Occlusion from Dental Anatomy
1/139
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Thank you Gracie Girl
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
140 Terms
What is occlusion
-contacts between teeth
-relationship btwn maxillary and mandibular teeth when they approach each other, as occurs during chewing or at rest
What is static occlusion
Contact between teeth when the jaw is closed and stationary
Dynamic occlusion
occlusal contacts made when jaw is moving
What structures does occlusion involve
periodontium, TMJ, neuromuscular system
How are tooth positions determined
Lips/cheeks/tongue, arch width + tooth size, oral habits, proximal/occlusal contacts
What happens to teeth when there is a tooth size-arch discrepancy
Teeth remain outside of the normal arch due to the tooth size-arch discrepancy until corrected
How do oral habits affect occlusion
- Thumb sucking
-Musical instruments placed between the maxillary
and mandibular teeth (clarinet) may place labial
forces to the lingual surfaces of the maxillary anterior
teeth, resulting in a labial flaring
Proximal and occlusal contacts
maintain the teeth in normal alignment, effect of caries or missing tooth can be dramatic in the loss of stability of the dental arches
What happens when proximal and occlusal contacts become worn down
Mesial drifting helps maintain contact between adjacent teeth and stabilizes the arch
What happens the tooth in the opposing arch when one tooth is lost
The opposing tooth may be lost over time, teeth can drift into the edentulous space
What is the plane of occlusion
Draw an imaginary line through all the buccal cusp tips and incisal edges of the mandibular teeth, then broadened into a plane- include the lingual cusp tips and continuing across the arch to include the opposite side buccal and lingual cups tips
The curved occlusal plane permits maximum utilization of ____ ______ during function
tooth contacts
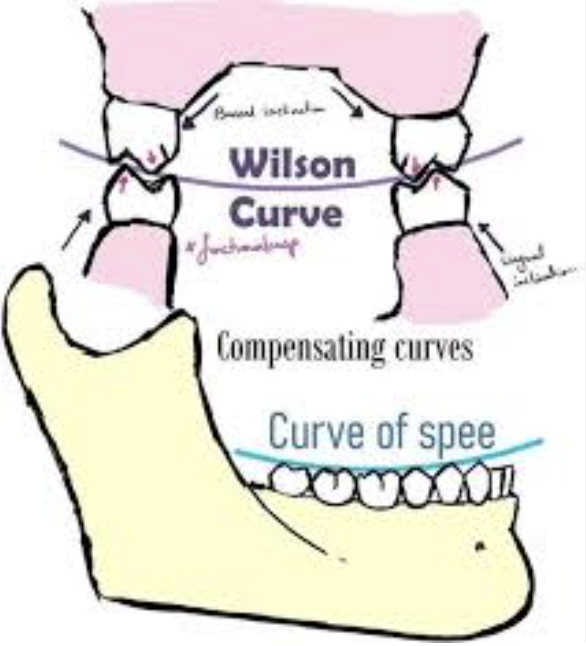
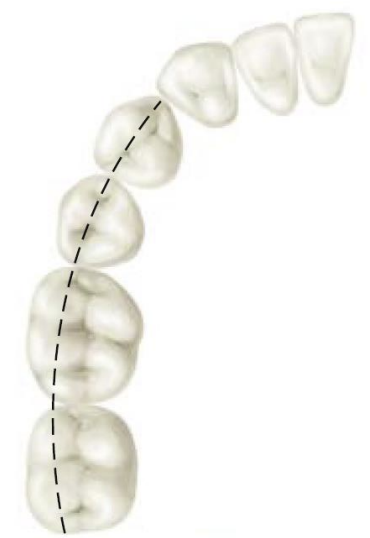
Curve of Spee (exam q)
Cusp tip of the mandibular canine and following the buccal cusp tips of the premolar and molar teeth (lateral view).
The maxillary arch’s normal curve of wilson and spee (occlusal plane) are convex or concave? exam q
convex
The mandibular arch’s normal curve of wilson and spee (occlusal plane) are convex or concave? exam q
concave
How is the maxillary arch inclined
Anterior mesially, most posterior distally/buccally inclined
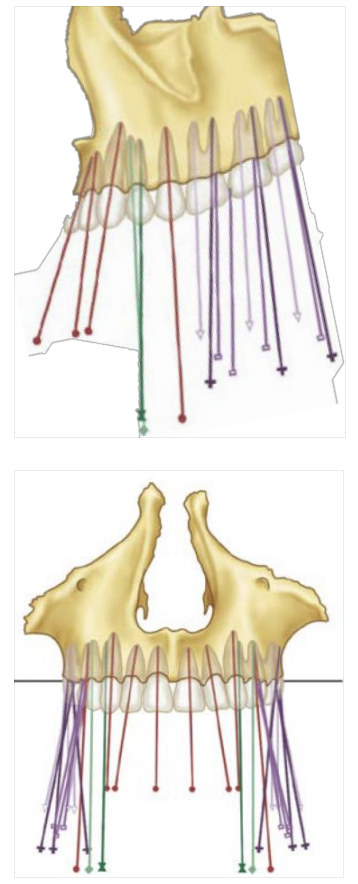
Curve of Wilson
Buccal and lingual cusp tips of both the right and the left posterior teeth
How is the mandibular arch inclined
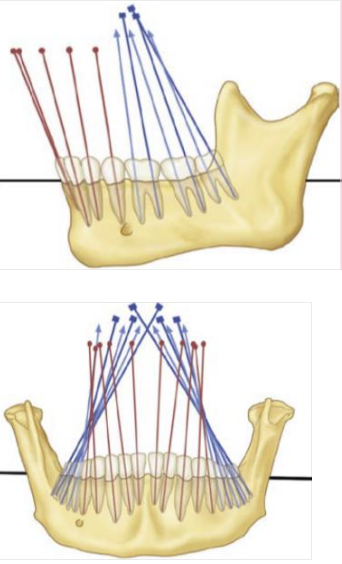
Mesially and lingually inclined
What does extrusion cause
interferes w smooth movement, creates abnormal height of molar occlusal plane
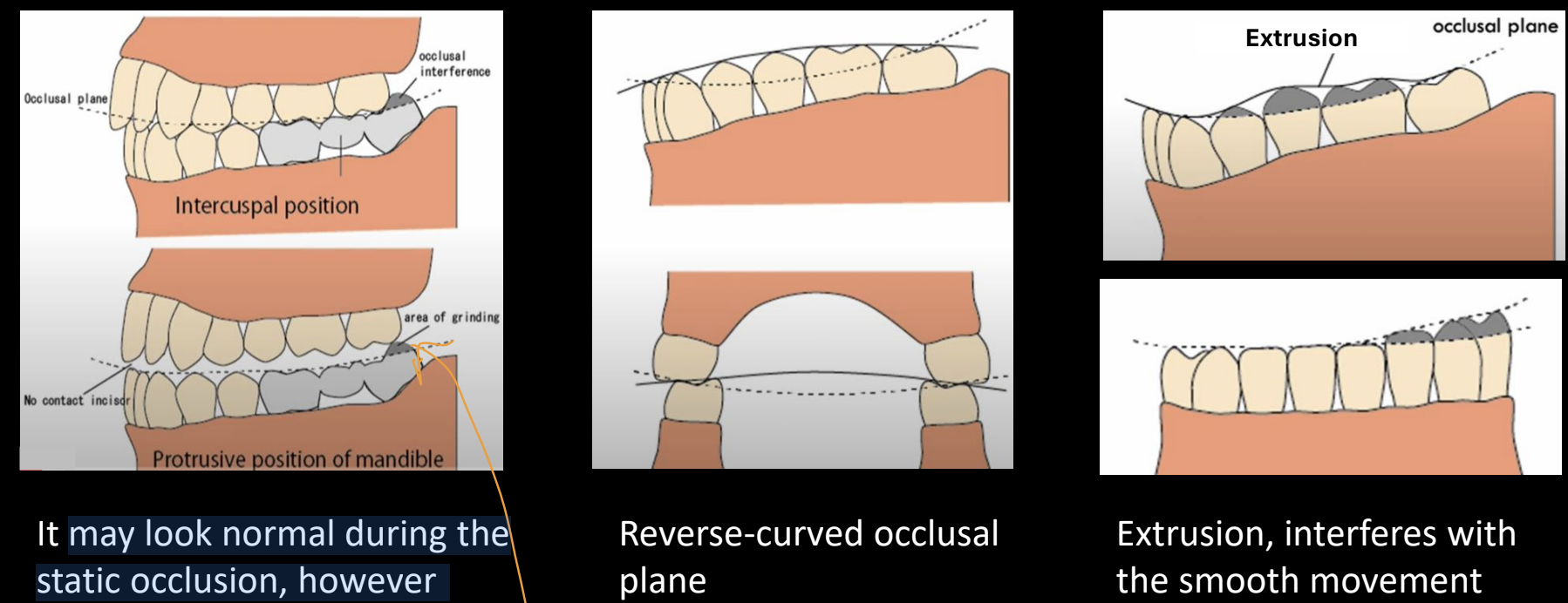
What does an occlusal interference of the last molars look like/cause (i.e. one restored tooth is too high)
May look normal during the static occlusion, however during the protrusion last molar, interferes with the smooth movement (dynamic occlusion)
Can damage muscles, causing TMJ problem
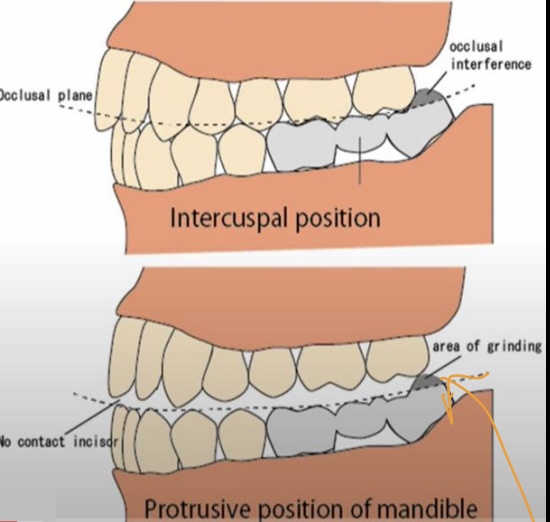
What are three examples given of abnormal intra-arch tooth alignment
protrusive mandible (caused by occlusal interference), reverse-curved occlusal plane- upward, extrusion
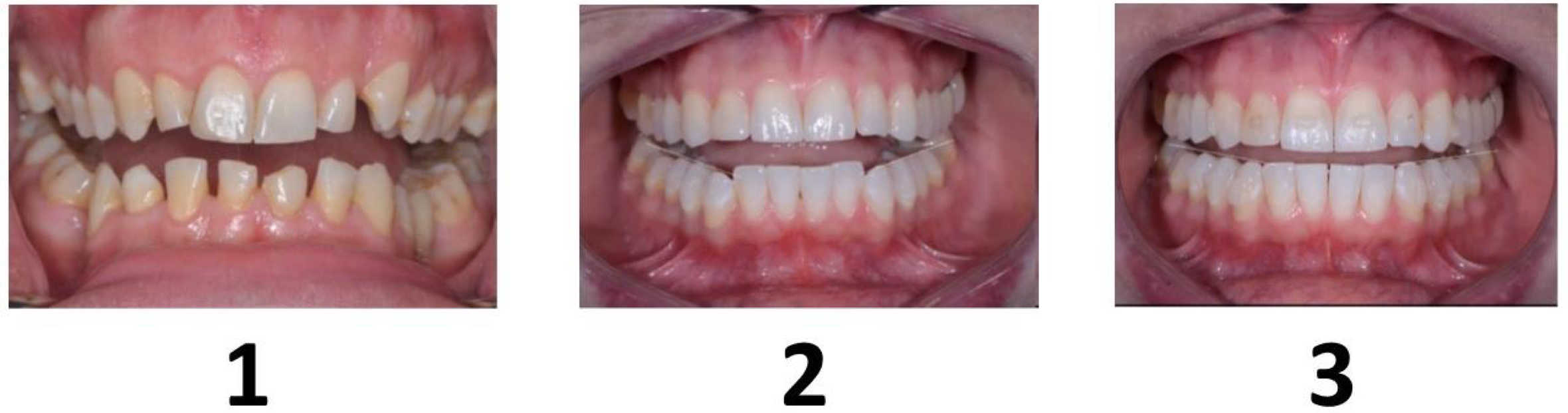
In which case is the occlusal plane appropriate? exam q
3
1= extrusion
2= mandibular incisors extruded
Which 3 occlusal surfaces of teeth break up food
*exam
cusps, grooves (shallow, linear), sulcus (long depression)
Not 1 of the surfaces that break up food, but fossa= irregular concavity
What are cusp tips to central fossa called
inner incline
What are cusp tips to HOC on lingual/labial surfaces of teeth called
outer inclines
Area between buccal+lingual cusp tips of posterior teeth
occlusal table
Where are the major forces of mastication applied?
occlusal table
Exam last yr: The occlusal table is ____% of the total buccolingual dimension of the posterior tooth and is positioned over the ___ axis of the root structure
50-60%, long axis
tooth inclines are identified with respect to which surface?
the surface toward which they’re directed
What would a high spot or in the occlusal table cause when biting down/ making lateral movements
possible fracture of the restoration or damage to the stomatognathic system
Stomatognathic system (not in slides, from internet)
compelx system of tissues/organs in oral/craniofacial cavities (teeth, jaw, tongue, muscle, glands, tmj)
What is interarch tooth alignment
relationship of teeth in one arch to those in the other, occlusal relationship protects surrounding soft tissue (cheek/tongue bite), maximizes, efficiency of musculature
Describe normal interarch positioning (maxillary)
Maxillary teeth are more facially positioned (protect muscle/from biting cheek), lingual cusps occlude along central fossa areas of mandibular teeth
Describe normal interarch positioning (mandibular)
Mandibular buccal cusps occlude along central fossa areas of maxillary teeth
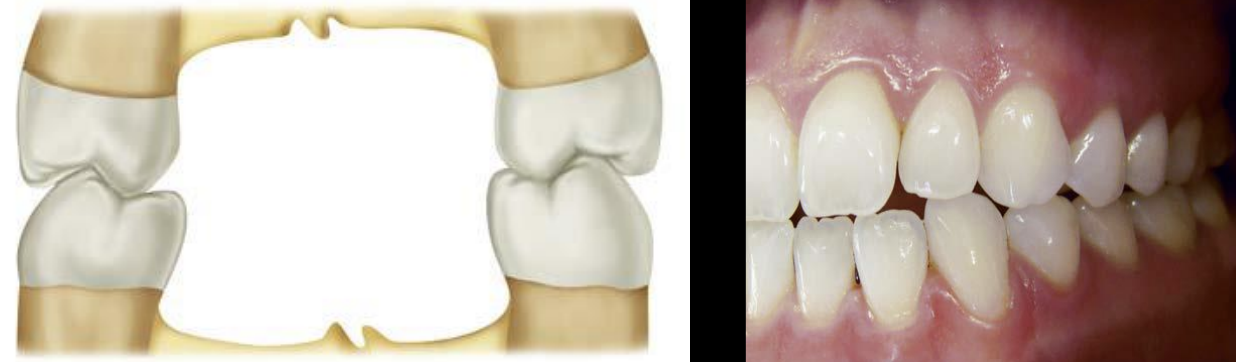
define crossbite + cause
Maxillary buccal cusps contact in central fossa area of mandibular teeth, caused by narrow maxilla compared to mandible
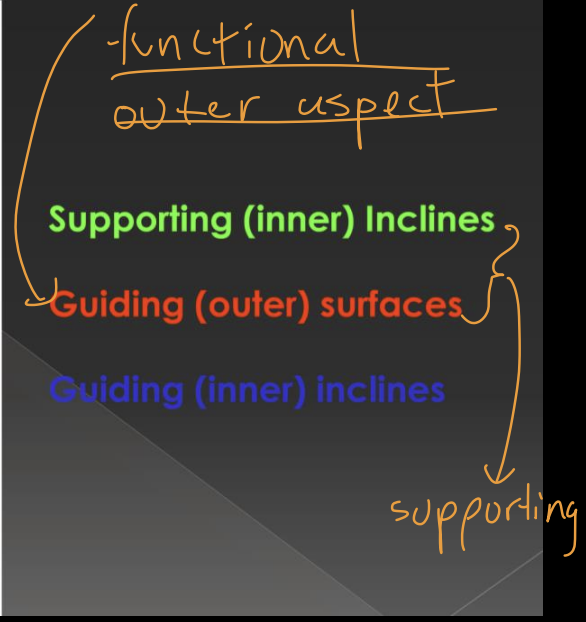
What are supporting cusps also known as (any terms can be used on exam)
centric or functional cusps
Supporting cusps are the ______ cusps of the mandibular posterior teeth and ______ cusps of maxillary posterior teeth occlude with opposing central fossa areas
buccal, lingual
What do supporting cusps do/maintain
VDO, mastication, rounded shape
What are guiding cusps also known as, are they more important than supporting cusps
non-centric, shearing, not as important
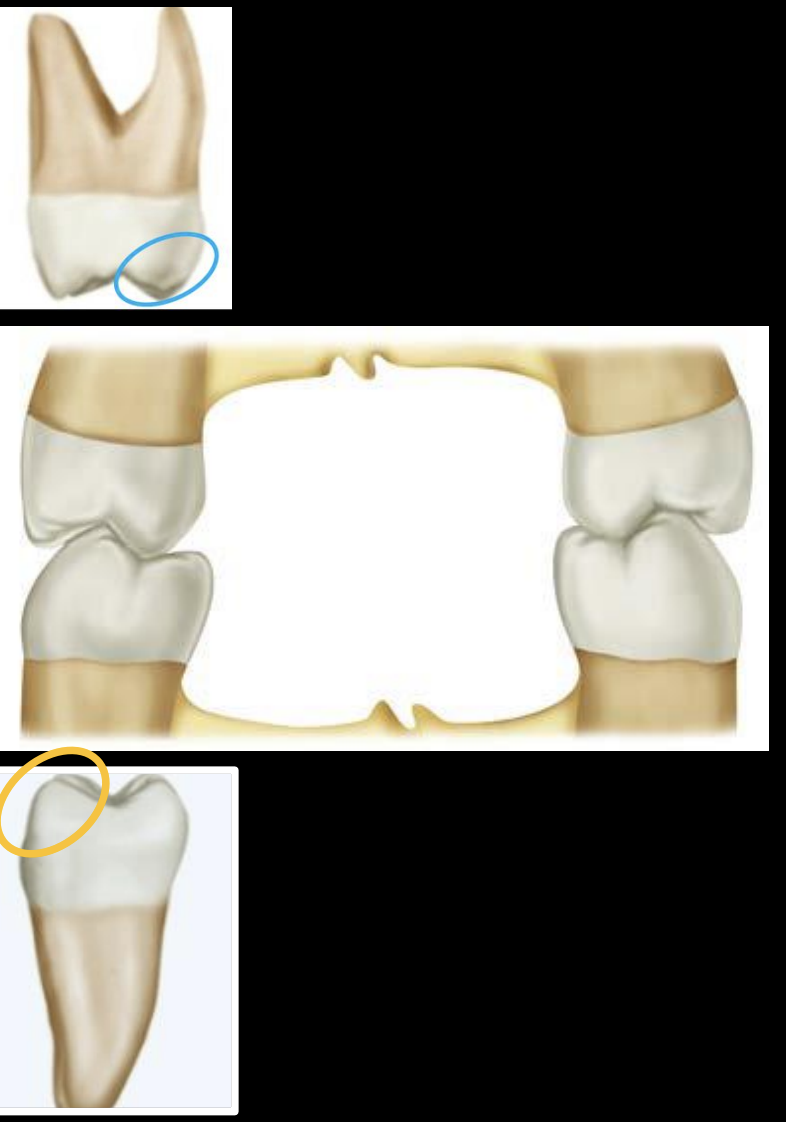
Guiding cusps are ____ cusps of maxillary posterior and ____ cusps of mandibular posterior
buccal, lingual
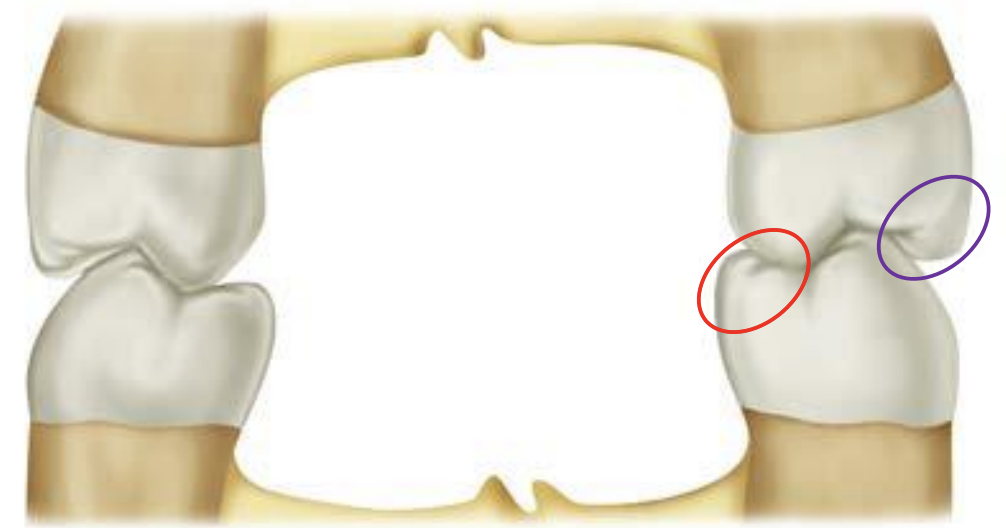
what do guiding cusps look like/do
sharp, definite tips, minimize tissue impingement, maintain food bolus on occlusal table during mastication, guide mandible into/out of intercuspal position (MIP)
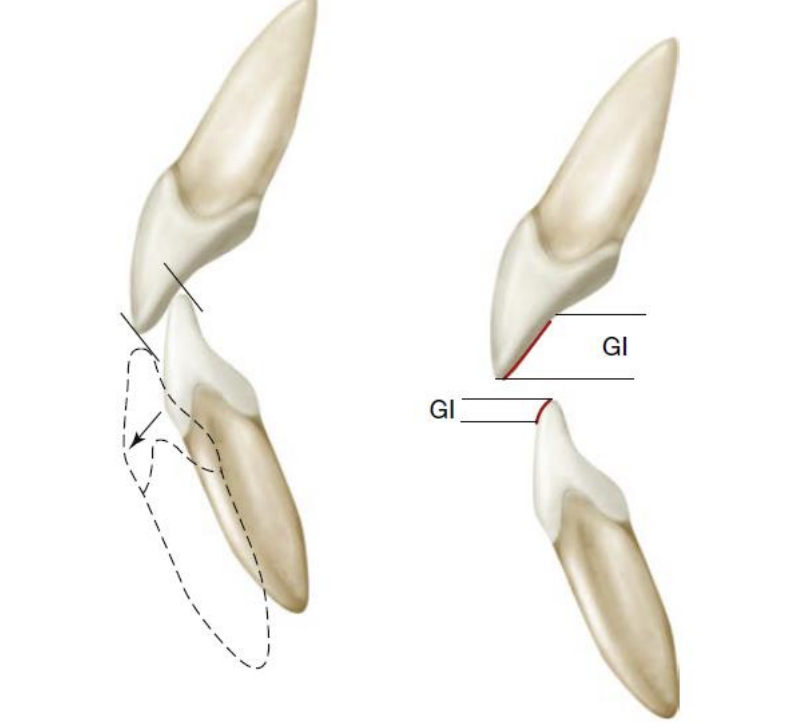
Functional outer aspect (FOA)
1 mm area on outer aspect of centric cusps (red), functions against inner incline of non-centric cusp
Assists in shearing of food during mastication
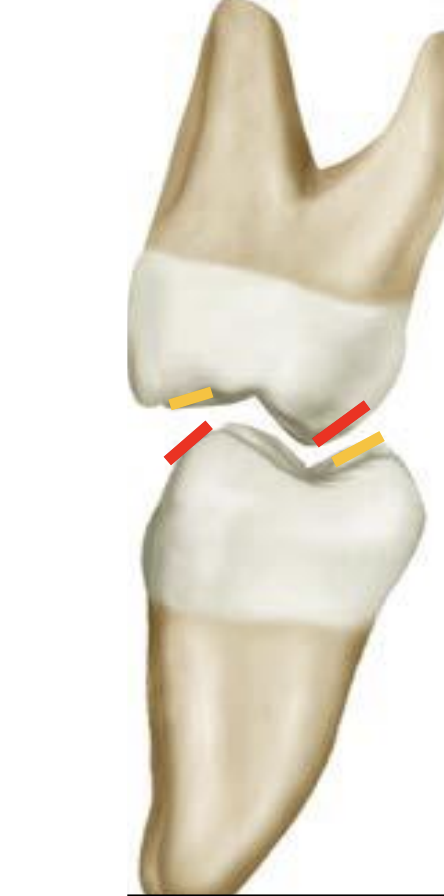
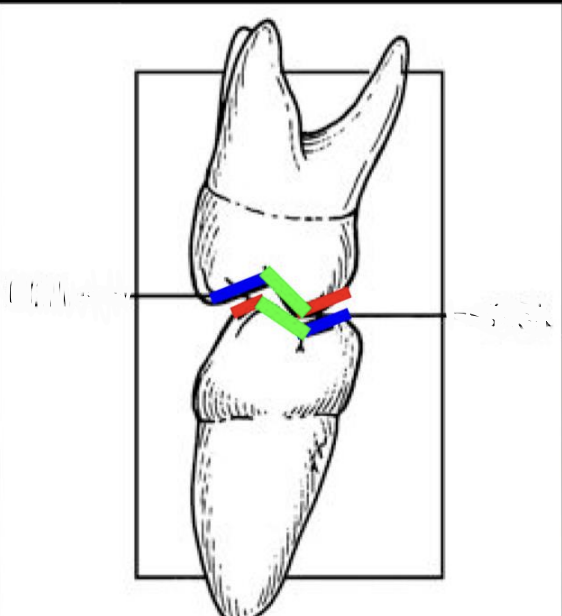
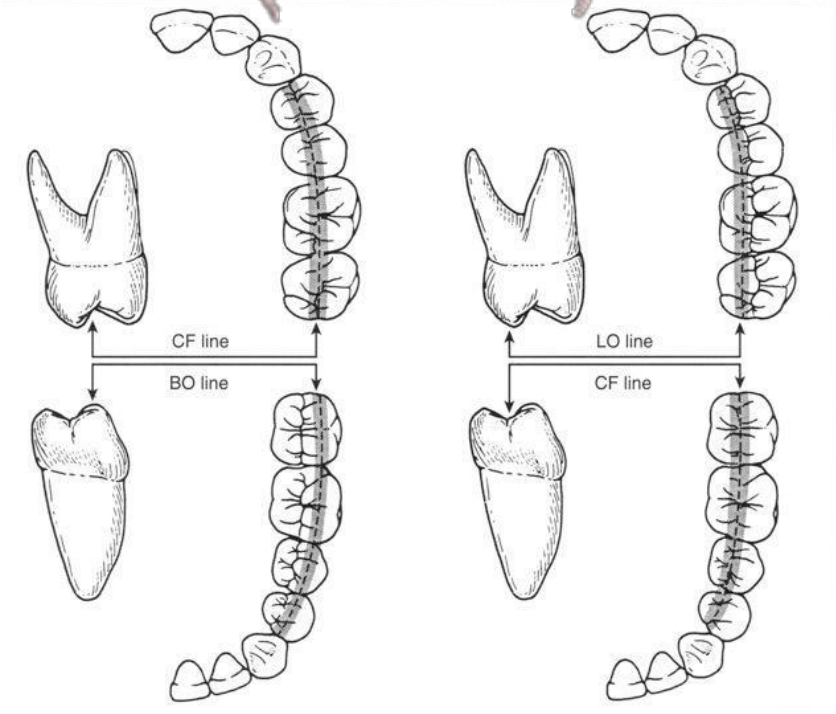
Which of the following line indicates the supporting cusp inner inclines? exam
what line is this/which quadrant
Buccoocclusal (BO) line of left mandibular arch

what line is this/which quadrant
Linguoocclusal (LO) Line of the Right Maxillary Arch.
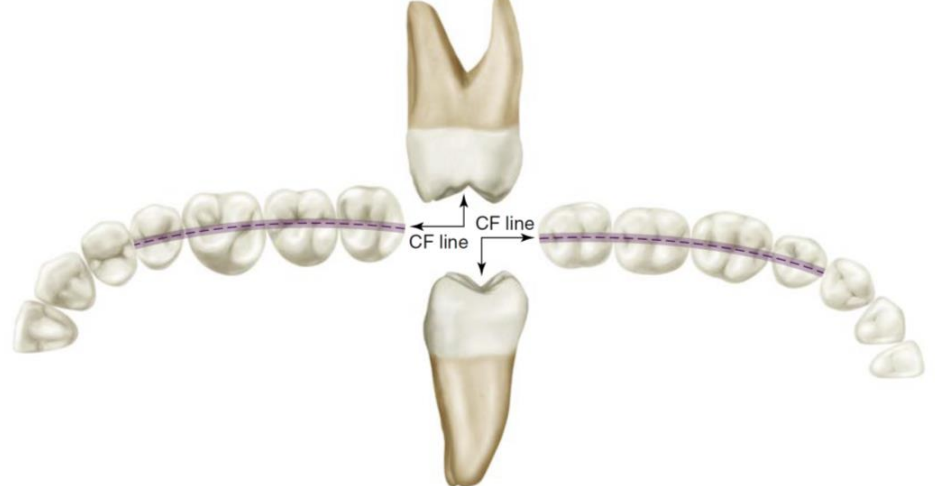
what line is this, which arch
Central Fossa (CF) Line of the left Dental Arches
In a normal arch, an imaginary line extended through the arch flows _____ and ________, revealing the general arch form.
smoothly and continuously
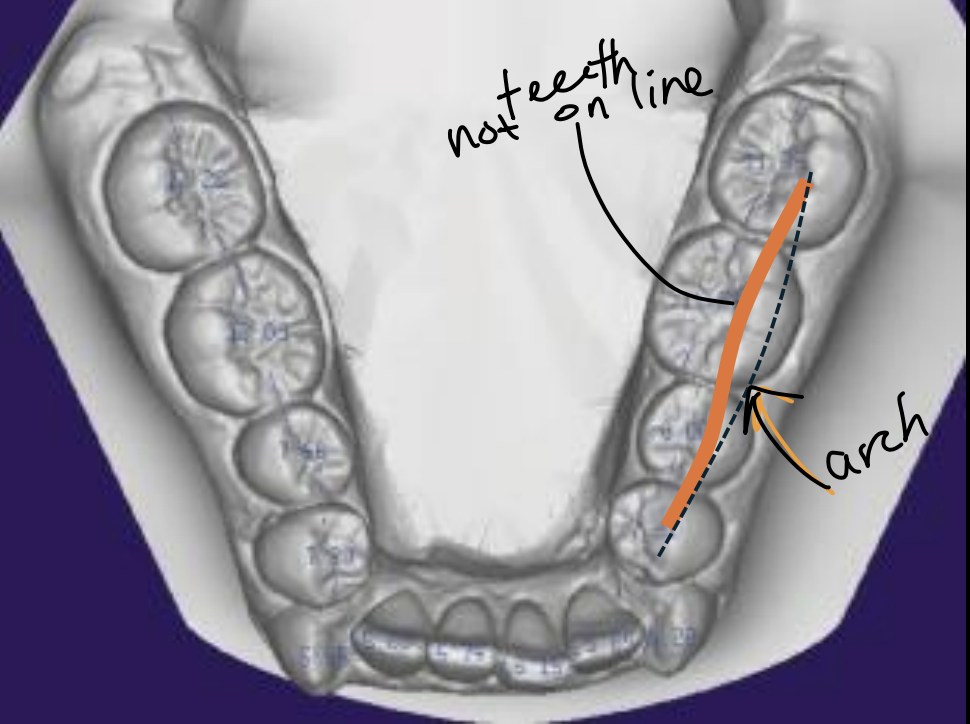
what line is this
BO line
In normo-occlusion, which lines (CF, BO, LO) are aligned together in which arches
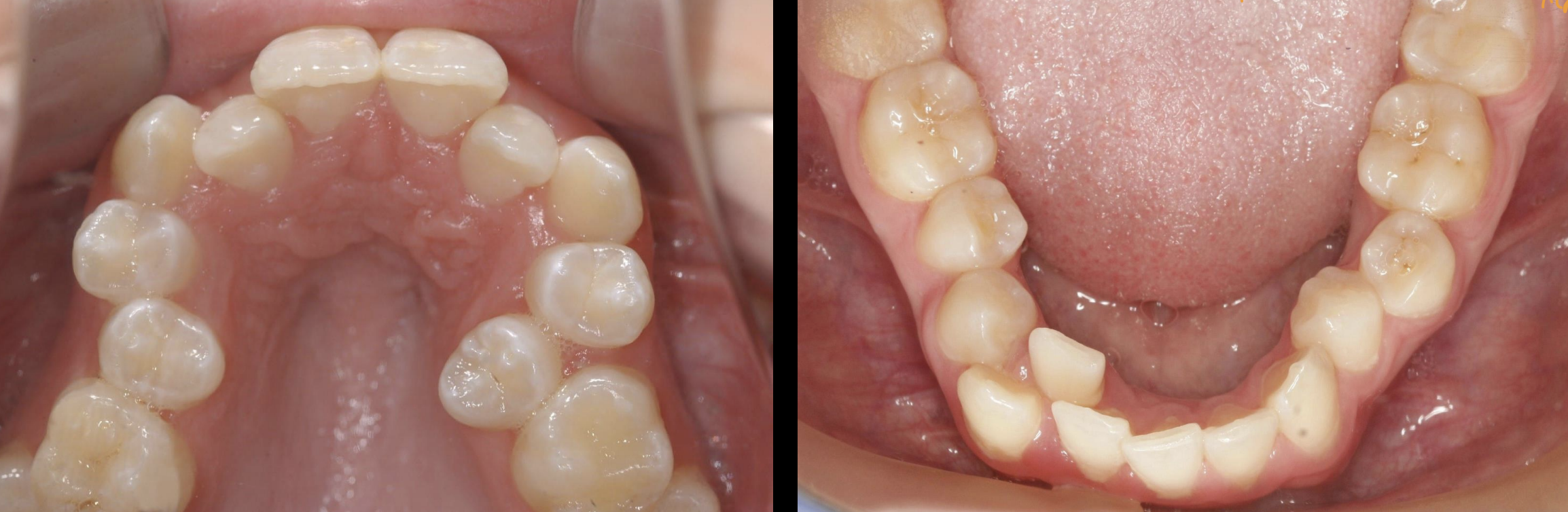
What’s going on… what’s happening
small jaw with big teeth- when the permanent dentition erupted, it created even more crowding
Where are the embrasure areas in the occlusal view
Area slightly buccal and lingual to the central fossa line
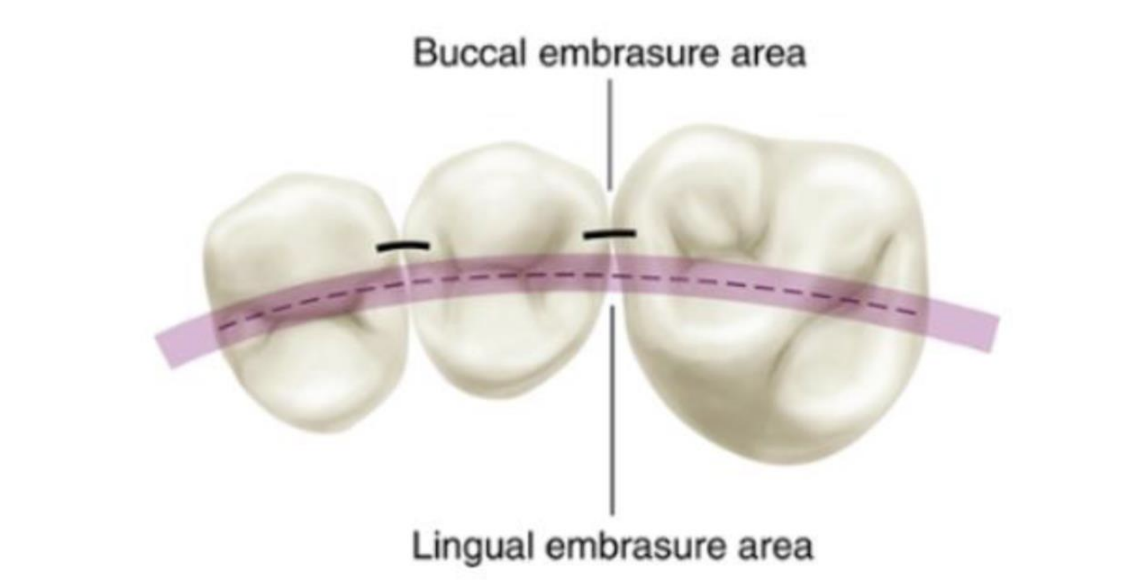
which is larger, lingual embrasure area or buccal embrasure- what is the function
lingual (major spillway for food, tongue is more efficient in returning food to the occlusal table than the buccinator and perioral musculature)
more simply- if there’s too much food in the mouth it allows to spill out, no buildup of pressure
When the normal interarch tooth relationship is viewed laterally, each tooth occludes with how many teeth, and what does it aid in
two opposing teeth, helps distribute occlusal forces to several teeth/over entire arch
What are the exceptions to the one-tooth-two-teeth relationship
Max 3rd molars, mand central incisors
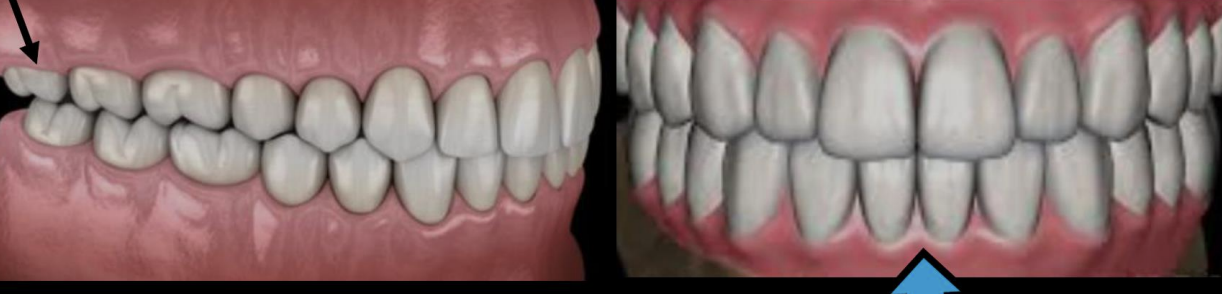
What tooth is Angle’s classification centered around?
first molar
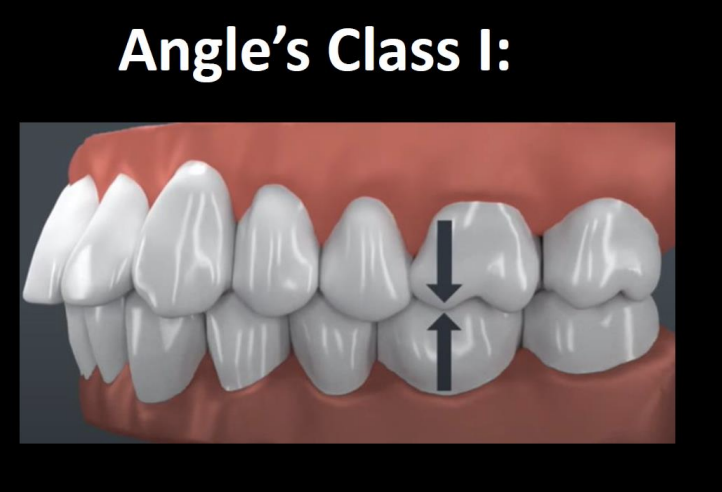
How is the maxillary first molar aligned in Class I occlusion
The MB cusp of max 1st molar is aligned directly over the buccal groove of the mand 1st molar
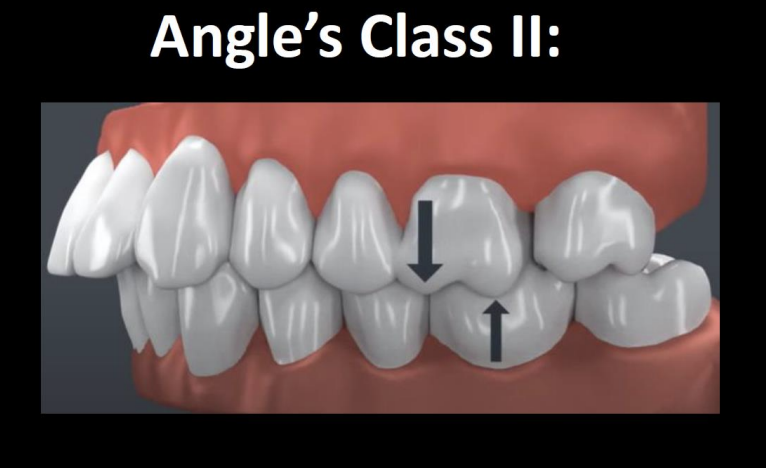
How is the maxillary first molar aligned in Class II occlusion
the MB cusp of max 1st is situated over the embrasure btwn the mand 2nd PM and 1st molar
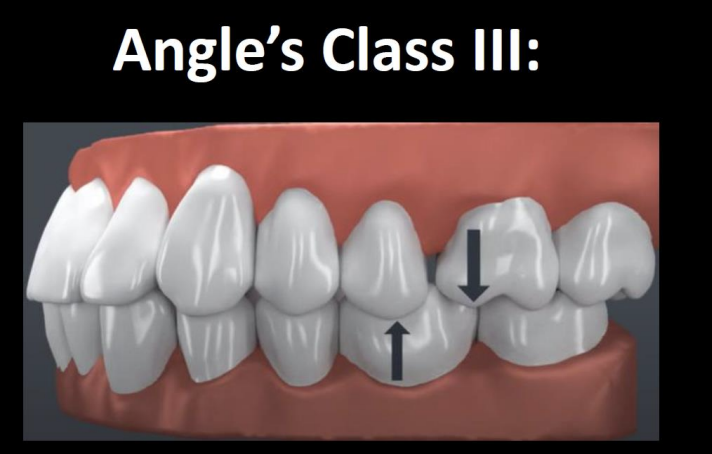
How is the maxillary first molar aligned in Class III occlusion
The MB cusp of max 1st is over the embrasure btwn the mand 1st and 2nd molar
The maxillary anterior teeth are normally positioned ____ to mandibular anterior teeth
labially
How are maxillary and mandibular anteriors inclined? What is the degree range from a vertical reference line
labial, 12-28 degrees
What is the purpose of anterior teeth in terms of lateral movement; what is it called
Anterior teeth contact and guide the mandible through various lateral movements- Anterior guidance
Which directions can the relationship of anterior teeth be examined
Horizontally and vertically
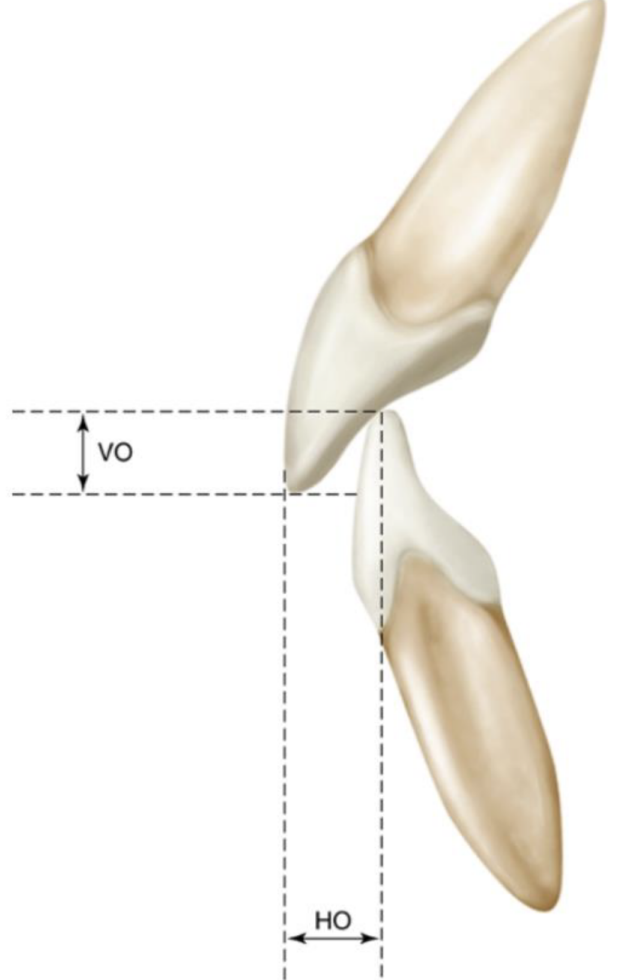
Overjet/horizontal overlap
horizontal distance by which max anteriors overlap mandib anteriors
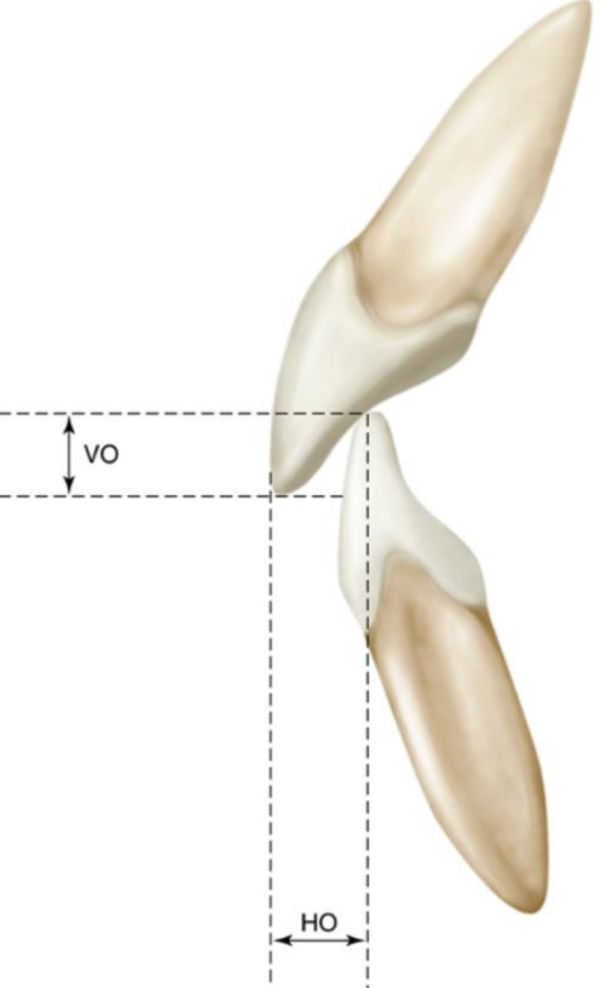
Overbite/vertical overlap, what is the normal amount in mm?
anterior guidance examined in the vertical plane, 3mm is normal
Class II Div 1
Malocclusion, deep bite, increased overjet
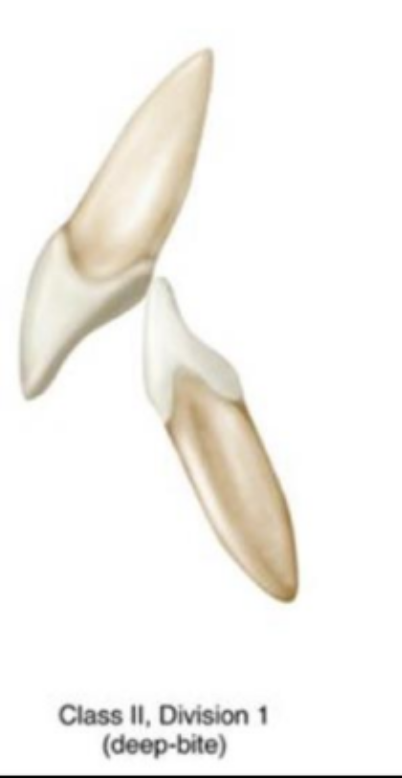

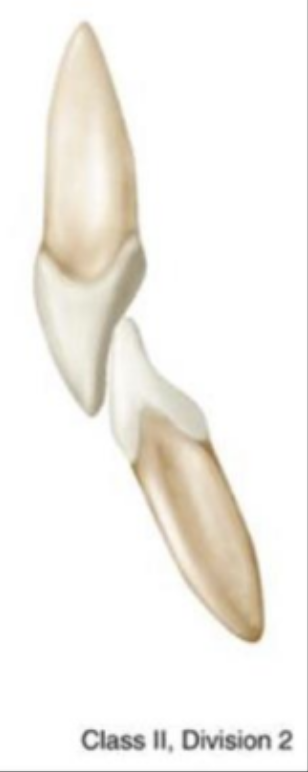
Class II Div 2
retroclined max central incisors, more rare
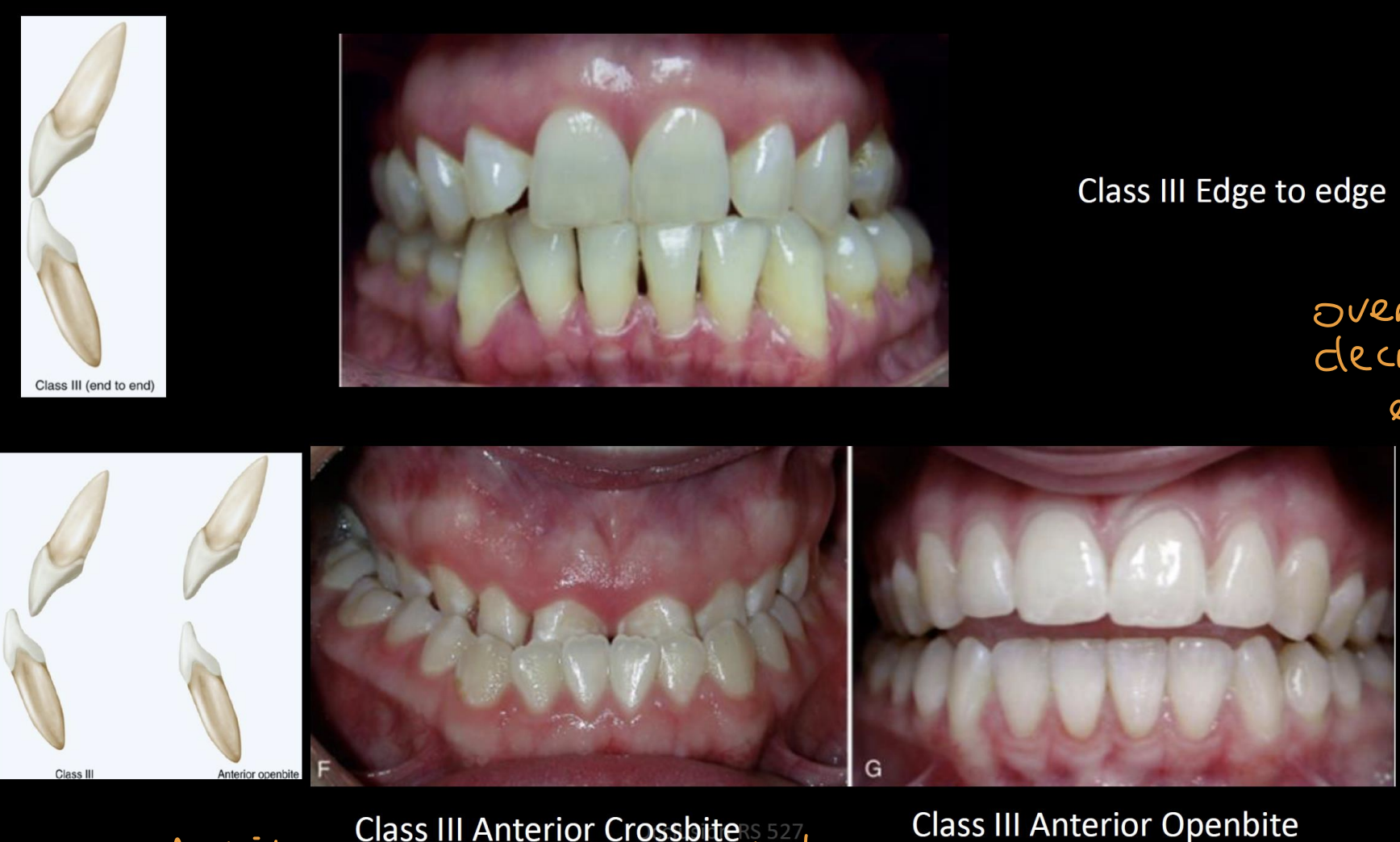
What are the 3 types of class III bites
Edge to edge, anterior crossbite, anterior openbite
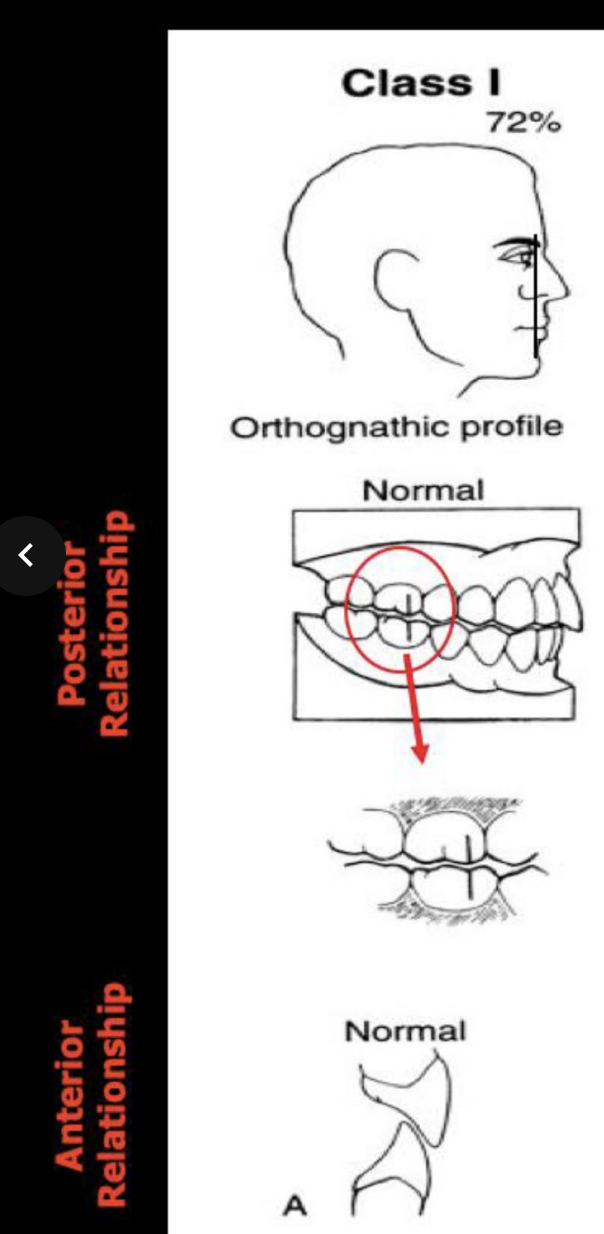
what is the profile name, angle of profile, posterior relationship, and anterior relationship of Class I bite
Orthognathic profile (72% angle), posterior- mesiobuccal cusp of 1st max molar aligns with buccal groove of mand 1st molar, anterior-lower incisors rest on the cingulum of the upper incisors
what is the profile name, angle of profile, posterior relationship, and anterior relationship of Class II bite; what are the divisions possible for Class II
Retrognathic profile (22% angle), distal occlusion, posterior- MB cusp of max 1st is situated over the embrasure btwn the mand 2nd PM and 1st molar, Anterior Div I, Anterior Div II
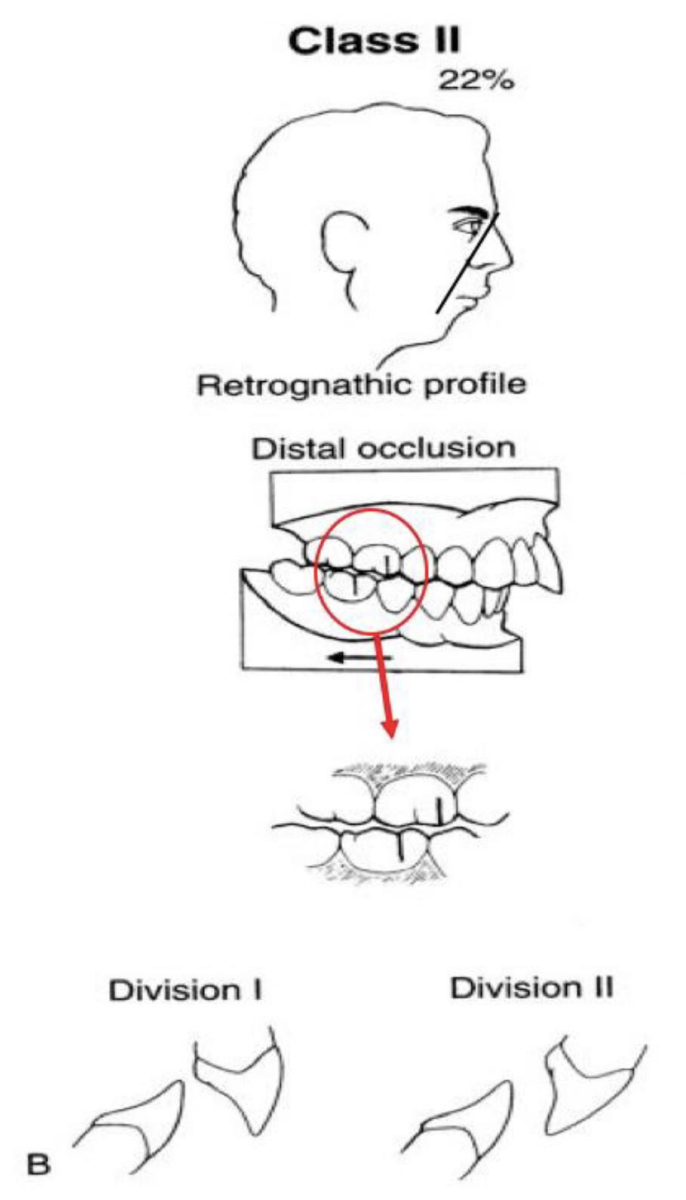
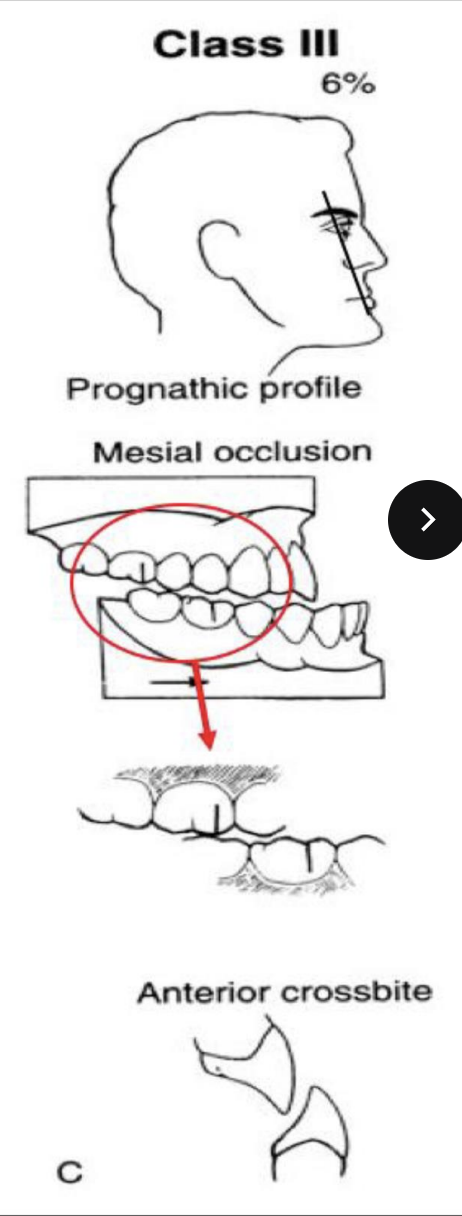
what is the profile name, angle of profile, posterior relationship, and anterior relationship of Class III bite
Prognathic profile, 6% angle, posteior mesial occlusion (MB cusp of max 1st is over the embrasure btwn the mand 1st and 2nd molar), anterior crossbite
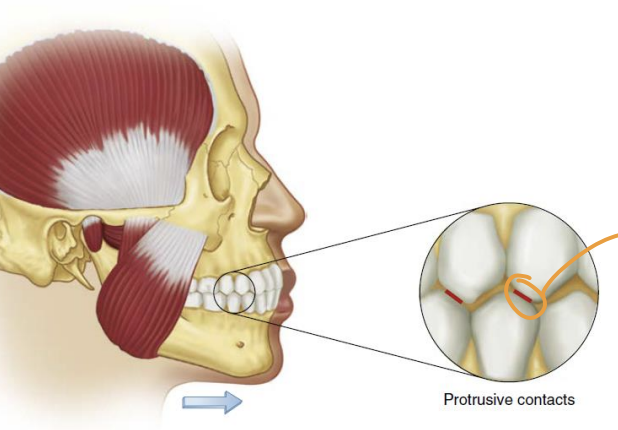
Eccentric movement
any movement of the mandible from the intercuspal position that results in tooth contact
Protrusive movement
mandible moves forward from intercuspal position
What surfaces create anterior guidance
Guiding inclines of anterior mand and maxillary teeth
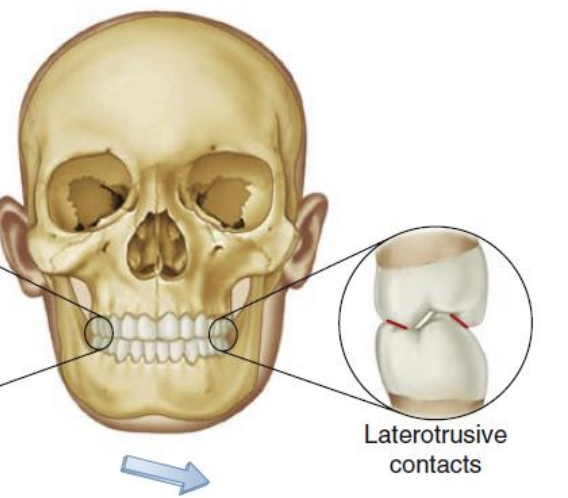
Laterotrusive movements/contact
Working side
Mediotrusive movements/contact
Non-working side
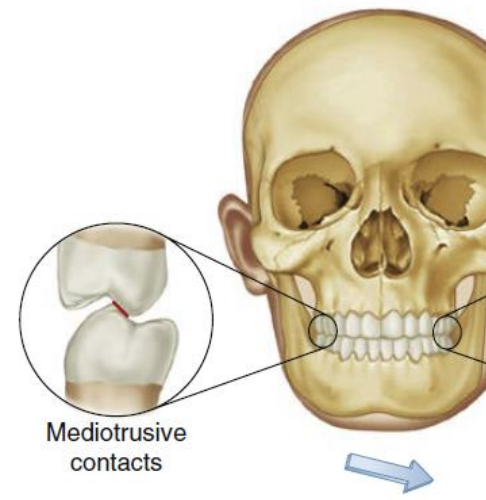
in normo-occlusion, which max and mandib teeth contact during right and left lateral movements/have laterotrusive contact? what is this known as
Canines, canine guidance
_____ surfaces and _____ edges of mandibular canines and ______ fossae and _____ edges of maxillary canines meet in canine guidance
labial surfaces and incisal edges, lingual fossae and incisal edges
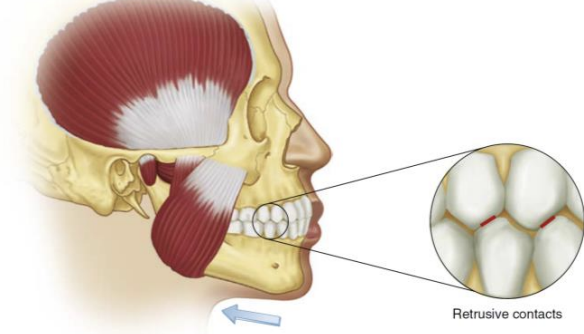
Retrusive movement
Backwards movement restricted by ligaments (1-2mm)
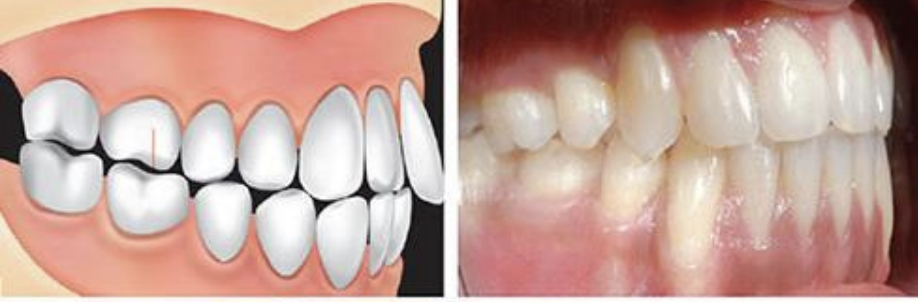
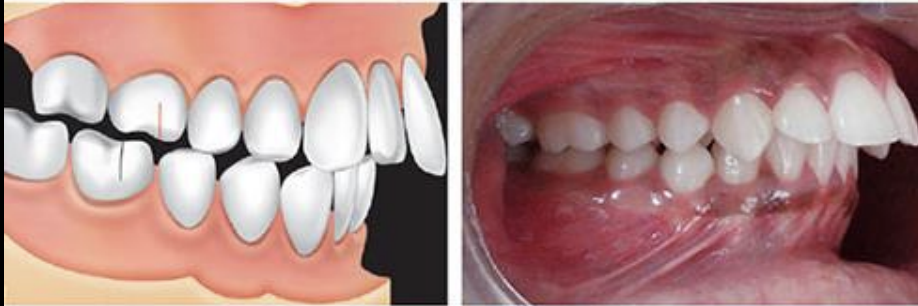
What angle class
Angle Class I
What angle class
Angle Class II
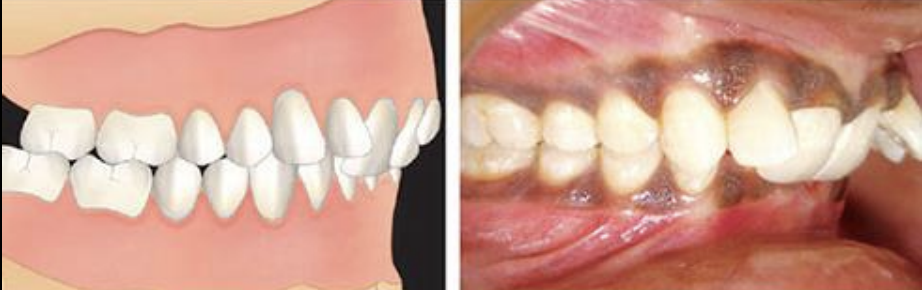
What angle class
Angle Class II Div II
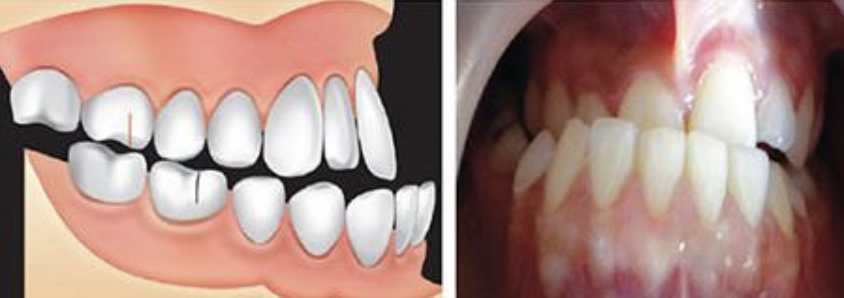
What angle class
Angle Class III
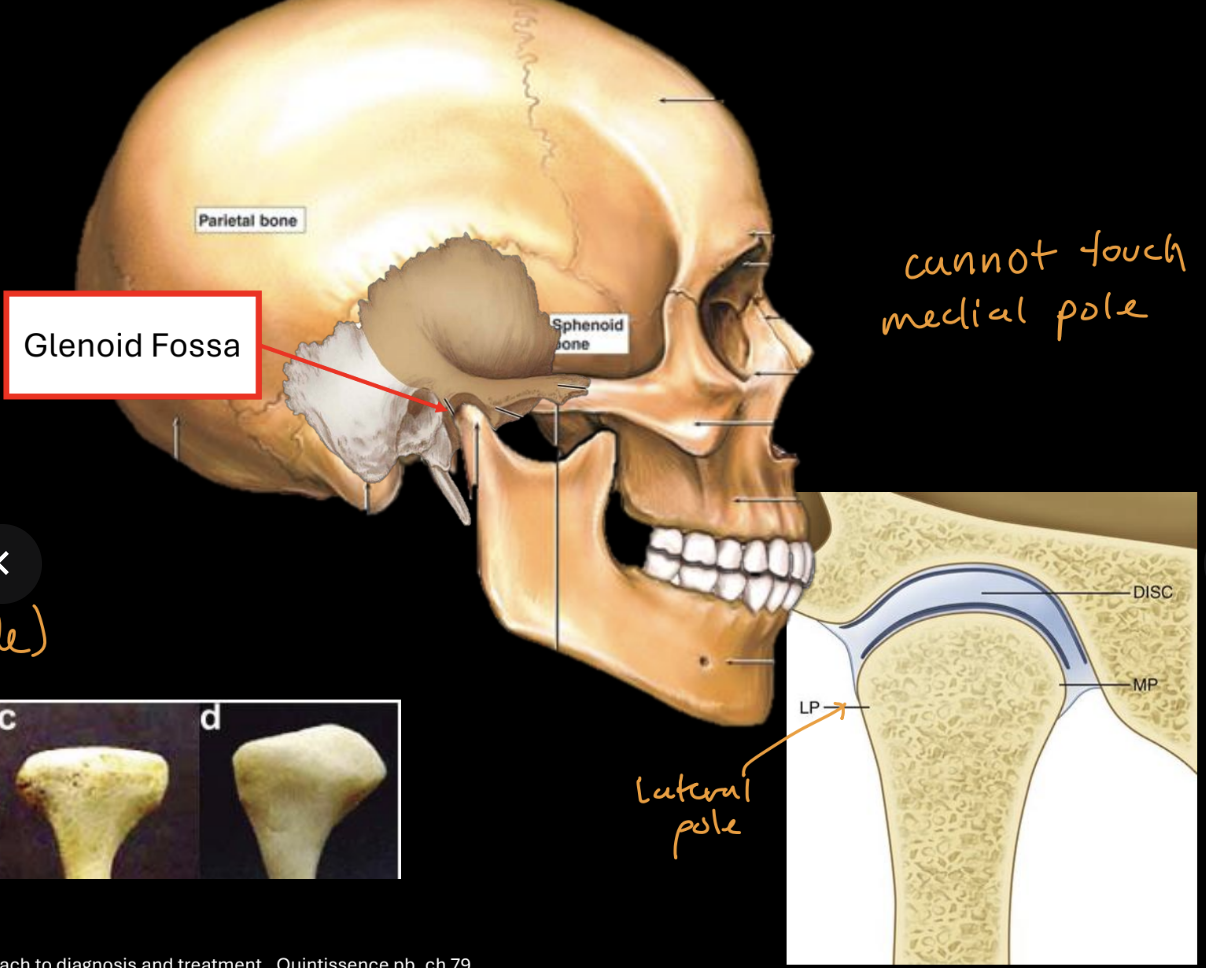
What are the two bones involved in the TMJ
Squamous temporal bone, mandibular condyle
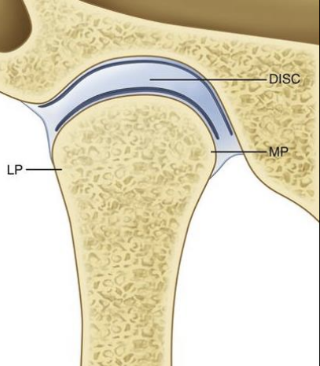
What is btwn the TMJ bones
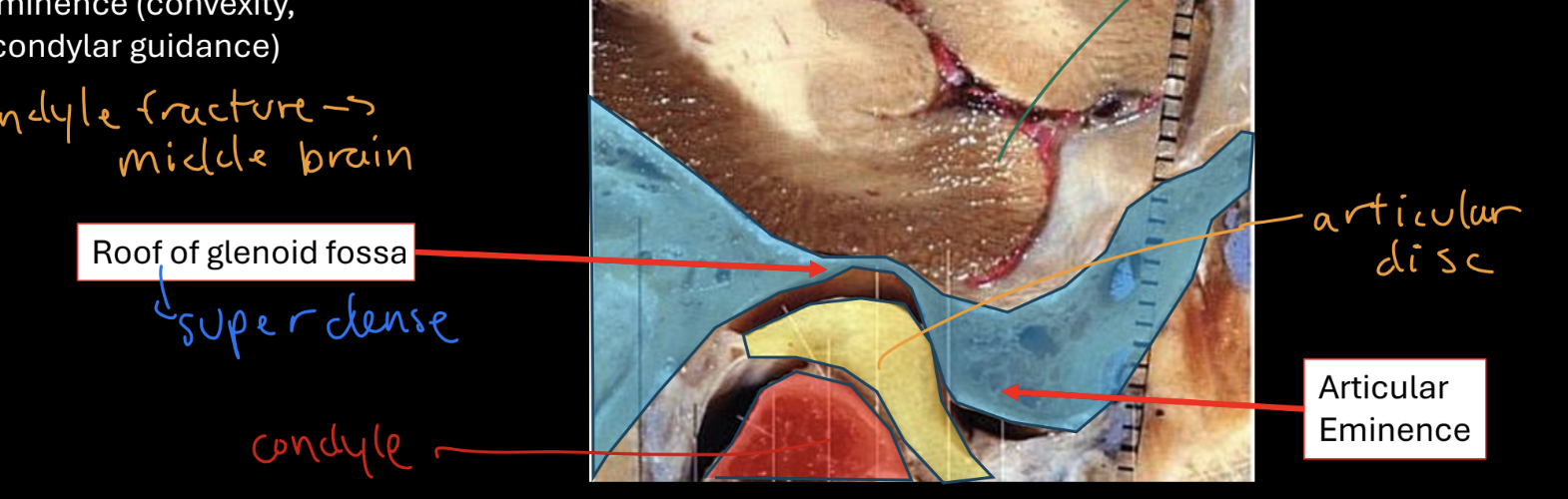
articular disc
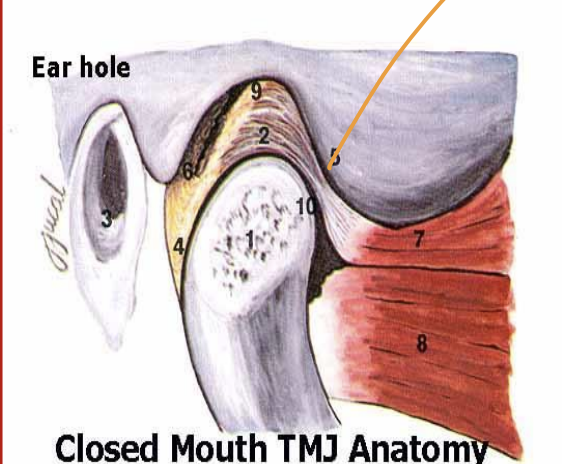
Mandibular condyle location, shape, etc
top of mandibular neck, articulates with glenoid (mandib) fossa, convex, elliptical, medial/lateral poles
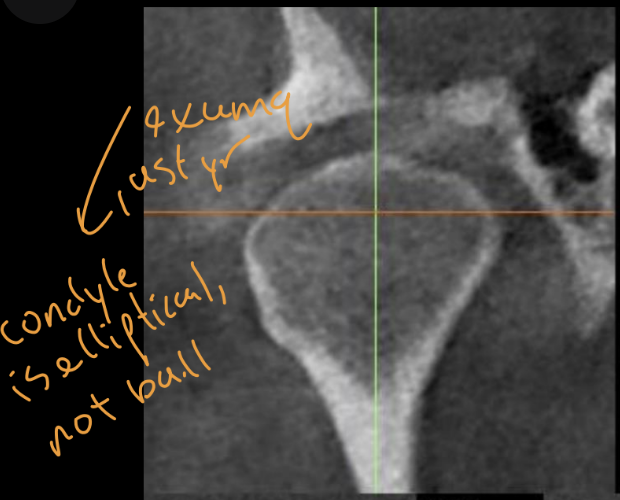
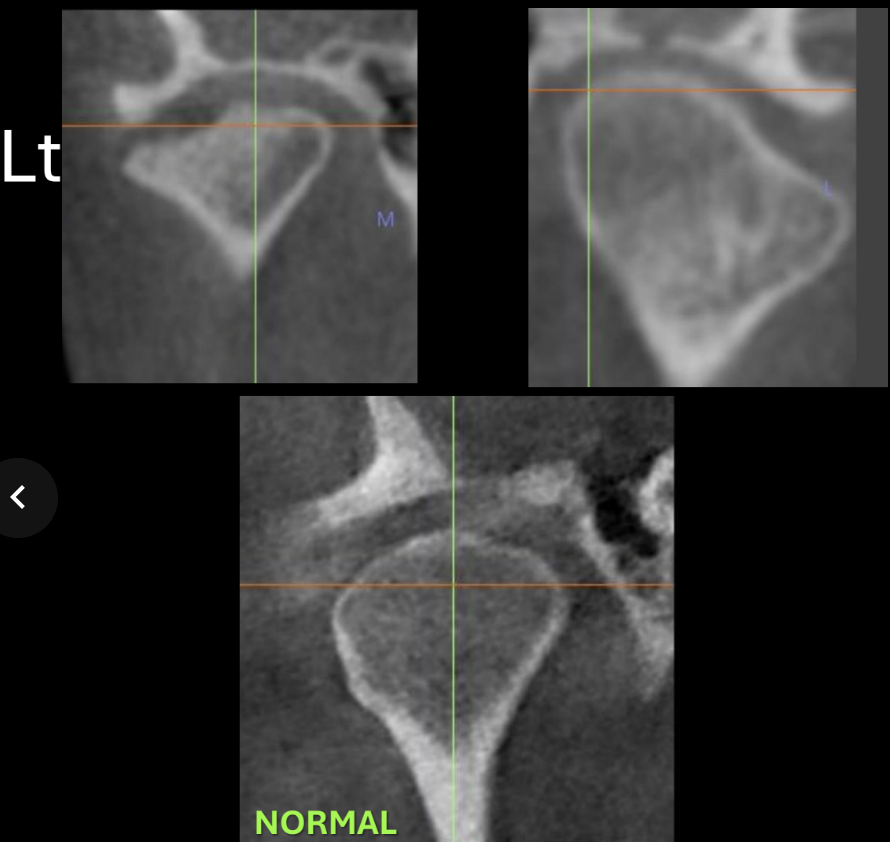
What type of xray is best for visualizing TMJ (what was this taken with), how would you describe this xray
computed tomography, normal condyle coronal section (cortical borders intact and continuous, condyle has convex and smooth surface)
What would the TMJ look like when pt has degenerative disorder
The convexity is disrupted (becomes concave), left side cortical borders are interrupted, visible bone spurs
Temporal bone (squamous portion)
upper part of tmj, glenoid fossa is thin roof, has articular eminence (convexity, steepness, condylar guidance)
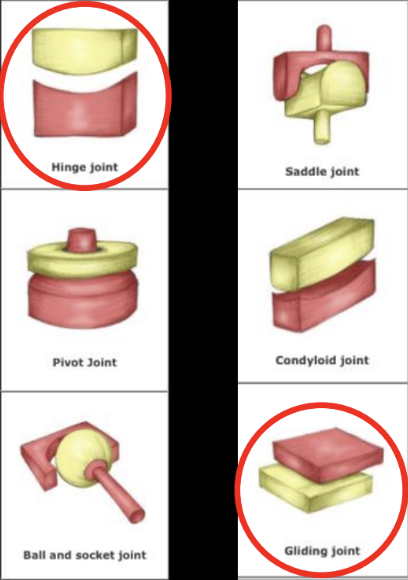
Ginglymoarthrodial joint components
2 types of joint mvmt (ginglymoid= hinge, arthrodial=plane joint)
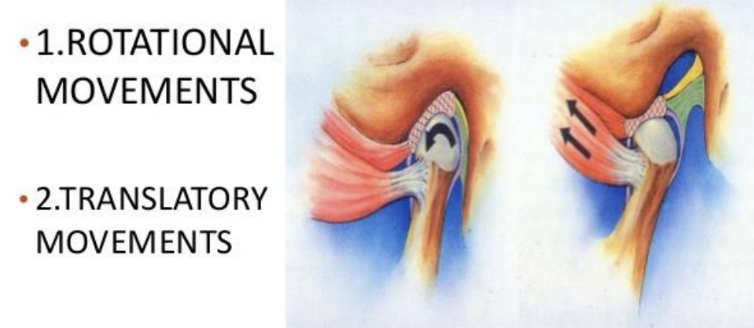
Condyle/ginglymoarthrodial joint movements
accommodated by articular disc
Rotate (hinging movement lower compartment),
translate (gliding movement upper compartment
Which pole do we palpate during TMJ palpation
lateral pole of TMJ
Which of the following is FALSE about mandibular condyle?
A. Articulates with glenoid (mandibular) fossa
B. Convex shape
C. Has medial and lateral poles
D. Rotates with hinging movement on the upper compartment
E. Translates with gliding movement on the upper compartment
D. Rotates with hinging movement on the upper lower compartment
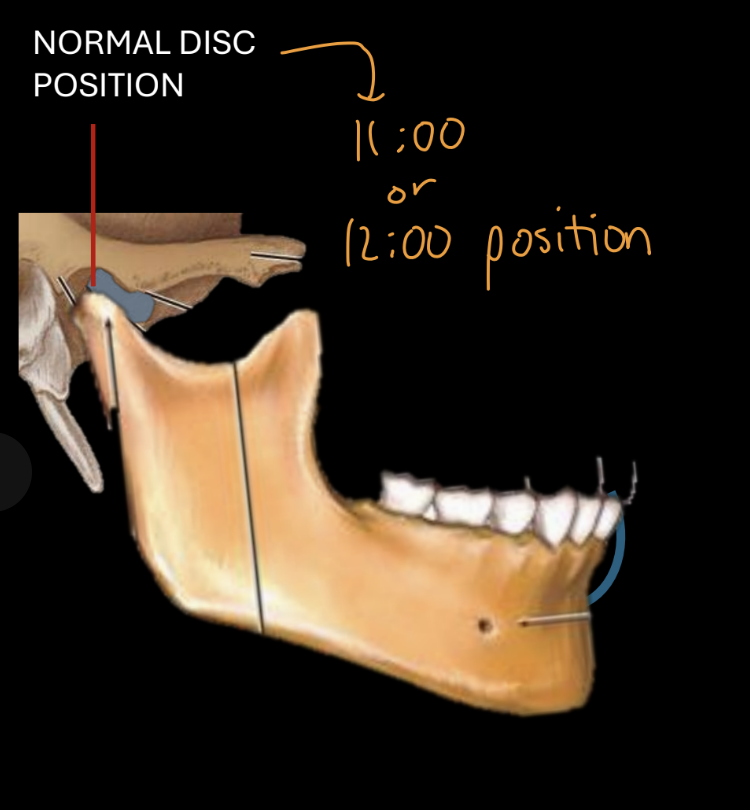
Normal articular disc position before movement
Posterior border-11-12:00 position on condyle
Anterior prominence of condyle: central thin part of disc
Disc follows condyle during opening
anterior disc displacement without reduction, at rest
articular eminence hits the posterior border of disc instead of normal resting position
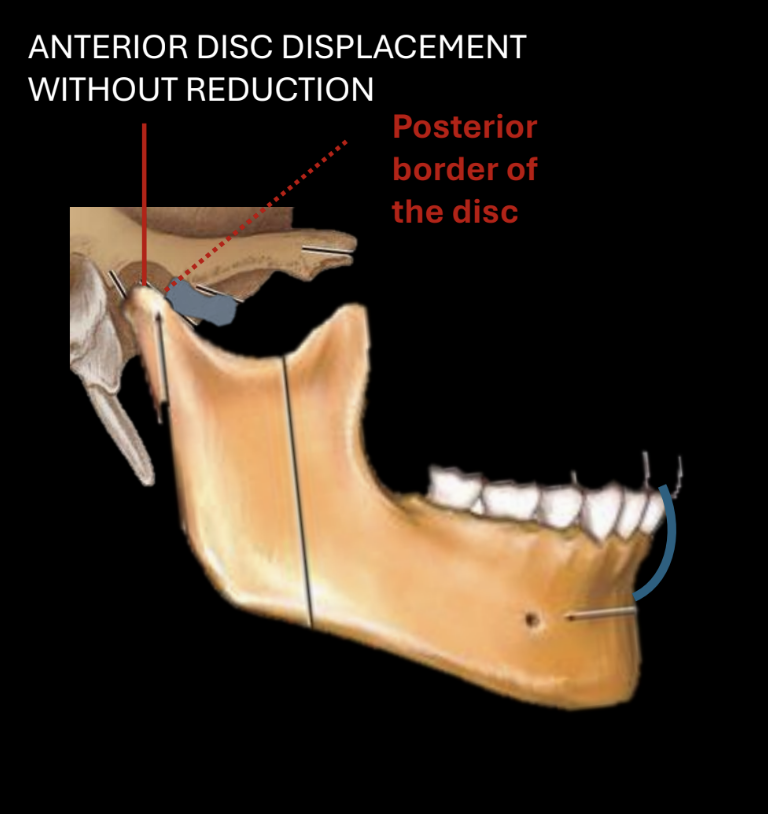
Rotation with normal disc position
Rotation 20-25 mm (mouth opening starts with rotation of condyle under disc)
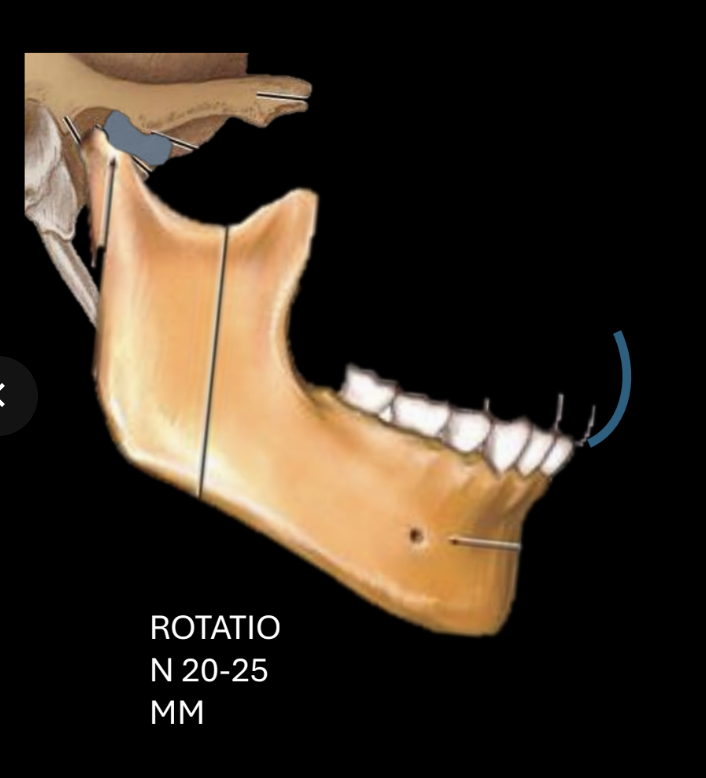
Translation with normal disc position
Translation normal max >40mm (rotation of condyle should be followed by translation)
anterior disc displacement without reduction during rotation
ROTATION 20-25 MM (normal)
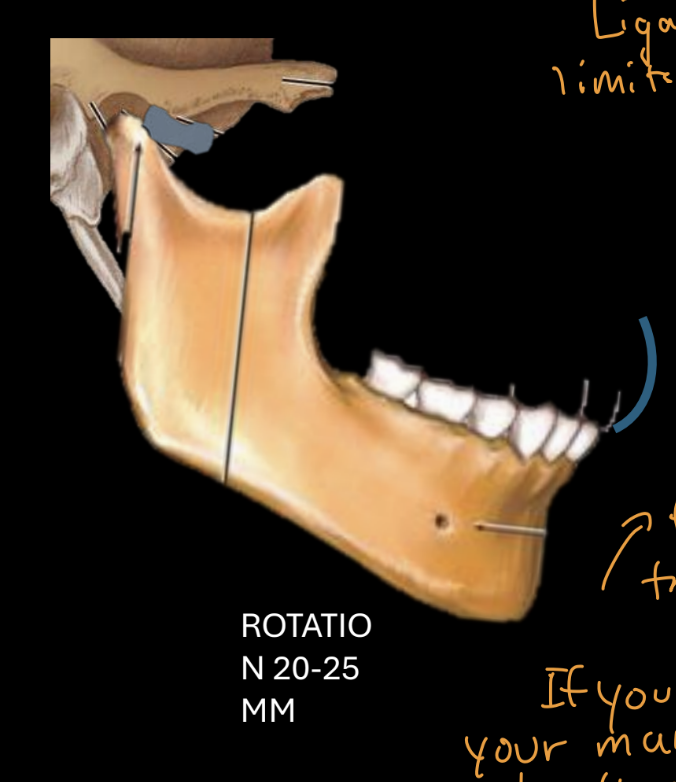
anterior disc displacement without reduction during translation
NO TRANSLATION- painful locking, limited mouth opening (if you move mandible down only, without translation, condyle hits muscle and bone instead of cartilage)
Articular surfaces of synovial joint
hyaline cartilage absorbs shock and reduce friction during movement- has limited capacity to heal and repair