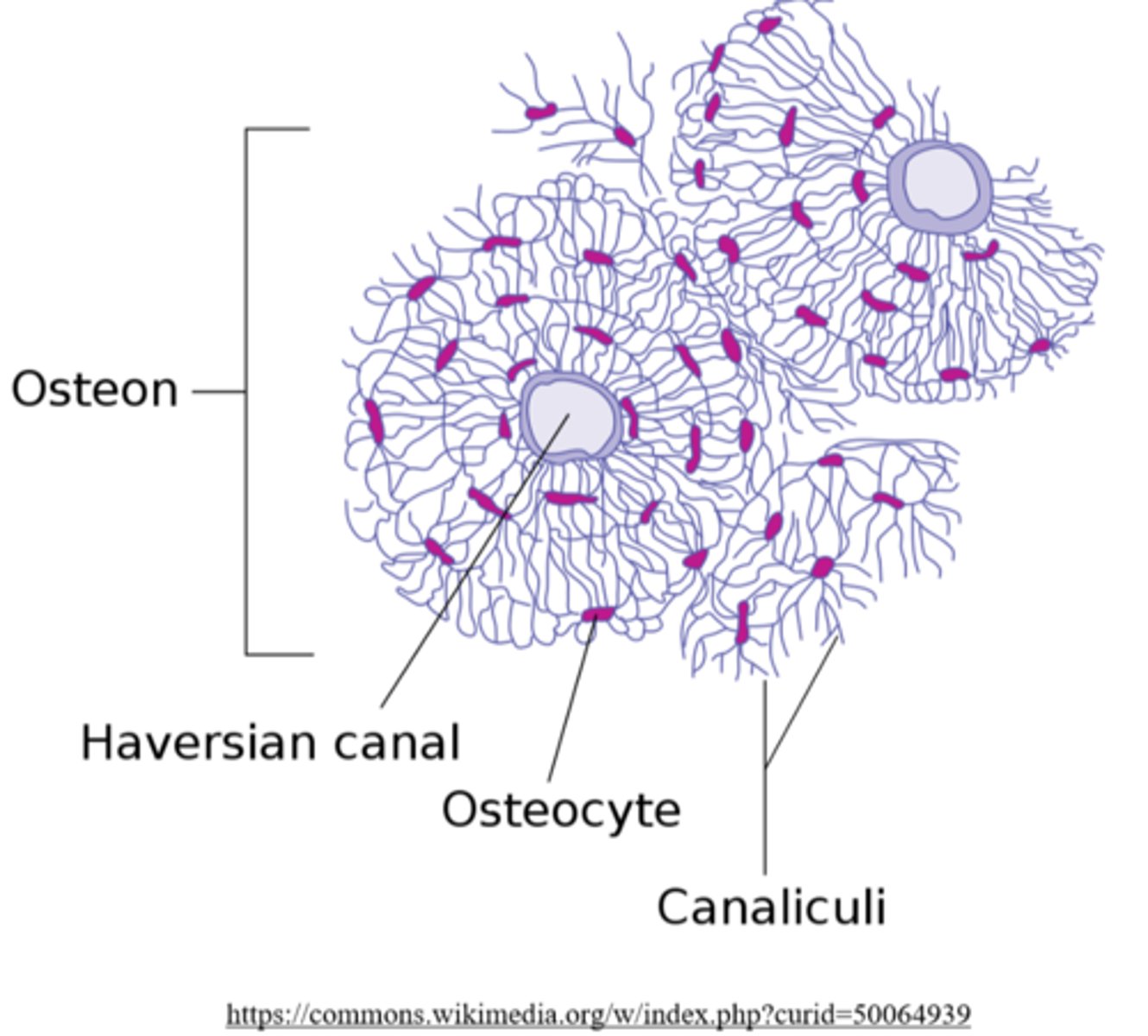
_____ are the functional unit of cortical bone, and they appear as multi-layer cylinders
osteons
what direction do osteons travel within cortical bone?
parallel to the bone's long axis
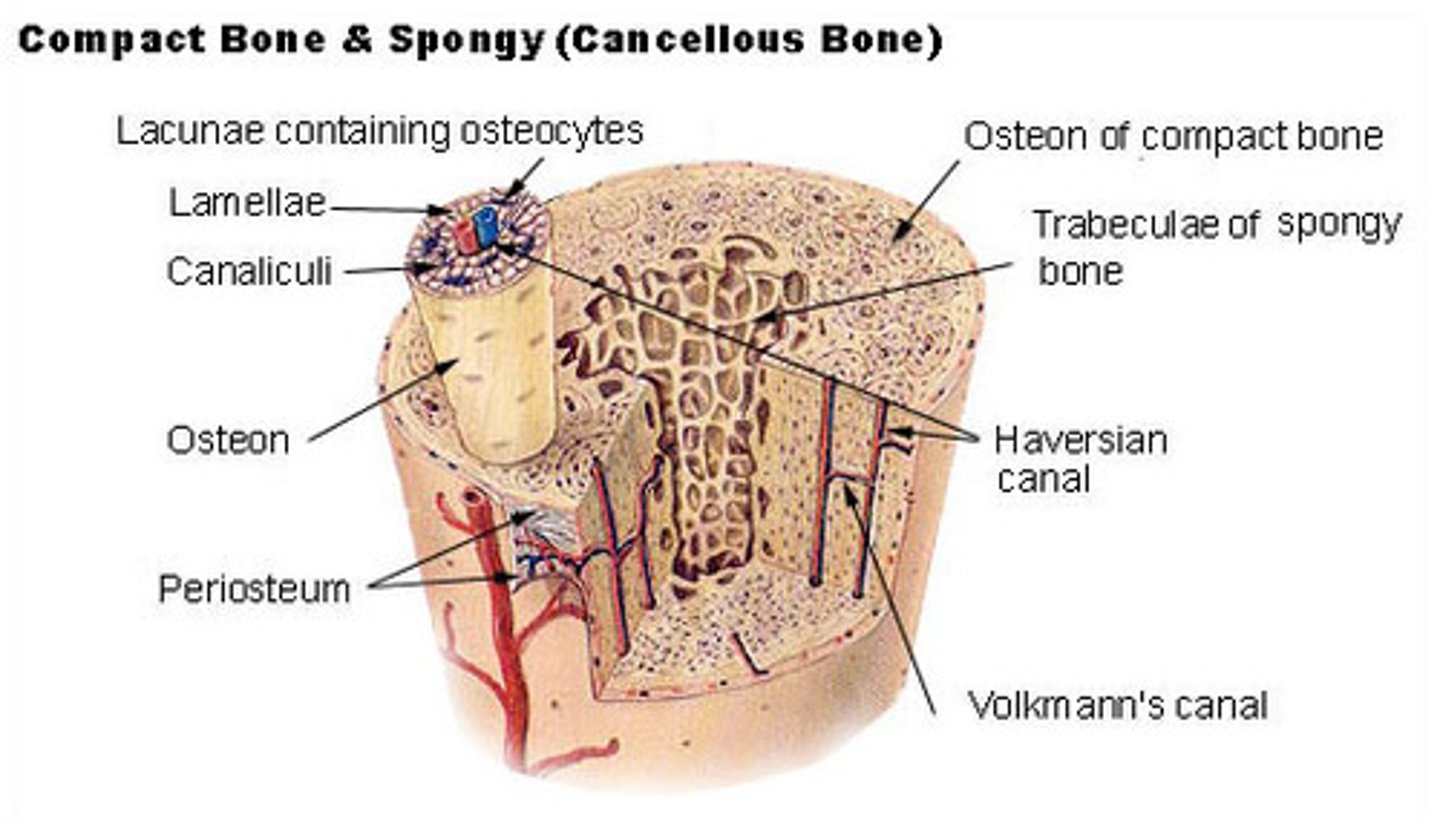
the layers that make-up an osteon are called _____
lamellae
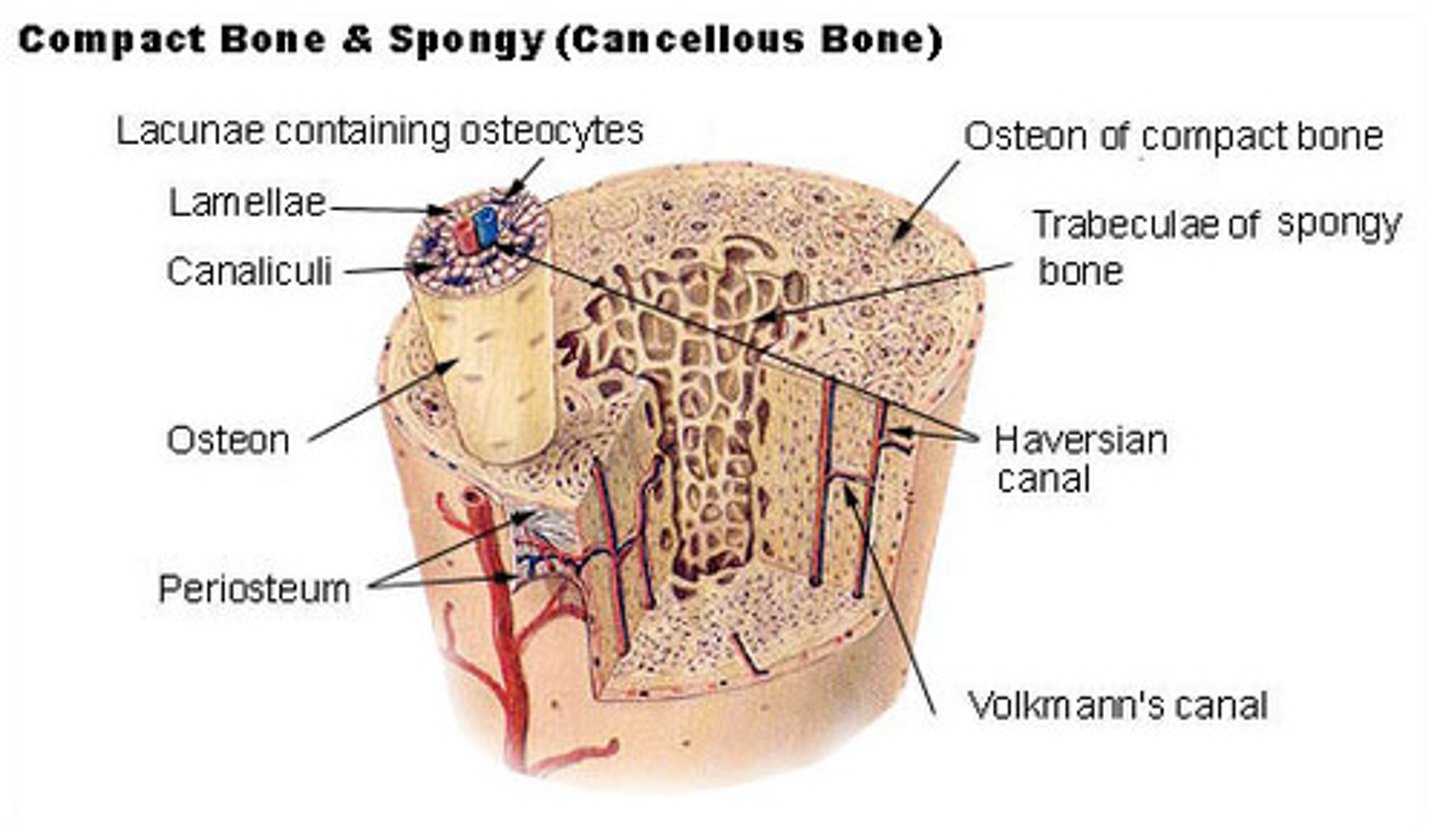
_____ contain cortical bone and collagen fibers
lamellae
_____ are the central canals of an osteon
Haversian canals
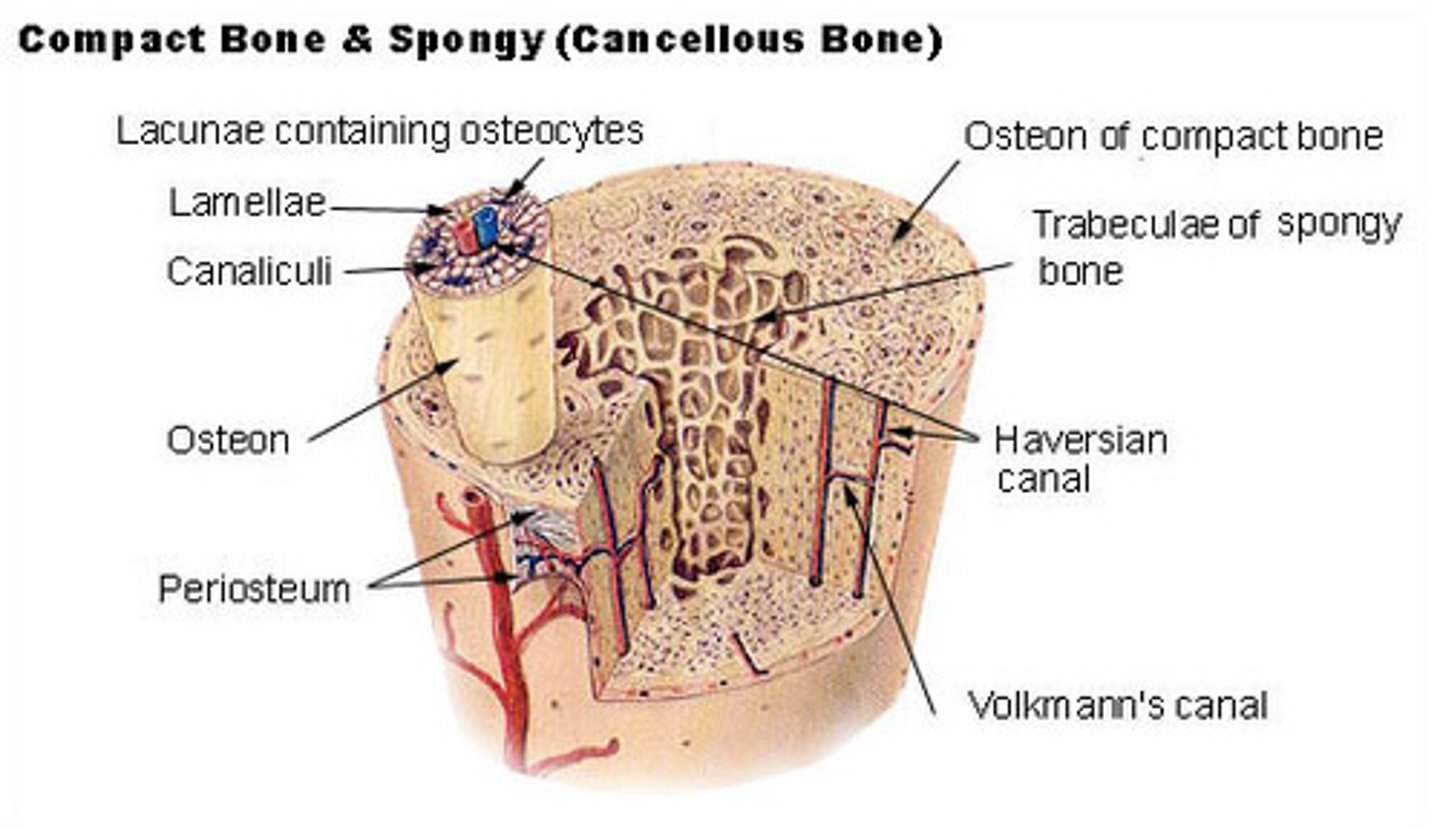
Haversian canals contain blood vessels to supply nutrients to the _____ of an osteon
osteocytes
(Haversian canals connect to osteocytes through canaliculi)
_____ are small spaces between lamellae that house bone cells
lacunae
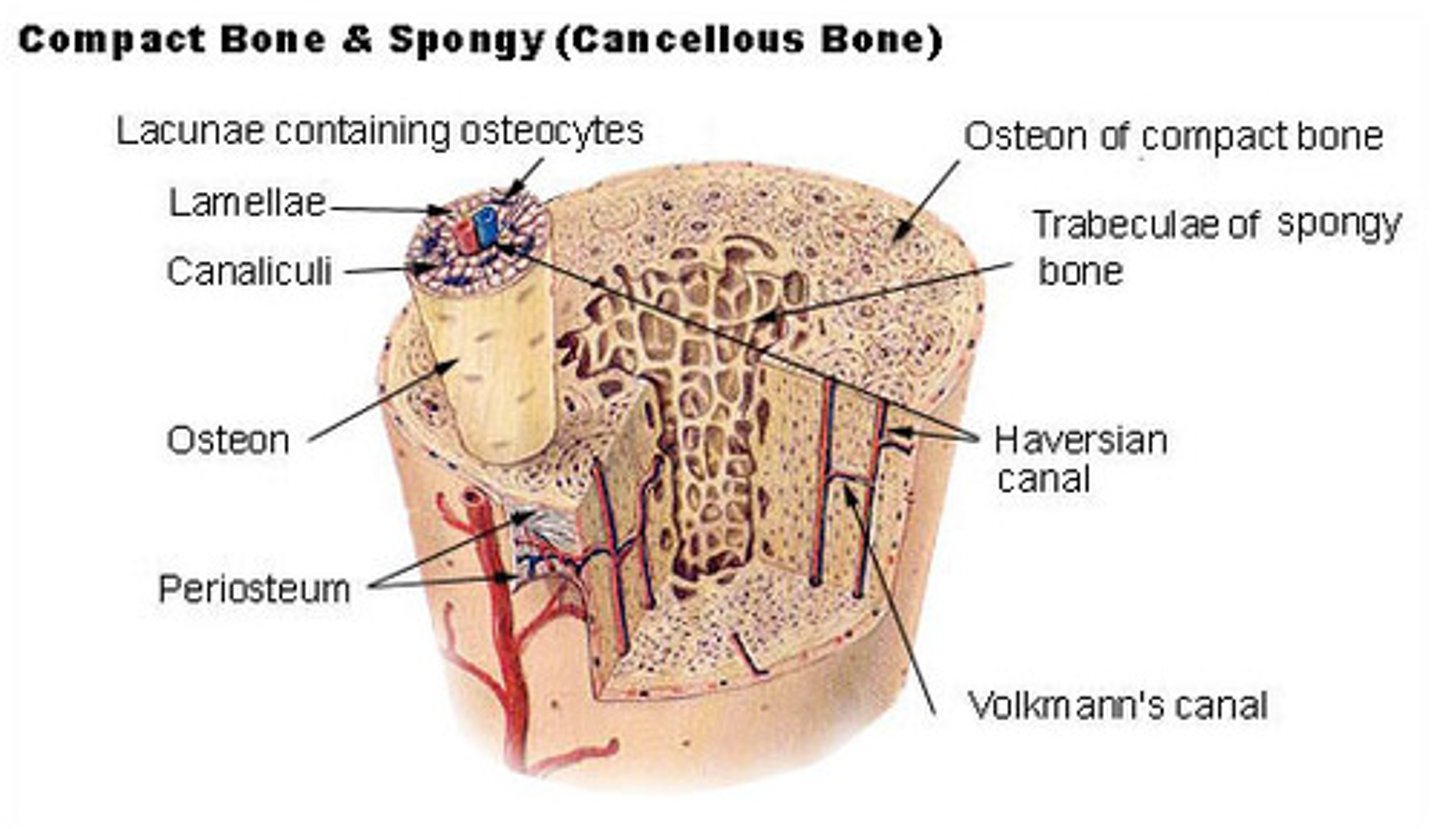
canaliculi connect _____ and _____ of a single osteon
lacunae (housing osteocytes); Haversian canals
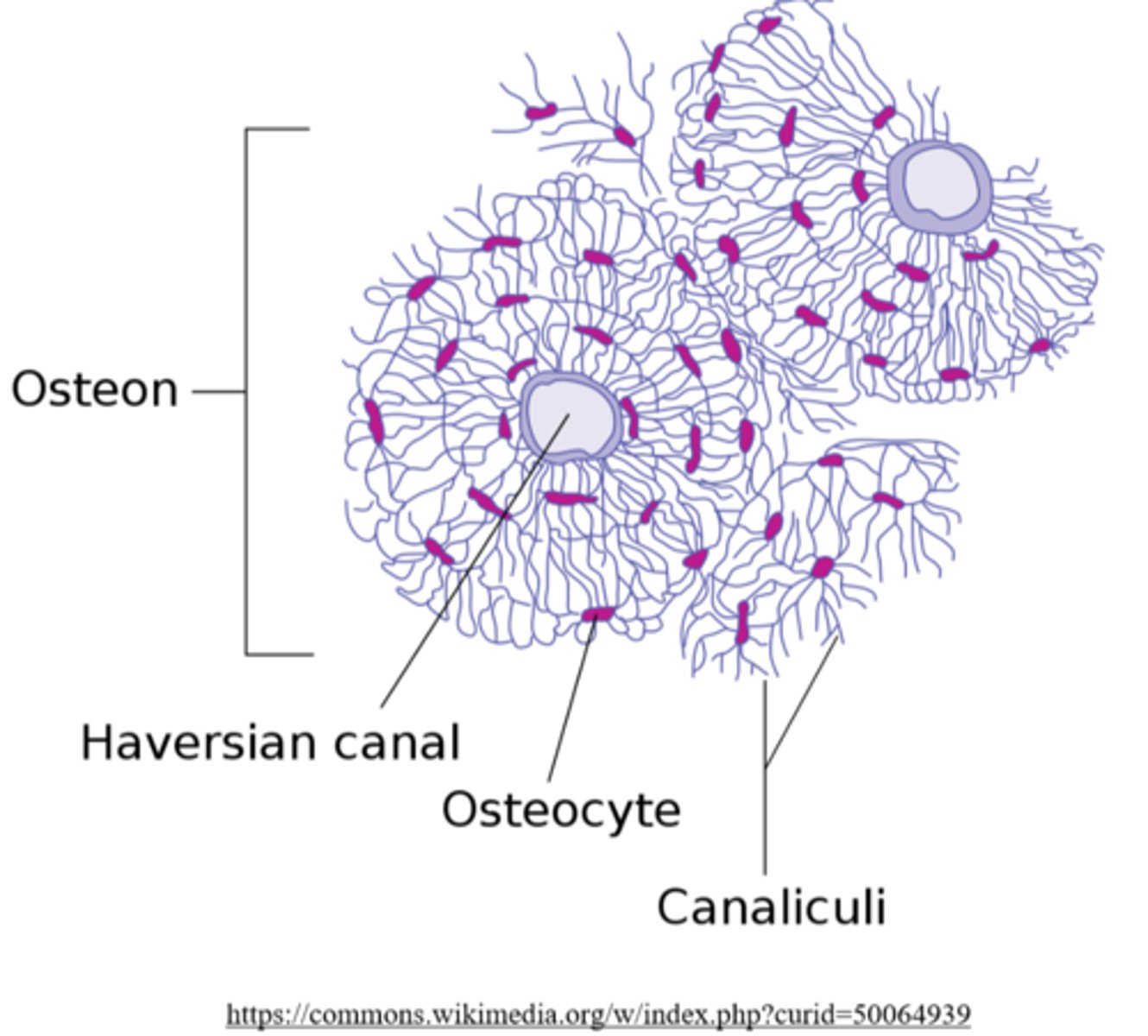
_____ connect adjacent Haversian systems as well as peripheral osteons to the periosteum
Volkmann's canals
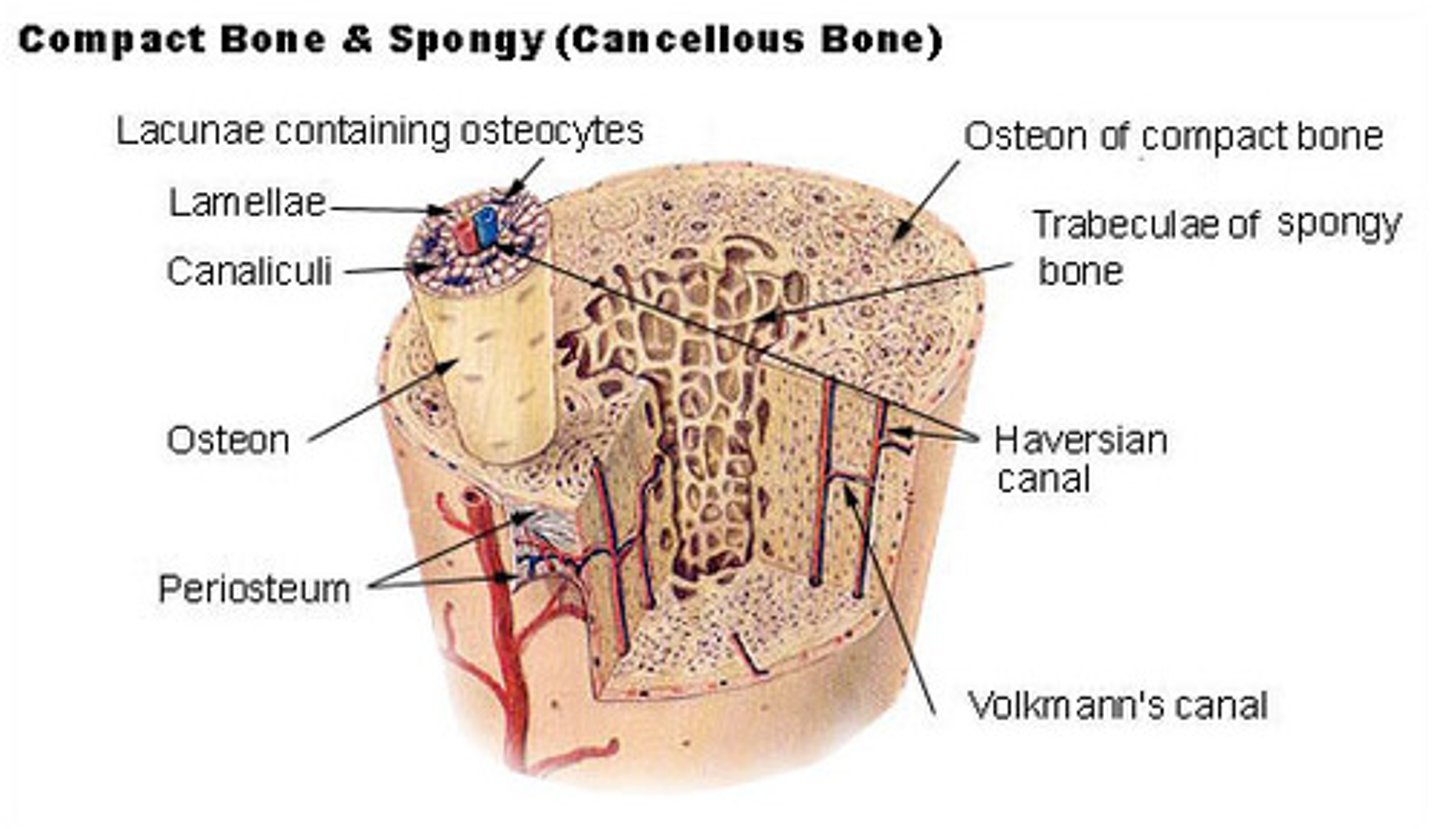
_____ bone is soft and flexible, and it is made of _____ that soak up bone marrow like a sponge
cancellous; trabeculae
(trabecular/cancellous bone = spongy bone)
_____ are precursors to osteoblasts
osteoprogenitors
osteoblasts contain _____ nucleus
1
what is the main function of osteoblasts?
to build bone (secrete collagen + proteins that make osteoid)
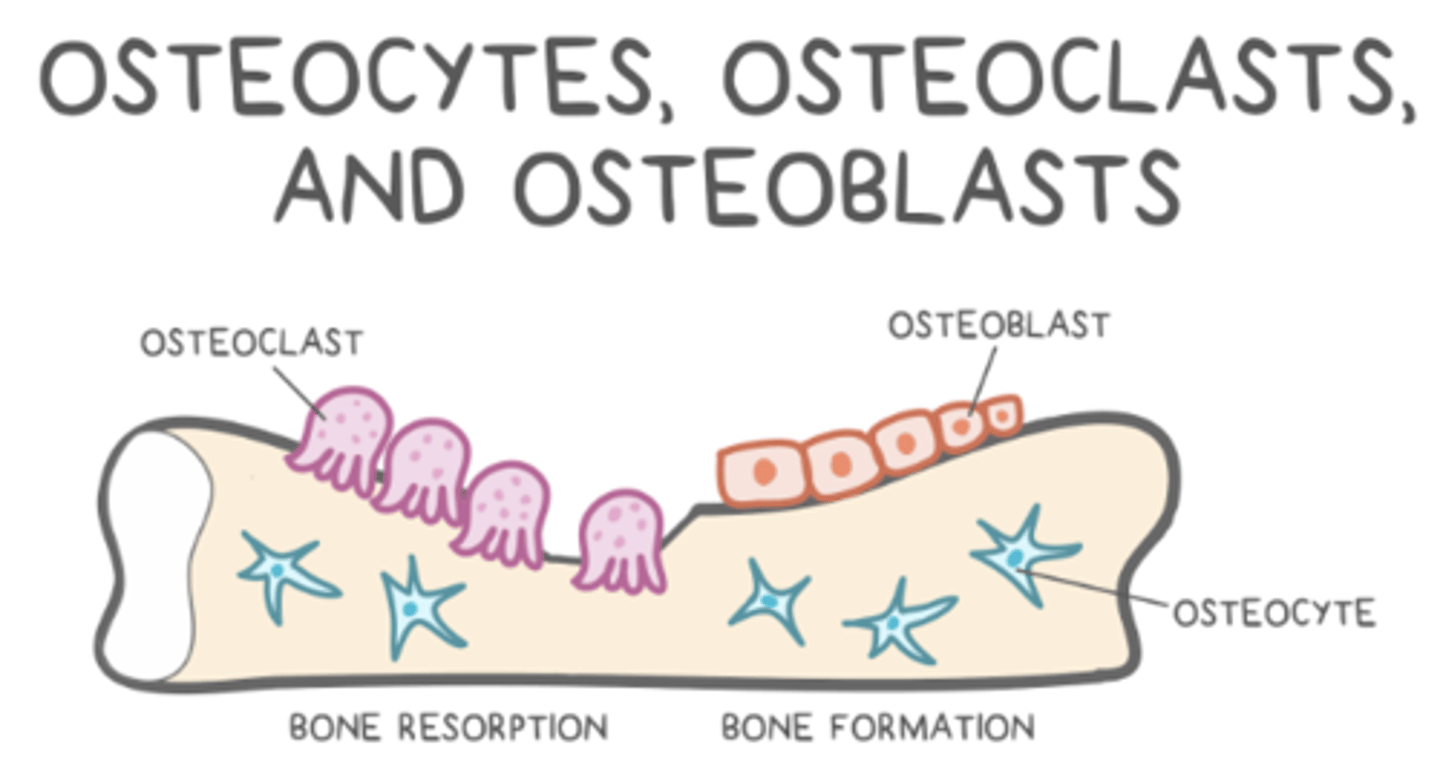
_____ are mature bone cells that develop from osteoblasts
osteocytes
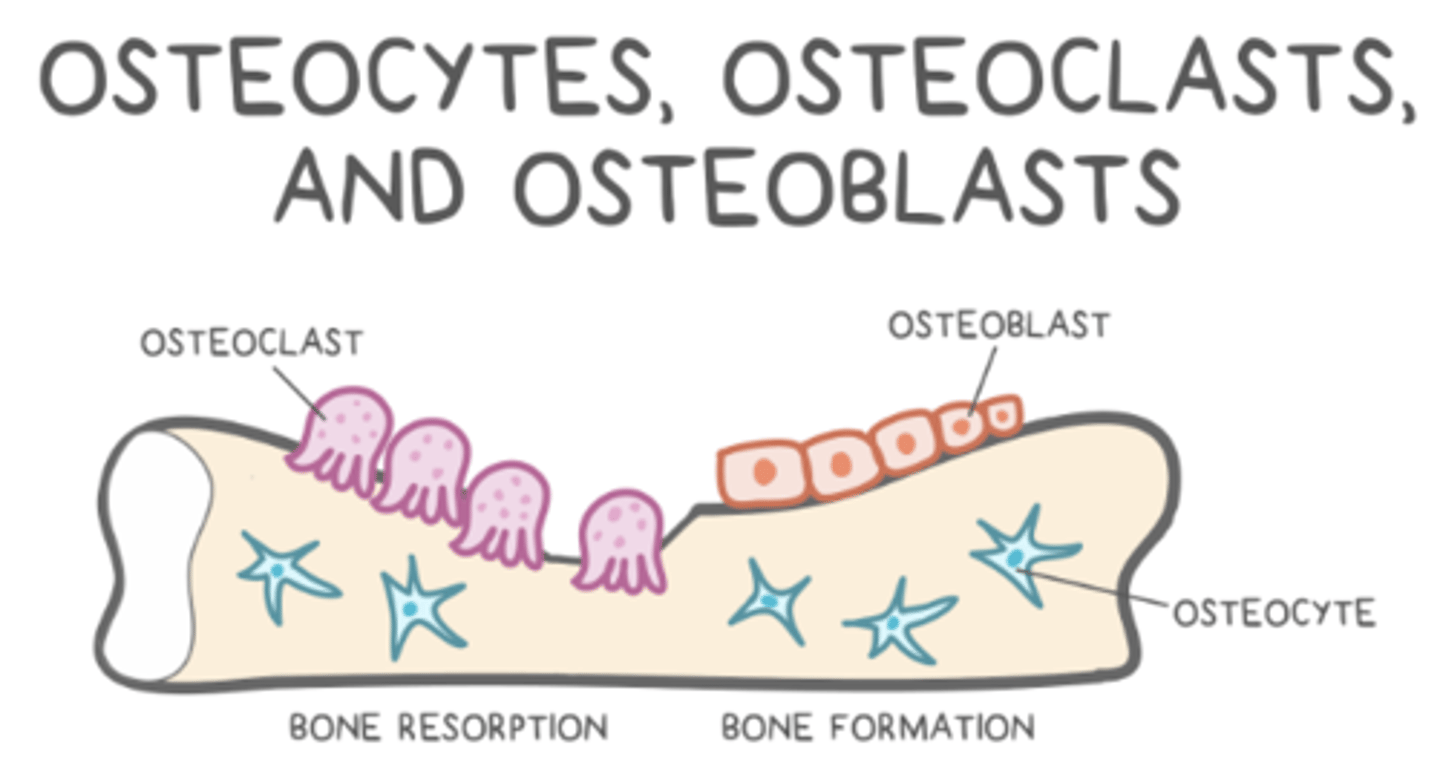
how do osteoblasts become osteocytes?
osteoblasts get trapped in the osteoid they secrete
osteoclasts contain _____ nuclei, and they are found in _____
multiple; Howship's lacunae
what cell type gives rise to osteoclasts?
monocytes
what is the main function of osteoclasts?
to resorb ("chew") bone
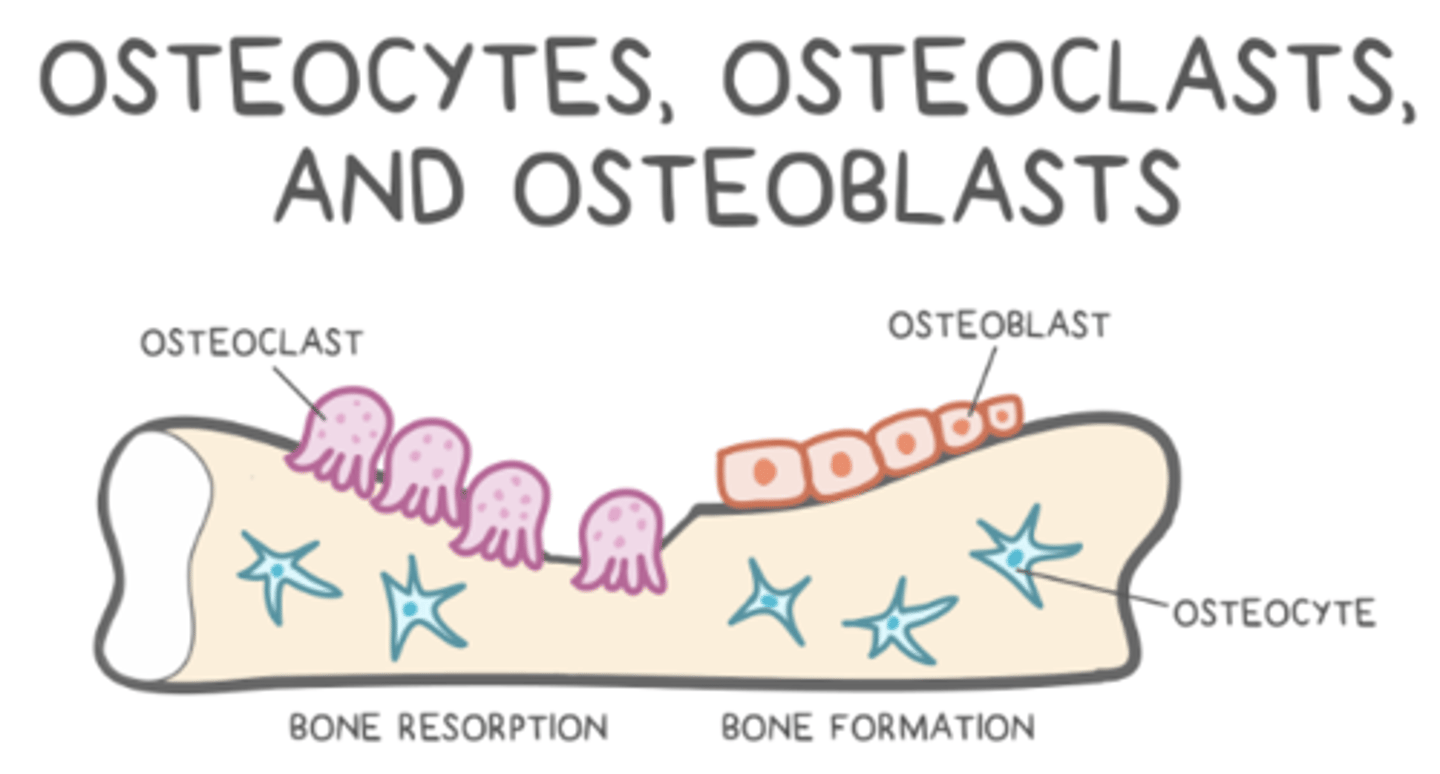
what are Howship's lacunae?
pits created by osteoclasts
what is bone remodeling?
the back and forth between resorption (osteoclasts) and ossification (osteoblasts)
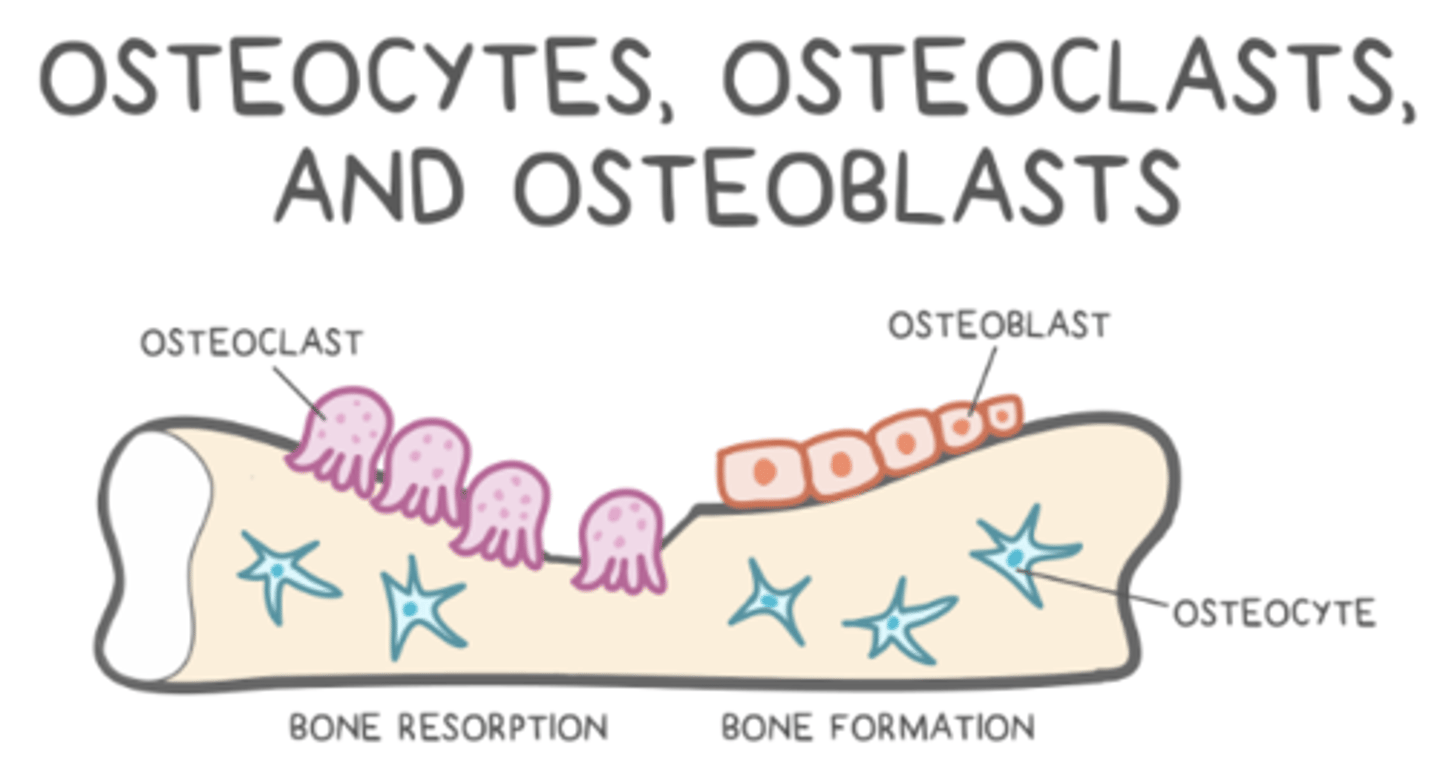
what are the primary factors that affect bone remodeling?
parathyroid hormone, vitamin D, calcitonin
parathyroid hormone (PTH) is secreted from the parathyroid gland, and it _____ (increases/decreases) blood Ca2+
increases
PTH stimulates _____ (bone cell) and depresses _____ (bone cell)
osteoclasts; osteoblasts
vitamin D is activated by _____ to _____ (increase/decrease) blood Ca2+
PTH; increase
through which type of feedback does activated vitamin D affect PTH secretion?
negative feedback
vitamin D stimulates Ca2+ _____ in the intestines, and increases the number of _____ for resorption
absorption; osteoclasts
calcitonin is secreted by the _____, and it opposes PTH to _____ (increase/decrease) blood Ca2+
thyroid gland; decrease
calcitonin decreases the activity of _____, so _____ have less competition
osteoclasts; osteoblasts
_____ is made of proteins and type 1 collagen fibers, to provide bones with tensile strength
osteoid
_____ provides bone density, and it is made of inorganic crystals of Ca2+, phosphate, & H2O
hydroxyapatite
what are the two types of embryonic ossification?
intramembranous and endochondral
what is the most common type of embryonic ossification?
endochondral ossification
_____ ossification occurs when bone is created directly within a fibrous membrane
intramembranous
list the steps of intramembranous ossification
1. osteoblasts secrete osteoid
2. osteocytes in the hardened bone matrix create trabeculae
3. the trabeculae gets wrapped in blood vessels and forms the periosteum
4. cortical bone grows between the periosteum and trabeculae
what types of bones are usually made by intramembranous ossification?
flat bones
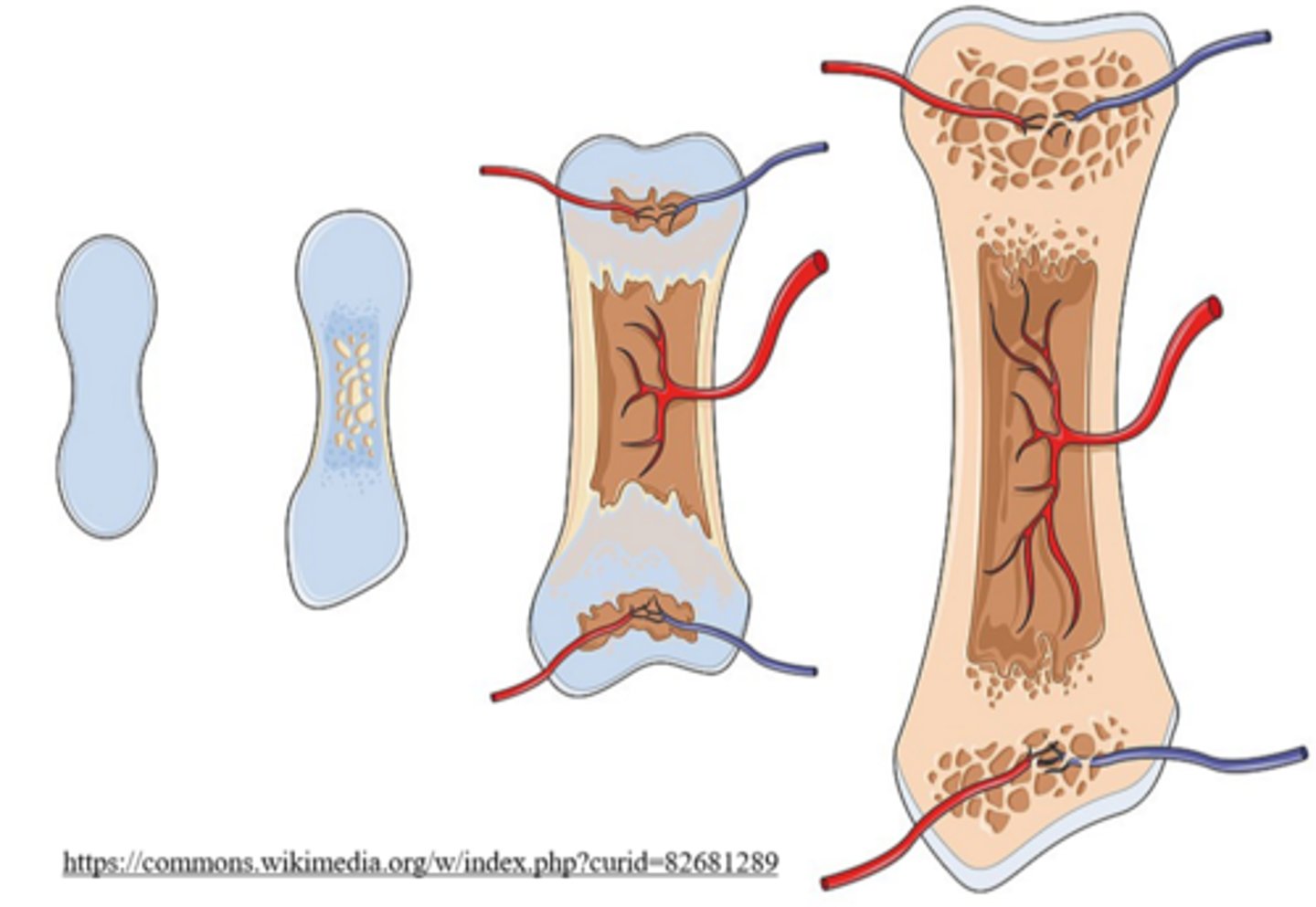
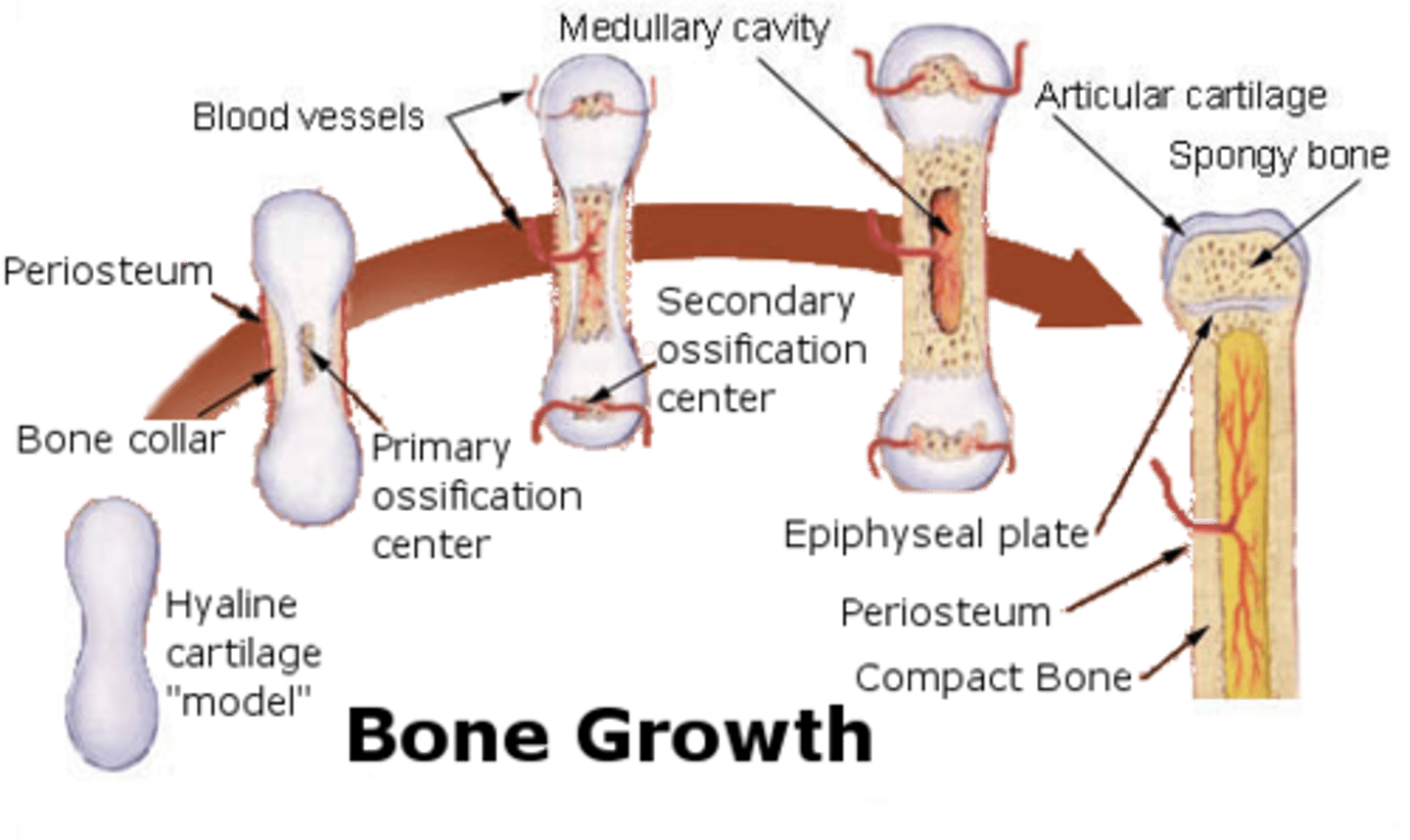
_____ ossification occurs when bones are created indirectly, from a cartilage model
endochondral
list the steps of endochondral ossification
1. hyaline cartilaginous matrix hardens into the cartilage model
2. the cartilage model's center calcifies
3. capillaries and osteoblasts invade the calcified center and establish the primary ossification center
4. secondary ossification sites are made at epiphyses
5. osteoclasts resorb the inside of the diaphysis, which creates the medullary cavity
what are the three main types of connective tissue?
fibrous; cartilage; joints
what bones are made through endochondral ossification?
long bones
fibrous connective tissue includes which three things?
tendons; ligaments; periosteum/endosteum
_____ connect bones to muscle
tendons
_____ connect bones to other bones
ligaments
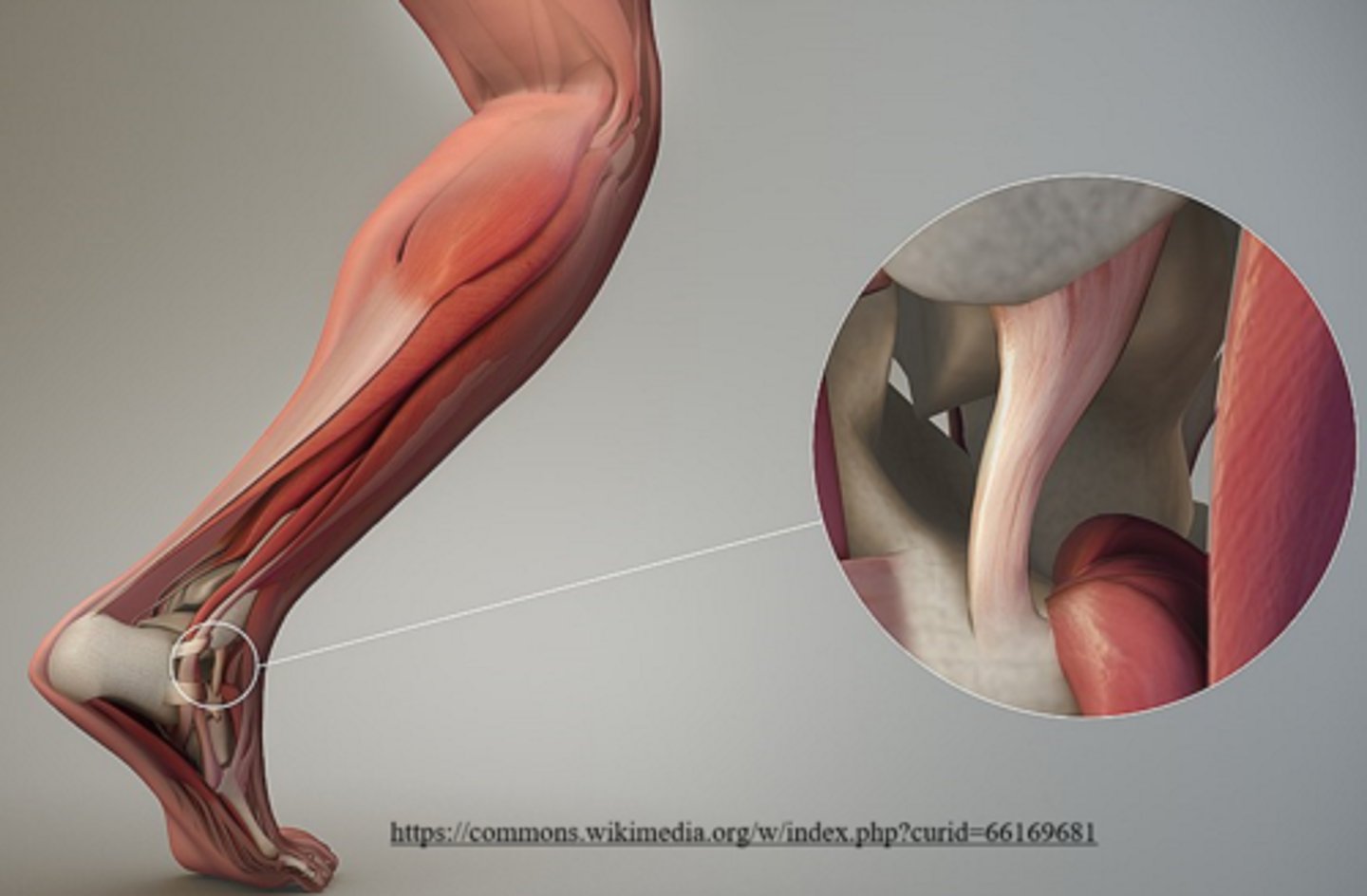
the _____ is a protective fibrous membrane that covers cortical bone
periosteum
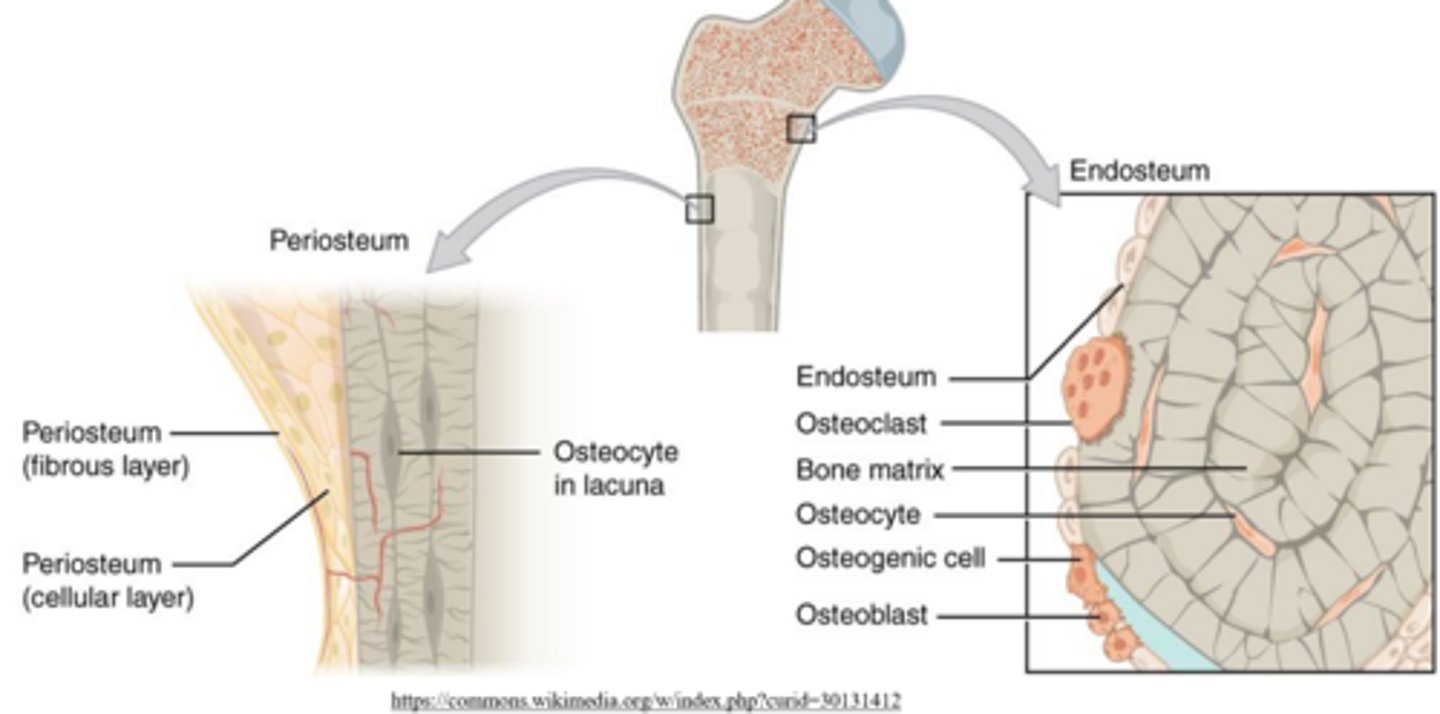
what are the two sublayers of the periosteum?
outer fibrous layer; inner/cambium layer
(cellular layer = inner/cambium layer)
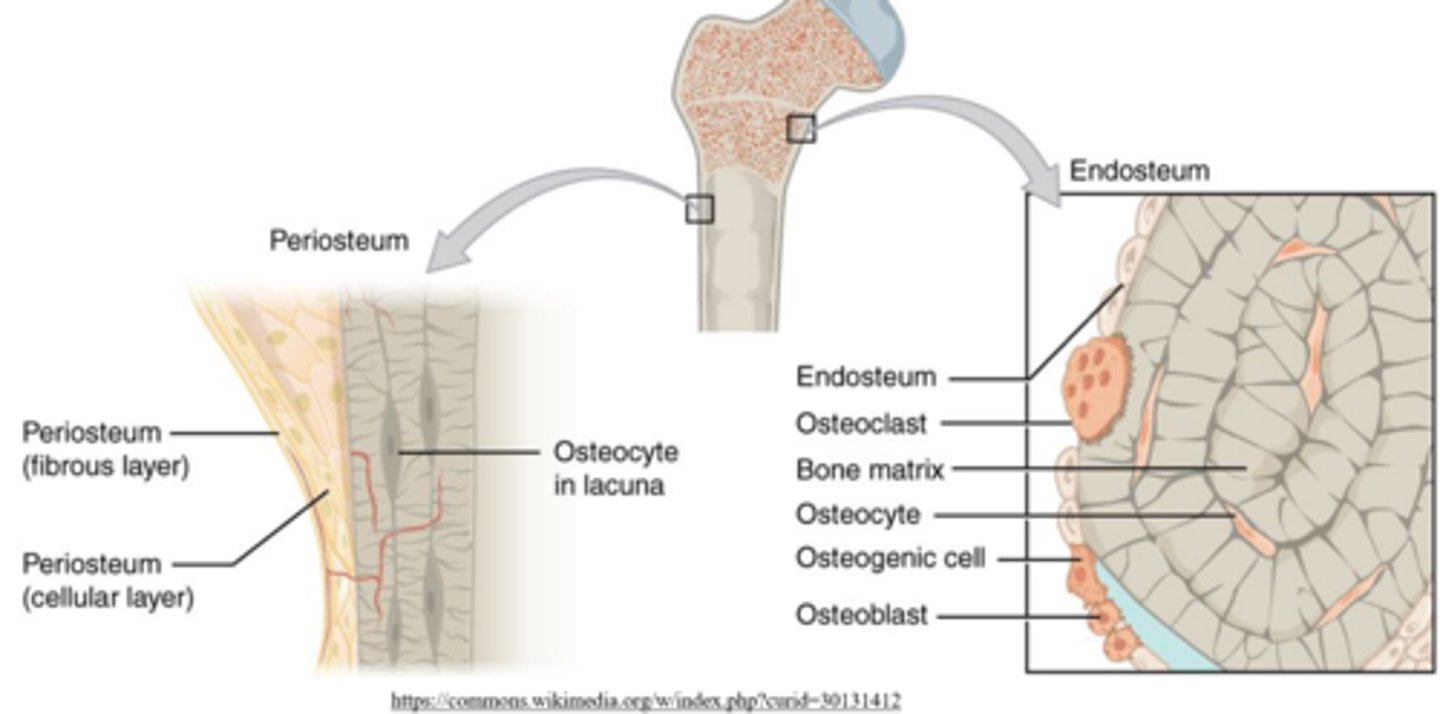
the outer fibrous layer of the periosteum is _____
vascularized
the _____ layer of the periosteum contains collagen and osteoprogenitor cells
inner/cambium
the _____ is a single layer membrane between cortical and cancellous bone
endosteum
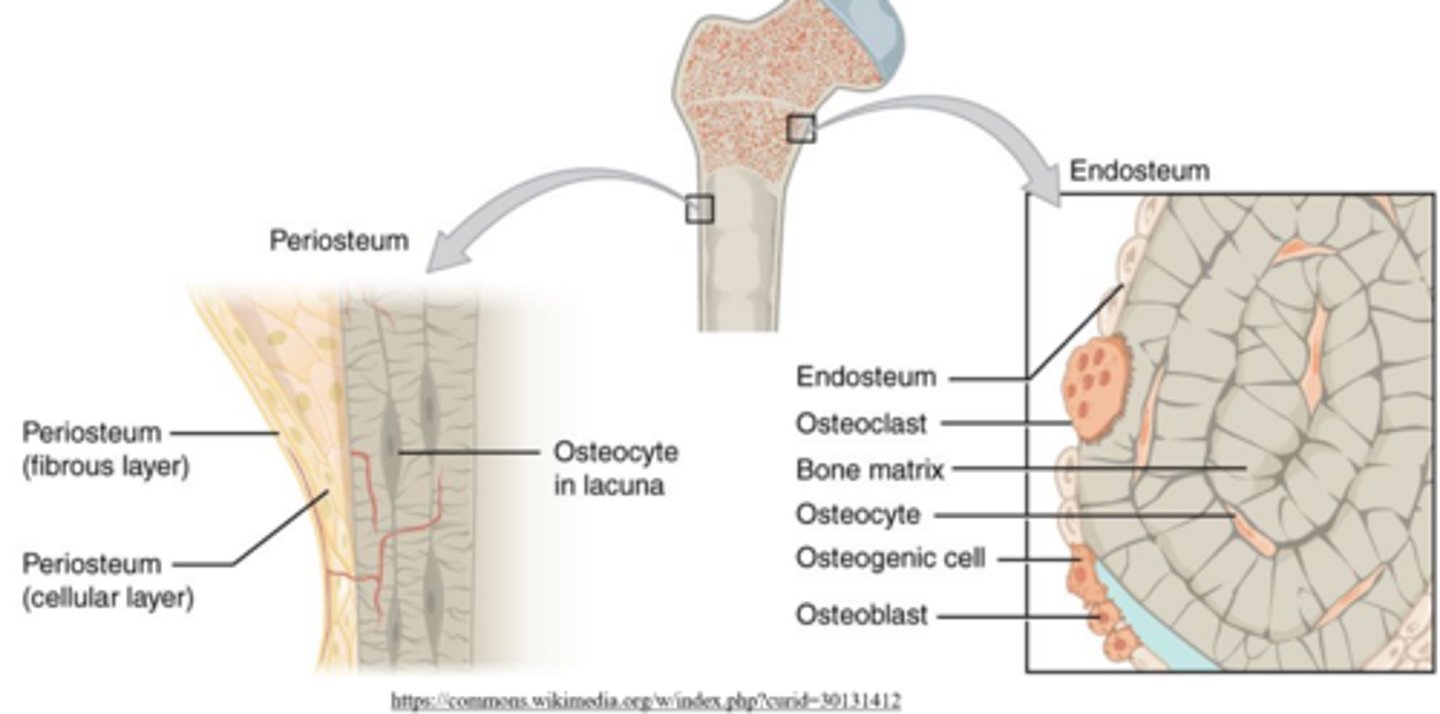
what processes are both the periosteum and endosteum involved in?
bone growth, repair, and remodeling with respect to bone thickness
cartilage is _____ and not _____
avascular; innervated
how do cells living in cartilage get nutrition/immune support?
from the surrounding fluid
cartilage building cells are called _____
chondroblasts
(analogous to osteoblasts)
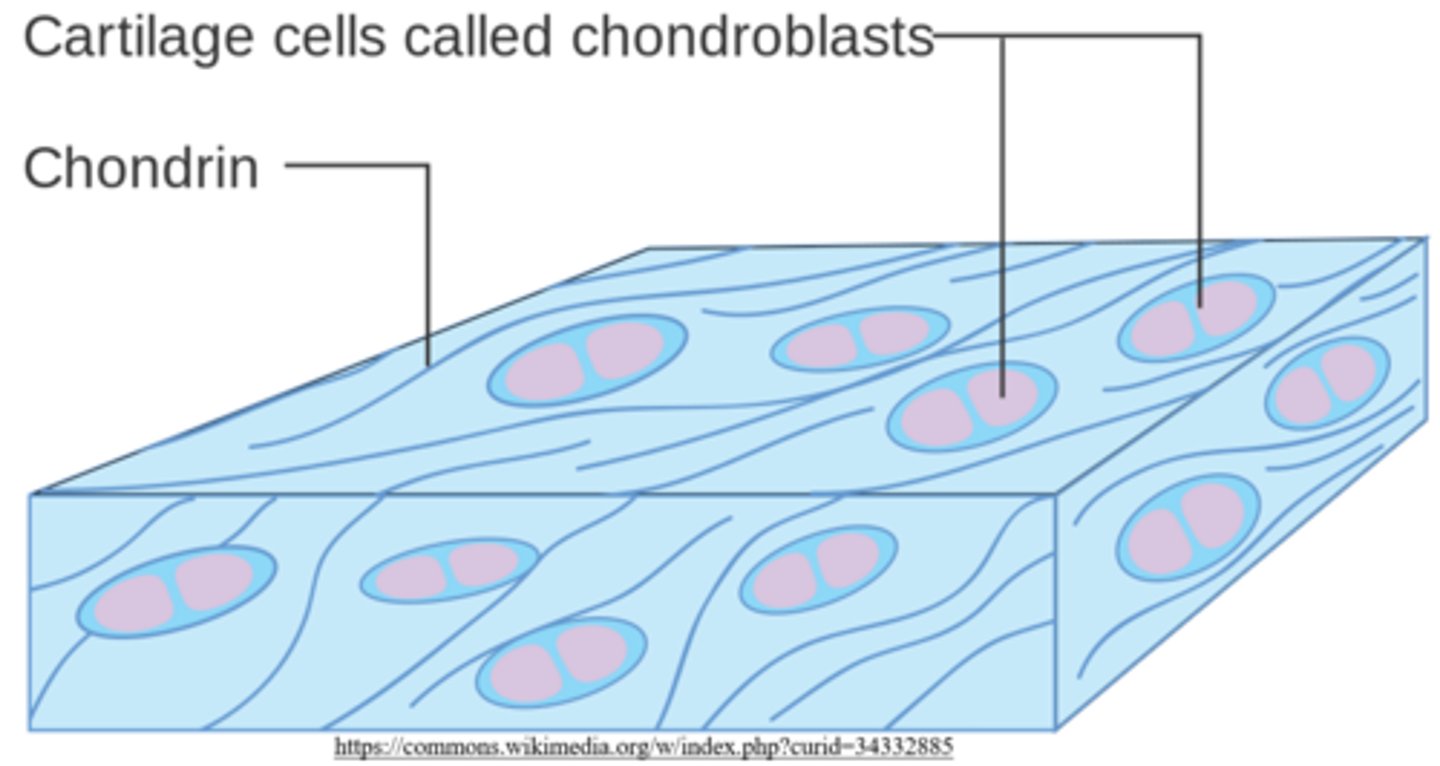
chondrocytes are mature _____
chondroblasts
(analogous to osteoblasts --> osteocytes)
how do chondroblasts give rise to chondrocytes?
chondroblasts get trapped by the matrix they secrete
(analogous to osteoblasts --> osteocytes)
what is the primary function of chondrocytes?
maintaining cartilage
(similar to osteocytes, which maintain bone)
where are chondrocytes found?
cartilaginous lacunae
(similar to osteocytes inhabiting lacunae of an osteon)
chondroblasts secrete a cartilaginous matrix containing:
collagen and elastin
how can you change the type of cartilage?
change the amounts of collagen and elastin
what is the most common protein in mammals?
collagen
what are the three types of cartilage?
hyaline; fibrous; elastic
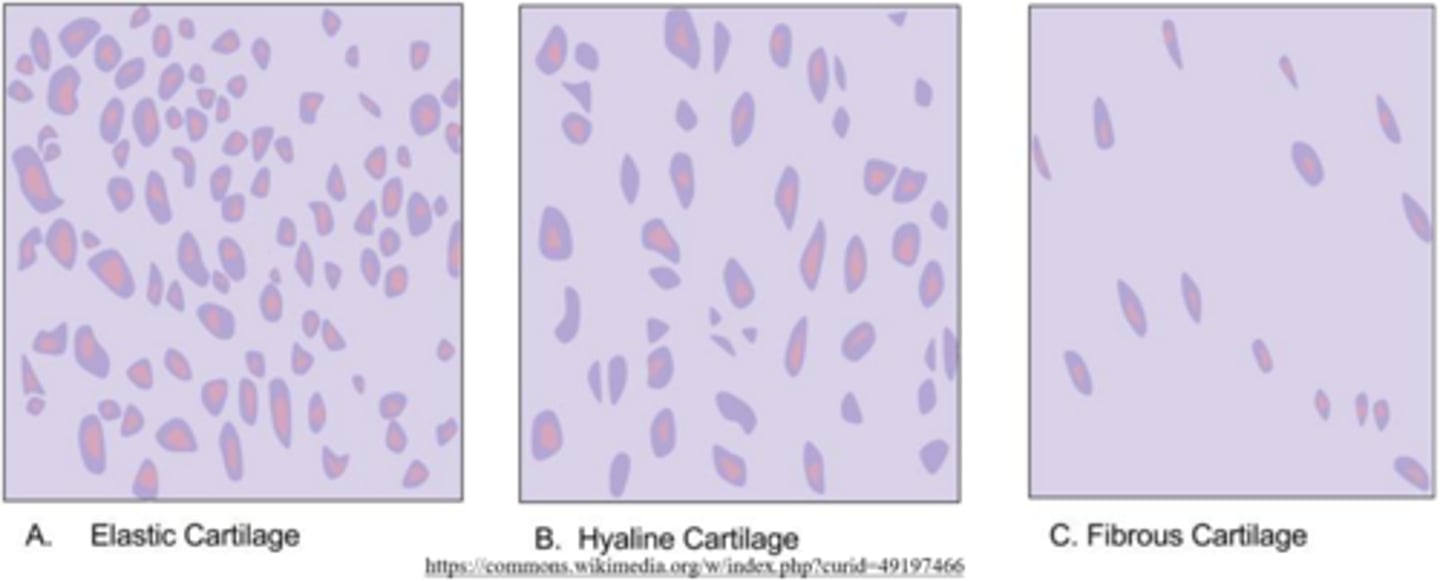
_____ cartilage has a glassy appearance, and it absorbs shock by supporting the ends of long bones at synovial joints
hyaline
(the articular cartilage found at synovial joints is hyaline cartilage)