CR Lecture 11 - Social Robotics, HRI and Trust
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Four incremental skills of social interaction and learning
Joint attention: Gaze and pointing gestures
Imitation: Body movement, action/goals
Cooperation: Spontaneous altruistic behaviour
Theory of Mind (ToM): Ability to attribute beliefs, goals and percepts to other people
Joint attention and Gaze stages
Sensitivity stage: Discriminate left or right side of caregiver’s gaze direction
Ecological stage: Scanning along the line of gaze for salient obejcts
Geometrical stage: Recognise orientation angle to localise distal target
Representational stage: Orient outside of the field of view
Robot set up for joint gaze model
Robot head with two cameras (pan/tilt rotation)
Human caregiver with various salient objects
Procedure:
Random object location
Caregiver looks at the object
Robot detect's caregiver’s face
Cognitive architecture for attention
Robot locates the salient objects
Cognitive architecture for joint gaze model
Salient feature detectors: colour, edge, motion and face
Visual feedback controller: to move the head towards the salient object in the robot’s view
Self-evaluator learning module: Neural network learns mapping between face image and head position, and desired motor signal
Internal evaluator: Check if there is an object at the center of the image
Gate module: Selects between outputs from the visual feedback controller and the learning module
Selection rate to model non-linear development changes
Nagai et al Joint Gaze model results
3 stages:
Robot mostly looks at objects located within its view, can only achieve joint attention at a chance level
Robot achieves joint attention in great majority of cases when object is within the image, increases the gazing at location outside the eye’s view
Robot achieves joint attention in almost all trials and positions
Joint Attention and Pointing
Attention manipulation via pointing
Imperative pointing: to request an object when other agent is not initially looking at it
Declarative pointing: to create shared attention on an object focus of the interaction
“Child” robot learns to recognise the partner’s pointing gesture (neural network)
Pointing entirely based in language
HAMMER architecture
Hierarchical Attentive Multiple Models
Parallel and hierarchical multiple pairs of inverse/forward models
Inverse model: Takes as inputs the current states of the system and target goal, outputs motor control commands for goal
Forward model: Takes as inputs current state of the system and control command, outputs predicted next state of the control
Top-down mechanism for control of attention during imitation
Models psychology Active Intermodal Matching
HAMMER robot applications
Used for robot imitation experiments:
Robot head ESCHeR that observes and imitates human head movements
Mobile robot Peoplebot with arm imitation actions
Imitation for robotic wheelchairs
Imitation of dancing (Nao)
HRI
Application of social robotics and language models to human-robot interaction scenarios
Technical and scientific challenges for HRI
Speech recognition/production
Action recognition and intention reading
Trust and acceptability
Emotion recognition/production
Long-term interaction
ASR
Automatic Speech Recognition
ASR examples
Hidden Markov Models to Deep Learning models
Nuance VoCon, Sphinx
Google, Bing, Alexa
Robot-specific ASRs
Speech Synthesis
Text-to-speech
Loquendo/Nuance
Google Cloud text-to-speech
ASR for HRI
State of speech recognition in Nao
Test with adults: Recognition of counting numbers and short sentences, 90% with Nao onboard mic and 99% with high quality mic
ASR for children
Child speech very different from adult speech
Higher pitch
Disfluencies
Utterances often ungrammatical
About 60%
Action/Pose recognition
1st revolution: Kinect and RGBD
2nd Revolution: Deep Learning, OpenPose 2016
Real time multi-person keypoint detection library for body, face, hands and foot estimation
Kinect/RGBD applications
On-board or add-on
Pepper
Nao
Applications
Teleoperation
Navigation
Action recognition
Human tracking
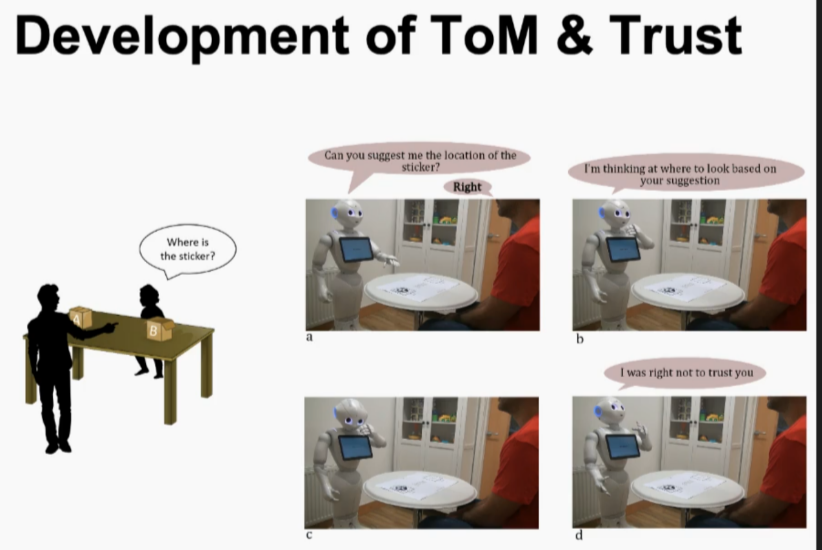
Trust in HRI
Robot’s trust of other agents
Theory of Mind and trust
Bayesian model for belief and ToM
People’s trust of robots
HRI experiments on social factors
HRI experiments on anthropomorphic factors
Theory of Mind
Social capability to recognise that other agents have their own mental states (they think, they have a goal, they have preferences)
Bayesian ToM Trust model
Similar to a mini neural network - each node has a meaning. Collects statistical information for tracking the reliability of their peer agents.
Explainability
Robot explains why it made the decision it did
Sally-Anne test
Deception detection test
HRI trust experiments
Anthropomorphic and social factors in human’s trust of robots
Social gaze
Speech
Anthropomorphic priming
Share actions
Imitation
HRI protocols for measuring trust
Price game judgement
Investment game
Social and Humanoid Priming
Exposure to social cues or stimuli (humanoid shape) subconciously influence a person’s behaviour
Anthropomorphic behaviour and trust
Anthropomorphic behaviour increases trust
Joint attention
Head tracking, gaze, and gestures when playing the game
Interactoin with the intentions of the robot