Ancient Egyptian - Early Christian
1/104
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Yellow highlight - Important to know, Blue highlight- VERY important to know, Green highlights - has been on the test before
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
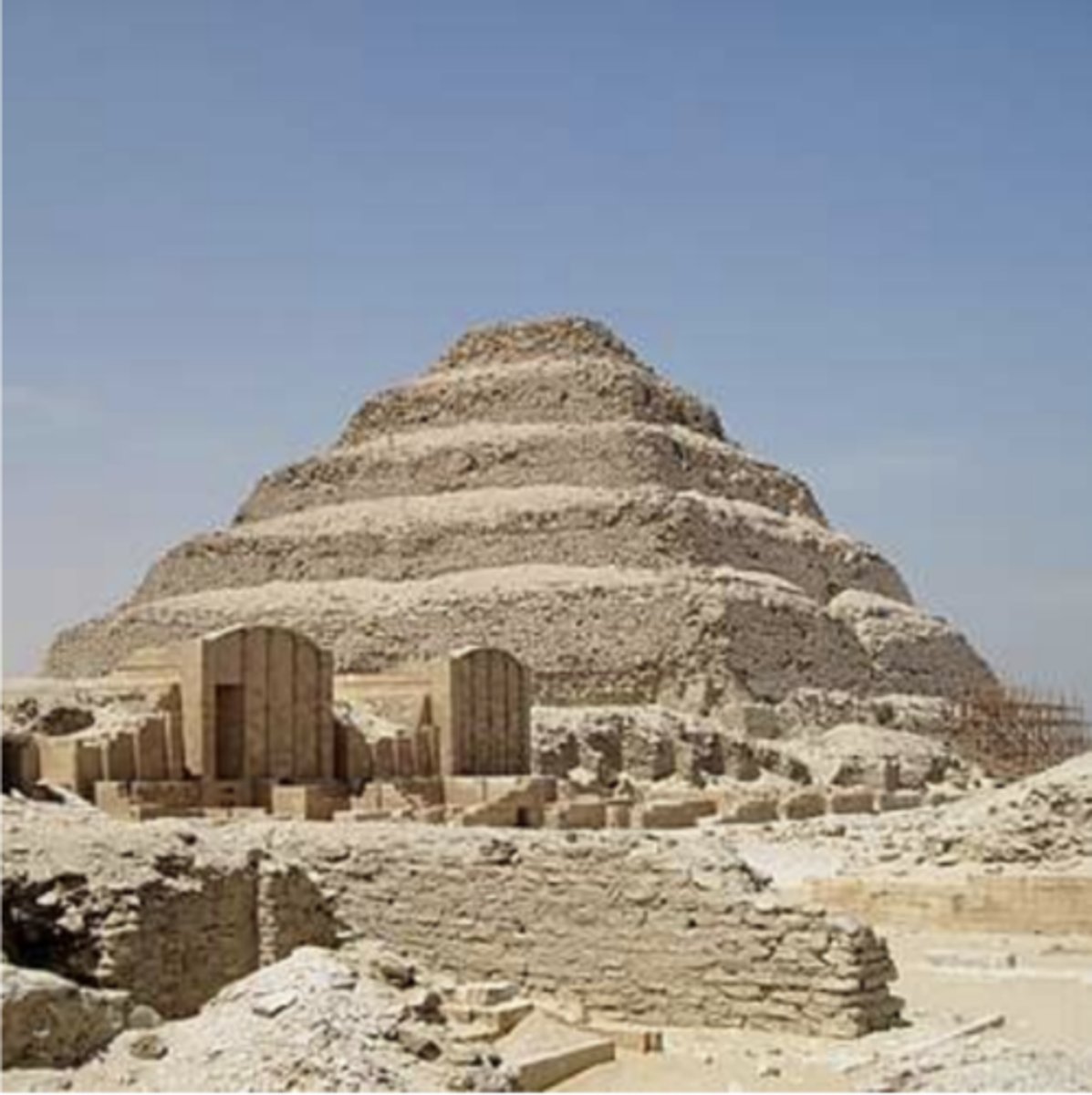

The Pyramid of Djoser, Saqqara, Egypt,
by Imhotep, 2667-2648 BC
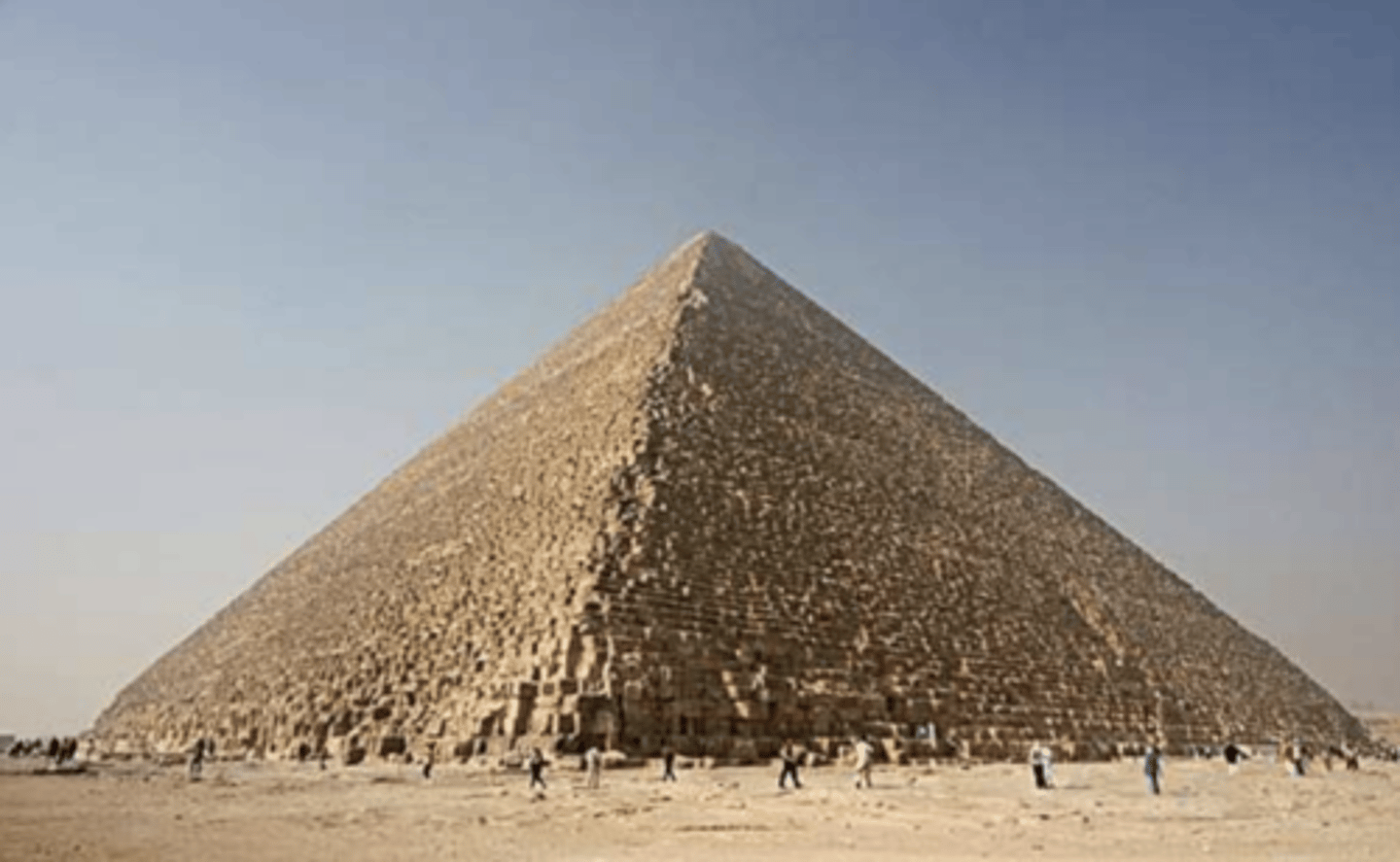

Great Pyramid of Giza, Giza, Egypt, by Hemiunu,
c.2589-2566 BC

Hypostyle Hall of the Karnak Temple Complex, Luxor, Egypt, unknown architect, c.1294-1213 BC
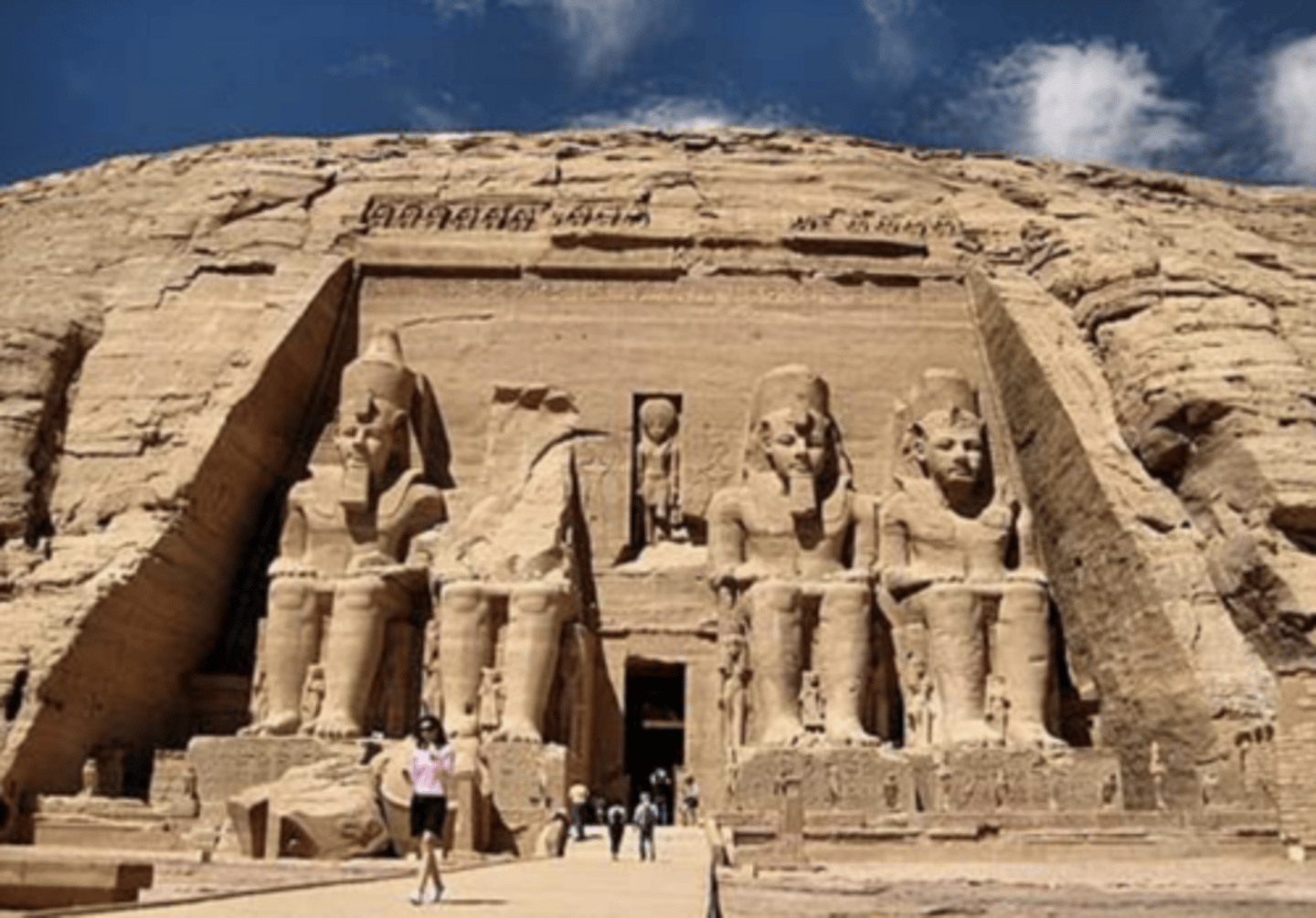

Great Temple of Abu Simbel, Egypt, unknown
architect, c.1264 BC
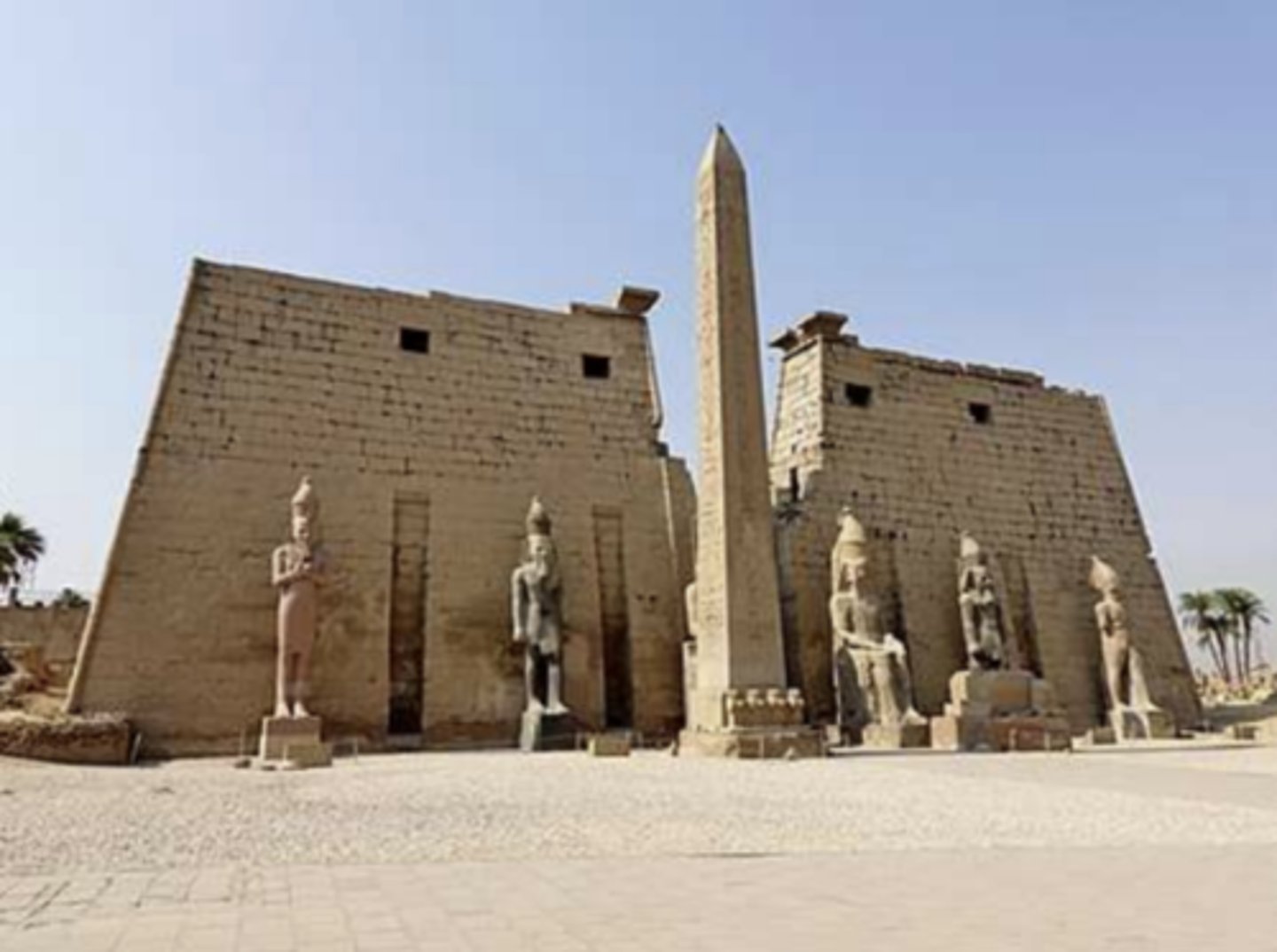


Entrance of the Luxor Temple complex, unknown architect, 1279-1212 BC

Temple of Philae, unknown architect, 380 BC-117
Mesopotamian Architecture
(21st century BC - 6th century BC)
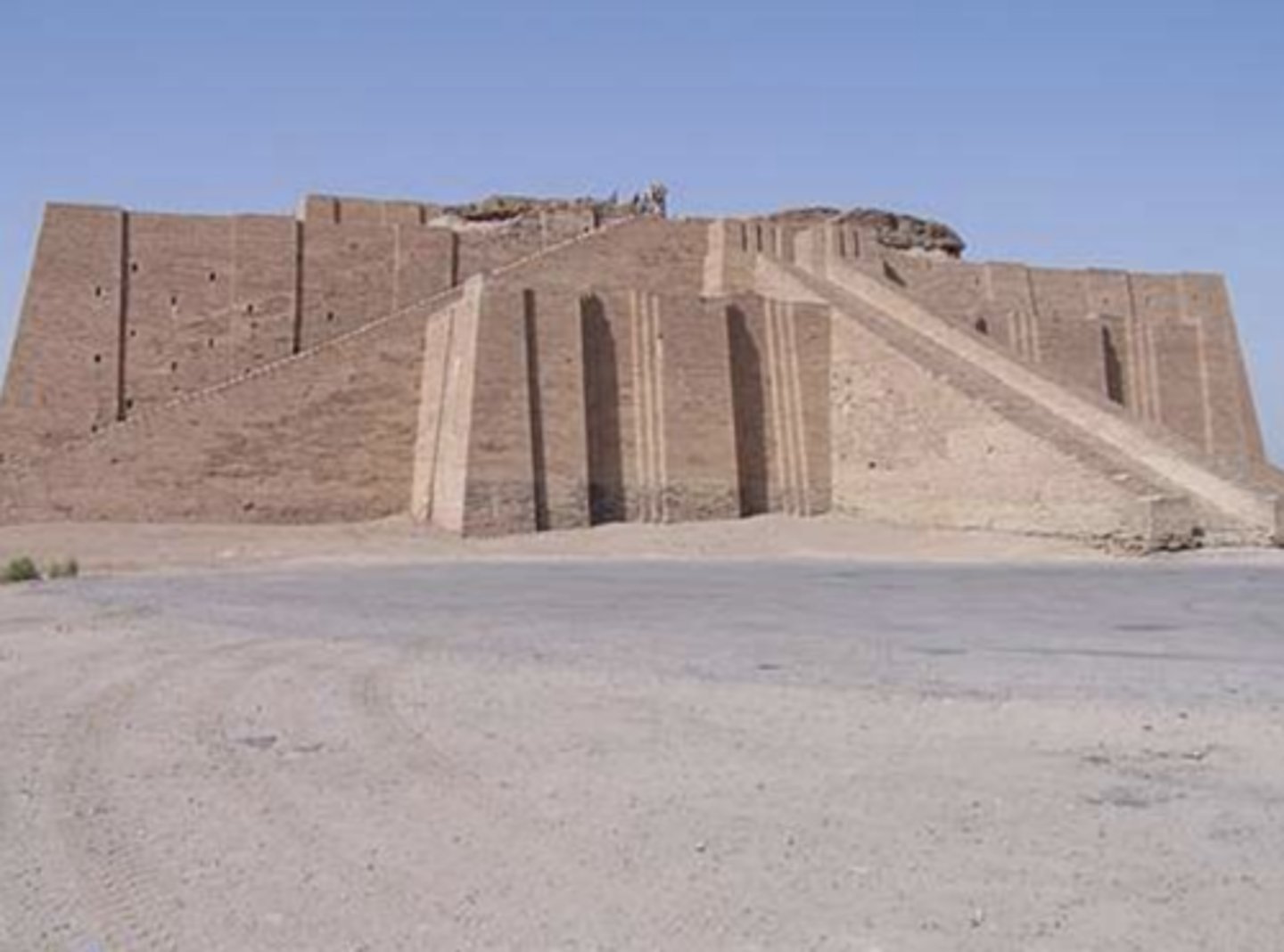

Ziggurat of Ur, Tell el-Muqayyar, Dhi Qar Province, Iraq, unknown architect, 21st century BC

Asked on a test
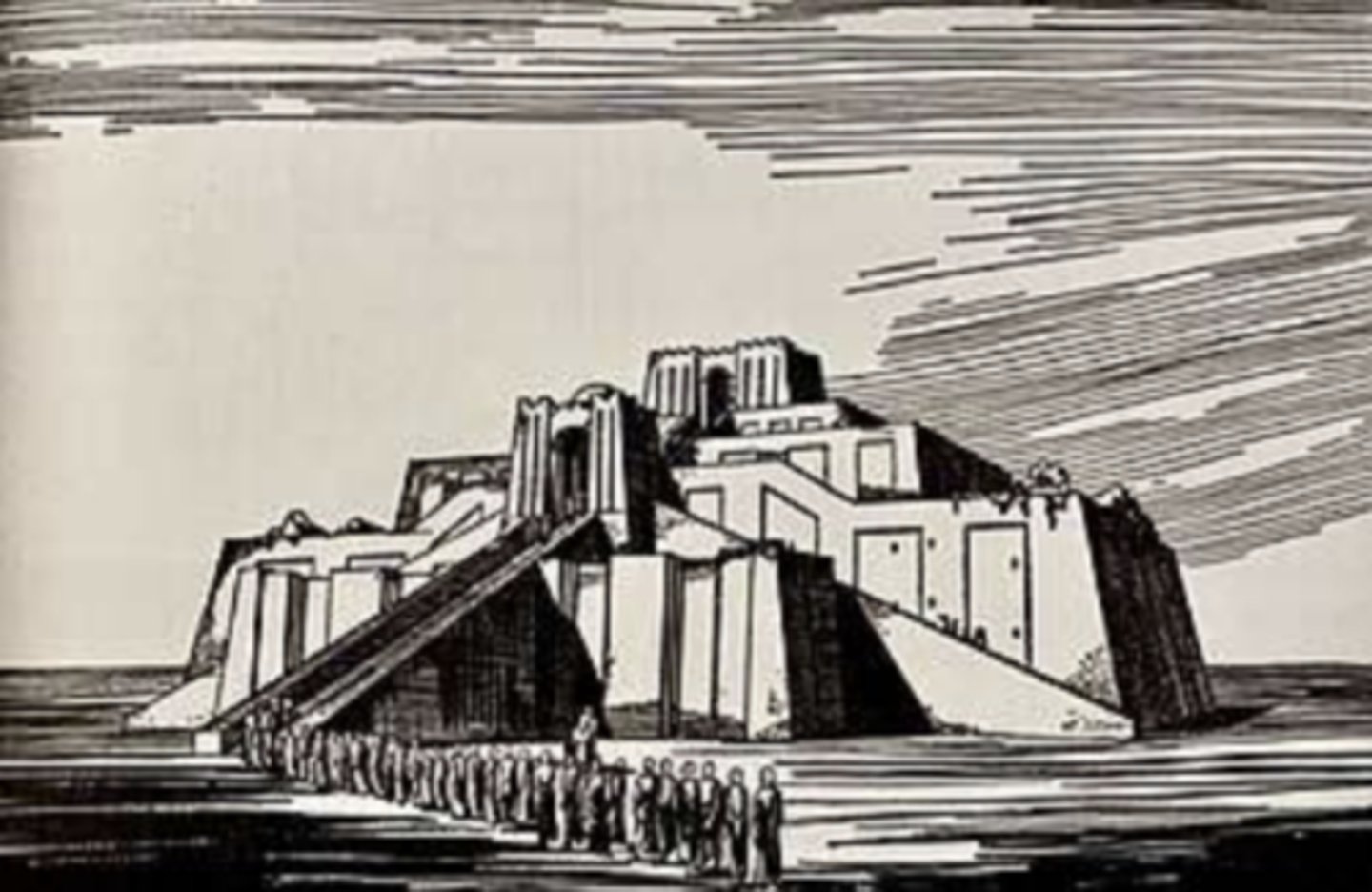
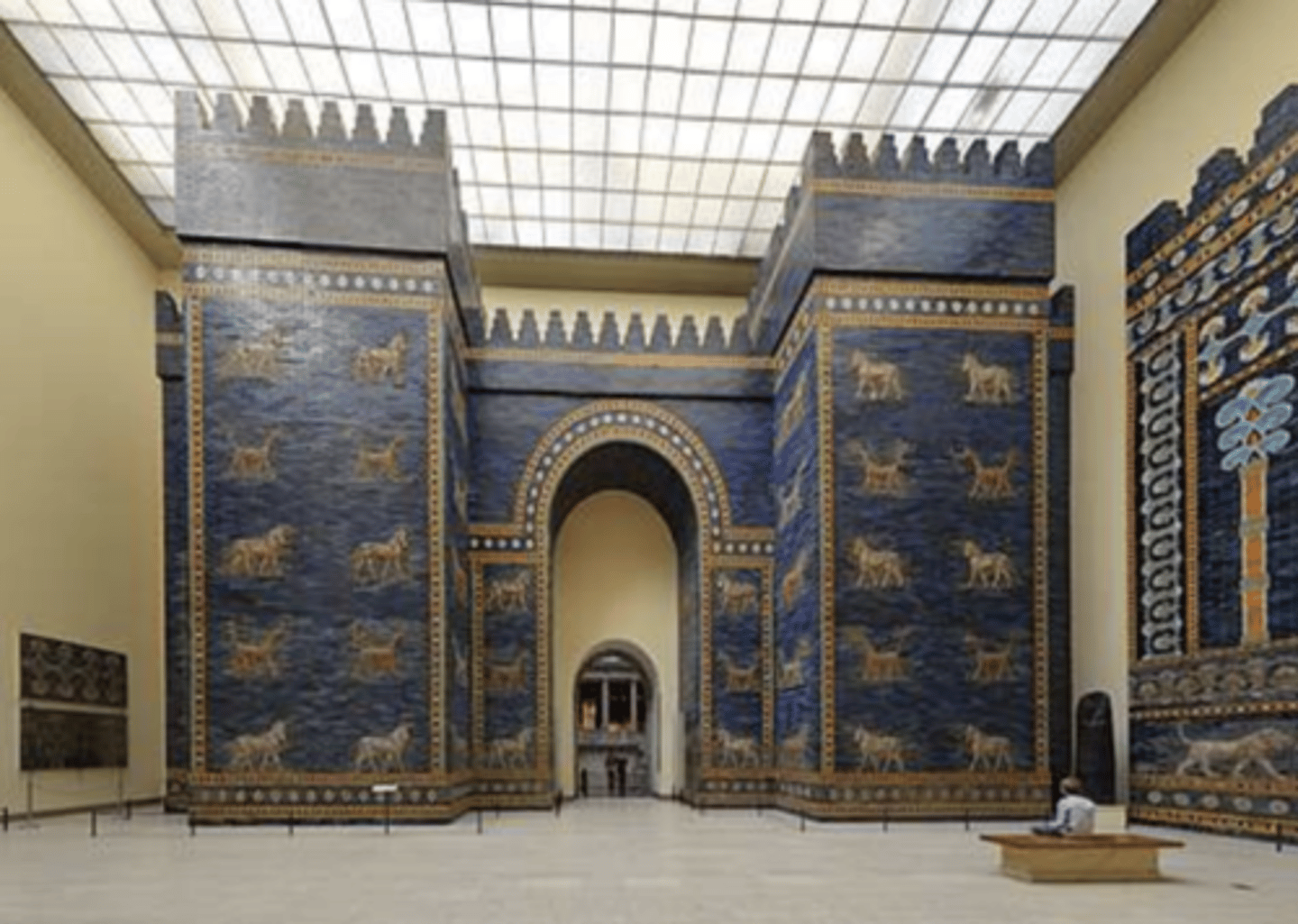


Reconstruction of the Ishtar Gate, Pergamon Museum, Berlin, Germany, unknown architect, c.605-539 BC (was part of walls on babylon)

About Mesopotamia
- Most noted for its construction of mud-brick buildings and the construction of ziggurats, occupying a prominent place in each city and consisting of an artificial mound, often rising in huge steps, surmounted by a temple. The great city of Uruk had a number of religious precincts, containing many temples larger and more ambitious than any buildings previously known.
"Ziggurat"
The word ziggurat is an anglicized form of the Akkadian word ziqqurratum, the name given to the solid stepped towers of mud brick. It derives from the verb zaqaru, ("to be high"). The buildings are described as being like mountains linking Earth and heaven. The Ziggurat of Ur, excavated by Leonard Woolley, is 64 by 46 meters at base and originally some 12 meters in height with three stories. It was built under Ur-Nammu (circa 2100 B.C.) and rebuilt under Nabonidus (555–539 B.C.), when it was increased in height to probably
seven stories.
Bronze Age Europe
3300 - 800 B.C.E
Minoan civilization the island of Crete
(27th century BC - 15th century BC)
First civilization on the island of Crete
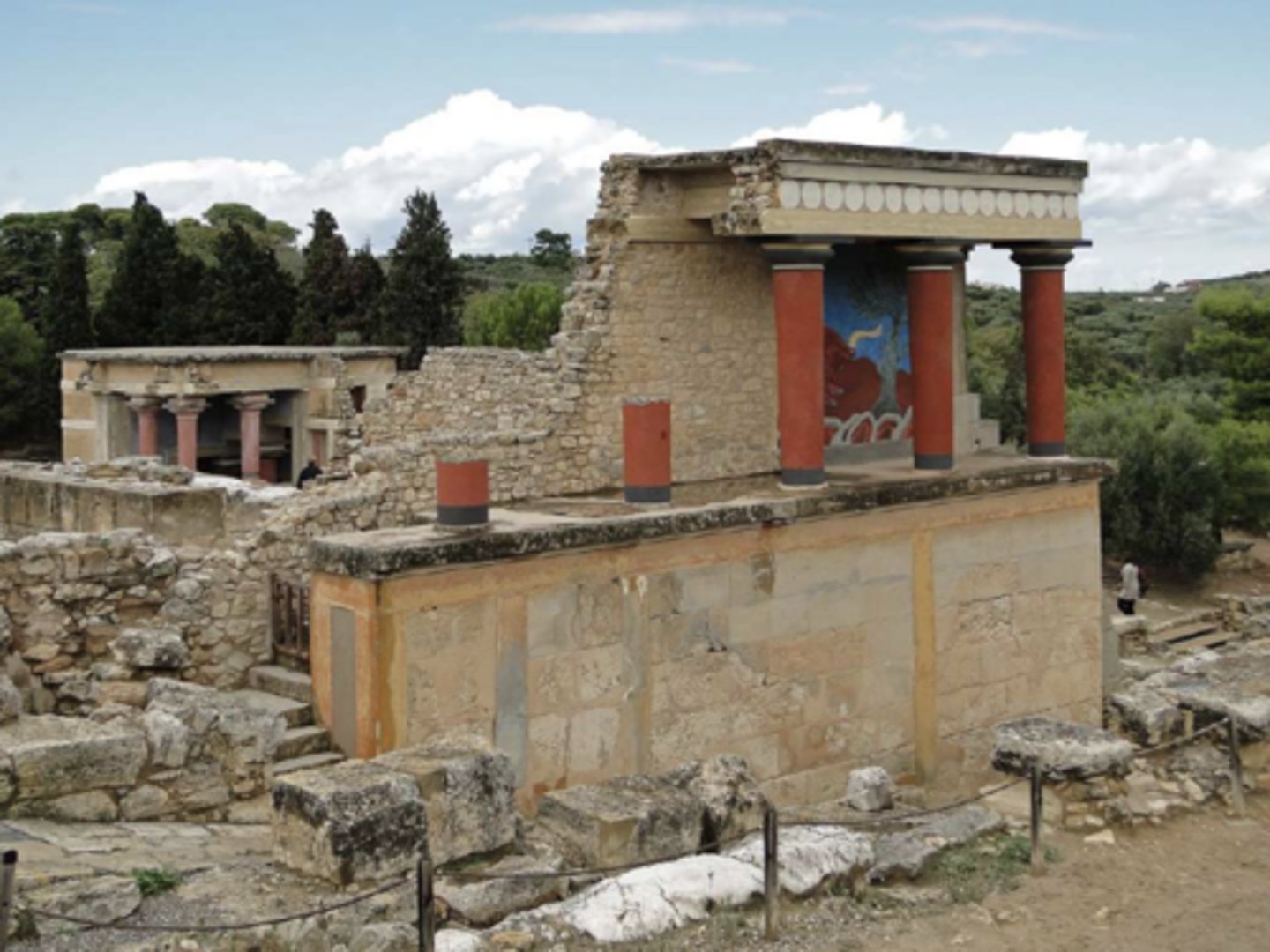

Partly reconstructed ruins of Knossos, Crete, c. 1700 BC (The Palace of Minos, famous for red columns)

Minoans and their history
The first well-known literate civilization in Europe was the Minoan civilization that arose on the island of Crete and flourished from approximately the 27th century BC to the 15th century BC.
The Minoans were replaced by the Mycenaean civilization which flourished during the period roughly between 1600 BC, when Helladic culture in mainland Greece was transformed under influences from Minoan Crete, and 1100 BC. Quite unlike the Minoans, whose society benefited from trade, the Mycenaeans advanced through conquest. Mycenaean civilization was dominated by a warrior aristocracy.
The plane of the palace of Minos
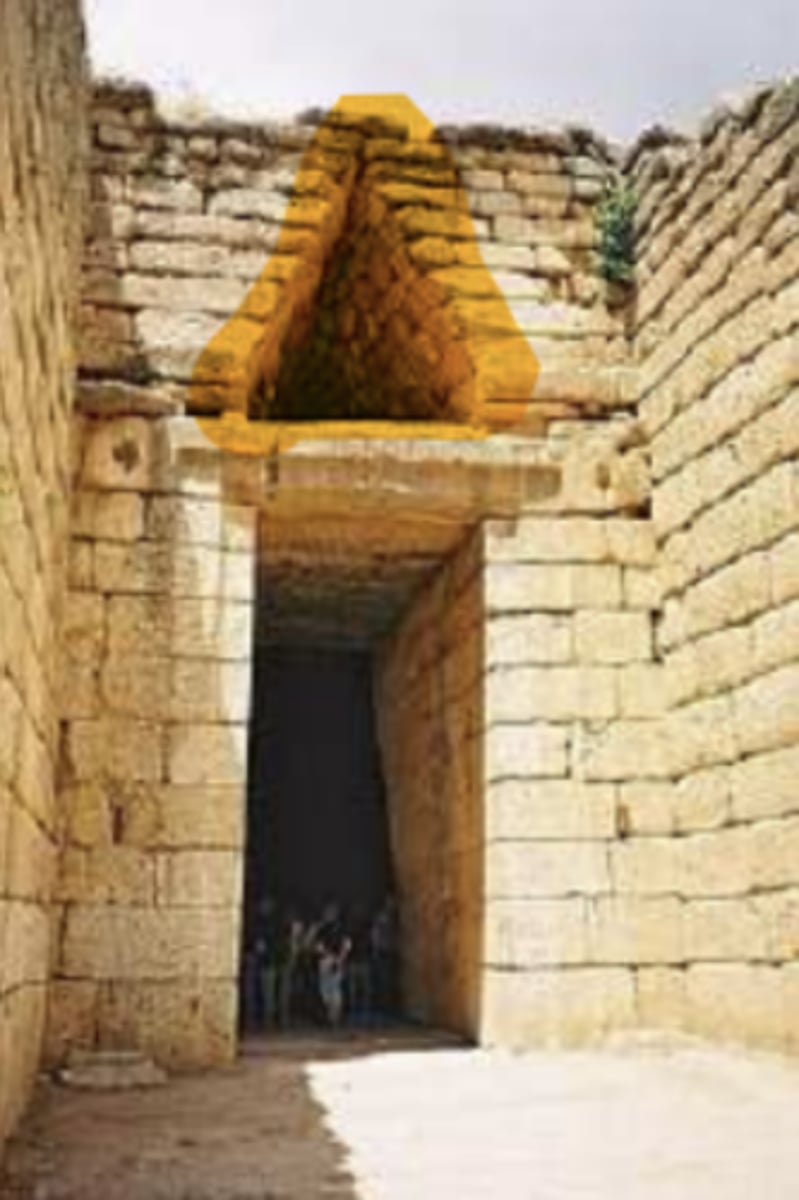

1) The Treasury of Atreus, or Tomb of Agamemnon in Mycenae 1250 BC
2) A "corbel" arch also considered a "fake" arch
Mycenaeans took over Minoans and built this arch.

Bronze Age Collapse
Around 1200 BCE. Bronze age collapse is called the Dark Ages. Very little is kept from that period because of the decline of culture and learning. Mycenaeans were ruling until the dark ages.
Ancient Greece
About 900 to 31 BC
Classical Greece
510-323 BC (death of Alexander)
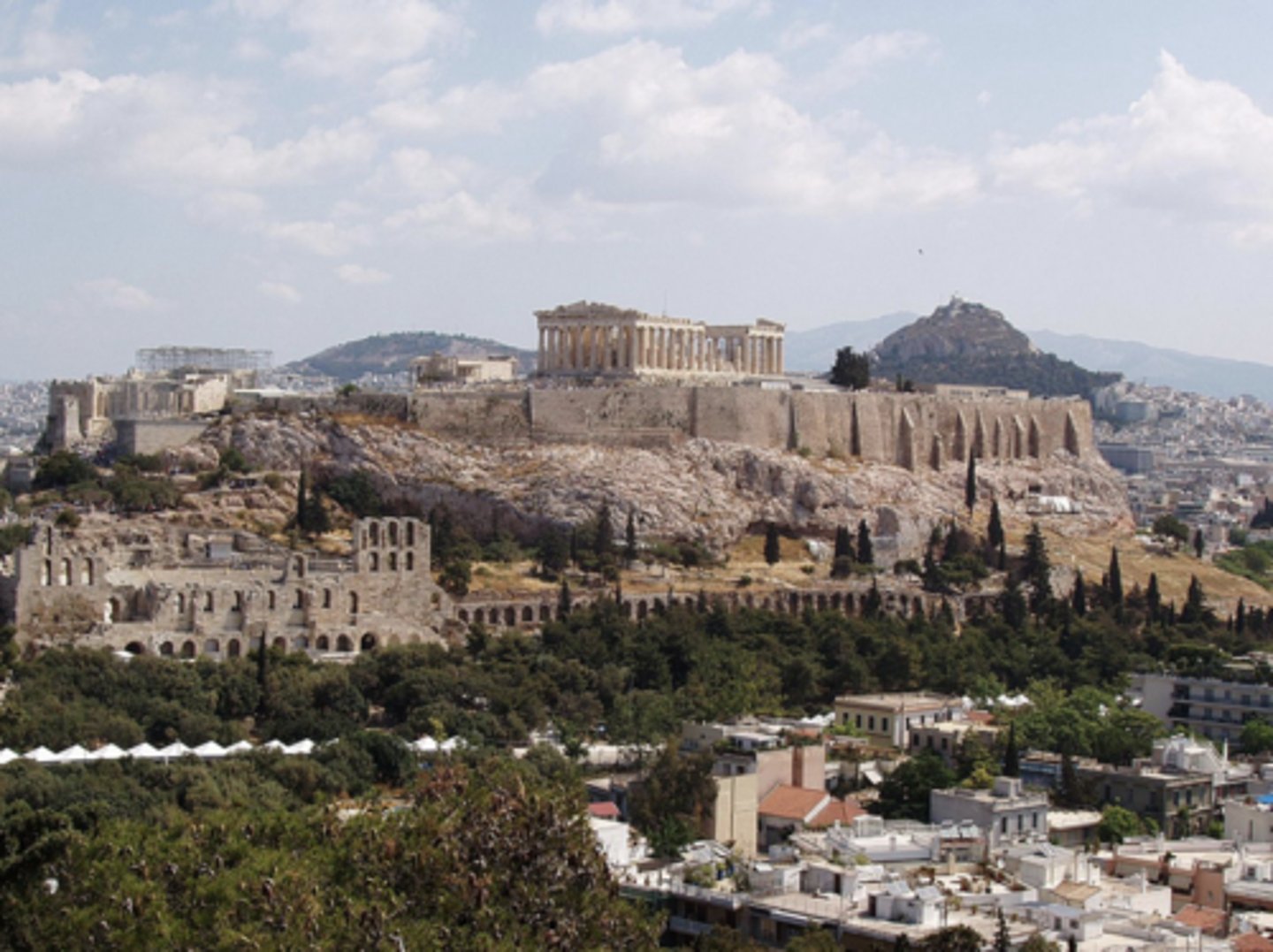

The Acropolis, Athens
Ancient Greek Architecture
Ancient Greek architecture is most renowned for its temples, with the Parthenon being considered the prime example both in ancient times and today. Another prevalent architectural form found throughout the Hellenic world is the open-air theatre, with the earliest dating back to around 525–480 BC. Additional surviving structures include processional gateways (propylon), public squares (agora) surrounded by colonnades (stoa), town council buildings (bouleuterion), public monuments, monumental tombs (mausoleum), and stadiums.
The formal vocabulary of Ancient Greek architecture, notably the division into three defined orders—the Doric Order, the Ionic Order, and the Corinthian Order—exerted a profound
influence on subsequent Western architecture. The architectural style of ancient Rome evolved from Greek influences. Classicism revivals during the Renaissance preserved not only the precise forms and details of Greek architecture but also its concept of beauty based on balance and proportion. Neoclassical architecture and Greek Revival architecture, with their successive styles, closely followed and adapted ancient Greek styles.

Stoa of Attalos
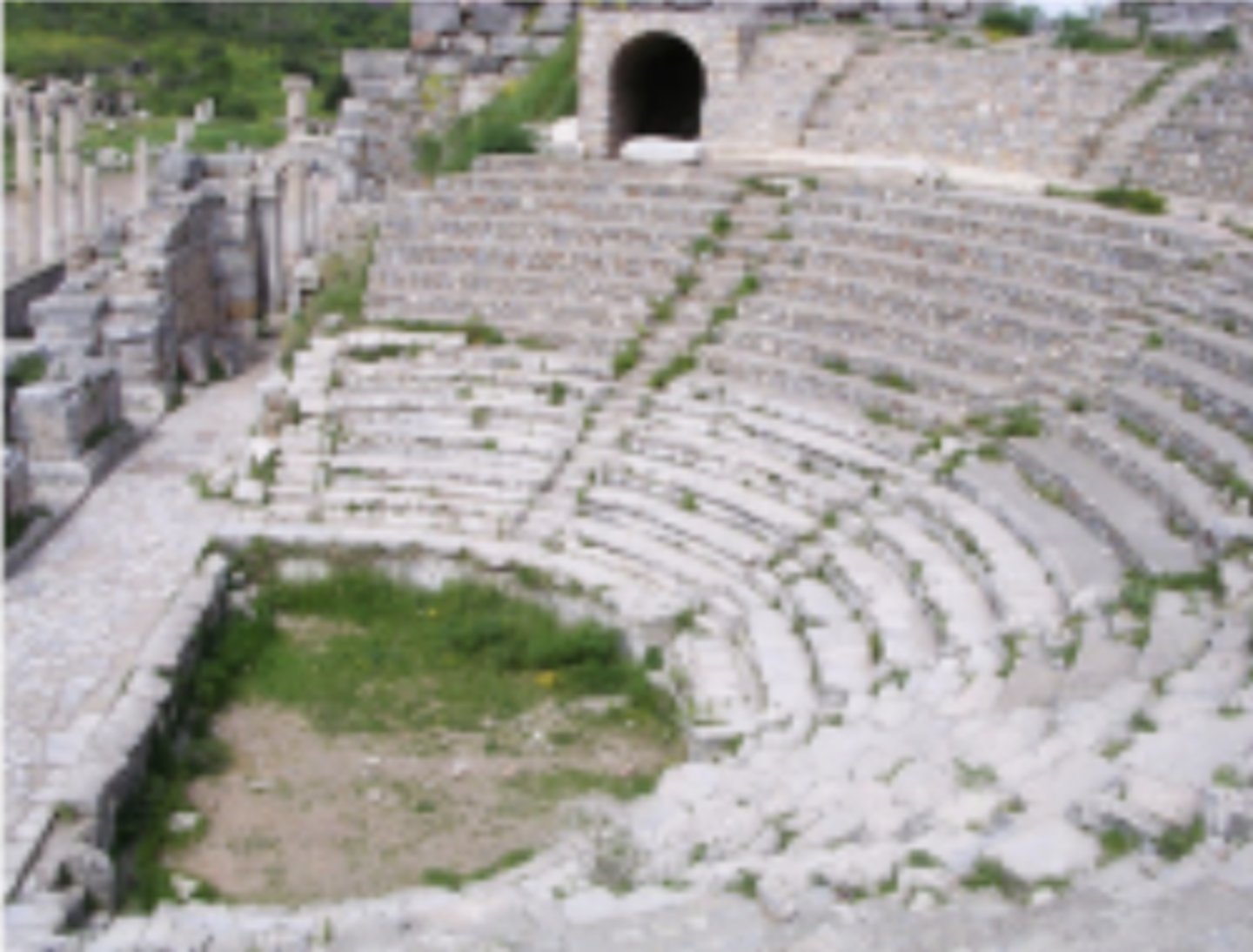

Bouleuterion of Ephesus
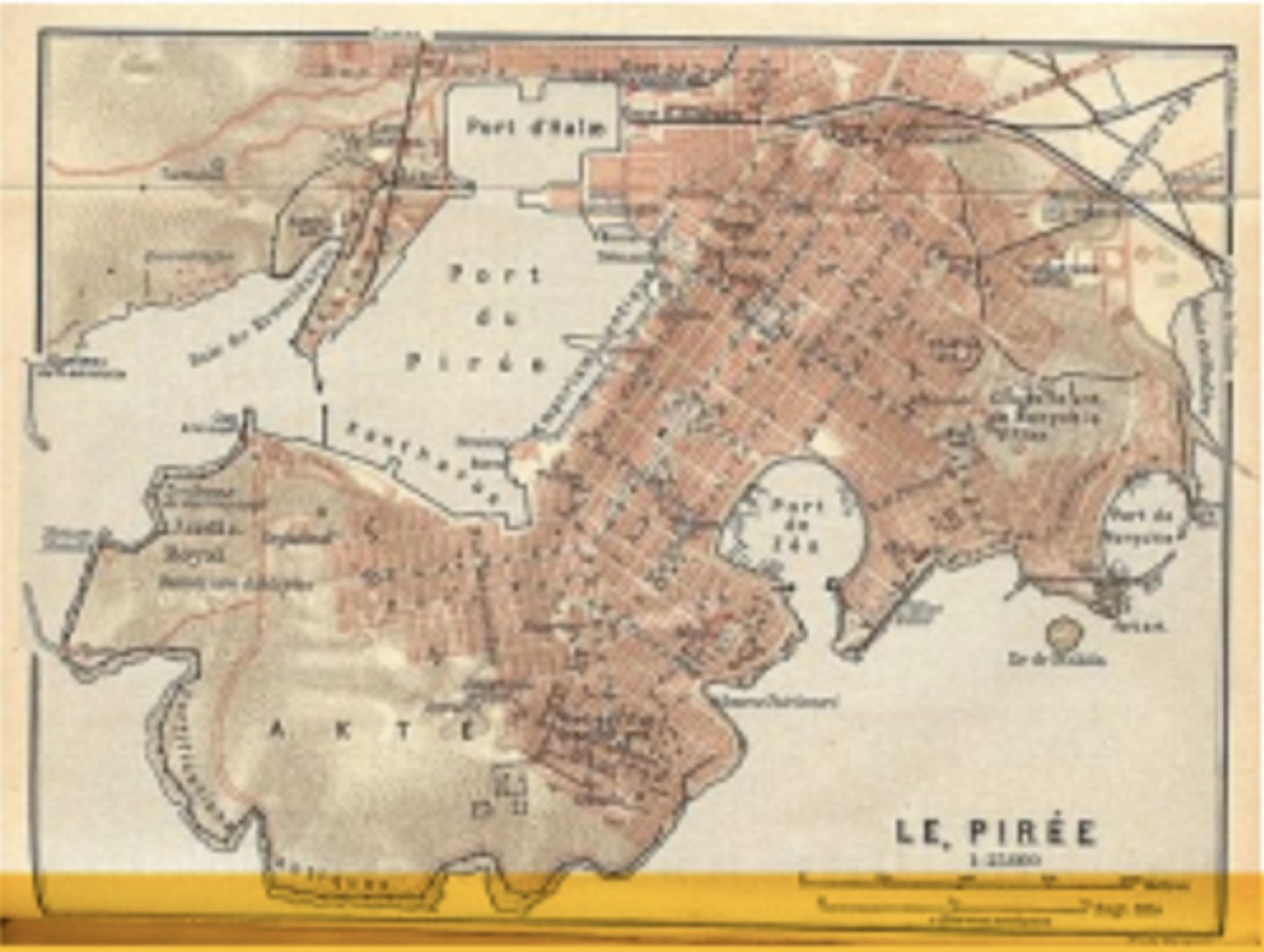
Map of Piraeus, port of Athens showing grid plan of city. Made by Hippodamus of Miletus, 470 BC. He was one of the first urban planners
Name, period
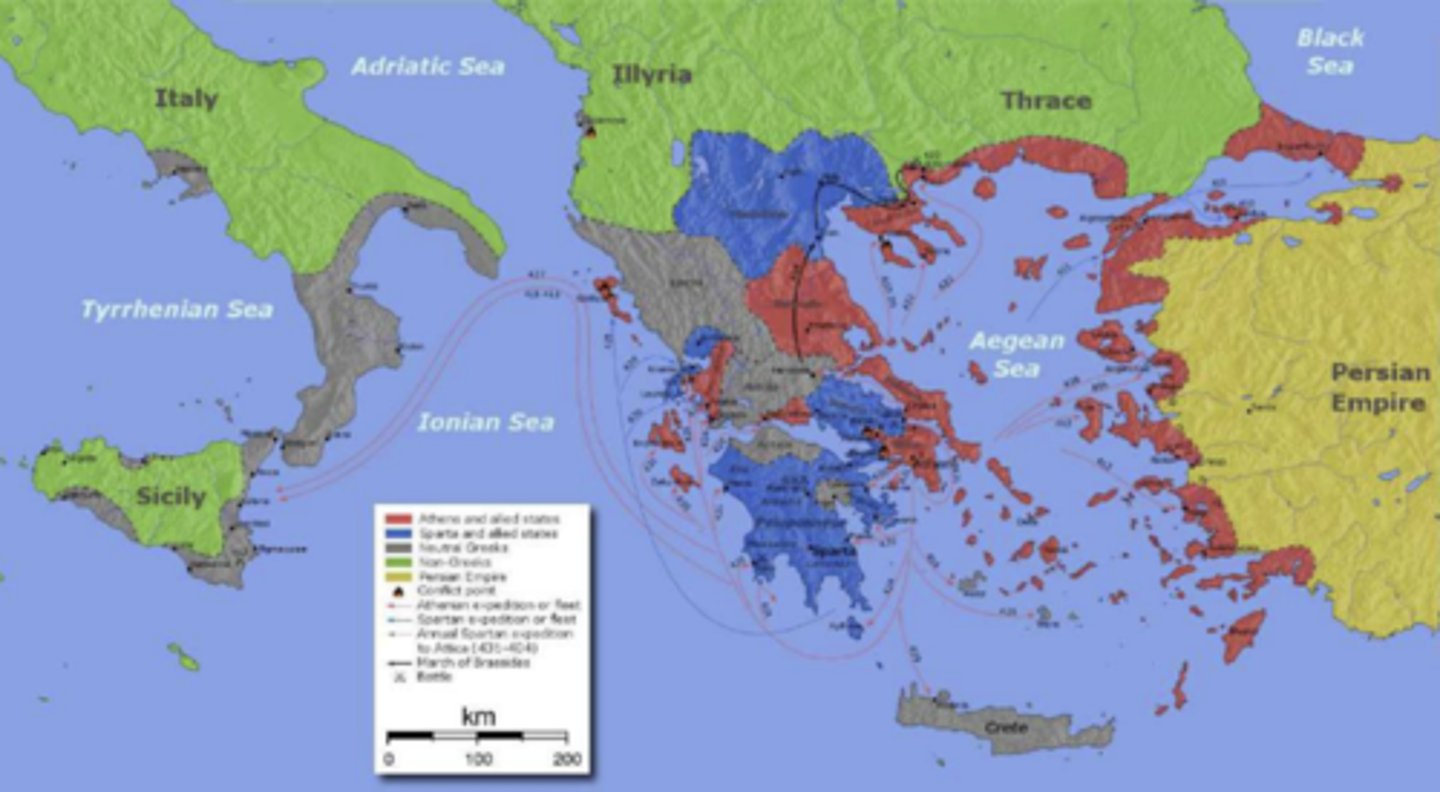
Greece during the Peloponnesian War (431-404 BC)
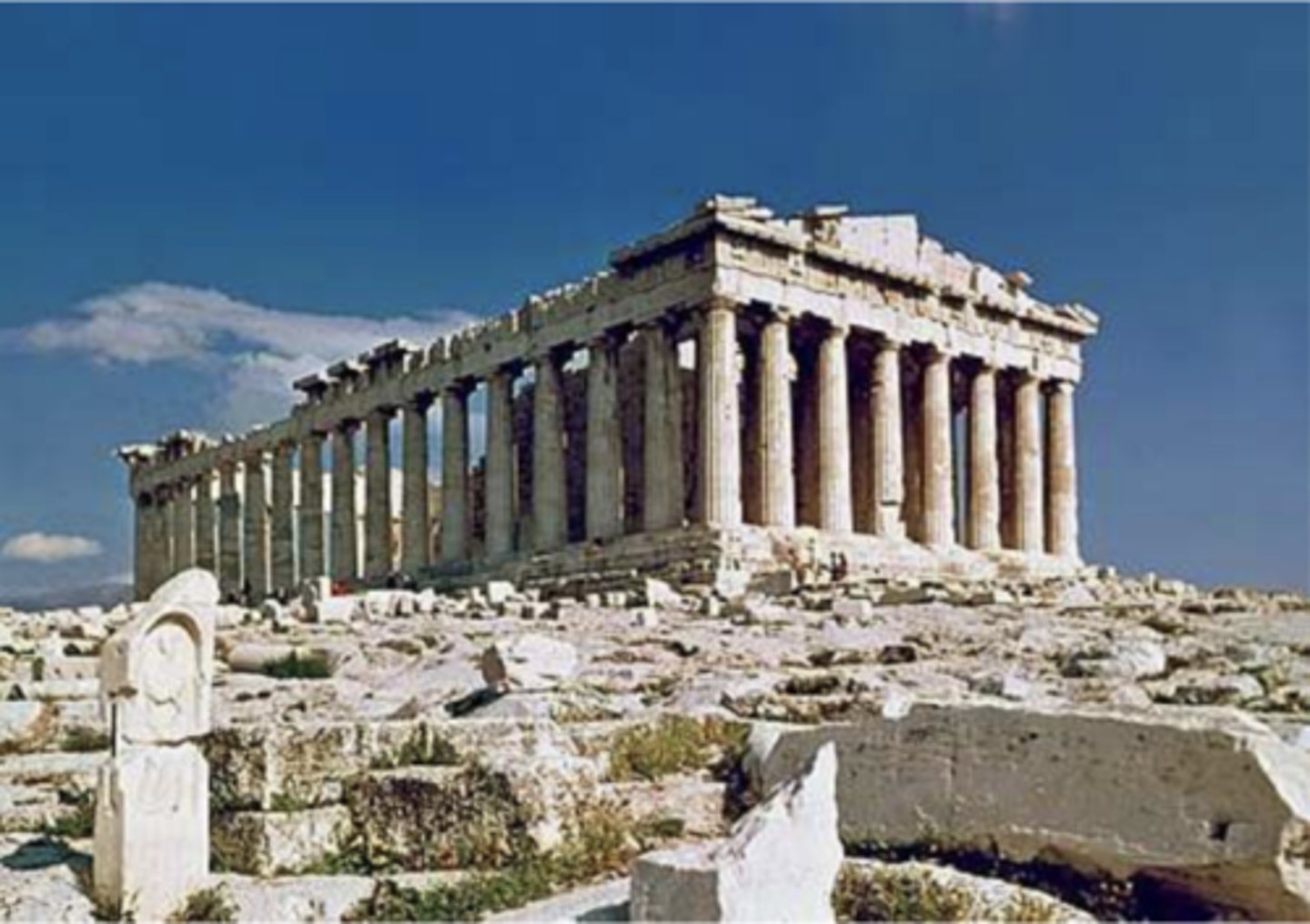

Parthenon, 432 BC, Athens. Architect: Ictinus, Sculptor: Phidias
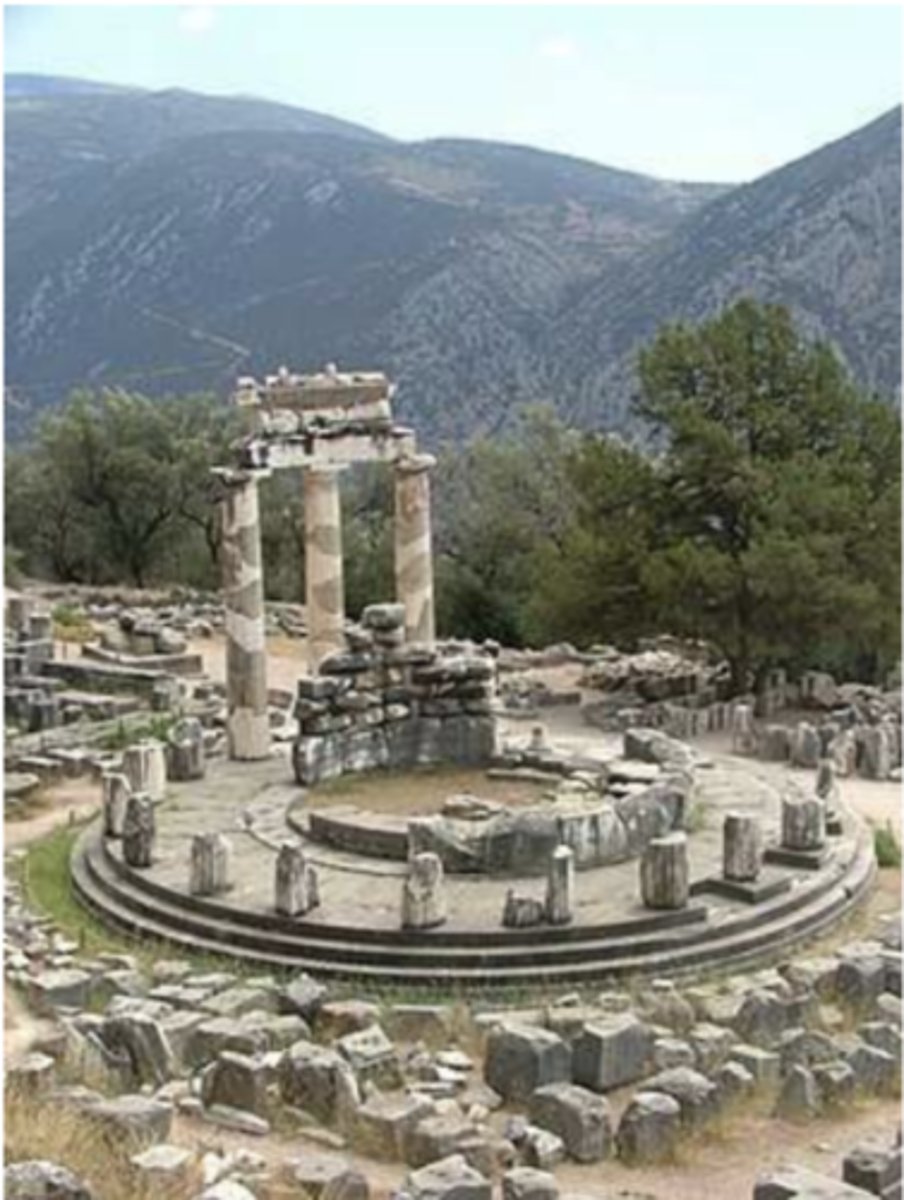

Architect: Theodore the Phocaean, Tholos of Delphi, 380 BC. Delphi means "someone who can predict the future" and back then it was a very important role. Tholos means "circular temple"
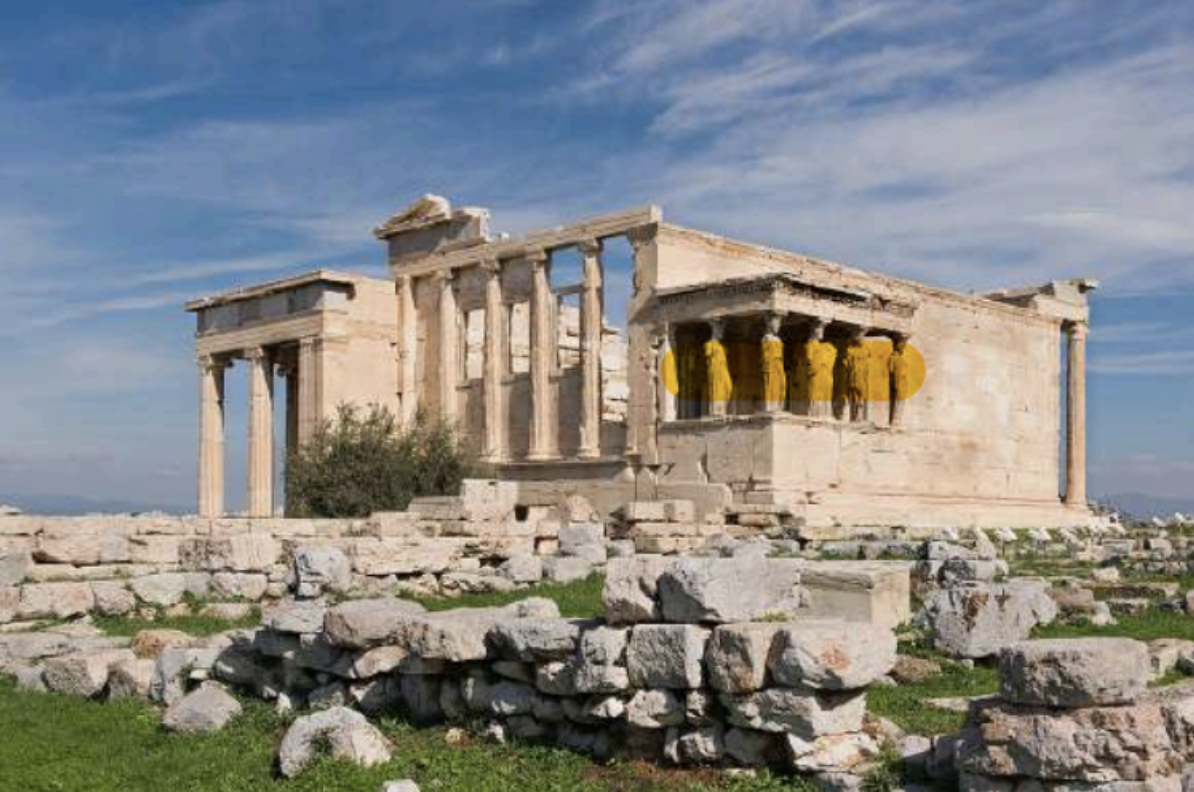

Erechtheion, 421 BC, Athens. Architect: Mnesikles. Female statues as columns are called "caryatids"
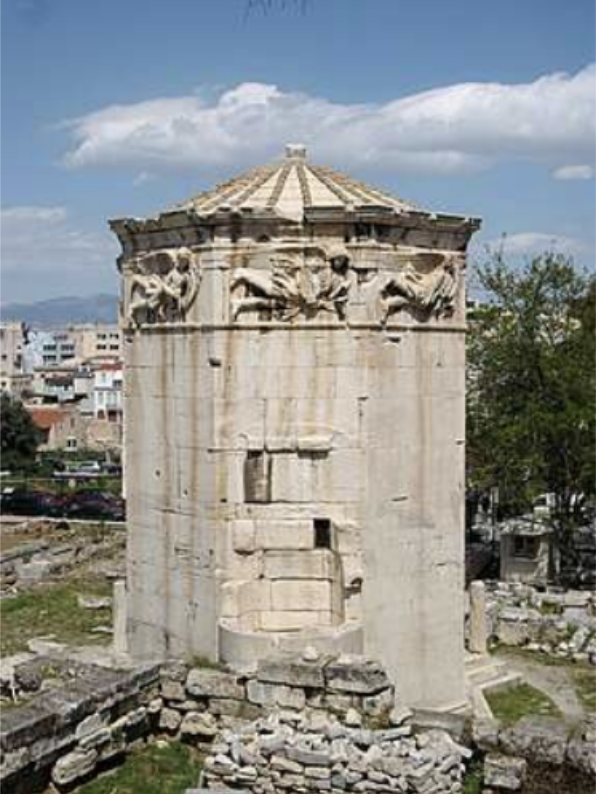

Tower of the Winds, Athens, 1st century BC
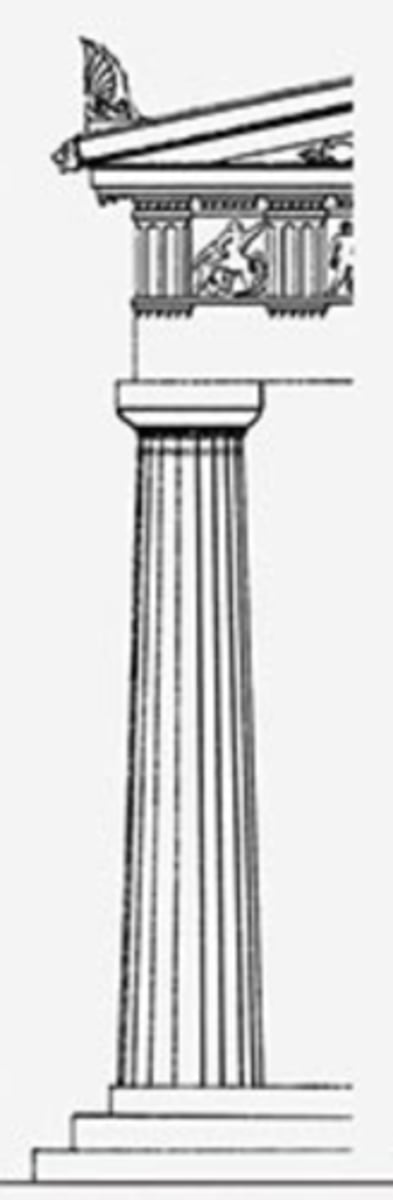
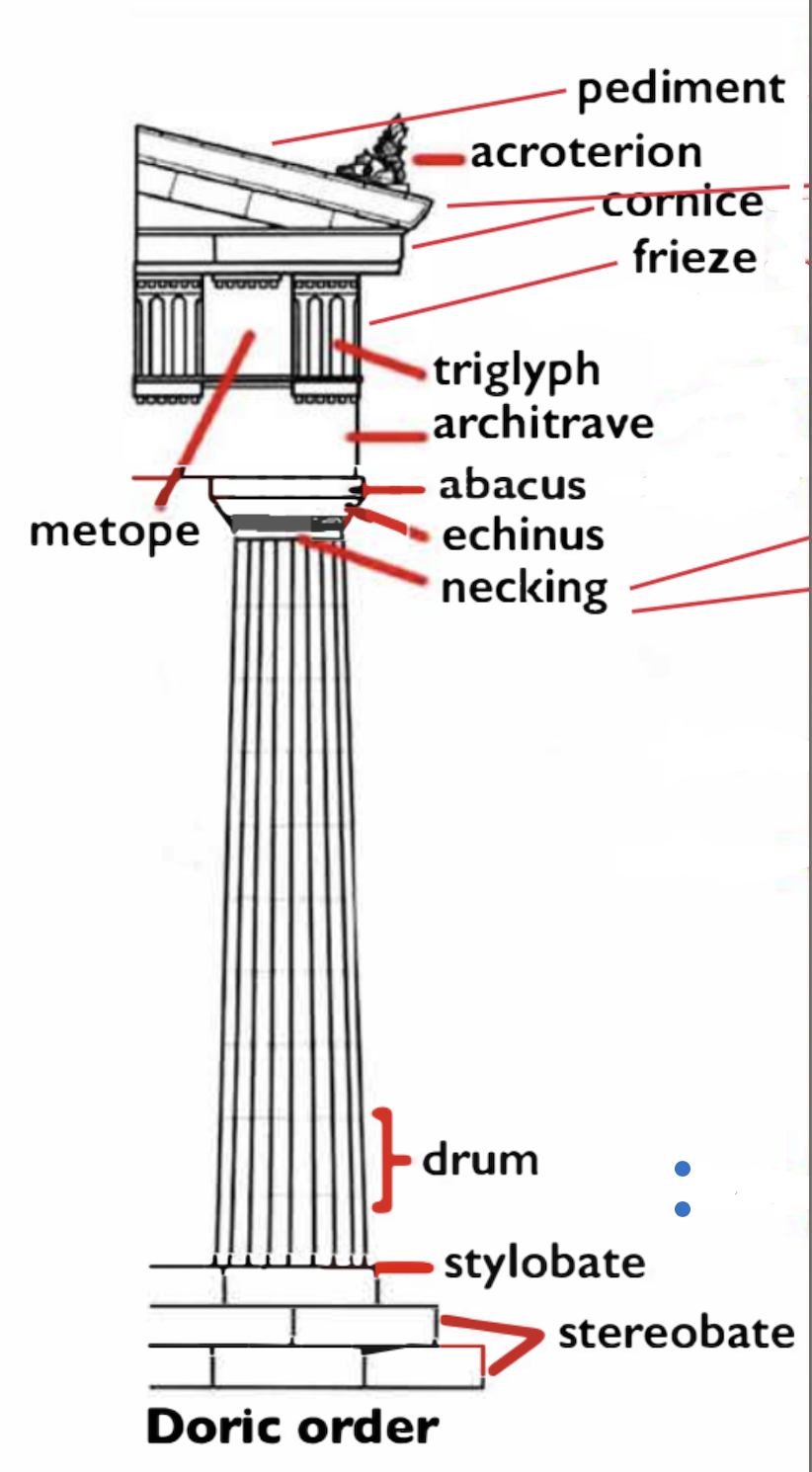

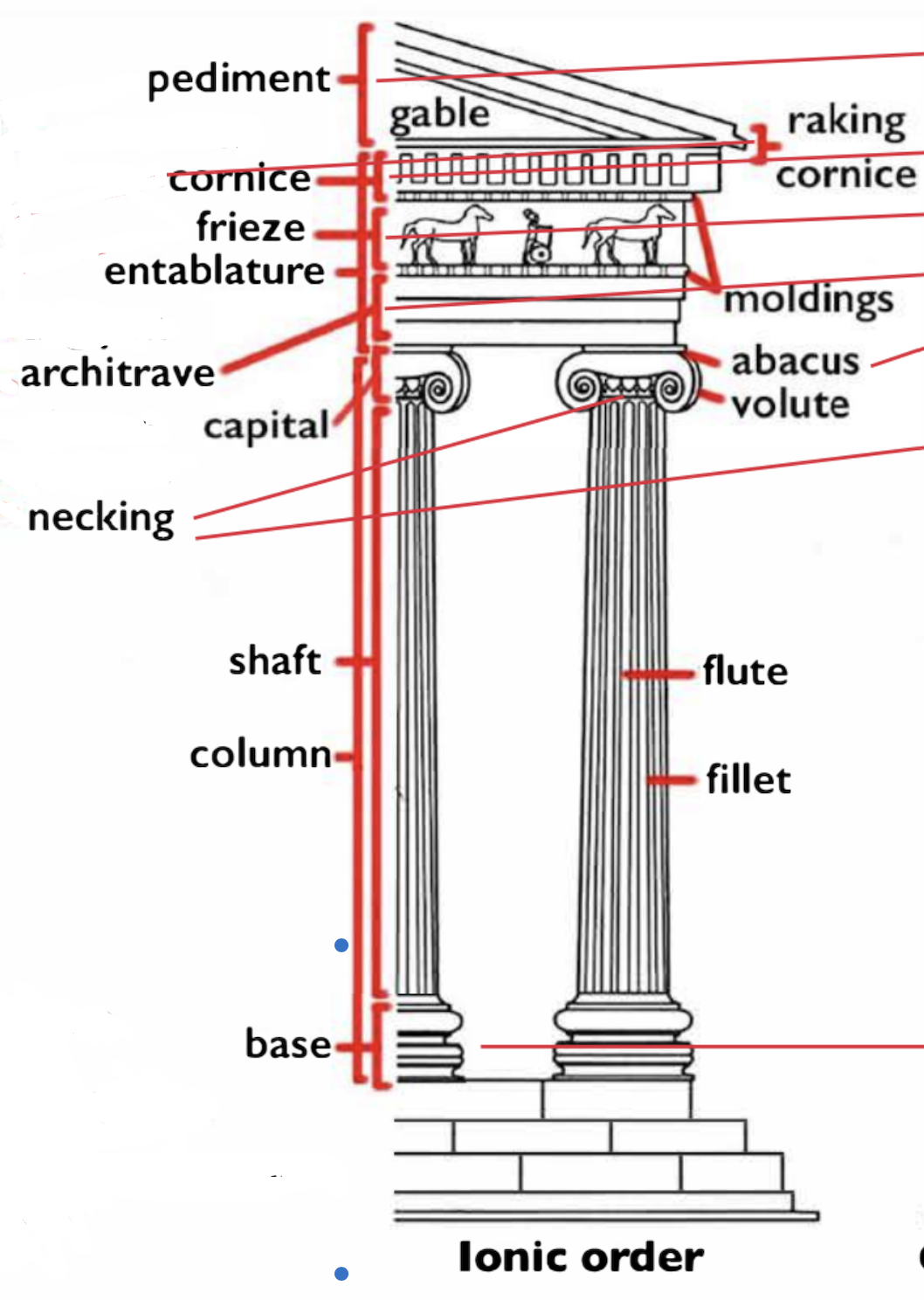

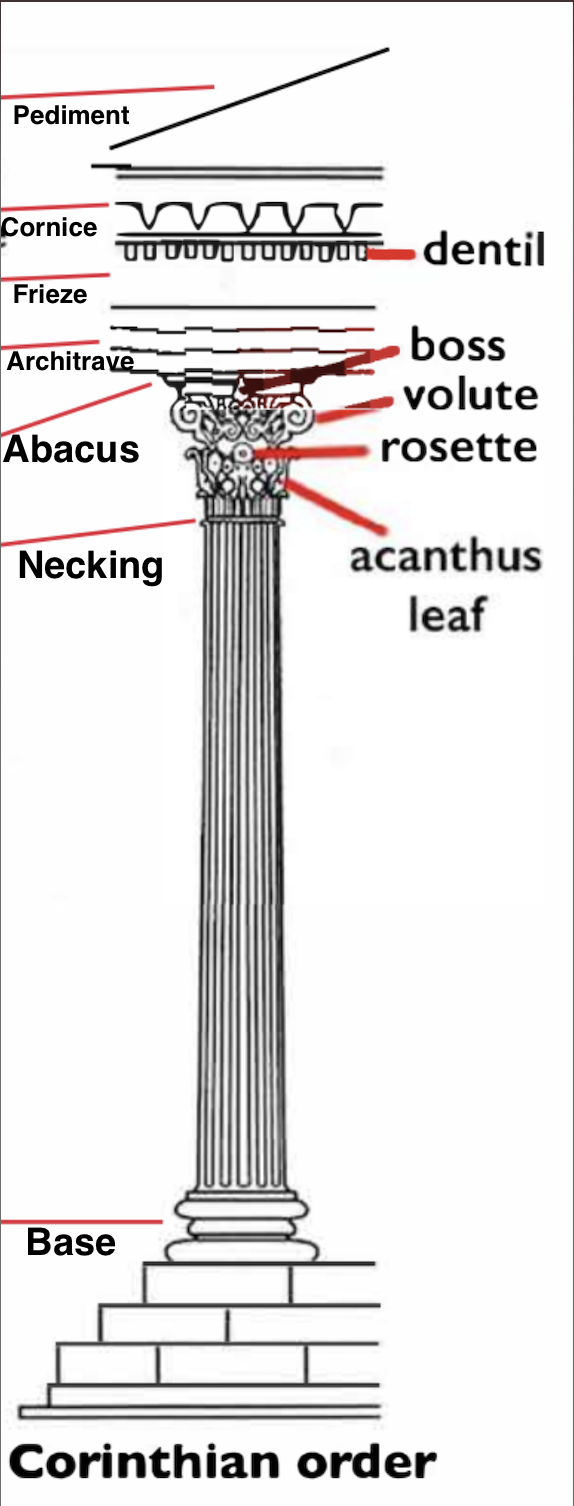
What are other types of columns?
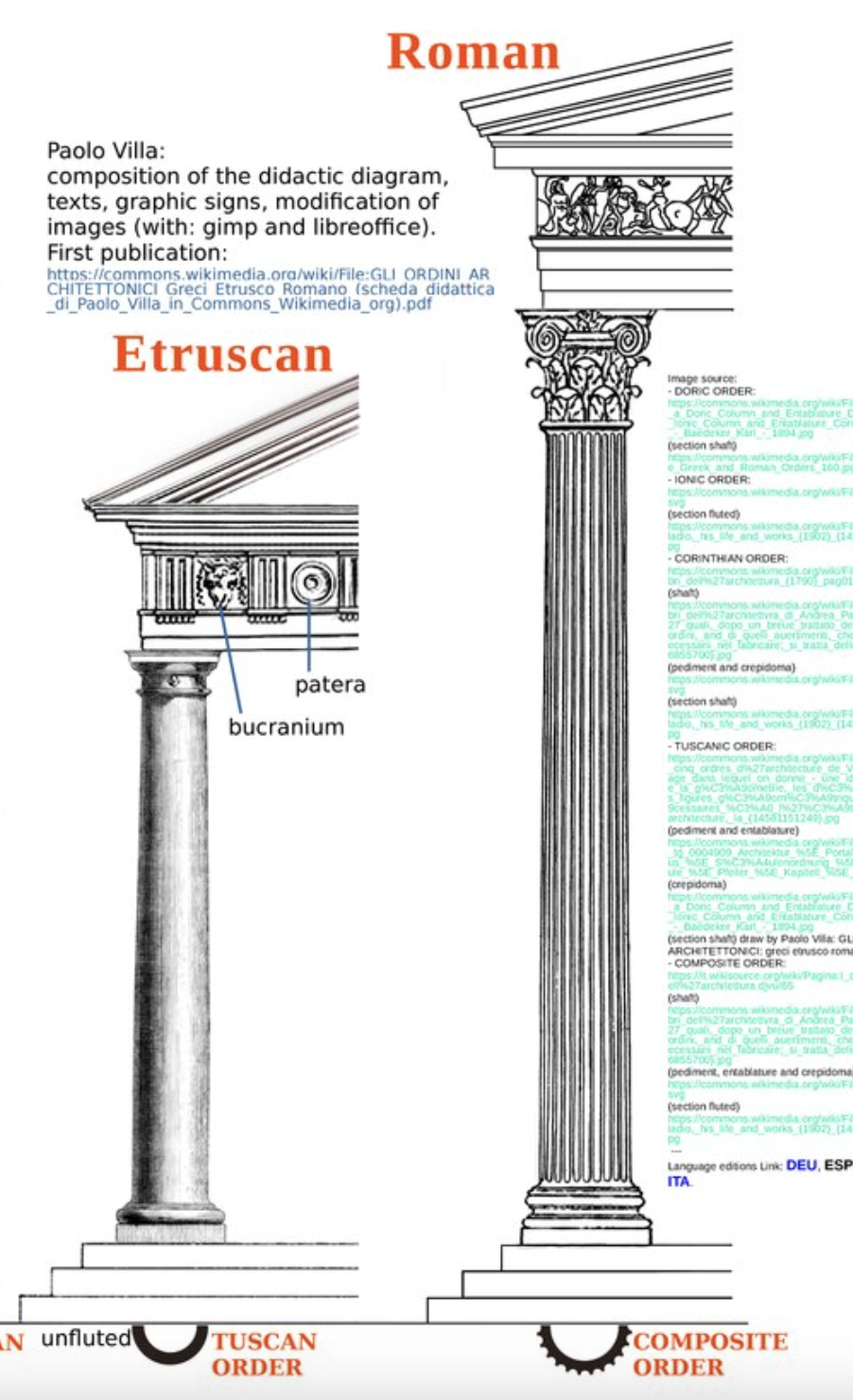
A composite orders volute is bigger than corinthians, a kind of mix of corinthian and ionic
Tuscan is like a more embellished doric
Roman Architecture
753 BC- 476 AD
Roman civilization
Since the beginning of Roman civilization, the focus has been on the "city" as the fundamental constituent element. In general, the history of the Romans does not begin with a major battle or the reign of a particular king. Their history begins with the founding of the city of Rome by Romelus and Remus in 753 BC. According to the legend, the two brothers, suckled by a female wolf, were the founders of Rome. The city will went to conquer the entire Mediterranean basin, becoming the "Caput Mundi" (aka Head of the World, europes biggest and wealthiest city).
Outline of Roman History 1
Kingdom Period: 753-509 BC
In this period, the city and territory of Rome was ruled by a monarchy. According to legend, the brothers Romulus and Remus founded Rome in 753 BC. The Latin aristocrats (Latins were the name of the people who inhabited in and around Rome) rose up after a couple of centuries, expelled the Etruscan Kings in 509 BC, establishing the Roman Republic. Romans didn’t like their king, so the republican period started.
Outline of Roman History 2
Republican Period 509-27 BC
The Roman Republic began with the overthrow of Roman monarchy in the year traditionally dated to 509 BC and its replacement by a government headed by two consuls, elected each year by the citizens and given power by a senate. A mixed constitution gradually evolved, centering on the principles of separation of powers and checks and balances.
Outline of Roman History 3
Empire Period 27 BC-476 AD
The Roman Empire was founded when the Republic was reorganized under the leadership of Augustus in the 1st century BC. The Empire experienced a long period of peace and stability, know as the Pax Romana, between 27 BC and 238 AD, when it was engulfed in turmoil due to the Crisis of the Third Century. It was divided into Eastern and Western parts in 395. The Western Roman Empire, collapsed in 476 as a result of the attacks of the Germanic tribes that came to Europe with the Migration of Tribes, while the eastern part continued its existence as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantine Empire until the Fall of Constantinople by Mehmet II, in 1453.
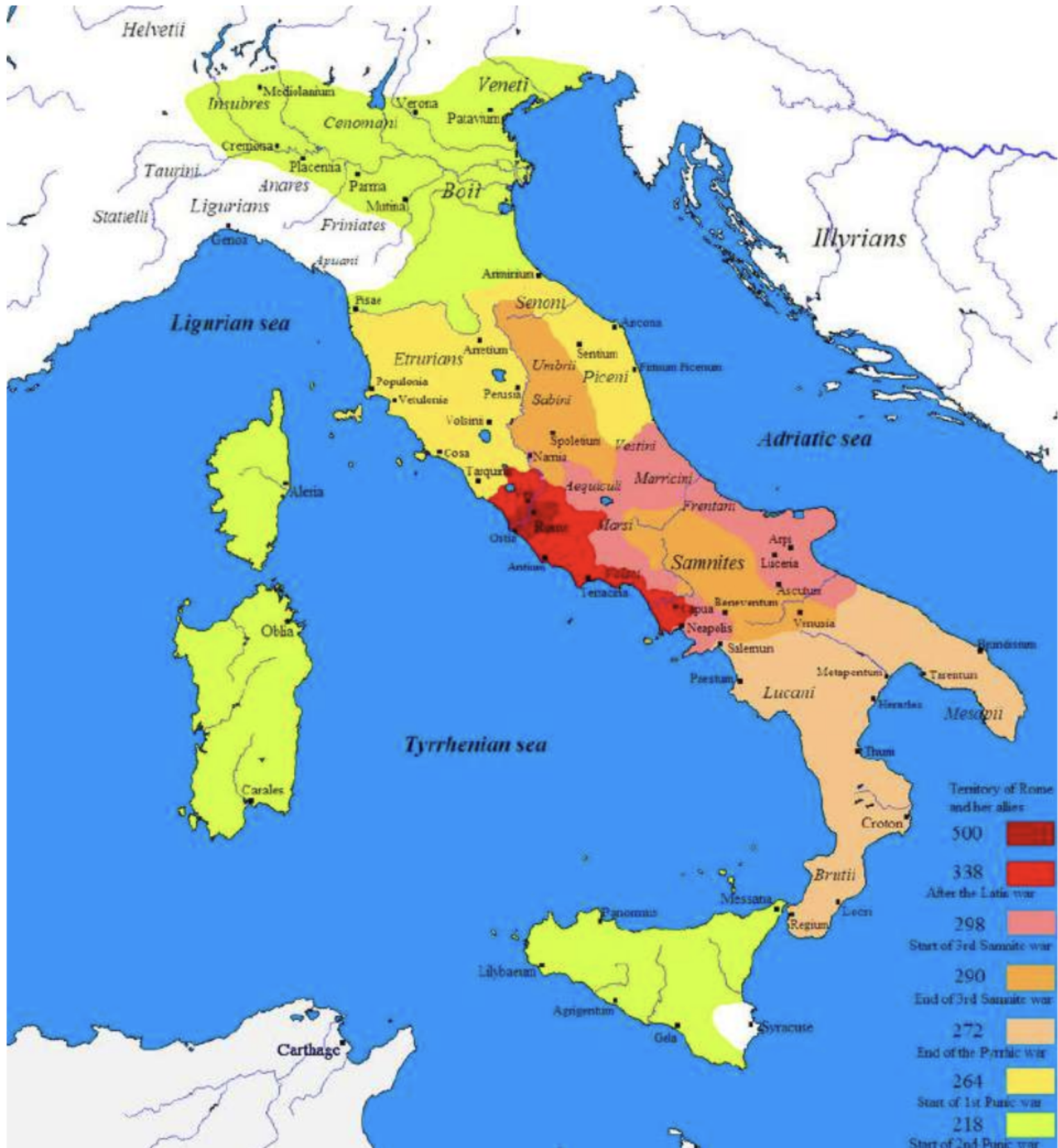
Roman Expansion in Italy
Roman Expansion in Italy (500 - 218 BC)
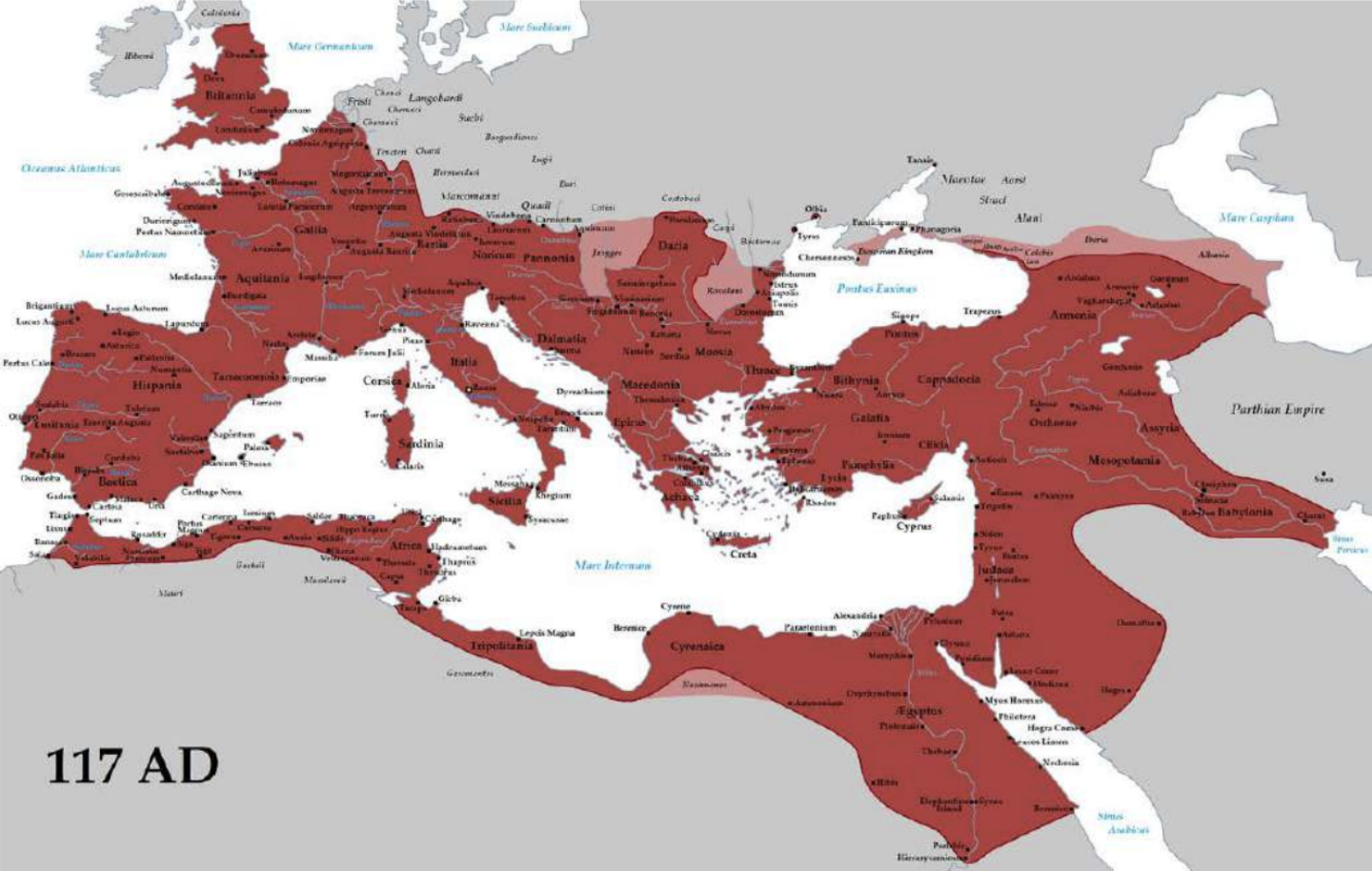
Peak Roman Territorial Expansion under Trajan
Peak Roman Territorial Expansion under Trajan, 117 AD
Different Typologies of Roman Architecture
Temple, Forum, Theatre, Roman Bath, Triumphal Arch, Basilica.
Temple
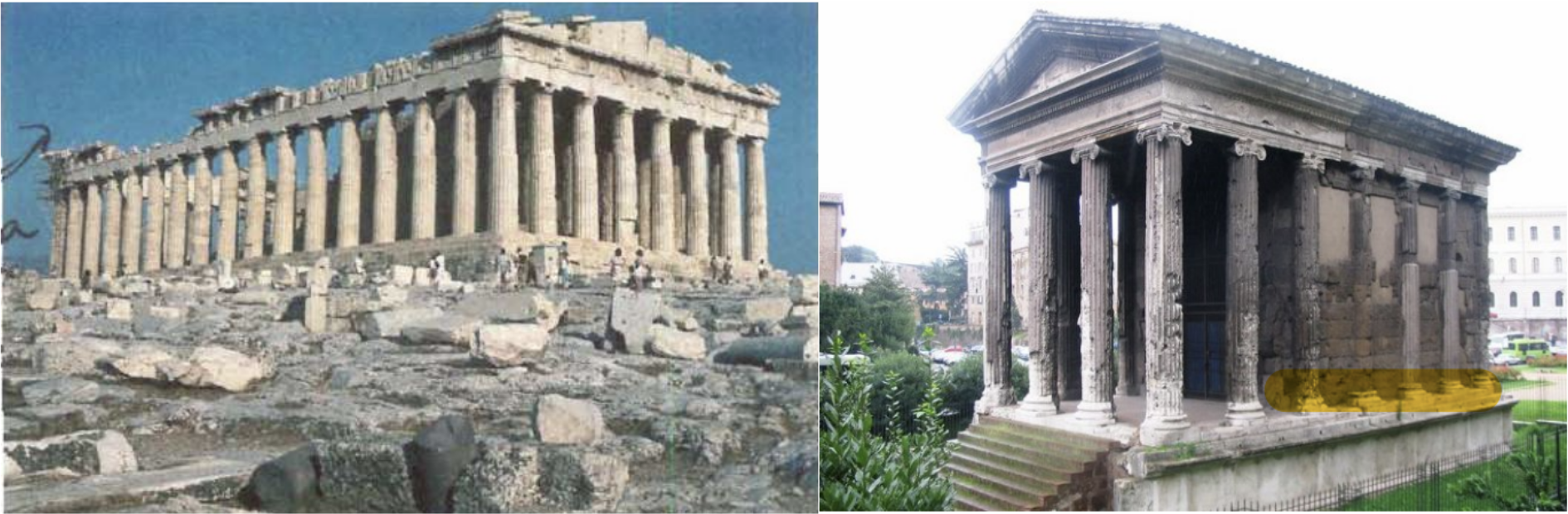

Greek temples are built on the highest hill of the city to be seen, and since they are surrounded by stairs on all four sides, it is possible to enter the temple from al sides. These features distinguish them from Roman temples. Roman temples are built inside the city, in the center, and are elevated on a pedestal, allowing access in only one direction. In this respect, the plans of a Greek and Roman temple look like this.
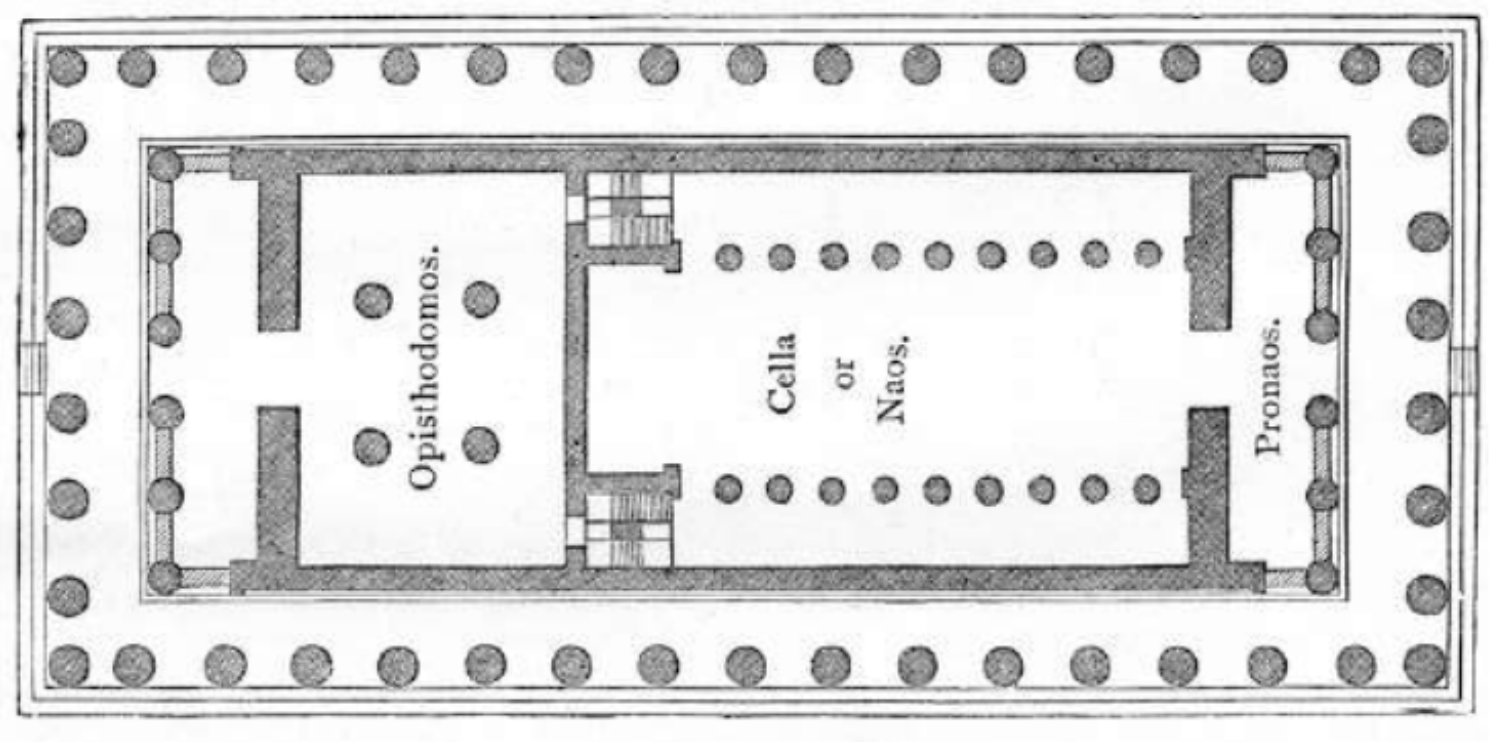
Name?
Name: Parthenon, Plan
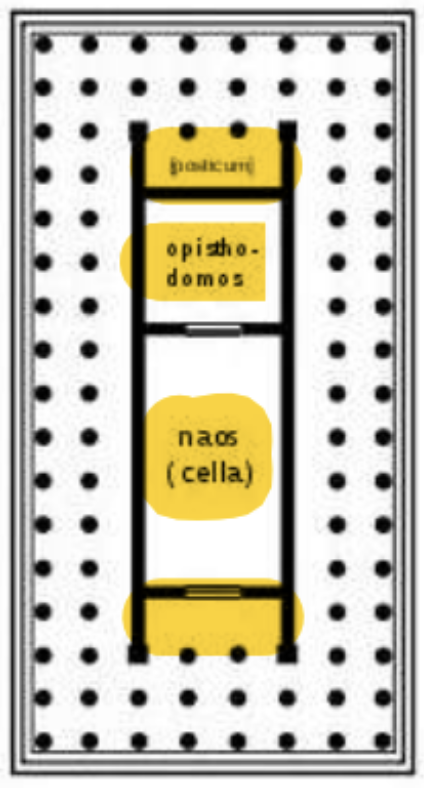
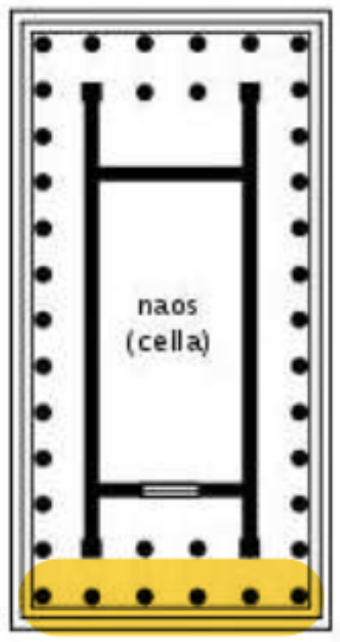
Middle/big room in the image calles “cella” or “naos” are mains rooms
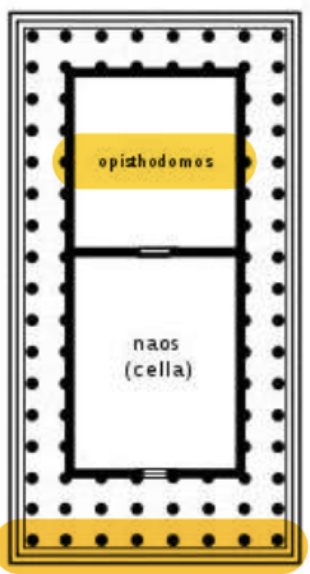
Opisdomodos is unique to Greek architecture
“Pronaos” at the right side of the plan in a “preroom”
Name: ___
Name: Temple of Portunus, Plan

Name: ___ Example:___
Name: Anta
Example: Athenian Treasury in Delphi, “Distyle” in Antis, has 2 columns


Name: ___
Name: Double anta
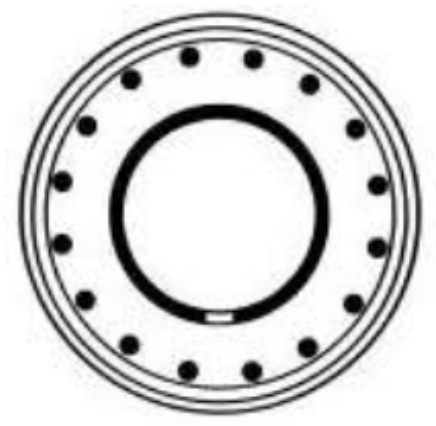

Name: ___
Name: Tholos

Name: ___
Prostyle

Name: ___
Name: Amphiprostyle
Name: ___
Name: Dipteral
the top part says “posticum”
Name: ___
Name: Peripteral (Hexastyle)

Name: ___
Name: Pseudoperipteral
Name: ___
Name: Pseudodipteral (Octostyle)
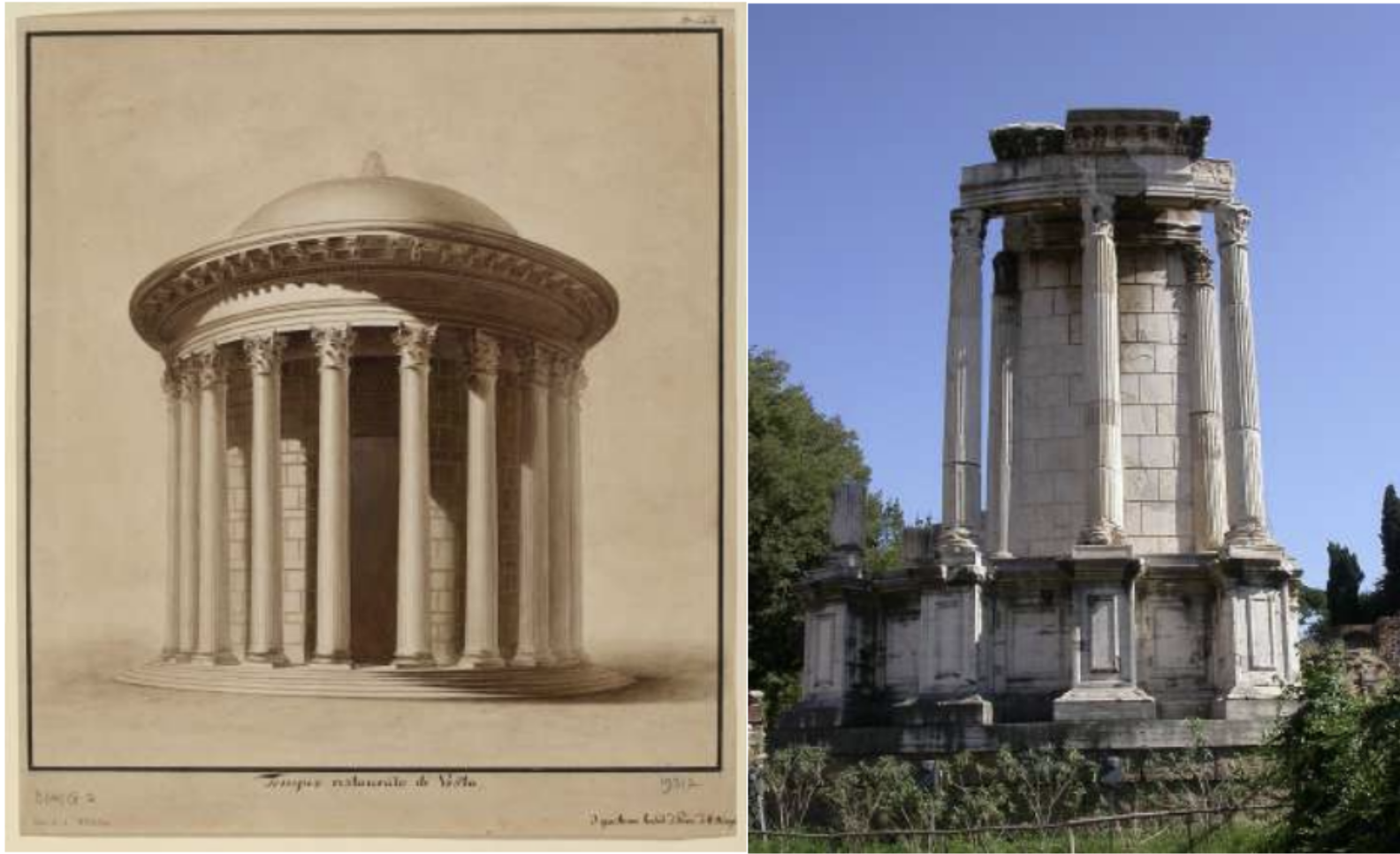
Temple of Vesta
(2nd century AD, the final version)
The only remaining round-plan temple (tholus) in Rome. The Vestal Virgins were the sacred virgin priestesses of Vesta, the goddess of the family in Ancient Rome. They were chosen for the priesthood from the young daughters of elite families in Rome. They had to preserve their virginity. Otherwise they were punished with death. Their primary duty was to guard Vesta's sacred fire in the temple of Vesta in the Forum Romanum (Roman Forum). The vestalate was a great honor and women who took on this role were given great privileges.

Roman Architectural Revolution
Monumental domes began to appear in the 1st century BC in Rome and the provinces around the Mediterranean Sea. Along with vaults, they gradually replaced the traditional post and lintel construction which makes use of the column and architrave. The construction of domes was greatly facilitated by the invention of concrete, a process which has been termed the Roman architectural revolution.
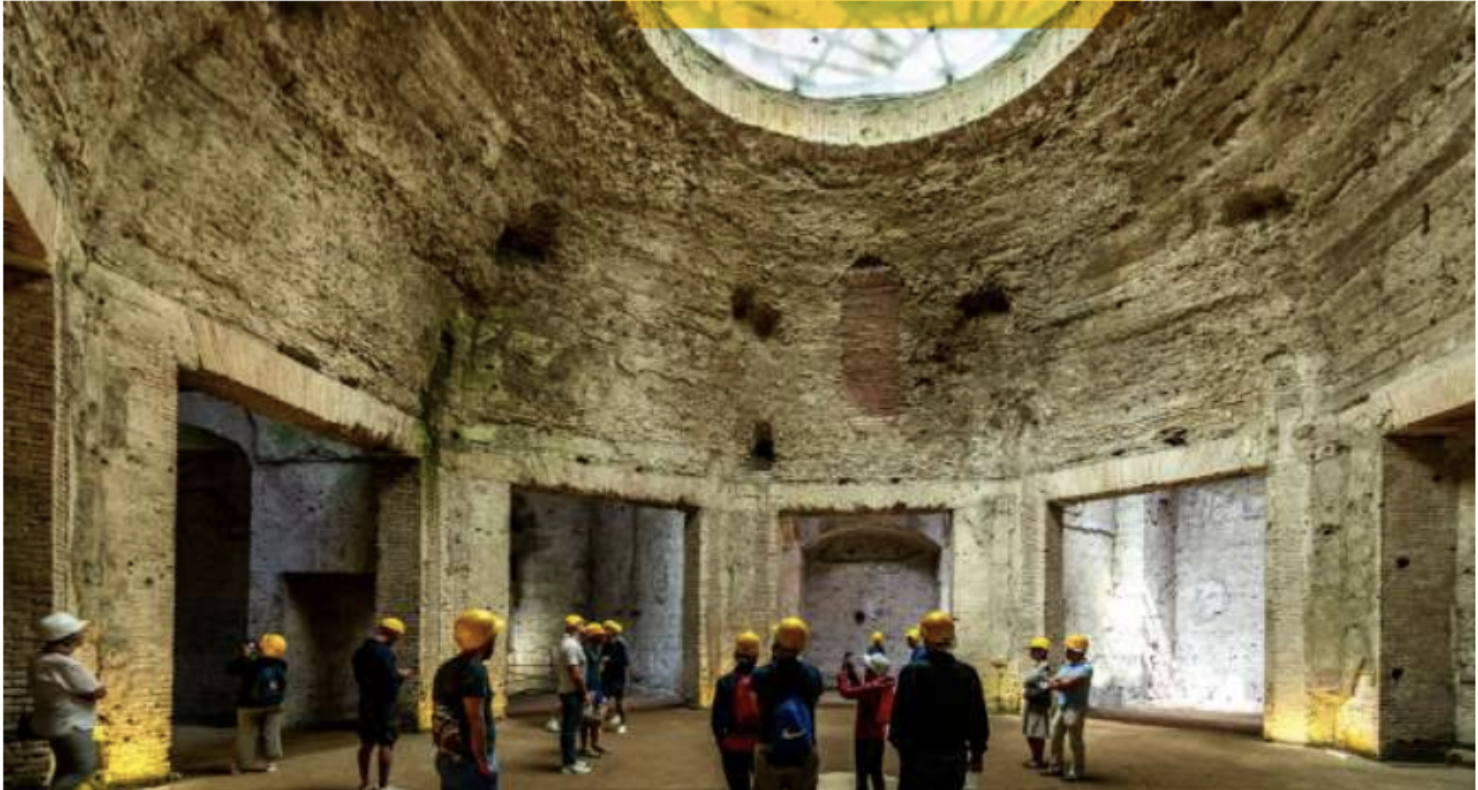

The Domus Aurea (64–68 AD)
The Domus Aurea (Latin, "Golden House") was a vast landscaped complex built by the Emperor Nero (famous for “The great fire of rome” 68) on the Oppian Hill in the heart of ancient Rome after the great fire in 64 AD had destroyed a large part of the city.
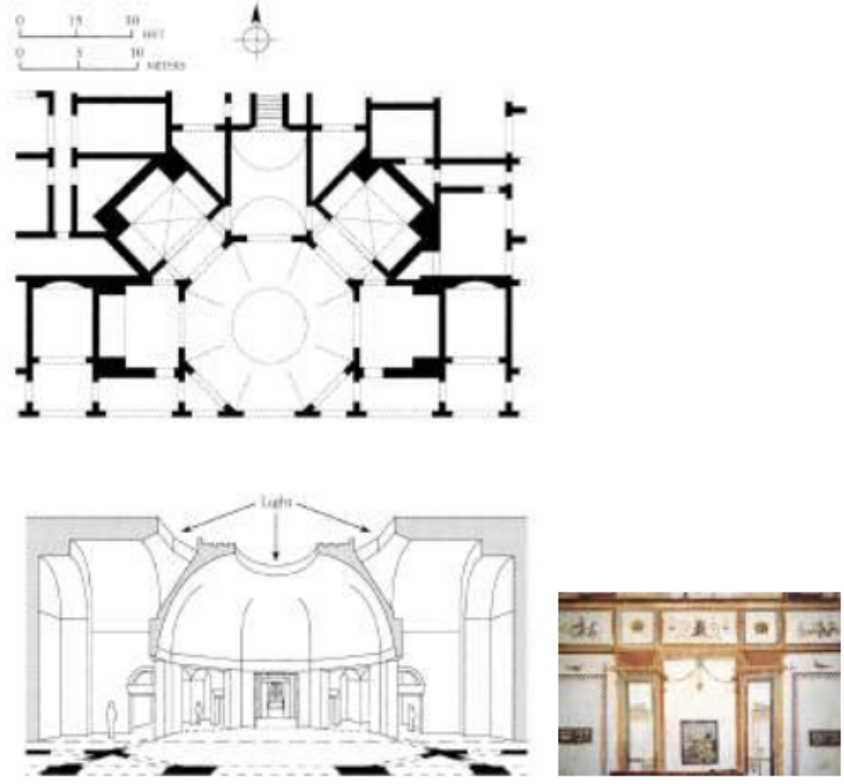
What is the name of the highlighted area?
What was named after these decorations?

Oculus- from latin means eye
Grotesque
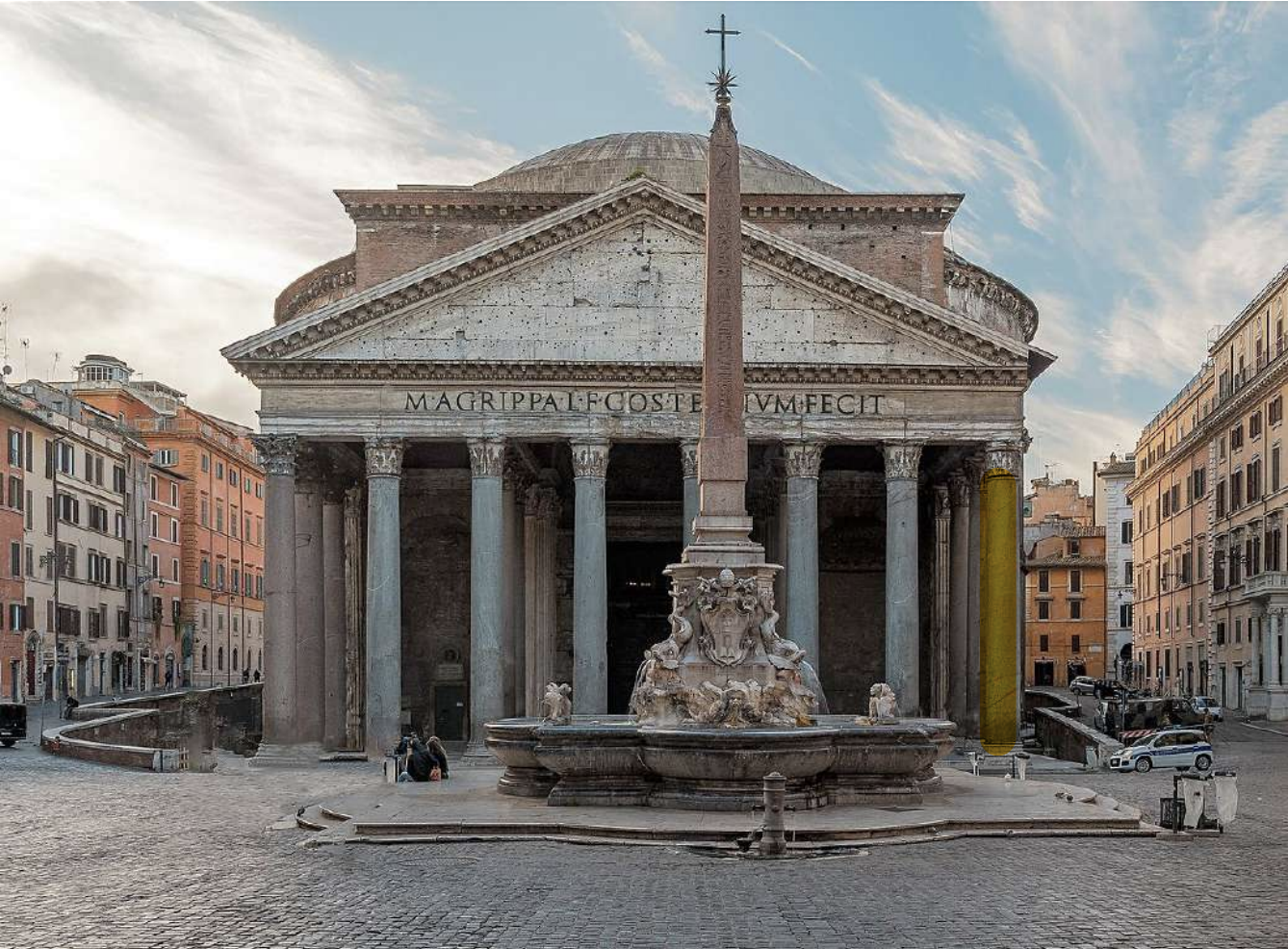

The Pantheon (113-125 AD), Rome, Italy
*The columns are called monolithic, therefore made out of stone
The Pantheon is a former Roman temple and, since AD 609, a Catholic church (Basilica Santa Maria ad Martyres or Basilica of St. Mary and the Martyrs) in Rome, Italy. It was built on the site of an earlier temple commissioned by Marcus Agrippa during the reign of Augustus (27 BC – AD 14), then after that burnt down, the present building was ordered by the emperor Hadrian and probably dedicated c. AD 126. Its date of construction is uncertain, because Hadrian chose not to inscribe the new temple but rather to retain the inscription of Agrippa's older temple.
The building is round in plan, except for the portico with large granite Corinthian columns (eight in the first rank and two groups of four behind) under a pediment. A rectangular vestibule links the porch to the rotunda, which is under a coffered concrete dome, with a central opening (oculus) to the sky. Almost two thousand years after it was built, the Pantheon's dome is still the world's largest unreinforced concrete dome. The height to the oculus and the diameter of the interior circle are the same, 43 metres (142 ft).
It is one of the best-preserved of all Ancient Roman buildings, in large part because it has been in continuous use throughout its history. Since the 7th century, it has been a church dedicated to St. Mary and the Martyrs (Latin: Sancta Maria ad Martyres), known as "Santa Maria Rotonda". The square in front of the Pantheon is called Piazza della Rotonda. The Pantheon is a state property, managed by Italy's Ministry of Cultural Heritage and Activities and Tourism through the Polo Museale del Lazio. In 2013, it was visited by over six million people.
The Pantheon's large circular domed cella, with a conventional temple portico front, was unique in Roman architecture. Nevertheless, it became a standard exemplar when classical styles were revived, and has been copied many times by later architects.
The Pantheon (Additional image 1)
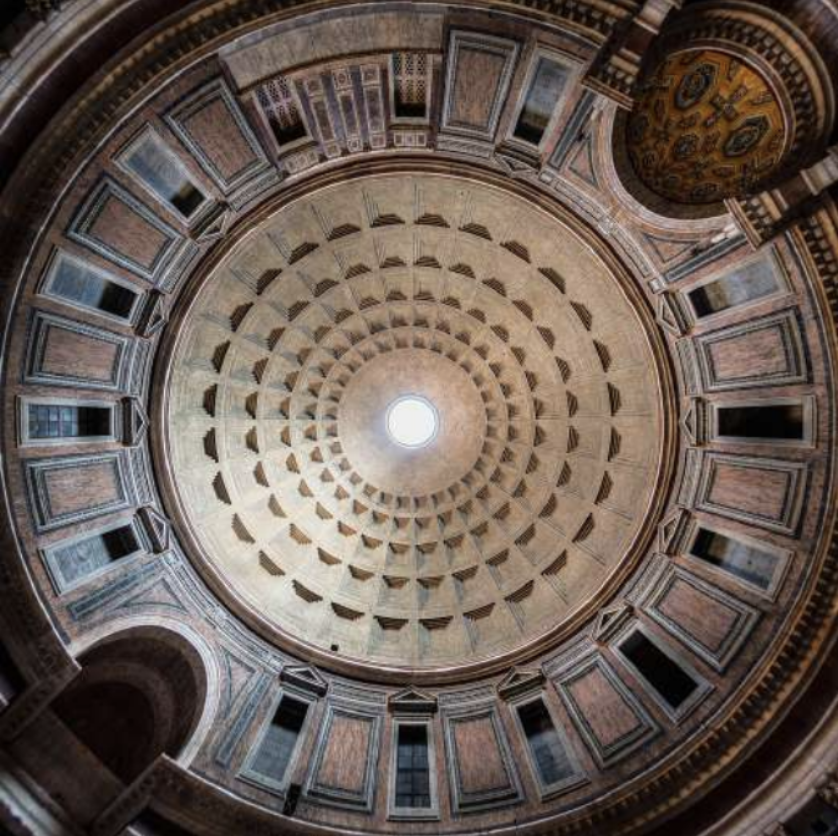

The whole in the middle is an oculus, while the indents around it are coffers that help with easy light access
The Pantheon (Additional image 2, the plan)
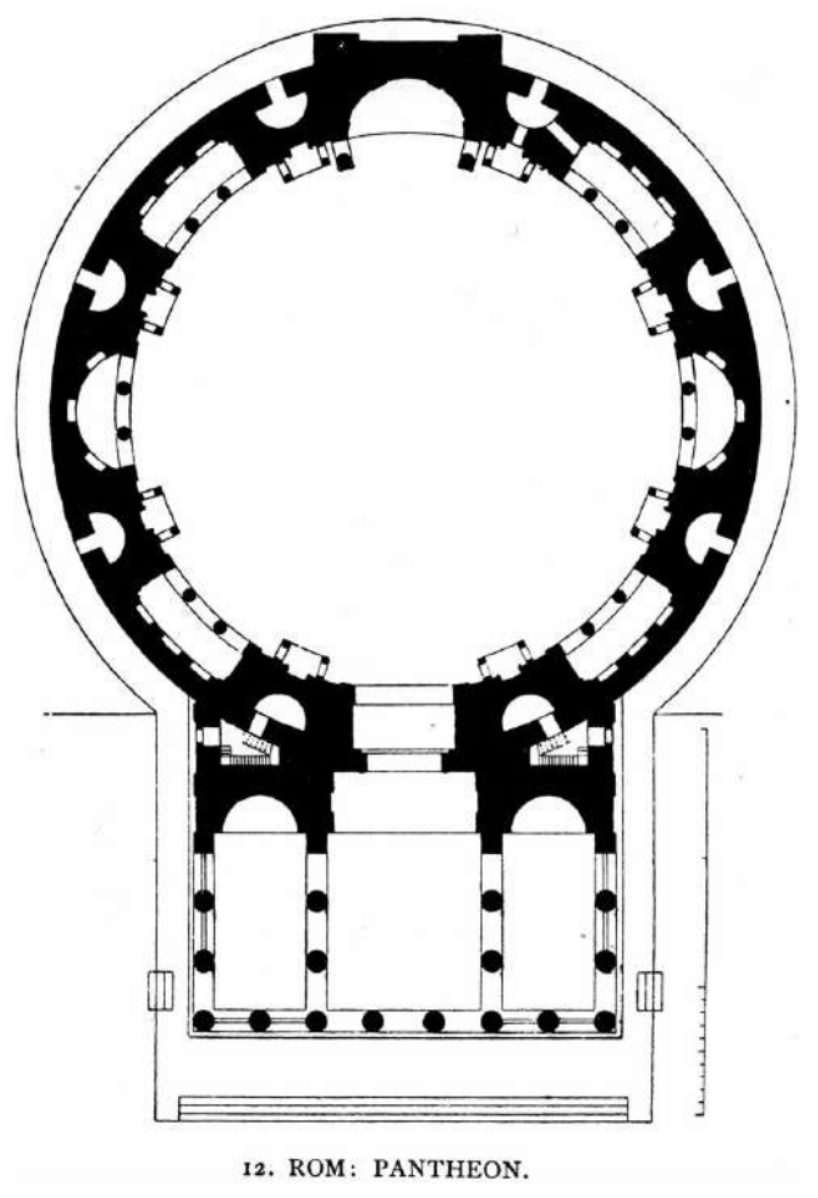
The Pantheon (Additional image 3, cross section)
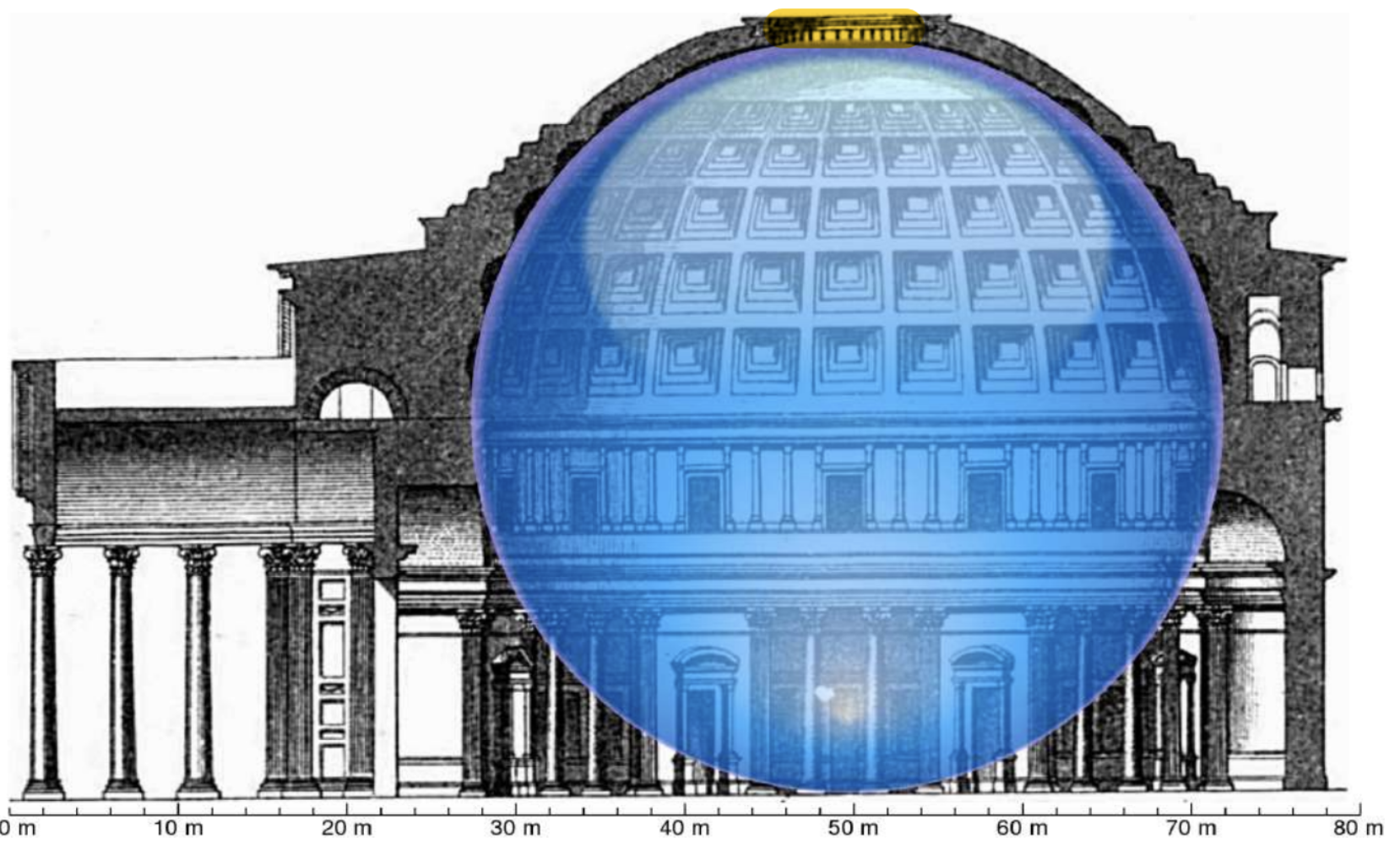
Cross-section of the Pantheon showing how a 43.3-metre diameter sphere fits under its dome.
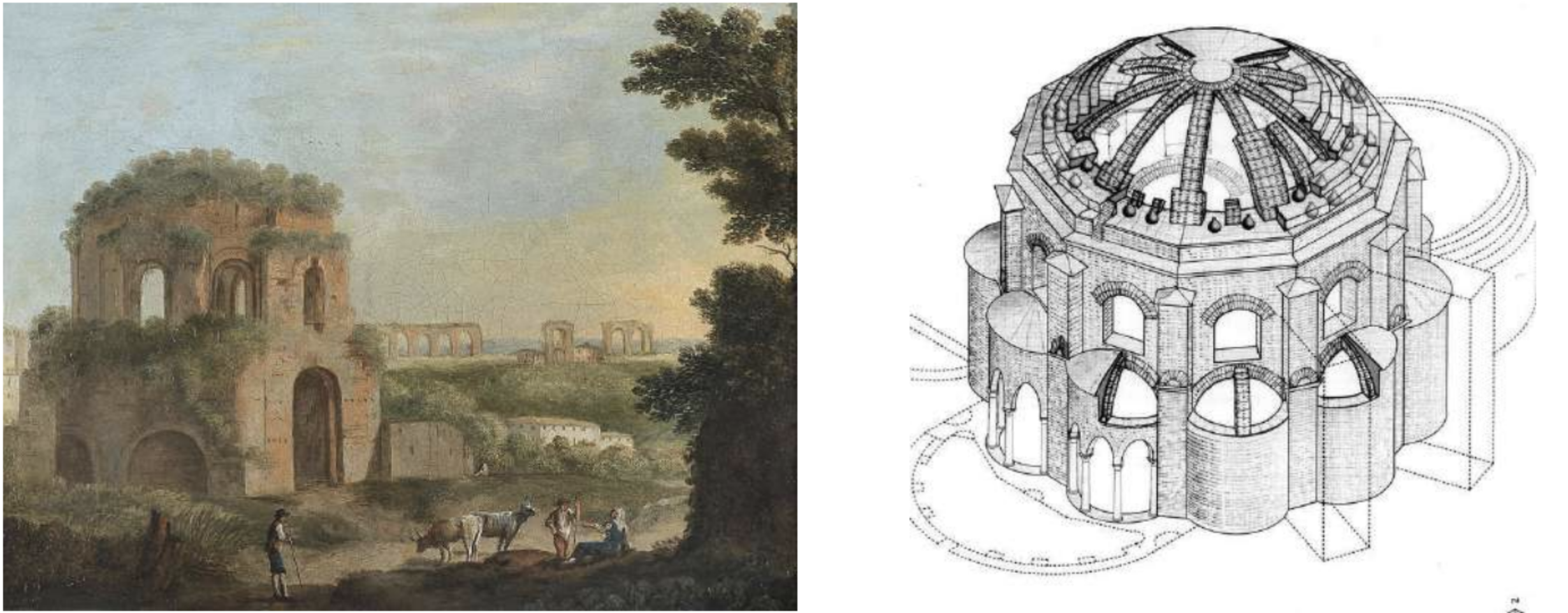
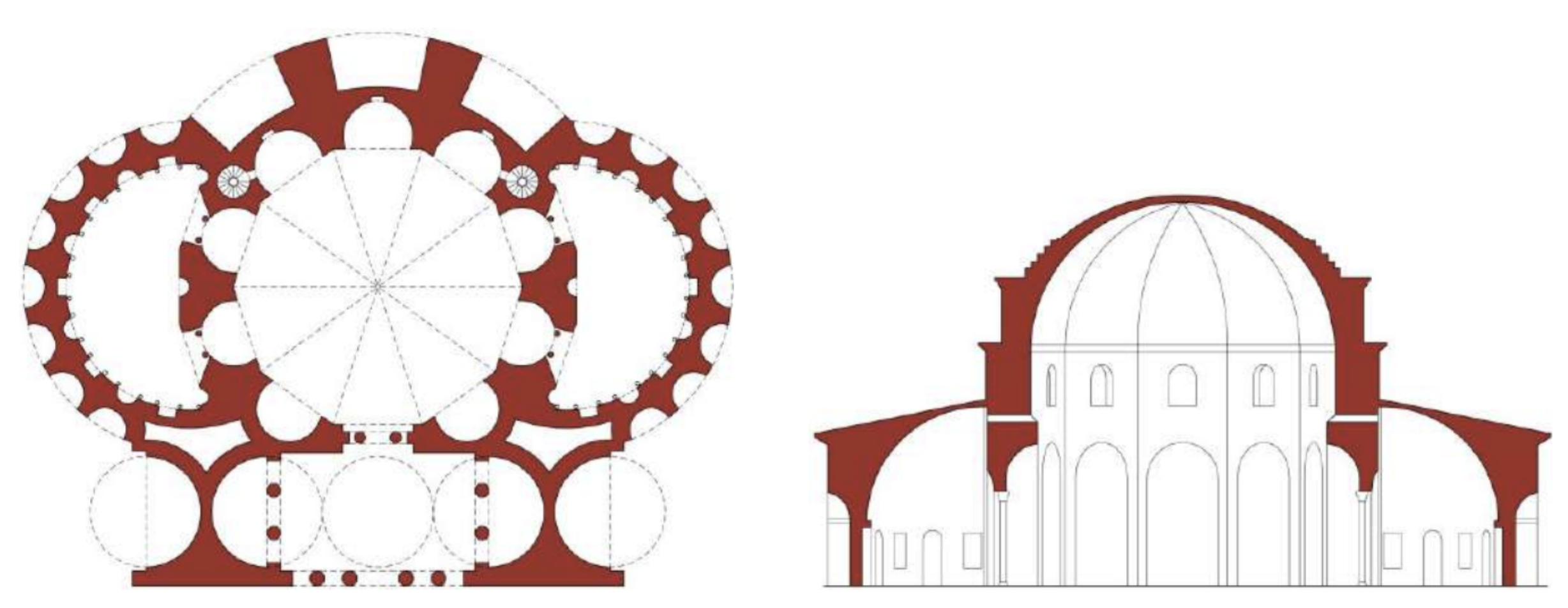
The Temple of Minerva Medica (4th Century)
The Temple of Minerva Medica is a ruined nymphaeum of Imperial Rome which dates to the 4th century CE. It is located between the Via Labicana and Aurelian Walls and just inside the line of the Anio Vetus. Once part of the Horti Liciniani on the Esquiline Hill, it now faces the modern Via Giolitti. It was once thought to be the temple to Minerva Medica ("Minerva the Doctor") mentioned by Cicero and other sources.
The decagonal structure in opus latericium is relatively well preserved, though the full dome collapsed in 1828. It is surrounded on three sides with other chambers which were added at a later date. There is no mention of it in ancient literature or inscriptions.
The structure represents a transition in Roman secular architecture between the octagonal dining room of the Domus Aurea and the dome of the Pantheon, and the architecture of nearby Byzantine churches. The diameter of the hall was approximately 24 meters, and the height was 33 meters. Inside the nymphaeum, there are nine niches beside the entrance, and above these niches are ten corresponding round-arched windows. Both the interior and exterior walls were once covered with marble.
2. Forum
Forums were squares surrounded by stoa and public buildings where people could come together. The Forum was an adaptation of the "Agora" of the Ancient Greeks. The Stoa were covered, columned galleries located next to a street or agora in Ancient Greece. They were used as administrative centers and trade hubs, and were open to the public. In Roman architecture, the "FORUM" functioned in a similar manner. The distinctive feature of the forum was its open architectural definition and its generally rectangular shape.
The Roman Forum (Forum Romanum)
"Forum Romanum" (Roman Forum), was considered to be center of the Roman World, aptly called the "Caput Mundi". As it developed slowly over several centuries, it is not as precise as the subsequently planned forums. Starting from the time of Julius Caesar, additional forums were built to the north and east of the original forum. Trade, business, prostitution, worship and the administration of justice took place here. It was the heart of the city. Following the Collapse of the Western Roman Empire, much of it was buried underground due to stratification, and was excavated in the 1930s to reach its current state today.
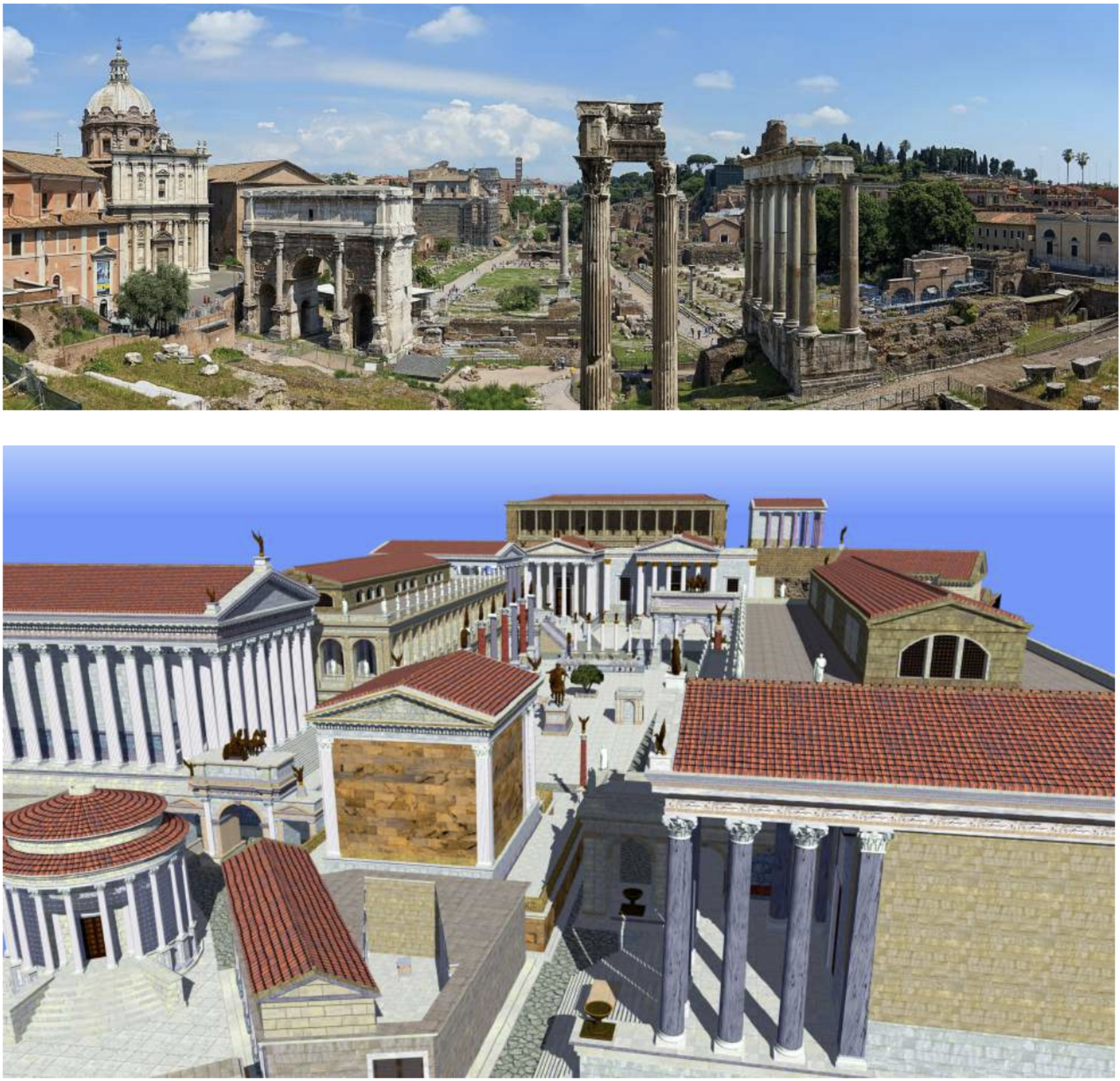

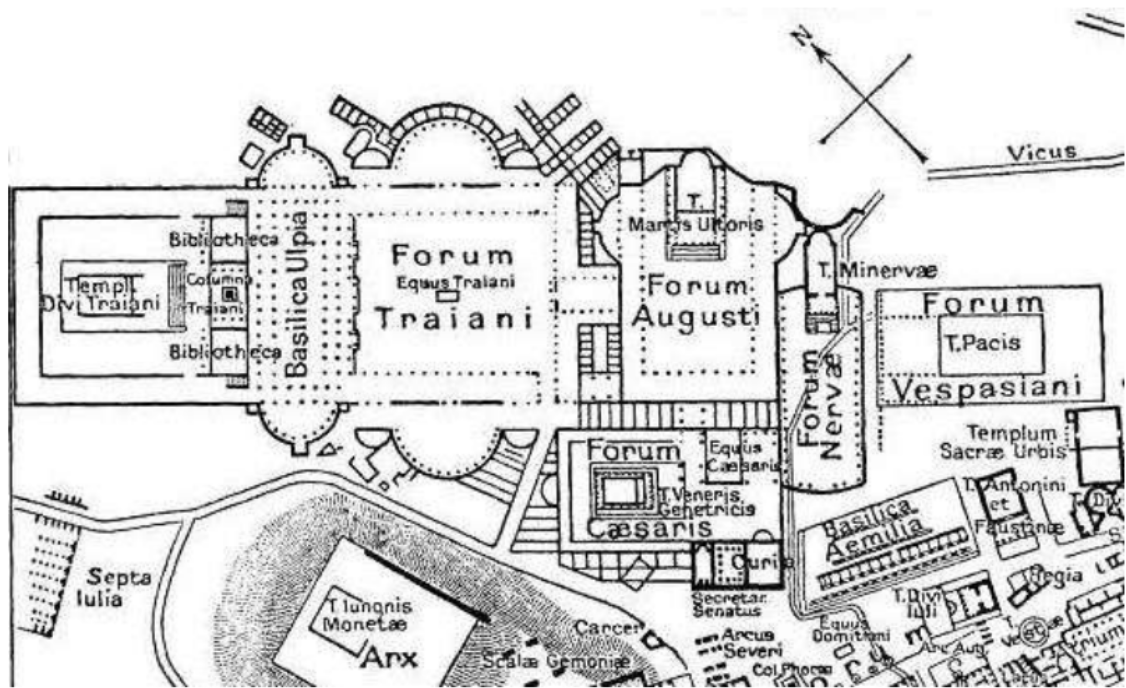
Unlike the agora in the Greek city, there were more than one forum in the Roman city. Roman rulers built forums with their own names to make their own propaganda and decorated them with statues, tombs and columns. In this context, these are the most well-known forums established by rulers:
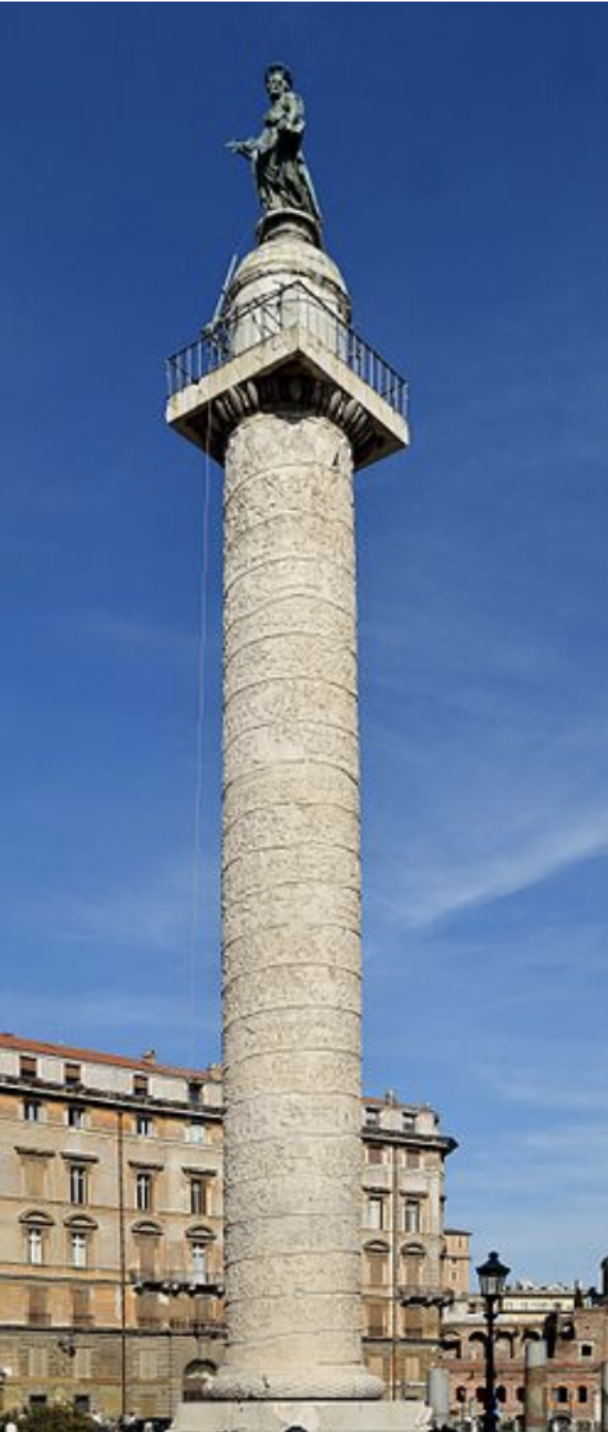

Trajan's Column (113 AD)
The monument was built by Trajan in his Forum (106-113), where it's still standing today. It is a marble column in the Roman Doric order. The outer face of the column is covered with a spiral band of decoration. There are low relief scenes depicting the two campaigns of Trajan in Dacia.

The image above is a high relief sculpture (there are and low relief sculptures)
3. Theatre
In Greek architecture, there is a theater in every city (polis); and their backs are against the hillside. Because mortar has not been discovered yet, arches and domes do not exist in Greek architecture. In addition, the necessity of resting its back on the slope brought the necessity of the plan to be a semicircle. The Greek theater was for education. In Rome, the theater was for entertainment. In Roman architecture, on the other hand, theaters do not have to rest their backs on a slope. They can be inside the city and in a semicircular or oval shape. While the column systems of Greek temples played an important structural role, Roman temples used these column forms in a decorative sense. Even three different column arrangements can be seen in a single building. A prominent example of this is the Colosseum.
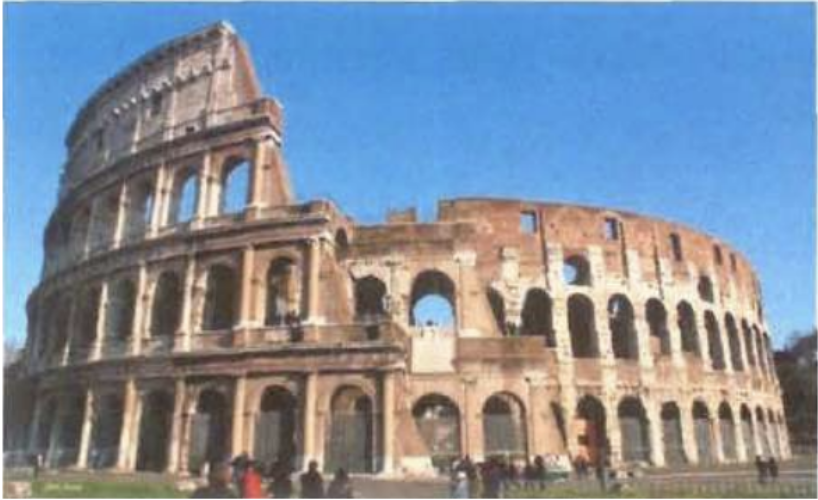

Colosseum (85 AD), the roman amphitheatre - The Colosseum is an ancient theater, formed by the union of two semicircles. When viewed from the outside, it is seen that the floors are decorated with doric, ionic, and corinthian orders.
*Roman theatres are round and free standing.
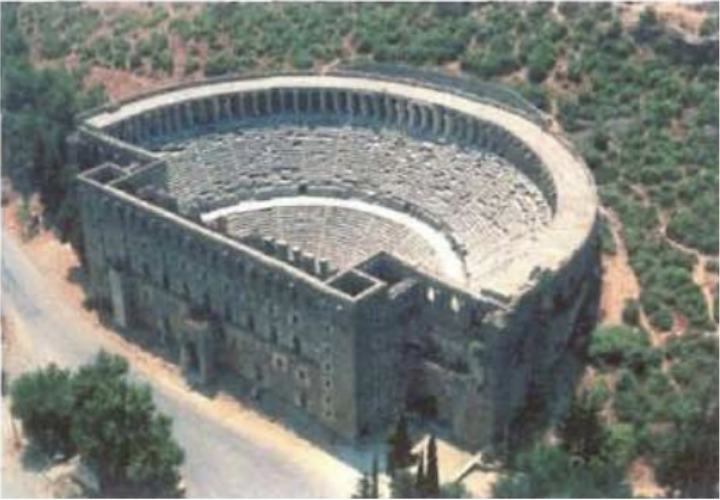

Aspendos - Greek theatre
Greek theatre are almost always semicircle and resting on a hill
4. Roman Bath
In Rome, baths were places where people gathered, chatted and ate. Underfloor heating kept the baths warm. Channels are heated with water. Below is a section of the Baths of Diocletian.
p.s. Ancient greeks didn’t have public baths
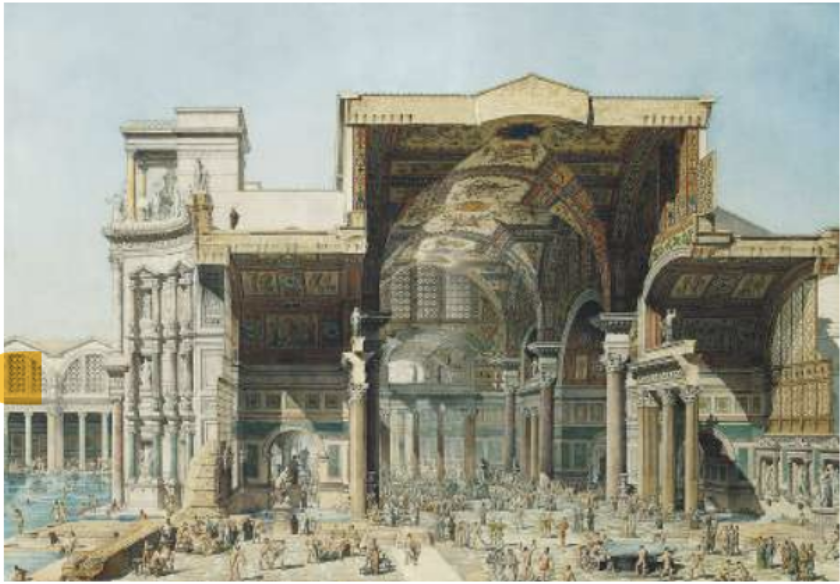

A Section of the Baths of Diocletian, Rome, Italy
The area in yellow shows windows known as the Diocletian windows or Thermal windows
5. Triumphal arch (just knowing the typology can be enough)
The oldest surviving Roman triumphal arches date from the Imperial Period from the 1st century BC. During the earlier period of the Old Roman Republic, arches to honor commanders have been documented, but not a single one survives today. Triumphal arches were built all over the former Roman imperial territories and their remains exerted an important influence on Renaissance Architecture.
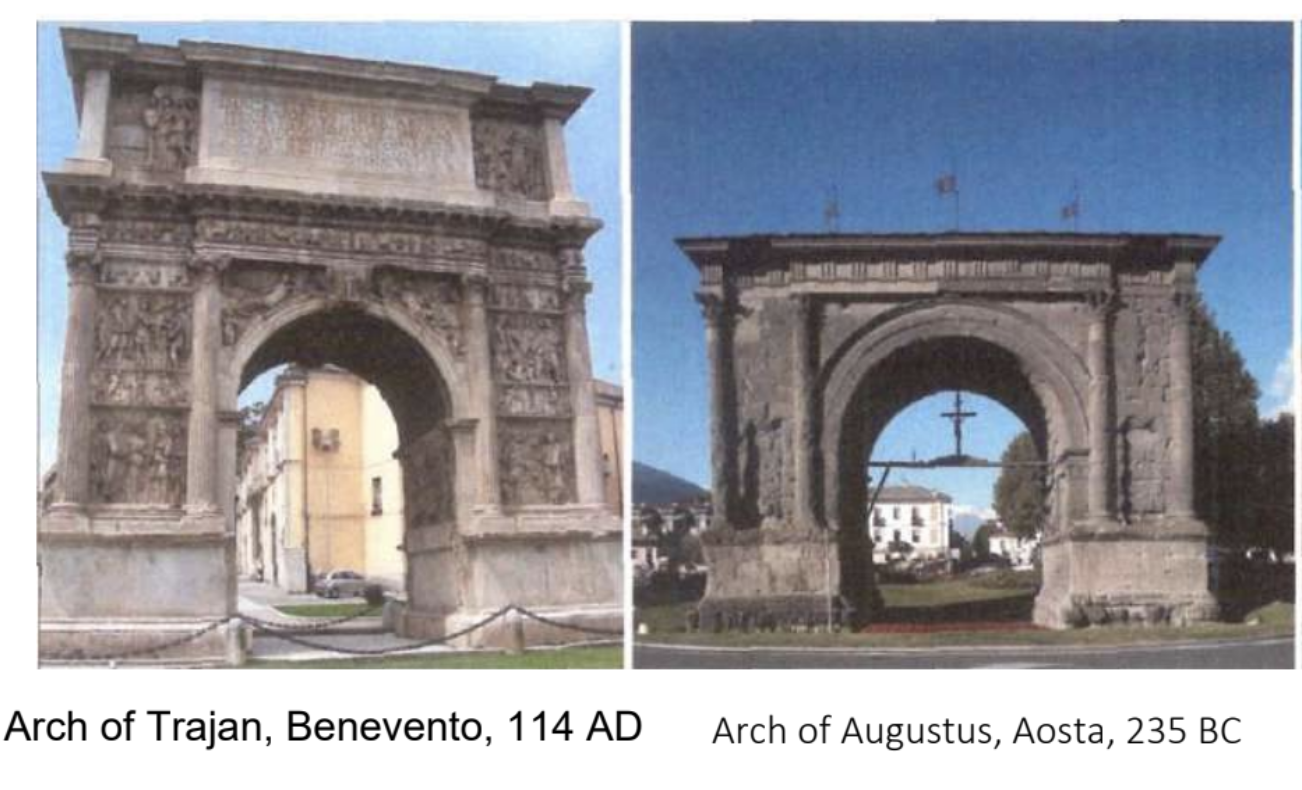
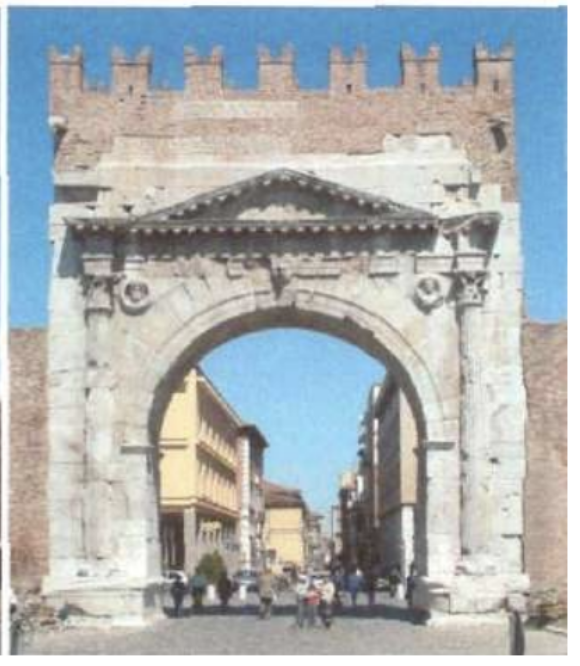


Arch of Augustus, Rimini, 27 BC
Inspired Tempio Malatestiano by Alberti + one of the first arches built
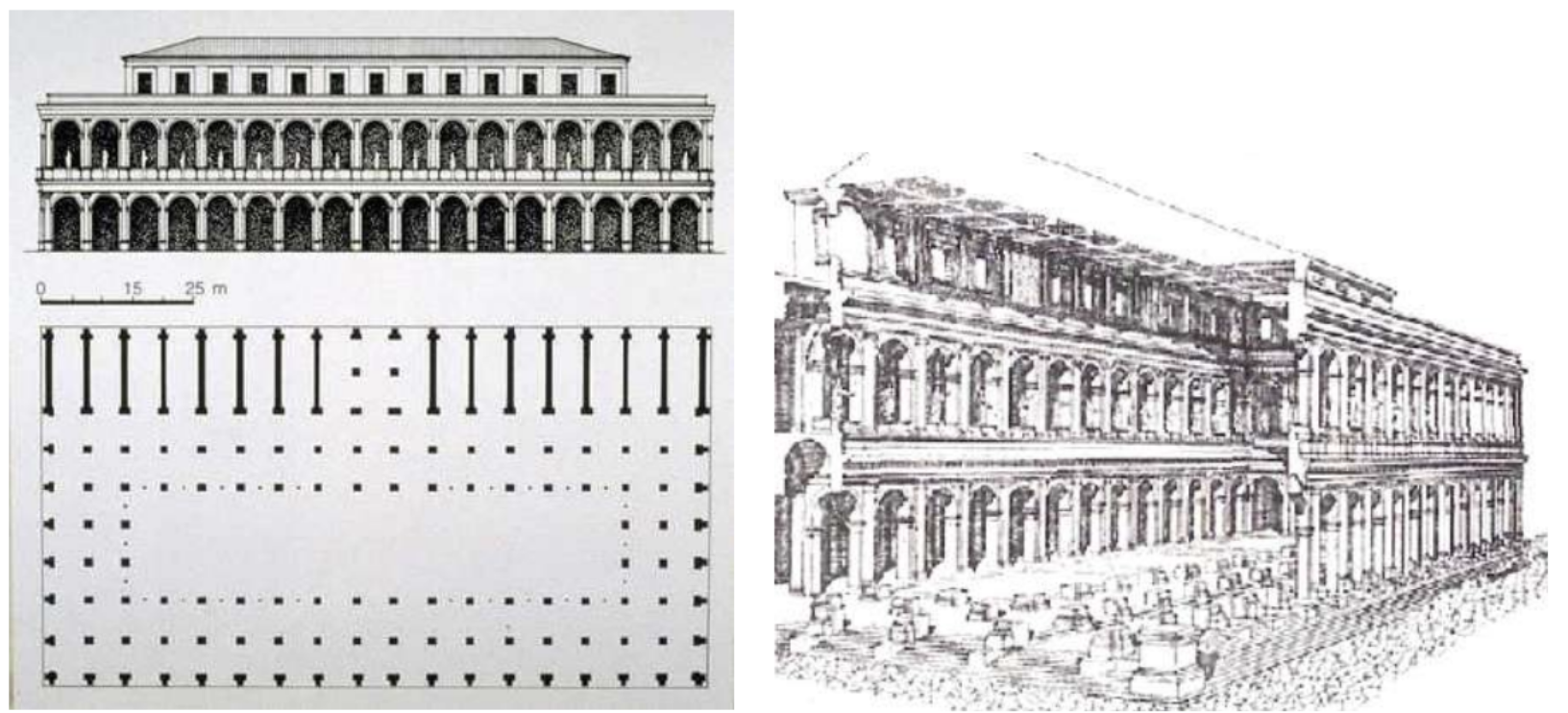
6. Basilica
long lasting building typology
The Basilica Julia, an ancient Roman structure, served as a model for early Christian basilicas. Its spacious layout and architectural features, such as a central nave and side aisles, influenced the design of early Christian churches. This archetype facilitated the transition of architectural styles from pagan to Christian worship spaces.
*
Early Christian and Byzantine Architecture (Architecture of Ravenna)
Early Christian Places of Worship before the Edict of Milan
The first 300 years Christianity was illegal. Romans believed in their own multiple gods, and were open to religions with multiple gods. Therefore no churches could be built. The art that emerged between the 1st century AD, when Christianity began to spread secretly, and the 4th century AD, when it was accepted as the official religion by various countries, is called Early Christian Art. Early Christian art is related to Roman art and emerged in the lands dominated by the Romans (such as Anatolia, Greece, Egypt, Italy).
In 313, Emperor Constantine legalized christianity in his Edict of Milan. In the years when Christianity emerged and spread secretly, the first Christians fleeing from the oppression of the pagan Romans built underground cities in various regions (Anatolia, Rome). After the 4th century, catacombs were replaced by churches and turned into places of religious visitation.
Another important type of architecture built by the early Christians was underground cities. The fact that people felt the need to hide from the oppression of the pagan Romans in the early periods of Christianity was also effective in this regard. The influence of the Cappadocia region on the development of early Christian art is very important. The paintings and frescoes on the walls of many monasteries, churches, chapels and houses built in this region were the pioneers of Byzantine painting.
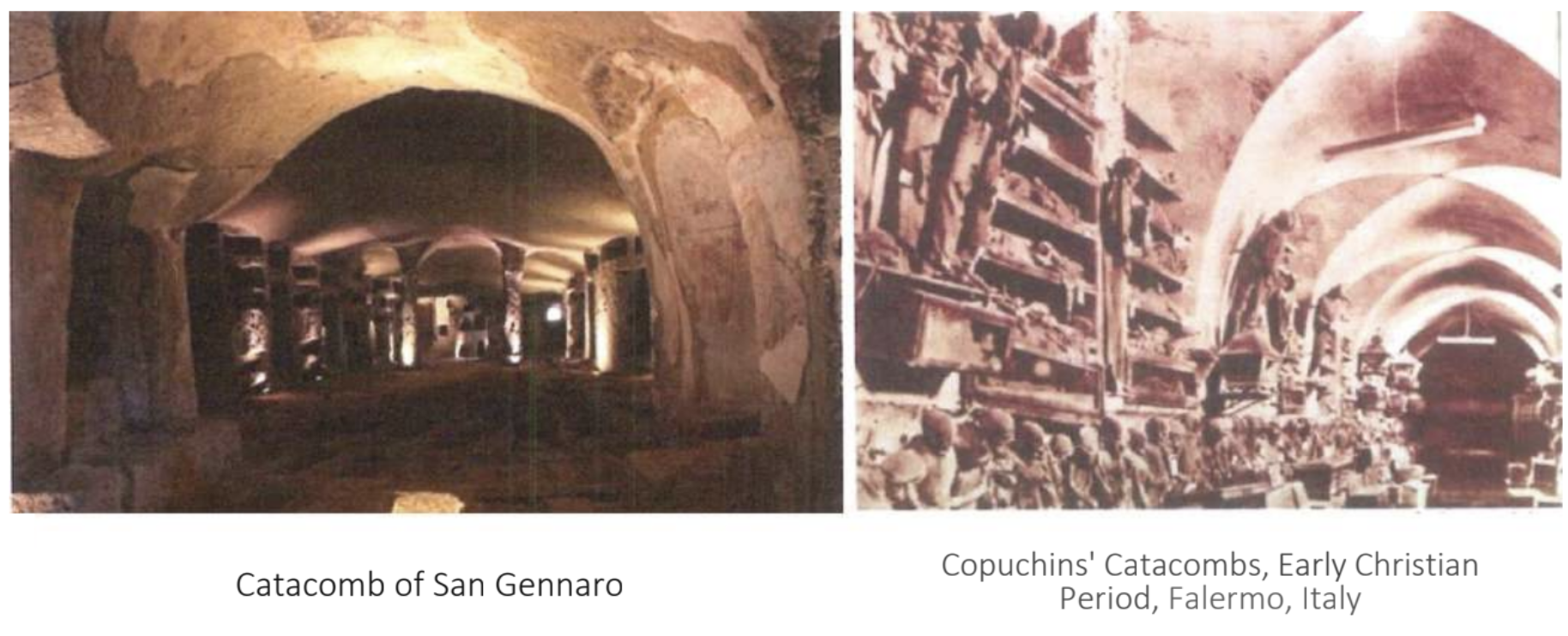

Early Christian Architecture after the Official Adoption of Christianity
As soon as Christianity became the official religion of the empire, the problem arose of designing a building type that was functionally and symbolically suitable for public worship. It was clear that the old temple form could not be used. Filled with symbols of worship of pagan gods, they were also not designed to hold large crowds of people. Constantine and the religious authorities turned to non-religious public buildings. The type of building they chose was the basilica. Basilicas were originally designed for public gatherings. It was a positive symbol of just government based on earthly justice.
Basilica Type 1: Rectangular Basilicas
This is the first type of basilica, and it is this basilical structure that Western Rome mostly used. Christian basilicas are large rectangular halls, longer than they are wide. On either side, there are narrower and lower chambers separated from the central chamber by colonnades. The important hall in the center, where the congregation gathers, is called the central nave, while the lower side bays are called the side naves or wings. In most basilicas, the central nave is covered high with wooden beams, while the side naves are flattened. At the end of the nave, there is a semicircular space called the apse, where the leader of the meeting or ritual stands. In front of the apse is the choir area. The semicircular apse is covered with a stone half dome.
Basilica Type 2: Central Plan Basilicas
This is the main church type of Byzantine architecture. Consequently, this church form, while mostly found in Constantinople (today's Istanbul), influenced the architectural forms in reconquered Italy (Gothic War 535-554), especially in the Ravenna region.
(Architecture of Ravenna)
Basilica Type 3: Domed Basilicas
By VI century, basilicas were covered with vaults or domes instead of wooden roofs. The most magnificent example of domed basilicas is "Hagia Sophia" in Istanbul. This work is based on a rectangular plan, which is crowned by a dome 55 meters above the ground.
Basilica Type 4: Cruciform (Greek Cross) Basilicas
The second church type of Byzantine architecture is the "cruciform" ones. These churches, built starting from the VIIIth century, have a square plan. In the center of the square, a dome sits on four pillars. The weight of the dome is supported from four sides by a barrel arch with axes perpendicular to each other. As this dome and arch system is reflected on the floor, a cross (Greek cross) is formed with four arms equal to each other. Apart from the main dome in the center, domes were placed on the four arms and the number was increased to five. There is an apse in the east and a narthex in the west. A good example of the Greek Cross Plan is the St Mark's Basilica in Venice, which was based on the plan of the Church of Holy Apostles in Constantinople.
BUILDING TYPOLOGIES IN THE WESTERN ROMAN EMPIRE
The Rectangular and Central Basilica
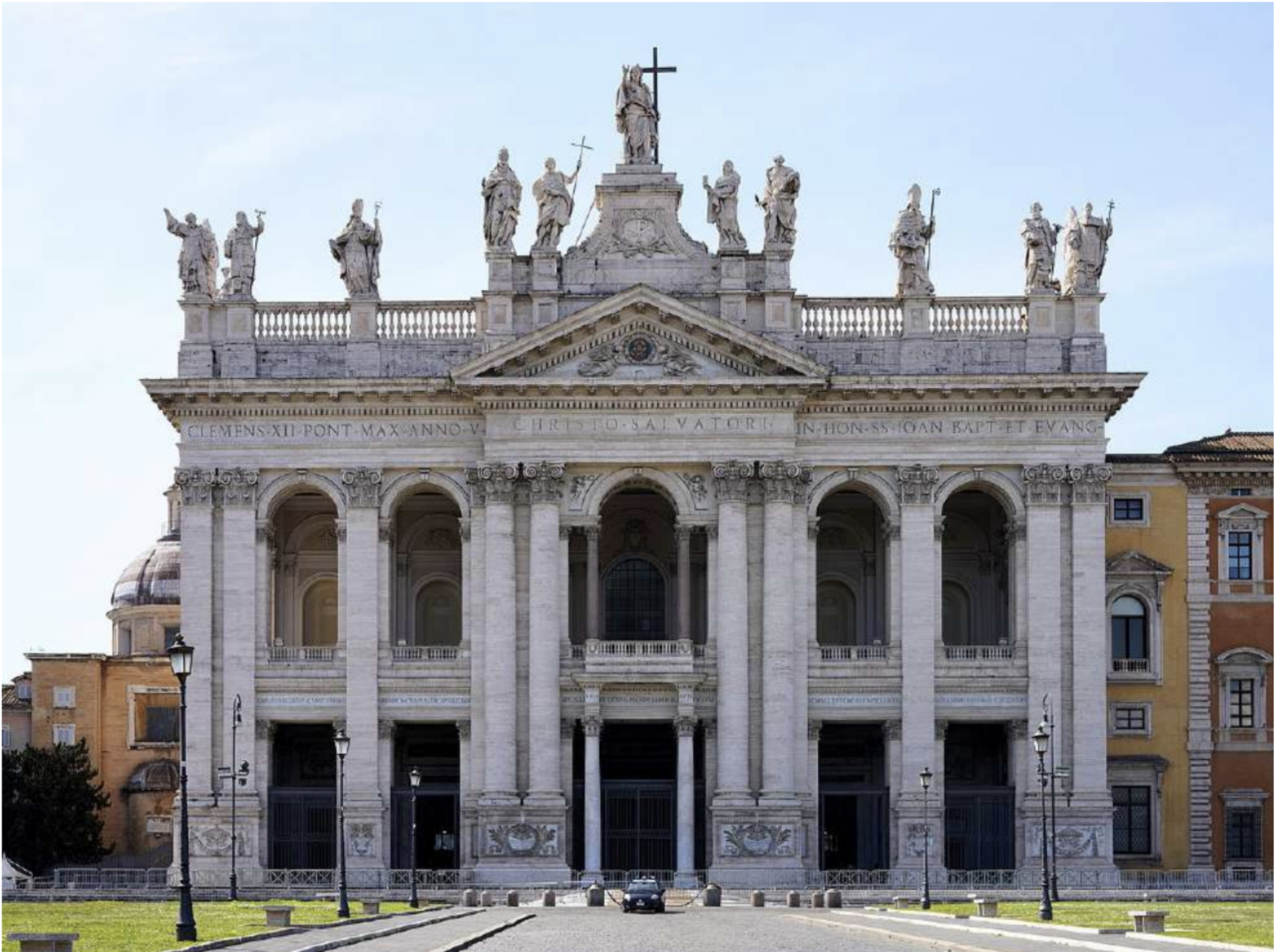

The Lateran Basilica (324 AD)
The cathedral of Rome and the second largest of the four Major Papal Basilicas. Unfortunately, it was rebuilt in the 17th and 18th century, so little remains of the Constantinian building. The facade was rebuilt in Baroque style in 1735.
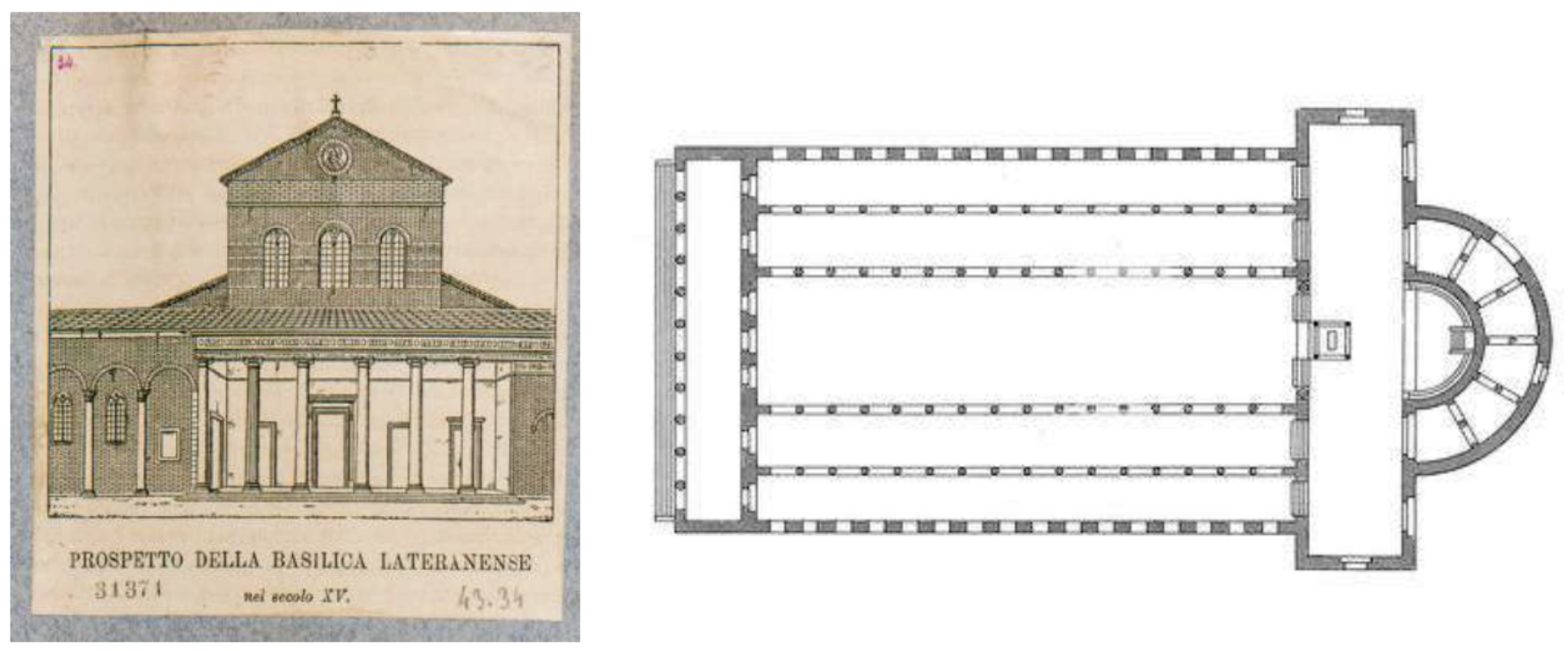
Basilica plane, typical of how early churches looked
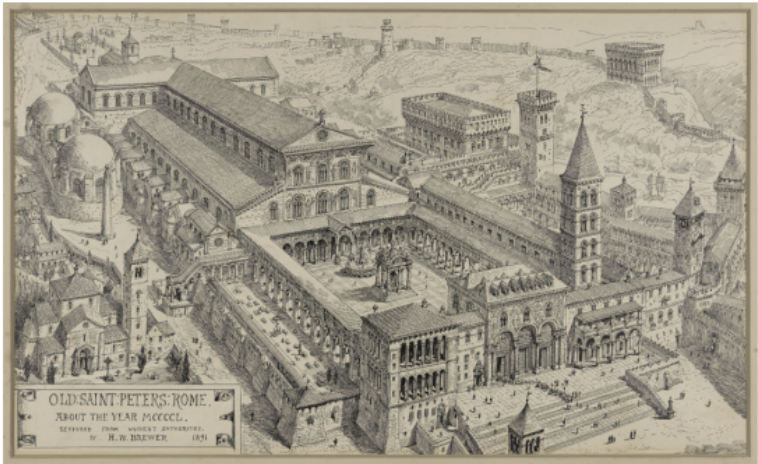

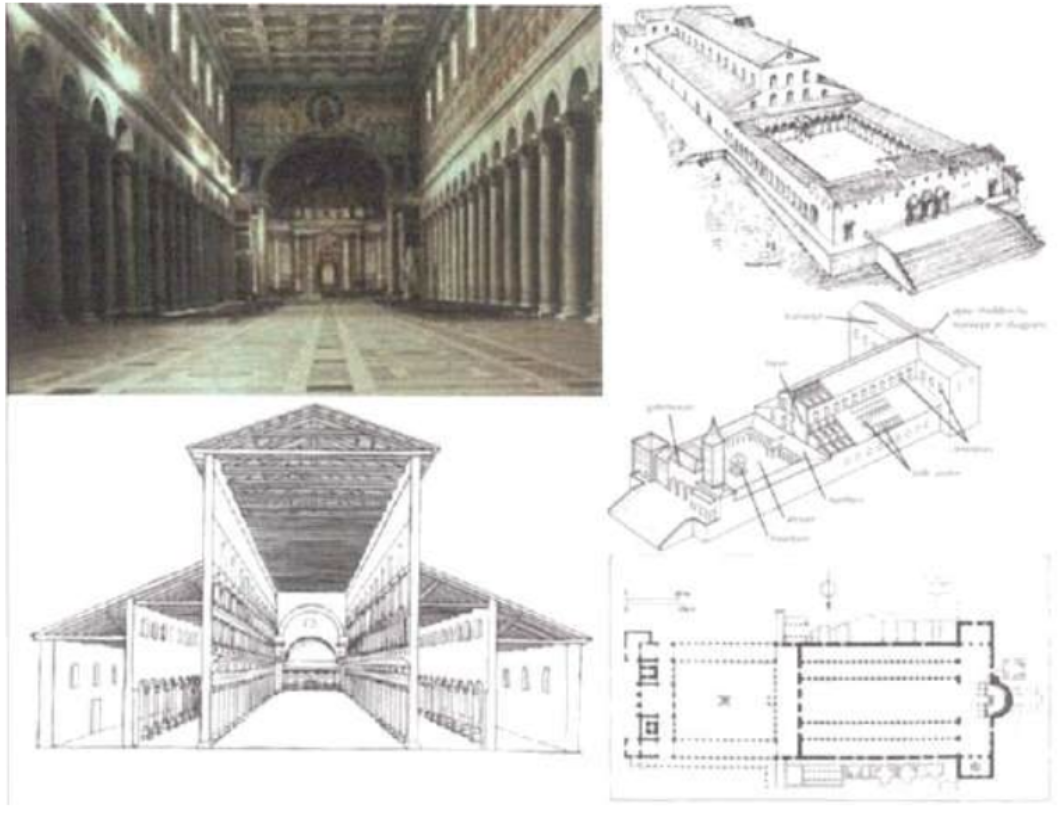
Saint Peter's Basilica (OLD) (324 AD)
Another Constantinian church in Rome, this was one of the largest basilicas in Rome. It was built by Constantine at the spot where the martyr Saint Peter is believed to be buried. It was later rebuilt between 1506-1620 to take its current form today.
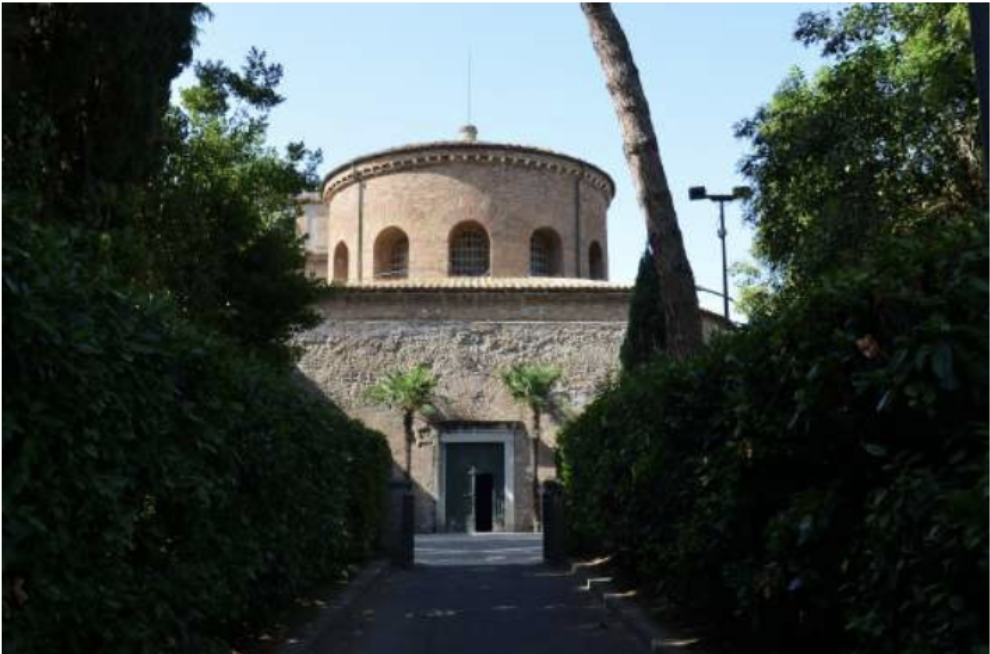

Santa Costanza, 360 AD, Rome, Italy
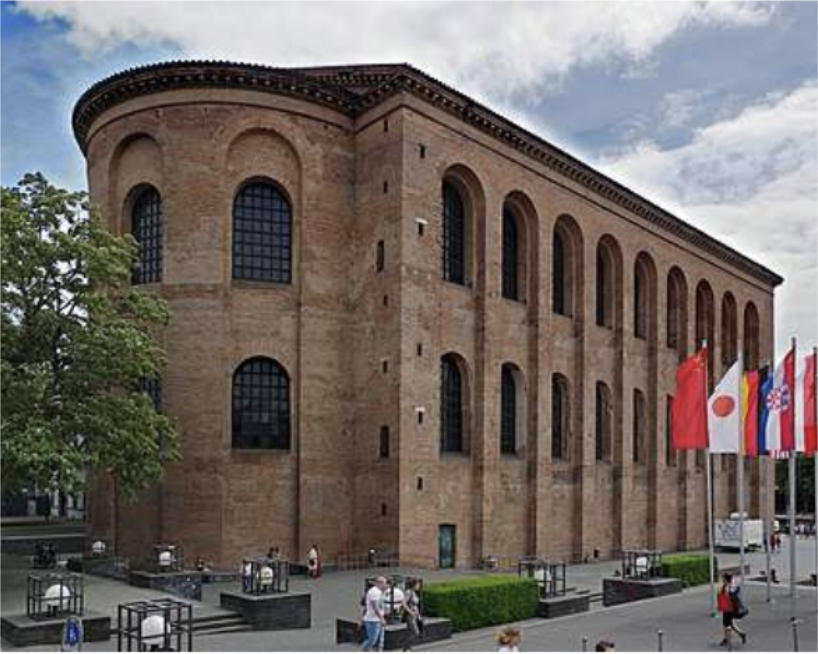

Aula Palatina, largest extant hall from antiquity, Trier, Germany, 300-310 AD
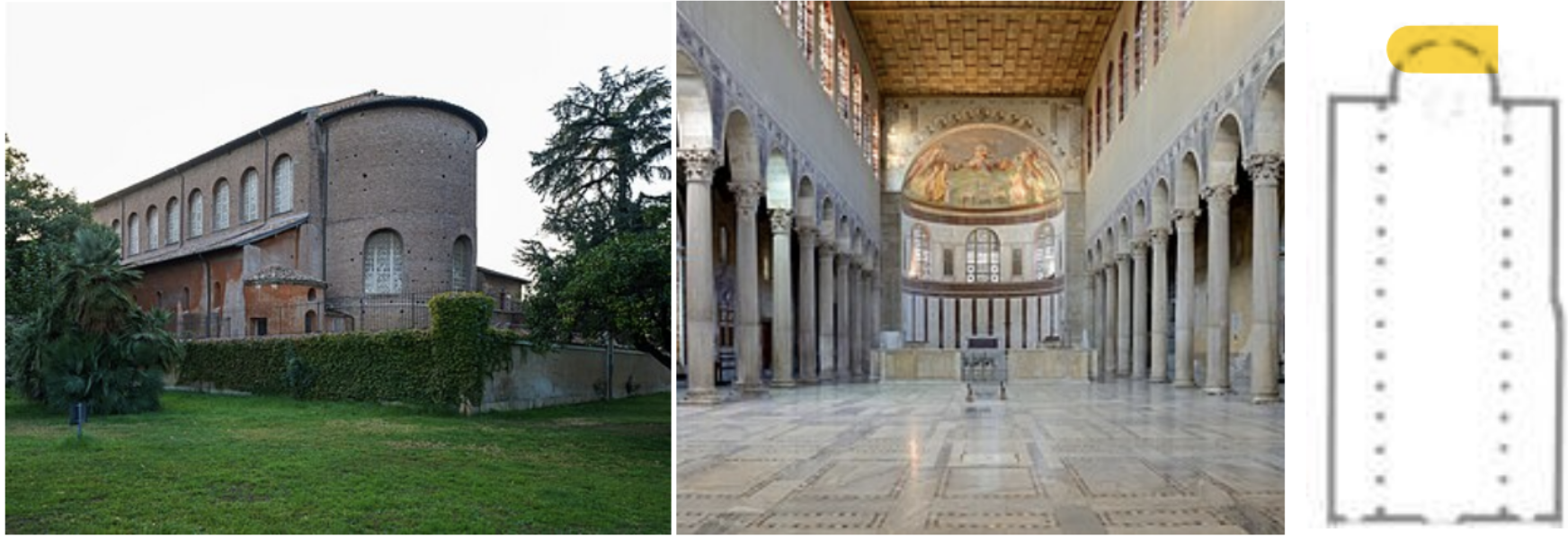

Santa Sabina, 432 AD, Rome, Italy
*Main idea is big rectangular space and semicircle
Architecture of Ravenna (500 - 550)
In Western Rome, centrally planned, domed and cruciform basilicas originate from Eastern Roman (Byzantine) influence. The main reason for the focus of early church architecture in Italian cities other than Istanbul (Constantinople) is that these regions were under intense Eastern Roman (Byzantine) influence in political and cultural terms. We see examples of this architectural structure especially in Ravenna, Rome and Milan in Early Christian Architecture.
RAVENNA
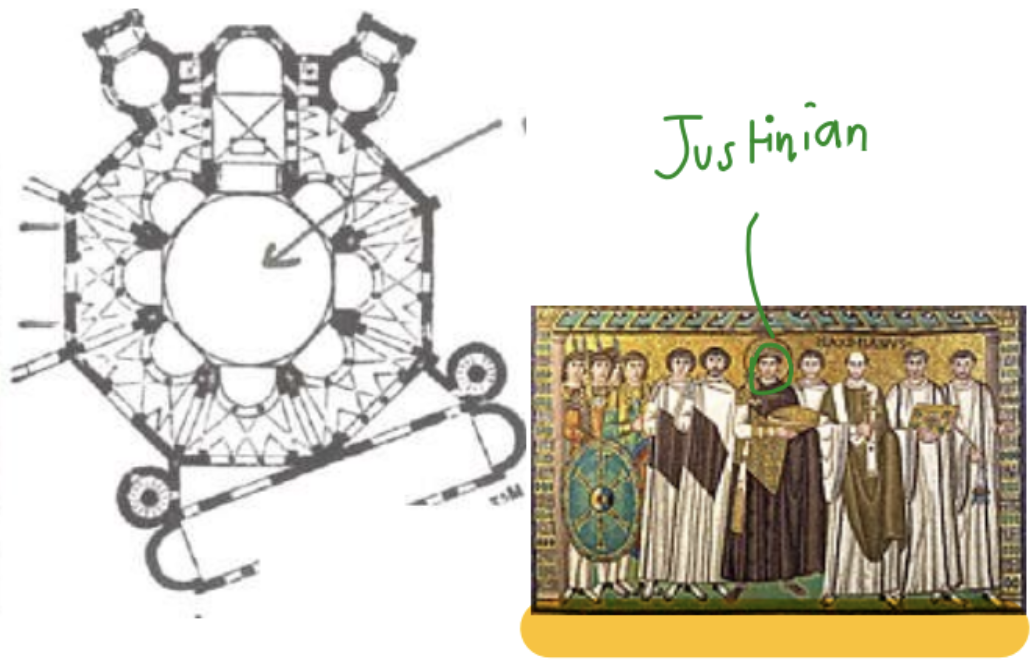
Early Christian monuments in the city and the mosaics in these monuments date back to the 5th and 6th centuries AD. In short, Ravenna was the architectural center of Western Rome between the 4th-6th centuries. At a time when the Western world was in disarray and the various monarchies were rapidly disintegrating, Eastern Rome was still dependent on the idea of empire. Ravenna, as the seat of the Eastern Roman governor, became a center of Eastern Roman (Byzantine) art, and as such the most prestigious place and representative of the peninsula. It experienced its heyday under Constantine in the 4th century and Justinian in the 6th century. Ravenna was especially important for Justinian, who reconquered the West, partically. It is possible to see the effects of Byzantine art primarily in the plans. We see the Byzantine central plan applications in the mausoleums, chapels or churches in Ravenna.
In Ravenna there was a mix of eastern and western traditions after the war in rome, and six buildings from that period need to be known. Which ones are they?
1.Mausoleum of Galla Placidia (430 AD)
2.Arian Baptistery (500 AD)
3.Basilica of Sant'Apollinare Nuovo (500 AD)
4.Mausoleum of Theodoric (520 AD)
5.Basilica of San Vitale (548 AD)!!!
6.Basilica of Sant'Apollinare in Classe (549 AD)
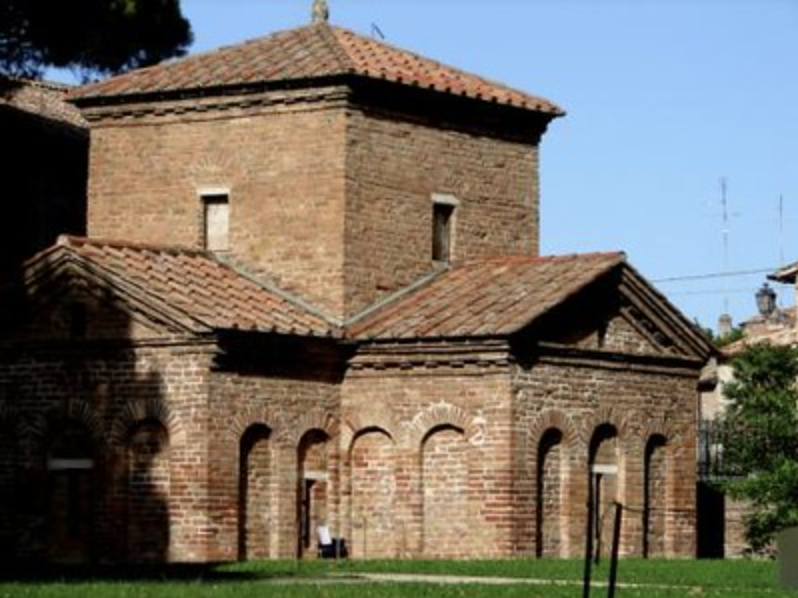

Mausoleum of Galla Placidia (430 AD)
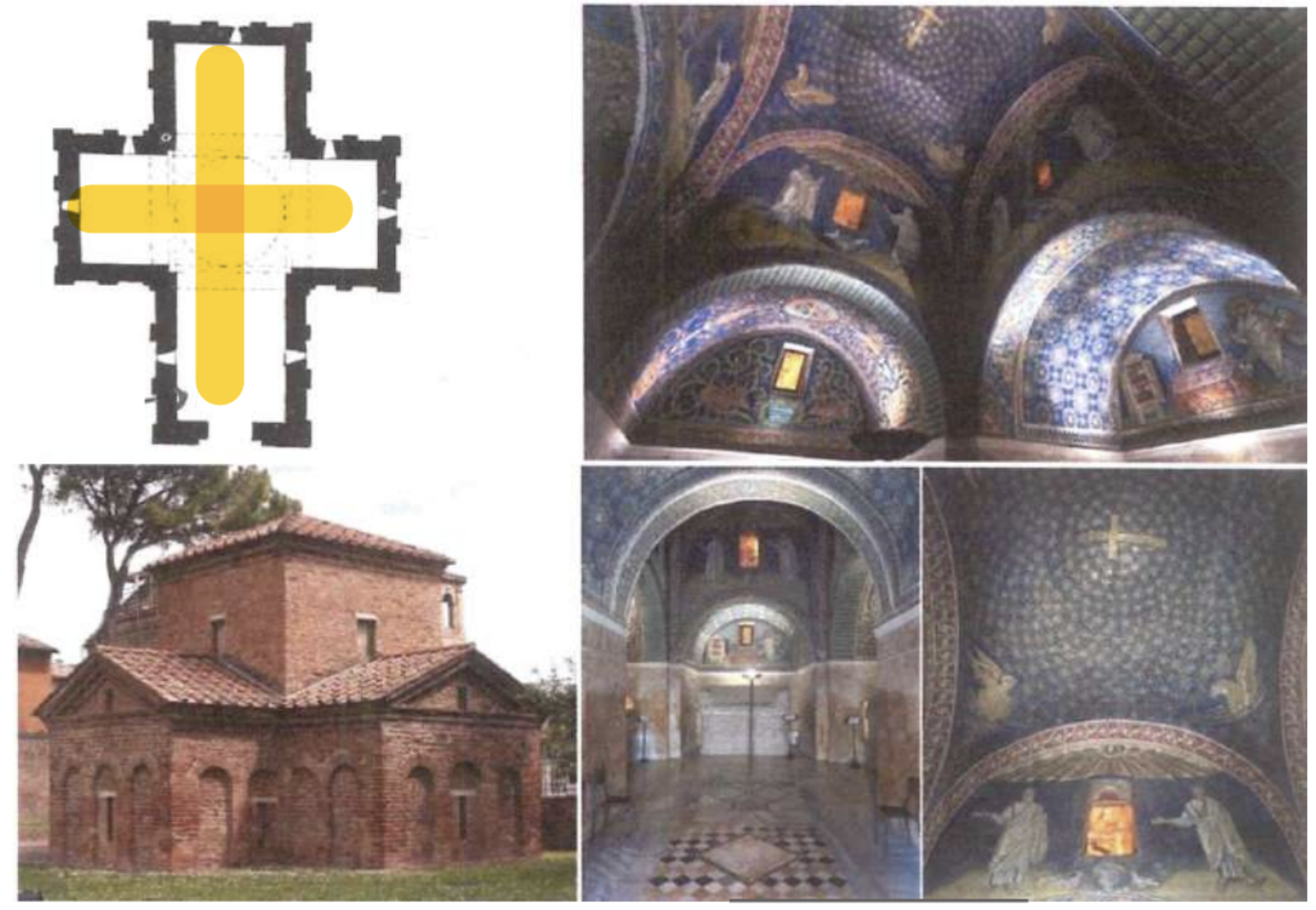

The plane (in yellow) is made like a greek cross
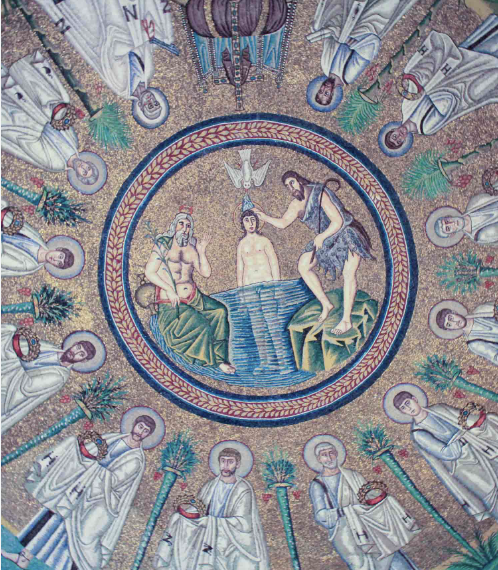


Arian Baptistery (500 AD)
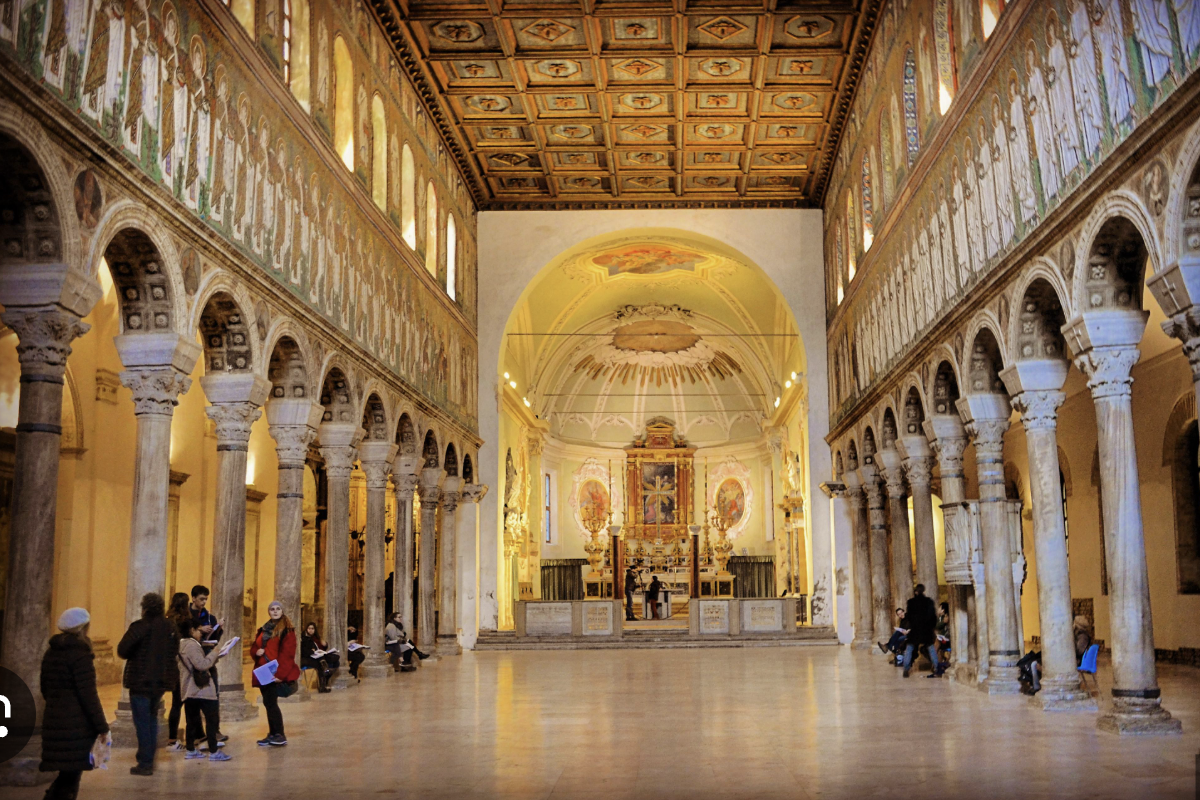


Basilica of Sant'Apollinare Nuovo (500 AD)

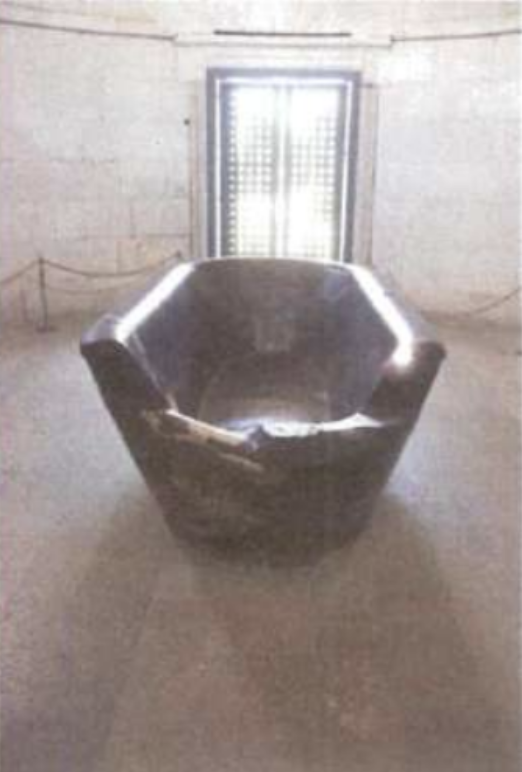
Mausoleum of Theodoric (520 AD)
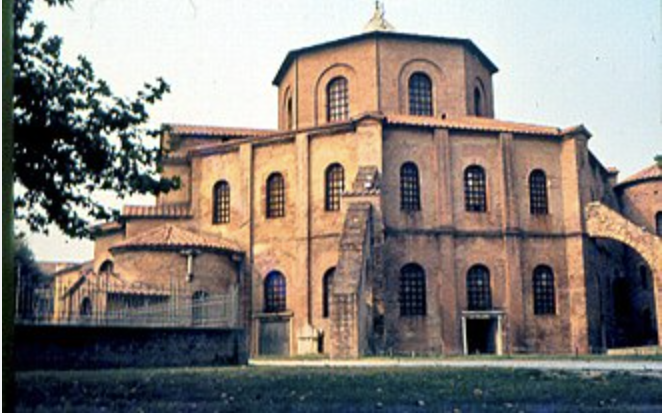


Basilica of San Vitale (548 AD)!!!
Most Important building as marks a switch from rectangular to multi sided church architecture. It new shape inspired many others. Justinian was the one who ordered to built it
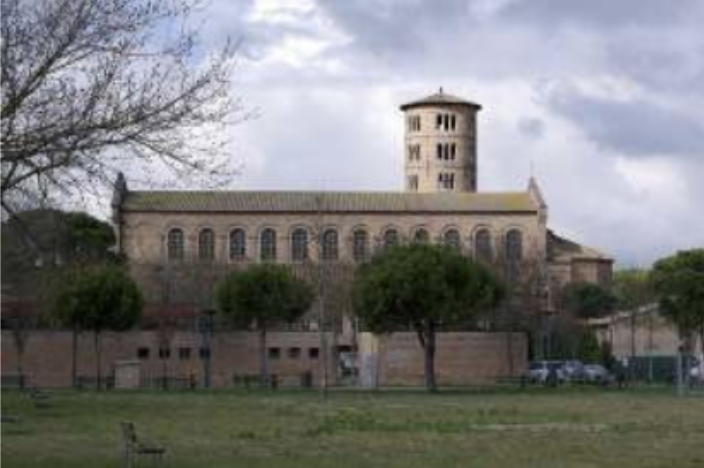
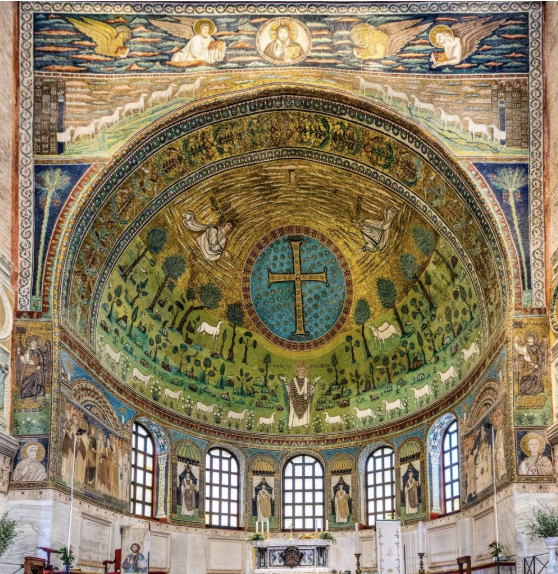


Basilica of Sant'Apollinare in Classe (549 AD)
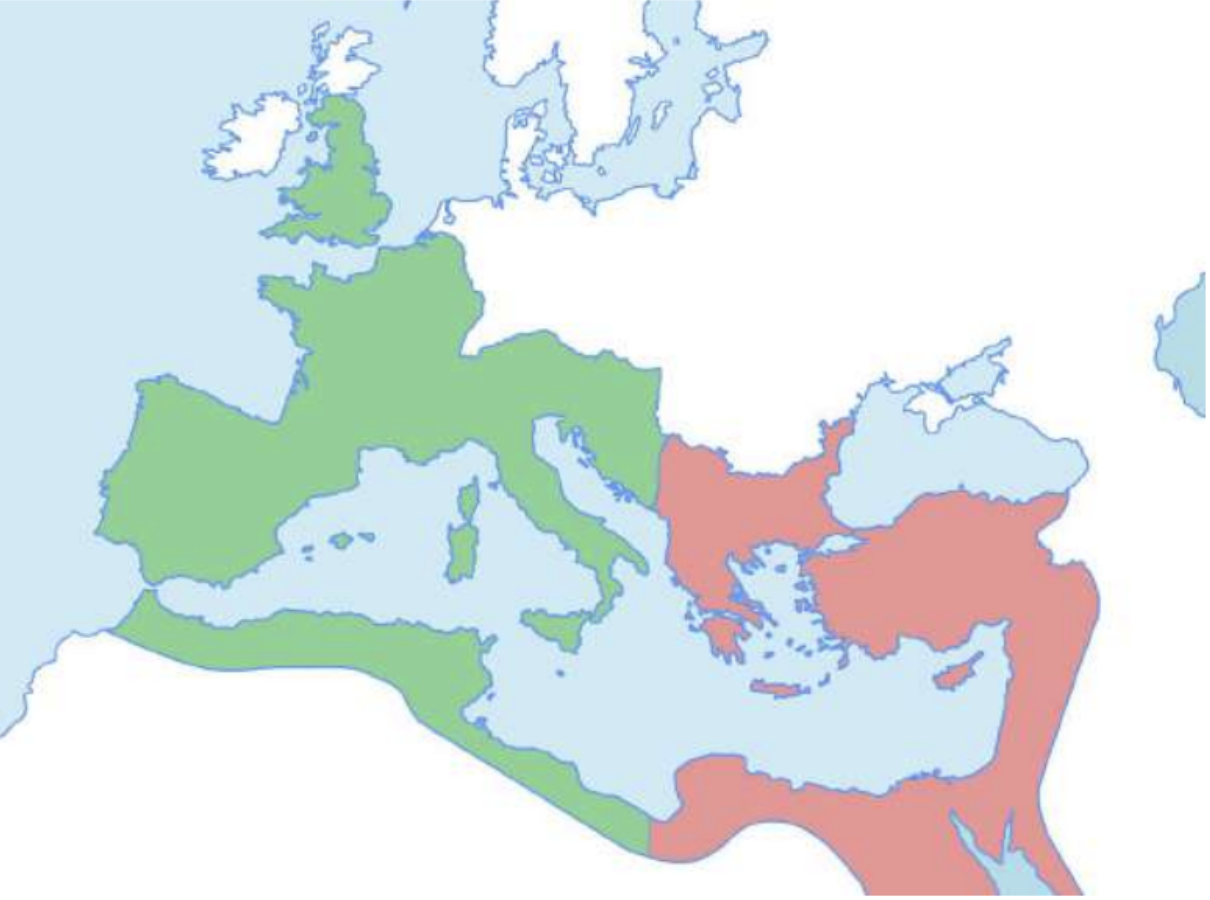
Roman East and West, 395 AD
Rome a whole country at first (green+red) in 117
395 it split into 2 (east and west)
Western Rome didi’t have the best time and within 100 years it collapsed (green) in 436
Then the easy reconquered the west and while doing so they made Ravenna the new administrative centre of Italy
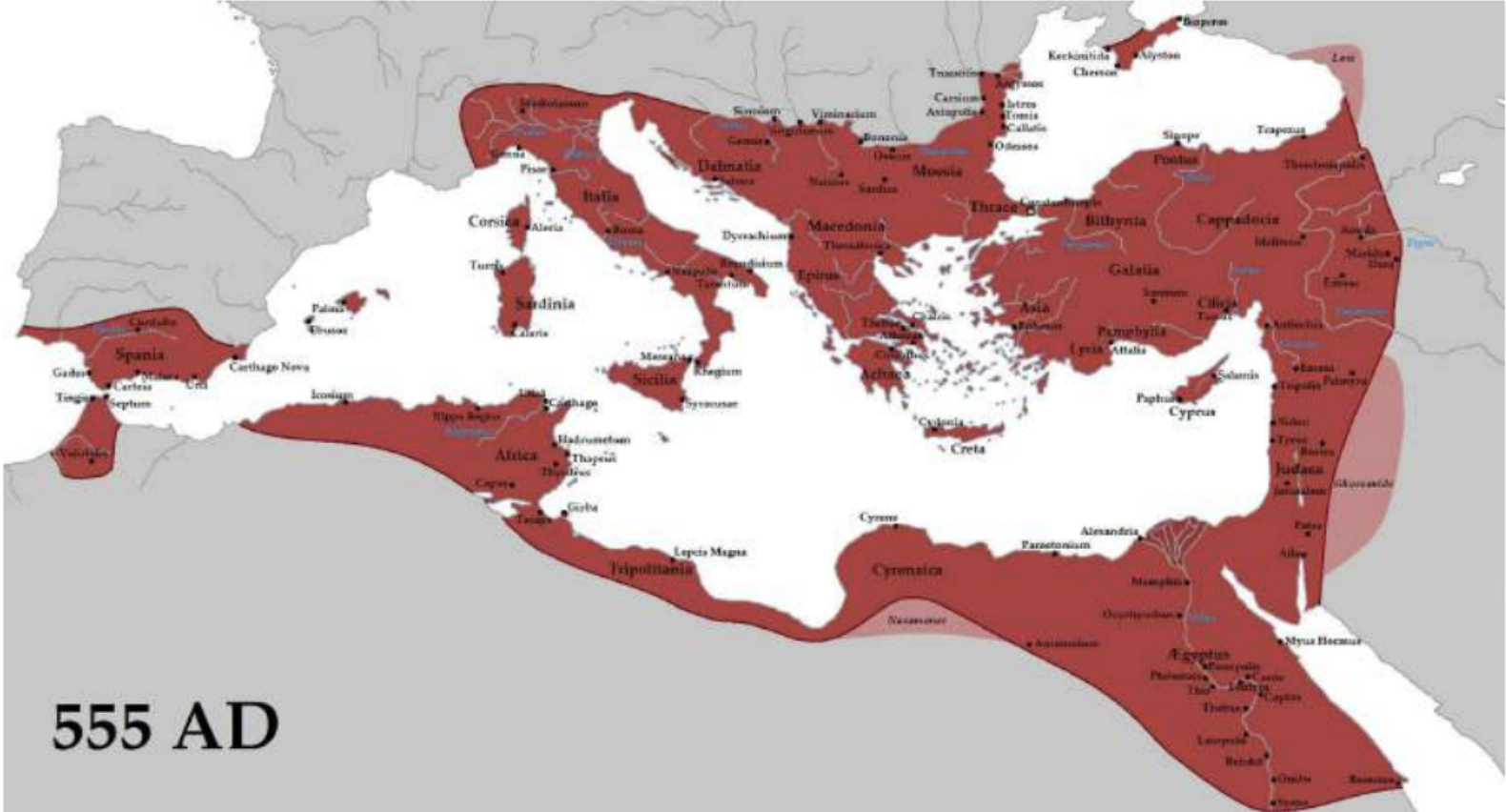
The Empire after Justinian's reconquest of the West 555 AD
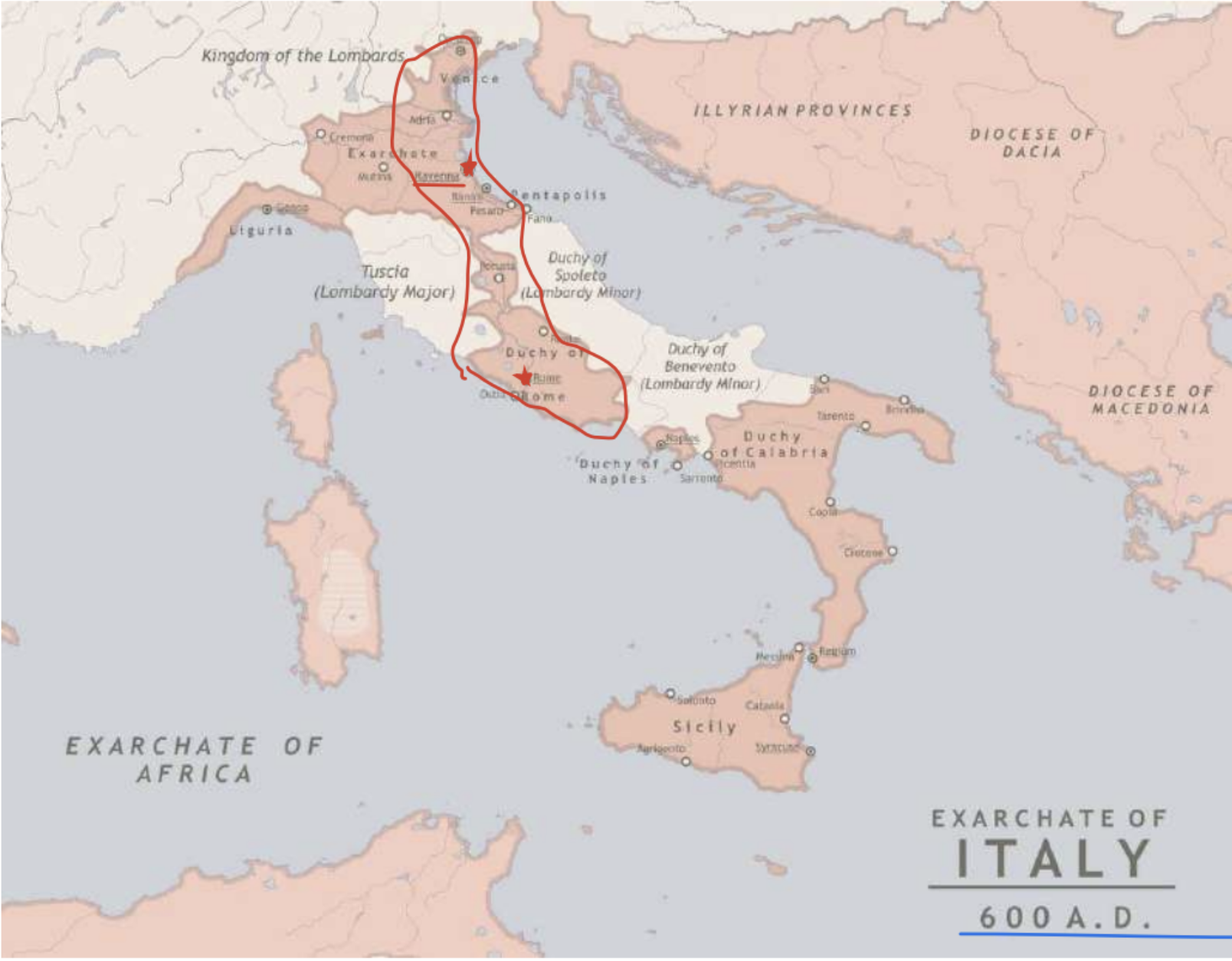
Exarchate of Ravenna 600 AD
Eastern Roman (Byzantine) Architecture (313 - 1453)
The Byzantine Empire, which dominated the Eastern Mediterranean, was one of the largest states in Europe and the Christian world during the Middle Ages. With the collapse of the Western Roman Empire, the influence of the Byzantine Empire grew larger. The capital city of the Byzantine Empire was Constantinople (Istanbul today). In 313, after the Roman Emperor Constantine granted Christians equal rights by the Edict of Milan, important developments took place in Byzantine art. The art that emerged after this date, 313, is considered Byzantine art.
Lasting until the 12th century, this brilliant period began to decline with the weakening of the state administration and the loss of territory. The Fourth Crusade (Sack of Constantinople) in 1204, and the subsequent advance of the Turks in Anatolia would culminate in the Fall of Constantinople in 1453 to the Ottomans led by Mehmed the Conqueror.
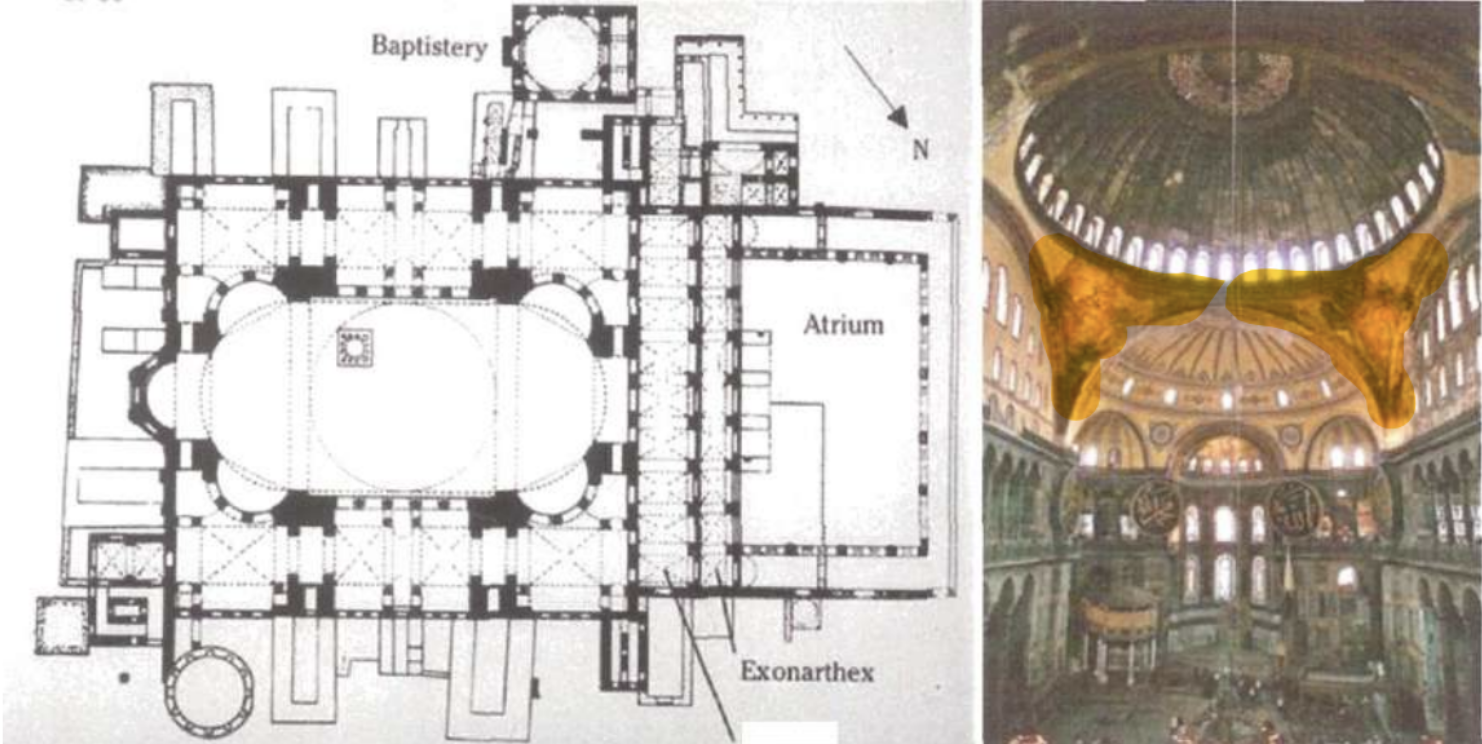
Byzantine Architecture fully adopted the centrally planned church typology. These square or polygonal buildings give the impression of a round space with their interior appearance. Hagia Sophia, Hagia Irene and the Church of Sergios and Bacchos in Istanbul are examples of this type of building, which was mostly used in early period of Byzantine architecture. The Hagia Sophia is especially important due to its role in the development of Pendentives, which would be very influential for Western Architecture during the Renaissance.
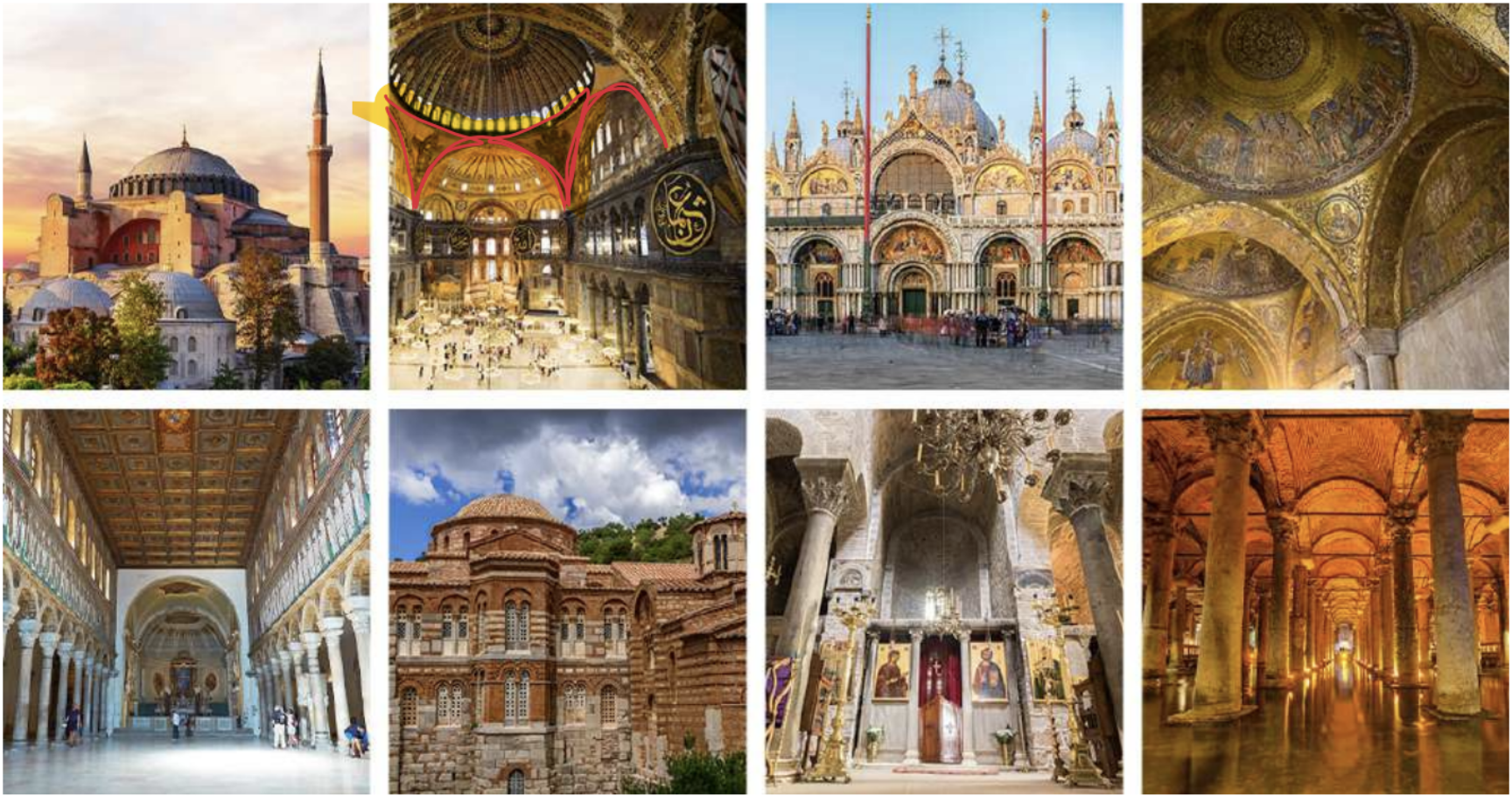
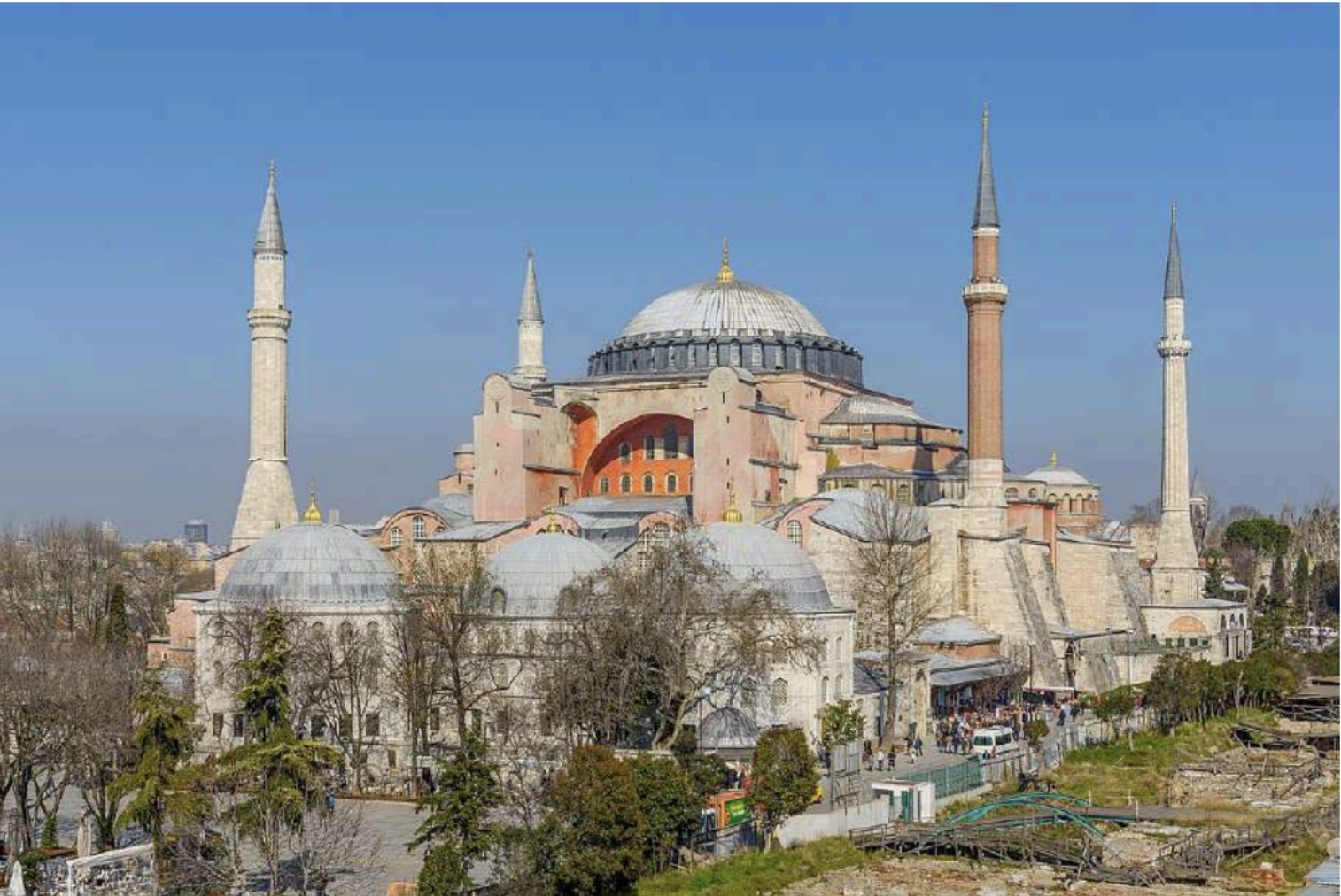


Hagia Sophia was built by the Byzantine emperor Justinian I (Codified roman law “Corpus Juris Civilis” 534 AD). Built between 532 and 537 AD in the old city center in the historical peninsula of Istanbul and was converted into a mosque by Mehmet the Conqueror after the Ottoman conquest of Istanbul in 1453. Since 1935, it has been serving as a museum. (Reconverted into a Mosque in 2020) In terms of architecture, Hagia Sophia is a domed basilica type building that combines the basilica plan with the central plan and is considered as an important milestone in the history of architecture with its dome transitional and structural system features.
It is stated that approximately 10.000 workers were employed in the construction of the Hagia Sophia, which was designed by Anthemius of Tralles and Isidore of Miletus. One of the peculiarities of this very old building is that some of the columns, doors and stones used in its construction were brought from older buildings and temples.