Biological molecules (M2)
1/65
Earn XP
Description and Tags
water carbs lipids membranes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
what type of molecule is water ?
polar molecule
why is water a polar molecule ?
it is a neutral molecule but has dipoles
what are dipoles in molecules ?
areas with a slight charge caused by having fewer or more electrons of different regions in the same molecule
how do water molecules bond in terms of dipoles ?
the positive ( hydrogen ) dipoles of one water molecule attract the negative dipoles (oxygen) forming hydrogen bonds
What is cohesion ?
water molecules ‘sticking tg ‘ bcs of hydrogen bonds .
Adhesion
water molecules ‘sticking’ to other molecules on surfaces because of hydrogen bonds
why is water a good solvent for ions or other polar molecules ?
the negative ions attract the positive dipoles in the water molecule while the positive ions attract the negative dipoles in the water which form hydration shells around the ions allowing the water molecules to dissolve the substances that are either ionic or polar
cohesion of water causes s____ t____
surface tension
What is surface tension?
A measure of how difficult it is to stretch or break the surface of a liquid.
How does surface tension benefit organisms?
It enables appropriately adapted organisms to use the surface of the water as a habitat.
biological consequences of water having a high shc
aquatic environments maintain a relatively stable temp throughput the year regardless of weather temps making them hospitable habitats for life
biological consequences of water having a high latent heat of vaporisation
plants and animals can lose excess heat energy by evaporation of water from their surfaces e.g transpiration or sweating which allows them to maintain a stable body temp
what are monosaccharides give 4 examples and what they have in common
single sugar molecule e.g. alpha/beta glucose fructose galactose all hexose sugars
what are pentose /hexose sugars
pentose contain 5 Carbons while hexose contains 6
disaccharide
two monosaccharides linked covalently by a glycosidic bond
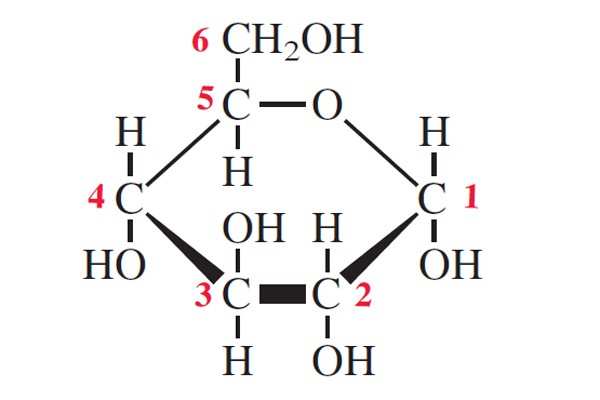
what type of glucose is this and how do u know
alpha glucose the OH on the right side is on the bottom not the top
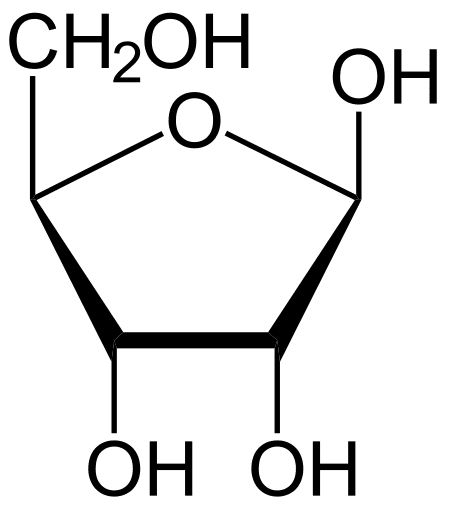
what is this
ribose -pentose monosaccharide
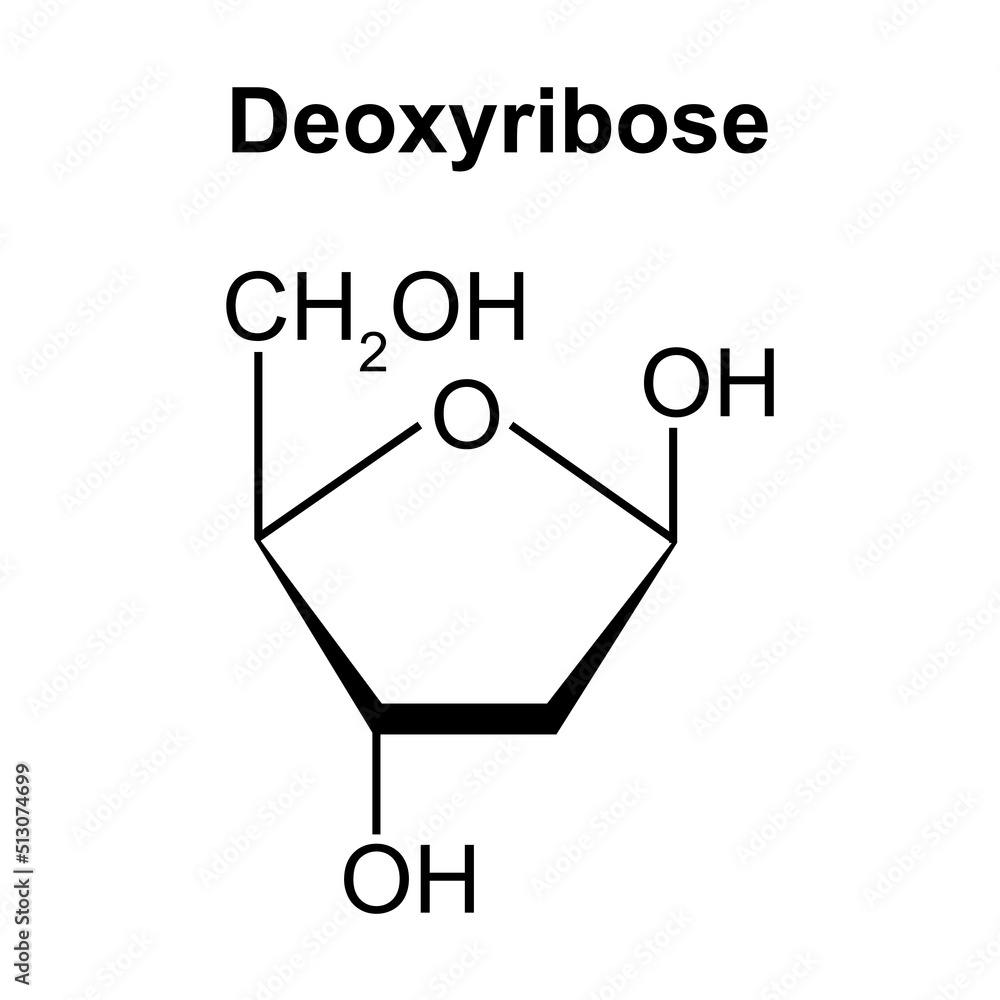
what is this
deoxyribose - pentose monosaccharide
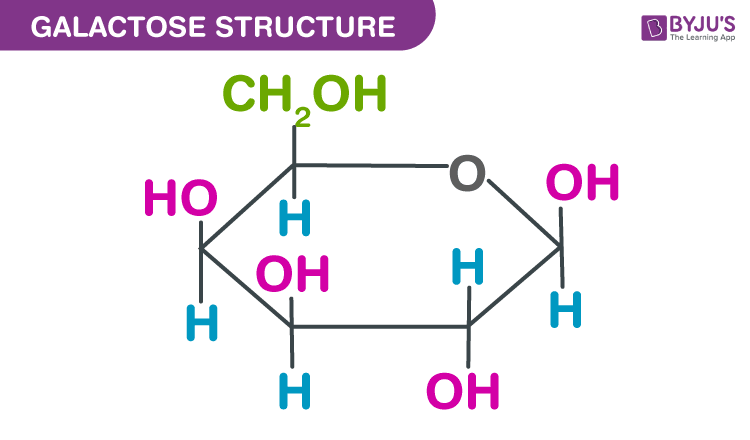
what molecule is this ?
galactose
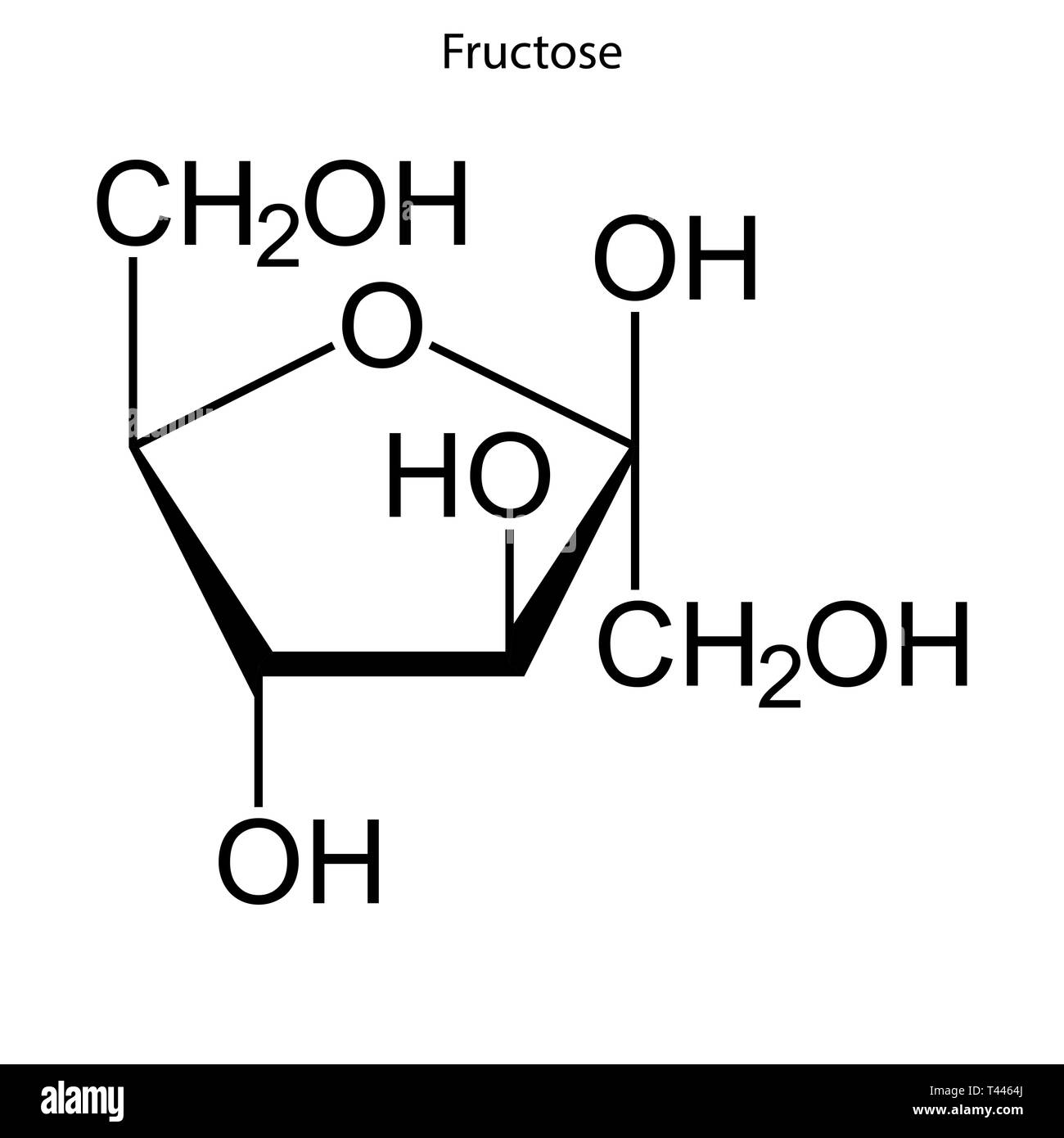
what is this ?
fructose
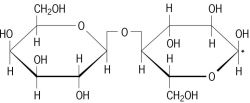
what two monosaccharides make up lactose ?
beta glucose and galactose with a beta 1-4 glycosidic bond
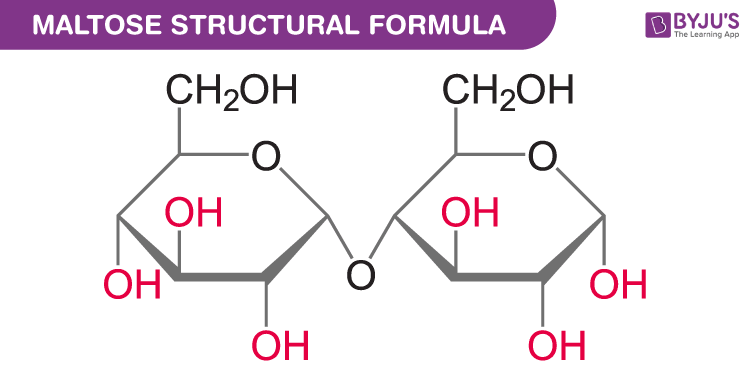
what two monosaccharides make up maltose
two alpha glucoses with an alpha 1-4 glycosidic bond
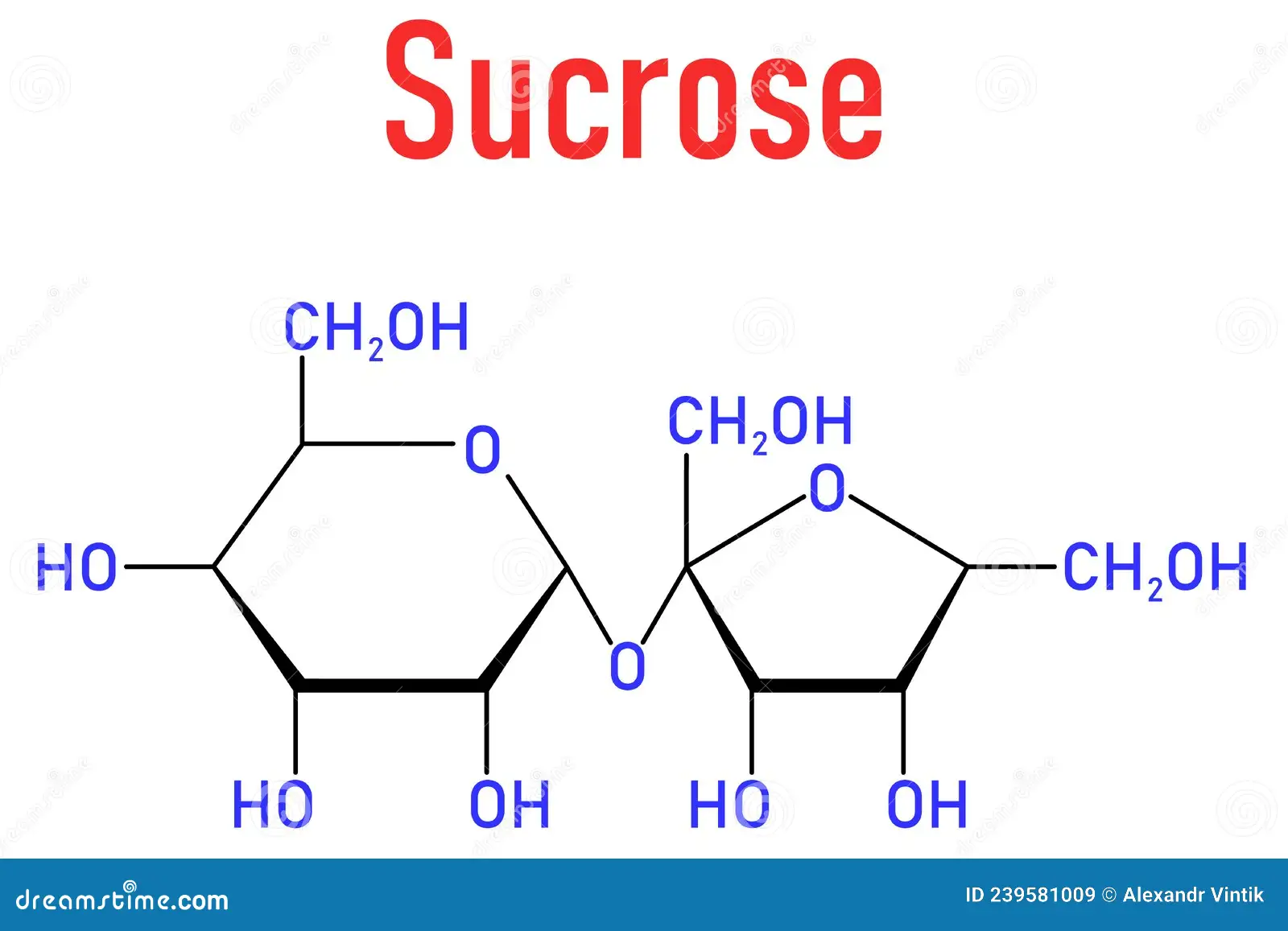
which monosaccharides make up sucrose ?
alpha glucose and fructose with an alpha 1-2 glycosidic bond (as the fructose is flipped)
how do yk if a bond is alpha or beta ?
alpha bond points downwards beta points upwards
what are the three hexose monosaccharides and why are they all soluble in water ?
glucose fructose and galactose which are all structural isomers .
they’re all soluble in water bcs they have OH grps which form hydrogen bonds w/ water molecules
what are isomers
molecules that have the same molecular formula but differ in their structural arrangement, leading to different properties and functions
glycosidic bond
covalent bond joining 2 monosaccharides
condensation reaction
removal of water to form a bond
hydrolysis
addition of water to break a bond
disaccharide
2 monosaccharides joined tg by a glycosidic bond
how are the structural features of glucose related to its functions ?
5 OH grps so… :
-high solubility in water / transport in the blood or phloem
-chemically reactive -can be oxidised to release energy
OH grps ring structure means :
-it forms polymers w/ other glucose molecules
-OH grps can condense to form glycosidic bonds
a and b isomers :
-form polymers w/ diff roles
-a glucose = energy storage
-b glucose = structural
how are disaccharides hydrolysed ?
by digesting each disaccharide using its specific hydrolytic enzyme (maltose , lactose and sucrase e.g. in our digestive systems ) or by heating in acid
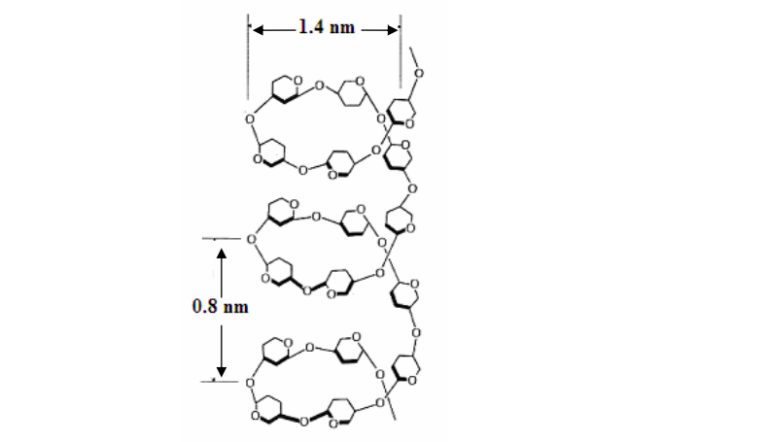
what is this ?
the polysaccharide amylose
consists of long chains of alpha glucose joined by 1-4 glycosidic bonds
coils up into a helix held tg by hydrogen bonds
insoluble due to its coiled structure preventing osmosis
makes up 20-30% of starch grains
only poly detectable by iodine which becomes trapped inside the long coil forming blue/black colour
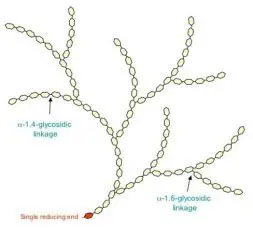
what is this ?
polysaccharide amylopectin
large molecule 10-100k a glucose units
makes up 70% of starch grains
consists of chains of a glucose linked by 1-4 glycosidic bonds with alpha 1-6 glycosidic bonds forming branches every 25-30 glucose residues
significance of branching in amylopectin ?
glucose molecules can be hydrolysed frm the free ends of each branch
so more branches means more glucose can be released for respiration
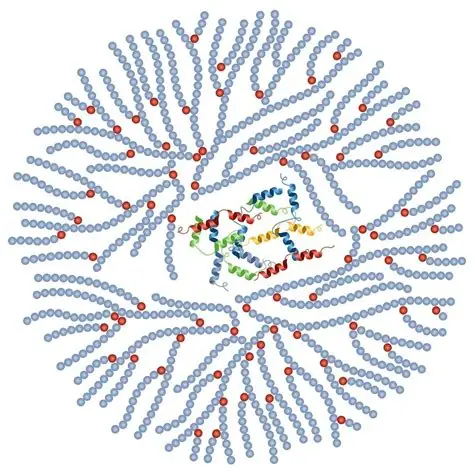
what is this ?
the polysaccharide glycogen
alpha glucose storage molecule of animal cells
more branches than amylopectin bcs animals need more energy so more glucose needs to be released at a time
chains o alpha glucose joined by alpha 1-4 glycosidic bonds with alpha 1-6 glycosidic bonds forming branches every 10-12 glucose residues
how is glycogen stored
stored in cells as glycogen granules
-30-50k a glucose monomers surrounding a core protein called glycogenin
more branches makes it compact so more energy can be stored in a smaller volume
what are the features of a good storage molecule ?
compact- doesn’t take up too much space in a cell
insoluble-cant dissolve in water then be lost in cells
no osmotic effect - doesn’t pull water into cells by osmosis
easily hydrolysed - releases glucose when needed for respiration
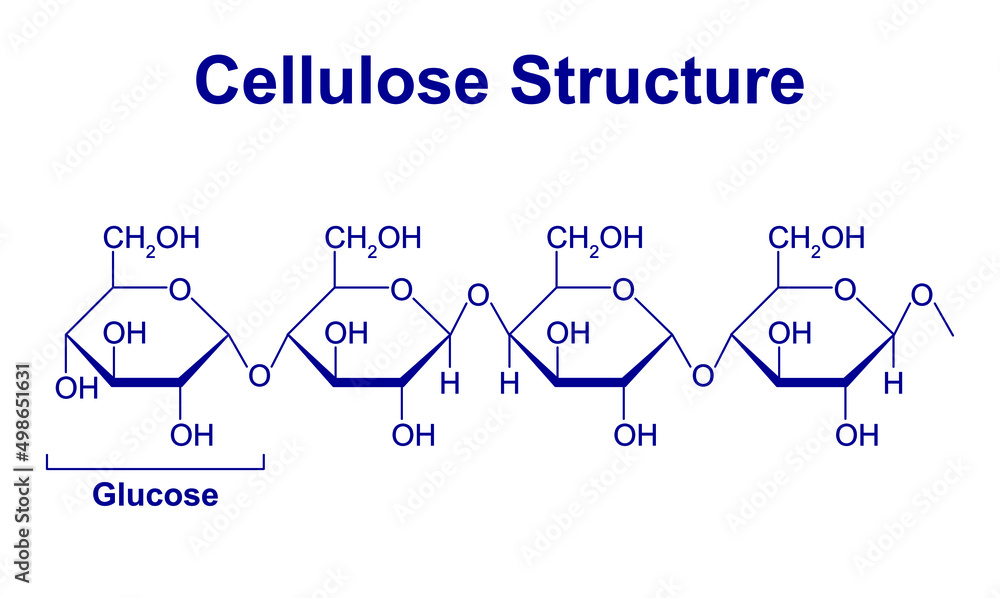
what is this ?
cellulose
polymer of B glucose monomers joined by 1-4 beta glycosidic bonds to form straight unbranched chains
every 2nd glucose must be flipped 180 degrees
individual chains are held tg by hydrogen bonds to form microfibils which bond tg to form fibres
fibres r laid down in diff directions to form a cell wall
cellulose has high tensile strength - means it can resist a large pulling force w/o breaking
reducing sugar test
add benedict’s reagent to sugar solution
heat in a boiling water bath for 5 mins
-sugars w/ aldehyde or ketone grps reduce Cu2+ ions in benedicts solution to Cu+ which forms brick red precipitate
what are the reducing sugars
all hexose monosaccharides ( glucose fructose galactose) as they can all open up to form straight chain aldehyde or ketone
the disaccharides lactose and maltose can open up one of their rings - so r also reducing sugars
results for sugar test
blue green - low conc
brown / orange - med conc
brick red - high conc
why is sucrose a non reducing sugar ?
bcs C1 of A glucose and C2 of fructose form the glycosidic bond neither of the two rings can open up
the glycosidic bond must first be hydrolysed to form its two monos
test for non reducing sugars
add benedict’s reagent and boil for 5 mins - neg result
add HCL to sugar solution and boil for 5 mins
neutralise w/ sodium hydrogencarbonate
add benedict’s reagent and boil for 5 mins
what are lipids?
macromolecules containing the elements carbon hydrogen and oxygen
what are the different functions of lipids ?
energy storage
thermal insulation
protection
membrane structure
electrical insulation
steroid hormones
why are lipids used as energy stores ?
they contain more energy per gram than any other type of food molecule
how are lipids used for thermal insulation ?
subcutaneous deposits of adipose tissue prevent heat loss
how are lipids used for protection
adipose tissue cushions internal body organs
what is the role of lipids in membrane structure?
all biological membranes are made from phospholipids
what is the role of lipids in electrical insulation?
nerve fibres are surrounded by a fatty myelin sheath
what is the role of lipids in steroid hormones ?
they’re all made of the lipid cholesterol
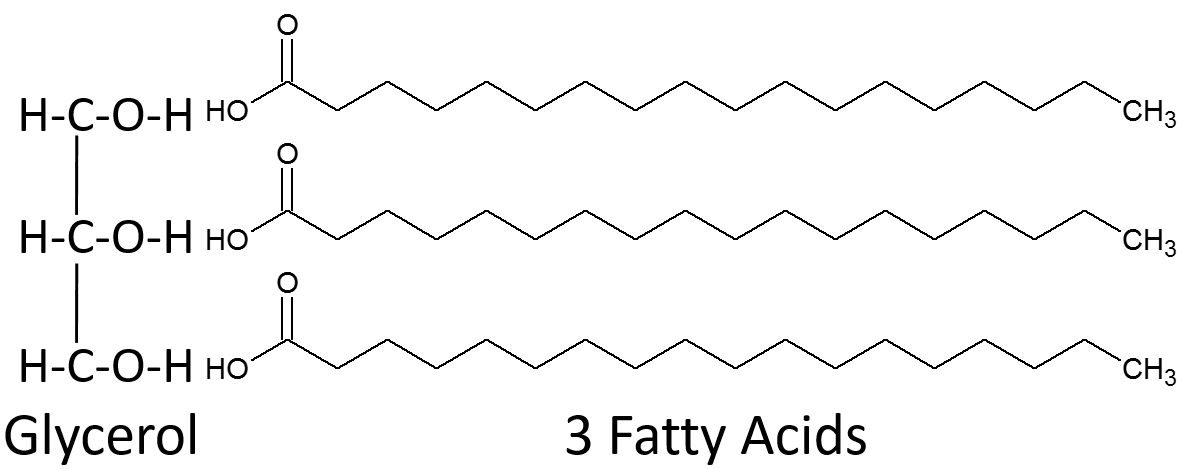
how are triglycerides formed
by the condensation reaction of 1 glycerol and 3 fatty acids
what are the two types of fatty acids and compare them
saturated :
more common in animals
high mps make them solid at room temp e.g. lard
no double bond bcs molecules is saturated w/ hydrogen atoms
unsaturated:
more common in plants
low mps make them liquid at room temp
do contain double bonds bcs molecule is not saturated w/ hydrogen atoms
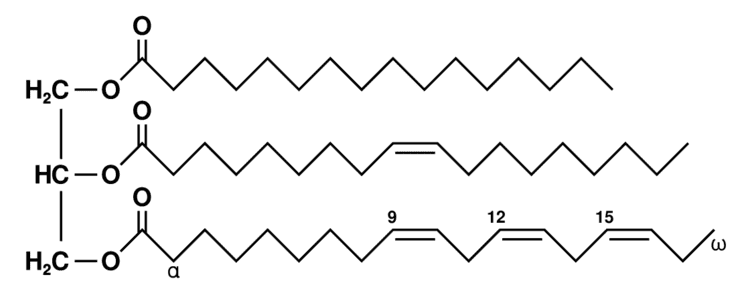
explain how triglycerides form by condensation reactions ?
a glycerol has 3 OH grps
each one of its OH groups interact with that of a fatty acid leading to the formation of three water molecules and three ester bonds
triglycerides consisting of saturated vs unsaturated fatty acid tails
saturated:
pack tighter
higher mp
less fluidity
tallow / lard
unsaturated :
packs less closely bcs of kinks
lower mp
more fluidity
olive oil
two types of unsaturated fatty acids
polyunsaturated - more than one double bond
monounsaturated - one double bond
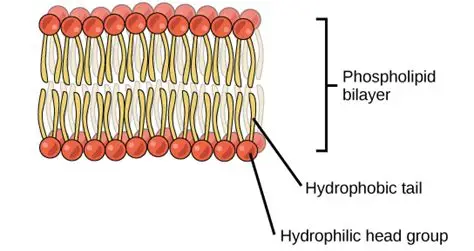
describe the role of phospholipids
they naturally form a bilayer
hydrophilic phosphate head grps make contact w/ water on the inside and outside
hydrophobic fatty acid tails cluster tg away frm water in the middle
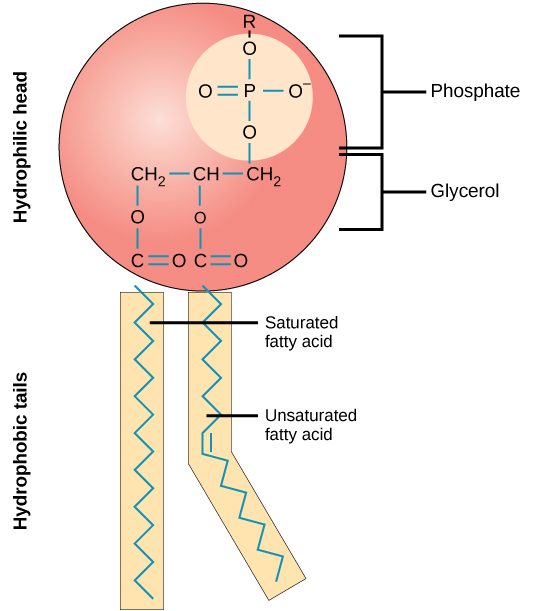
structure of phospholipids
1 phosphate group - neg charge so water soluble( hydrophilic )
1 glycerol
2 fatty acids form the tail (being uncharged and non polar makes them water repelling (hydrophobic) )
what are phospholipids ?
modified triglycerides that contain the element phosphorus as well as Carbon hydrogen and oxygen
one of the fatty acids chains in a triglyceride molecule is replaced with a phosphate grp to make a phosphate lipid
describe the structure of cholesterol
central sterol nucleus made of 4 HC rings (found in all steroid hormones )
HC tail
hydroxyl grp
what are sterols ?
another type of lipid found in cells . complex alcohol molecules based on a four C ring structure with an OH grp at one end e.g. cholesterol
describe the functions of cholesterol
to maintain stability and regulate the fluidity of cell membranes
precursor for the synthesis of steroid hormones , bile acids and vitamin D
how does cholesterol form part of the cellular membrane ?
makes membranes less fluid (it holds the phospholipids tg so they dont move as much )
OH grp sits between the phosphate head grps and the rest of cholesterol is hydrophobic so sits w/ the fatty acids
effect of cholesterol in the phospholipid bilayer
tighter packing
incs mp
decreases fluidity
test for lipids
dissolve the sample in alcohol and mix well
pour the alc into water
if a lipids present a milky white emulsion forms