Physics - Section One: Forces and motion
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Velocity and Acceleration
Velocity and Acceleration
What is the difference between speed and velocity?
Speed is how fast you're going (e.g., 30 m/s or 20 m/h) without regard to direction. Velocity includes direction (e.g., 30 m/s north).
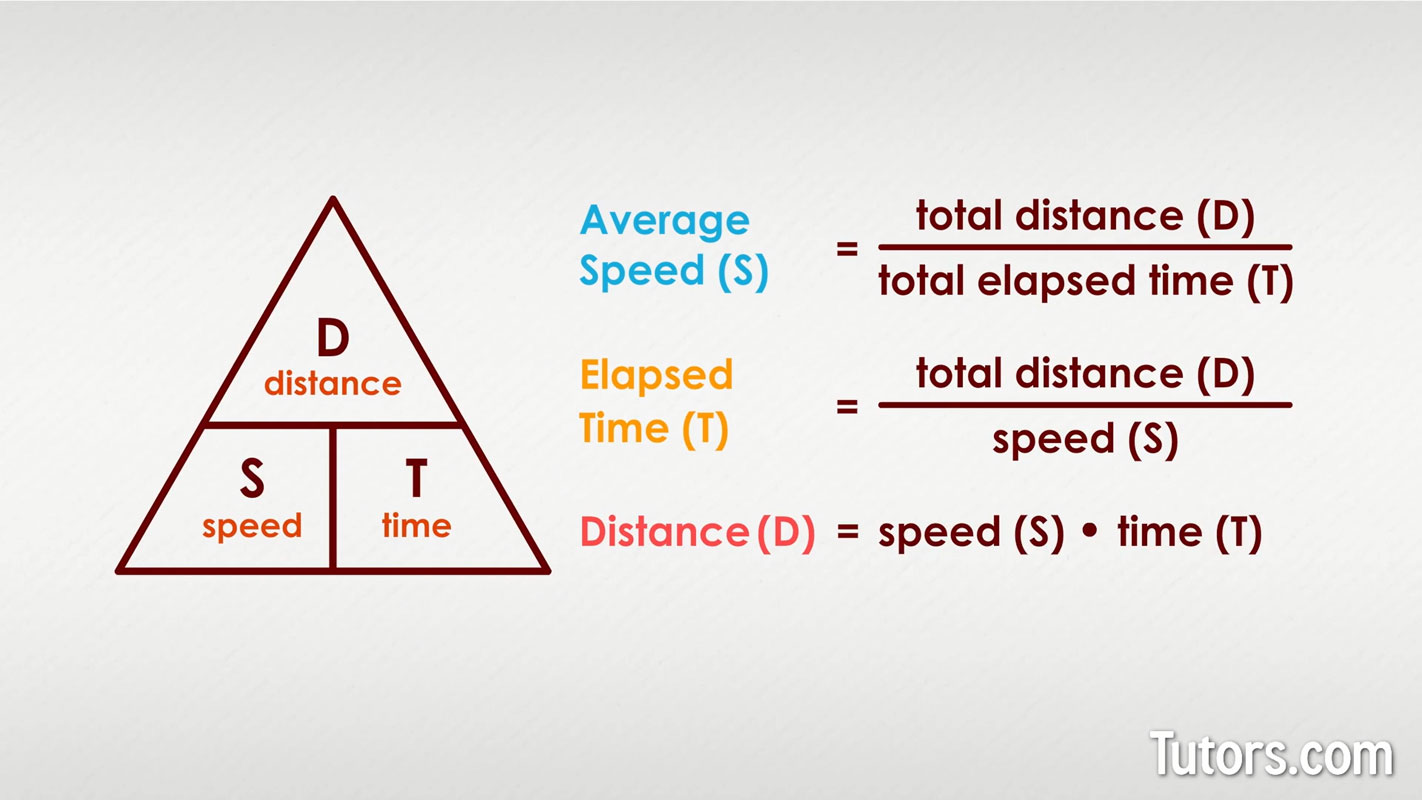
What is the formula for average speed?
Average speed (m/s) = Distance moved (m) / Time taken (s)

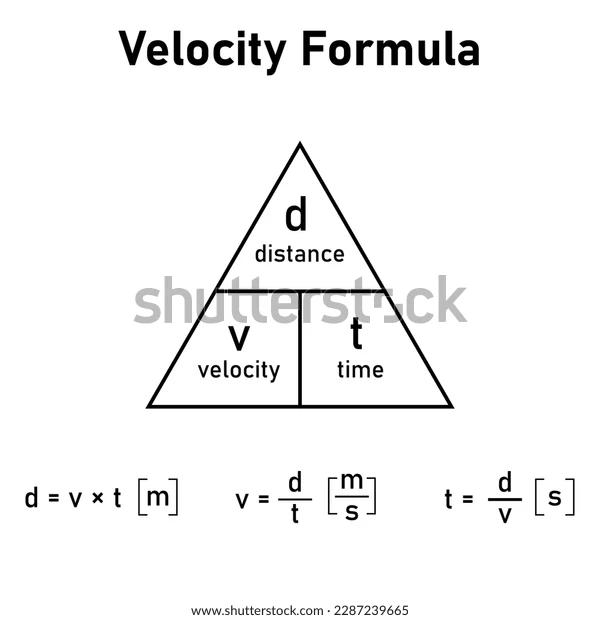
What is the formula for Velocity?
Velocity (m/s) = Distance (m) / time (s)

What is acceleration?
Acceleration (m/s²) is how quickly velocity is changing. It can result from a change in speed, direction, or both.
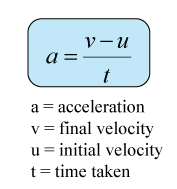
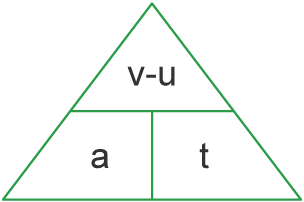
What is the formula for acceleration?
Acceleration = Change in velocity / Time taken

What is the formula for velocity using acceleration and displacement?
v^2 = u^2 + 2as
How do you handle negative acceleration?
Negative acceleration (deceleration) indicates slowing down. Ensure to include the negative sign in calculations.
Distance- Time and Velocity- Time Graphs
Distance- Time and Velocity- Time Graphs
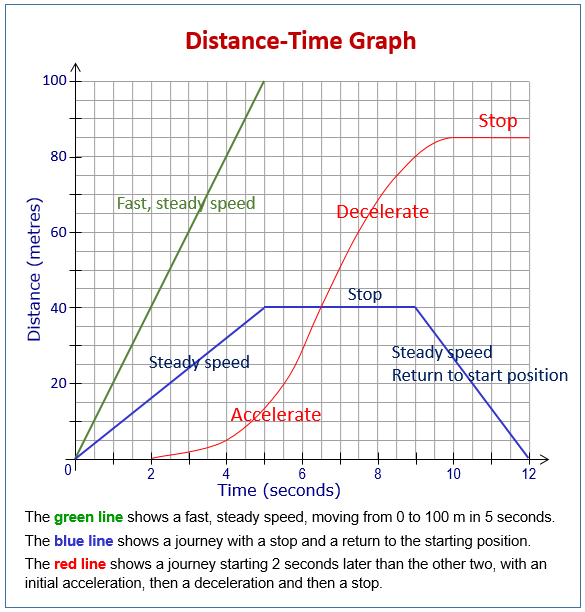
What are the key points of a Distance time Graph?
Key Points:
Gradient (slope) = speed at any point.
Flat sections: Object is stopped.
Steeper graphs: Higher speed.
Curved graphs: Acceleration or deceleration.
Levelling off: Slowing down (decreasing gradient).
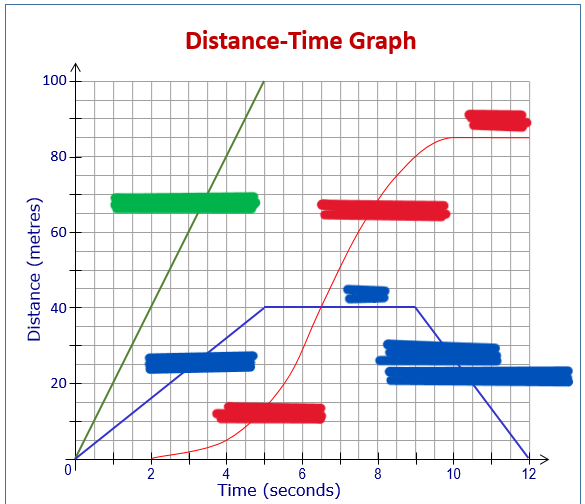
What are the correct words/ terms that describe what the graph shows where there is a box?


What is the formula for speed using a distance-time graph?
Speed = Gradient = Vertical/ horizontal (change in y/ change in x)
What is the formula for average speed using a distance-time graph?
Average speed = total distance/ total time
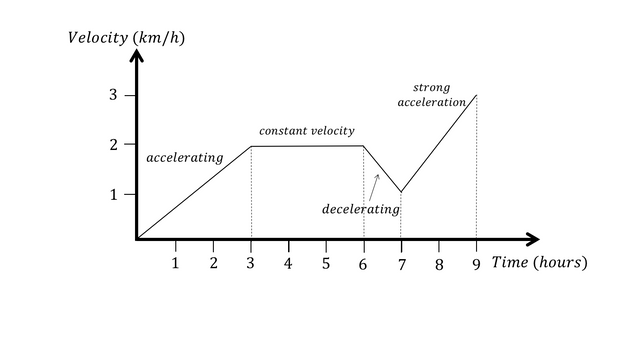
What are the key points of a Velocity time Graph?
Key Points:
Gradient = Acceleration.
Flat sections: Steady speed.
Steeper gradient: Greater acceleration or deceleration.
Uphill sections (/): Acceleration.
Downhill sections (\): Deceleration.
Area under graph = Distance travelled.
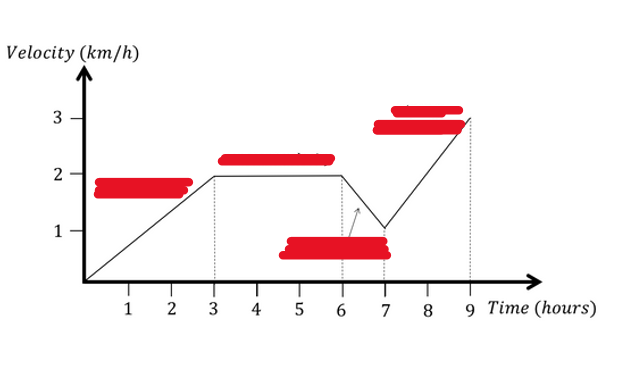
What are the correct words/ terms that describe what the graph shows where there is a box?


What is the formula for acceleration using a velocity time graph?
Acceleration = gradient = vertical/ horizontal
How do you find the speed on a velocity time graph?
By reading the value off the velocity axis
How do you find the distance travelled on a velocity time graph?
Area under the graph
Mass, Weight and Gravity
Mass, Weight and Gravity
What is gravity?
Gravity is the force of attraction between all masses
What does gravity do?
Gravity attracts all masses but it is only noticeable when one mass is very large (e.g., planets).
What are the effects of gravity?
1. Causes all objects to accelerate towards the ground at on Earth.
2. Gives weight to objects.
3. Keeps planets, moons, and satellites in orbit by balancing forward motion and inward pull of gravity.
What are the differences between weight and mass?
Mass: Amount of matter in an object, constant everywhere in the universe (measured in kilograms, kg).
Weight: Force of gravity acting on mass, varies by location (measured in newtons, N).
Weight depends on gravitational field strength.
How do you measure weight and mass?
Mass (Kg): Using a mass balance.
Weight (N): Using a newton meter or spring balance.
What is the formula relating mass, weight and gravity?
W = m \times g
m: Mass in kilograms (kg).
g: Gravitational field strength (N/Kg).
How does gravity create orbit?
Gravity creates orbits by balancing the forward motion of objects (like satellites) with the inward pull of gravity.
Forces and Friction
Forces and Friction