Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
MRI
Uses a powerful magnetic field and radio waves to proved an image - does not use radiation making it a lot safer
The two types of MRI scanners used in veterinary practice
Superconducting magnets
Permanent magnet
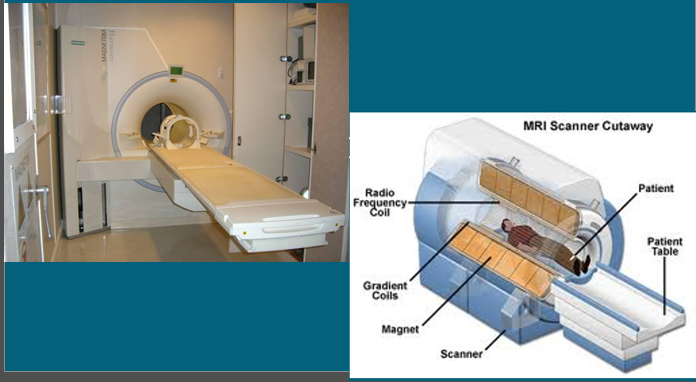
Superconducting magnets
Usually tube shaped, and the animal being scanned is moved into the centre of the scanner on a moveable table top
Usually used by companies providing mobile MRI services, some referral practices and universities
Unlikely to see this type of scanner in general practice due to the level of power source that’s needed
Permanent Magnet
Tend to be C-shaped and open at the sides
Whilst they do not provide such a string magnetic field and scan may take longer to acquire, they have the advantage of being less expensive to purchase and maintain, and are often the scanner of choice for centres where the electricity supply is inadequate for running a superconducting magnet
Not as powerful, take longer, lower power source
Magnetic Field Strength
The type of MRI scanners available also vary depending on their magnetic field strength (measured in Tesla), low-field and high-field
Low field (usually 0.2-0.5T)
High field (1.5T and above)
The majority of MRI scanners in veterinary use are between 0.4T and 1.5T (Perspective - 1T magnet on a crane is strong enough to pick up a car)
The image provided is cross-sectional
It gives good soft-tissue detail as the tissues contain differing amounts of water and therefore hydrogen nuclei
Bone is less easily imaged - because bone has got an incredibly high specific gravity
MRI safety
Due to the strength of the magnetic field great care must be taken with equipment, staff and personnel when working with MRI scanners
Equipment should be made of NON-FERROUS materials. This includes GA equipment and trolleys, and can be very expensive
Pre MRI checks - Health and Safety!
Does the patient have a microchip? Some microchips can distort the MRI image
Is there any chance the patient could have eaten any foreign body containing metal? - an x-ray could be advised to check before having an MRI
Does the patient have any implants? If so where are they and what are they made of?
Even if the patient has implants which aren’t made of ferrous metal, they can heat up in an MRI scanner which can cause pain, discomfort and can damage the implants
Check personnel!
Do you or anyone who will be working with the MRI scanner have:
Any metal objects on their person?
Any implants?
A pacemaker?
Fringe Field
If the MRI scanner can affect implants within the body, it follows that other objects taken into the room could also be affected
The magnetic field is strongest within the scanner itself, but the field reaches out into the area surrounding the scanner. This is called the fringe field from weak to string very rapidly as you approach the scanner
Fringe field goes from weak to string very rapidly as you approach the scanner
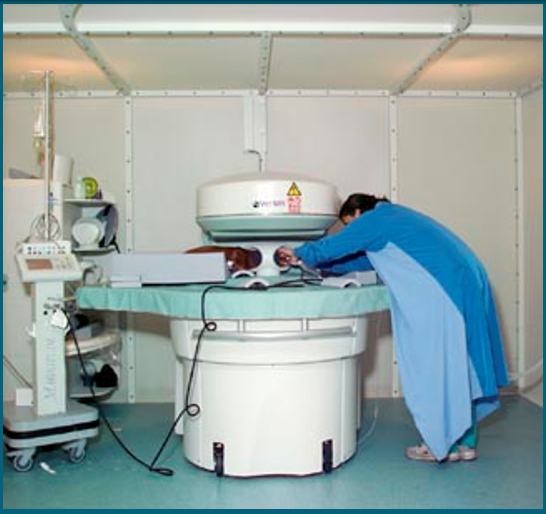
Patient preparation
All patient have to be anaesthetised as the image takes several minutes or up to an hour to acquit, therefore any movement can blur the image and render it non-diagnostic (can take from half and hour up to an hour)
All collars and metal tags should be removed, and patient with metal implants are not suitable for MRI
The magnets can even heat up non-ferrous metal causing potential problems (e.g. pain, discomfort, damage to implants, burns)
Indications for use
Head trauma
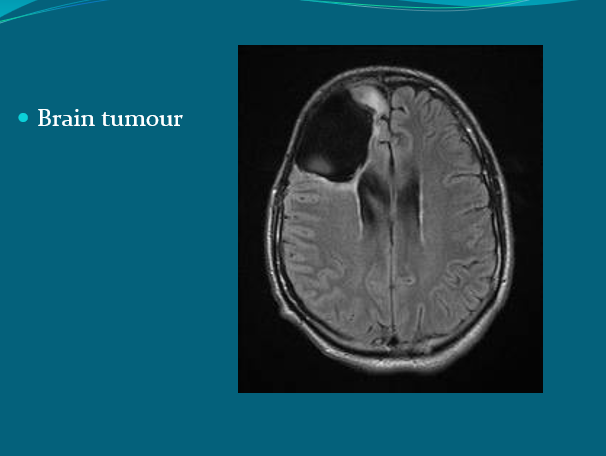
Epilepsy (diagnosing brain tumours)
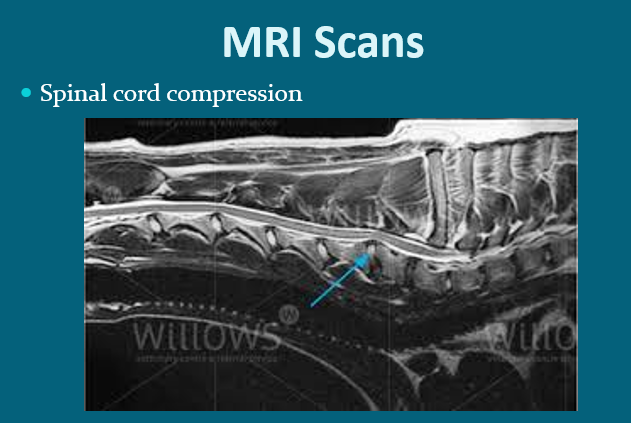
Spinal disease
Middle/Inner ear disease
Lameness/orthopaedic conditions (ruptured cruciate)
MRI is generally considered ‘gold standards’ for imaging of the brain and spinal cord
Advantages
Does not use ionising radiation, so is considered safer than x-rays
Helps to show the full extent of a disease and plan surgery on the animal
Can be used on pregnant patients (no effect on foetus reported)
Good detail shown on scans, i.e. investigation of the nervous system. Also shows muscle and joint composition ad thoraces abnormalities (i.e. tumour) and vascular abnormalities
Disadvantages
Not ideal for investigating bone structure containing calcium
It is a noisy and long process
People or patient with metal implants should not enter the room or undergo MRI scanning
It is expensive
Recording Information
Images are produced in digital format; this can be emailed, burnt to CD or copied to an x-ray film and stored accordingly
Note that when compared to x-rays and CT, calcified material is black on an MRI scan
Use of contrast media
Contrast media can be used to highlight parts of the body to assist in achieving a diagnosis
With MRI scanning, the most commonly used contrast media is Gadolinium