Exam 2 - psy1400
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/80
Earn XP
Description and Tags
USU gregory madden; analysis behavior.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
1
New cards
What’s the definition of antecedent?
an observable stimulus that is present **before** the behavior occurs
2
New cards
what’s the definition of a consequence?
observable stimulus change that happens **after** behavior occurs
3
New cards
a **consequence** occurs _______ a behavior
after
4
New cards
An **antecedent** occurs ________ a behavior
before
5
New cards
What is the response-consequence contingency?
describes the causal (IF → THEN) relation between operant behavior and its consequence
6
New cards
What is a contingent reinforcement?
delivered following the occurrence of the target response
7
New cards
What is a noncontingent reinforcement?
* delivered independently from response
* usually via time based schedule
* usually via time based schedule
8
New cards
if reinforcement is given contingently, response rates will…
go up, increase
9
New cards
if reinforcement is changed and now its delivered non-contingently, response rates will…
not increase, stay the same
10
New cards
What is superstitious behavior?
occurs when the individual behaves as though a response–consequence contingency exists when the relation between response and consequence is **noncontingent**
11
New cards
Define reinforcement…
**process or procedure** whereby a reinforcer **increases** operant behavior above its baseline level
12
New cards
define reinforcer…
a **consequence** that **increases** operant behavior above its baseline level
13
New cards
define reward…
beneficial consequences that we think will function as reinforcers, but we don’t know yet if they will
14
New cards
Who discovered Reinforcement?
Edward L. Thorndike
15
New cards
Define operant behavior
a generic class of responses influenced by antecedents, with each response in the class producing the same consequence
16
New cards
What’s an everyday example of reinforcement?
clapping
cheering
giving a high five, thumbs up
gaming
cheering
giving a high five, thumbs up
gaming
17
New cards
What’s an everyday **non**-example of reinforcement?
training a dog, them losing focus
18
New cards
Recognize the Reinforcement flowchart
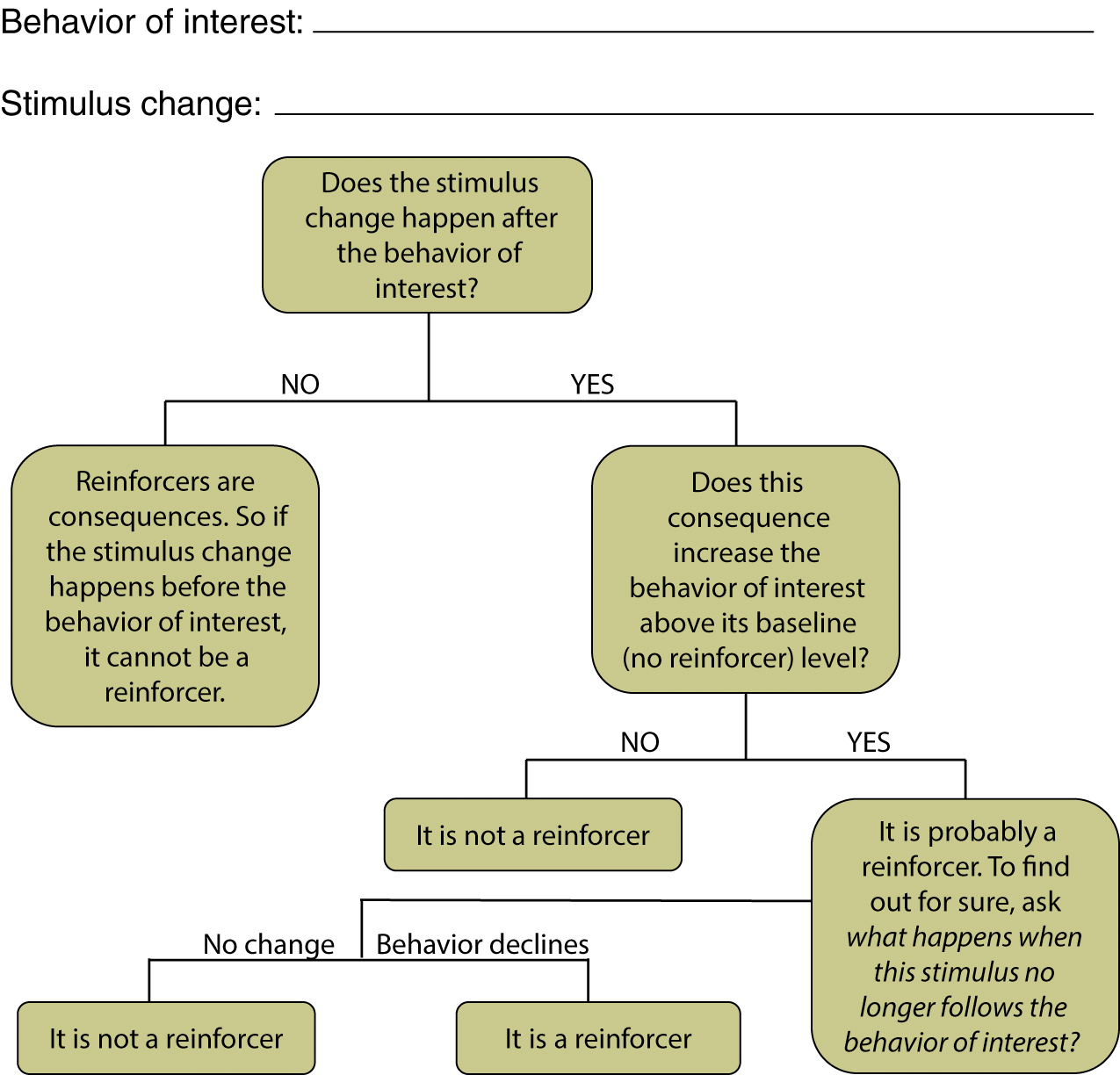
19
New cards
What role does exploration play in operant behavior?
* response variability when exposed to something new (trial and error)
* moves to exploitation when you find an efficient way to do something and don't ever change
* can lead to finding reinforcers and consistently doing behavior
* moves to exploitation when you find an efficient way to do something and don't ever change
* can lead to finding reinforcers and consistently doing behavior
20
New cards
Define positive reinforcement
The presentation of a consequence, the effect of which is to increase operant behavior above its no-reinforcer baseline level
21
New cards
Which goes along with positive reinforcement -
SR+, SRE-, or SRA-?
SR+, SRE-, or SRA-?
SR+
22
New cards
Which goes along with negative reinforcement - (two answers)
SR+, SRE-, or SRA-?
SR+, SRE-, or SRA-?
SRE- & SRA-
23
New cards
Define negative reinforcement SRE- (escape variety)
consequent **removal** **or reduction** of a stimulus, the effect of which is to increase operant behavior above its no-reinforcer baseline level
24
New cards
Define negative reinforcement SRA- (avoidance variety)
consequent **prevention** of a stimulus change, the effect of which is to increase operant behavior above its no-reinforcer baseline level
25
New cards
Why’s it important to distinguish between positive and negative reinforcers?
heuristics
loss aversion
preference for positive reinforcement
loss aversion
preference for positive reinforcement
26
New cards
Know options when it’s time to positively influence behavior (consequences)
consequences can be:
* presented
* removed/reduced
* prevented
* presented
* removed/reduced
* prevented
27
New cards
Define loss aversion
* The tendency for loss prevention (SRA−) to influence behavior more than presentation of the same stimulus (SR+)
* People are less likely to do behavior if it means they’ll lose something, even if they could gain something
* People are less likely to do behavior if it means they’ll lose something, even if they could gain something
28
New cards
Why do people prefer positive reinforcement?
people are happier with interventions in which they can earn something (SR+) rather than avoiding something
29
New cards
What are 3 objections to using reinforcement?
1. Intrinsic Motivation
2. Performance-Inhibiting Properties of Reinforcement
3. Cheating
30
New cards
Define intrinsic motivation
the natural drive to engage in a behavior because it fosters a sense of competence
31
New cards
define extrinsic reinforcer
* those reinforcers that are not automatically obtained by engaging in the behavior
* instead, they are artificially arranged
* instead, they are artificially arranged
32
New cards
Do extrinsic reinforcers decrease intrinsic motivation?
No, they do not decrease
33
New cards
What goes along with performance-inhibiting properties of reinforcement?
Two answers
Two answers
* “choking under pressure”
* reinforcers reduce creativity
* reinforcers reduce creativity
34
New cards
Does reinforcement inhibit creativity and cause people to choke under pressure?
* if reward is at stake, creativity can be limited to meet others’ expectations
* with too high of reward, people can choke under pressure - they fail to meet what they could normally
* with too high of reward, people can choke under pressure - they fail to meet what they could normally
35
New cards
Does reinforcement increase probability of cheating?
if it can produce positive reinforcer easier, some will succumb
36
New cards
What are the 2 theories of reinforcement?
* Response Strengthening Theory
* Information Theory
* Information Theory
37
New cards
What does response strengthening theory say?
* frequency of behavior is followed by reinforcer
* more firmly its established, the harder it’ll be to disrupt
* more firmly its established, the harder it’ll be to disrupt
38
New cards
what does the information theory say?
* agrees that reinforcers increase operant behavior above a baseline level, but it disagrees about how this happens
* allows us to predict when/where subsequent reinforcers may be obtained
* allows us to predict when/where subsequent reinforcers may be obtained
39
New cards
define operant extinction
Responding that meets the reinforcement contingency no longer produces the reinforcer and, as a result, it falls to baseline levels
40
New cards
How does operate extinction apply to positive reinforcement?
when positive reinforcement is removed, behavior returns to baseline level
41
New cards
How does operant extinction apply to negative reinforcement?
* when negative reinforcement is removed, behavior returns to baseline level (SRE- & SRA-)
* (if pushing a button doesnt stop noise, eventually well stop pushing it)
* (if pushing a button doesnt stop noise, eventually well stop pushing it)
42
New cards
define escape extinction
* Responding that meets the negative reinforcement contingency, no longer removes or reduces the aversive event
* As a result, responding decreases to baseline levels
* As a result, responding decreases to baseline levels
43
New cards
What’s the partial reinforcement extinction effect (PREE)?
What does it allow us to predict?
What does it allow us to predict?
* direct relation between prior reinforcement rate and how quickly behavior undergoes extinction
* (ex: when highly reinforced before extinction (reinforced every time), then extinction will be faster)
* (ex: when highly reinforced before extinction (reinforced every time), then extinction will be faster)
44
New cards
What effect does motivation have on operant extinction?
* if motivation is higher, the reinforcer will be needed less
* if highly motivated, will continue the behavior even when it doesn't work (e.g., keep trying to start the car)
* if highly motivated, will continue the behavior even when it doesn't work (e.g., keep trying to start the car)
45
New cards
What’s spontaneous recovery of operant extinction?
temporary resumption in responding following time away from the extinction session
46
New cards
What are the primary effects of operant extinction?
returning to baseline levels
47
New cards
What are the secondary (other) effects of operant extinction?
1. extinction-induced emotional behavior
2. extinction burst
3. extinction-induced variability
4. extinction-induced resurgence
48
New cards
define extinction-induced emotional behavior
shift in emotions following extinction (usually negative)
49
New cards
define extinction burst
temporary increase in the rate, magnitude, or duration of the previously reinforced response
50
New cards
define extinction-induced variability
increase in the variety of operant response topographies following extinction
51
New cards
define extinction-induced resurgence
* when one operant behavior is extinguished, other (different) behaviors that were previously reinforced are emitted again
* Ex: bully figures out your regular route home, you avoid that route, then a while later you resume that route
* Ex: bully figures out your regular route home, you avoid that route, then a while later you resume that route
52
New cards
Define functional analysis of behavior
the scientific method used to:
1. determine if a problem behavior is an operant
2. identify the reinforcer that maintains that operant (alternating treatments)
3. develop an intervention (can we eliminate the reinforcement?)
1. determine if a problem behavior is an operant
2. identify the reinforcer that maintains that operant (alternating treatments)
3. develop an intervention (can we eliminate the reinforcement?)
53
New cards
Why do we use functional analysis?
to determine whether or not the consequence functions as a reinforcer (operant, automatic) *or* that the behavior isn't operant
54
New cards
define automatic reinforcer
consequence that is directly produced by the response - it is not provided by someone else - and which increases the behavior above a baseline level
55
New cards
define differential reinforcement
procedure in which a previously reinforced behavior is placed on extinction while a second behavior is reinforced
56
New cards
define differential reinforcement of alternative behavior (DHA)
* "something else" that’s being reinforced is incompatible with the problem behavior
* can't be done at the same time
* can't be done at the same time
57
New cards
Define differential reinforcement of incompatible behavior (DRI)
reinforced response can be any adaptive behavior (doesn't have to be incompatible)
58
New cards
define differential reinforcement of other behavior (DRO)
* reinforcement is provided contingent upon abstaining from the problem behavior for a specified interval of time
* can be gradually modified to require longer intervals
* can be gradually modified to require longer intervals
59
New cards
Define differential reinforcement of variability
responses (or patterns) that haven't been emitted, ever or in a long time, that are reinforced and recent response topographies are extinguished
60
New cards
define differential reinforcement of high-rate behavior (DRH)
* low-rate responding is put on extinction and high-rate responding is reinforced
* ex: 5-second rule game - learn to respond faster and not slower
* ex: 5-second rule game - learn to respond faster and not slower
61
New cards
define differential reinforcement of low-rate behavior (DRL)
* high-rate responding is put on extinction and low-rate responding is reinforced
* ex: thanking someone for talking slower so you can understand them
* ex: thanking someone for talking slower so you can understand them
62
New cards
define functional communication training
problematic demands for attention (ex: tantruming) are extinguished while appropriate requests (ex: "will you play with me please") are established and reinforced
63
New cards
define primary reinforcer
* consequence that functions as a reinforcer because it is important in sustaining the life of the individual or the continuation of the species
* (ex: food, water, escape, etc)
* (ex: food, water, escape, etc)
64
New cards
define conditioned reinforcer
consequences that function as reinforcers only after learning occurs
65
New cards
2 ways an individual can learn the relation between: conditioned reinforcer and backup reinforcer
1. Pavlovian learning; learning via association, if action then consequence
2. through verbal learning; information provided indicating that the reinforcer signals a delay reduction to another reinforcer
66
New cards
define token economy
set of rules governing the delivery of response-contingent conditioned reinforcers (tokens, points, etc.) that may be later exchanged for one or more backup reinforcers
67
New cards
define backup reinforcer
the reinforcer provided after the conditioned reinforcer signals the delay reduction to its delivery
68
New cards
attractive features of token economies:
* motivationally robust
* nondisruptive
* fair compensation
* portability
* delay-bridging
* nondisruptive
* fair compensation
* portability
* delay-bridging
69
New cards
What is the good behavior game?
type of behavior management used to increase physical activity and improve academic performance (specifically in schools)
70
New cards
What is the first principle of conditioned reinforcement?
* use of an effective backup reinforcer
* ex: token for ice cream vs token for concert admission
* ex: token for ice cream vs token for concert admission
71
New cards
What’s the second principle of conditioned reinforcement?
* use of a salient conditioned reinforcer
* ex: something that stands out or is unique; clickers in dog training, having a child put the token in their own piggy bank instead of the parent doing it
* ex: something that stands out or is unique; clickers in dog training, having a child put the token in their own piggy bank instead of the parent doing it
72
New cards
What’s the third principle of conditioned reinforcement
* use of a conditioned reinforcer that signals a large delay reduction to the backup reinforcer
* the bigger the delay reduction to the BR, the more effective the CR will be
* the bigger the delay reduction to the BR, the more effective the CR will be
73
New cards
What’s the fourth principle of conditioned reinforcement?
* make sure the conditioned reinforcer is not redundant
* want the conditioned reinforcer to be the only stimulus signaling a delay reduction to the backup reinforcer
* want the conditioned reinforcer to be the only stimulus signaling a delay reduction to the backup reinforcer
74
New cards
use delay-reduction ratio to evaluate efficacy of conditioned reinforcer
* US --> US interval/
* CS --> US interval
* if bigger, it’s more effective
* CS --> US interval
* if bigger, it’s more effective
75
New cards
define generalized conditioned reinforcer
* when a conditioned reinforcer is paired with a wide variety of other reinforcers
* when a conditioned reinforcer signals a delay reduction to more than one backup reinforcer
* when a conditioned reinforcer signals a delay reduction to more than one backup reinforcer
76
New cards
define marking
conditioned reinforcer immediately follows the response, and this helps the individual learn which response produced the backup reinforcer
77
New cards
what’s marker clicker-training?
use clicker to make brief sound indicating which behavior was good and then treat after
78
New cards
define shaping
differential reinforcement of successive approximations to a terminal behavior
79
New cards
what are the principles of effective shaping?
(6 principles)
(6 principles)
1. objectively define the terminal behavior
2. evaluate what the novice can currently do and how that falls short
3. advice for setting the reinforcement contingencies (should be challenging but not too much)
4. differential reinforcement (reinforcing one response and extinguishing another)
5. ensure the learner has mastered the current phase approximation before moving to the next one
6. lower the criterion for reinforcement if current sequence is too difficult
80
New cards
define percentile schedule of reinforcement
a simple automated training technique incorporating the six principles of effective shaping
81
New cards
define flow
a state in which one feels immersed in a rewarding activity and in which we lose track of time and self