A.1.3.1 (1) The Cardiovascular System
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What is its function?
transport blood, oxygen and nutrients to the body
What are the three main parts?
heart
blood vessels
blood
What is blood and its components?
special fluid containing RBC’s, WBC’s, platelets and plasma
What is heamoglobin?
pigment that binds oxygen for transport in the blood
Red blood cells are…
erythrocytes, carry oxygen nutrients and wastes
White blood cells are…
leucocytes, fight diseases and protect the body from infections
Platelets are…
thrombocytes, gather at the site of injury helping with clotting
Plasma is…
mixture of water and dissolved substances
What are blood vessles?
tubes/channels that carry blood throughout the body
What are the three types of blood vesssles?
veins
arteries
capillaries
What do arteries do?
carry blood away from the heart
What are arteries structure and why?
thickest wall, withstand high pressure
What do veins do?
carry blood towards the heart
What are veins’ structure?
less muscular and stretchy, blood moves at low pressure
What do capillaries do?
form an extensive branching network through tissues
What are capillaries’ structure?
thinnest wall, act as a site of exchange between blood and tissues
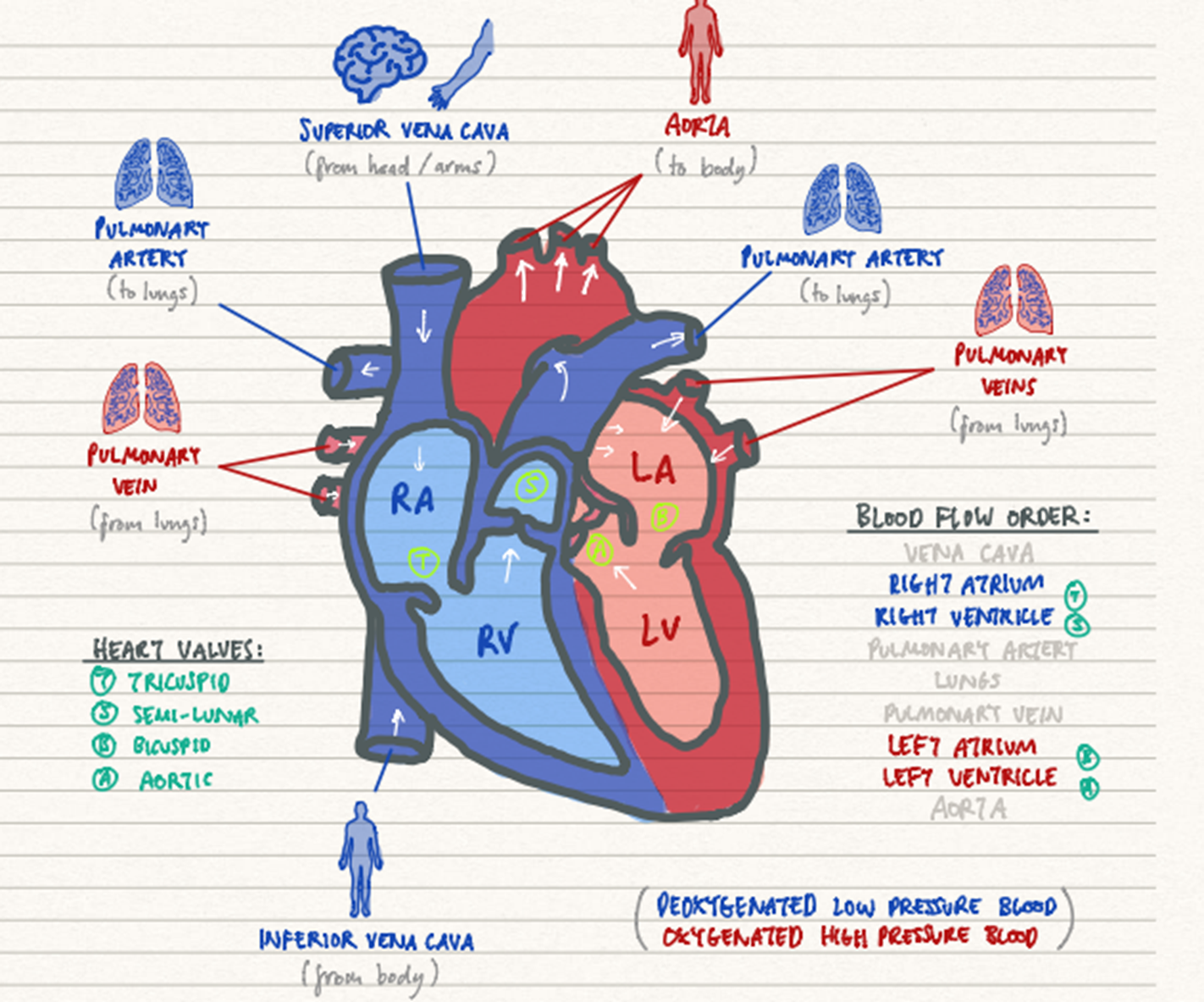
What are the 4 main chmabers of the heart?
right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium and left ventricle
What do the atria do?
receive blood
What do the ventricles do?
eject blood from the heart
What are the two main circuits of blood flow in the heart?
Pulmonary circuit (deoxygenated to oxygenated)
Systemic circuit (oxygenated to the body)
The pulmonary circuit..
involves deoxygenated blood to the lungs
Step 1 - pulmonary circuit
the RA takes in deoxygenated blood from the superior/inferior vena cava
Step 2 - pulmonary circuit
blood moves to the RV and is taken to the lungs through the pulmonary artery
The systemic circuit…
transports oxygenated blood to the body
Step 1 - systemic circuit
oxygenated blood from the lungs enters the LA through the pulmonary veins
Step 2 - systemic circuit
blood is pumped into the LV and is sent to the body through aorta
The cardiac cycle
What two phases is blood pressure split into?
Diastolic
Systolic
What is diastolic blood pressure?
force exerted by blood on arterial walls during ventricular relaxation
What is systolic blood pressure?
force exerted by blood on arterial walls during ventricular contraction
What is the healthy adults typical systolic and diastolic BP range?
90-120mmHg (S), 60-80mmHg (D)
How would this BP be described?
“120/80 mmHg”
What are the two types of exercise BP can respond to?
Dynamic
Static
What is dynamic exercise?
repetitive movement promoting blood flow keeping dBP from rising
What happens to systolic and diastolic BP during dynamic exercise?
systolic BP increase (up to 200)
diastolic BP remains constant
What happens to systolic and diastolic BP during static exercise?
systolic increases
diastolic also increases
What main two things happen to blood flow during exercise?
more O2 and nutrients required
more heat and waste need to be removed