med micro microbial disease of the cardiovascular and lymphatic systems
1/245
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
246 Terms
cardiovascular system
circulates blood through the bodys tissues
cardiovascular system includes what?
heart and associated arteries, veins, and capillares
cardiovascular system delivers...
substances to and removes substances from the cells
-emia
infection of the blood
viremia
viruses that cause meningitis
fungemia
fungi in the blood
bacteremia
presence of bacteria in the blood
septicemia
flourishing/growing bacteria in the blood; can lead to decreased blood pressure and septic shock
toxemia
toxins in the blood; intoxication
what are the 3 layers of the heart?
endocardium, myocardium, epicardium
whats the inner layer of the heart?
endocardium
whats the outer layer of the heart?
epicardium
plasma leaves blood capillaries becoming ___________ _________
interstitial fluid
lymph capillaries
transport interstitial fluid (lymph) to lymph vessels (lymphatics) and lymph nodes
lymph nodes have fixed ________, ________, ________
macrophages, B cells, T cells
buboes
swollen lymph nodes
the thoracic duct from the lymphatic system intersects what from the cardiovascular system?
left subclavian vein
septicemia
acute illness due to the presence of pathogens or their toxins in the blood
sepsis
systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS)
lymphangitis
inflamed lymph vessels
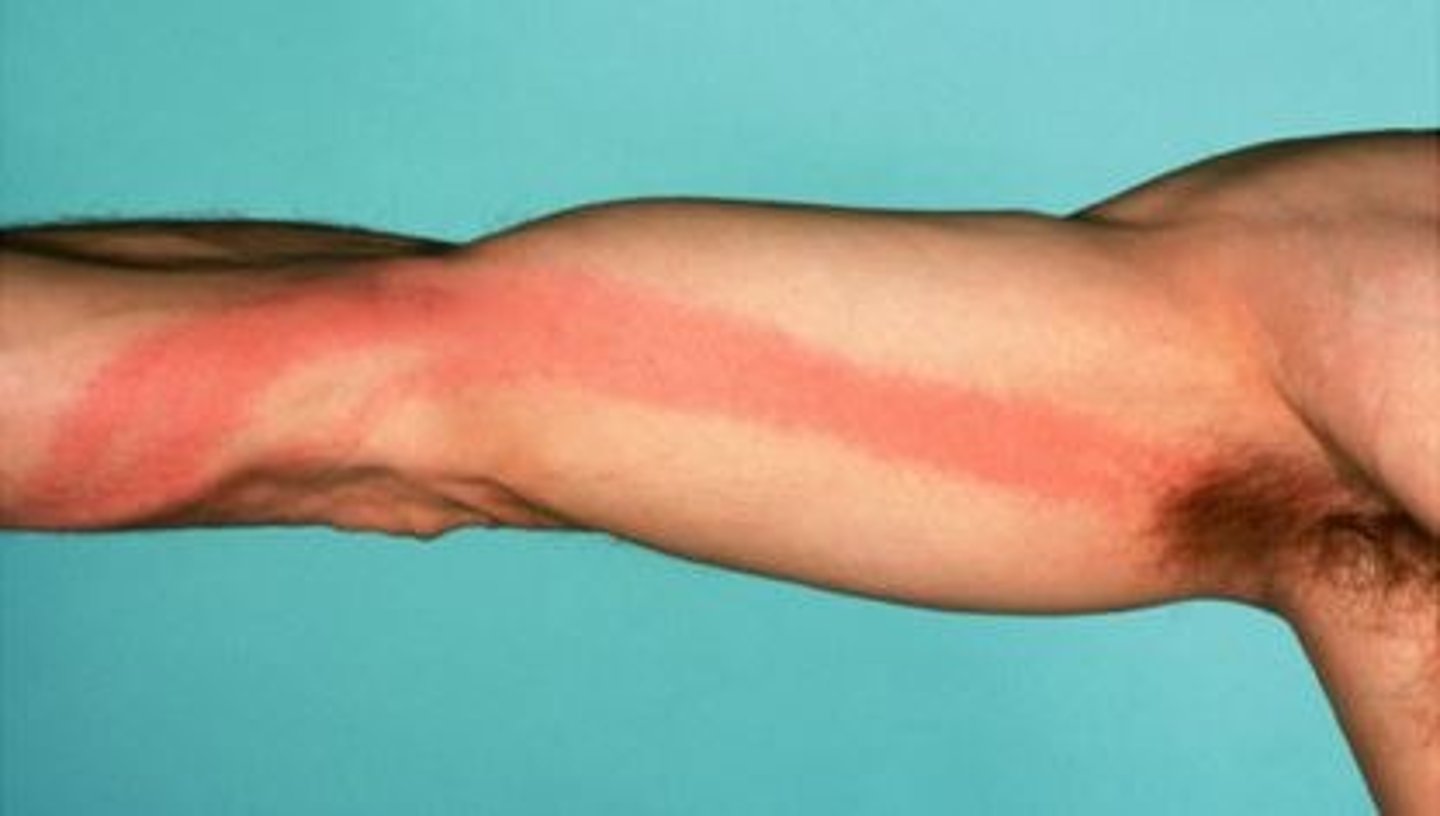
severe sepsis
decreased blood pressure and dysfunction of at least one organ
septic shock
sepsis and uncontrollable decreased blood pressure; high mortality if patient progresses to this state
gram negative sepsis
also called endotoxin shock; endotoxins (LPS) cause a serve drop in blood pressure
what are 3 bacteria that are most frequently involved in gram negative sepsis?
Klebsiella spp, E. coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa
antibiotics can worsen gram negative sepsis by killing bacteria t/f
true
treatment for gram negative sepsis
neutralizing the LPS components and inflammatory causing cytokines
gram positive sepsis
potent exotoxins that cause toxic shock syndrome; hospital acquired infections
potent exotoxins that cause toxic shock syndrome
superantigen exotoxin (TSST)
what are 2 superantigen exotoxin bacteria that cause gram positive sepsis?
Streptococcus pyogenes, Staphylococcus aureus
what are 3 bacteria that are hospital acquired infections that cause gram positive sepsis?
Enterococcus faecium, Enterococcus faecalis, Streptococcus agalactiae
Enterococcus faecium and Enterococcus faecalis
inhabit the colon; colonize wounds and the urinary tract; resistant to many antibiotics
Streptococcus agalactiae
neonatal sepsis
puerperal sepsis
also called puerperal fever and childbirth fever; caused by Streptococcus pyogenes; transmitted to the mother during childbirth
puerperal sepsis infects the ________ and progresses to an infection of the abdominal cavity called _________
uterus; peritonitis
endocarditis
inflammation of the endocardium
subacute bacterial endocarditis
impairs the function of the heart values; caused by alpha-hemolytic streptococci from an oral infection
acute bacterial endocarditis
caused by Staphylococcus aureus
pericarditis
inflammation of the sac around the heart; Streptococci
subacute bacterial endocarditis causes what caused by the immune system response to bacteria?
fibrin platelet vegetations
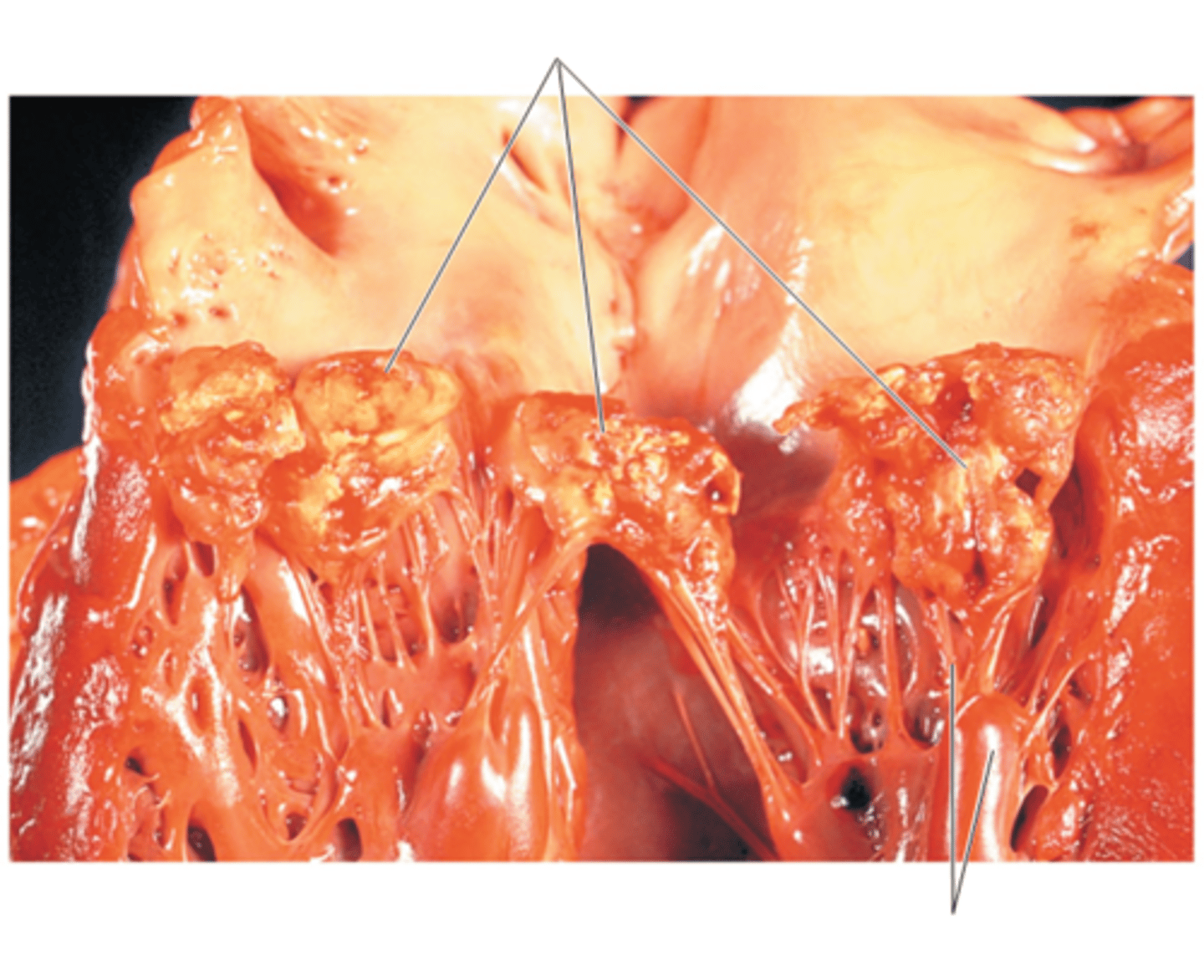
rheumatic fever
autoimmune complication of S. pyogenes infections
rheumatic fever initially starts as what then subsequentally what?
initially streptococcal sore throat; subsequentally inflammation of the heart valves from an immune reaction against streptococcal M protein
whats a key sign of rheumatic fever?
subcutaneous nodules at the joints
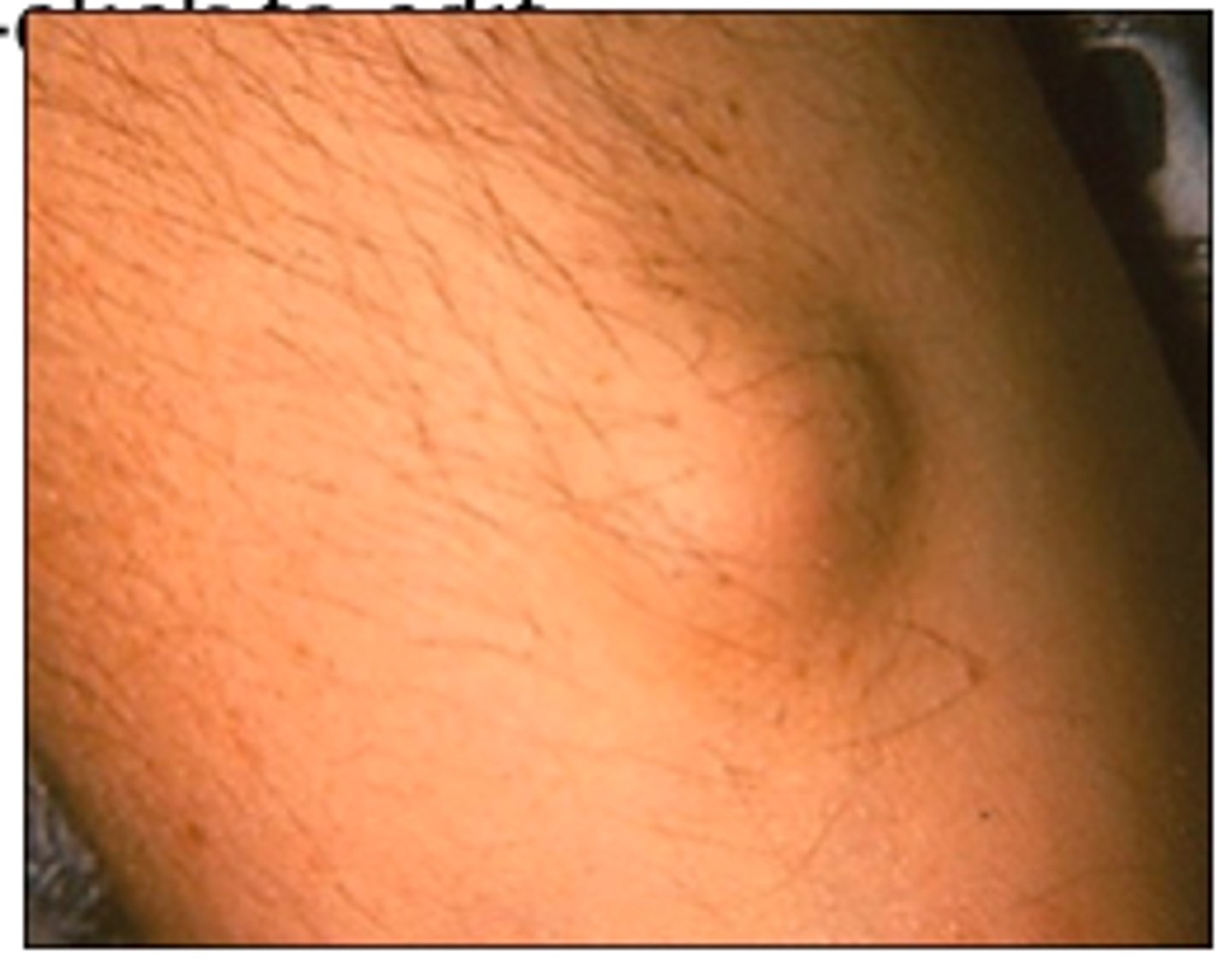
tularemia
caused by Francisella tularensis; zoonotic disease
tularemia transmission
rabbits, ticks, deer flies
tularemia creates an ______ at the site of entry
ulcer
where do bacteria reproduce and what does this cause in tularemia?
bacteria reproduce in phagocytes which enlarges the regional lymph nodes (pus filled)
parenteral skin infection tularemia mortality rate
3%
respiratory infection tularemia (tularemia pneumonia) mortality rate
30%
A 27 year old women has a fever and cough for 5 days. She is hospitalized when her blood pressure drops. Despite aggressive treatment with fluids and massive doses of antibiotics, she dies 5 hours after hospitalization. Catalase negative, gram positive cocci are isolated from her blood. what infections could cause these symptoms?
gram positive sepsis from S. pyogenes
Brucellosis
caused by Brucella spp; undulant fever
Brucella spp.
aerobic gram negative coccobacilli; Brucella abortus, Brucella suis, Brucella melitensis
Brucella abortus
elk, bison, cows
Brucella suis
swine
Brucella melitensis
goats, sheep, camels
Brucellosis transmission
transmitted via milk from infected animals or contact with infected animals
Brucellosis persists where and evades what?
in the reticuloendothelial system; evades phagocytes
symptoms of undulant fever
malaise, night sweats, muscle aches
is undulant fever usually fatal?
no
anthrax
caused by Bacillus anthracis
Bacillus anthracis
gram postive, endospore forming aerobic rod; found in soil
anthrax primarily affects what?
grazing animals
anthrax spores introduced into the body are taken up by __________ and germinate. bacteria enter the bloodstream and release _______.
macrophages; toxins
Bacillus anthracis virulence factors
protective antigen, edema toxin, lethal toxin, amino acid capsule
protective antigen
binds the toxins to target cells, permitting their entry
edema toxin
causes local swelling and interferes with phagocytosis
lethal toxin
targets and kills macrophages
amino acid capsule
avoids an immune response
cutaneous anthrax
endospores enter through a minor cut; sign: depressed, black papule
gastrointestinal anthrax
ingestion of undercooked, contaminated food
inhalational (pulomnary) anthrax
inhalation of endospores, bacteremia/toxemia drives septic shock, death within 36 hours of septic shock
cutaneous anthrax mortality rate
20%
gastrointestinal anthrax mortality rate
50%
inhalational anthrax mortality rate
100%
ischemia
loss of blood supply to tissue
necrosis
death of tissue
gangrene
death of soft tissue
gas gangrene
caused by Clostridium perfringens
Clostridium perfringens
gram positive, endospore forming anaerobic; grows in necrotic tissue, produces toxins that move along muscle bundles
gas gangrene treatment
surgical removal of necrotic tissue and/or use of a hyperbaric chamber
hyperbaric chamber
floods area with oxygen
what are 1% of ER visits annually?
animal bites and scratches (dogs make up 80% of reported bites; cats about 10%)
Pasteurella multocida
gram negative rod; causes severe swelling and pain; pneumonia and sepsis may result
cat scratch disease
caused by Bartonella henselae
Bartonella henselae
aerobic, gram negative; inhabits cat RBCs; multiplies in the digestive system of cat fleas
Bartonella henselae is carried in the blood of what percent of cats?
50%
in cat scratch disease cat claws or mouth get contaminated with what
flea feces
cat scratch disease forms a _________ at the infection site and causes what?
papule; swollen lymph nodes
cat scratch disease is self limiting t/f
true
1 multiple choice option
rat bite fever
transmitted via rat bites
what are the 2 types of rat bite fever?
streptobacillary rat bite fever and spirillar fever
streptobacillary rat bite fever
found in north america; caused by Streptobacillus moniliformis
Streptobacillus moniliformis
filamentous, gram negative, pleomorphic, fastidious
symptoms of streptobacillary rat bite fever
fever, chills, muscle pain
mortality rate of streptobacillary rat bit fever
10%
spirillar fever
caused by Spirillum minus; similar to streptobacillary rat bite fever
plague
caused by Yersinia pestis
Yersinia pestis
gram negative rod
plague transmission
rat flea (Xenopsylla cheopis)
plague is endemic to
rats, ground squirrels, prairie dogs
Yersinia _______ blocks the fleas digestive tract so when a flea bites a human host, ingested blood is regurgutated into host
biofilm