A level Bio 1.3 Lipids
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
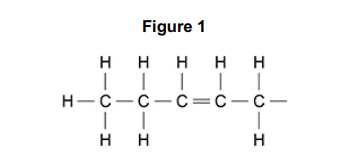
Figure 1 shows the structure of a fatty acid R group
Type of R group-
Explanation (2)
Type of R group - Unsaturated (fatty acid/hydrocarbon) (1)
Explanation- Double bond (between carbons) (1)
Describe how you would test for the presence of a lipid in a liquid sample of food. (2)
Add ethanol/alcohol then add water and shake/mix (1)
White/milky (emulsion) (1)
Describe how an ester bond is formed in a phospholipid molecule (2)
Condensation (reaction) (1)
Between of glycerol and fatty acid (1)
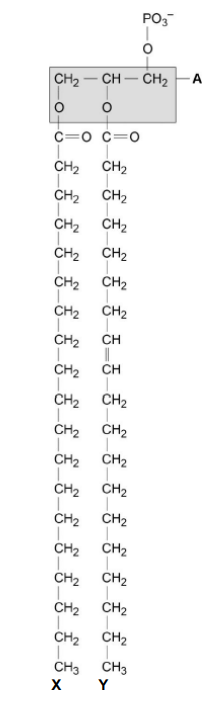
The part of the phospholipid labelled A is formed from a particular molecule. Name this molecule. (1)
Glycerol (1)
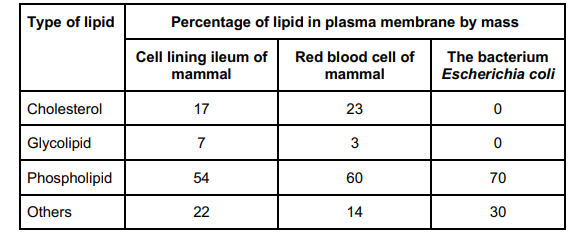
Scientists investigated the percentages of different types of lipid in plasma membranes from different types of cell. The table shows some of their results.
The scientists expressed their results as Percentage of lipid in plasma membrane by mass. Explain how they would find these values (2)
Divide mass of each lipid by total mass of all lipids (in that type of cell) (1)
Multiply answer by 100 (1)
The ratio of saturated to unsaturated fatty acids in a cell-surface membrane determines the extent of the membrane’s fluidity.
Scientists provided a cell culture of mouse phagocytes with liquid broth rich in unsaturated fatty acids.
The scientists observed:
• an increase in the proportion of phospholipids in the phagocytes containing unsaturated fatty acids
• more phagocytosis.
Suggest and explain why there was more phagocytosis. (3)
More unsaturated fatty acids increases fluidity (in cell-surface membrane) (1)
(Making cell-surface) membrane more fluid/flexible (1)
Easy to engulf (1)
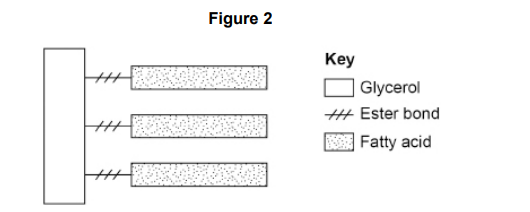
Explain why phospholipids can form a bilayer but triglycerides cannot (3)
Phospholipid both hydrophobic and hydrophilic (1)
Triglycerides only hydrophobic (1)
Hydrophilic/phosphate group attracts water (to either side of bilayer) (1)
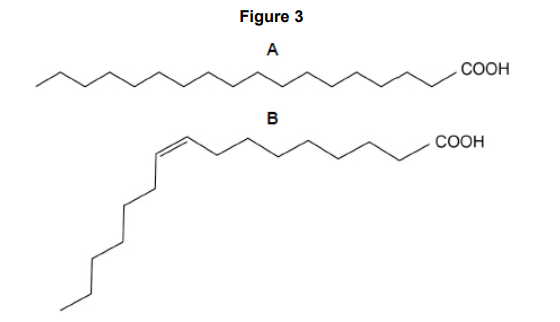
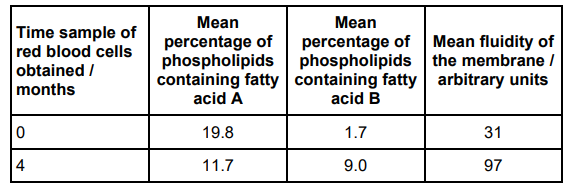
Scientists fed rats a diet with added fish oil for 4 months.
They obtained samples of red blood cells from the rats before starting this diet (0 months) and after 4 months on this diet.
For each red blood cell sample, they separated the cell-surface membranes and measured:
• the percentage of phospholipids containing each of the fatty acids A and B
• the fluidity of the membrane.
Suggest why the fluidity of the membrane was higher after 4 months. Use all the information provided in the question (3)
Fatty acid A is saturated (1)
(At 4 months) less fatty acid A and more fatty acid B (1)
Increase in fluidity caused by increased unsaturated fatty acids (1)
All mammals produce a lipase called CEL. CEL digests triglycerides. CEL is activated by bile salts binding to the enzyme. Describe two other functions of bile salts. (2)
Emulsify lipids/fats (1)
Increases surface area (of lipid/fat) for (increased) lipase activity (1)
Mammals feed their young on milk. CEL digests the triglycerides in milk. The ability to produce CEL occurred due to a gene mutation. Describe how natural selection may have led to all mammals in a population producing CEL. (4)
Mutation results in (a new) allele (1)
Those with the (new) allele able to digest milk/triglycerides (1)
Individuals with CEL/allele more likely to (survive and) reproduce (1)
Increase in frequency of (this) allele in population (1)
State 3 roles of lipids (3)
it is waterproof (as it is only soluble in organic solvents) (1)
Insulator to retain body heat (1)
Provide energy when oxidised and release water (1)
State and explain three properties of triglycerides (3)
Source of energy as there is a high ratio of energy storing carbon-hydrogen bonds to carbon atoms (1)
Storage molecule as it has a low mass to energy ratio (1)
it releases water when oxidised due to a high ratio of hydrogen to oxygen atoms (1)