The Origins of Agriculture
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
reading: carey 2023
QUIZ: carey (2023) mentions that the domestication process of plants was:
Rapid
gradual
QUIZ: according to Carey (2023), which one of the following lifestyles brought about malnutrition, epidemic diseases, and social inequality in human society?
Hunter-gatherer
Agriculture-sedentism
Metalsmith
All of the above
gradual
Agriculture-sedentism
sedentary life - what were effects
people living in permanent settlements year-round
hunting: cultural images and social reality
We were all hunter-gatherers
Sports: metaphor of hunting?
Many HG societies: heavy reliance on plants, fish, or shell
the origins of agriculture
early views
The Bushman (!Kung) is a “Classic illustration of a people whose economic resources are of the scantist”
“Only the most intense application makes survival possible”
(Herskovits 1958 Economic Anthropology)
current facts
Hunter-gatherers were not nasty, brutish, starving, and short
Monumental architecture came before agriculture
Why did almost all our hunter-gatherer ancestors adopt sedentary life and agriculture?
Did sedentary life and agriculture give us a better life?
diet and health
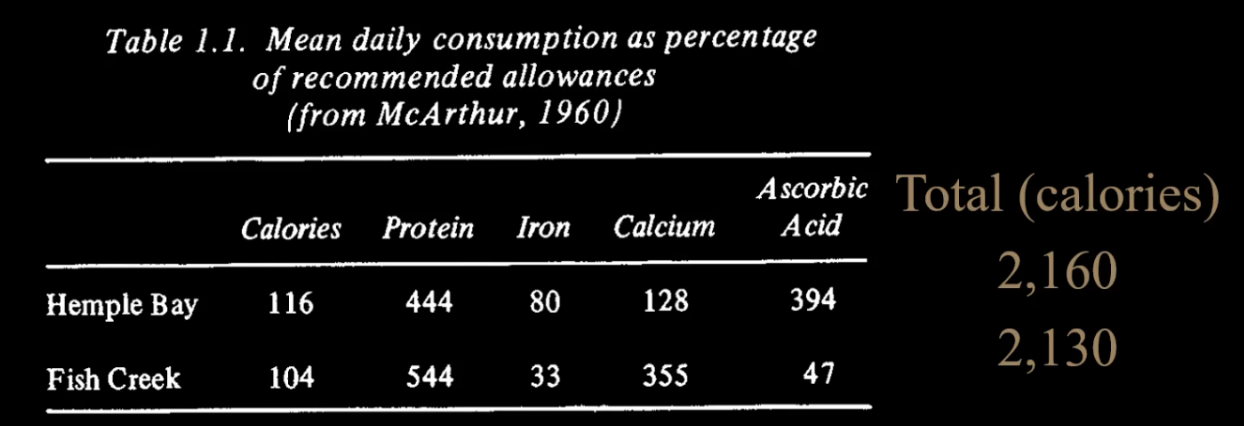
Balanced rich diet
Sleep a good deal
Work less hard
agriculturalists
professionals or individuals involved in the science, practice, and management of farming and food production
Natufian (12,500-9,500 BCE)
what is material evidence of the transition from H-G to domestication?
Transition to sedentism and agriculture
Wild plant us
Grinding stones
Sickles
incipient agricultre in southwest asia (near east)
Abu Hureyre (9500-6500 BCE)
jericho (10000 BCE)
catalhoyuk (7000 BCE)
Abu Hureyra (Syria): PPNA 9500-8500 BCE
Wheat, barley, rye
Pits and silos were located inside and outside houses:
Group storage
cultivation; domestication?
More sedentary?
Jericho (Palestine): oldest town:
Wallas village by 10000 BCE
Massive walls by 9000 BCE
Wall and tower:PPNA
Defense?
Floods?
Catalhoyuk (“”)
7000-6500 BCE: large, complex settlement; 32 acres (!Abu H)
8000 people
A large village or town with numerous small houses 3.7ha
the origin of rice cultivation in China 6000 BCE
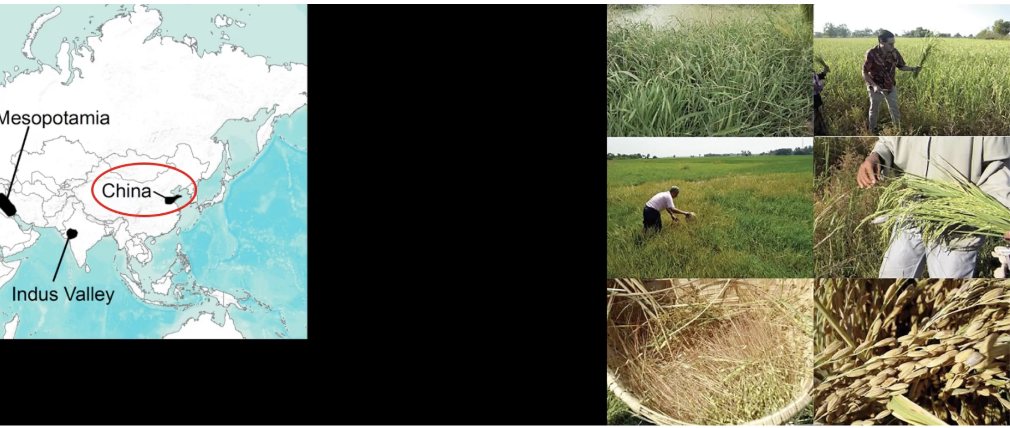

enviornmental effects or cultural preferences?
SW asia vs east asiashunayqa 1 : what did researchers find?
Wheat and barley
Grinding and baking
Rice and millet
Steam and boil
effects of agriculture
population growth
disease
the spread of insects
family-orientated society
social inequality
conflicts
gender division
impacts on the environment
original affluent society
Marshall Sahlins
“They lived in a kind of material plenty.
With advent of agriculture. People had to work harder.”
diet between hunter-gatherers and agriculturalists
Hunter-gatherer
diets were highly varied, featuring diverse wild plants, lean meats, fish, nuts, and fruits, rich in fiber and micronutrients, offering a balanced protein/carb/fat intake
agriculturalist
diets became less varied, centered on starchy staples like grains (rice, wheat) and tubers (potatoes), leading to more carbohydrates, less fiber, and vulnerability to crop failure, though providing more consistent calorie access
transition to agriculture and sedentism
Relief from hunger = no?
Poorer health status, less diverse diet
Less work and more leisure time = no
More work
domestication in the americas
Domestication before sedentism
Monumental architecture before sedentism
Gradual development, but rapid change after the building of monumental architecture
Maize, lack of significant animals
domestication of turkey, sweet potato
where were their origins?
when?
Mesoamerica: 800 BCE-100 BCE
American southeast: 200 BCE-500BCE
Independent domestication?
effects of turkey domestication
commercial turkey
domesticated turkeys from europe
domestication of bottlee gourds
why domesticated?
From the Old World around 8000 BCE or earlier?
Drift from Africa and domestication around 8000 BCE?
Early domestication = not for food
Paso de la Amada
what happens?
why maize domestication?
Productive plant
1 kernel: 200 or more
Medivela european wheat 1:3-5
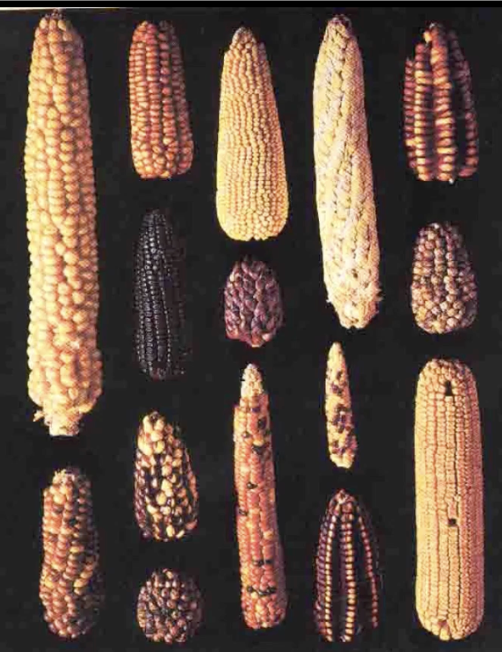

different processes of agriculture between SW aisa and mesoamerica
Southwest asia
Monument architecture before sedentism
Sedentism before agriculture
Relatively rapid change after domestication
What, barley, animal
Mesoamerica
Domestication before sedentism
Monumental architecture before sedentism
Gradual development, but rapid change after the building of monumental architecture
Maize, lack of significant animals
why agriculture?
More options along with hunting and gathering
Climate change warmer and wetter
Storage = risk-management
Animals
mixed substances
Monumental architecture = feast/ceremony/competiton
Intensification of face to face interactions
Intensification of production
Diverse processes
Unintended consequences
why didnt we go back?
Population growth ← sedentism
Environmental change
Social change