Exam 3: Soil Colloids and Soil Acidity: Types, Development, and Effects
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
122 Terms
What are soil colloids?
The smallest particles in soil, which are electrically charged and chemically reactive.
What is the soil colloidal fraction?
A collective term for clay and other tiny particles in soil, less than 1 µm in diameter, that behave as colloids.
What are the four main types of soil colloids?
1. Crystalline Silicate Clays, 2. Noncrystalline Silicate Clays, 3. Iron/Aluminum Oxides, 4. Organic particles (Humus).
How do crystalline silicate clays develop?
Through alteration (slight changes in structure or charge) and recrystallization (complete degradation and formation of new structures).
What is isomorphous substitution?
The substitution of one element for another in a mineral without a significant change in the crystal structure, affecting charge.
What are tetrahedral and octahedral sheets?
Tetrahedral sheets are made of Si and O, while octahedral sheets are made of O/OH and Al, Mg, or Fe.

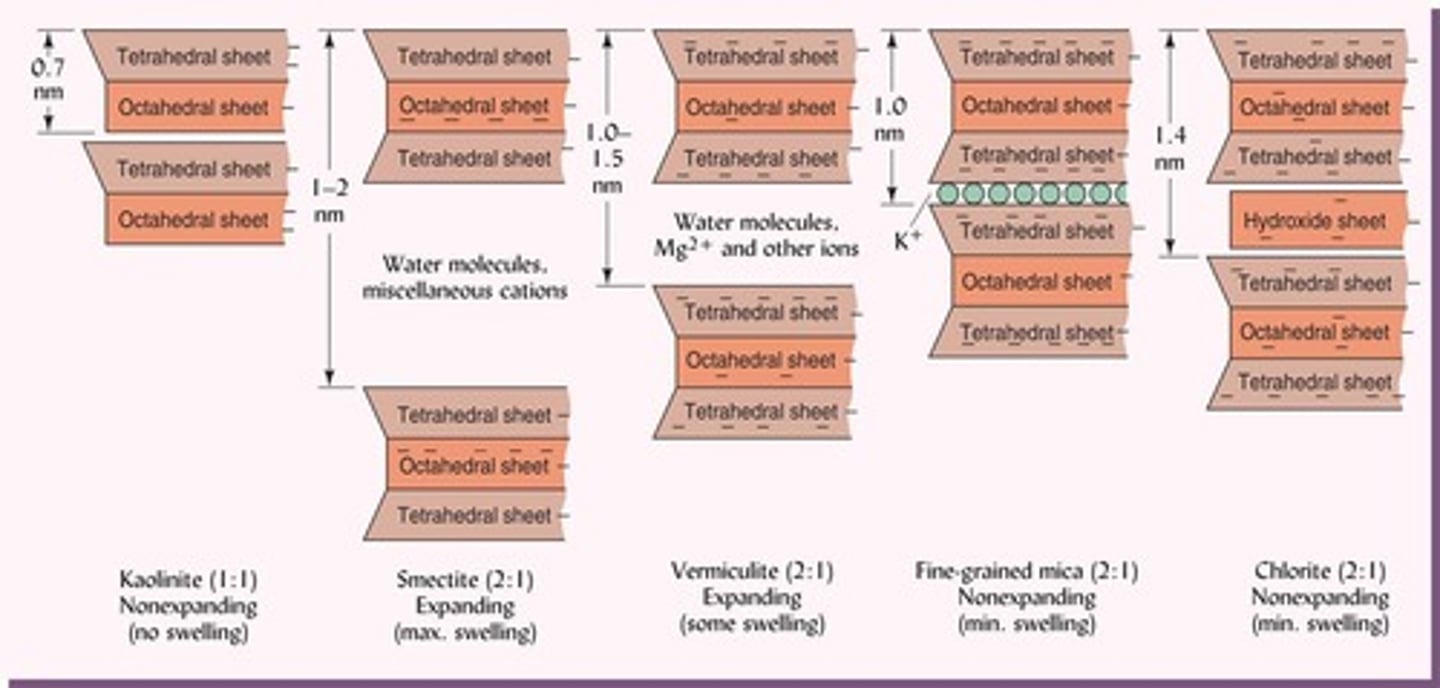
What is the structure of 1:1 silicate clays?
They consist of one tetrahedral sheet and one octahedral sheet, tightly bound with no interlayer space.
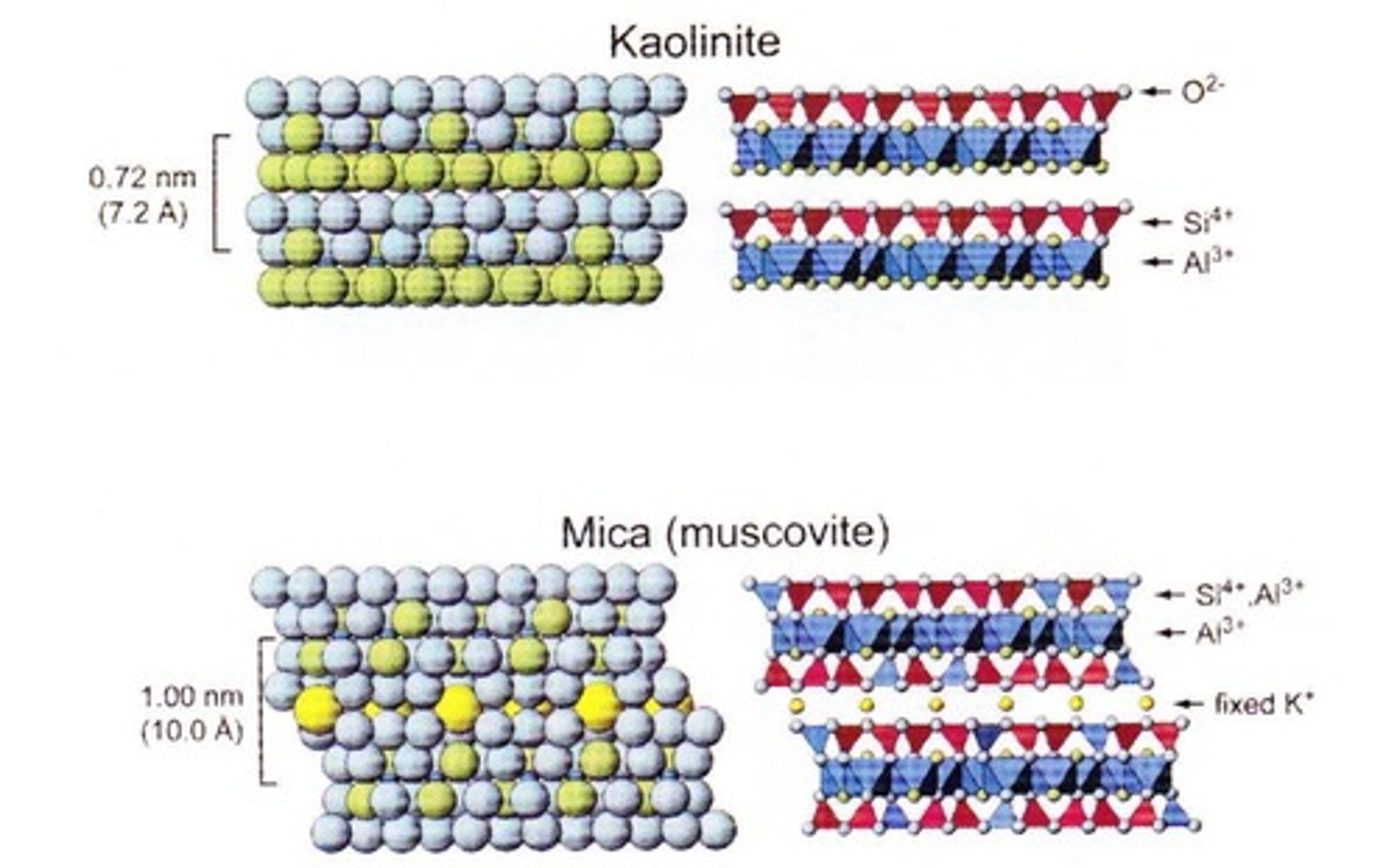
What is an example of a 1:1 silicate clay?
Kaolinite, which is less sticky and reactive, commonly used in ceramics and foundations.
What characterizes 2:1 silicate clays?
They have two tetrahedral sheets surrounding one octahedral sheet, allowing for greater expansion and cation exchange.
What happens during the weathering of silicate clays?
Si is lost over time, leading to a low Si:Al ratio in highly weathered soils.
What types of clays dominate highly weathered soils?
Kaolinites and iron/aluminum oxides.
What is the significance of surface area in soil colloids?
A larger surface area makes colloids the most chemically active soil fraction, enhancing their reactivity.
What is the role of cation and anion adsorption in soil colloids?
Colloids adsorb cations and anions, which are essential for soil fertility and water retention.
What is the charge on soil colloids due to isomorphous substitution?
Negative charge results from substituting a lower charge ion for a higher charge ion, while positive charge occurs when a higher charge ion replaces a lower charge ion.
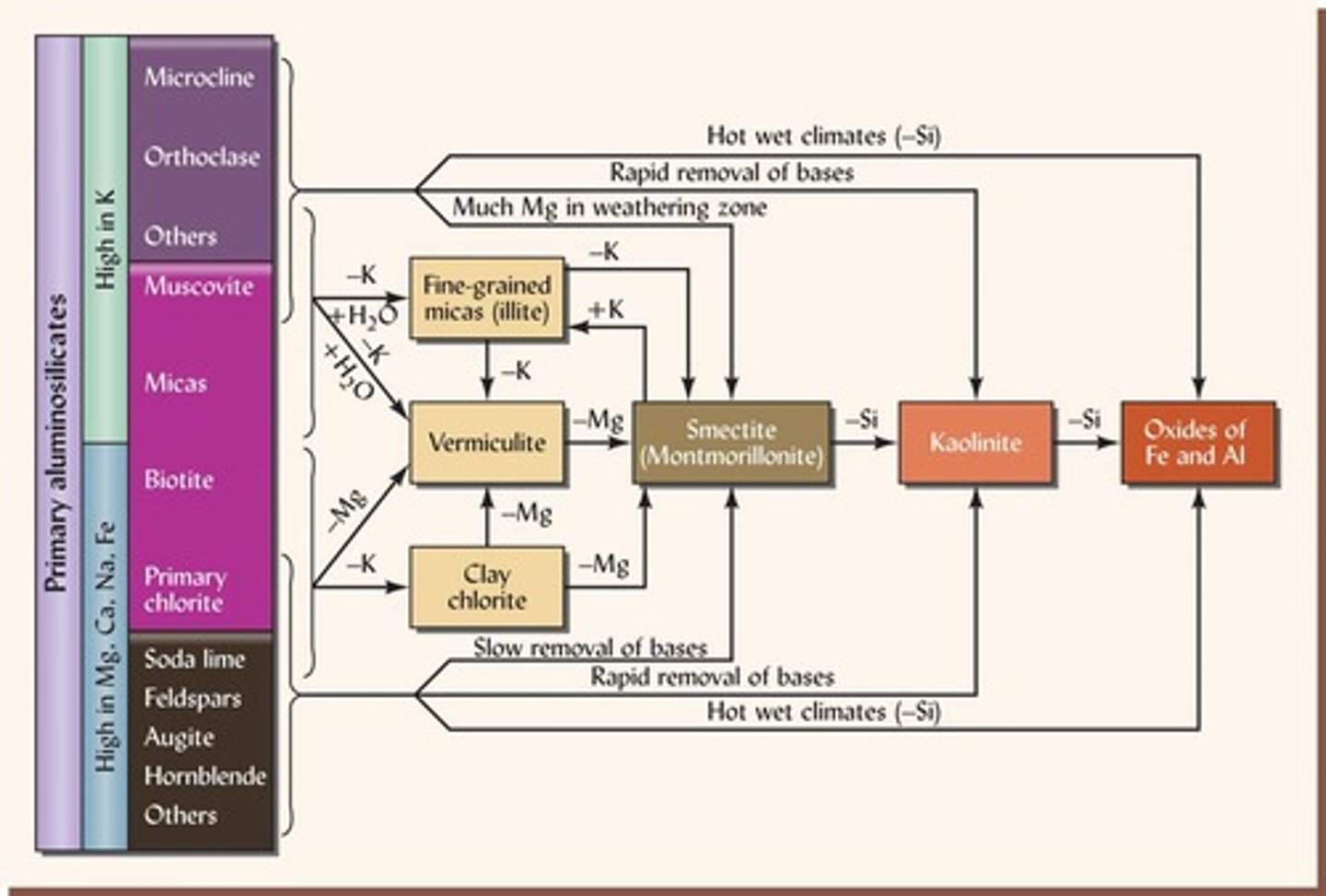
What are the stages of weathering for soil colloids?
1. Early: Micas/Chlorites, 2. Intermediate: Smectites/Vermiculites, 3. Advanced: Kaolinites, 4. Extreme: Fe/Al Oxides.
What is the difference between crystalline and noncrystalline silicate clays?
Crystalline silicate clays have a layered sheet structure, while noncrystalline silicate clays are amorphous and poorly structured.

What is the primary source of permanent charge in silicate clays?
Isomorphic substitution, which occurs in both octahedral and tetrahedral sheets.
How does the structure of kaolinite affect its nutrient capacity?
Kaolinite has little to no isomorphous substitution, resulting in low nutrient capacity and CEC.
What are the characteristics of organic particles in soil?
Organic particles (humus) are not minerals, lack crystalline structure, and are the most chemically active fraction of organic matter.
What is the significance of the tetrahedron and octahedron shapes in soil mineralogy?
They are fundamental geometric forms that make up the tetrahedral and octahedral sheets in silicate clays.
What is the effect of low pH on kaolinite formation?
Kaolinite is a product of acid weathering, common in soils of the southeastern USA.
What distinguishes the 2:1:1 phyllosilicate clays?
They have two tetrahedral sheets and one octahedral sheet, allowing for unique structural and functional properties.
What are 2:1 silicate clays composed of?
Two tetrahedral sheets and one octahedral sheet (TOT).
What is a common sub-group of 2:1 silicate clay?
Montmorillonite, which is a type of smectite.
What is a characteristic of smectite clays?
They have a large internal surface area and can swell and shrink significantly.
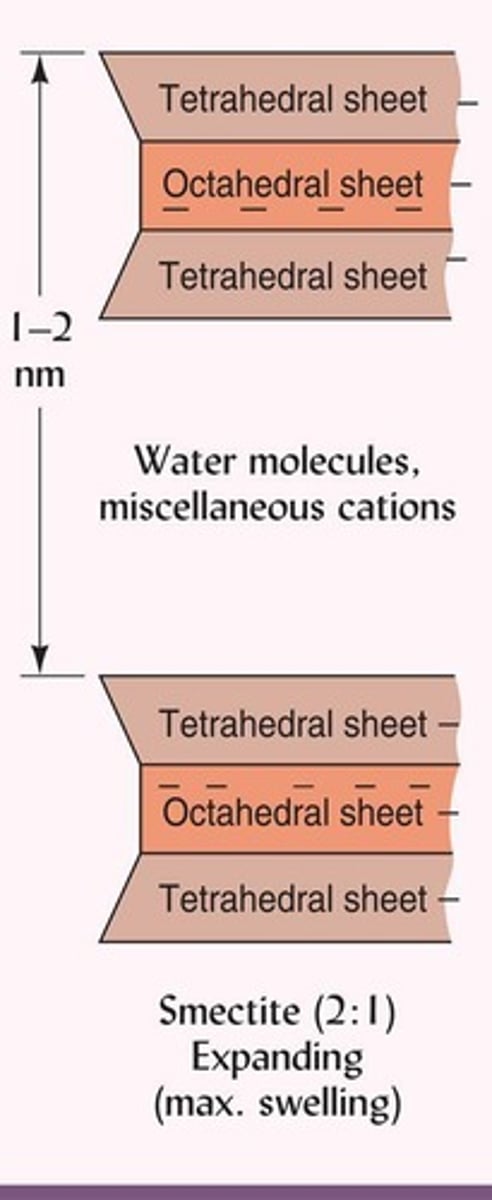
What causes the layer charge in smectite clays?
The substitution of Mg2+ for Al3+ in the dioctahedral sheet.
Under what conditions do smectite clays become unstable?
Under low pH and high moisture.
What is the primary alteration product of micas in vermiculite clays?
Loss of K+ ions.
What is the nutrient characteristic of vermiculite clays?
They have a high cation exchange capacity (CEC) and are nutrient-rich.
What type of charge do fine-grained mica clays have?
Strong surface charge, but they are non-swelling and only moderately plastic.
What is the composition of 2:1:1 silicate clays like chlorite?
Fe or Mg occupies many octahedral sheets, with a hydroxy sheet in the interlayer.
What is a defining feature of noncrystalline silicate clays?
They have an amorphous structure and high nutrient and water-holding capacity.
What are examples of noncrystalline silicate clays?
Allophane and imogolite.
What type of charge do Fe/Al oxides typically have?
They do not expand and can strongly adsorb anions.
What is the role of organic molecules (humus) in soil?
They have a large net negative charge and can adsorb nutrients and water.
What are the two sources of charge on soil colloids?
Constant/permanent charge and pH-dependent charge.
What causes permanent charge in soil colloids?
Isomorphic substitution within the clay crystal structure.
How does pH affect the charge on soil colloids?
Increased pH can lead to negative charge by removing H+ ions, while decreased pH can lead to positive charge by adding H+ ions.
What is cation exchange in soils?
The process where cations adsorbed to soil colloids can be replaced by different cations from the soil solution.
What is cation exchange capacity (CEC)?
The sum of exchangeable cations that a soil can adsorb.
What is the difference between buffered CEC and effective CEC?
Buffered CEC is measured under stable conditions, while effective CEC is measured under variable conditions.
What happens to cations during cation exchange?
One cation enters the soil while another is released into the solution.
What is isomorphic substitution?
The substitution of one atom for another within the clay structure, affecting charge.
What types of colloids typically have a constant negative charge?
2:1 clays such as smectite and vermiculite.
What is the significance of soil colloids in agriculture?
They are crucial for nutrient retention and soil chemical activity.
What is the effect of high moisture on smectite clays?
They can swell significantly, affecting soil structure.
What role do soil colloids play in preventing groundwater contamination?
They can sorb charged organic and inorganic compounds, holding toxins for microbial degradation.
What does CEC stand for in soil science?
Cation Exchange Capacity
How is CEC expressed in soil measurements?
In centimoles of charge per kg of soil (cmolc/kg) or milliequivalents per 100 grams (meq/100 g).
What does a CEC of 15 cmolc/kg indicate?
1 kg of soil can hold/exchange 15 H+ ions' worth of charge.
What factors influence Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC)?
Type of clay, quantity of clay, quantity of organic matter, and soil pH.
How does the type of clay affect CEC?
2:1 clays have higher CEC than 1:1 clays.
What is the relationship between organic matter and CEC?
Soils with more organic matter generally have higher CEC.
How does pH affect CEC?
CEC generally increases with higher pH levels.
What is the charge behavior of smectite clay at different pH levels?
Smectite has a constant charge below pH 6.0 and increases slightly above that due to ionization.
What is the charge behavior of kaolinite clay and humus with pH changes?
Both kaolinite and humus have variable charges that increase with higher pH.
What role does organic matter play in CEC?
Organic matter increases negative sites, enhancing CEC.
What is base saturation in relation to CEC?
Base saturation is the percentage of CEC satisfied by base cations that reduce acidity.
What are base cations?
Base cations include Ca2+, Mg2+, K+, and Na+.
What are acid cations?
Acid cations include Al3+ and H+.
What does the term 'saturation percentage' refer to in CEC?
It refers to the proportion of a given cation that satisfies the total CEC.
What is the principle of charge equivalence in cation exchange?
Exchange occurs on a charge-for-charge basis, balancing the charges.
What is the Ratio Law in cation exchange?
At equilibrium, the ratio of cations on the colloid matches the ratio in the overall system.
How do anions affect cation exchange reactions?
An exchange reaction is more likely to proceed if the released ion is prevented from reacting in reverse.
What is cation selectivity in soil?
Cation selectivity is influenced by positive charge and hydrated radius, affecting which cations are exchanged.
What is the significance of complementary ions in cation exchange?
Ions on exchange sites can impact each other's activity, affecting nutrient availability.
What is buffered CEC?
Buffered CEC measures potential or maximum CEC at a specific pH with ammonium or barium.
What is effective CEC?
Effective CEC measures CEC at the actual soil pH without buffering, important for acidic soils.
How is CEC calculated from lab data?
By leaching soil with ammonium and potassium solutions to displace exchangeable cations and measuring their concentrations.
What is the role of soil texture in determining CEC?
Soils with high clay content generally have higher CEC compared to sandy soils.
What happens to nutrient mobility when CEC is high?
Higher CEC enhances nutrient mobility and availability for plants.
How is CEC calculated using NH4+?
CEC is calculated by summing the contributions from various cations like NH4+, Ca2+, Mg2+, K+, H+, and Al3+.
What is the formula for calculating CEC from NH4+?
CEC = (mg NH4+ / 1 g) x (1 mole / 100 cmol) x (1 cmol NH4+ / kg soil).
What is the significance of the total base cations in CEC?
Total base cations are the sum of cations like Ca2+, Mg2+, and K+, which contribute to soil fertility.
What is base saturation in soil?
Base saturation is the percentage of total CEC occupied by base cations, indicating soil fertility.
What factors contribute to soil acidity?
Sources include carbonic and organic acids, oxidation of nitrogen and sulfur, and plant cation uptake.
What is the pH definition in soil science?
pH is the negative logarithm of the hydrogen ion concentration in a solution.
How does organic matter affect soil acidity?
Organic matter can acidify soils by forming soluble complexes with basic cations and releasing H+ ions.
What role does aluminum play in soil acidity?
Aluminum ions (Al3+) contribute to soil acidity and can be toxic to plants and microbes.
What is the difference between active and exchangeable acidity?
Active acidity refers to H+ ions in soil solution, while exchangeable acidity refers to H+ ions held on soil colloids.
What is buffering capacity in soil?
Buffering capacity is the ability of soil to resist changes in pH, influenced by the presence of acidic and basic cations.
What are the negative effects of soil acidification?
Negative effects include reduced nutrient availability, increased aluminum toxicity, impaired microbial activity, and decreased plant growth.
What is the impact of rainfall on soil acidity?
High rainfall can leach away base cations, leading to increased soil acidity.
How does liming affect soil pH?
Liming materials react with soil to neutralize acidity and raise pH.
What factors affect the amount of liming material needed?
Factors include soil texture, initial pH, target pH, and the type of crops grown.
What is the relationship between pH and soil acidity?
Every 1-unit decrease in pH represents a tenfold increase in soil acidity.
What are common sources of H+ ions in soil?
Sources include carbonic acid, organic acids from microbial activity, and acids from precipitation.
What is the effect of plant cation uptake on soil pH?
Plant uptake of cations can lead to the release of H+ ions, contributing to soil acidity.
How does the oxidation of nitrogen contribute to soil acidity?
Nitrification of ammonium ions produces H+ ions, increasing soil acidity.
What is the significance of the global distribution of soil acidity?
Soil acidity is often related to annual rainfall patterns and vegetation types.
What is the effect of organic matter accumulation on soil pH?
Accumulation of organic matter can lead to increased soil acidity due to the release of H+ ions.
What is the role of acid rain in soil acidity?
Acid rain introduces additional H+ ions into the soil, increasing acidity.
What is the chemical reaction for the dissolution of Al(OH)3 in acidic conditions?
Al(OH)3 + 3H+ → Al3+ + 3H2O, showing how Al3+ increases as pH decreases.
What are the two roles of aluminum in soil acidity?
Aluminum contributes to acidity as an acid cation and can be toxic to plants.
What is the formula for calculating the contribution of Ca2+ to CEC?
Ca2+ contribution can be calculated using the formula: (mg Ca2+ / 1 g) x (1 mole / 100 cmol).
What is the process by which Al3+ hydrolyzes in soil?
Al3+ hydrolyzes in several steps depending on pH, forming various aluminum hydroxide species.
What are the three major pools of soil acidity?
1. Active acidity, 2. Exchangeable acidity, 3. Residual acidity.
What is active acidity in soil?
Active acidity refers to H+ ions in soil solution and is the smallest pool of acidity.
How does exchangeable acidity relate to soil pH?
Exchangeable acidity involves Al3+ and H+ ions on soil solids that can be released into the soil solution, affecting pH.
What is residual acidity?
Residual acidity consists of non-exchangeable Al3+ and H+ ions bound to colloids, contributing to soil's buffering capacity.