Unit 5: Agriculture and Rural Land-Use Patterns and Processes
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
agriculture
The deliberate effort to modify a portion of Earth's surface through the cultivation of crops and the raising of livestock for sustenance or economic gain.

climate
Overall weather in an area over a long period of time
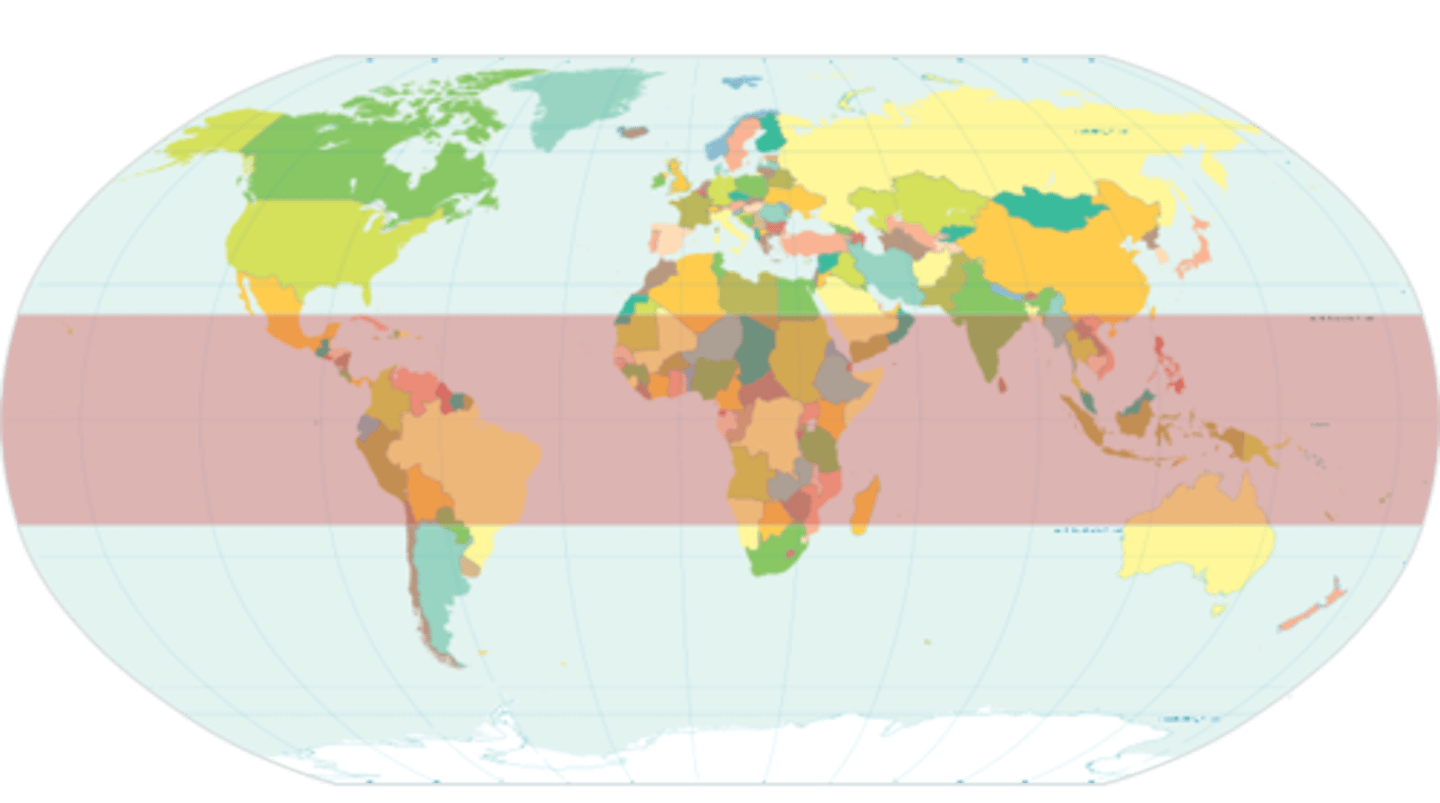
Tropical Climate Zone
warm, moist climate zone near the equator
Subtropical (humid) Climate Zone
The Humid Subtropical climate is mostly found on the east coast of continents between 20 degrees and 40 degrees north and south of the equator. The southeast United States is a good example of this climate. Florida and other parts of the South has a Humid Subtropical climate.
https://www.climatetypesforkids.com/humid-subtropical-climate

Mediterranean Climate Zone
warm or hot, dry summers and mild or cool, wet winters. Found coastal regions around the Mediterranean, Southwest coast of CA, tip of South Africa, Southwest and South Australia
Midlatitudes
Between 30 N and 60 N and 30 S and 60 S
high latitudes
are located between 60° and 90° latitude, in both the Northern and Southern Hemispheres
Desert (arid) climate
bands of desert that is characterized by dry climate and little rainfall - Sahara, Central Australia, Southwest US
intensive agriculture
Agriculture that involves effective and efficient use of labor on smaller plots of land to maximize crop yield.
extensive agriculture
Agriculture that produces lower yields and therefore uses large quantities of land
Pastoral Nomadism
the herding of domesticated animals in dry climates where planting crops is impossible
Example: Bedouins in Saudi Arabia and North Africa; Maasai of East Africa
(extensive agriculture)
Transhumance
The seasonal migration of livestock between mountains and lowland pastures.
Livestock Ranching
type of commercial farming in which livestock roams over an established area while the farmer remains settled
EX: cattle ranching in western US
(extensive agriculture)
shifting cultivation
type of agriculture in which people shift frequently from one field to another, slash and burn and frequent relocation are 2 defining factors
Ex: Brazil
(extensive)
slash and burn agriculture
Another name for shifting cultivation, so named because fields are cleared by slashing the vegetation and burning the debris.
Swidden
A patch of land cleared for planting through slashing and burning.
fallow
inactive; unproductive (field)
mixed crop and livestock farming
type of commercial farming that integrates cultivation of crops and livestock
Crops are fed to animals, livestock provides manure to fertilize soil
Majority of land devoted to growing crops, but majority of income comes from the sale of animal products (beef, milk, eggs)
Stabilizes workload and income throughout the year
Example: United States, France, Russia
(intensive)
plantation agriculture
large commercial farm in a developing country that specializes in one or two crops
Often in the tropics or subtropics and operated by Europeans or North Americans for sale to developed countries
Cotton, sugarcane, rubber, coffee, tobacco
Example: cotton/tobacco in the South (US), sugar, coffee, rubber in Latin America, cotton and cocoa in Africa, and rubber and coffee in Asia
(intensive)
Market Gardening (Truck Farming)
The small scale production of fruits, vegetables, and flowers as cash crops sold directly to local consumers.
Distinguishable by the large diversity of crops grown on a small area of land during a single growing season
Labor is done manually
Example: Southeastern US because of the long growing season and humid climate / accessibility to large markets (NY, D.C., Philly)
(intensive)
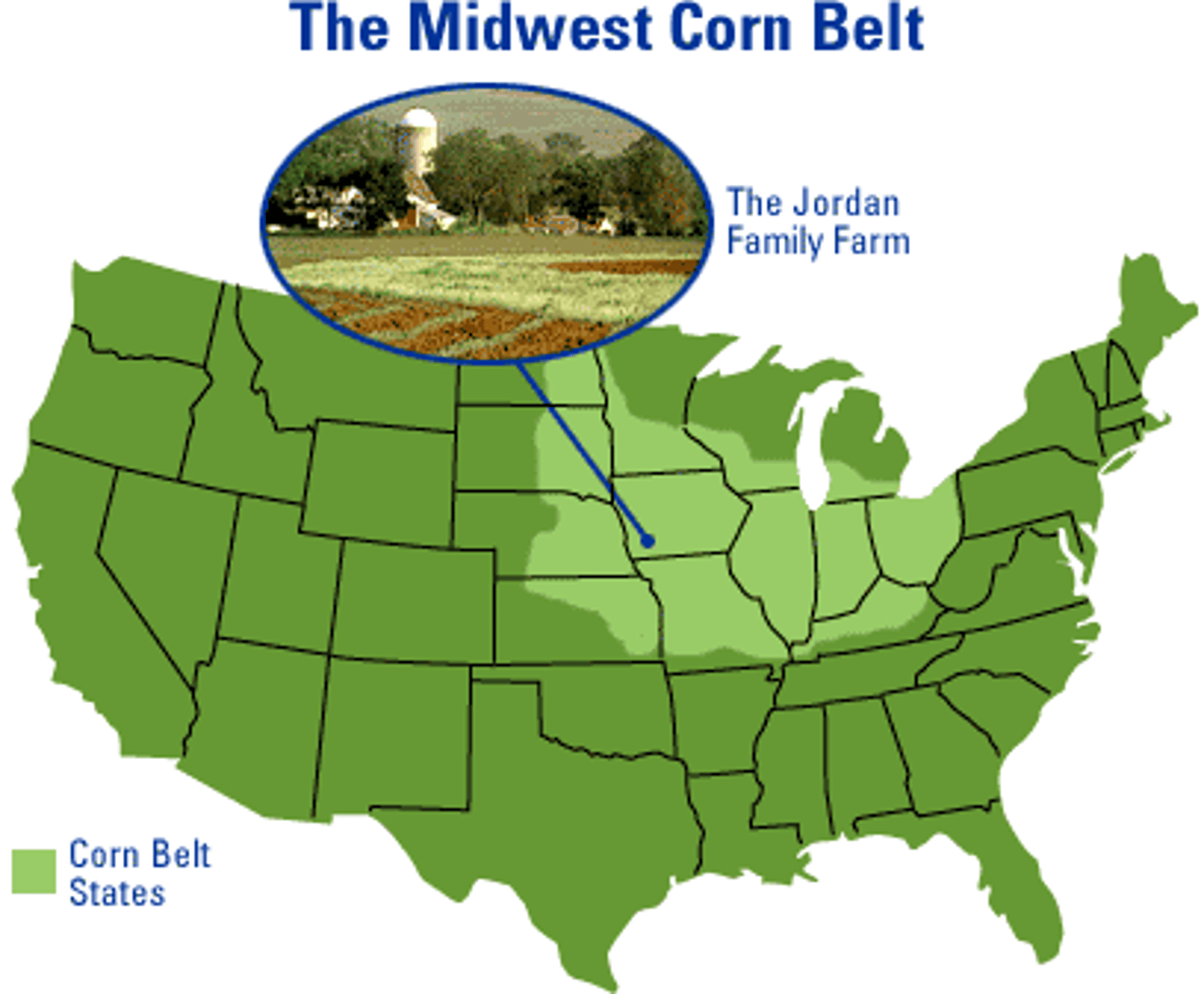
Corn Belt
most important mixed crop and livestock farming region in the U.S.; extending from Ohio to the Dakotas, with its center in Iowa; approximately half the crop land is planted in corn
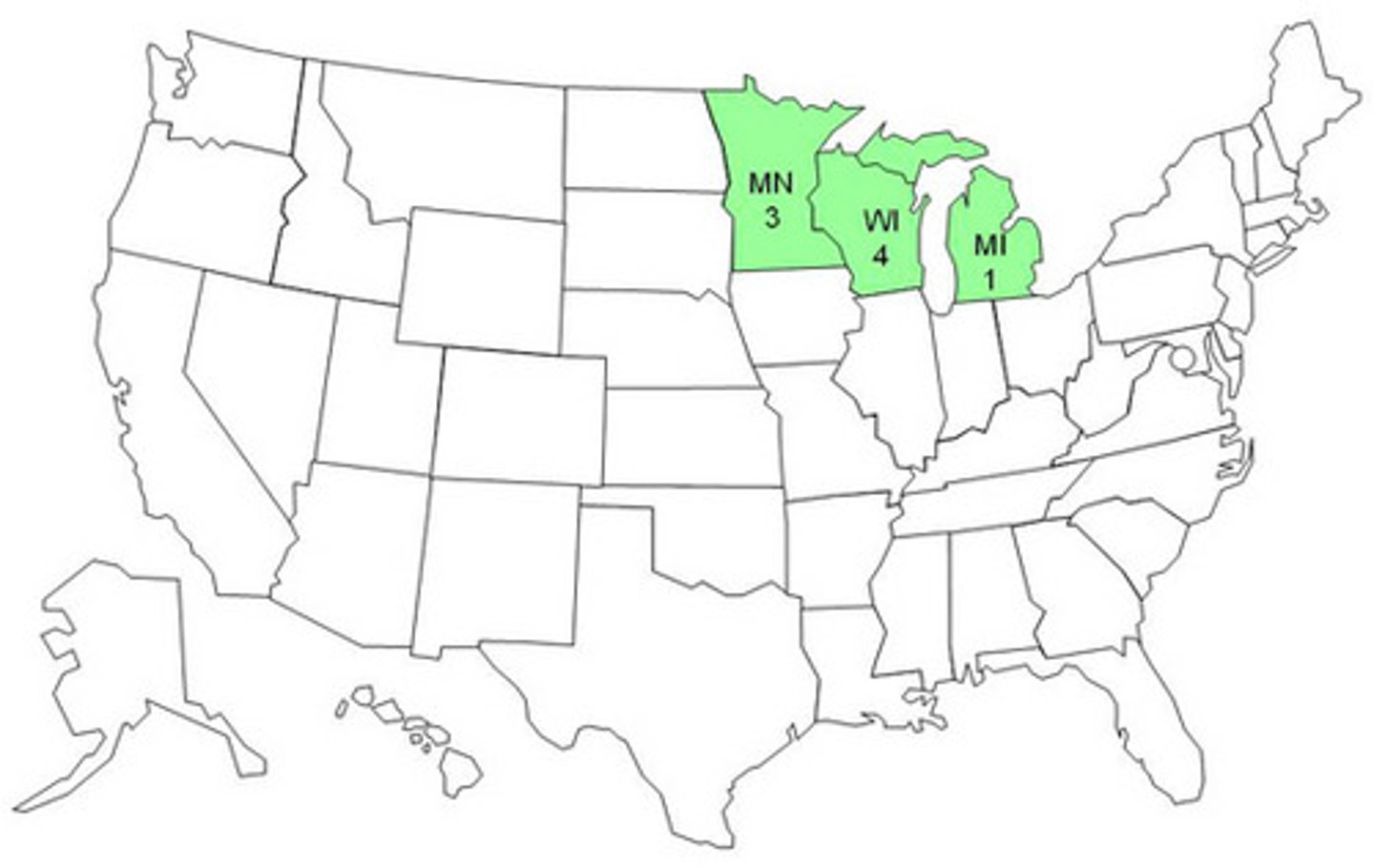
Dairy Belt
the area of the Midwestern United States north of the Corn Belt in which dairy farming is a major economic activity
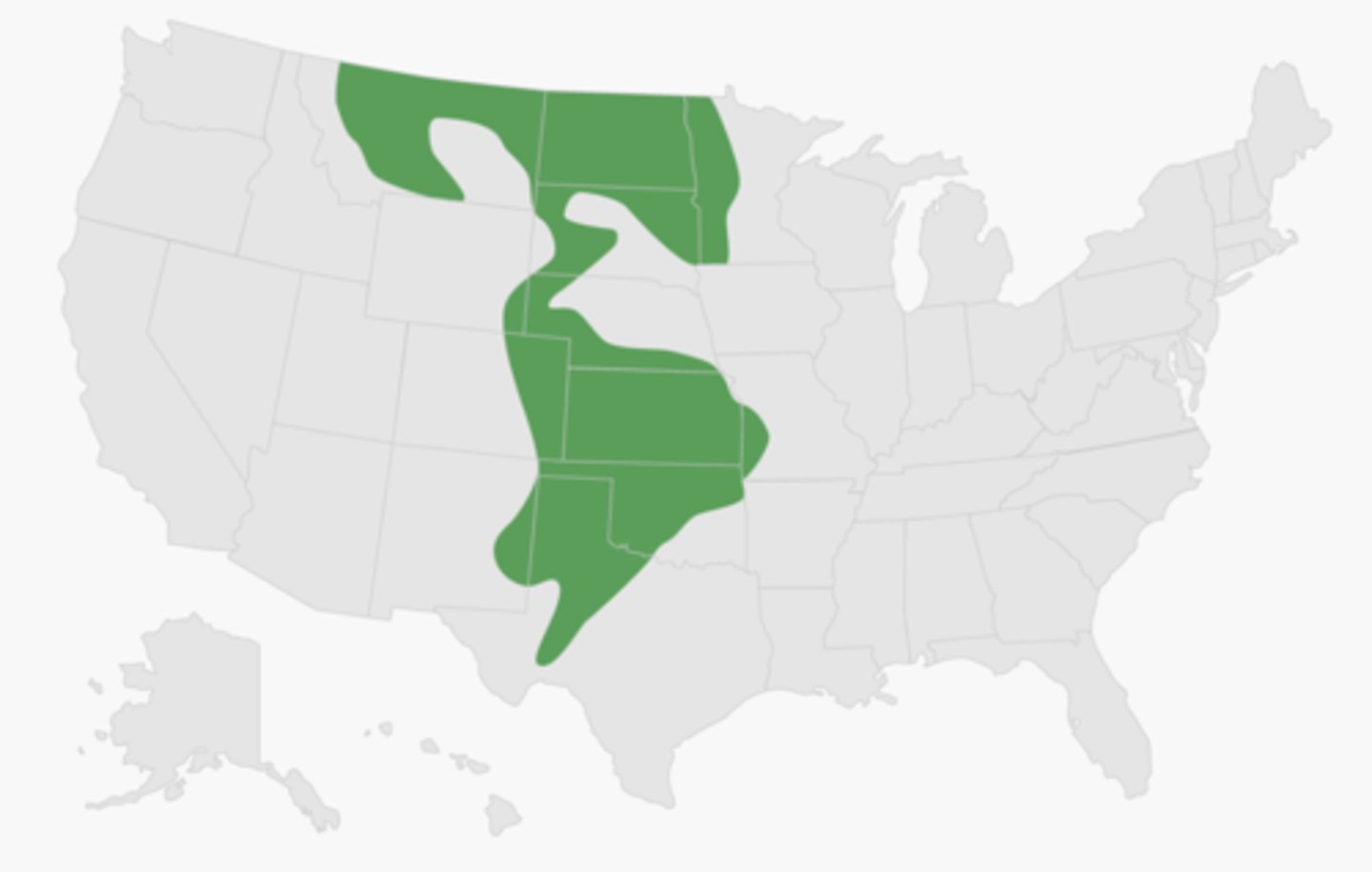
Wheat Belt
Productive farm area that began at the eastern edge of the Great Plains
Spring Wheat
Wheat planted in the spring and harvested in the late summer.
Winter Wheat
wheat planted in the fall and harvested in the early summer
animal domestication
animals kept for some utilitarian purpose whose breeding is controlled by humans and whose survival is dependent on humans; differ genetically and behaviorally from wild animals.
Cows, pigs, chicken, horses, dog first to be domesticated
rural
relating to farm areas and life in the country
urban
in, relating to, or characteristic of a city or town.
First (Neolithic) Agricultural Revolution
the wide-scale transition of many human cultures from a lifestyle of hunting and gathering to one of agriculture and settlement, making large populations possible
Happened in multiple locations at the same time (around 8,000 BCE) in Fertile Crescent, Indus River Valley, Southeast Asia, and Central America
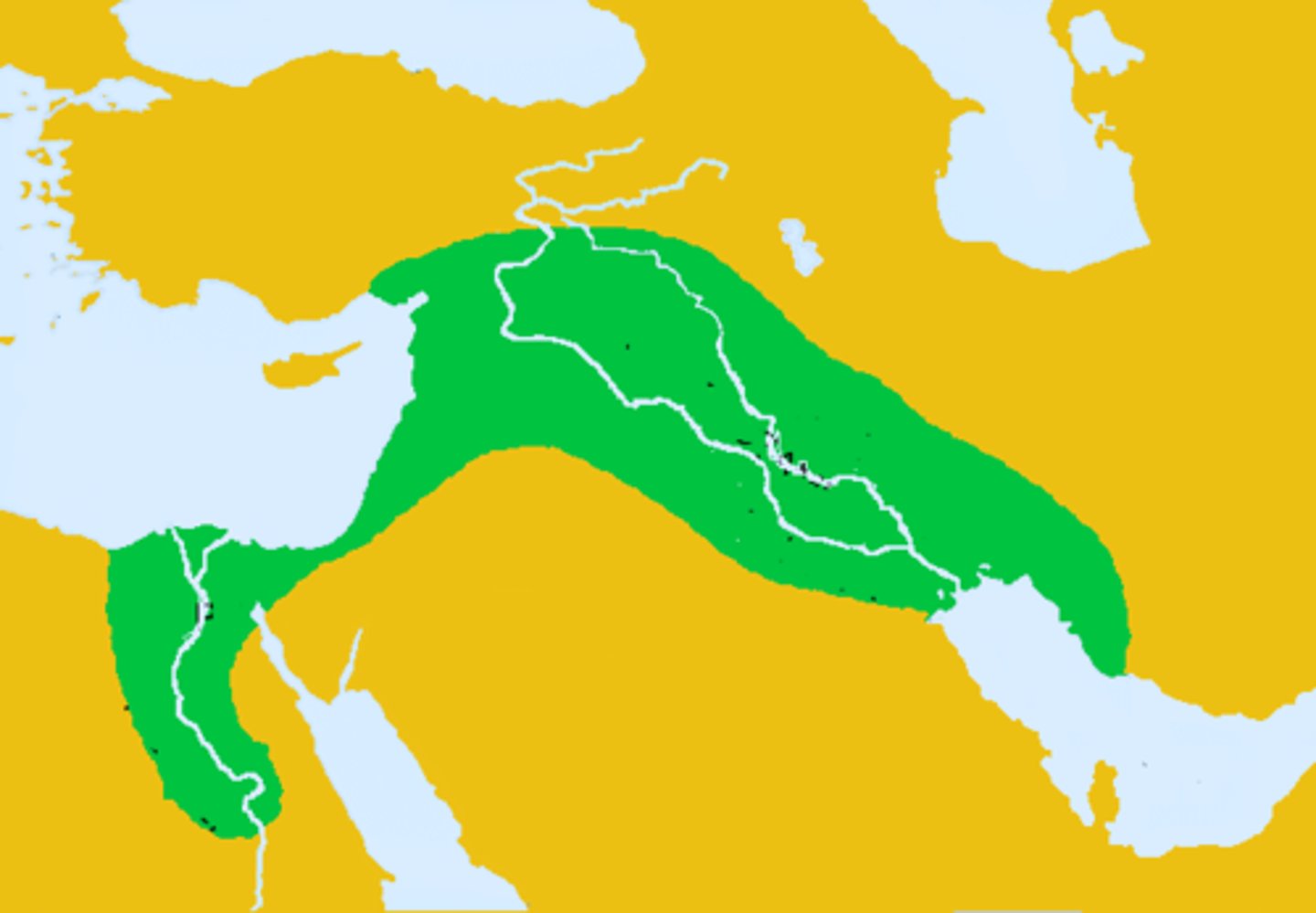
Fertile Crescent / Southwest Asia
A geographical area of fertile land in the Middle East stretching in a broad semicircle from the Nile to the Tigris and Euphrates
Barley, Cattle, Dog, Wheat, Goat, LEntil, Oats, Pig, Rye, Olive
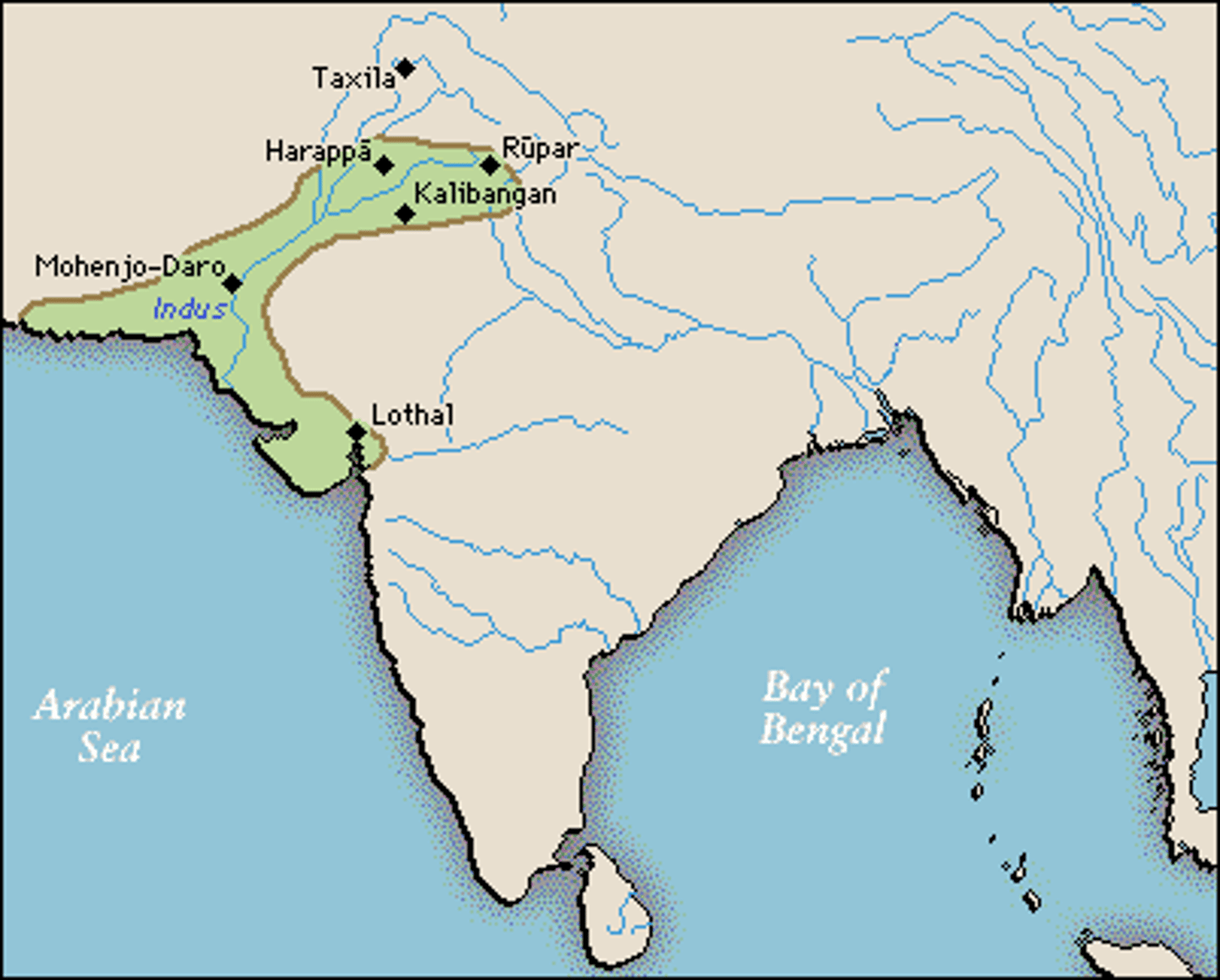
Indus River Valley / South & Central Asia
A valley and early civilization along the Indus River, one of the longest rivers in the world. One of the first civilizations
Chicken and Finger Millet / Sheep, walnut, Broad Bean
Columbian Exchange
An exchange of goods, ideas and skills from the Old World (Europe, Asia and Africa) to the New World (North and South America) and vice versa.
Second Agricultural Revolution
1600s & 1700s in England, advanced technology and agricultural practices led to increased food production, population growth, and migration of farmers into the cities
Yellow River Valley / East Asia
Rice, Millet
Chinese Chestnut, Soybean,
Southeast Asia
coconut, mango, taro, pigeon pea
Latin America / Central America
Cassava, Squash
Pepper, Potato
Alpaca, Cotton, Lima Bean, Llama, Maize, Sweet potato
Sub Saharan Africa
Sorghum, Yam
African Rive, Cowpea
Coffee
Enclosure Movement
The process of consolidating small landholdings into a smaller number of larger farms in England during the eighteenth century.
crop rotation
The practice of rotating use of different fields from crop to crop each year, to avoid exhausting the soil.
selective breeding
the human practice of breeding animals or plants that have certain desired traits - common practice during 2nd agricultural revolution
Green Revolution (Third Agricultural Revolution)
The development of higher-yield and fast-growing crops through increased technology, pesticides, and fertilizers transferred from the developed to developing world to alleviate the problem of food supply in those regions of the globe.
Led by Norman Borlaug in Mexico, China, Indonesia, India, Vietnam, Philippines
Technology of the Green Revolution
Crossbreeding Plants
Artificial fertilizer
Irrigation
Insecticides & Herbicides
Mechanical Machinery
subsistence agriculture
Agriculture designed primarily to provide food for direct consumption by the farmer and the farmer's family
Commercial Agriculture
Agriculture undertaken primarily to generate products for sale off the farm.
Agribusiness
Businesses that provide a vast array of goods and services to support the agricultural industry
factory farm
a large scale farm in which animals are bred and fattened using modern industrial methods
industrial agriculture
modern, commercial farming that refers to the industrialized process of the production of livestock and crops
subsidy
A government payment that supports a business or market
Commodity (supply) Chains
process used by firms to gather resources, transform them into goods (commodities), and distribute them to consumers
4 stages: Production, manufacturing, storage/distribution, and retail
Vertical Integration
An approach typical of traditional mass production in which a company controls all phases of a highly complex production process.
single crop economy
Economy of a country depend on a single crop. Very dangerous
ex- Latin America- coffee and sugar cane
(economic) complementarity
when one country produces or has the potential to produce an agricultural product another country cannot
Climate, location, size, availability of labor, or level of development
Monoculture
farming strategy in which large fields are planted with a single crop, year after year
Biotechnology
A form of technology that uses living organisms, usually genes, to modify products, to make or modify plants and animals, or to develop other microorganisms for specific purposes.
GMOs
genetically modified organisms
plants, animals, and organisms that have genetically modified DNA
selective breeding
The process of selecting a few organisms with desired traits to serve as parents of the next generation
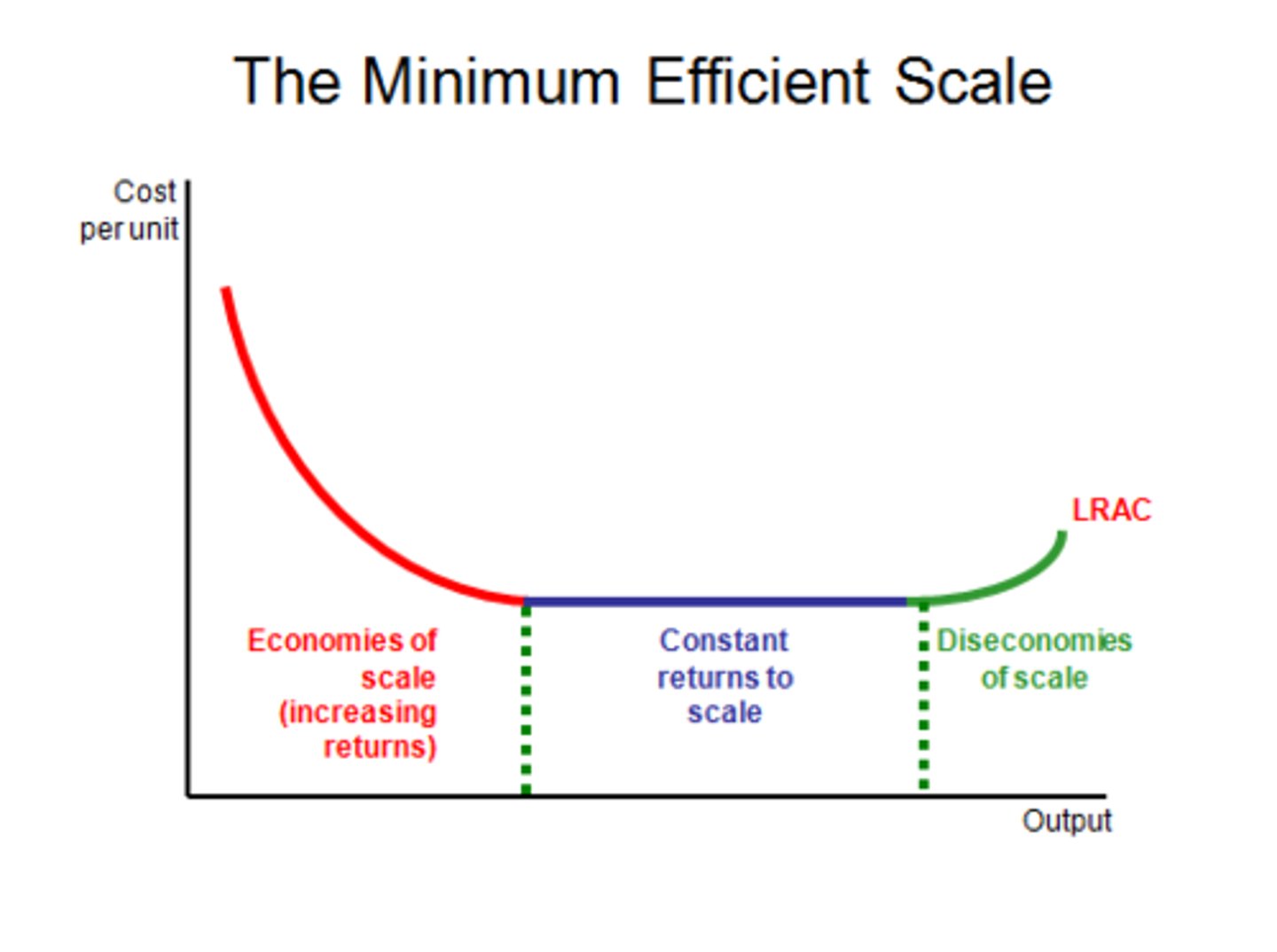
economies of scale
a proportionate saving in costs gained by an increased level of production.
Aquaculture
Raising marine and freshwater fish in ponds and underwater cages/ controlled conditions
Blue Revolution
New techniques of fish farming that may contribute as much to human nutrition as miracle cereal grains but also may create social and environmental problems.
pollution
the presence in or introduction into the environment of a substance or thing that has harmful or poisonous effects.
Consequence of factory & machinery runoff, also pesticides and chemical fertilizers

Desertification
Degradation of land, especially in semiarid areas, primarily because of human actions like excessive crop planting, animal grazing, and tree cutting.
soil salinization
in arid regions, water from irrigated areas evaporates leaving salts behind and leaving the soil infertile.
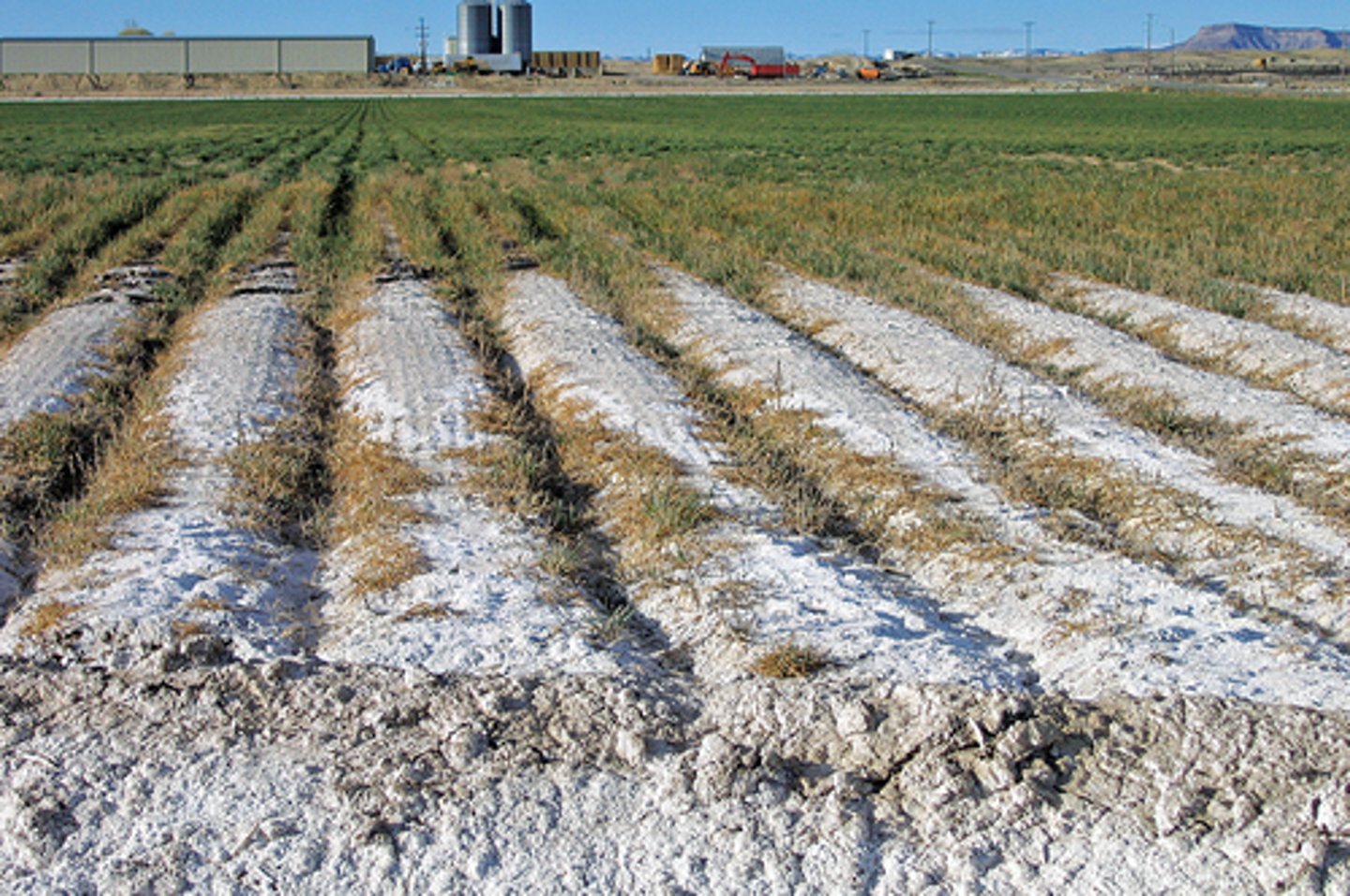

Waterlogging
A form of soil degradation that occurs when soil remains under water for prolonged periods.
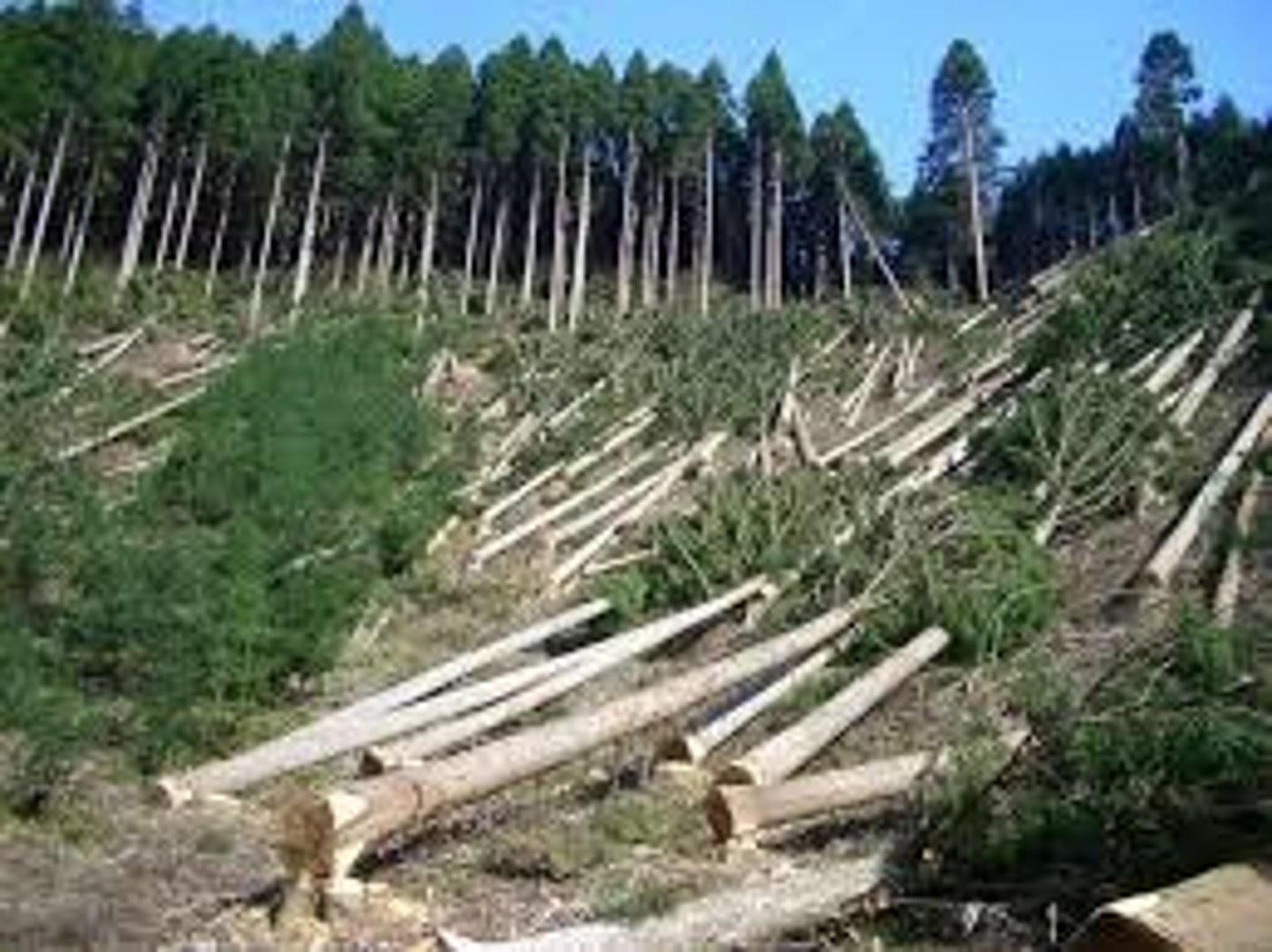
deforestation
Reduction of the forest at a faster rate than replaced
-Conversion of forests to agricultural land to feed people
-development of cash crops and cattle raising
-unregulated commercial logging
-poor soils in humid tropics that do not support agriculture for long
-slash and burn ag
Amazon

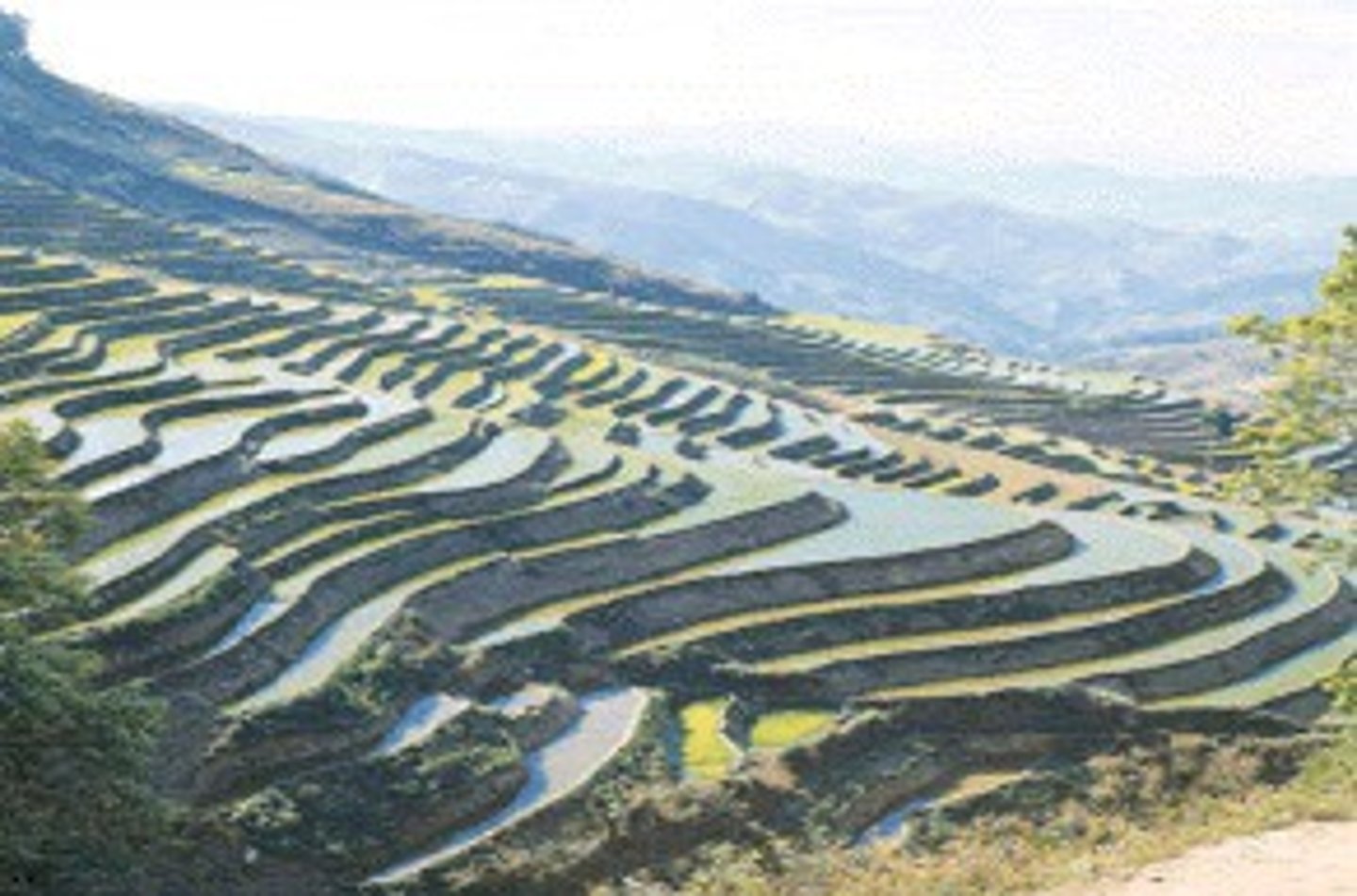
Terrace Farming
The cutting out of flat areas (terraces) into near vertical slopes to allow farming. Terrace farms appears as steps cut into a mountainside. This adaptation allowed both the early Chinese, and the Inca of Mesoamerica to grow enough food for their large populations.

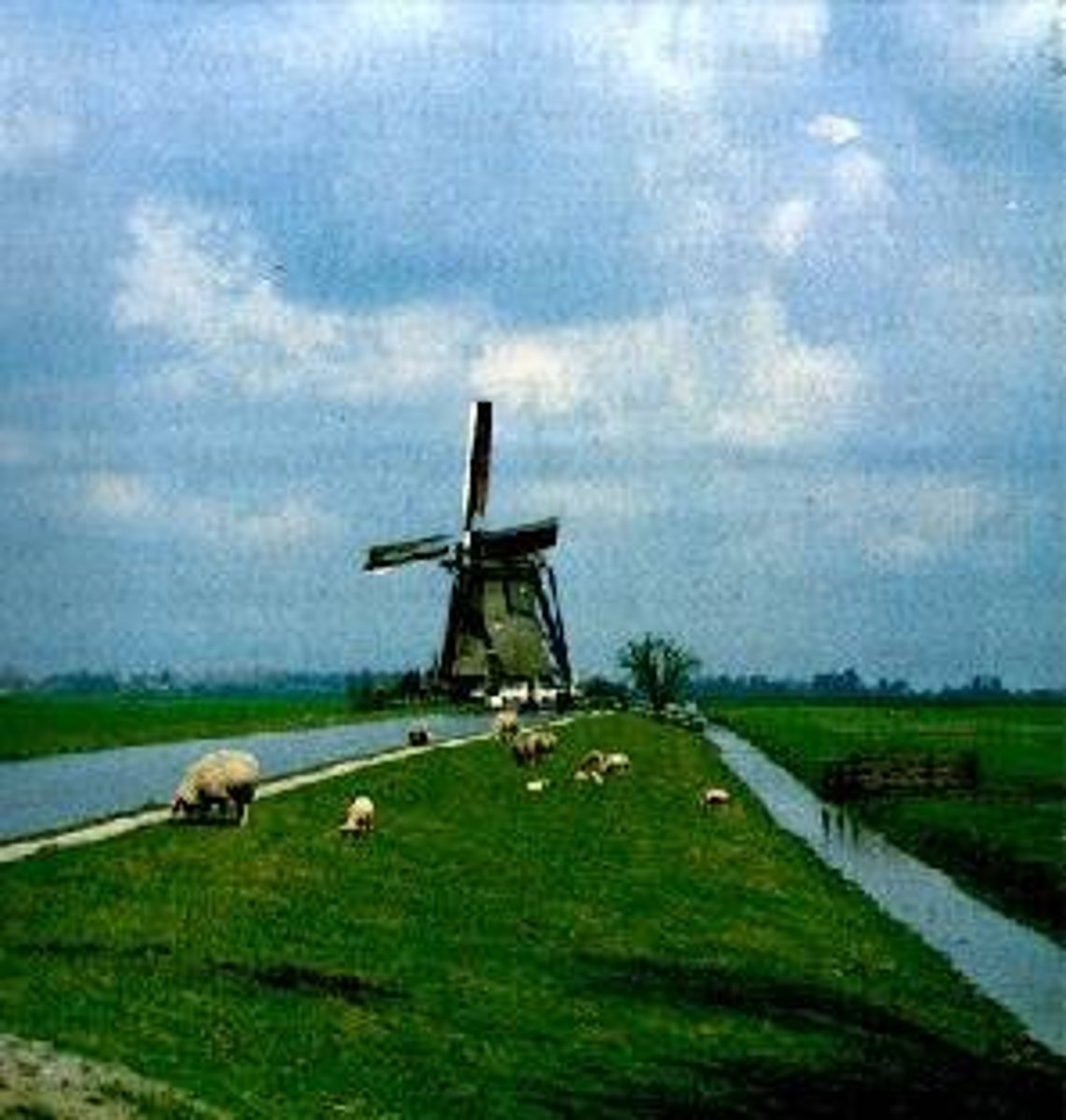
wetland draining / removal
draining water from a wetland to clear an area for farming; may have negative affects on the environment
Polder
low-lying area from which seawater has been drained to create new land

Community Supported Agriculture (CSA)
network between agricultural producers and consumers whereby consumers pledge support to a farming operation in order to receive a share of the output from the farming operation
fair trade
An alternative to international trade that emphasizes small businesses and worker-owned and democratically run cooperatives and requires employers to pay workers fair wages, permit union organization, and comply with minimum environmental and safety standards.
Locovore
a person who tries to only eat 'local' foods
organic food production
involves growing and producing food without the use of synthetic chemicals such as pesticides and artificial fertilizers
The Ugly Food Movement*
The idea that foods that are not breed to look perfect on a store shelf (kind of like dogs who are mutts), are genetically heartier and possibly more healthy than foods that have been primarily made to look perfect.
Biofuels
Fuels, such as ethanol or methanol, that are created from the fermentation of plants or plant products.
food insecurity
the state of being without reliable access to a sufficient quantity of affordable, nutritious food
food desert
an area typically in a highly populated, lower income urban environment, where healthy, fresh food is difficult to find
food swamp
Communities that are flooded with unhealthy, highly processed, low-nutrient food combined with disproportionate advertising for unhealthy food compared to wealthier neighborhoods.
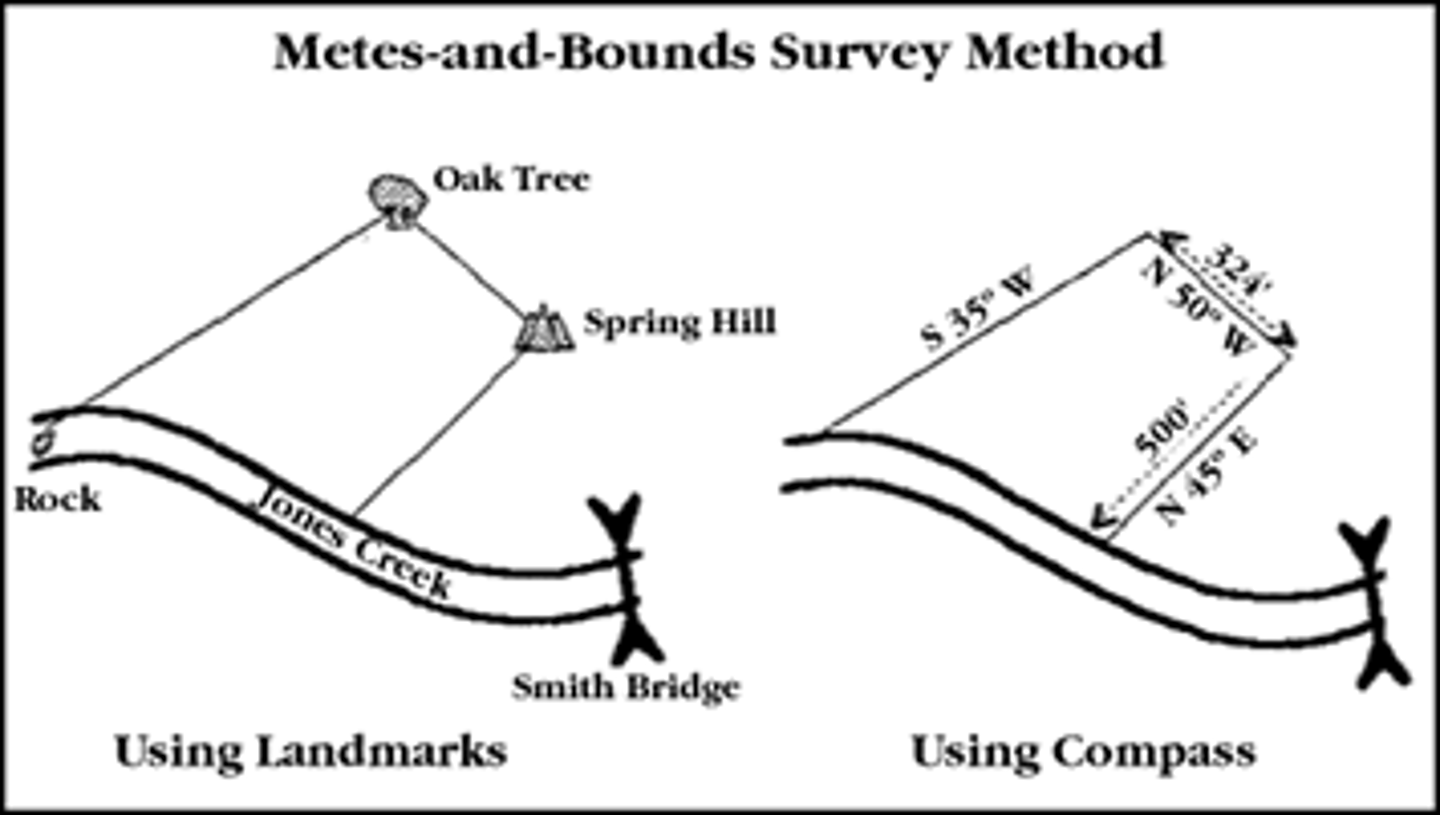
Metes and Bounds
system uses physical features of local geography along with directions and distances to define and describe boundaries of land parcels.
Native to England and brought into 13th colonies
Looks like parcels irregular in size and shape, clustered
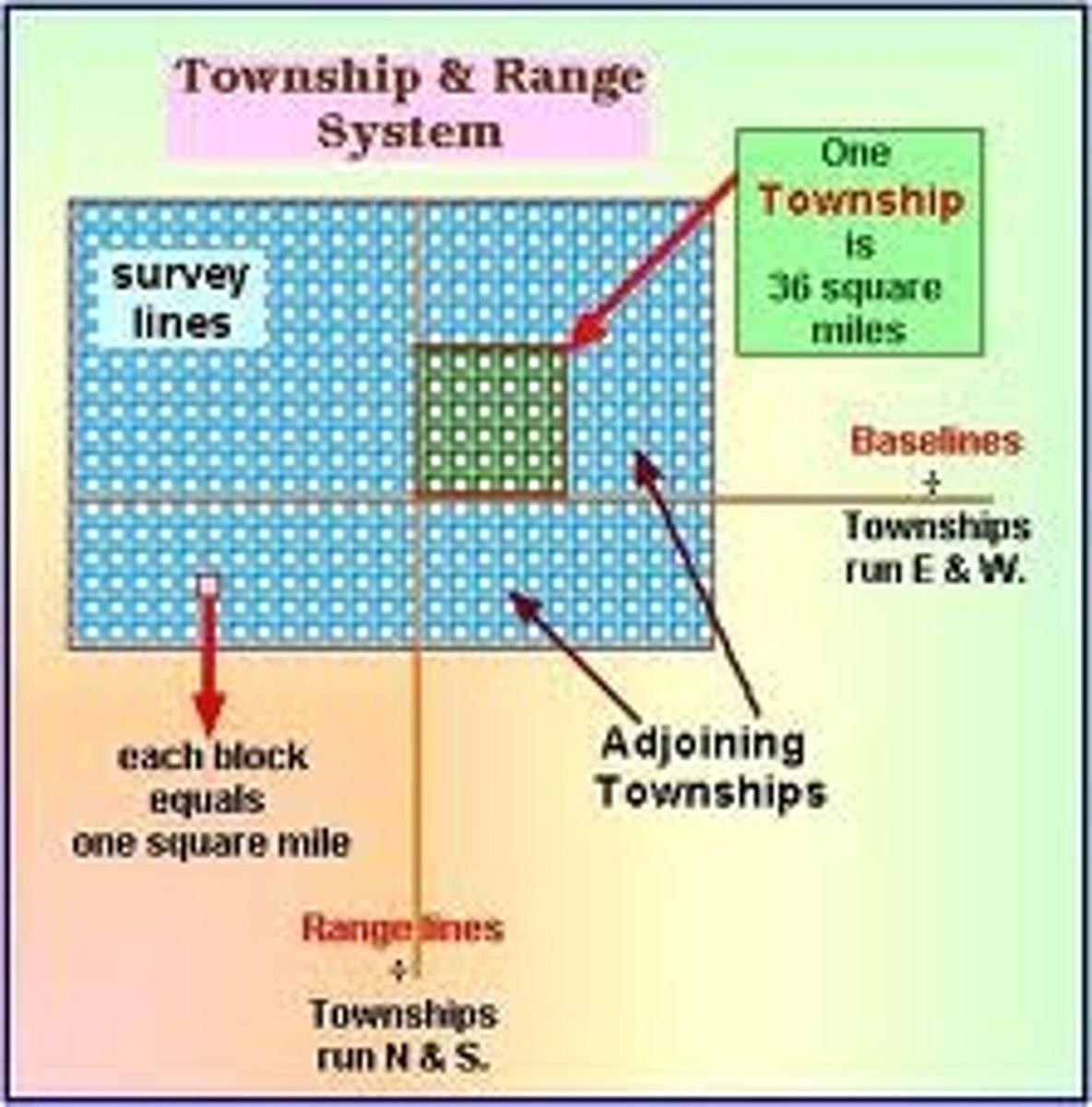
township and range system
system that divides land into 6 mile-square townships and can be subdivided into 1 mile square sections, then further divided into quarters, etc.
US farmland and towns
Looks like square, uniform parcels of land, dispersed
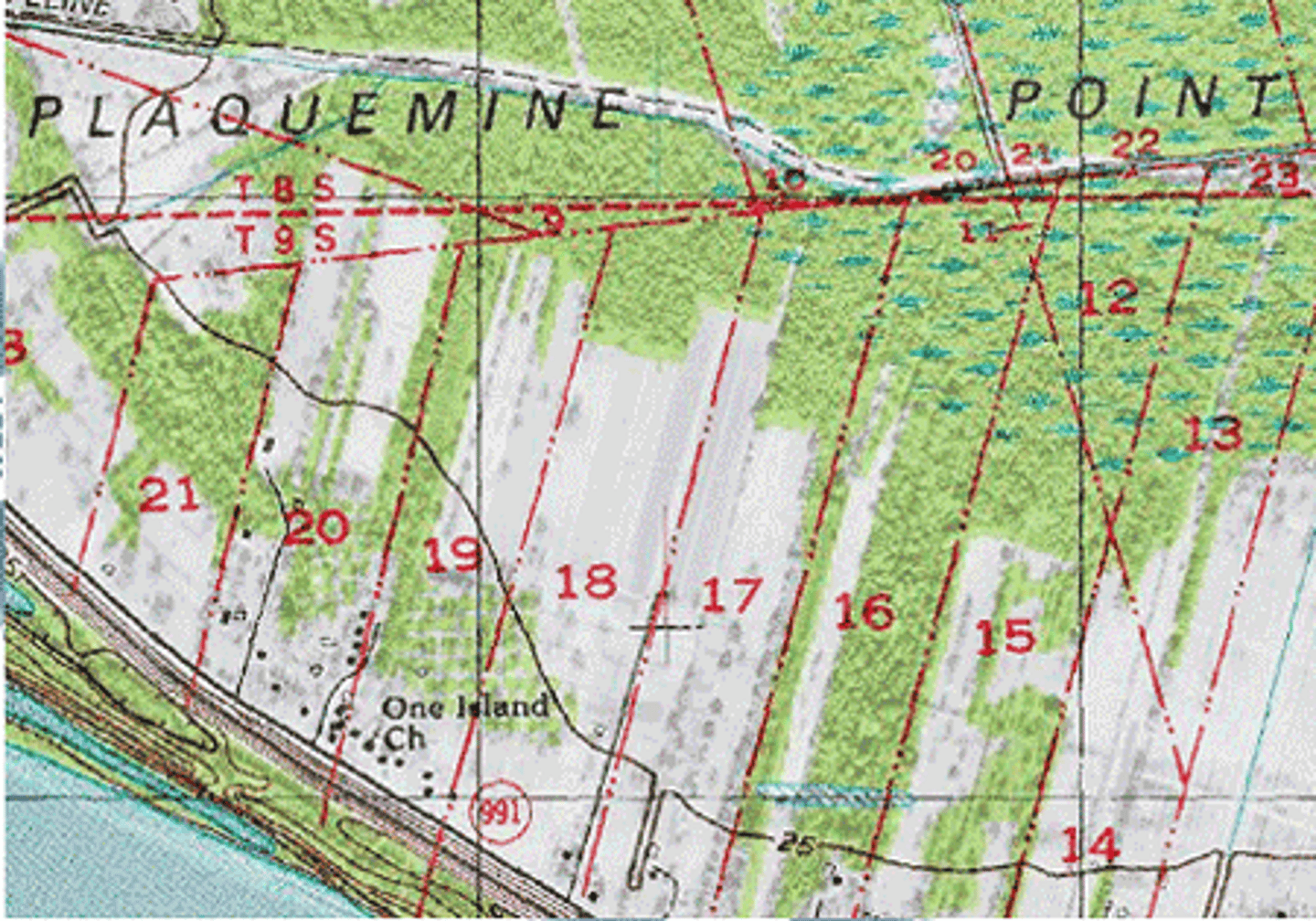
French long-lot system
system, often along rivers, created long rectangular plots of farmland to give equal access to river
French! Found in Canada and Louisiana, linear
Greenbelt
A ring of land maintained as parks, agriculture, or other types of open space to limit the sprawl of an urban area.
Bid rent theory
geographical economic theory that refers to how the price and demand on real estate changes as the distance towards the urban center increases.
Land Rent
the return that a particular parcel of land will bring in the open market