Decentralization
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Don’t send a national bulldozer to fix a village pothole (Bockenforde, M. (2011).
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Decentralization
Is the territorial dispersal of governmental authority from the national center to subnational levels—regional, provincial, or local.
Transfer of power of authority
It also includes upward transfers to international institutions (two-way street).
Upward Transfer of Power

Reality of the Systems of Government
There exists none today that strictly follows one system (federal, unitary, confederal) only.
Meaning that some Unitary nations can have hints of decentralization amid the spectrum.
The Bockenforde Framework
One of the frameworks that helps to understand the streams of decentralization practiced by different countries.
Divides decentralization into two aspects: (1) Formal and (2) Substantive
Formal Aspect of Decentralization
Formal - the backbone, organizational structure of an administrative system. If a policy-maker is aiming to revise the decentralization set-up of the nation, looking into the formal aspect is the best option.
(1) Checks how many levels of governments are there in a nation.
Types:
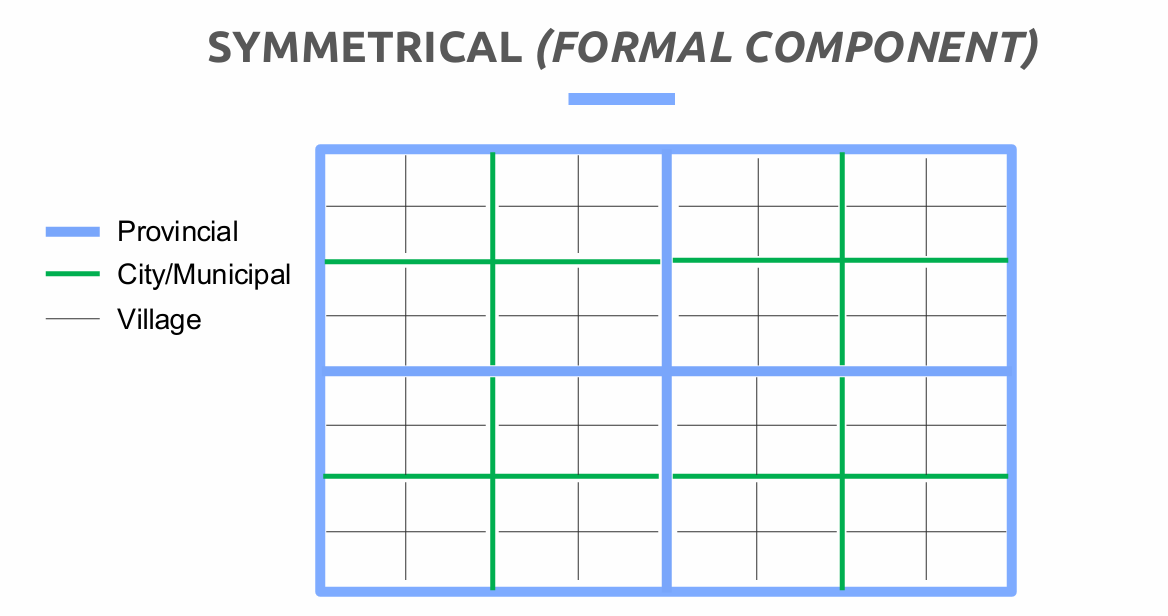
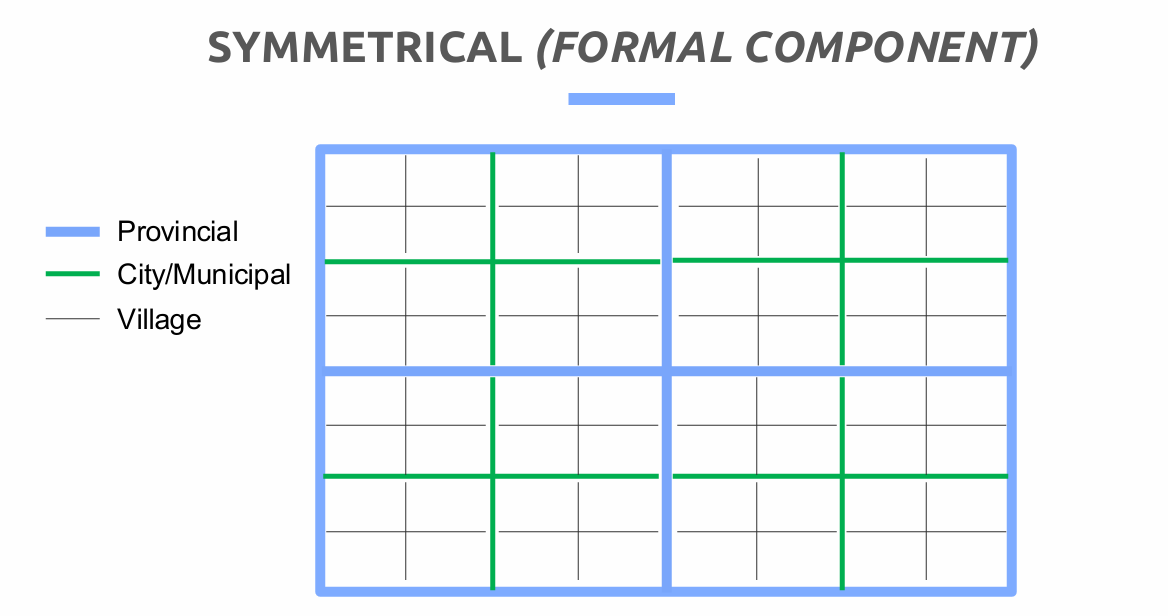
Symmetrical - equal numbers of level of government
Asymmetrical - some areas have more levels of gov/adm.
(2) Checks for institutional set up of the branches of the sub-national level of governments.
The Philippines has two levels of governments, the National and the Local. Meanwhile, the region is not a government but an administration. Symmetrical, but with a feature of asymmetry because of BARMM.
Symmetric Formal Component
Asymmetric Formal Component
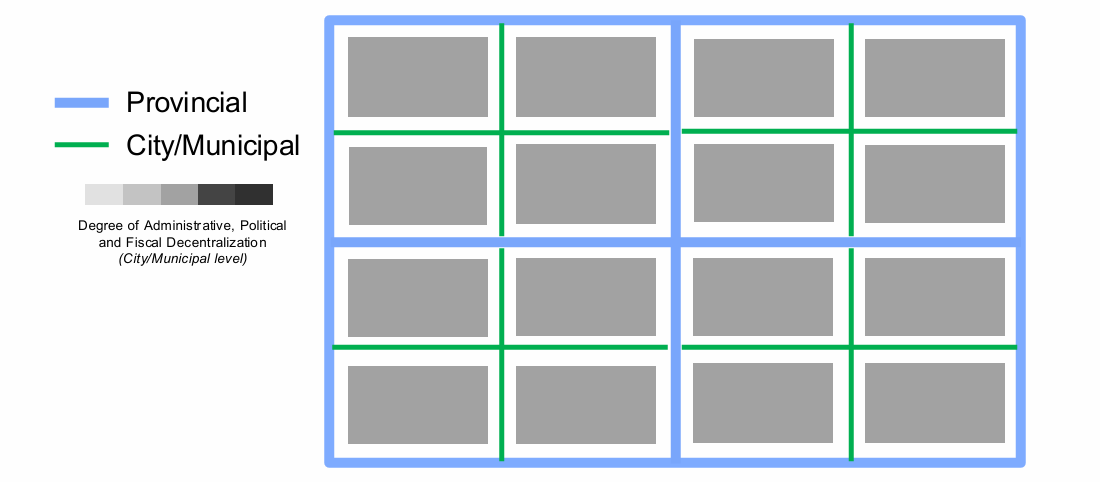
Symmetric Substantive Component
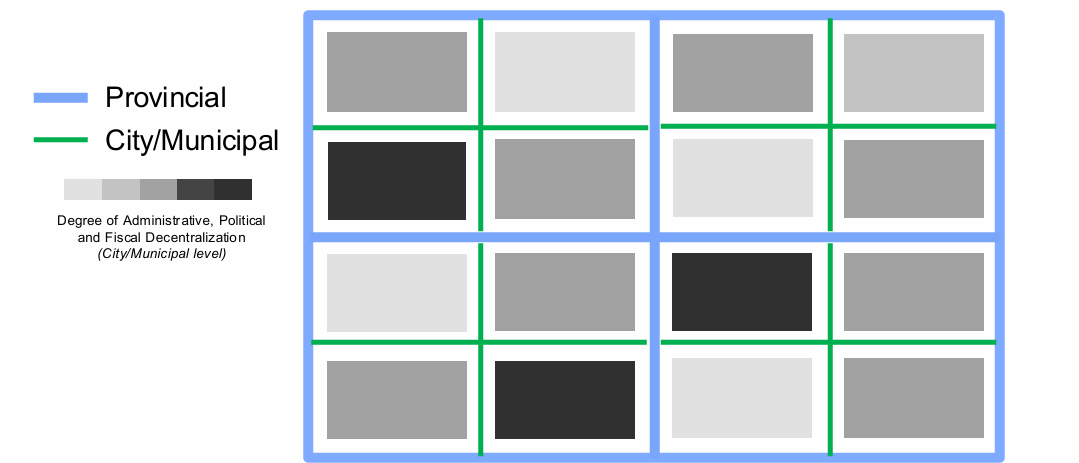
Asymmetric Substantive Component

Substantive Aspect of Decentralization
Substantive - the assigned functional, extent of authority to different levels of government.
(1) Checks for the Degree of administrative, political, and fiscal decentralization
Administrative - How are the plans of the government operationalized?
Political - Who can decide and to what extent can they decide?
In the Philippines, the section 17 of the Local Government code answers this question.
Fiscal - What are the sources of revenue of the subnational government? What are their limitations in terms of expenditure?
Sources of Revenues:
Internal Source:
Tax
Non-Tax
External Source:
National allotment
(2) Symmetry of power/authority
Types:
Symmetrical - same held powers and authority in all sub-nations
Asymmetrical - unequal held powers and authorities in some sub-nations. This is valid option that can be chosen to cater for the varying contexts of different sub-nations.
(3) Degree of legal safeguard against unilateral abolition
Are the sub-national units safe from abolishment when the national decides to abolish it?
Different Dimensions of Decentralization
Administrative - redistribution/transfer of responsibility and authority for carrying-out governmental functions.
Political - involves transfer of power to decide and to choose local elective and appointive officials. Transfers of authority to structure (organizational and functional) government at the subnational level
Fiscal - focuses on the degree of fiscal autonomy (assignment of expenditure responsibilities, revenue generation power), intergovernmental power (40% of the national revenue is apportioned to the subnational), and credit financing (exemplified by the dual nature of the LGU, not on its nature as a subdivision, but specifically as a corporation where it can create its own revenues).
Types of Decentralization (Atienza)
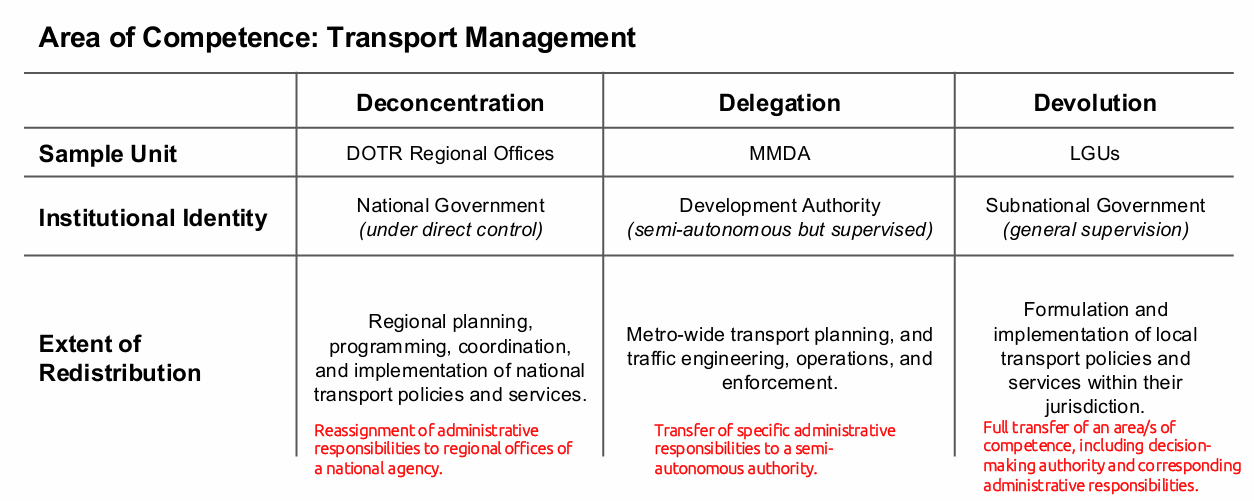
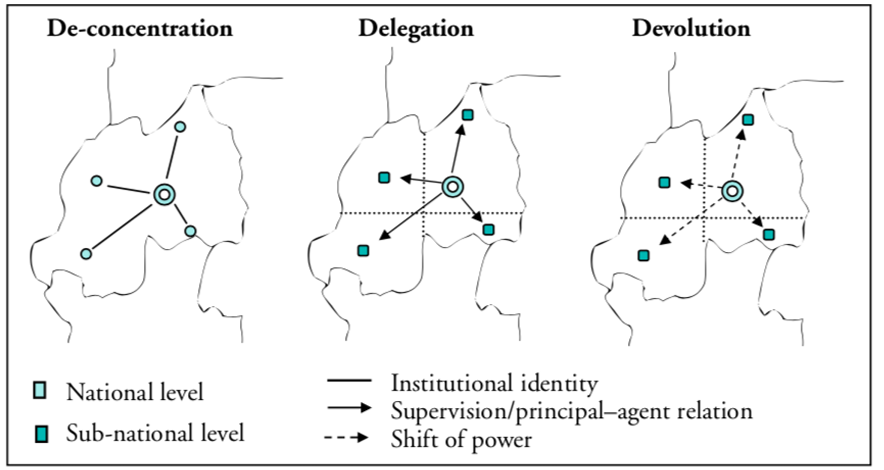
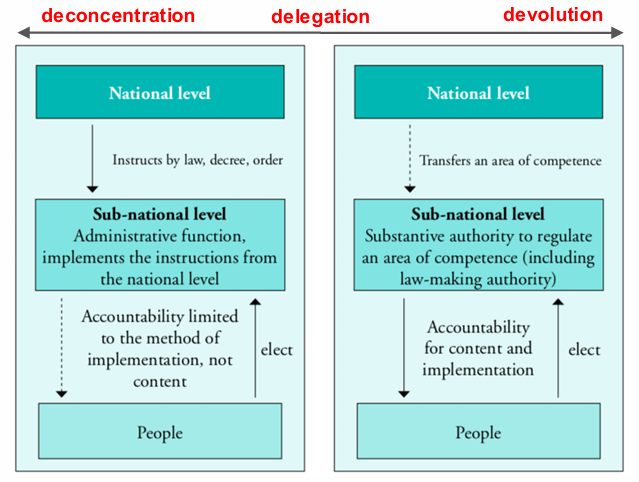
De-concentration (Geographical Decentralization): institutional identity is shared from the national to the sub-national; the central unit assigns its members to different geographs.
Utilizes the Old PA theory. e.g. field offices.
Delegation (principal-agent relation): the national provides supervision to the sub-national; decision-making and management authority for specific functions is delegated to organizations that are not under the direct control of central government ministries. Utilizes New Public Management theory.
Examples are regional planning and area development authorities, special project implementation units, and public corporations (MMDA, and GOCCs).
Devolution (extreme decentralization): the central government relinquishes certain functions or creates new units of government that are outside its control. In this type, voting happens. Utilizes Government to Governance Model.
Examples are the LGUs as implicitly stated in section 16 of the LG code, titled General Welfare.
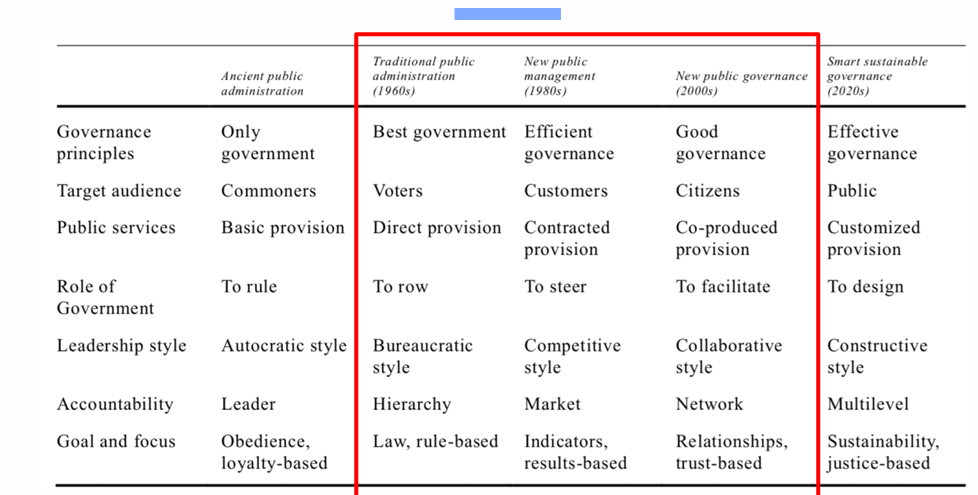
Where do the Types of Decentralization fit into the Paradigms of Public Administration?
Deconcentration vs. Delegation vs. Devolution -example thru Transport Management
Administrative Dimension of Decentralization (Atienza)
Redistribution/Transfer of responsibility and authority for carrying-out governmental functions.
Political Dimension of Decentralization (Atienza)
Transfer of power to decide and to choose local elective and appointive officials.
Transfer of authority to structure (organizational & functional) government at the subnational level.
Fiscal Dimension of Decentralization (Atienza)
Degree of fiscal autonomy
Assignment of expenditure responsibilities
Revenue generation powers
Intergovernmental transfers - 40% of the national revenue is apportioned to the subnational
Credit Financing - (exemplified by the dual nature of the LGU, not on its nature as a subdivision, but specifically as a corporation where it can create its own revenues
Centralization: Dimensions vs. Types
Administrative Decentralization = Deconcentration
Political Decentralization = Devolution
“A degree of political decentralization must accompany devolution, given that the central government no longer has sanctions over the subunits; the electorate must assume that responsibility by voting in popular elections” (Bockenforde, 2011)
Centralization vs Decentralization
Centralization
Lack of capacity at the local level
Priority to address national concerns
Legacy: Historical Centralization. Ex: PH structure can be traced back to our history
Decentralization
Easier to decentralized when you globalise, devt Competitive advantage through decentralization
Call from communities. Ex: BARMM
Economic efficiency: Hindi na kailangan dumaan sa natl govt
Nene Pimintel: Father of LGC
Operational efficiency, service delivery
Decentratlization: Positive vs. Negative Effects
