AP Biology - Evolution Chapter 22-26
1/101
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
Evolution
The Change over a period of time
Charles Darwin and the Origin of the Species
Came up with the phrase “Descent with Modification.’
Sedimentary Rock
Fossils end up sediments and can be used for relative dating.
Artificial Selection
Humans choose specific characteristics to breed.
Homology
Similar characteristics in related organisms due to common ancestors
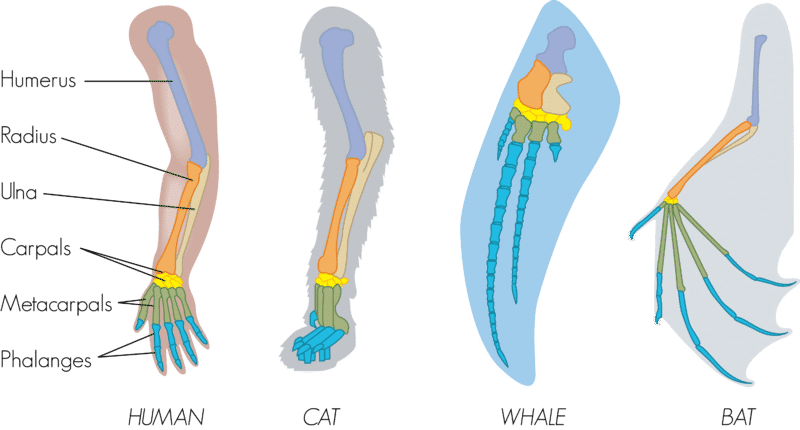
Anatomical Homology
Physical structures like the forelimb that are common to multiple organisms.
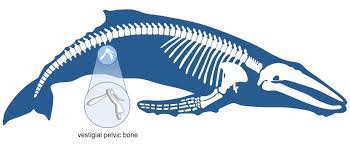
Vestigial Structures
Structures with little to no use in an organism in the present day. It had some use in the past.
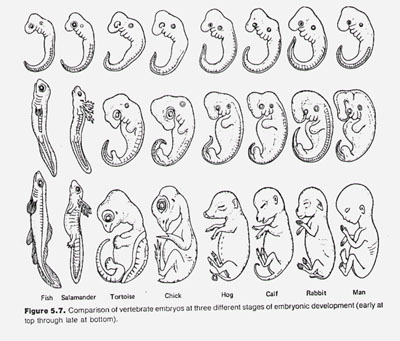
Embryological Homology
Common ancestry by looking at forms of the embryo. The more similar the embryos, the closer related the 2 organisms are.
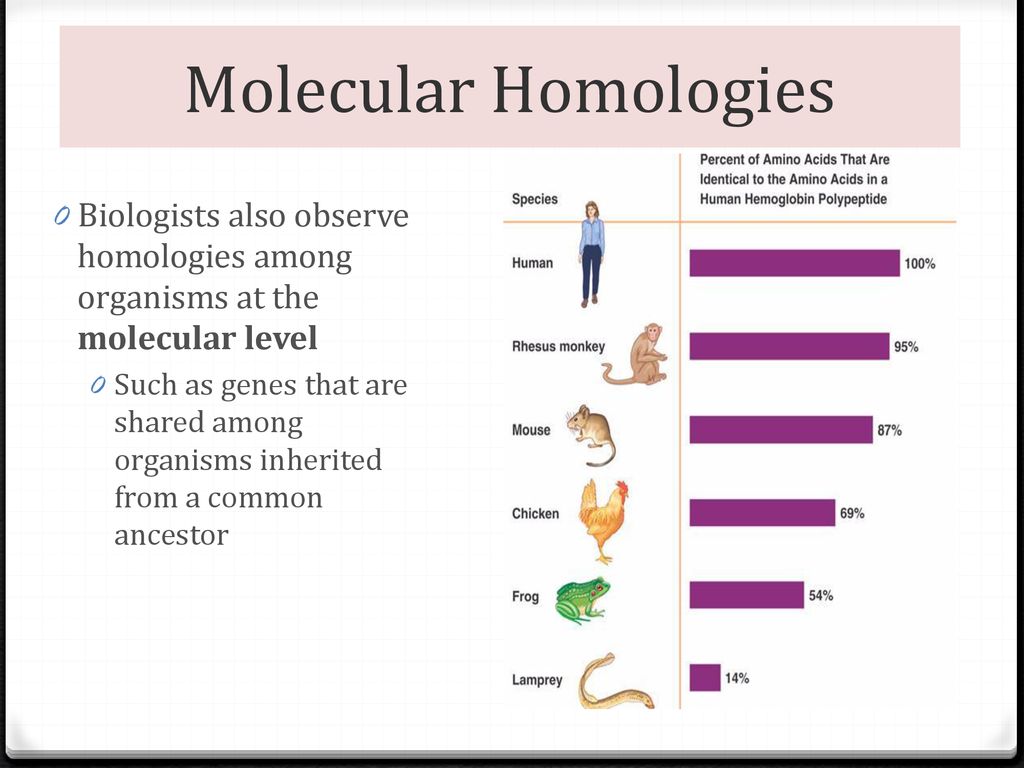
Molecular Homology
Similarities in the sequences of DNA/Amino Acids. The more similar the DNA, the more similar the organisms are.
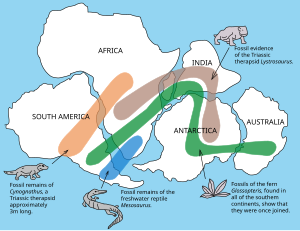
Biogeography
The distribution of species on the planet.

Endemic Species
Species that are only discovered in specific locations.
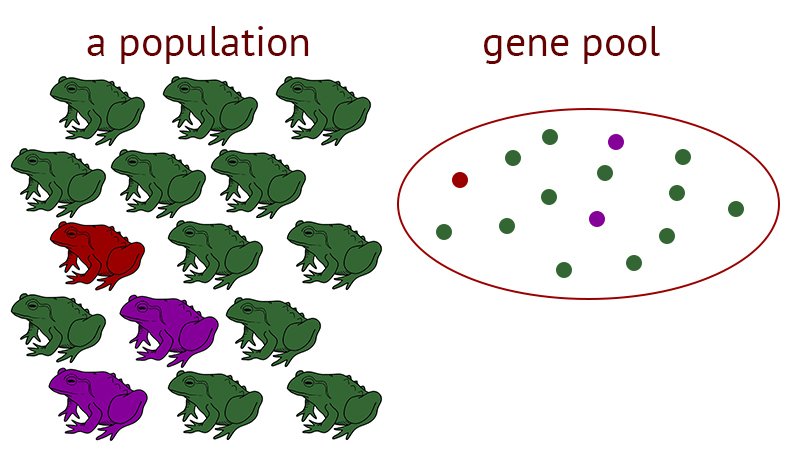
Genepool
All of the genes and alleles in a population
Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium
A set of conditions where evolution won’t occur:
1) No Sexual selection
2) No Natural Selection
3) Infinitely large population
4) No Migration
5) No Mutations
Microevolution
Change in the frequency of alleles over a period of time due to chance
Hardy-Weinberg Equations
p + q = 1
p²+2pq + q² = 1
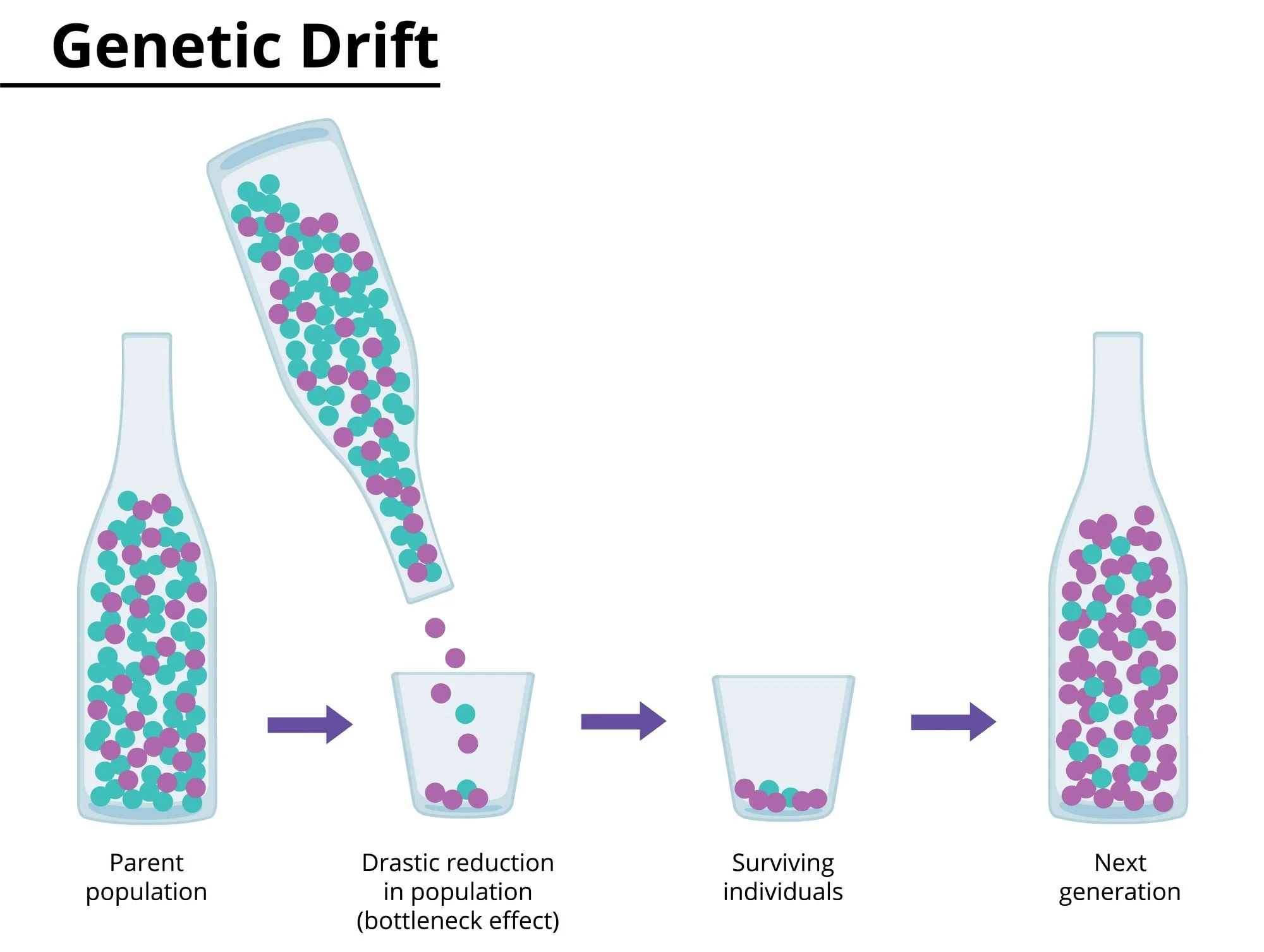
Bottleneck Effect
Something, like a disaster, that causes some animals with a specific trait to survive over others by chance.
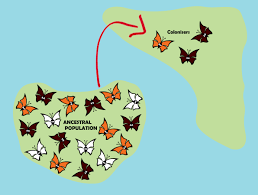
Founder Effect
A small group finds a new location to inhabit.
Adaptation
A trait that increases survival/reproduction rates
Fitness
The number of offspring an organism produces.
Gene Flow
New alleles entering/exiting a population based on migration
Mutation
A change in the genetic material/DNA. It does not have a major impact on humans but does have a bigger effect on bacteria.
Polymorphism
2 or more versions of a characteristic
Balanced
Nature can sustain different versions of a characteristic
1) Hetero zygote Advantage
2) The more common a characteristic becomes, the more it will be selected against
3) Nature doesn’t select for or against the allele (like blood type)
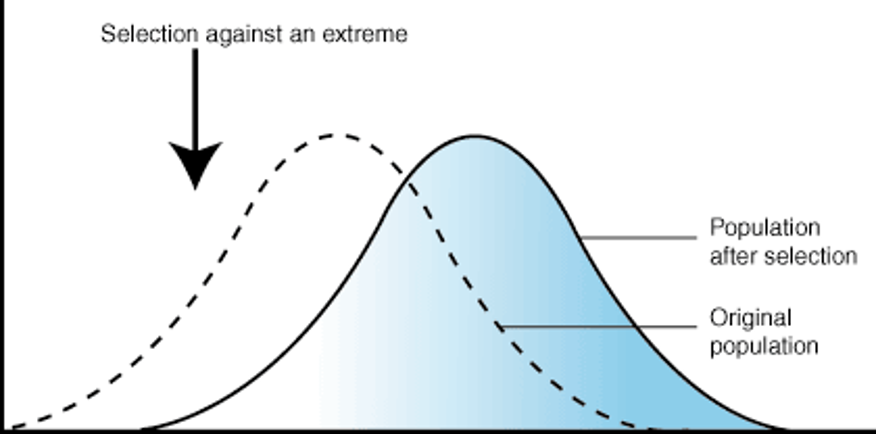
Directional Selection
One of the extremes of the curve is more successful than the average and other extrema.
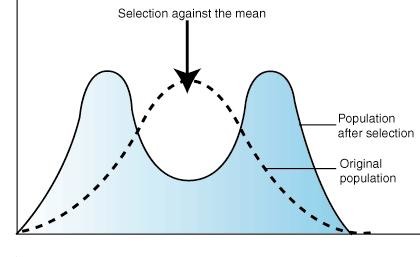
Disruptive/Diversifying Selection
The fitness of the average declines and the extremes increase. This leads to speciation.
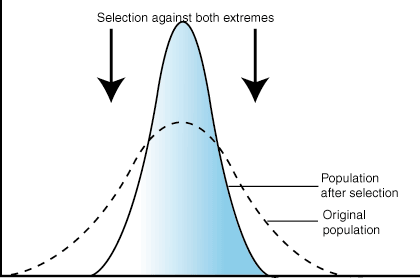
Stabilizing Selection
The environment doesn’t change and the average continues to be the most fit.
Sexual Selection
Animals choose their mates
Intrasexual Selection
The males compete for the rights to a female. Competition meaning showing off because fighting is not viable as it reduces the fitness of both parties.
Intersexual Selection
Female chooses the mate.
Coevolution
2 species are dependent on each other for survival and they evolve together
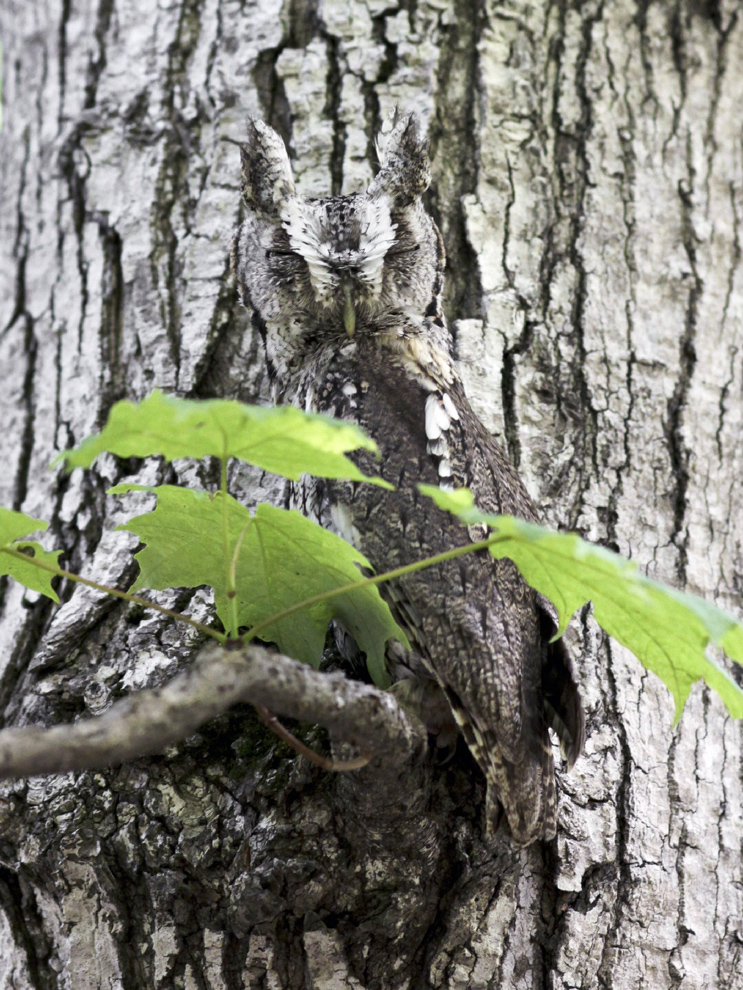

Cryptic Appearance
Camouflage (industrial melanism)
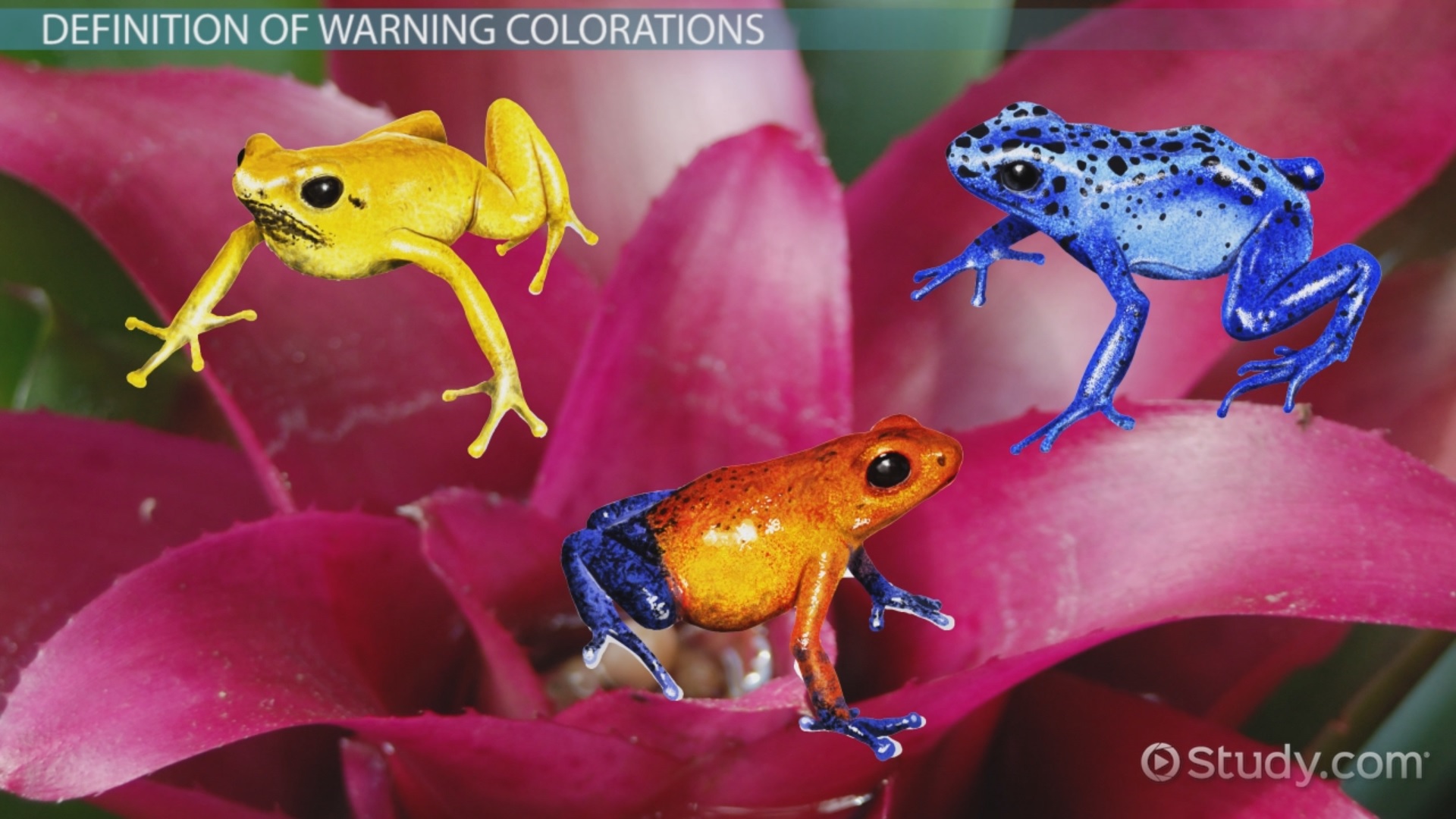

Warning Coloration
Bright colors to signify an animal is poisonous
Mimicry
Species that mimic other species
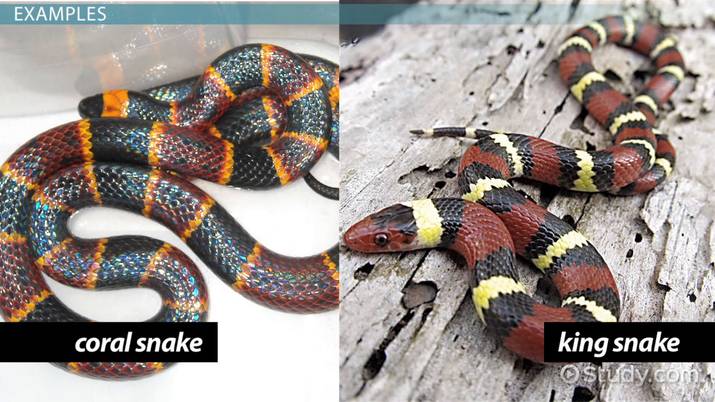

Batesian Mimicry
Something not dangerous imitating something that is

Mullerian Mimicry
2 or more venomous species mimic each other.
Species
Animals grouped based on fertility/the ability of them to reproduce and produce fertile offspring.
Population
A group of organisms in a specific area
Deme
A localized population. The organisms usually stay and mate within their group
Related Demes
Populations that have the ability to go to each other.
Climal Variation
Change in characteristics based on geography.
Subspecies
Species that can mate with each other but usually don’t because they are characteristically different and it prevents them from being attracted to each other.
Reproductive isolation
Prevents species from reproducing successfully.
Prezygotic Barriers
Prevents the actual mating from even occuring.
Postzygotic Barriers
Mating has happened and the hybrid is born but not viable or not fertile.
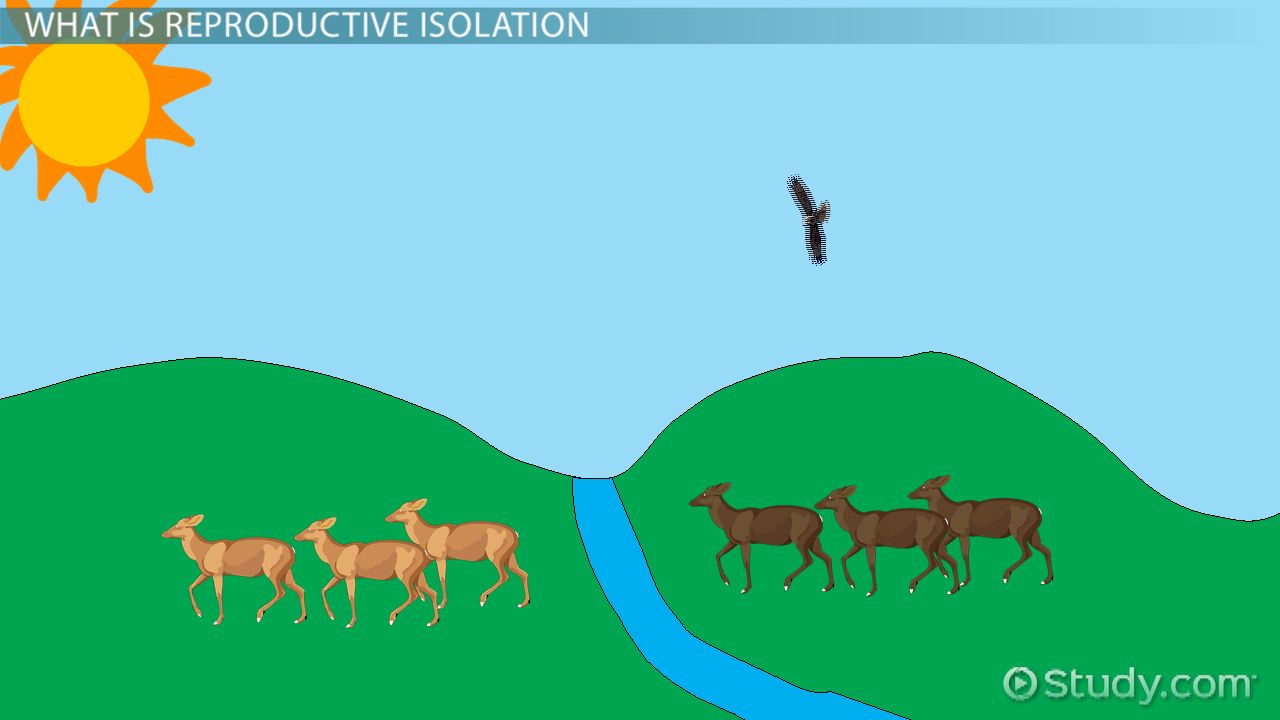
Habitat isolation
Prevents any concern of physical mating because they are located in different places.
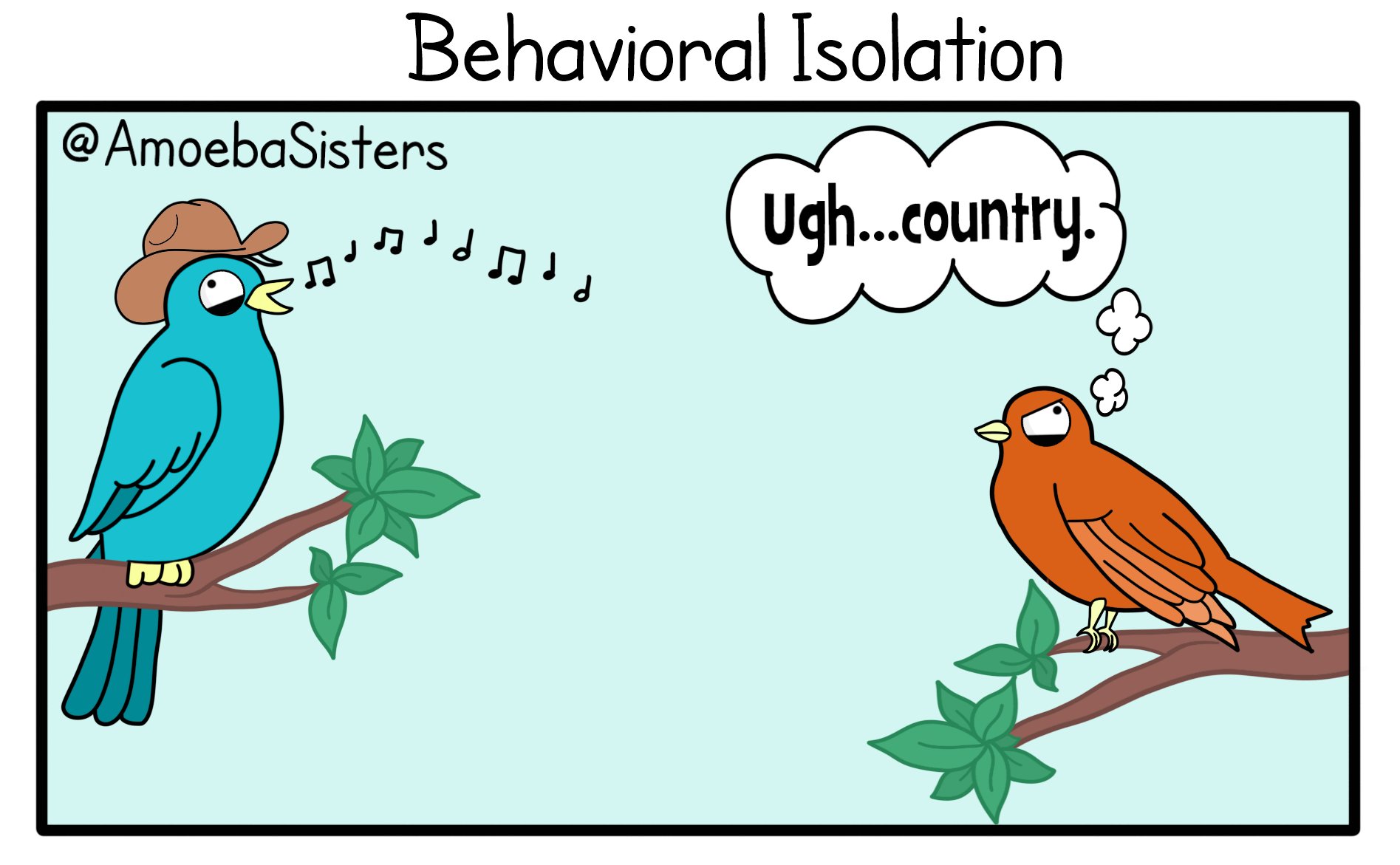
Behavorial Isolation
No interest in the courtship rituals of the other.
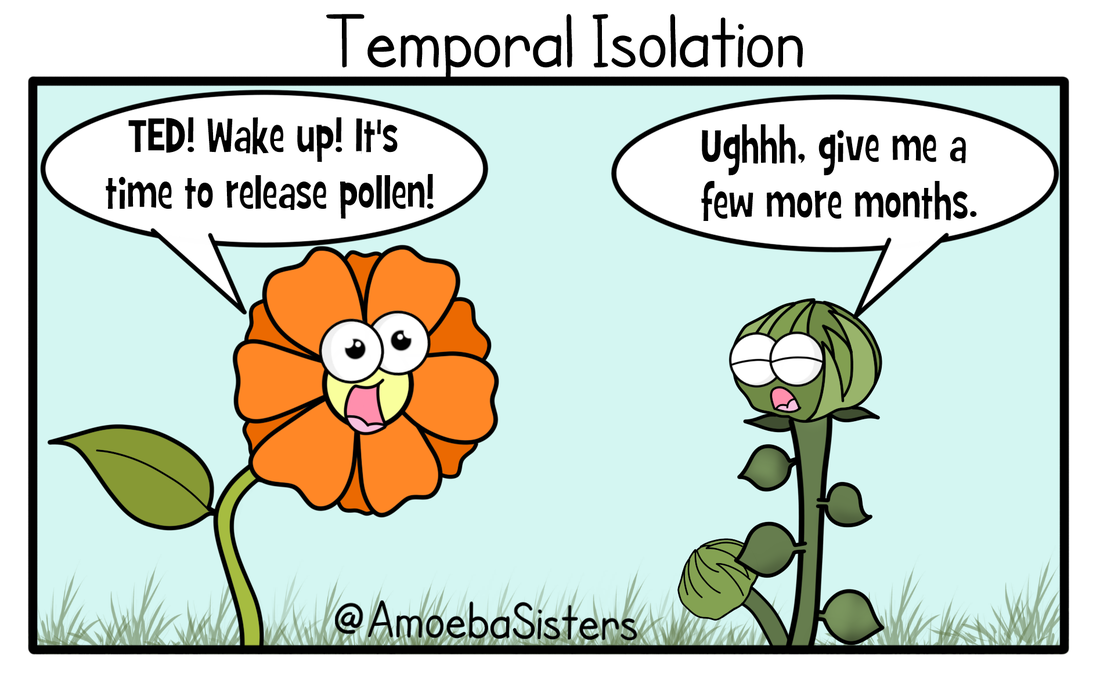
Temporal Isolation
Different Mating Seasons
Mechanical Isolation
Difference in genitalia or stamen/pistil of a flower
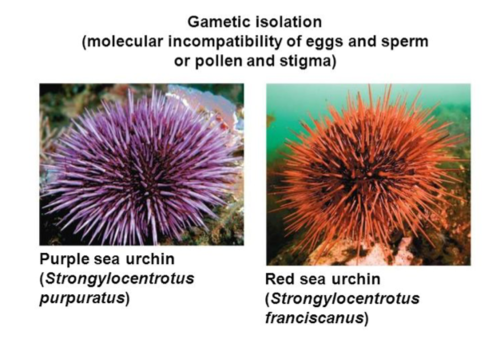
Gametic Isolation
Sperm can’t fertilize the egg or the gametes don’t fuse
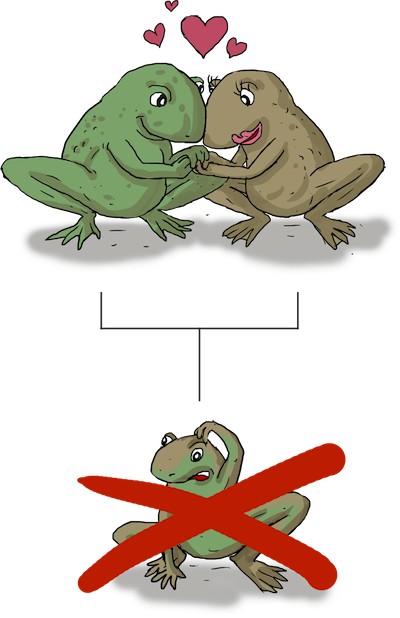

Reduced Hybrid Viability
The hybrid does not last long and does not survive to reproductive age

Reduced hybrid fertility
The hybrid does reach reproductive years but cannot make eggs or spern
Hybrid Breakdown
The offspring of the hybrid have reduced fertility/viability
Speciation
The formation of a new species
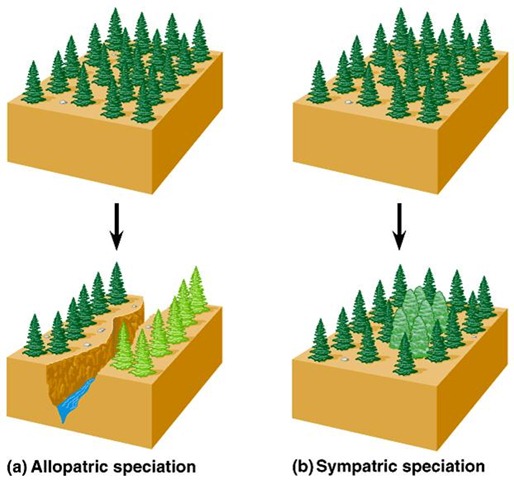
Sympatric Speciation
A new species from in the same location as the original species
Character Displacement
When a species starts to differentiate itself physically.
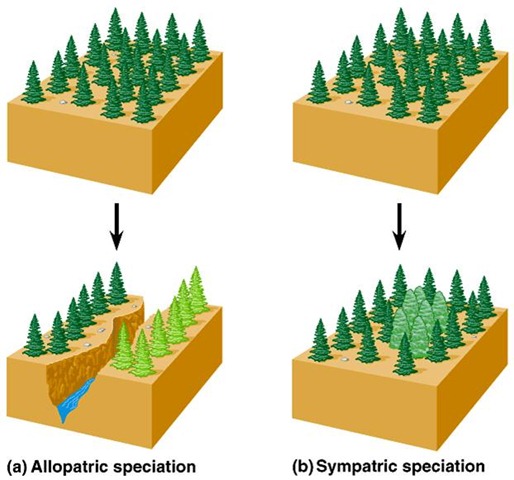
Allopatric Speciation
New species arise that has been geographically separated from the original population.
Polyploidy
Multiple sets of chromosomes (Usually found in plants)
Autopolyploidy
Greater sets of chromosomes from within the same species.
Hybrid Zone
A region in which members of different species meet and mate, producing at least some offspring of mixed ancestry.
Allopolyploidy
Separate species with polyploidy mate and produce a zygote with polyploidy.
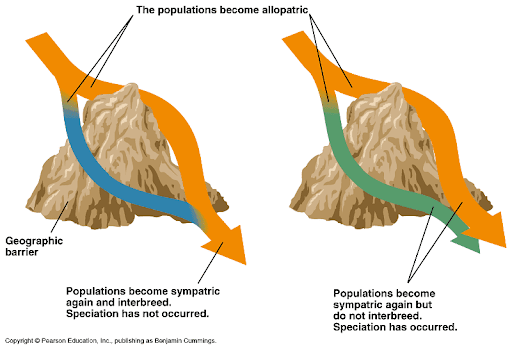
Reinforcement
The continuation of hybridization
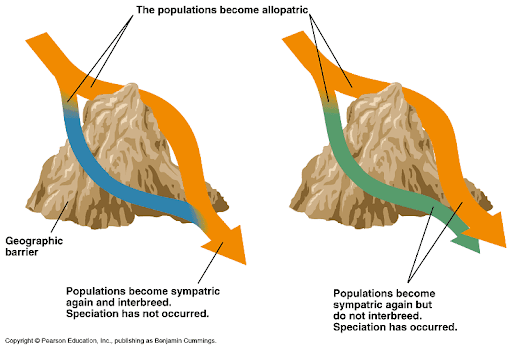
Fusion
When the hybrid species is more successful and the original species fuses
Anagenesis
One species form a new species that is more successful than the original.
Cladogenesis
New species branch off but the original one still exists.
Adaptive Radiation
A lot of speciation from a single species in a relatively short period of time due to the founder effect and bottleneck effect.
Gradualism
Evolution happens slowly over time
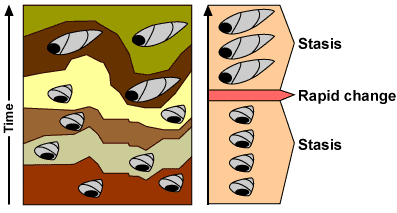
Punctuated Equilibrium
Things stay the same for long periods of time and then quickly change. For example, fossils in rocks are suddenly lost and new species arise (quick changes)
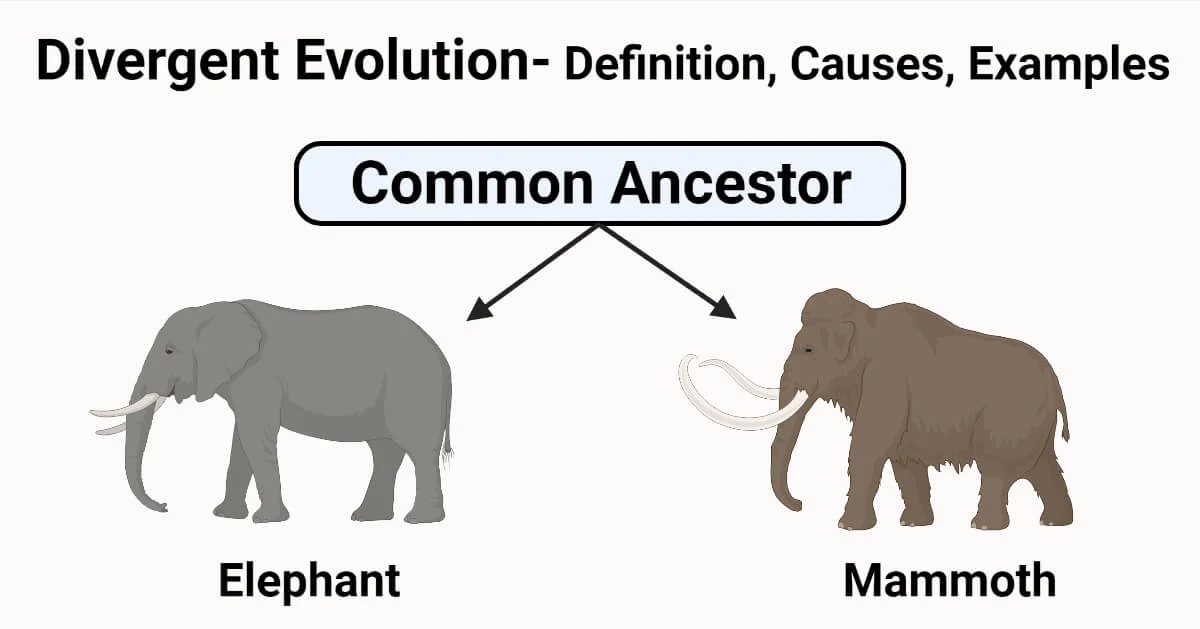
Divergent Evolution
There is a common ancestor and new species branch off from it.
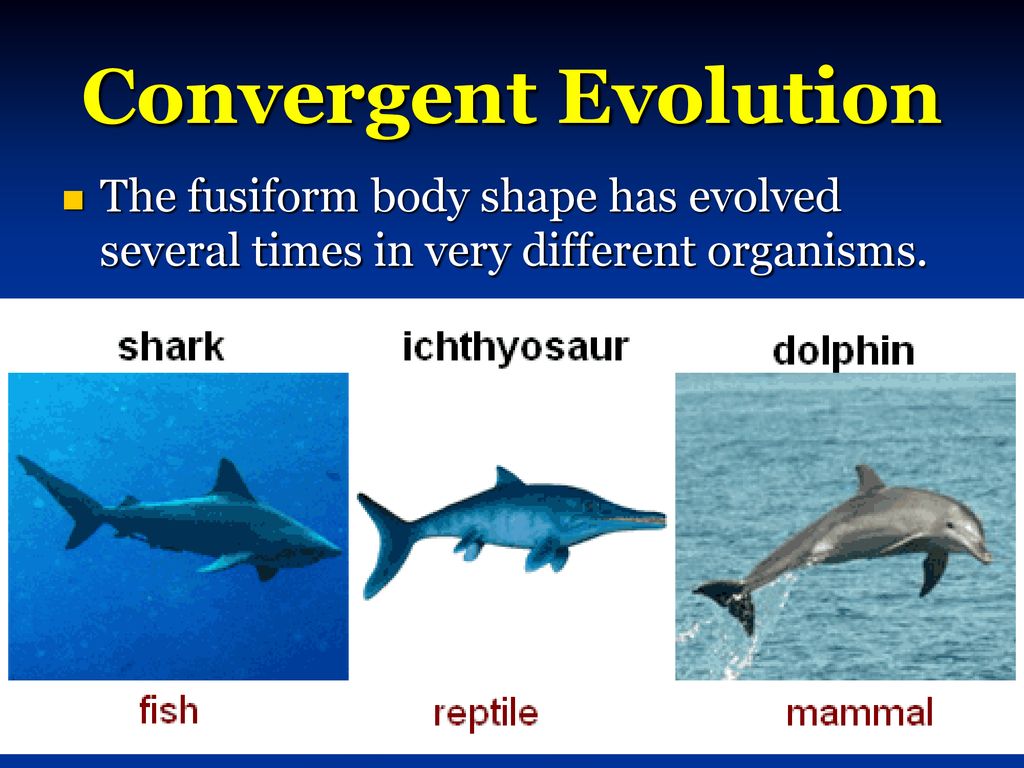
Convergent Evolution
Species that appear or behave similarly to each other

Analogous Structures
Structures not from common ancestors but have the same appearance/function.
Exaptation
A feature that was produced by natural selection for a function other than the one it currently performs and was then co-opted for its current function.
For example, wings developed in birds to match their hollow bones
Oparin and Haldane
The Earth is different from when life began which is the reason why we don’t see life being created today. The current atmosphere is oxidizing and attacking bonds which is not suitable for creating life.
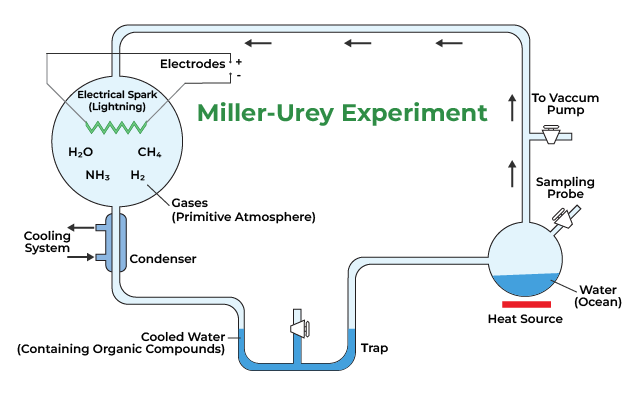
Miller and Urey
An attempt to create the conditions for the origin and life. They were able to produce amino acids and organic monomers.
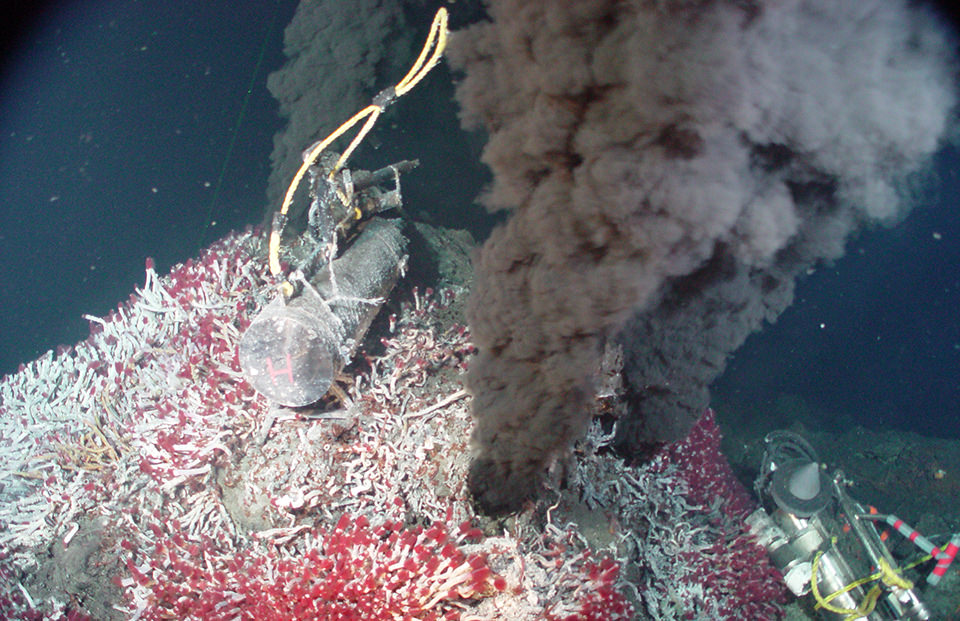

Hydrothermal vents
Openings on the ocean floor that release hot, mineral-rich fluids.
Alkaline Vents
Openings on the ocean floor that release hot, mineral-rich fluids but at a higher pH level.
Protocells
A self-organized, spherical structure considered a rudimentary precursor to living cells
Relative dating
Approximating the age of a fossil using sedimentary rock.

Stromatalites
Fossilized bacteria (also one of the older that we have found)
Absolute Dating
Using half-life (half of the atoms of a radioactive isotope to decay into a more stable isotope form)
Radiometric Dating
Uses elements like C-14 and U-238
Tectonic plates
Pieces of crust that move along the mantel
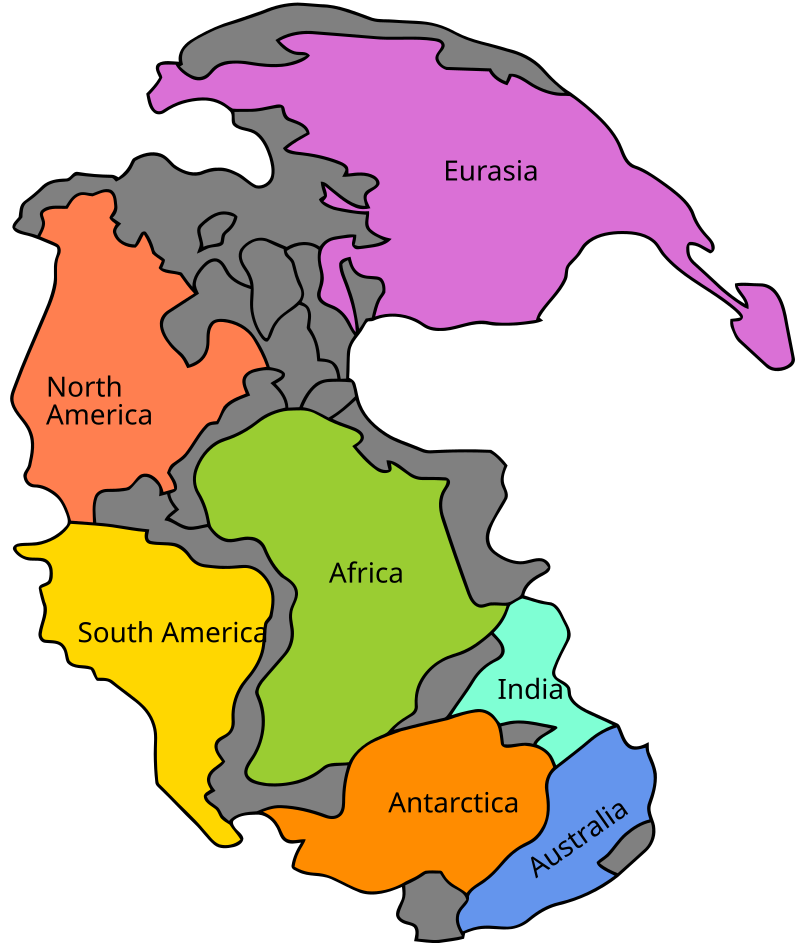
Continental Drift
The moving tectonic plates cause the continents to move slowly. It also formed Pangaea.
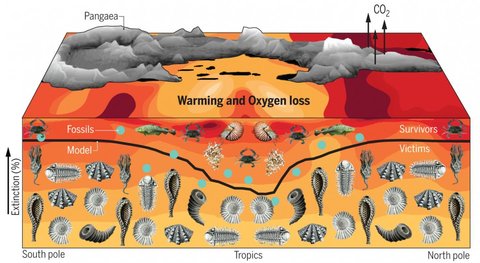
Permian Mass Extinction
Greatest mass extinction event. Resulted from the formation of Pangaea and led to the Mesozoic Era. 81% of sea animals and 70% of land animals disappeared.
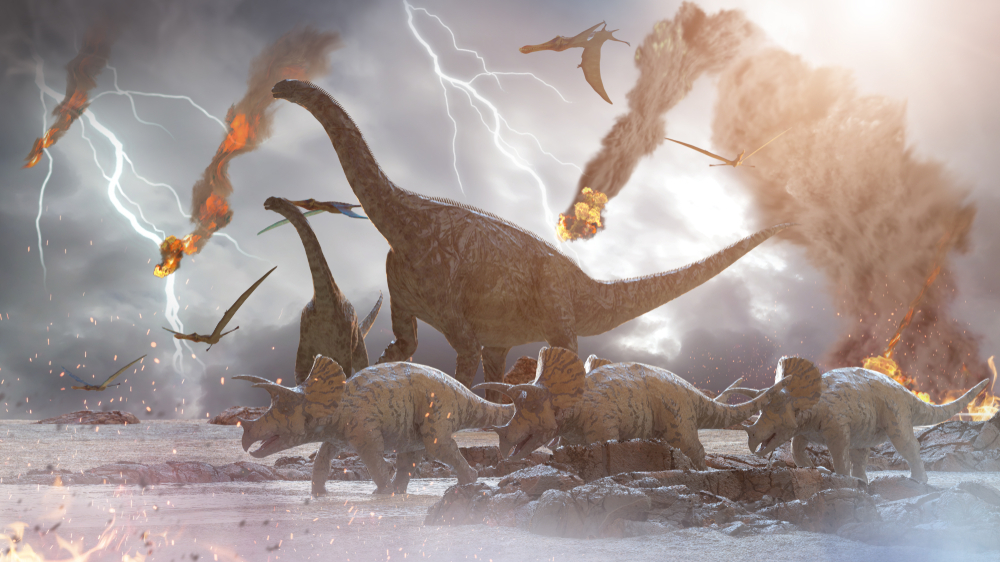

Cretaceous Mass Extinction
The end of dinosaurs and large tetrapods
Evo Devo
Small genetic changes cause large changes in morphology. Compares different developmental processes.
Heterochrony
Changes in rate and timing of change that can cause huge morphological changes
Paedomorphosis
Reproductive organs develop to majority before the rest of the organs.
Phylogenics
The evolutionary history of a species
Binomial Nomenclature
2 word name classification (Panthera Pardue)
Hierarchical Classification
A system of grouping based off of hierarchy
Taxon
The name that is assigned to the group at any level (family, genus, etc)
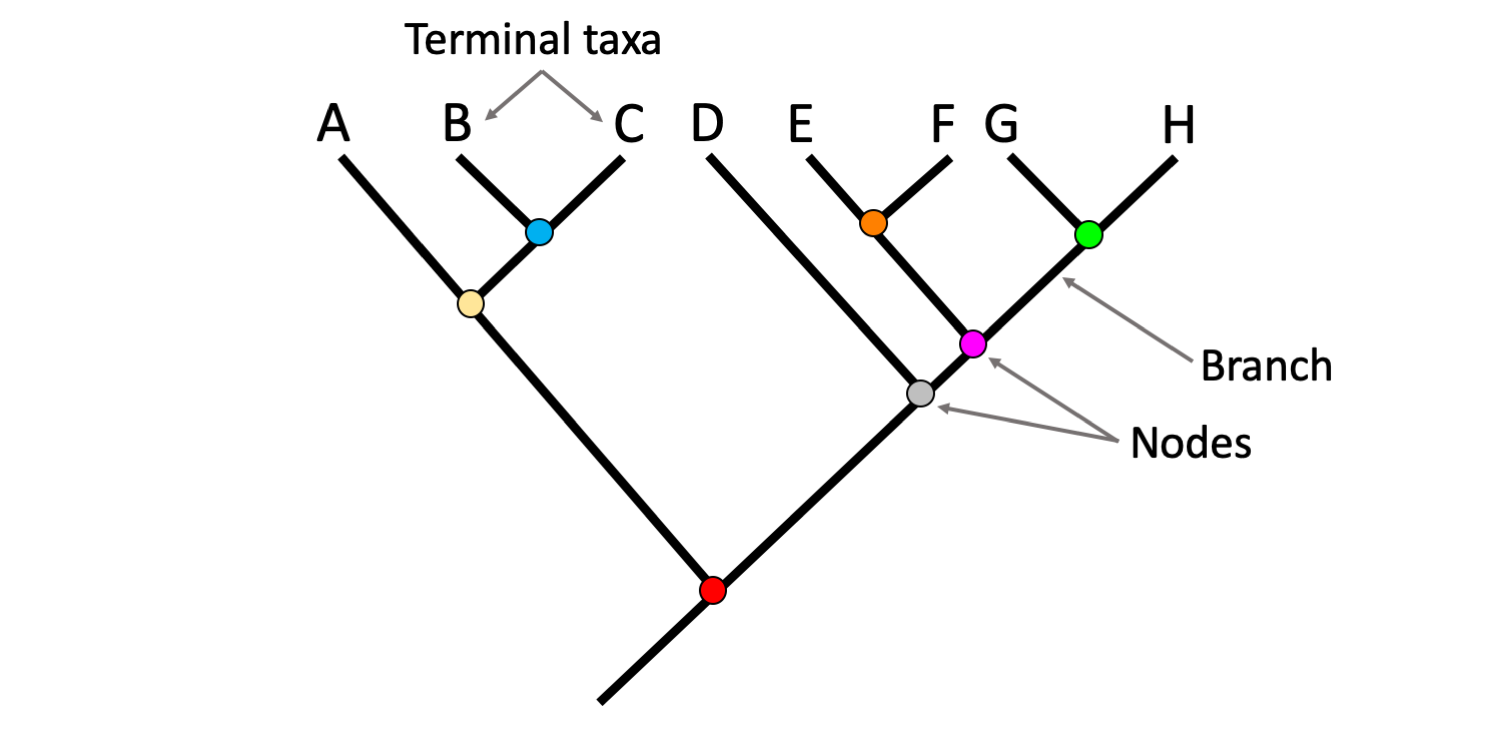
Branch point
When a common ancestor diverges and splits into new species.
Cladistics
Classifying based on phylogeny and is always based on a common ancestor
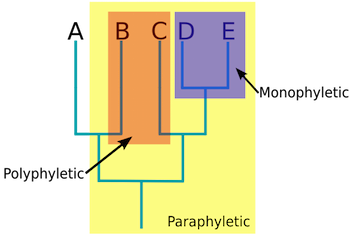
Monphyletic/True Clade
Ancestor and all of it’s descendants, whether living or extince
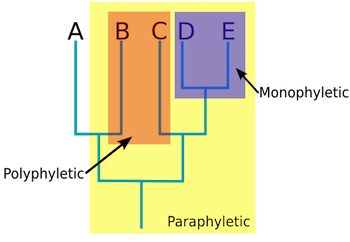
Paraphyletic
The ancestor and some but not all of it’s descedants
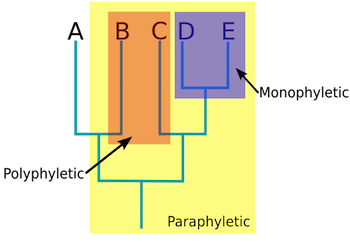
Polyphyletic
Multiple descendants but no common ancestor
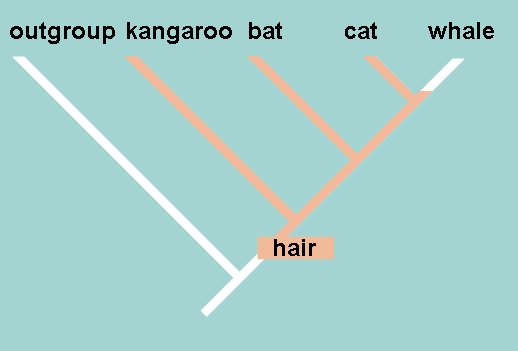
Shared ancestral Character
Characteristics that evolved in an ancestor but also includes other descendants as well (shared outside of the clade)
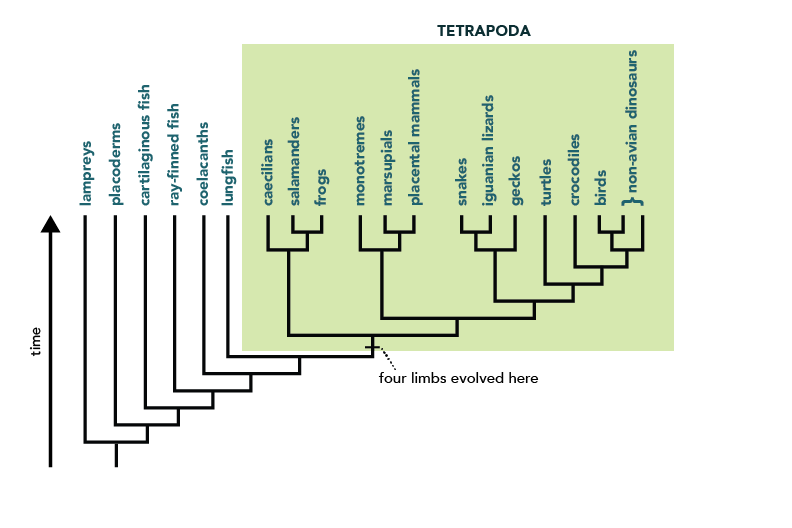
Shared Derived character
Characteristics unique to the Clade
Maximum Parsimony
Fewest amount of changes that occur before the division of species. It is the simplest and least amount of mutations that would lead to the final result.
Maximum Likelihood
Most likely steps (not the least amount of steps)