Oxygen Binding Proteins
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Myoglobin
Binds oxygen and stores it for use when muscles expend energy and need to convert molecules from food into useable forms
Heme
The prosthetic group of myoglobin and haemoglobin and consists of an organic constituent, protoporphyrin IX, and an iron atom
Myoglobin binding O2
Myoglobin binds O2 as the O2 partial pressure increases
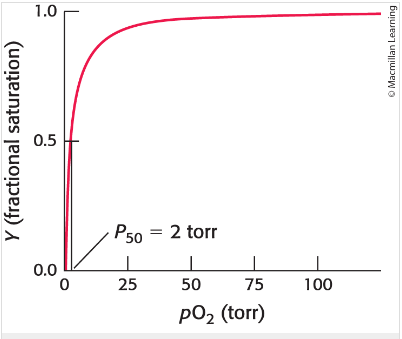
Oxygen binding curve
Plots the fraction of possible binding sites that contain O2 , the curve rises as O2 partial pressure increases then levels off
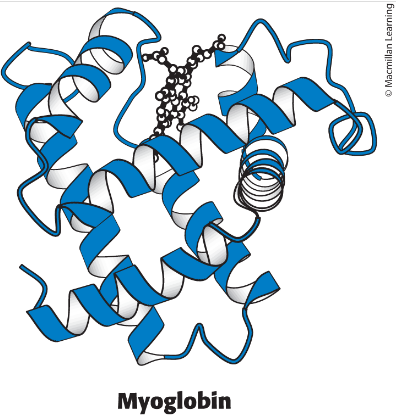
Structure of myoglobin
a single polypeptide chain, made up of alpha-helixes, and a heme ligand
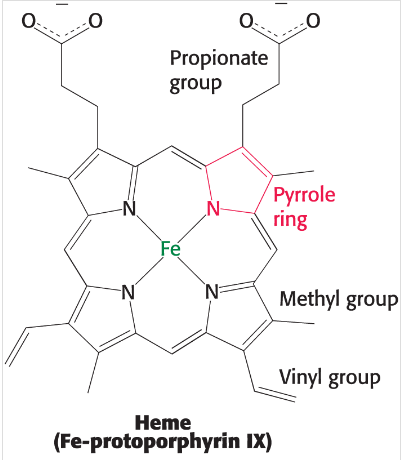
Structure of Heme
Organic compound, made of four linked pyrrole rings attached with a central iron atom by nitrogen and its binding sites are referred to as the 5th and 6th coordination sites
Deoxymyoglobin
Oxygen-free myoglobin
Structure of Deoxymyoglobin
The iron is in a ferrous oxidation state and is too large to fit in porphyrin ring. The sixth site unoccupied
Oxymyoglobin
Bound oxygen myoglobin
Structure Oxymyoglobin
Forms when oxygen binding occurs in the 6th coordination site and rearranges the electrons within the iron so that the ion becomes smaller, allowing it to move into the plane of the porphyrin
Myoglobin and Carbon Monoxide
CO blocks and inactivates the binding site of myoglobin, preventing the binding of O2
Haemoglobin
Heme-containing oxygen carrier found in the bloodstream
Structure of Haemoglobin
Four polypeptide chains, two alpha-helices and two beta-sheets
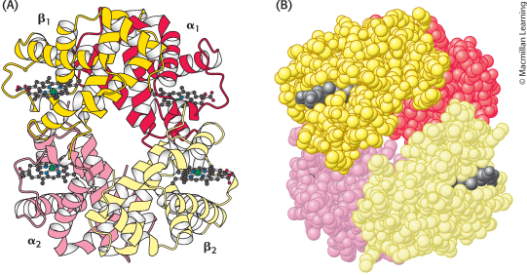
Haemoglobin binding
O2 binding for haemoglobin is weaker than for myoglobin
Cooperative binding behaviour
Binding reactions of individual sites are not independent
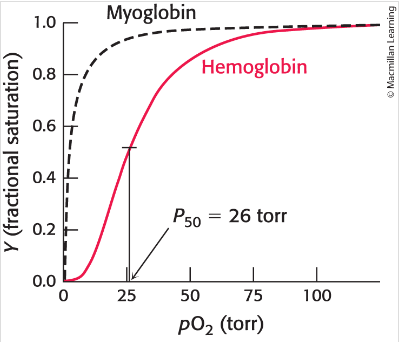
Haemoglobin oxygen binding curve
Sigmoidal curve indicates that the binding site of oxygen at one site within haemoglobin increases likelihood of O2 binding at the remaining unoccupied sites
Advantages of cooperative binding behavior
Efficient O2 transport, release of O2 favours more complete delivery to tissue, O2 delivered to tissue where needed most
Oxygen binding in Haemoglobin
Alpha1,Beta1 dimers in quaternary structure rotate 15 degrees with respect to one another, the interface between Alpha1,Beta1 and Alpha2,Beta2 dimers affected as free to move with respect to one another in oxygenated state
T state
Quaternary structure in deoxy form of haemoglobin (tense)
R state
Quaternary structure of oxy form of haemoglobin (relaxed)
2,3 Bisphosphoglycerate
In the presence of 2,3-BPG, haemoglobin can transition from a high-oxygen-affinity state to a low-oxygen-affinity state, making oxygen transport more efficient
How does 2,3-BPG work
Single molecule of 2,3-BPG binds in a pocket in the centre of the tetramer of haemoglobin (only present in T-state), During T-state to R-state transition the pocket collapses, releasing 2,3-BPG. Therefore in order for the structural transition from T to R, the interactions between 2,3-BPG and haemoglobin must be disrupted. In the presence of 2,3-BPG, more O2 binding sites within haemoglobin tetramer must be occupied for the T-to-R transition and so haemoglobin remains in lower-affinity T-state until higher O2 concentrations are reached
Affect of Hydrogen and Carbon Dioxide in O2 release
Haemoglobin responds to higher levels of hydrogen and carbon dioxide in tissues and will release O2 to where it is needed most
Hydrogen ions
O2 affinity of haemoglobin decreased as pH decreases from value of 7.4, ionic interactions stabilise T-state leading to a greater tendency to release O2
Carbon Dioxide effect
CO2 reacts with water to form bicarbonate ion (H3O+ and H+), dropping the pH that stabilises T-state
Sickle Cell Anemia
Abnormal sickle shape of red blood cells deprived of oxygen
How sickle cell anaemia works
Haemoglobin molecules form large fibrous aggregates which extend across the red blood cell, distorting them so they clog small capillaries and impair blood flow. They don’t remain in circulation for long as when sickling occurs, can increase tendency of cells to lyse, leading to anaemia