Modern Western Civilizations Exam 1
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
111 Terms
What was the significance of the Peace of Augsburg (1555)?
It made Lutheranism a legal religion in the predominantly Catholic Roman Empire, but it did not extend recognition to Calvinism.
What was the staple food of European peasants in the 16th, 17th, and 18th centuries?
Grain
Which of the following was the only European state to emerge unscathed from the economic downturn of the early 17th century, thanks to its growing population and a tradition of agricultural innovation?
The Dutch Republic
By the end of the Thirty Years’ War, the balance of power in Europe
had shifted away from the Habsburg powers toward France, England, and the Dutch Republic.
Which French Catholic ruler ushered in the French Wars of Religion after a disastrous attempt to play rival factions against one another?
Catherine de Medicis
Demographic historians who have studied the 16th and 17th centuries confirm that in times of economic crisis Europeans tended to
postpone marriage, often until their late twenties, and have fewer children.
How did the long-term process known as secularization affect the study of science and the natural world?
Religion because a matter of private conscience rather than public policy, this allowing people to seek nonreligious explanations for natural phenomena.
The career of Cardinal Richelieu (1585-1642) as chief member of France
reflected a new belief in raison d’stat, or the primacy of the state’s interest above all else.
Why was Galileo Galilei (1564-1642) put on trial before the inquisition in 1633?
He was accused of disobeying the Catholic church’s order that he not teach that the earth revolves around the sun.
Why did King Henry IV declare “Paris is worth a Mass”?
He converted to Catholicism to ensure his control over France, believing that he needed to place the interests of the state ahead of his Protestant faith.
What divided the northern and southern provinces of the Netherlands even after they drove out the Spaniards in 1576?
The southern provinces remained largely Catholic, while the northern Protestants were predominantly Protestant.
Although William Shakespeare did not set plays like Hamlet (1601) in his own era, they nevertheless reflect what primary concern of his age?
The nature of power and the crisis of authority
The artistic style known as the baroque was most closely tied to which religious movement?
The Catholic resurgence after the Reformation
Which of the following was argued by the French scholar René Descartes (1596–1650)?
A scientific approach to knowledge could lead to a secure understanding of nature and human behavior.
What was the significance of the Church of England's Thirty-Nine Articles of Religion, which were issued in 1563 under the authority of Queen Elizabeth I?
They combined elements of Catholic ritual with Calvinist doctrines.
What was one of the chief goals of Ivan the Terrible and his successors?
To expand and make Muscovy the heart of a mighty Russian Empire
The Thirty Years' War ended in 1648 after the signing of which of the following documents?
The Peace of Westphalia
Why did France join in the Thirty Years' War in 1635, more than twenty years after the war began?
The French king Louis XIII hoped to profit from Spain's troubles in the Netherlands and from the Austrian emperor's conflicts with Protestants in his empire.
Why did witchcraft trials begin to decline in the mid-seventeenth century?
Scientists, physicians, lawyers, and clergy came to believe that the accusations were based on superstition.
Although serfdom had virtually disappeared in Western Europe by the 17th century, where did it intensify?
Eastern Europe
Principia Mathematica (1687), which synthesized the laws of movement and universal gravitation, was the work of what great scholar?
Issac Newton
How did the Edict of Nantes, issued by Henry IV in 1598, end the French Wars of Religion?
It granted Protestants a large measure of toleration, such as freedom to worship in specified towns and the right to retain their own troops, courts, and fortresses.
What 1571 event ended Turkish dominance of the Mediterranean Sea?
Philip II’s naval victory at Lepanto off the Greek coast.
What prompted Philip II to send his Spanish Armada against England and Elizabeth I in 1588?
Elizabeth’s execution of her Catholic Cousin Mary, queen of Scots.
The French Catholic Lawyer Jean Boudin (1530-1596) is perhaps best known for his defense of what doctrine?
Monarchical absolutism
By about 1648, western and central Europe were primarily
Catholic
How did the Thirty Years’ War affect European civilians?
It resulted in widespread suffering and devastation and led to peasant revolts and even outbreaks of plague.
In what ways did European states engage in economic and political competition in the New World?
They chartered private joint-stock companies to import new goods and natural resources, and they invested in the burgeoning slave trade and plantation economies in the New World.
Which European ruling family had lost a significant amount of political and economic power by the end of the 17th century?
The Habsburgs
Which of the following was a result of the flood of precious metals from the Americas and the tremendous growth in population that took place during the 16th century?
A drastic inflation of food prices that reached up to 400 percent.
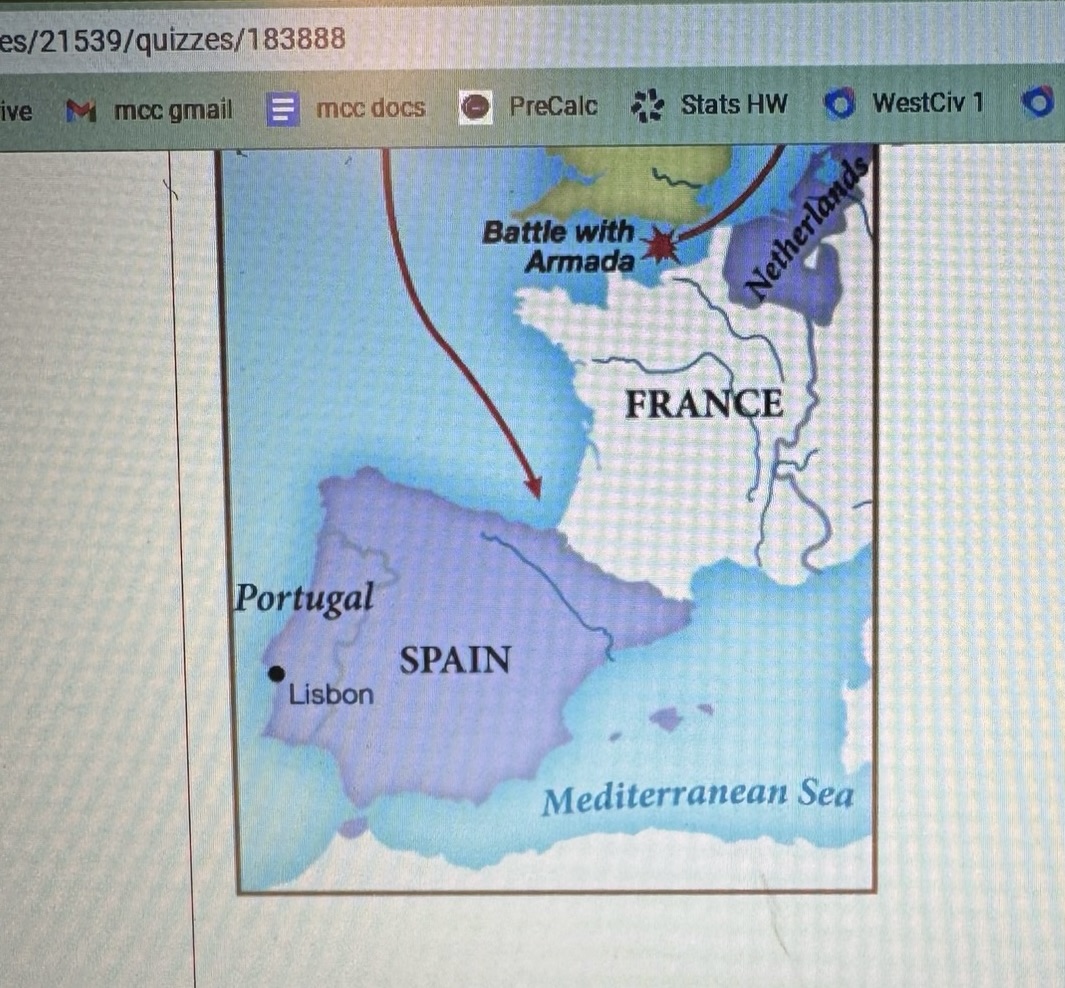
Saved the English from a Spanish invasion.
What was the purpose of Louis XIV's expansion and professionalization of the French military?
To expand French power in Europe and increase France's territorial holdings on the continent
What was the name given to runaway serfs and poor nobles who formed outlaw bands in the no-man's-land of southern Russia and Ukraine?
Cossacks
The series of revolts in France known as the Fronde (1648–1653) broke out when Cardinal Mazarin
arrested his opponents for demanding that the parlements be given the right to approve new taxes.
How did the breakdown of constitutionalism, the violence of the Cossack revolts, and a Russo-Polish war affect religious toleration in Poland-Lithuania?
Religious toleration ended, as Jews fled to shtetls and Protestants fled Catholic reprisals for their support of Sweden during the war.
For more than 150 years, the Austrian Habsburgs and the Ottoman Turks fought over what territory?
Hungary
Seventeenth-century absolutism was a political response to which of the following French developments?
The fear of disorder and breakdown that was the legacy of the Fronde revolts
In the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries, the poor were no longer perceived as deserving of charity but as
dangerous degenerates in need of moral reform through harsh discipline.
By agreeing to Parliament's demand for a Petition of Right in 1628, Charles I
promised not to levy taxes without Parliament's consent.
What were the consequences of Louis XIV's revocation of the Edict of Nantes in 1685?
The Calvinists lost all their rights, their churches and schools were closed, and they were forced to convert to Catholicism, leading thousands to flee the country.
Which region did Louis XIV acquire following the Treaty of Rijswijk in 1697?
Alsace
Who was the titular head of the Dutch Republic’s decentralized constitutional state?
The stadholder
Why do some historians view the English civil war of 1642-1646 as the last Great War of religion?
It pitted Puritans against those trying to push the Church of England toward Catholicism
By agreeing to Parliament’s demand for a Petition of Right in 1628, Charles I
promised not to levy taxes without Parliament’s consent
Which of the following statements about Europe at the end of the 17th century is supported by this map?
Austria expanded its territory by acquiring lands from the Ottoman Empire.
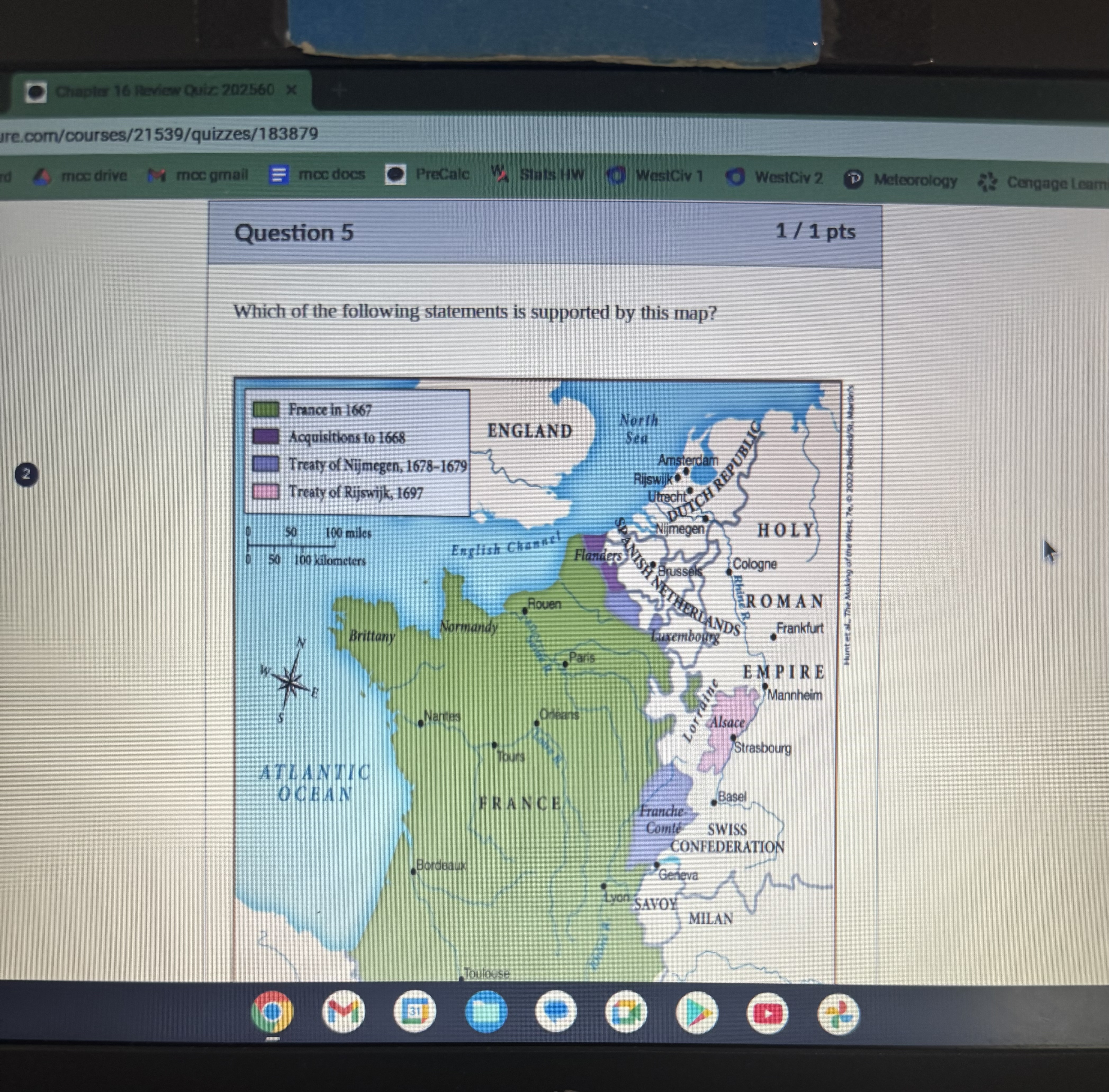
Which of the following statements is supported by this map?
Louis XIV was able to expand France by acquiring territory through the passage of treaties
Why did the philosophy of the Jewish scholar Benedict Spinoza (1633-1677) alarm so many people?
He wrote that God was not influenced by any human action or prayer.
How did European peasants and colonized subjects resist attempts to reform popular religious rituals?
They reinterpreted religious festivals and combined Christian symbols with their own.
Although John Milton’s Paradise Lost explores the fall of Adam and Eve, it can also be seen as
a response to the turmoil of the English civil war
When he reportedly uttered the phrase “L’etat, c’est moi” (“I am the state”), Louis XIV demonstrated the attachment to what form of rule?
Absolutism
Parliament offered the throne jointly to William (r. 1689-1702) and Mary (r. 1689-1694) on the condition that they accept which of the following?
A bill of rights making Parliament a full partner in state governance
The Tories and the Whigs invited the Dutch ruler William of Orange and his wife, James II’s daughter Mary, to invade England in 1688 after
James produced a male heir who Parliament feared would be reared as a Catholic
The 1699 Treaty of Karlowitz marked the beginning of the decline of what empire?
The Ottoman Empire
Why did Thomas Hobbes’s Leviathan (1651) enrage both royalists and supporters of Parliament?
Hobbes favored social contract as the basis for governmental legitimacy while championing absolutist rule (by either king or Parliament).
Historians have advanced several different ideas about the increase in the slave trade during the 17th century. Which of the following factors might explain this increase?
Improvements in muskets, the rising price of slaves, and growing conflict between African tribes made slave capture easier and more profitable.
Which of the following did Louis XIV employ as a counter to the parlements, provincial estates, aristocratic governors, and hereditary officials, many of whom had purchased their offices?
Intendants
The English civil war of the 1640s led to the emergence of which new religious sects in England?
Baptists, Quakers, and Diggers
When Louis XIV’s wars with much of western and Central Europe finally ended with the Treaty of Rijswijk in 1697, Louis
returned much of what he had seized since 1678, with the exception of Strasbourg.
In what ways did governments become involved in the sciences during the 17th century?
They saw science as a means to enhance their prestige and invested monetary and social resources in scientific research.
The legacy of Sir Robert Walpole (1676–1745) can be described as the establishment of which of the following?
An enduring pattern of parliamentary government in which a prime minister from the majority party guided legislation through the House of Commons
During the eighteenth century, most slaves ended up working on plantations that produced which of the following?
Sugar
How did the Dutch respond to their decline in international affairs and manufacturing during the eighteenth century?
They shifted their interest away from international power politics and began to focus on areas of trade and finance where they could establish an enduring presence.
Which of the following was characteristic of the rococo style of painting that developed in the eighteenth century?
The depiction of scenes of intimate sensuality and a decorative quality
Enlightenment writers saw the solution for all social problems in which of the following systems of thought?
The scientific method
The population explosion that took place in Europe around the turn of the eighteenth century can be attributed to
a decline in the death rate thanks to better weather, improved agricultural techniques, and the disappearance of the plague.
This map of European trading patterns c. 1740 demonstrates that, by the middle of the eighteenth century,
seventeenth-century mercantilism was widely adopted in Europe.
After some two hundred years of tolerating and even supporting piracy, why did the English and Dutch governments suddenly try to stamp it out around 1700?
English, Dutch, and French bands of sailors began to form associations of pirates, especially in the Caribbean, that preyed indiscriminately on shipping lines of every national origin.
What did critics of the Enlightenment find so dangerous about the new intellectual movement?
Its proponents subjected everything to criticism and challenged both political and religious authority.
What sorts of professions made up the developing urban middle classes of the eighteenth century?
Government officials, merchants, professionals, and small landowners
What steps did the Duke of Orleans (1674-1723), regent to Louis XV, take to shore up France’s crumbling finances?
He founded a state bank to help the government service its debt, only to see the bank crash within a few months in the wake of a speculative bubble.
Which of the following is true of the 17th century Protestant revival known as pietism, which became popular in the German Lutheran states, the Dutch Republic, and Scandinavia?
It encouraged a deeply emotional, even ecstatic religious experience as well as participation in daily catechism instruction and frequent prayer meetings.
In the Act of Union of 1707, Scottish Protestant leaders abolished the Scottish Parliament and agreed to obey the Parliament of Great Britain
because they feared the threat of Jacobitism in Scotland.
In the 1740s, which of the following regions would most likely export coffee to Europe?
Indonesia
How were ambassadors chosen for the new diplomatic services that France and other Europeans states created in the 17th and 18th centuries?
They were chosen from among nobles of ancient families and royal officials who could pay for their own staff.
What main critique of organized Christianity did Voltaire include in his influential Philosophical Dictionary (1764)?
That Christianity had been the prime source of fanaticism and brutality among humans
What new artistic movement developed in the eighteenth century in reaction to what some saw as the Enlightenment's excessive reliance on the authority of human reason?
Romanticism
Over the course of the eighteenth century, what was the trend in the number of out-of-wedlock births?
They quadrupled, as more women began to move to cities and out of the control of their families.
What was the opinion of Enlightenment writers on the role of religion in society?
They did not necessarily oppose organized religion, but they strenuously objected to religious intolerance.
The artistic and architectural style known as neoclassicism gained popularity in the eighteenth century thanks to what cultural phenomenon?
The rise of “grand tours,” in which upper-class youths traveled to Greek and Roman ruins
One way in which nobles and the landed gentry in Britain protected their social status and reasserted their privilege in the face of financial and political challenges was that
they defended their exclusive right to hunt game and severely punished poachers, who could even be sentenced to death.
How did Jean-Jacques Rousseau first become well-known?
He wrote a prize-winning essay about the corruption of public morality.
What new texts did abolitionists use in their petitions and campaigns to end the slave trade and slavery in the New World?
Firsthand accounts of slavery written by freed slaves
Who among the following leaders was the only enlightened ruler to end the personal aspects of serfdom?
Joseph II of Austria
Although most intellectuals of the Enlightenment publicly embraced the doctrine of religious toleration, many of them were still intolerant of which group?
Jews
After the revolutions of 1848, political power across most of Europe belonged to which of the following?
The aristocracy
Which of the following diseases had the most devastating impact on cities in the first half of the nineteenth century?
Cholera
What was the reasoning behind the 1834 passage of a new poor law in Great Britain, dubbed by its critics the “Starvation Act”?
That the distress caused by the separation of family members from one another in workhouses would encourage the poor to move to areas of higher employment
Key inventions in which industry drove the development of the Industrial Revolution?
Textile manufacturing
Where was the most significant nationalist movement in western Europe?
Ireland
The advent of what new artistic medium in 1839 created enormous potential for portraying the social realities of the industrial age?
Photography
The rapid urbanization that developed as a result of industrialization caused European cities to
become overcrowded and filthy, as the population expanded much more rapidly than the housing stock, and sanitation developed slowly.
The subject of the map reproduced here directly relates to the rise of what nineteenth-century phenomenon?
Nationalism
Between 1800 and 1840, many European countries began to close the industrial gap with Great Britain,
but by 1850, continental Europe was still almost twenty years behind Great Britain in industrialization.
The failure of the 1848 uprisings in Italy, Germany, and the Austrian Empire had their individual causes, but they shared which major problem?
The rebels' failure to agree on goals beyond overthrowing the existing government
What differentiated Karl Marx's views about the possibilities for social change from those of utopian socialists?
Unlike utopian socialists, who believed in cooperation, Marx was a realist whose views were based on scientific analysis and who saw class struggle as the basis for social change.
Which of the following was the most dramatic of Alexander II's Great Reforms?
The emancipation of almost fifty million serfs
How did Giuseppe Garibaldi help derail Napoleon III's plan to prevent Italian unification?
He liberated Sicily and southern Italy with the assistance of his red-shirted volunteers and then threw his support behind King Victor Emmanuel.
Realism in the arts rejected which of the following?
Romanticism and fervent religious sentiment
East Indian troops of the British army launched the Indian Rebellion of 1857 because they were angered by tightening British control and by
the rumor that Britain would force soldiers to use cartridges greased with cow and pig fat, which violated Hindu and Muslim religious rules, respectively.
Why was the English naturalist Charles Darwin's book On the Origin of Species(1859) so controversial?
Darwin challenged Judeo-Christian dogma, arguing that life had taken shape over millions of years through a process called evolution, not through God's miraculous creation of the universe in six days.