theme 3 : monopolies
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
assumptions of a monopoly
can only be established where there is a single seller in the market i.e. there are no close substitutes - therefore market demand is equal to the firms demand curve
high barriers to entry - new entrants to the market find it impossible to match the costs and prices of the established firm in the industry, only remain a monopoly if these barriers exist
in the uk a firm is classified as a monopoly if it has more than 25% of the total market
main barriers to entry that uk supermarkets have
land purchases / land holding : may be used to prevent rivals from opening shops close by which means smaller firms can’t expand
if a company has dominance over a local market, may prevent other firms from being close to maintain dominance
putting pressure on suppliers : can put pressure on suppliers and transfer the risk and cost disadvantages to suppliers instead of having it themselves
total revenue curve
price on y axis
output on x axis
upside down ‘u’ shape
average and marginal revenue curve
price on y axis
output on x axis
average revenue curve is a downward sloping curve
marginal revenue curve falls at twice the rate and becomes negative
how are the total revenue curve and the average and marginal revenue curve related
the peak of the total revenue curve plotted down is where the marginal revenue curve becomes negative
see notes from 20/01/25 to see graph
when is total revenue maximised
maximised where MR is 0
abnormal profit making monopoly in the short run
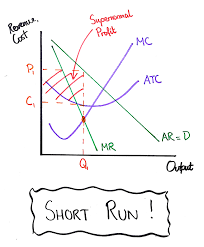
price on y axis
output on x axis
abnormal profit is the red box
loss making monopoly
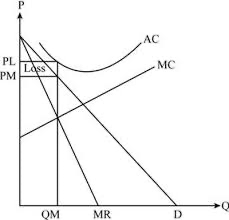
price on y axis
output on x axis
price from demand curve is lower than profit maximising price so firm makes a loss
summary of a monopoly
a pure monopoly is the sole supplier in an industry
as a result, the monopolist can take the market demand curve as its own demand curve
a monopolist therefore faces a downward sloping AR curve
with an MR curve falling at twice the rate of AR
where is profit maximised
where MR = MC
equilibrium profit maximising output point
this is where you track down from MR = MC
consumers will be willing to pay the price up for this output
perfectly competitive firms vs monopolise
perfectly competitive firms operate with allocate efficiency which means their output is where MC=P
monopolies set their output where MR=MC if they are profit maximising