UNIT 6: cephalocaudal (EYES)
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
orbicularis oculi
muscle that allows you to close your eyes, squint, blink and wink
the lens bulges to focus on close objects and flattens to focus on far objects, possible due to the refractive ability of the lens.
snellen or snellen E chart
hand-held snellen card or near vision screener (eg Rosenbaum)
ishihara plates
penlight, opaque cards, ophthalmoscope
cotton pedget, disposable gloves
equipment for eye and vision assessment:
eyeballs
eyebrows
eyelids
bulbar conjunctivae & sclerae
palpebral conjunctivae
lacrimal apparatus
cornea & lens
iris
pupils
corneal light reflex
cover test
cardinal gaze
color vision
visual acuity (distant vision)
visual acuity (near vision)
peripheral vision
what to assess for eye and vision assessment:
note symmetry of eyeballs & for any protrusion or sinking
what to note for eyeball symmetry
symmetrically aligned in sockets s̅ protruding or sinking
sample documentation for eyeball symmetry
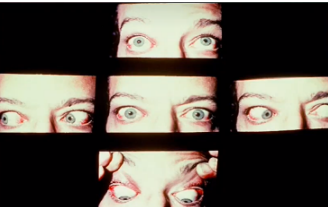
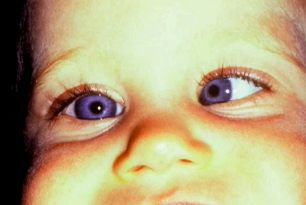
exophthalmos
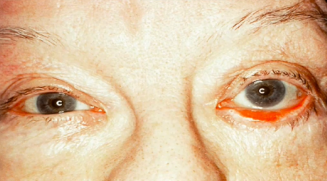
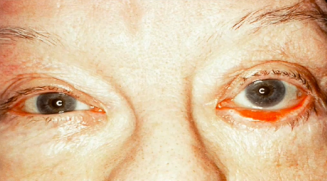
sunken eyeballs
abnormal findings for eyeball symmetry:
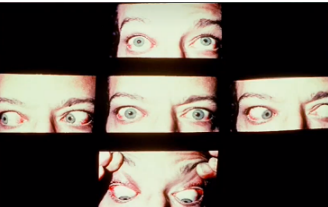
exophthalmos
(abnormal findings for eyeball symmetry)
bulging eyes
could be a sign of thyroid gland problems; it can be treated but it needs to be checked quickly as your vision can be affected

sunken eyeballs
(abnormal findings for eyeball symmetry)
“eyebags” or enopthalmos, sunk in your face. Family history, dehydration and lack of sleep.
usual to severely dehydrated px

note color, symmetry and distribution
what to note for eyebrows
same c̅ hair color; symmetric; evenly distributed
sample documentation for eyebrows
note position and appearance of eyelids and eyelashes, color changes and blinking
what to note for eyelids
let patient open and close eyes
how to assess the eyelids
lashes short, evenly spaced and curled outward;
lower lid margins at the bottom edge of iris;
upper lid margins cover approximately 2 mm of iris;
lid margins pink and moist without swelling or lesions;
upper and lower lids close easily and meet with each other
sample documentation for eyelids
ectropion
entropion
chalazion
hordeolum (stye)
blepharitis
ptosis
lagophthalmos
eye trauma
abnormal findings for eyelids:
ectropion
(abnormal findings for eyelids)
where the lower eyelids droops away from the eye and turns outward
everted lower eyelid
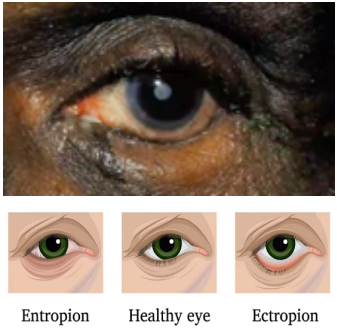
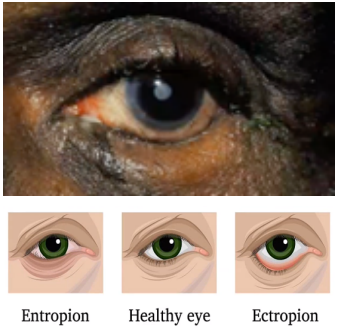
entropion
(abnormal findings for eyelids)
an inward turning of the eyelid margin and appendages such that the pilosebaceous unit and mucocutaneous junction are directed posteriorly towards the cornea and ocular surface.
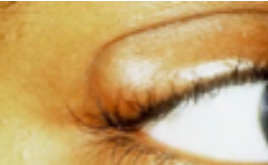
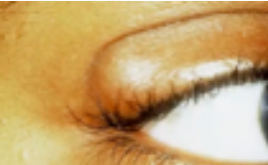
chalazion
(abnormal findings for eyelids)
a red bump on your eyelid (upper lid)
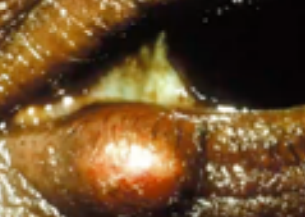
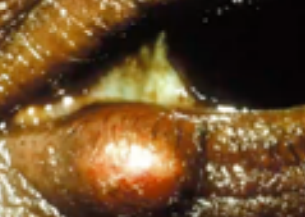
hordeolum (stye)
(abnormal findings for eyelids)
an infection of an oil gland at the edge of the eyelid. (lower lid)
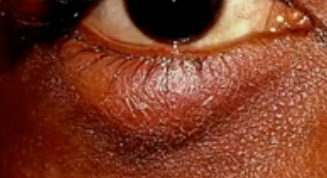
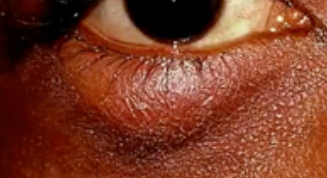
blepharitis
(abnormal findings for eyelids)
a common eye condition that makes your eyelids red, swollen, irritated, and itchy
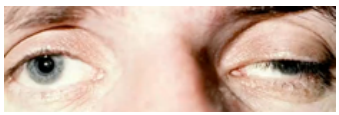
ptosis
(abnormal findings for eyelids)
drooping of the upper eyelids
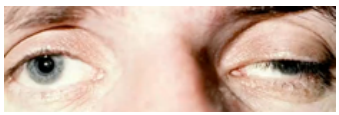
lagophthalmos
(abnormal findings for eyelids)
incomplete or abnormal closure of the eyelids
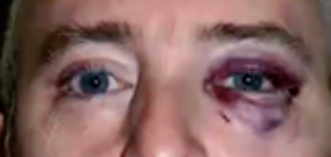
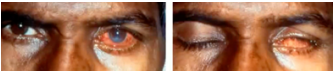
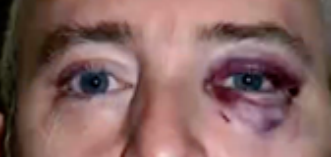
eye trauma
(abnormal findings for eyelids)
bruises, punctures, and scratches. They can result from accidents, exposure to chemicals, or foreign objects in the eye.
note for clarity, color & texture
what to note for bulbar conjunctivae
let patient look above, using object
how to assess bulbar conjunctivae
clear, moist, smooth and c̅ tiny vessels visible; sclerae are white
sample documentation for bulbar conjunctivae
conjunctivitis
pinguecula
subconjunctival hemorrhage
episcleritis
abnormal findings for bulbar conjunctivae:
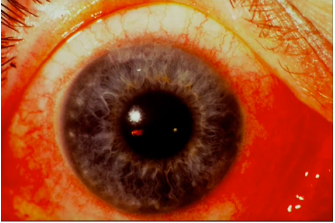
conjunctivitis
(abnormal findings for bulbar conjunctivae)
pink eye or piskat
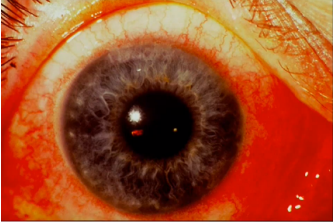
pinguecula
(abnormal findings for bulbar conjunctivae)
common type of conjunctival stromal degeneration in the eye. It appears as an elevated yellow-white plaque in their bulbar conjunctiva near the limbus
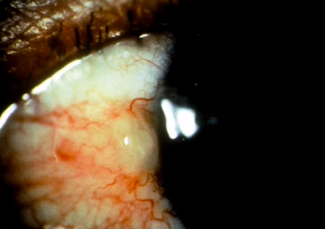
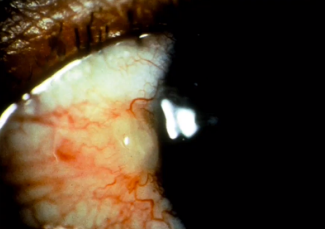
subconjunctival hemorrhage
(abnormal findings for bulbar conjunctivae)
occurs when a tiny blood vessel breaks just underneath the clear surface of your eye (conjunctiva); hypertension (HPN)
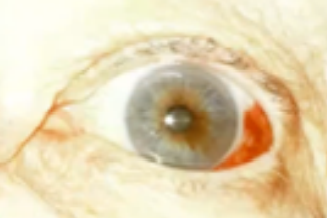
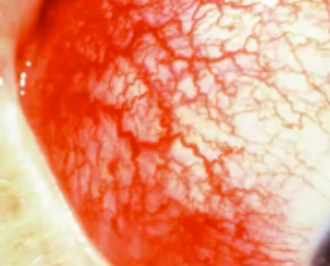
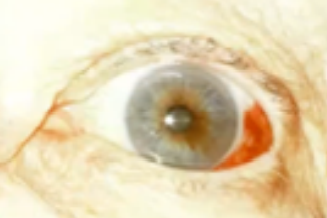
episcleritis
(abnormal findings for bulbar conjunctivae)
common, benign, self-limited cause of red eye, due to inflammation of the episcleral tissue
note for swelling, lesions, foreign bodies, trauma or discharges) / membranous membrane
what to note for palpebral conjunctivae
pull lower palpebrae down and let patient look above; use ear buds fold upper palpebrae with eyelash and pull up look down
how to assess palpebral conjunctivae
pallor
abnormal findings for palpebral conjunctivae:

pallor
(abnormal findings for palpebral conjunctivae)
pale palpebral conjunctivae;
signifies anemia, low blood count, low blood pressure

note appearance
what to note for cornea and lens
transparent, moist, and s̅ opacities; lens are clear
sample documentation for cornea and lens
arcus senilis
normal variation for cornea and lens:
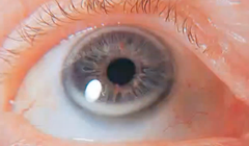
arcus senilis
(normal variation for cornea and lens)
depositing of phospholipids and cholesterol in peripheral cornea
whitish ring surrounding the cornea around the iris; normal in aging, young high cholesterol level or lipids
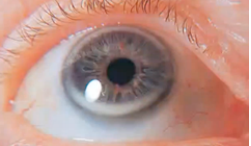
corneal scar
pterygium
cataract
abnormal findings for cornea and lens:
corneal scar
(abnormal findings for cornea and lens)
opacity of the cornea
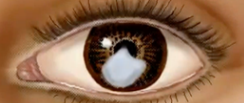
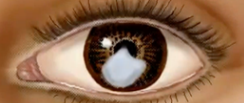
pterygium
(abnormal findings for cornea and lens)
pinkish triangular tissue growth in cornea treated with scraping
bulbar conjunctiva moves toward the cornea
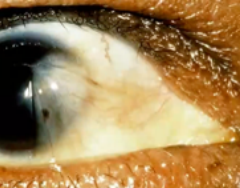
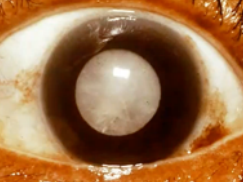
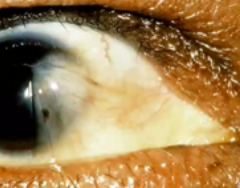
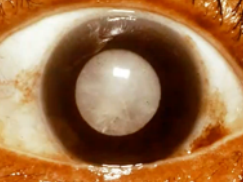
cataract
(abnormal findings for cornea and lens)
opacity of the lens, blurring of vision
note shape and color
what to note for iris
round; uniform color
sample documentation for iris
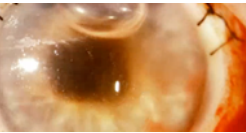
hyphema
hypopyon
abnormal findings for iris:
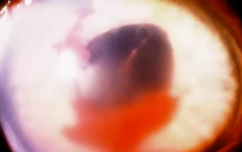
hyphema
(abnormal findings for iris)
collection of blood inside anterior chamber of eye (space between cornea and iris)
pooling or collection of blood inside the anterior chamber of the eye (the space between the cornea and the iris); trauma
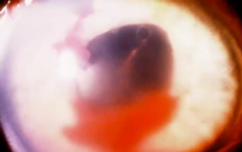
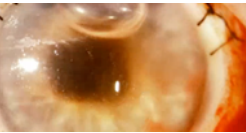
hypopyon
(abnormal findings for iris)
condition involving inflammatory cells in anterior chamber of eyes
the accumulation of white blood cells that form a whitish layer of fluid in the lower portion of the eye’s anterior chamber (front part); infection of internal eye.
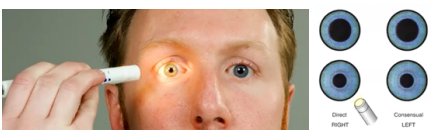
note shape, size, direct and consensual reaction to light and accommodation; 3 or 4 is normal
what to note for pupil:
P-E-R-R-L-A
pupils equally round
testing pupillary reaction to light (direct and consensual)
testing accommodation of pupils
3 procedures for assessing the pupil:
in checking the pupils - the pupils will constrict when there is light, the pupil will dilate when it is dark
(3 procedures for assessing the pupil)
testing pupillary reaction to light (direct and consensual)
equally round about 3 mm in size; illuminated pupil constricts and pupil opposite the one illuminated constricts simultaneously; pupils converge and constricts as object moves in toward nose; pupil responses uniform
(3 procedures for assessing the pupil)
sample documentation for testing accommodation of pupils
miosis
anisocoria
mydriasis
abnormal findings for pupil:
miosis
(abnormal findings for pupil)
small or constricted and fixed pupils; shrinking of pupils
drug addicts
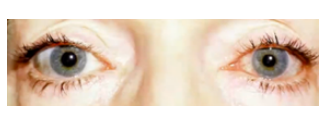
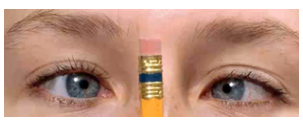
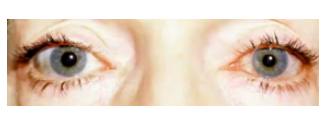
anisocoria
(abnormal findings for pupil)
pupil of one eye differs in size from the other
brain lesions.
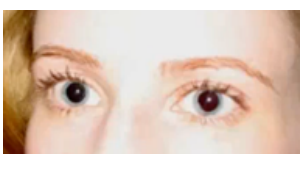
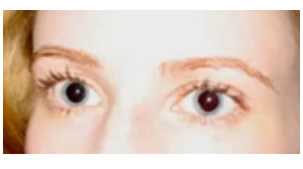
mydriasis
(abnormal findings for pupil)
unusual dilation or widening of pupil
when the black center of your eyes are larger than normal (dilated pupils); high on drugs, coffee, or stimulants
note for swelling, redness, drainage & tenderness); gland and nasolacrimal duct
what to note for lacrimal apparatus
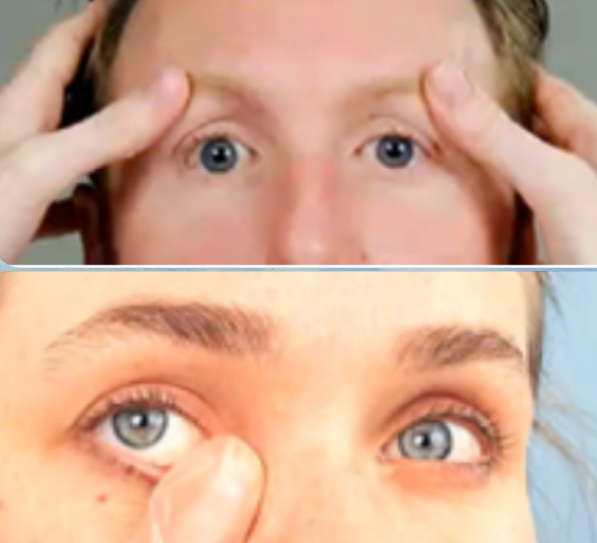
palpating lacrimal glands
palpating nasolacrimal duct
procedures in assessing lacrimal apparatus:
puncta visible s̅ without swelling or redness; no tenderness or drainage noted; minimal lacrimation
sample documentation for lacrimal apparatus
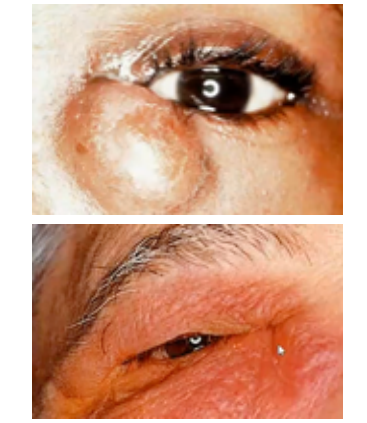
dacryocystitis
abnormal findings for lacrimal apparatus:
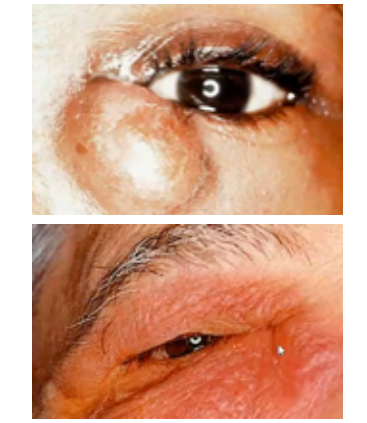
dacryocystitis
(abnormal findings for lacrimal apparatus)
characterized as an inflammatory state of the nasolacrimal sac/ lacrimal apparatus
infection in lacrimal duct due to blockage
corneal light reflex test
cover test
cardinal gaze
tests used in the assessment of extraocular muscle function inspection:
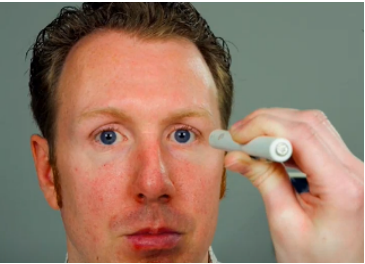
12 inches away from the client on the bridge of nose
procedure for the corneal light reflex
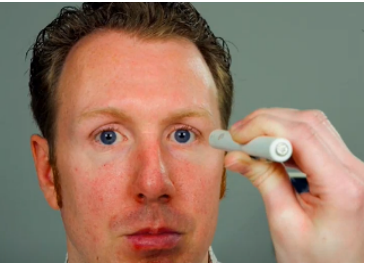
reflections of light noted at same location on both eyes.
sample documentation for corneal light reflex
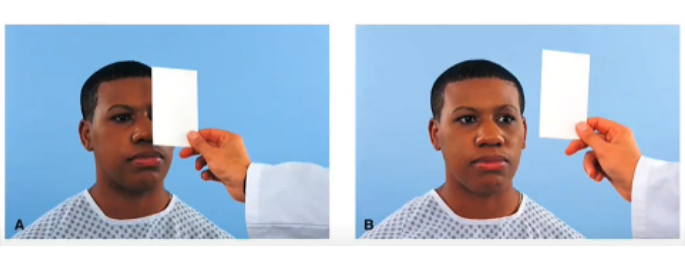
cover other eye and remove, repeat with other eye
procedure for the cover test
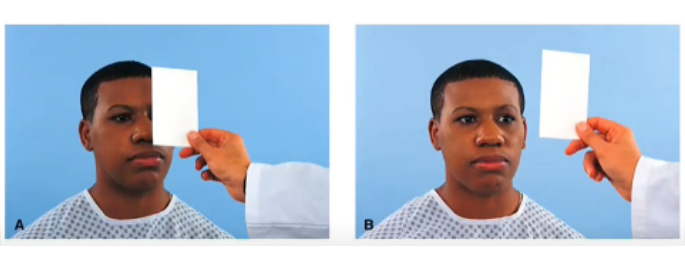
uncovered eye remains fixed; covered eye does not move as cover is removed
sample documentation for cover test
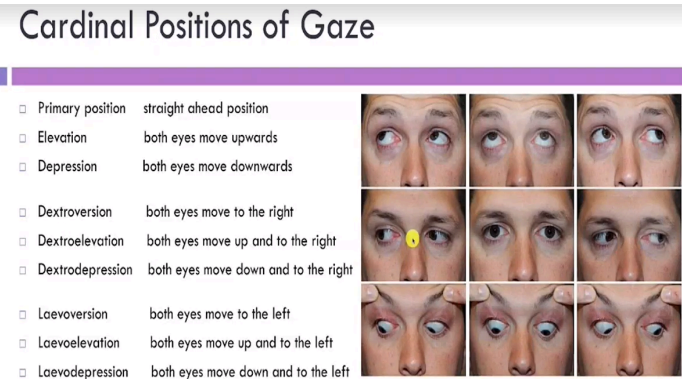
let client stare at object in 6-9 directions. Laevoeversion, Laevoelevation, and Laevodepression may not be necessary. But the other 6 are required
procedure for the cardinal gaze
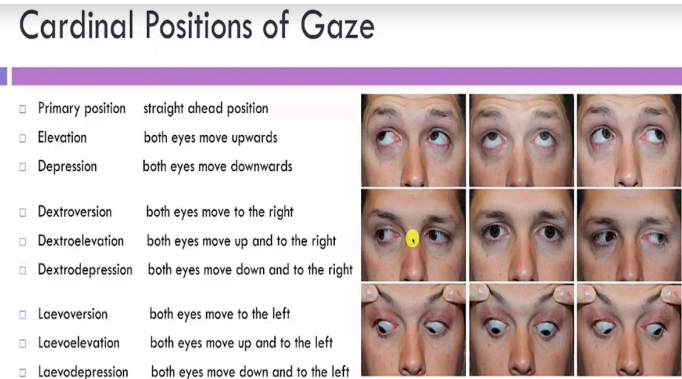
both eyes move in a smooth, coordinated manner in all 6 directions
sample documentation for cardinal gaze
strabismus (tropia)
esotropia
exotropia
nystagmus
abnormal findings for extraocular muscle function:
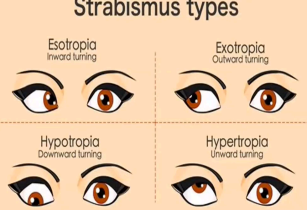
strabismus (tropia)
(abnormal findings for extraocular muscle function)
a disorder in which both eyes do not line up in the same direction; crossed eye.
constant malalignment of the eyes
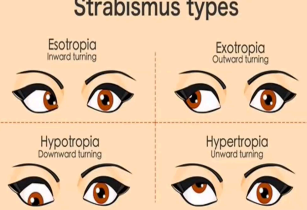
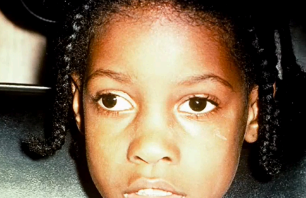
esotropia
(abnormal findings for extraocular muscle function)
an eye misalignment in which one eye is deviated inwards, or nasally
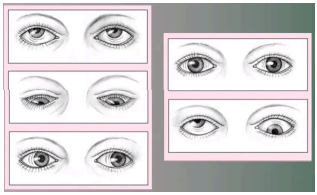
exotropia
(abnormal findings for extraocular muscle function)
a type of eye misalignment , where one eye deviates outwards

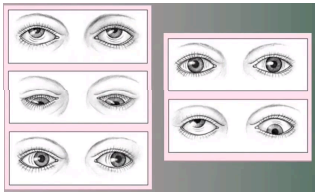
nystagmus
(abnormal findings for extraocular muscle function)
a vision condition in which the eye makes repetitive, uncontrolled movements; inner ear problem
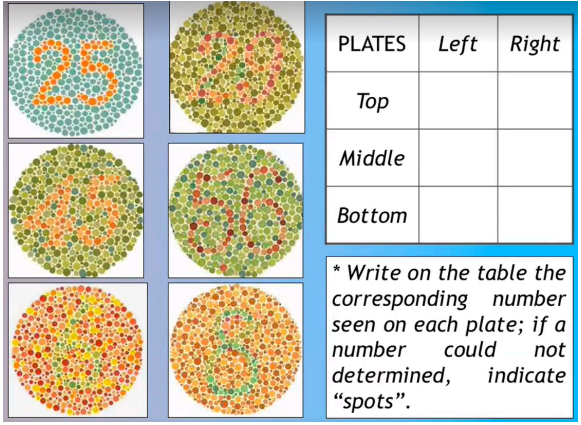
six screening ishihara plates; write on the table the corresponding number seen on each plate; if a number could not determined, indicate “spots”
procedure in assessing color vision
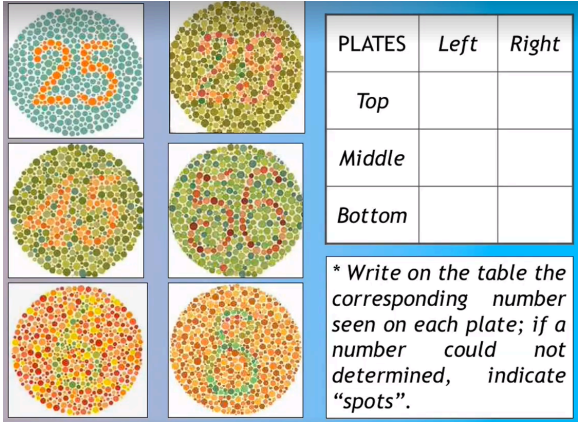
able to identify primary colors in snellen chart & in exam room; identifies all six screening ishihara plates correctly
sample documentation for color vision
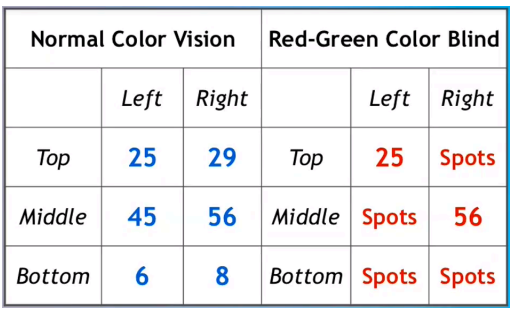
interpretation of ishihara test (sample)
snellen chart / snellen e-chart away 20 feet or 6 meters
procedure in assessing visual acuity: distant vision
20/20 OD & OS s̅ hesitation, frowning or squinting
sample documentation for visual acuity: distant vision
astigmatism
myopia
amblyopia
abnormal findings for visual acuity: distant vision:
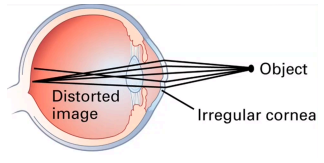
astigmatism
(abnormal findings for visual acuity: distant vision)
happens when your cornea (the clear front layer of your eye) or lens (an inner part of your eye that helps the eye focus) has a different shape than normal; irregular cornea
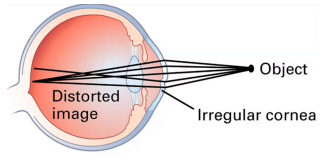
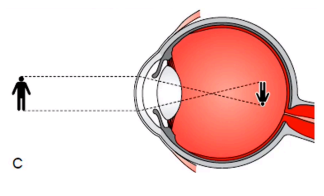
myopia
(abnormal findings for visual acuity: distant vision)
a common vision condition in which near objects appear clear, but objects farther away look blurry (nearsighted)

amblyopia
(abnormal findings for visual acuity: distant vision)
also called lazy eye. a type of poor vision that usually happens in just 1 eye but less common in both eyes; legally blind. The lazy eye cannot see
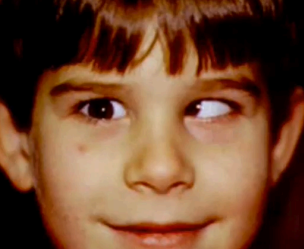
cover other eye and read rosenbaum 14 inches away
procedure in assessing visual acuity: near vision
pocket snellen chart, rosebaum card, jaeger test card
variations used in assessing visual acuity: near vision
reads print at 14 inches s̅ difficulty
sample documentation for visual acuity: near vision
hyperopia
presbyopia
abnormal findings for visual acuity: near vision:
hyperopia
(abnormal findings for visual acuity: near vision)
far sighted
presbyopia
(abnormal findings for visual acuity: near vision)
aging
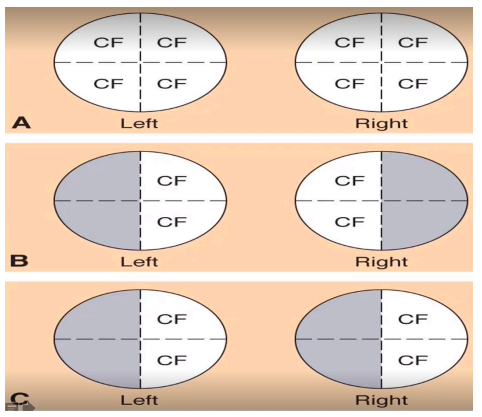
cover other eye and let client signal if object can be seen in their peripheral vision
procedure in assessing peripheral vision (confrontation test)
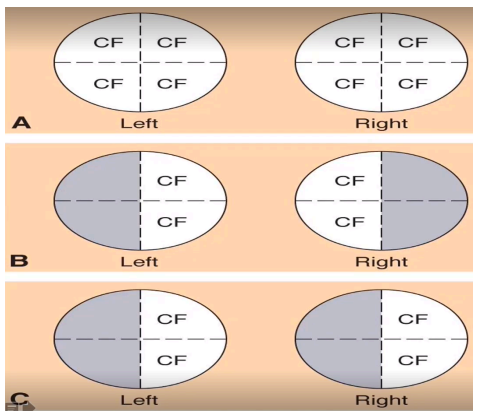
client sees examiner’s finger at the same time the examiner sees it (visual fields full by confrontation)
sample documentation for peripheral vision (confrontation test)