Neuroscience Lecture 3: Anatomy and Physiology of Neurons
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Neurons
primary cell type in nervous system
processes information
86 billion cells in the human brain that transmit information.
filaments extending out from the cell body
convey signals from point A to point B
Anatomy of a neuron
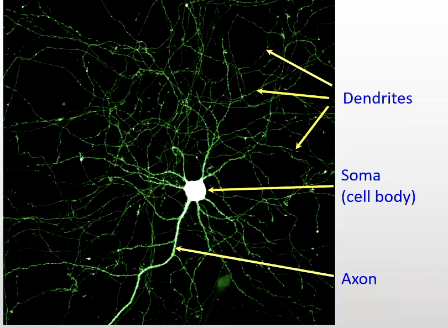
centre is soma (with nucleus etc)
filaments — fibres extending out — Axon is the thickest filament
complex web of fibres around neuron
Anatomy of a neuron
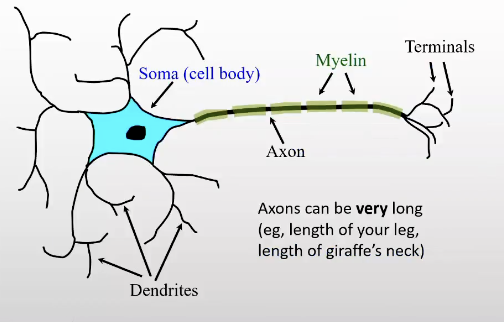
dendrites - thin filaments
axon extending out
length of the axon varies between neurons — can be very long, varies a lot in length
end of axon is terminal — forms connections to other neurons
What do neurons do?
neurons pick up signals at the end where dendrites are and they transmit those signals down the axon to the end of the axon where those signals are sent to other neurons
conveys signals from point A to point B
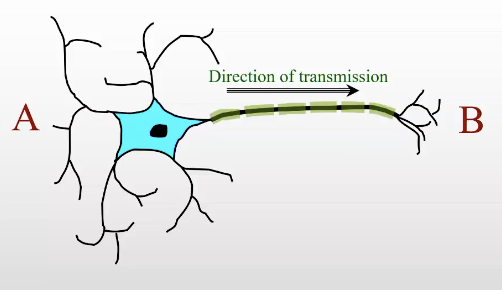
What signals do neurons convey?
binary signals
signalling whether it is on or off
Cellular makeup of a neuron
neurons covered in lipid membrane
doesn’t really let water pass through
semipermeable (control ion concentration) - can control the flux of ions across the membrane
neuron can control the charge of ions inside it
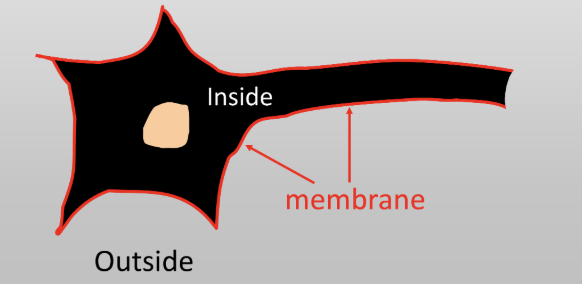
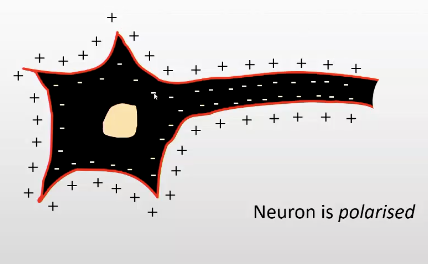
Electrical charge of neurons
in resting state — inside is negatively charged (vs outside which is positively charged)
sodium potassium pump in the membrane — swaps out 3 sodium ions for every 2 potassium ions it lets in
net result build up of positively charged sodium ions outside the membrane
electrical difference between inside and outside of neuron — form of stored energy which neuron uses in its signalling mechanism
neuron is polarised
Action potential (or not)
Moments when neuron acc sending signal - neuron becomes depolarised
Channels within the membrane that are normally closed – open up for brief moments and let the sodium ions sitting outside flow through – flood into neuron
Becomes positively charged
Triggers large scale change that drives neuron into flipped polarity
Flips electrical difference
If enough positive electrical charge introduced inside the neuron – starts opening up sodium channels everywhere else in surrounding membrane
Sudden cascade of response called action potential – flips from being negatively charged to positively charged
Only lasts a few milliseconds – repeats it over and over
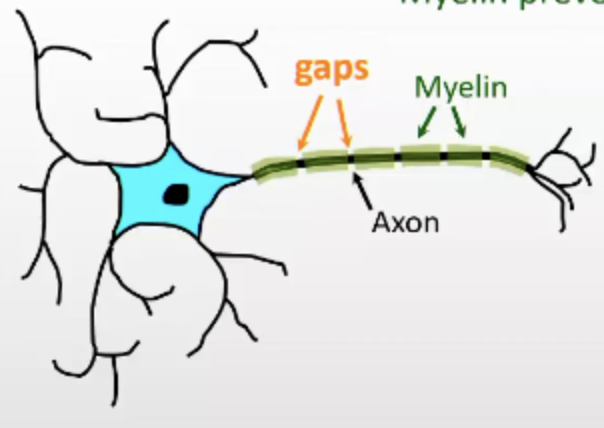
Myelin
Insulating material which covers ion channels underneath it
When they open up sodium ions can't come in
Stops action potential happening where covered by myelin
Small gaps between them – action potential is able to jump from one gap to another
Long axons use myelin to speed up the transmission of action potential
Prevents depolarisation
Knowledge of neuronal function?
Neurons are digital – convey only one bit of info
Sophistication of brain function due to
High speed of info transmission
Enormous number of neurons
Complexity of connections between neurons (circuitry)
certain drugs (anesthetics and alcohol) work by interfering with action potential
How do neurons interact?
form small junctions called synapses (space between neurons)
they communicate across synapses
10-20 nanometers
chemical synapses
vast majority of neurons communicate via chemical transmission across the synapse
Neurotransmission
end of axon is swollen - contains vesicles full of neurotransmitter chemical
calcium ions also entered during action potential which triggers NT vesicles — causes them to move from inside to fuse onto the wall of the membrane and spill the NT content out into synapse
once it is in synapse - immediately finds a receptor site in the membrane of the other neuron
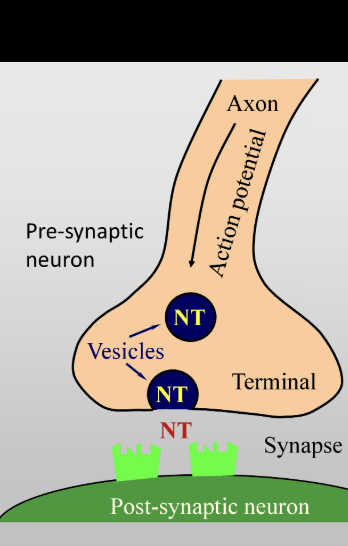
NT and Receptor
right receptor on the synapse for it to work - highly specific (lock and key process)
receptor is big protein molecule that has ion channel within it — normally closed
when NT binds w receptor — electrochemical force of the interaction changes the structure of protein slightly
opens the ion channel
most common transmitter — glutamate e.g when it bind w glutamate receptor which has sodium channel within it and lets sodium ions it — depolarises the membrane — can trigger action potential in this neuron
Excitatory transmission
when one neuron has excited another to have action potential
Inhibitory transmission
Gaba has opposite effect — inhibits the neuron
gaba receptor has chloride ion channel (-vely charged) - so when let in you hyperpolarise the membrane
makes it more negative than before and stops it from having action potential
Re-uptake
when released NT into synapse — only want it to be there for short amount of time
enzymes located in the tissue which target and destroy NT when come in contact w it
pre-synaptic terminal has pumps in membrane that sucks up the NT as soon as released
makes sure process it brief and synapse is ready for new signal to be sent
Neuropharmacology
psychoactive drugs affect functioning of neurons
many mimic or block NTs
can influence the release, re-uptake, enzymatic destruction or receptor binding of NTs
work as agonists (increase effect of NT) or antagonists (decrease effect of NT)
Psychoactive drugs — recreational
opiates (heroin, morphine, codeine) mimic brain’s opioid NTs
cocaine, amphetamines and ecstasy promote transmission of dopamine, noradrenaline and serotonin
nicotine - stimulates acetylcholine receptors
caffeine - blocks adenosine receptors
Psychoactive drugs — therapeutic drugs
benzodiazepines (e.g. valium) — enhances inhibitory effects of GABA (same as barbiturates and alcohol)
most anti-schizophrenic drugs block dopamine
antidepressant drugs enhance serotonin and noradrenaline transmission by blocking re-uptake