Blood Cells & Morphology
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
Red Blood Cell
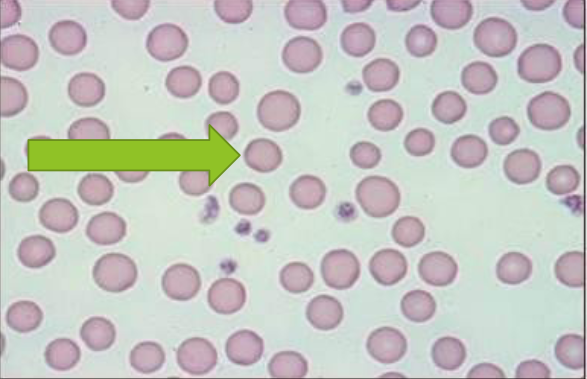
Platelet
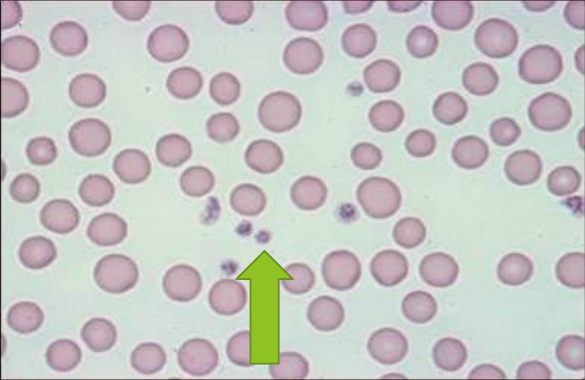
Neutrophil
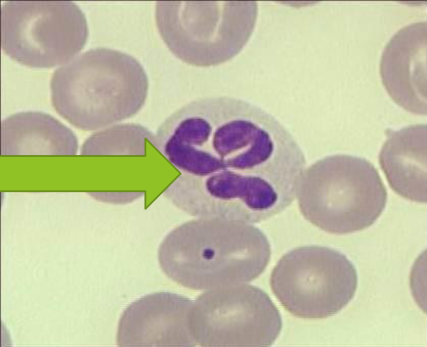
Lymphocyte
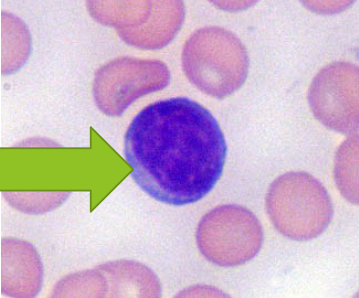
Monocyte
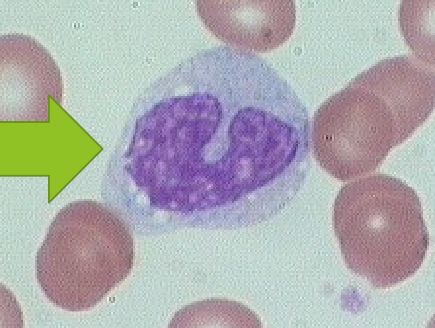
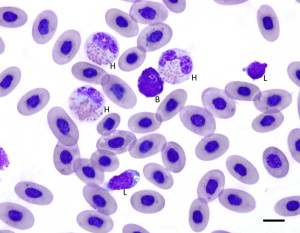
Feline Eosinophil
pink
rod shaped granules
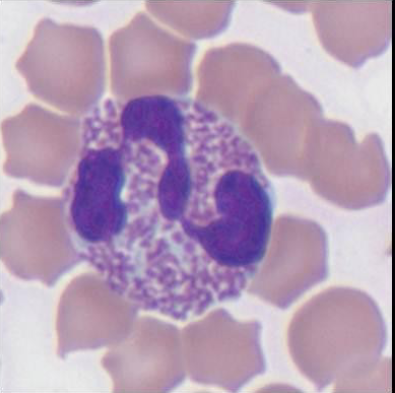
Canine Eosinophil
pink
round granules
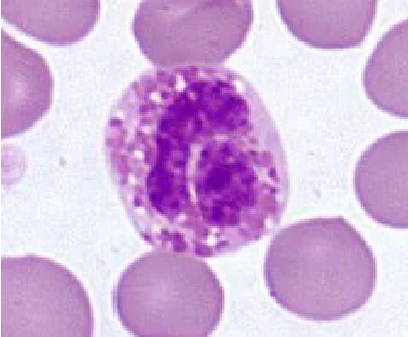
Equine Eosinophil
looks like a raspberry
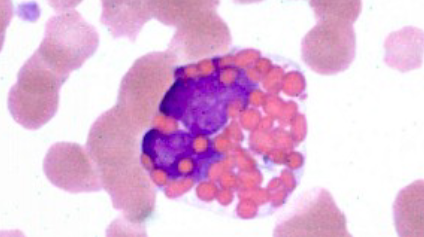
Feline Basophil
lavender
oval shaped granules
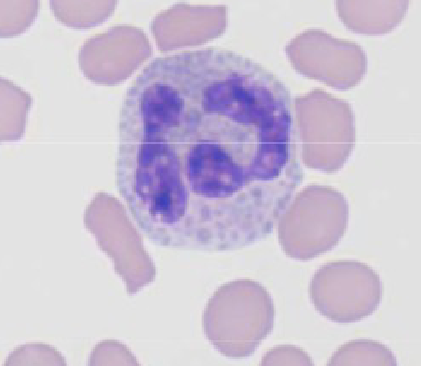
Canine Basophil
ribbon shaped nucleus
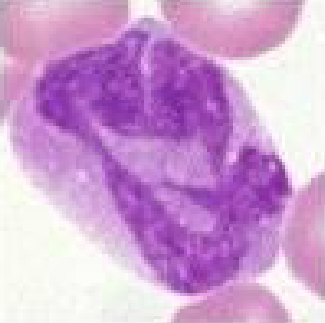
Equine Basophil
dark colored granules
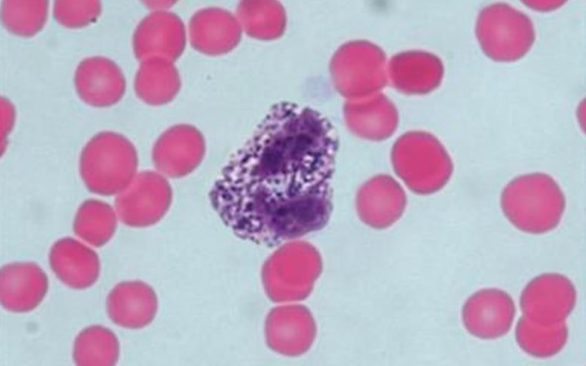
Nuclear Hypersegmentation
nuclei with 5 or more lobes
can be due to aging neutrophils
common in poodles w macrocytosis
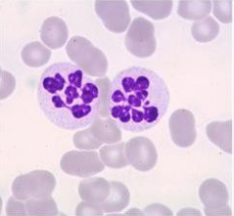
Dohle Body
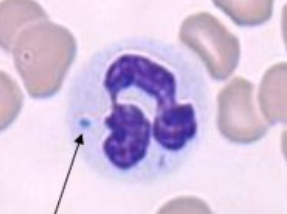
Reactive Lymphocyte
increased basophilia in cytoplasm
more abundant cytoplasm than normal
kidney bean shaped nucleus
caused by antigenic stimulation
vaccines or infection
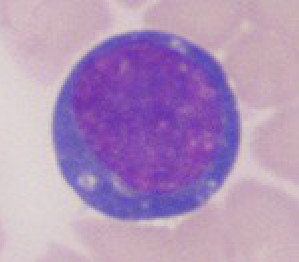
Blast Cell
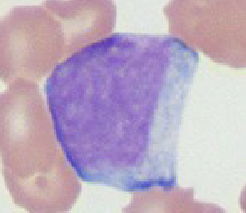
Toxic Granulation
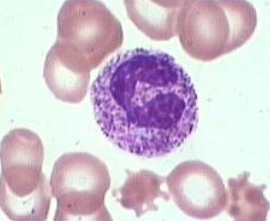
Pelger-Huet Anomaly
nuclear hyposegmentation
nuclear chromatin appears unsegmented
congenital defect (Aussie Shepherds)
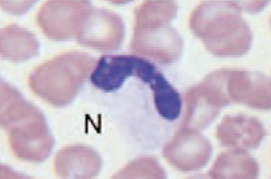
Smudge Cells
leukocytes that have ruptured
not significant unless in large numbers
associated with leukemia
artifact when making blood smear
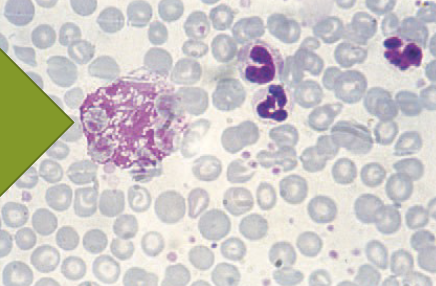
Pyknosis
condensing of nucleus as cell dies
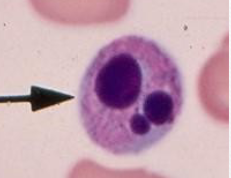
Karyorrhexis
fragmentation of nucleus after cell death
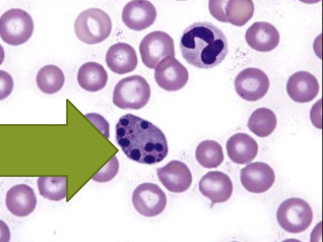
Karyolysis
degeneration of nucleus by dissolution of nuclear membrane
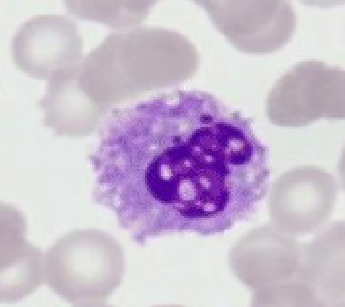
Rouleaux
stacking of RBC
only when found right behind feathered edge
common to see on butt end
can be seen in normal horses or cat & pigs
sticky RBC’s
seen w increased fibrinogen & globulin concentrations
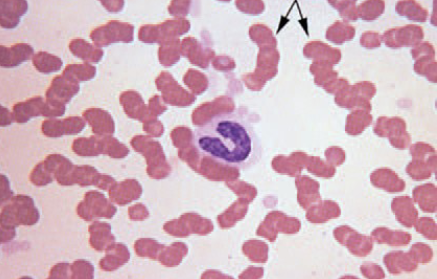
Autoagglutination
occurs in immune mediated disorders
body attacks itself
cells coat with antibodies & stick together
differentiate from rouleaux with drop of saline
rouleaux will disperse
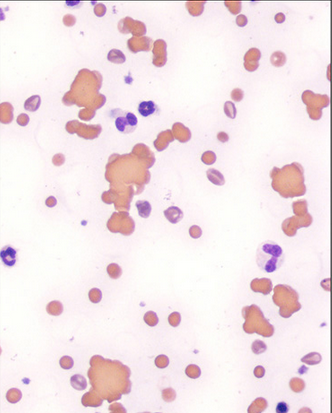
Anisocytosis
variation in size of RBC’s
macrocytes, microcytes, or both
common in normal bovine blood

Polychromasia
RBC’s with blueish tint
organelles remain in cytoplasm
indicate young RBC’s
appear as reticulocytes when stained with NMB
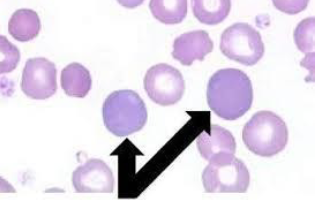
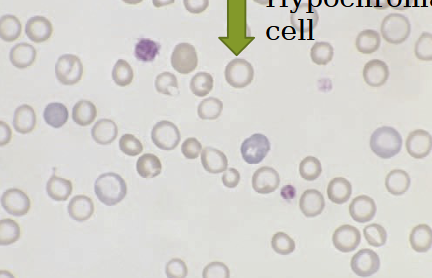
Hypochromasia
RBC’s with decreased color
periphery appears darker, gradually lose color in central region
vary pale central region
insufficient hemoglobin in cell
iron deficiency
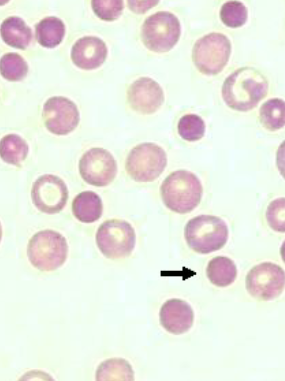
Hyperchromatophilic
RBC’s that stain darker than normal
usually microcytes or spherocytes
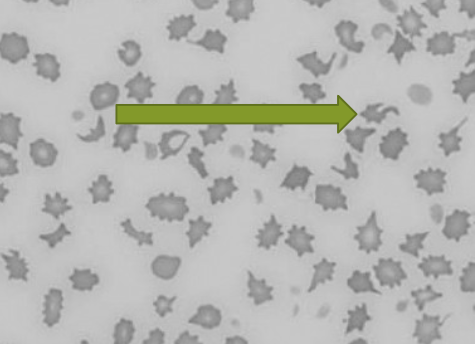
Poikilocytes
abnormally shaped RBC’s
does not suggest specific dx or cause for change
term used only when abnormalities cannot be described by another term
Schistocytes
RBC fragment
shearing of RBC via IV trauma
disseminated introvascular coagulopathy - DIC
RBC broken by fibrin strands & iron deficiency
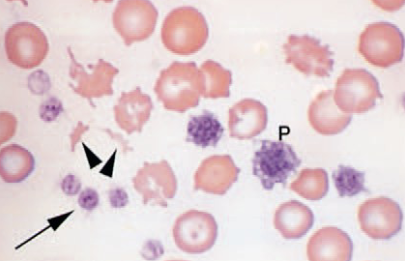
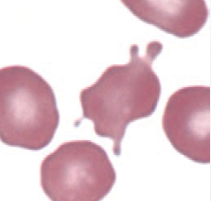
Acanthocytes
hemangiosarcoma
irregular spike-like projections
unevenly distributed
variable length & diameter
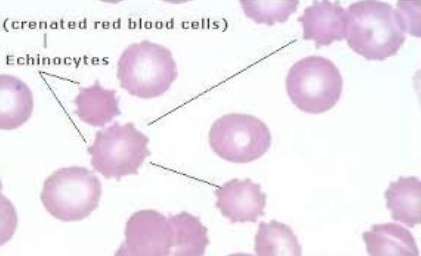
Echinocytes
crenated cells
numerous short, evenly spaced surface projections
uniform size & shape
can be due to slow drying/prolonged storage
seen with renal dz & lymphosarcoma in dogs
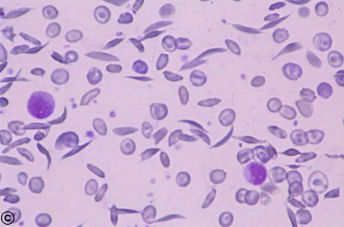
Drepanocytes
sickle cells
seen in deer & angora goats
Heterophils
normal in avian & reptiles
equivalent of neutrophil
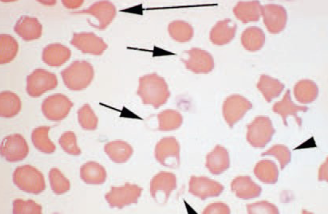
Keratocytes
helmet cells, blister cells
appear to contain vacuole attached to side of cell
associated with hepatic disease, neoplasia, IV trauma
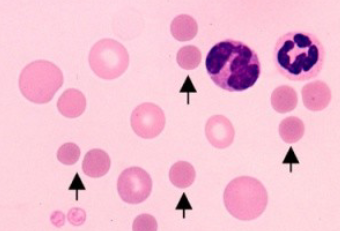
Spherocytes
dark staining RBC’s with reduced or no central pallor
partial phagocytosis of cell
response to antibodies
suggest immune-mediated destruction of RBC
hard to detect in species other than canine
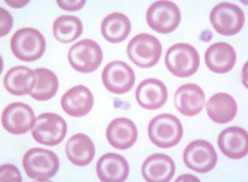
Target Cell
leptocyte with central area of pigment
surrounded by clear area & ring of peripheral cytoplasm
resemble target/bullseye
associated with anemia, liver dz, inherited disorders
Stomatocytes
transverse fold across center of cell
clear slit-like pale region in center
is an artifact if slit is perpendicular to feathered edge
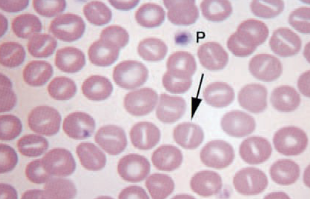
Torocytes
created by force of blood going through small vessels
area of central pallor
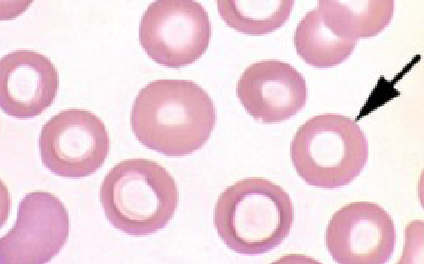
Elliptocytes
ovalcytes
normal in camelids & nonmammals
associated with leukemia, hepatic dz, etc.
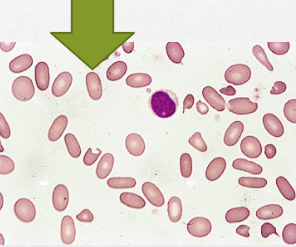
Eccentrocytes
appear to have hemoglobin pushed to one side
seen in patients with diabetes, neoplasia, babesia
can be due to toxicities
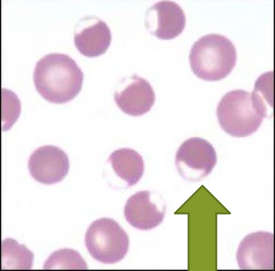
Dacrocytes
tear drop shaped RBC
if tails all face the same way = artifact
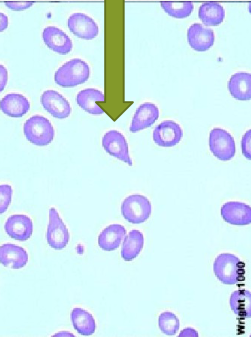
Basophilic Stippling
lead poisoning
small, dark blue bodies
from residual RNA
common in immature ruminant RBC’s
can be seen in anemic cats
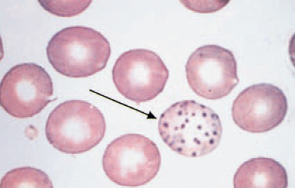
Howell-Jolly Bodies
basophilic nuclear remnants in young RBC
response to anemia
removed via phagocytosis when passing through spleen
can be seen after removal of spleen
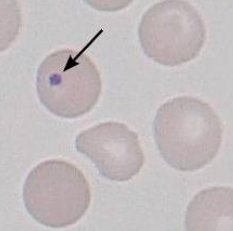
Heinz Body
round blue structures
denatured hemoglobin
normal in cats in 5% of RBC
increased # indicate diabetes, lymphosarcoma, etc.
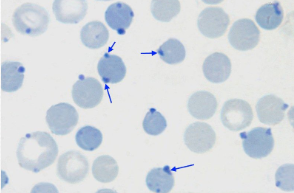
Nucleated RBC’s
immature cells in anemia
early release of RBC
can be seen in nonanemic animals
normal in nonmammals
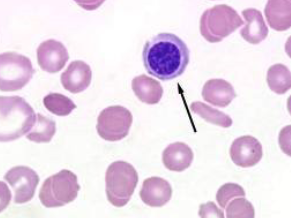
Parabasal Cell
estrus
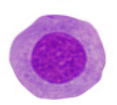
Intermediate Cell
proestrus
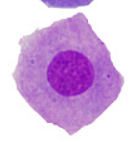
Hyaline Cast
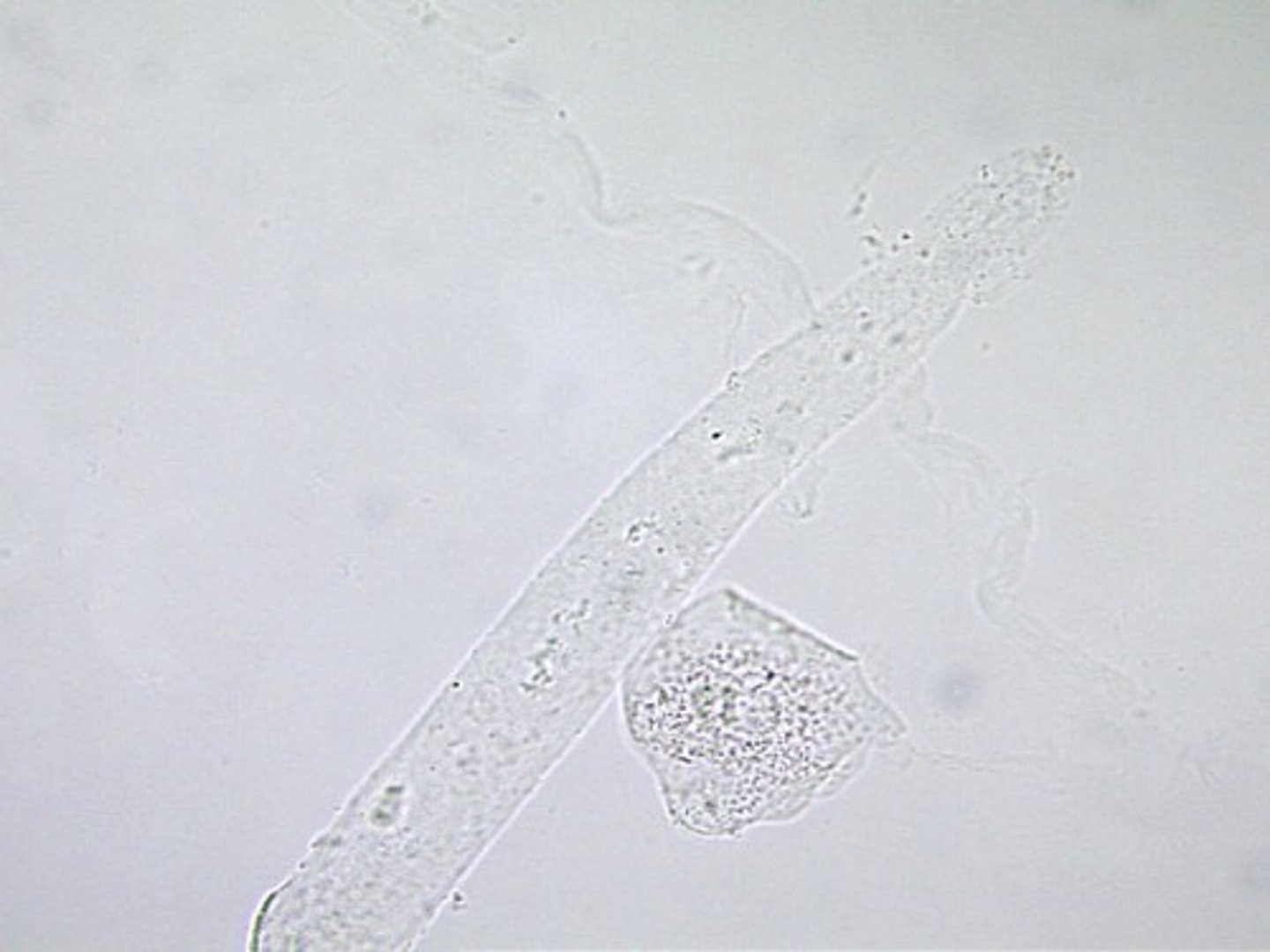
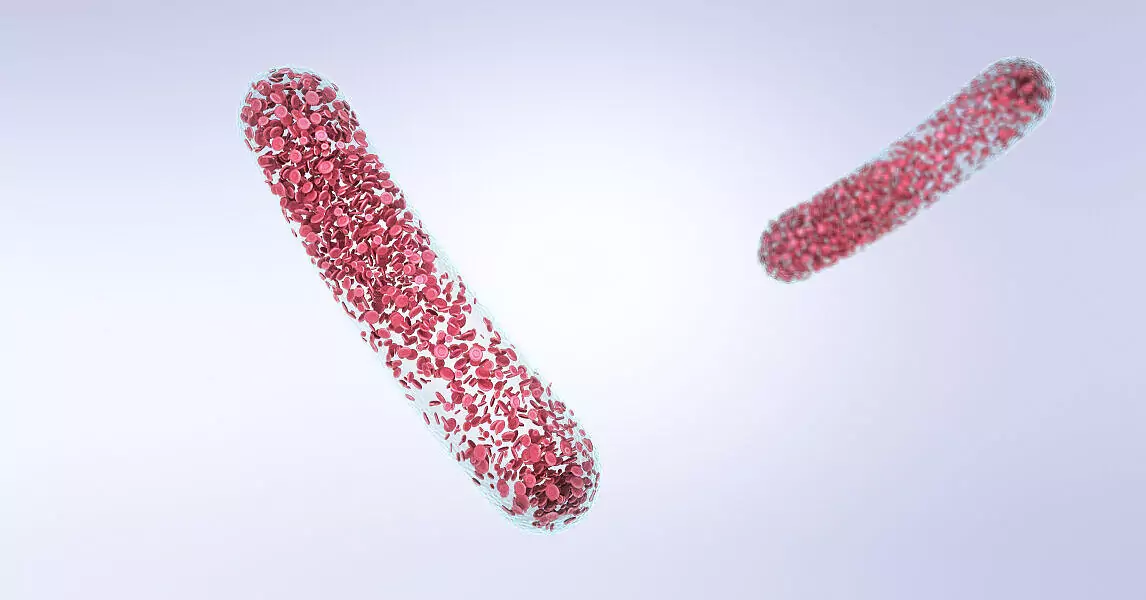
RBC Cast

WBC Cast
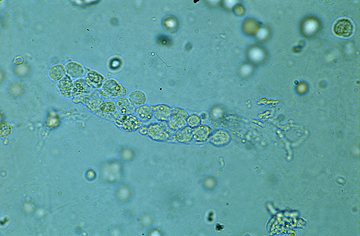
Fatty Cast
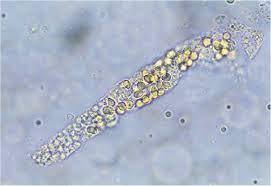
Mast Cell
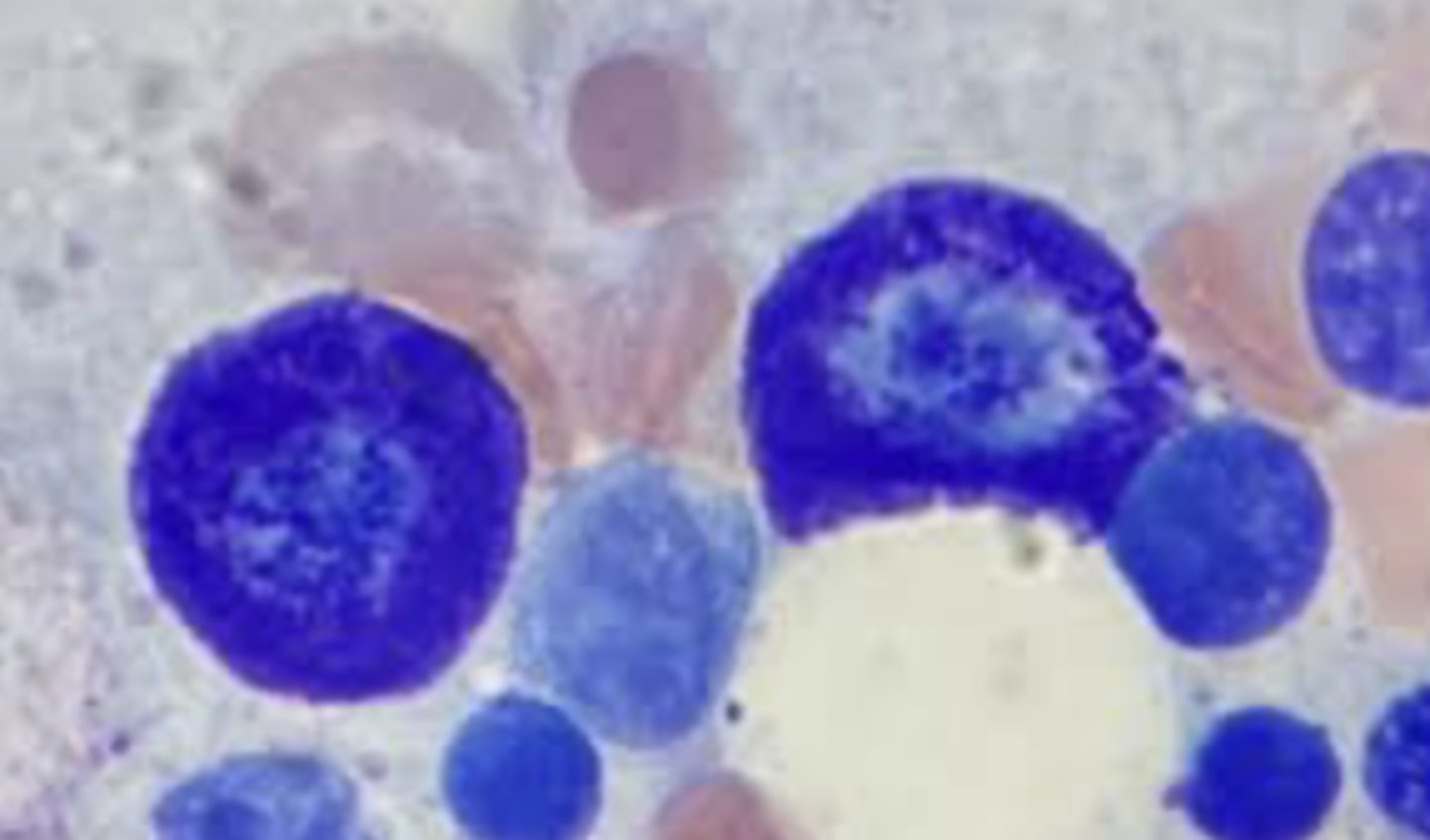
Superficial Cell
estrus

Squamous Cell
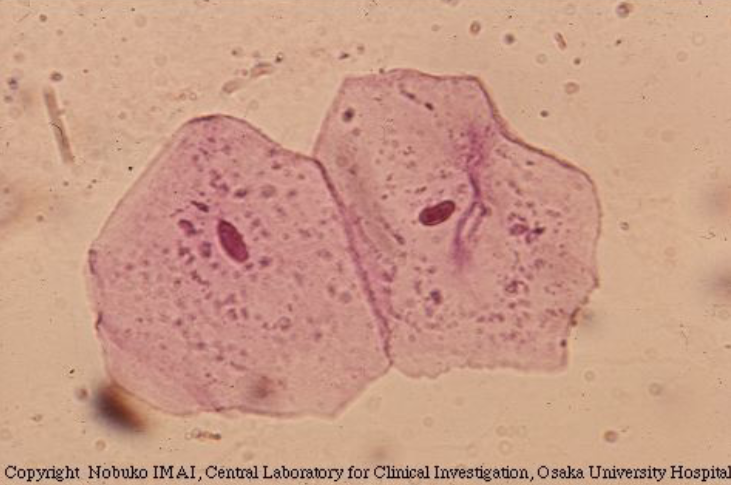
Renal Transitional Epithelial
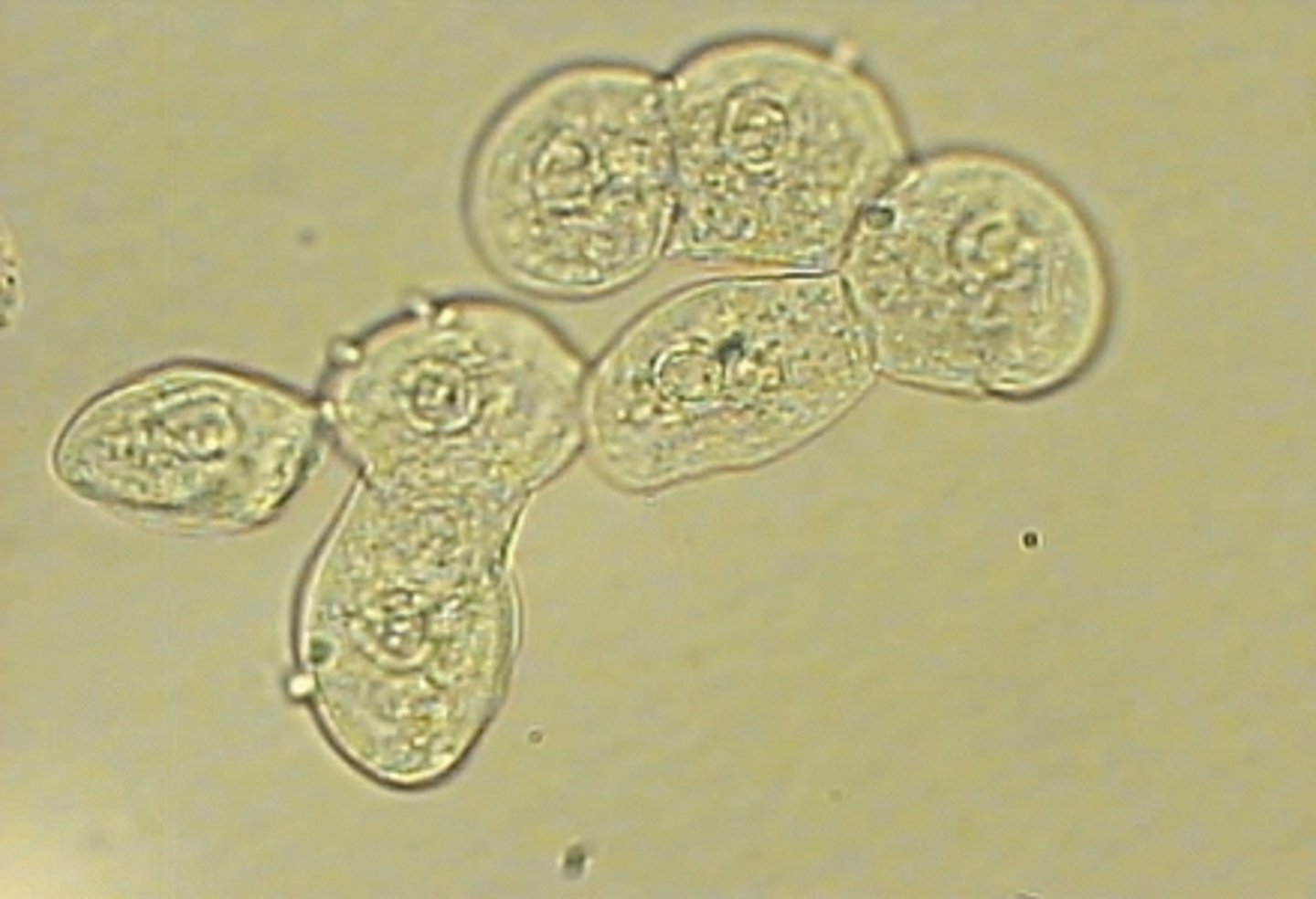
Struvite Crystal
alkaline urine
triple phosphate
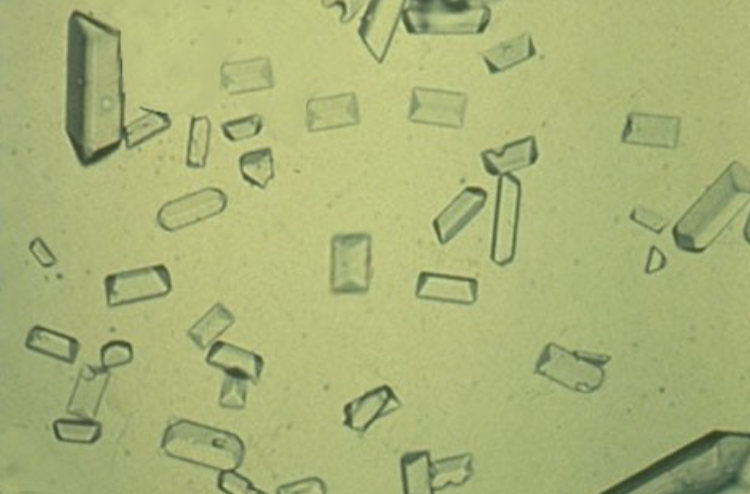
Calcium Oxalate Monohydrate
antifreeze ingestion
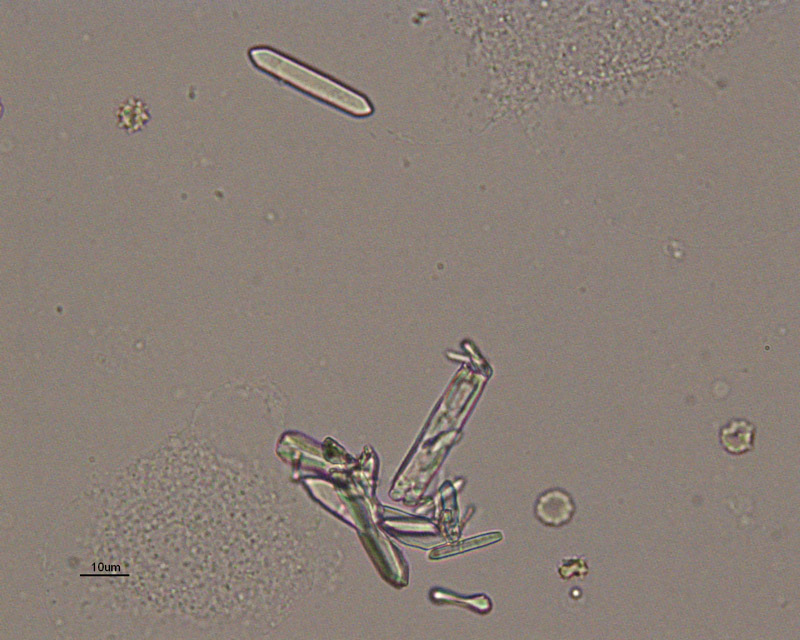
Calcium Oxalate Dihydrate
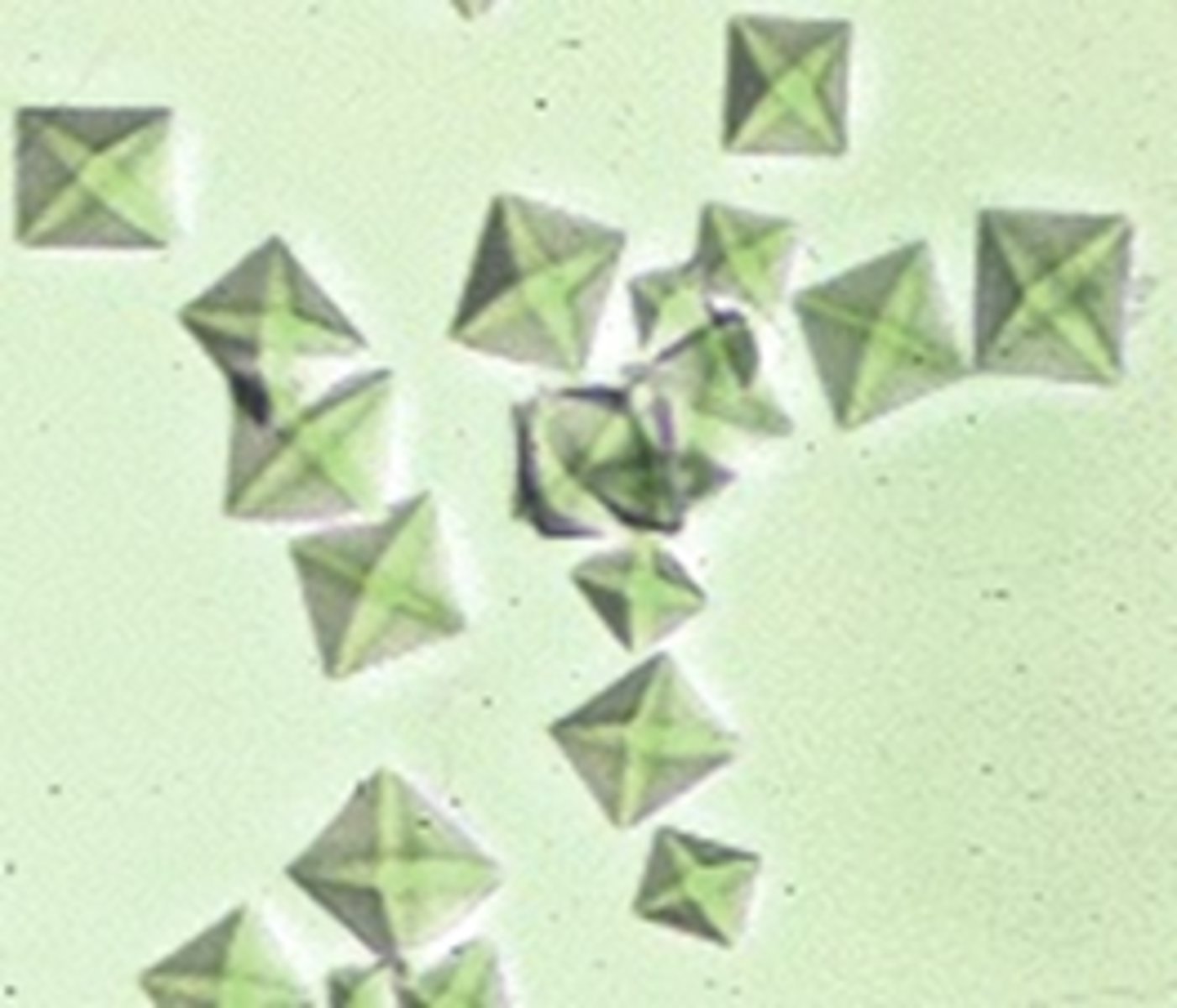
Bilirubin Crystal
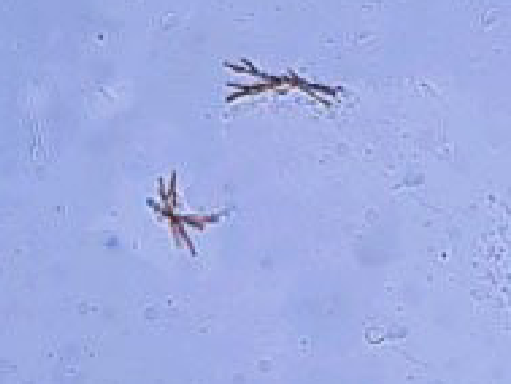
Calcium Carbonate Crystals
equine & rabbits
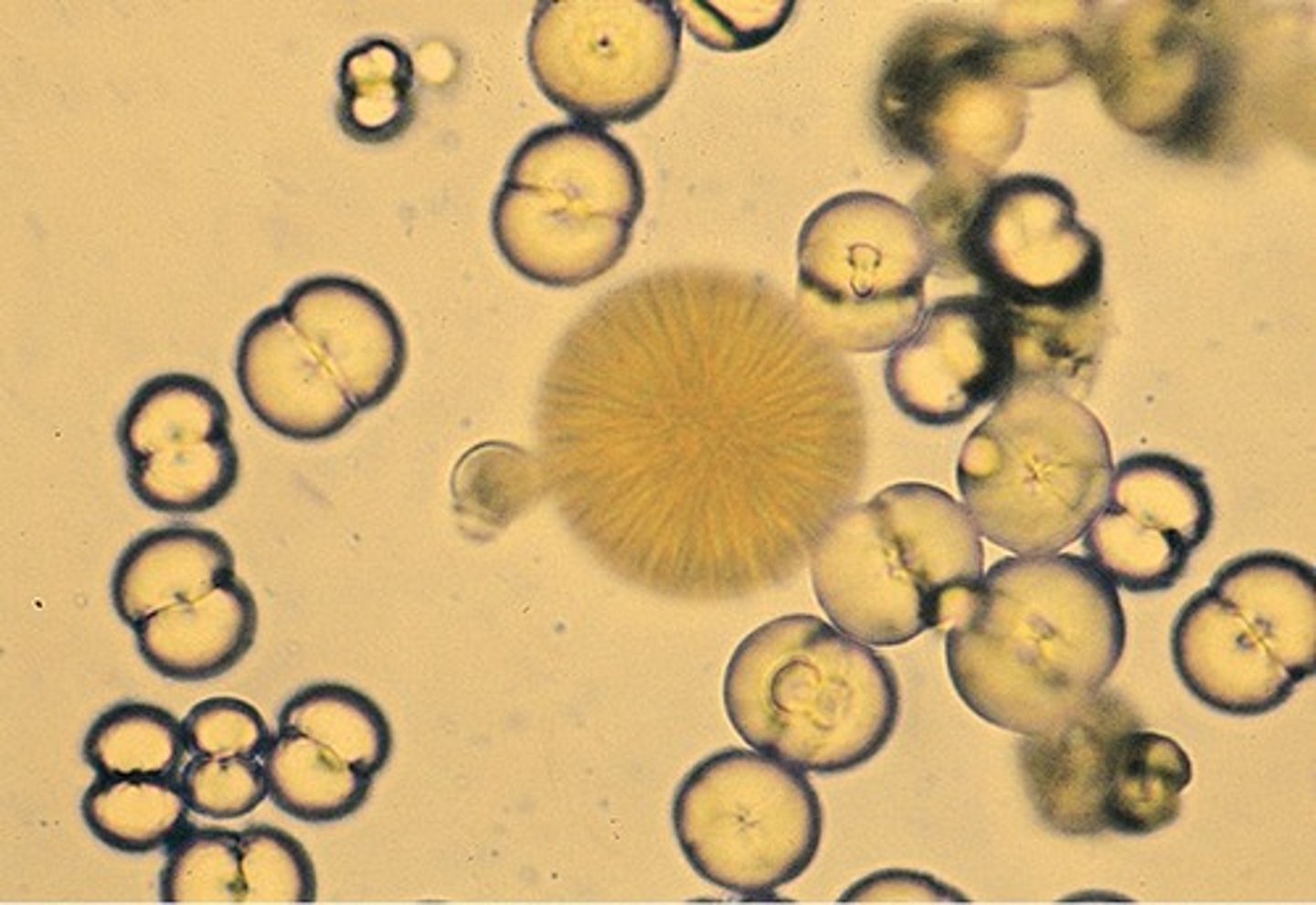
Fine Granular Cast
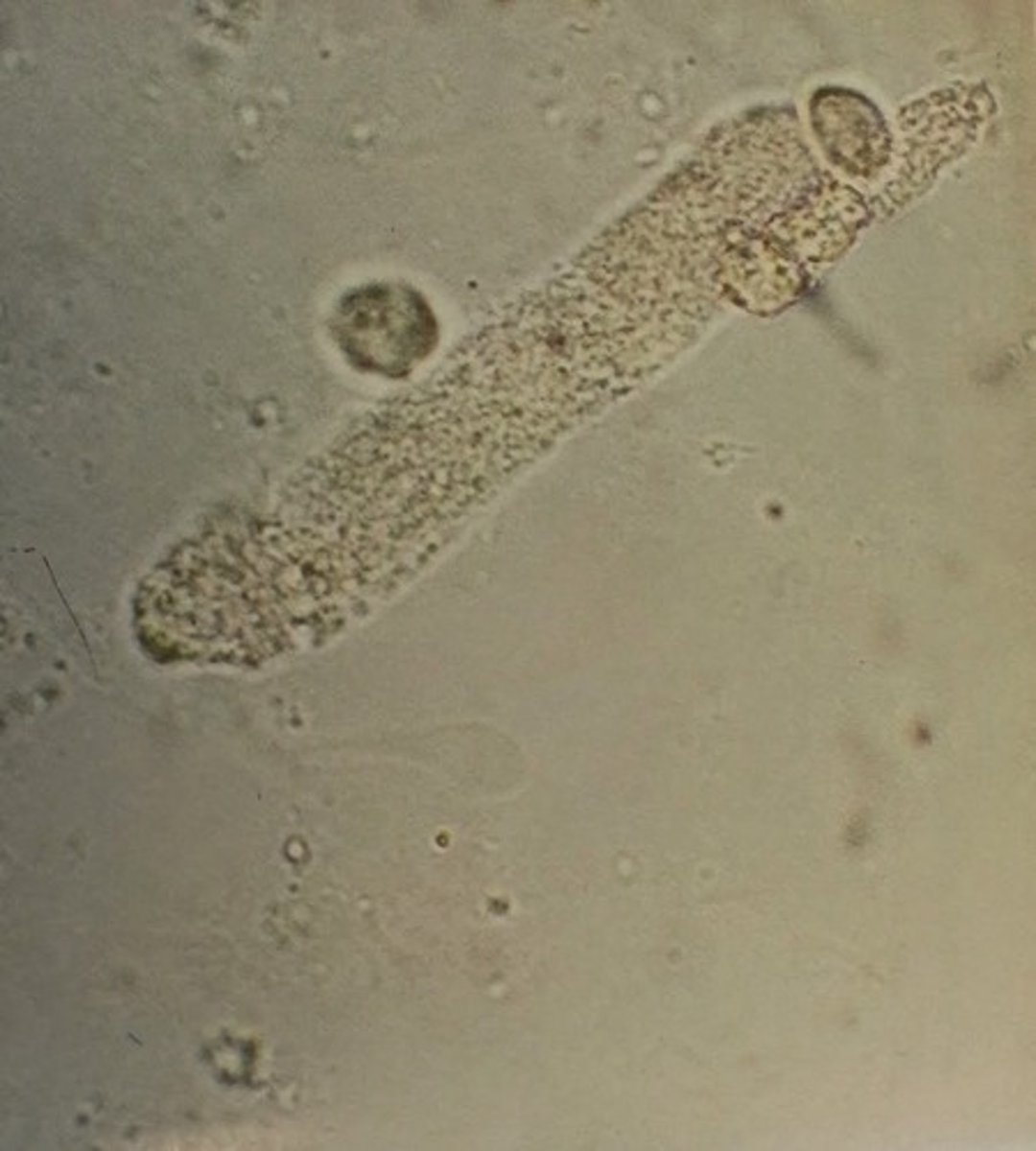
Coarse Granular Cast
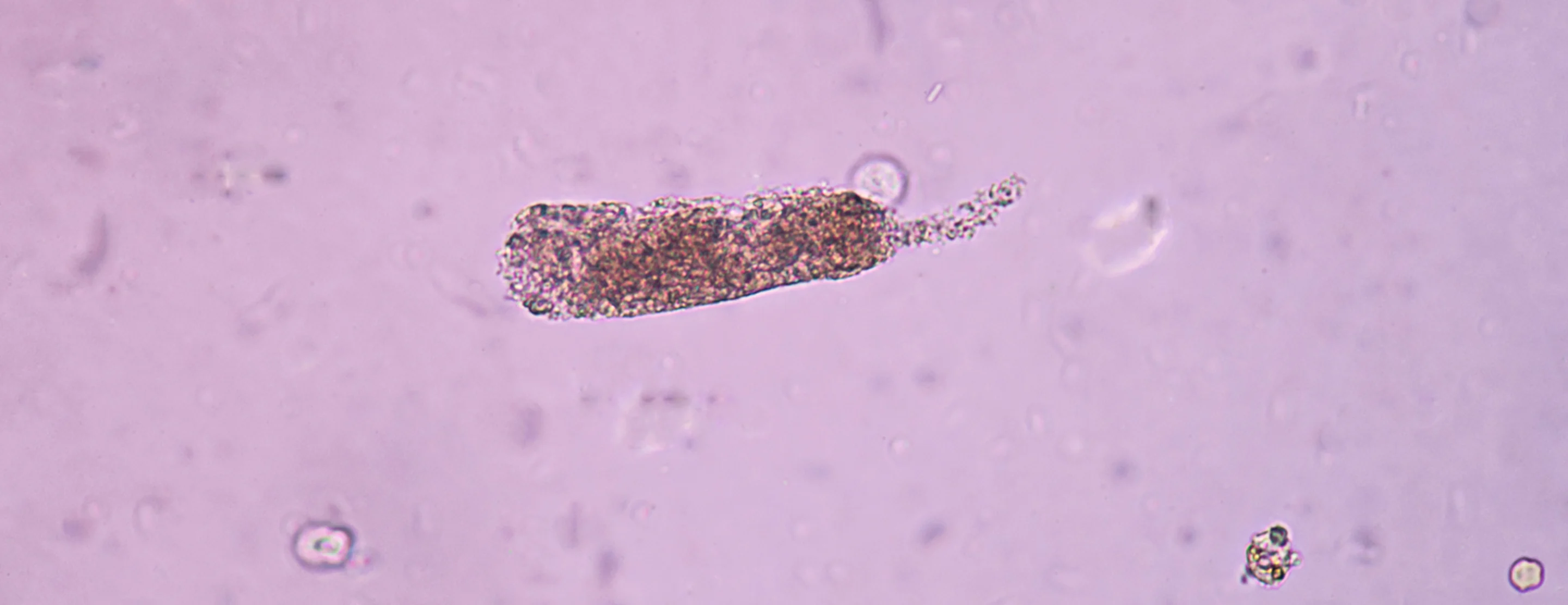
Waxy Cast
indicates renal failure
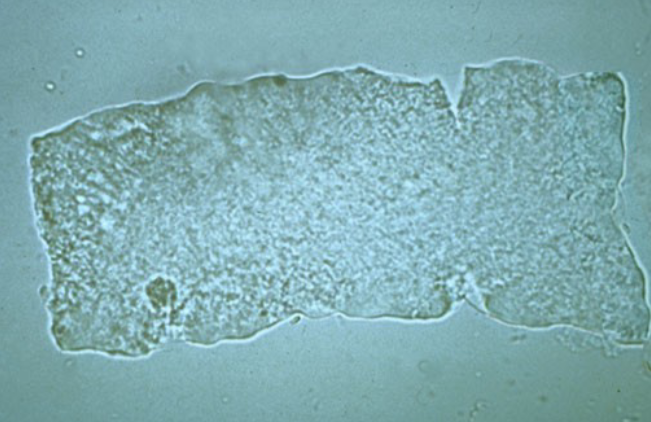
Uric Acid
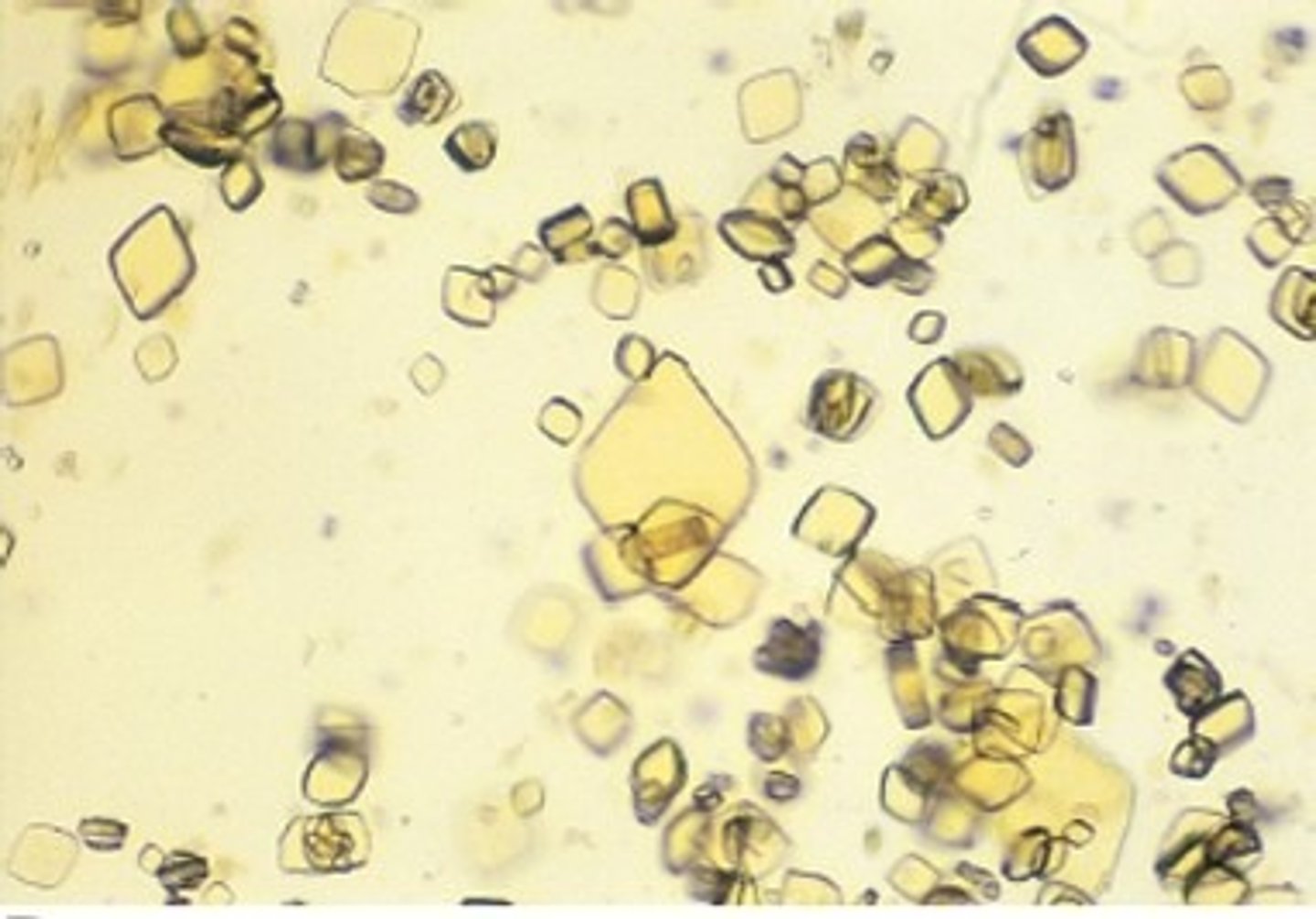
Mesothelial Cells
line body cavities
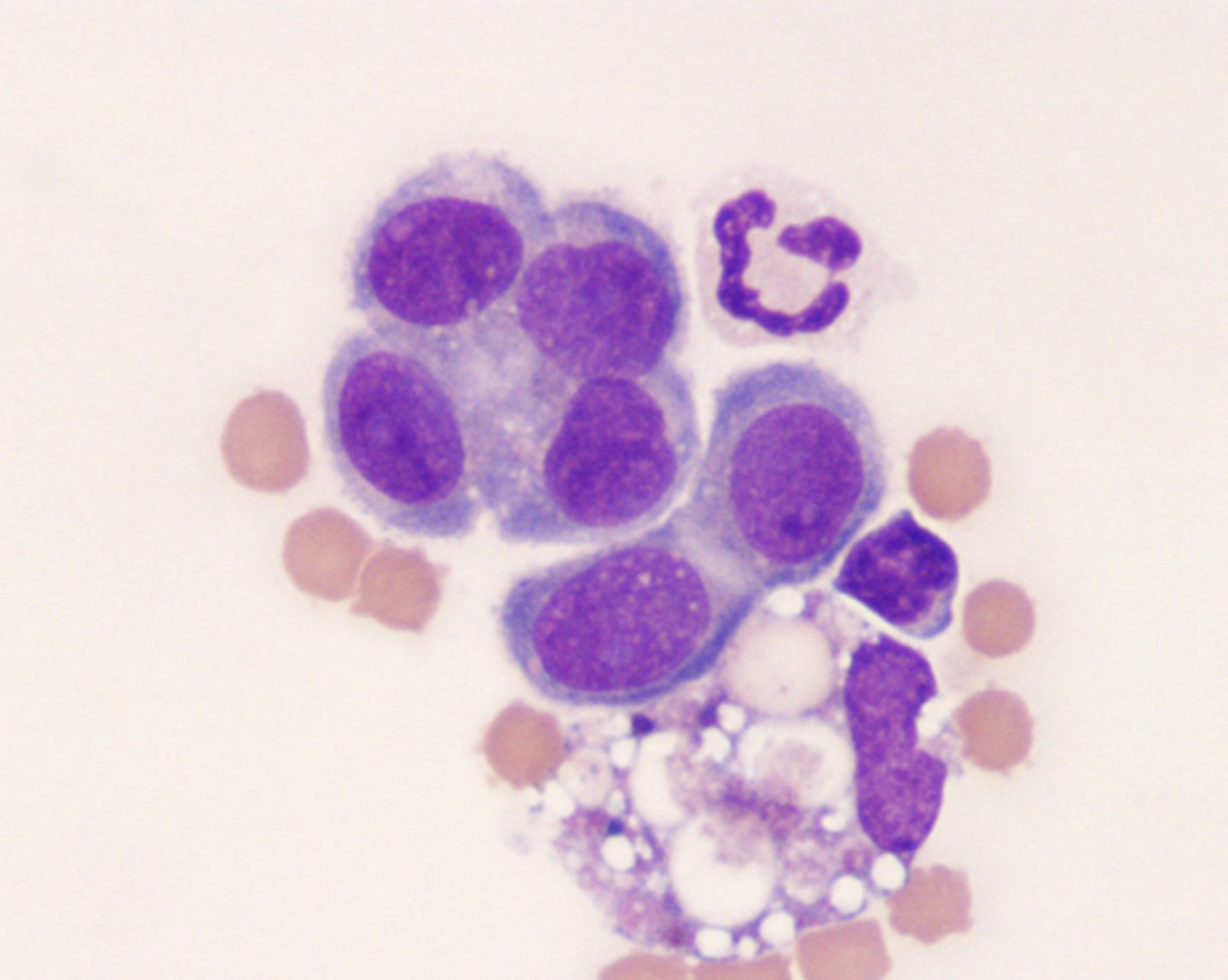
Macrophages
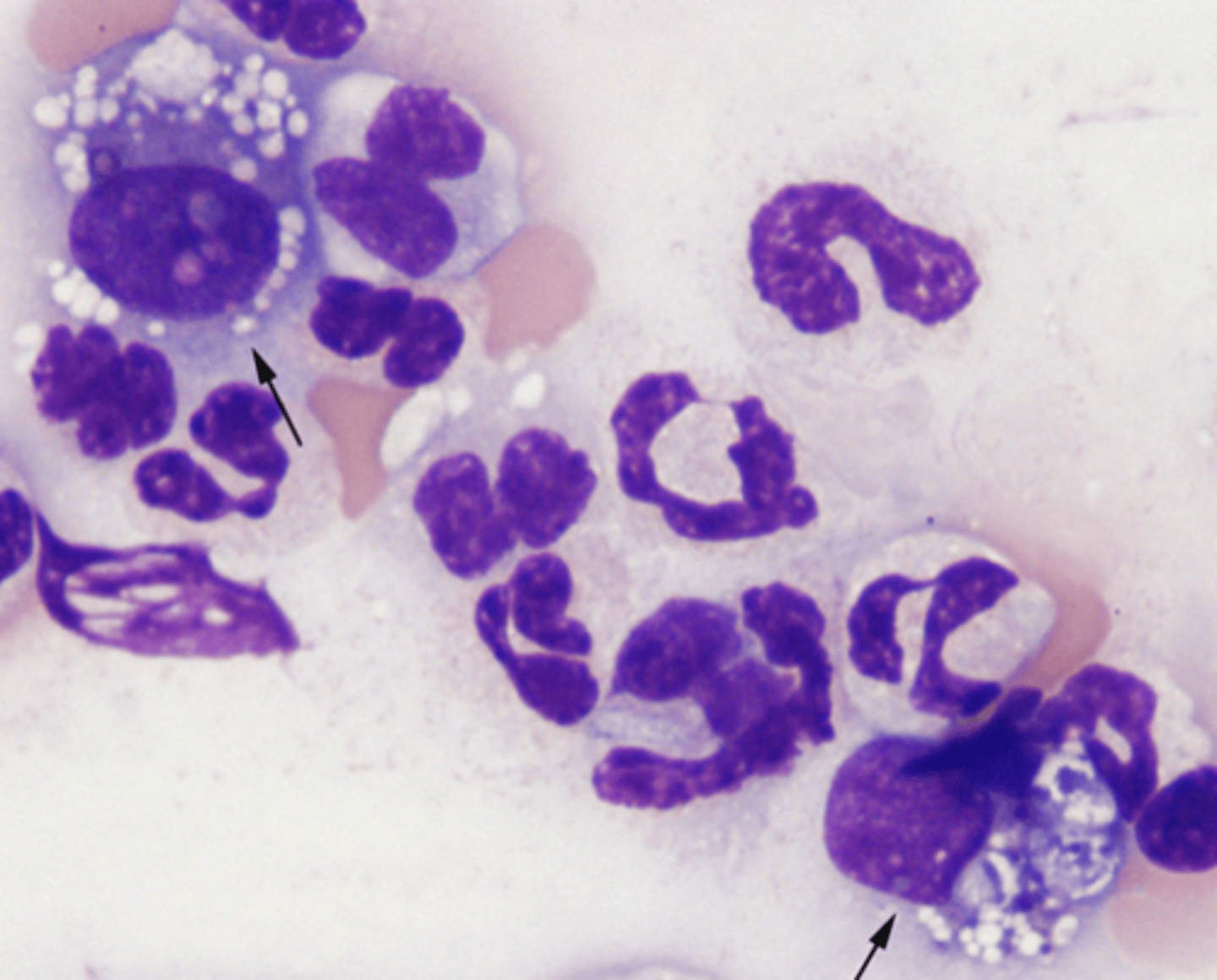
Suppurative Inflammation
Pyogranulatomous Inflammation
Eosinophilic Inflammation