(Completed) FInal: Connective Tissue and the Skin
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
131 Terms
The extracellular matrix (ECM) is composed of ___ and ___.
1) Ground Substance
2) Protein fibers
What is Ground substance?
a small amount of tissue fluid that has an amorphous gel-like consistency.
What is ground substance composed of? (3)
Glycosaminoglycans (GAG)
Proteoglycans (PG)
Multi-adhesive glycoprotein (MAG)
Which cell secretes Collagen fibers?
Fibroblasts
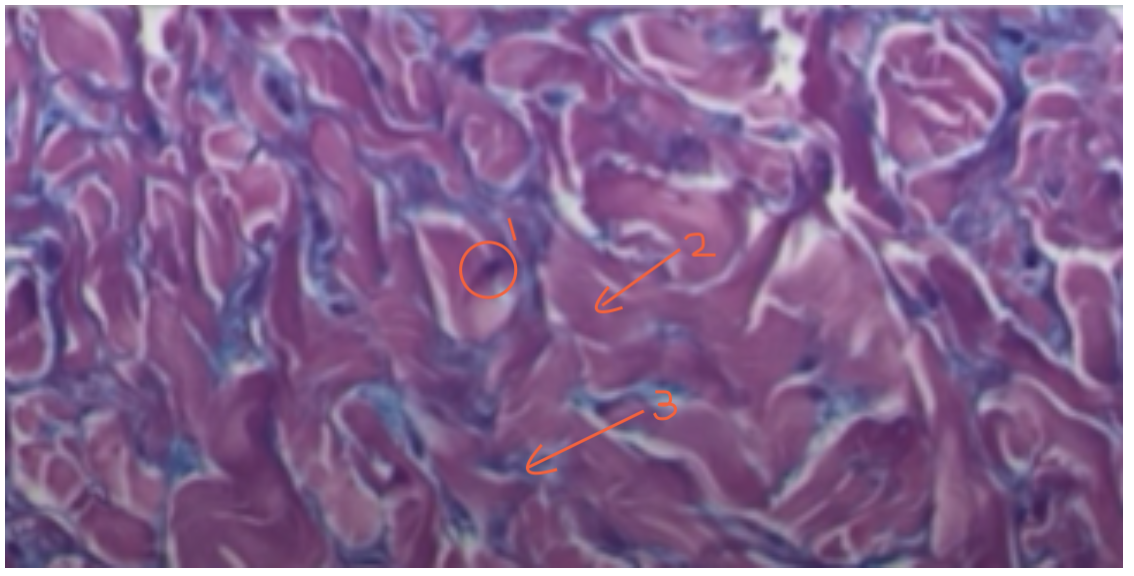
Identify the pointed structures.
Fibroblast cell
Collagen fibers
Ground substance
Which is the most abundant type of collagen and can be found in the dermis, tendons, ligaments? (Type 1,2,3,4)
Type 1
Which type of collagen provides resistance to pressure and can be found in Hyaline & Elastic cartilage? (Type 1,2,3,4)
Type 2
Give an example of Type 3 collagen.
Reticular fibers.
What type of collagen is present in the Basal Lamina of the Basement membrane? (Type 1,2,3,4)
Type 4
What type of collagen is found in the cartilage found in the nose? (Type 1,2,3,4)
Type 2
Elastic fibers are composed of ___?
a. Fibrilin
b. Elastin
A. Fibrilin
What cell produces elastic fibers?
Fibroblasts
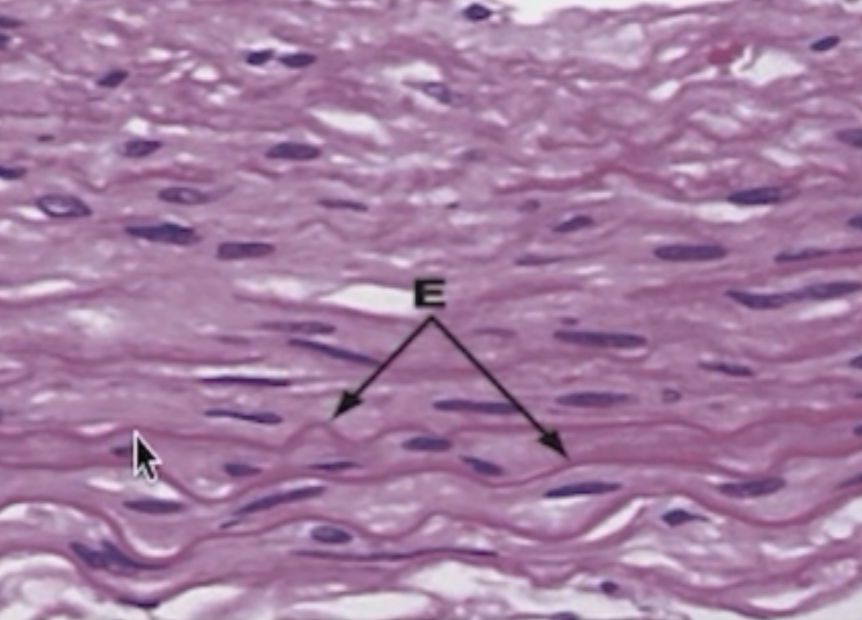
Identify the pointed structures.
Elastic Fibers
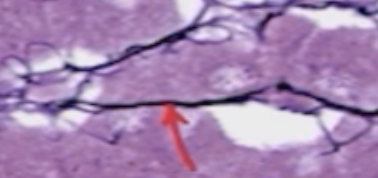
Identify the pointed structure. Note how darkly-stained it is due to its attraction to Silver stain.
Reticular fiber
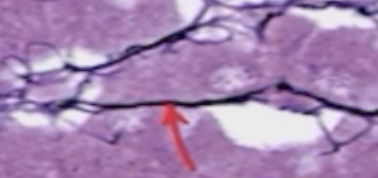
Identify what type collagen fiber this is.
Type 3 = Reticular fiber
ECM is composed of Ground substance and Protein fibers. Give the 3 types of Protein fibers.
Collagen
Elastic
Reticular
Which one is active and which is inactive?
Fibroblast
FIbrocyte
Fibrocyte - inactive
Fibroblast - active (seen during tissue repair)
An ovoid shaped fibroblast/fibrocyte = active or inactive?
Inactive
Small ELOMGA
Active
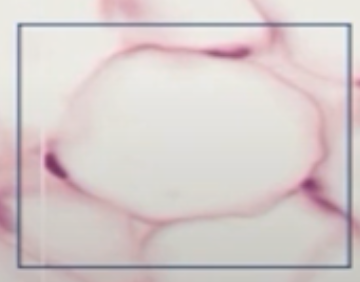
Identify the cell.
note the Signet Ring shape
note that the nucleus is located peripherally
Adipose cell
Macrophages are derived from what cell?
Monocytes from the bone marrow
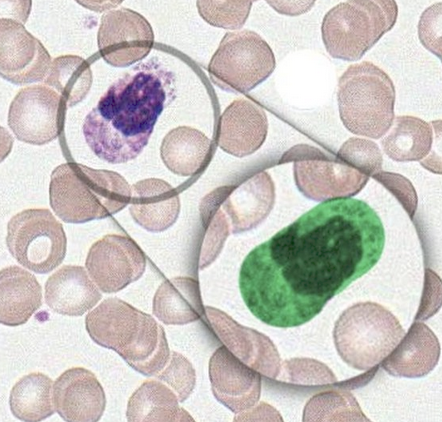
Identify this cell.
Macrophage
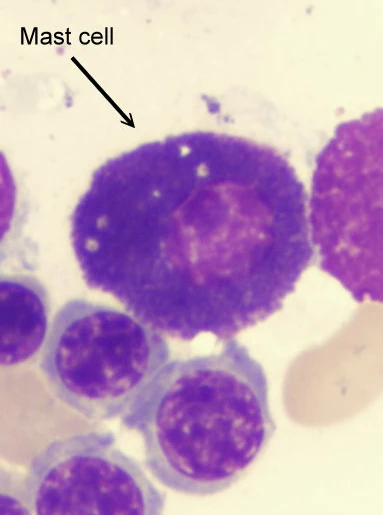
Identify this cell stained with toluidine blue
note the pale stained nucleus
note the cytoplasm filled with basophilic glanules
Mast cell
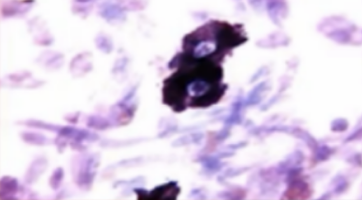
Identify the cell.
note the clock-face/spokes of a wheel
Plasma cell
____ cells migrate in between the endothelial cells of venues to enter CT via diapedesis.
Leukocytes
- Give the 5 types of leukocytes
Neutrophils, Eosinophils, Basophils, Monocytes & Lymphocytes
- Which leukocytes are classified as granulocytes?
Neutrophils, Eosinophils and Basophils
Which leukocytes are classified as Agranulocytes?
Monocytes and Lymphocytes
- Give the 3 kinds of Lymphocytes.
B cell T cell and NK cells
- Which (Loose or dense) CT contains minimal ground substance, fewer fibroblasts and densely packed collagen fibres?
Dense CT
- Which type of adipose tissue (White or Brown) functions as lipid storage and metabolism
White adipose tissue
- Which type of adipose tissue (White or Brown) is used for thermogenesis.
Brown adipose tissue
- Which type of adipose tissue (White or Brown) is found in newborns and hibernating animals?
brown adipose tissue
- Which type of adipose tissue (White or Brown) is multi-locular and has plenty of mitochondria?
brown
- Which type of adipose tissue (White or Brown) has a centrally located nucleus instead of peripherally located?
Brown
- Where is the (embryonic) origin of all connective tissues?
Mesenchyme
- Which embryonic CT has spindle-shaped cells, large nucleus and prominent nucleolus.
Mesenchymal CT
- Which embryonic CT is the gelatinous substance found within the umbilical cord?
Mucoid CT (a.k.a Wharton’s Jelly)
- Name the 2 types of Connective Tissue Proper: Loose and Dense CT
Name the 2 types of specialised CT
Reticular and Adipose CT
Name the 2 types of Embryonal CT
Mesenchymal CT
Mucoid/ Wharton’s Jelly
Name the 2 layers of the Skin.(ONLY 2 KASI HYPO ISNT PART OF THE SKIN)
Epidermis & Dermis
- Where is embryonic origin of the Epidermis?
Ectoderm
- True or false? The Epidermis is vascular.
False. Avascular
- Where is the embryonic origin of the Dermis?
Mesoderm
- What is the characteristic feature of the Dermis?
Dermal Papillae
- What is subcutaneous tissue also known by?
Hypodermis
- Which layer binds the skin to the underlying muscle?
Hypodermis
- Which layer of the skin has an extensive vascular supply?
Hypodermis
- The classify the type of epithelium of the Epidermis.
Stratified squamous keratinized epithelium.
- What are the 4 layers of the Epidermis?
Stratum Corneum, Stratum Granulosum, Stratum spinosum and Stratum basal.
- What layer can only be found in the epidermis of THICK skin?
Stratum Lucidum. (Found between Cornereum and Granulosum).
- *** INSERT IMAGE OF LAYERS OF EPIDERMIS: Stratum Corneum, Stratum Lucidum, Stratum Granulosum, Stratum spinosum and Stratum basal.
- What are some cells you can find in the Epidermis?
Melanocytes, Langerhans cells & Tactile/Merkel cells
- What is the single layer of cuboidal cells resting on the basement membrane between the Epidermis and dermis?
Stratum basal
- Which layer of the epidermis has actively dividing cells
stratum basal
- What type of junctional complex joins the Cell with the ECM ?
Hemidesmosomes
- What type of junctional complex joins the Cell with another Cell?
Desmosomes or Macula adheres.
Desmosomes form links between cells, and provide a connection between intermediate filaments of the cell cytoskeletons of adjacent cells. This structure gives strength to tissues.
- What are desmosomes also known as?
Macula adherens
- What is the thickest layer of the Epidermis?
Stratum Spinosum
- Which epidermal layer is the site of Keratin synthesis?
Stratum spinosum
- Which epidermal layer has 3-5 layers of flattened cells containing granules, and where nucleus starts to disappear?
Stratum Granulosum
- What is the most superficial layer of the epidermis?
Statrum corneum
- True or False? Thin skin have numerous hair follicles associated with sebaceous glands.
TRUE! Thin skin HAS neumerous wet glands, and hair follicles that are associated with sebaceous glands and the Arrector pili muscle.
REMEMBER: Thick skin DOES NOT have hair follicles, sebaceous glands ONLY and arrector pili muscles.
- Which cell is a neural crest derivative?
Melanocytes
- Which epidermal layer can langerhan cells be found?
Spinosum
- What type of macrophage is specifically found in the skin?
Langerhan cells
- What are the intra-epidermal sensory receptors for LIGHT TOUCH?
Merkel cells
- What are the 2 Layers of the Dermis?
Papillary & Reticular layers
- Which layer of the dermis is seem immediately below the epidermis?
Papillary layer
- Which layer of the dermis can Meissner’s corpuscles be found?
Paillary layer
- True or False? Meissner’s corpuscles are mechanoreptors for Light Touch.
true!
- True or False? The reticular layer of the dermis has loose connective tissue.
False. Dense connective tissue
- True or false? Surgeons make incisions along Langer Lines to produce least scarring and better wound closure.
TRUE
- Which layer of the skin has a rich network of blood and lymphatic vessels?
Dermis
- Which layer of the skin has Nutritive and Thermoregulatory functions?
Dermis
Which of these sensory receptors are encapsulated?
Meissner’s Corpuscles
Pacinian Copruscle
BOTH ARE ENCAPSULATED
- True or False? Meissner’s corpuscle and Merkel cells BOTH sense Light touch.
true
- Which mechanoreceptor cell detects course touch, sustained touch and vibrations?
Pacinian Corpuscle
- Which mechanoreptor is stimulated by stretch, tension or twisting of the skin?
Ruffini Corpuscle.
- Which mechanoreptor can sense low frequency vibration and is primarily found in the skin of the Penis and Clitoris?
Krause End bulb
- What are the 5 layers of the Hair Follicle?
Medulla
Cortex
Cuticle
Epithelial Root sheath
Connective tissue sheath.
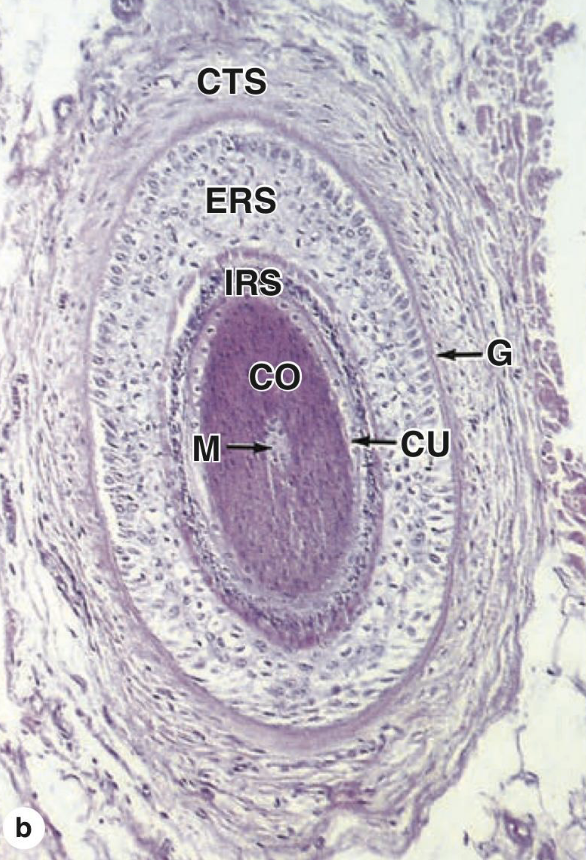
- Which layer of the hair follicle is composed of keratin?
Cuticle
- What makes up the Pilosebaceous unit?
Hair Follicle, Sebaceous gland & Arrector Pili Muscle.
Classify the sebaceous gland based on Morphology.
Simple branched acinar
Classify the eccrine sweat gland based on morphology
Simple Coiled tubular
- Which sweat gland has a smaller lumen? (Eccrine or Apocrine)
Eccrine
- ____ cells are found in the basal lamina to propel sweat into the duct.
Myoepithelial Cells
- Which type of sweat gland is largely confined in the axillary and perineal regions?
Apocrine glands.
True or False?
Apocrine glands only secrete watery secretions without proteins.
False!
Apocrine glands releases fluid containing:
Watery proteins
Lipids
Carbohydrates
Ammonium
other organic compounds
*PROTEIN RICH PRODUCT MIXED WITH SEBUM!
usually odorless but gets odor from bacterial activity.
- What are the 3 histological classifications of cells that engage in secretion?
Merocrine, Holocene & Apocrine
- True or False. Sweat glands are histologically classified as Merocrine.
True
What do you call the cresent-shaped structure found at the proximal ends of the nail body?
Lunula.
- Which part of the nail (also known as the cuticle) is an extension of the Stratum corner of the epidermis?
Eponychium
- True or False? The nail bed only contains the epidermal stratum basal.
False. The nail bed contains the epidermal stratum basal & Stratum spinosum.
- This is the condition where Mast cells present in the skin CT release vasoactive substances from their granules (histamine, cytokines and other neuropeptides) which leads to inflammatory reactions.
Hives.
- This is the condition where there is increased skin elasticity, joint hyper mobility and poor wound healing.
Ehlers-danlos syndrome.
Which of the following statements is TRUE about the blood supply to the skin?
AV shunts in the epidermis regulates blood flow to the skin
The cutaneous plexus is found between the papillary and reticular dermis.
1 is True.
2 is False. Cutaneous plexus is found in-between the Reticular dermis and Subcutaneous tissue.
- Movement of cells within hematopoeitic organisms is made possible by the stroma formed by which type of collagen fiber?
Type 3, they are usually the type found in the Lymph nodes, spleen and Bone marrow.
- Spooning of the nails is seen in which condition?
Iron deficiency anemia