Oligopoly and Pure Monopoly
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This covers terms from Chapters 14 and 15
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Oligopoly
A market structure in which a small number of firms compete
Do oligopolists affect each other?
Yes, they are large enough and know their actions affect one another
Are their barriers to entry?
Yes
Can oligopolists earn long-run proft?
Yes, because of barriers to entry
Most important barrier of entry for oligopolists
Economies of scale
How do we know a market structure is an oligopoly?
The four-firm concentration
The four-firm concentration ratio
The fraction of an industry’s sales accounted for by its four largest firms
A four-firm concentration ratio larger than ____ tends to indicate an oligopoly
40%
What firms are more likely to charge inefficiently high prices?
Firms in industries with the highest four-firm concentration ration
Why do monopolies/oligopolies exist?
Barriers to entry
Examples of barriers to entry
Control of a key input is held by one or a small number of firms
Examples:
Alcoa - bauxite for aluminum production
Ocean spray - cranberries
Government imposed barriers: governments might grant exclusive rights to some industry to one or a small number of firms
Examples:
Occupational licensing (ex: dentists and doctors)
Patents
Tariffs and quotas imposed on foreign companies
Game theory
The study of how people or firms make decisions in situations in which attaining their goals depends on their interactions with others
Duopoly Game
Apple’s dominant strategy is the same as Spotify (9.99)
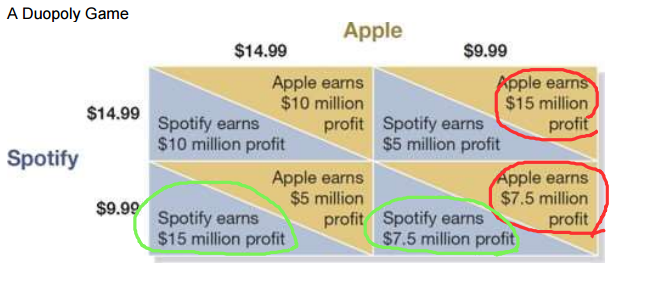
Nash Equilibrium
A situation in which each firm chooses the best strategy, given the strategies chosen the by the other firm
If Apple and Spotify work together to charge 14.99, that is…
Collusion
Collusion
When firms illegally cooperate to artificially raise prices to bring in more profits
Prisoner’s dilemma
A game in which pursuing dominant strategies results in noncooperating that leaves everyone worse off
5 Competitive Forces that Determine Overall Competition
Competition from existing firms
Threat from new entrants
Competition from substitute goods and services
Bargaining power of buyers
Bargaining power of suppliers
Most efficient market structure
Perfection competition
Least efficient market structure
Pure monopoly
Characteristics of the Monopoly Structure
One seller
No close substitutes for the good
Barriers to entry
Many buyers
Firms are price searchers (price makers)
Earning a positive economic profit
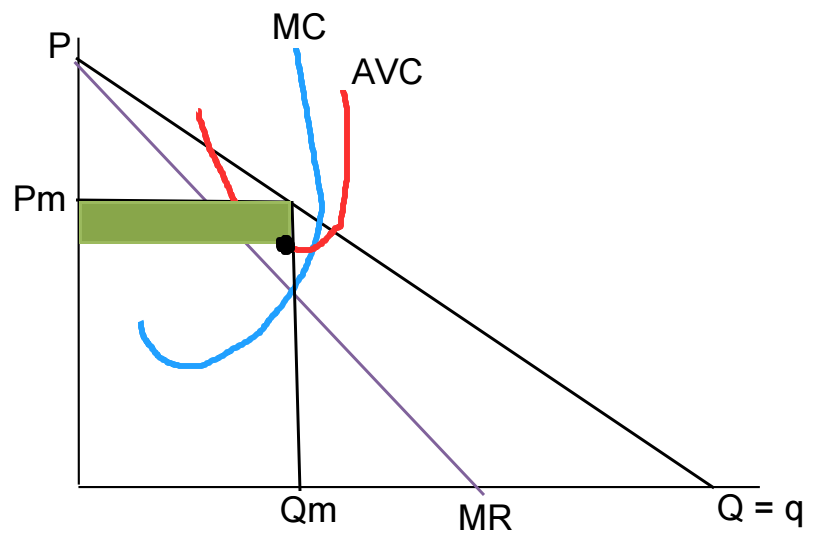
Is there a supply curve in monopolistic structure
No, only supply points
Why doesn’t the monopolist charge a higher price
Monopolists maximize profit, not price
Earning a negative economic profit
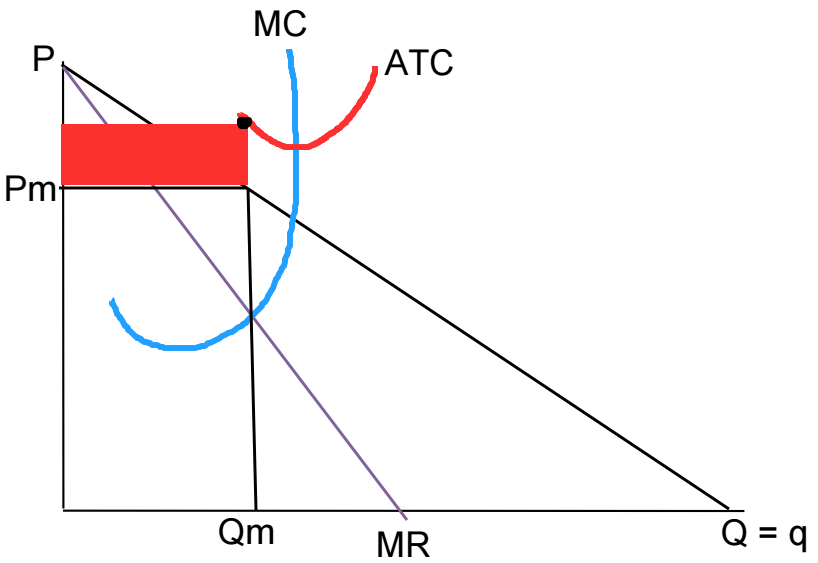
Are monopolies subject to the shutdown rule?
Yes
Monopolists can’t charge highest price possible because…
Profit must be maximized and demand must be acknowledged
Breaking even
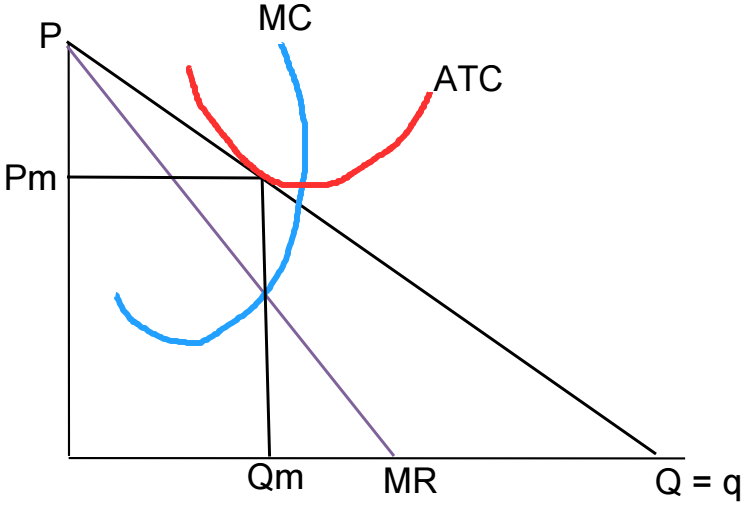
Can monopolists earn profit in the long-run?
Yes
Advantages of monopolistic structures
Provides incentive for innovation
Take advantage of economies of scale and scope
Take advantage of being a natural monopolist with lower average costs
Take advantage of producing a variety of products using the same inputs
Disadvantages of monopolistic structures
Limits options to consumers
Rent-seeking (profit-seeking) behavior
Spending money to obtain monopoly
Productive inefficiency (P > min ATC)
Deadweight loss or welfare loss (allocative inefficiency)