5 - Waves and Sound (fuck magnetism)
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
F = -kx
F = restoring force (back to equilibrium)
k = spring constant [k] = N/m
x = displacement from EQ
hooke’s law formula
simple harmonic function
back and forth motion (ex: waves, sound, spring, etc.)
PEelastic = (1/2)kx² OR Etotal = (1/2)kA²
A = amplitude (in case displacement is not used)
formula for nrg stored in spring as it stretches/compresses (potential energy)
Wby spring = -ΔPEelastic = -(1/2)kx²
ALL Work formulas are ±PE
formula for work by the spring (hint: it’s a conservative force)
period (T)
the time it takes to complete 1 cycle (returns to same position and velocity)
frequency (f)
f = 1/T → in Hertz (Hz = 1/second)
number of cycles in ONE second (1/second = Hz)
f = 1/T in hertz
simple harmonic motion frequency formula
waves
propagating oscillations that transfers nrg
medium is not propagating with the energy
medium oscillates with a series of identical oscillations slightly out of phase
particles oscillate in mechanical waves. Whereas electric & magnetic fields oscillate in EM waves
difference between mechanical and EM wave?
wavelength (λ): length of 1 cycle (crest → crest; trough → trough)
amplitude (A): max displacement of medium from EQ
wave speed (v): speed of wave moving to the right (d = vt)
period (T): time for 1 cycle to go by, or for 1 particle to finish 1 oscillation
frequency (f): # of pulse that passes per second
5 properties of waves:
wavelength (λ)
length of 1 cycle (crest → crest; trough → trough)
amplitude (A)
max displacement of medium from EQ
wave speed (v)
speed of wave moving to the right (d = vt)
period (T)
time for 1 cycle to go by, or for 1 particle to finish 1 oscillation
frequency (f)
# of pulse that passes per second
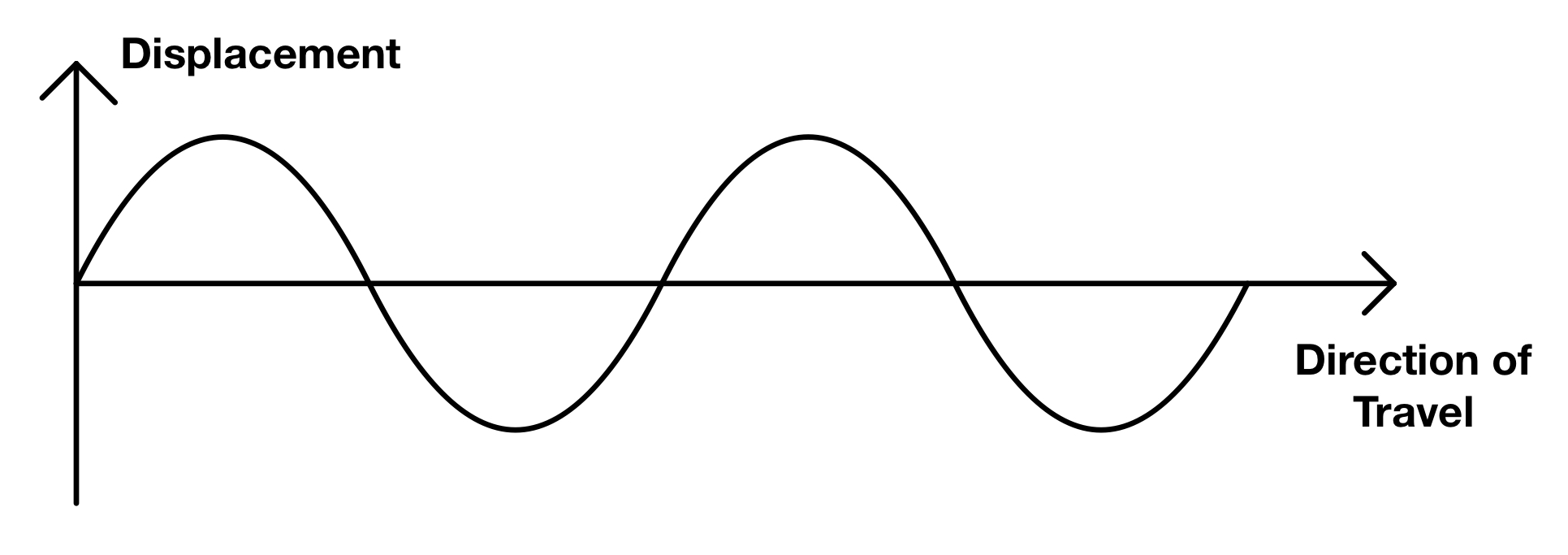
transverse waves
type of wave where medium oscillates that’s perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation (ex: ocean waves, waves on string, EM wave)
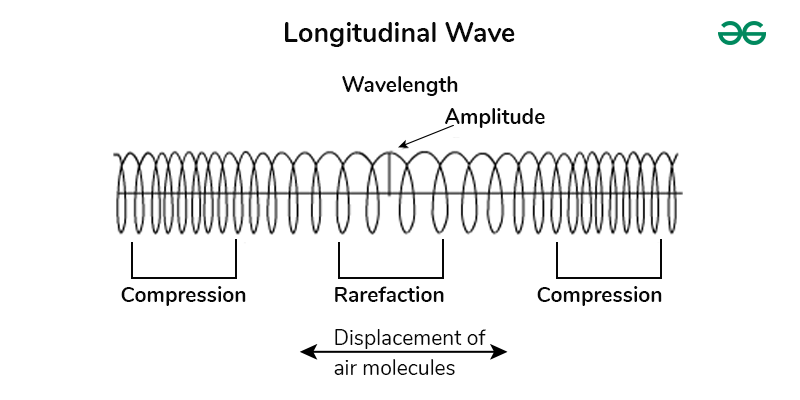
longitudinal wave
type of wave where medium oscillates parallel to the direction of wave propagation (ex: sound)
v = λf
formula for speed (v) using wavelength (λ) and frequency (f)
type of wave, physical properties of medium
speed of a wave (v) depends on:
______________ of wave
______________ of medium
frequency
a wave moving from 1 medium to another will maintain its ______________
velocity (v)
_____________ is constant in a medium, regardless of the frequency or length of it
gas, liquid, solid
sound waves travel the SLOWEST in ___________ (gas/liquid/solid) < (gas/liq/solid) < FASTEST in __________ (gas/liq/solid)
solid > liquid > gas
rank the type of medium sound waves travel the FASTEST to SLOWEST in
intensity (I)
I = Power (P) / Area (A) = W / m²
energy of a wave incident per unit area per unit time
I = Power (P) / Area (A) = W / m²
formula for intensity
doppler shift
shift in the detected frequency of wave due to relative motion between detector and sound source
detector and source getting closer together = higher frequency
detector and source getting farther = lower freq
v = 350 m/s
whats the speed of sound in air?
v = 3×10^8
what’s the speed of light wave in a medium?
fd = f[(v ± vD) / (v ± vS)]
fd = observed frequency
f = actual frequency
vD = velocity of detector (hears the sound)
vS = velocity of source (makes the sound)
doppler shift formula
vD = 10 m/s, vS = 20 m/s
f = 500 Hz
cyclist moving TOWARD the beep (+vD), bus moving AWAY from beep (-vS)
500(350
A cyclist is riding behind a bus, both traveling on a straight road. The bus is moving at a constant velocity of 20 m/s, and the cyclist is riding at a constant velocity of 10 m/s. The bus driver honks the horn, emitting a sound wave with a frequency of 500 Hz. If the speed of sound in air is 343 m/s, what is the frequency of the sound wave heard by the cyclist?
A) 465 Hz
B) 500 Hz
C) 535 Hz
D) 570 Hz