07.3A U7P1 (PART A) Organization of the Nervous System
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Nervous System (Functions)
Fast-acting control that uses electrical impulses to respond to stimuli and maintain homeostasis; responsible for every sensation, thought, action and emotion.
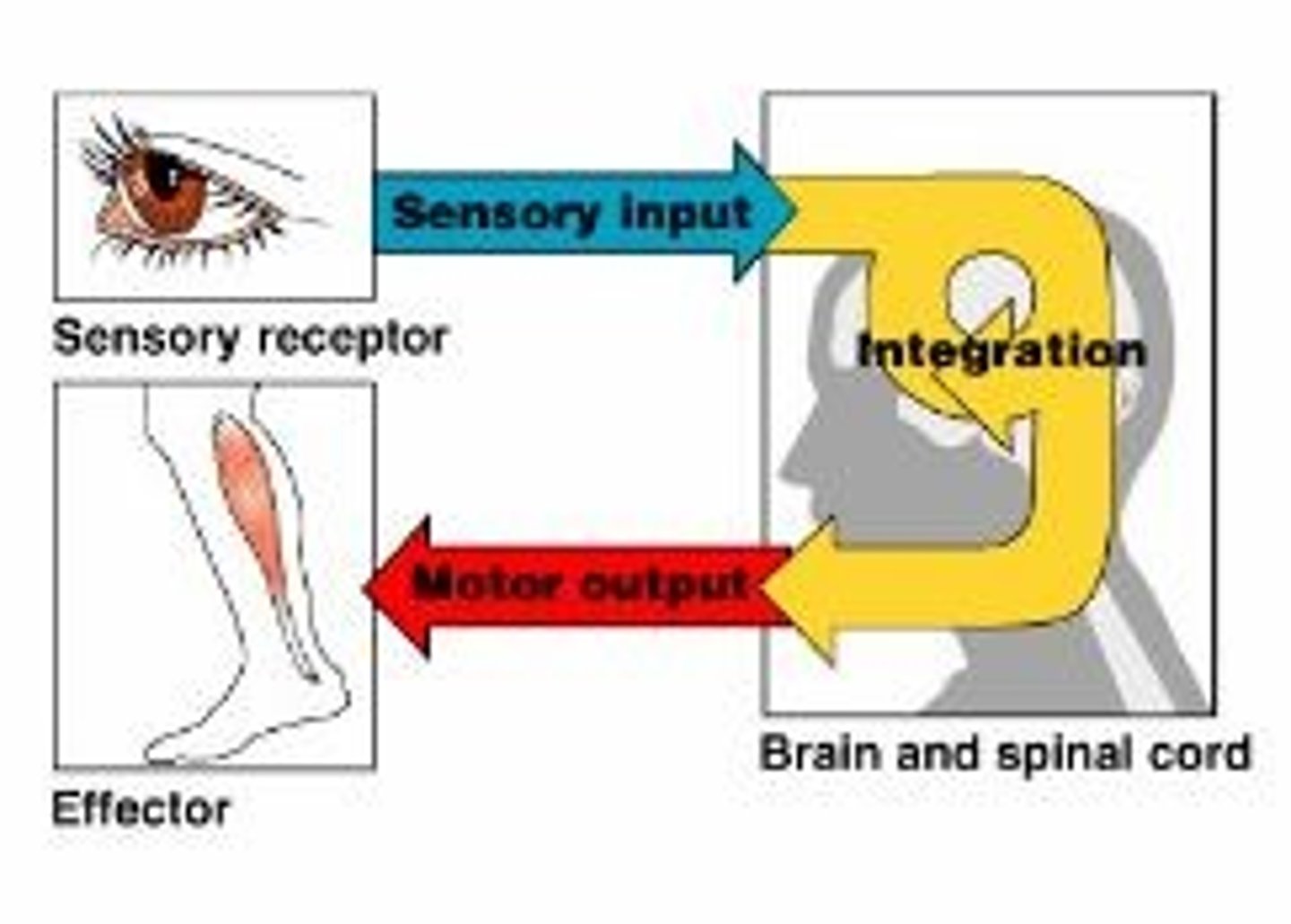
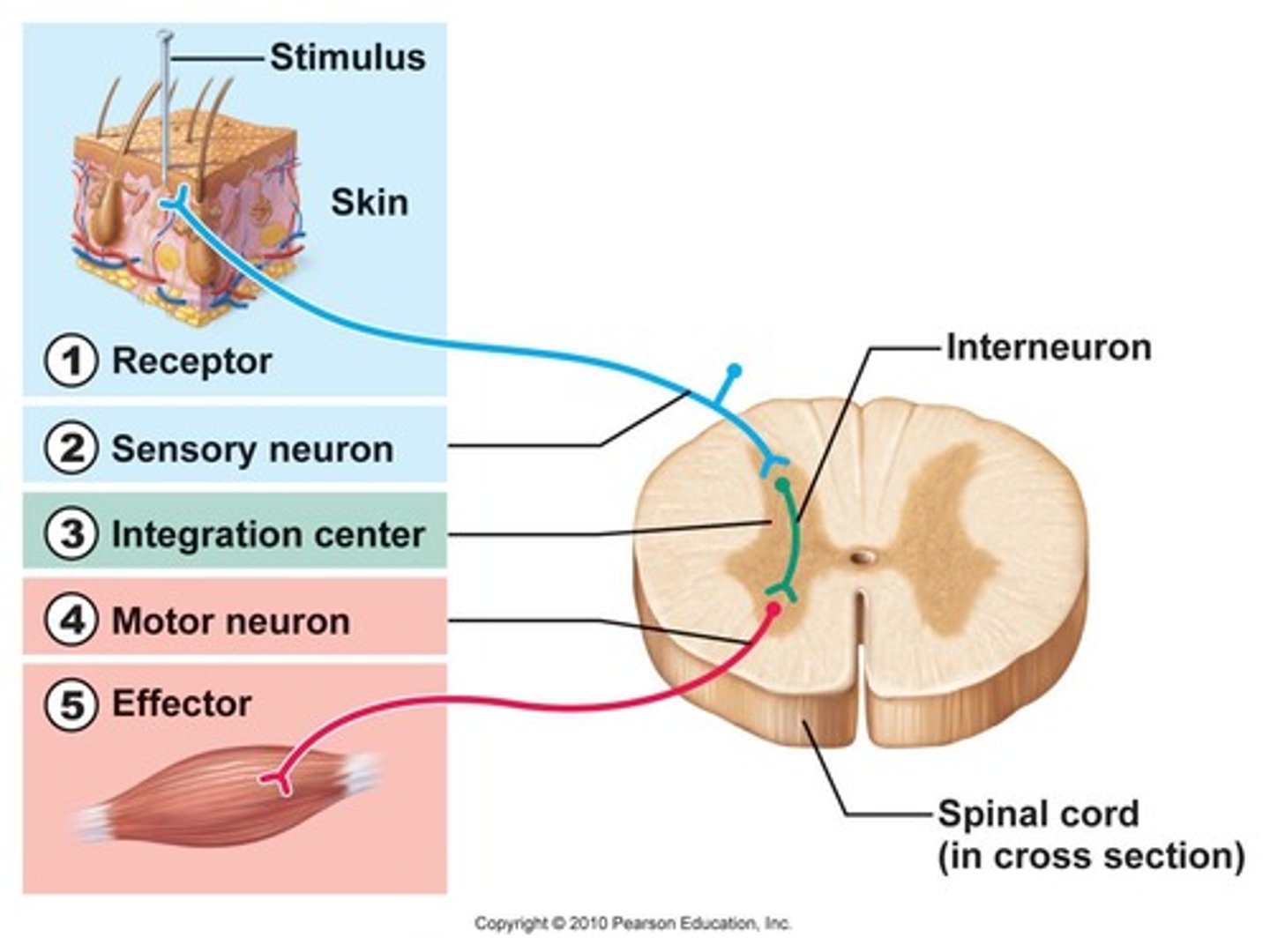
Sensory Receptor (Description)
Nerve ending that responds to a stimulus in the internal or external environment of an organism
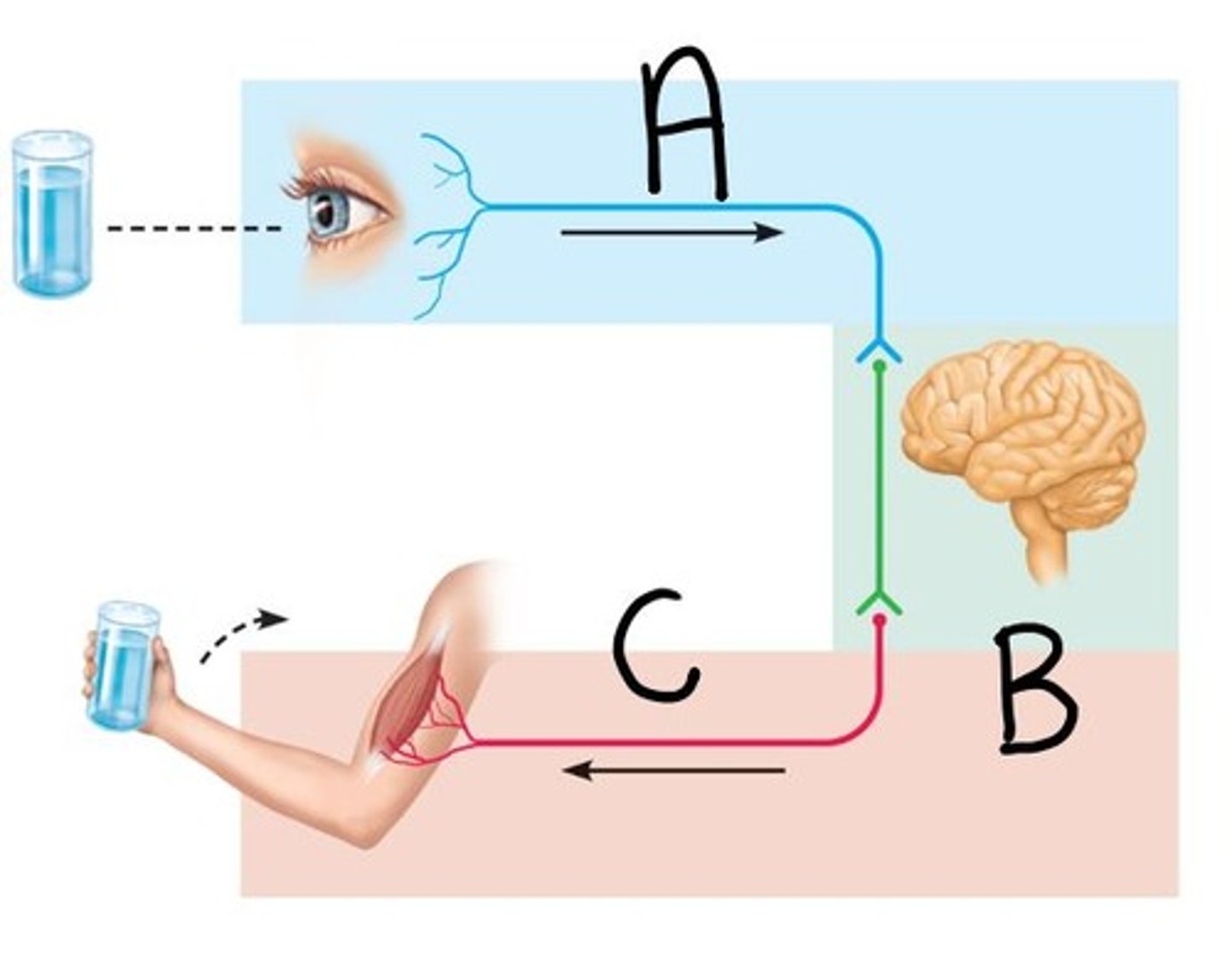
Input (Letter A)
Sensory information gathered both inside and outside the body (Letter A)
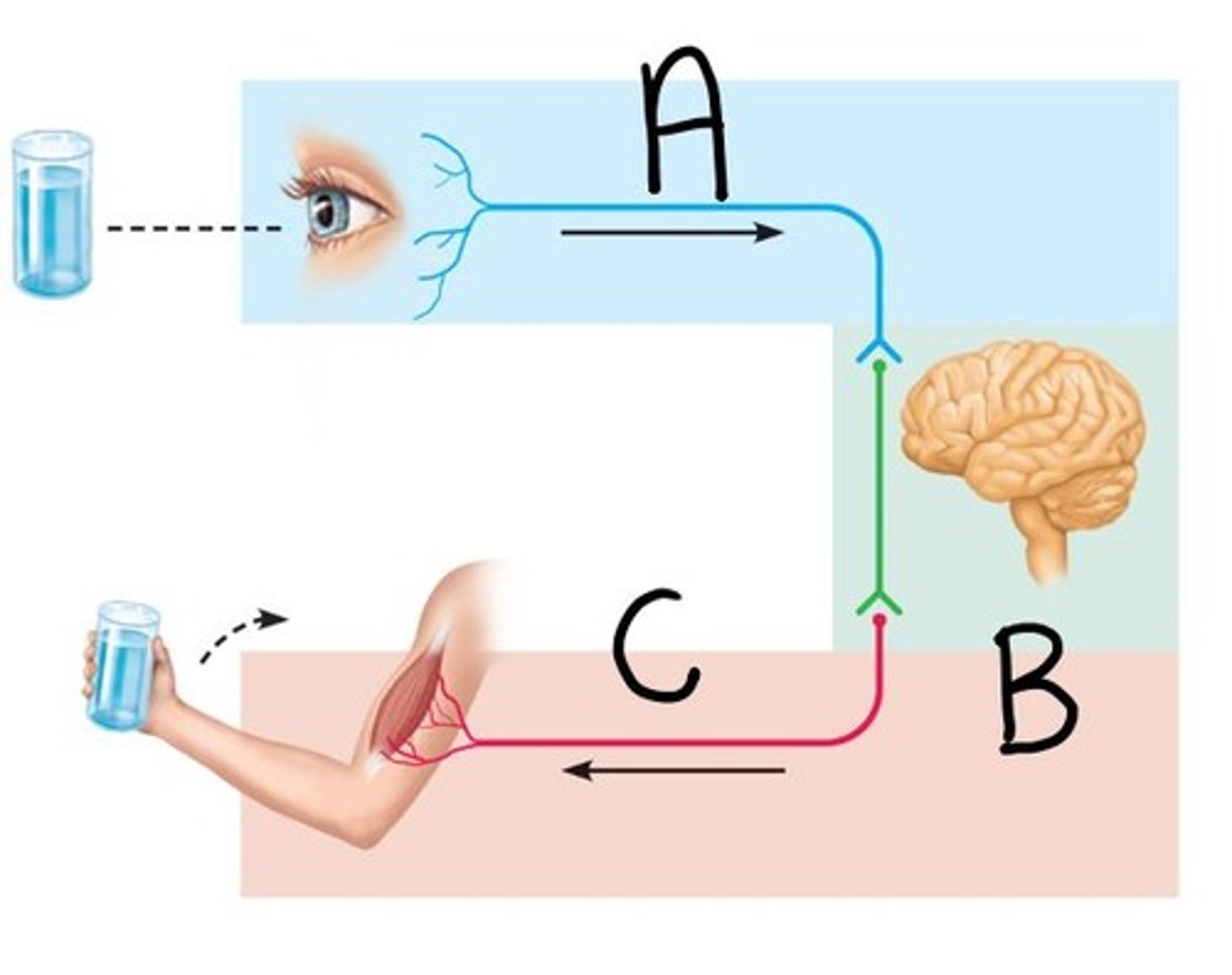
Integration (Letter B)
To process and interpret sensory input and decide if action is needed; occurs in the brain & spinal cord (Letter B)
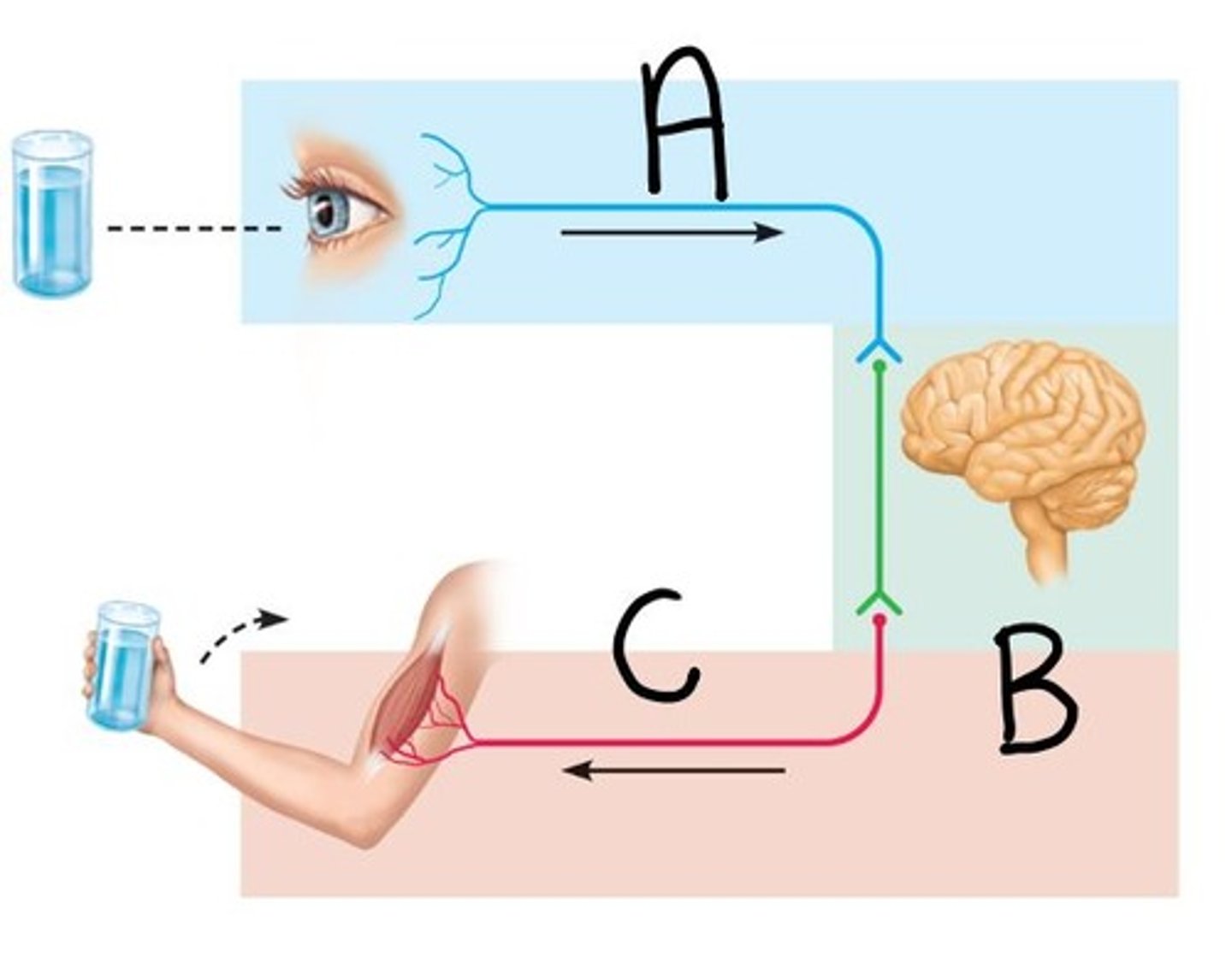
Output (Letter C)
A response to a stimuli that activates muscles or glands
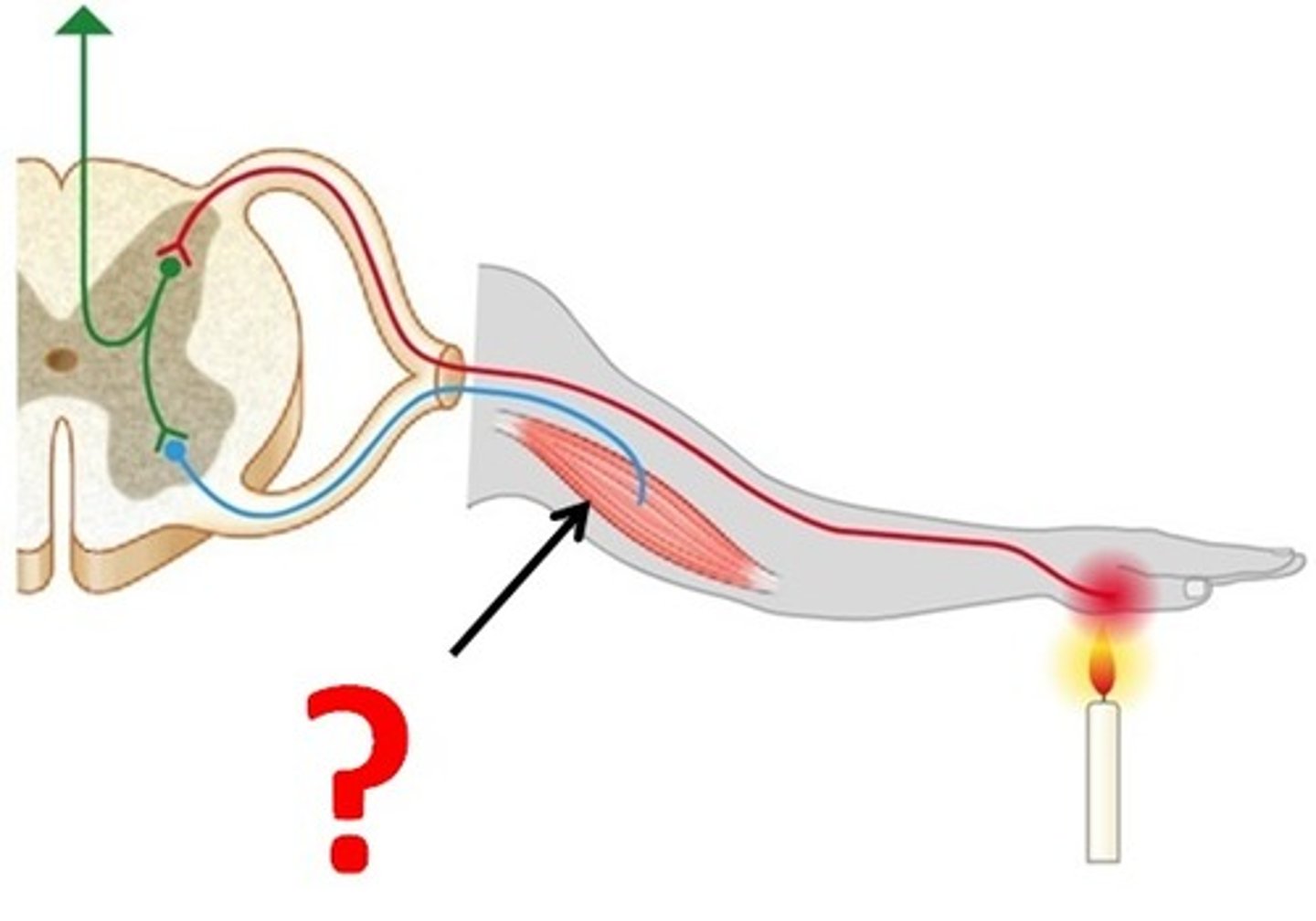
Effector
An organ, gland, or cell that acts in response to a stimuli
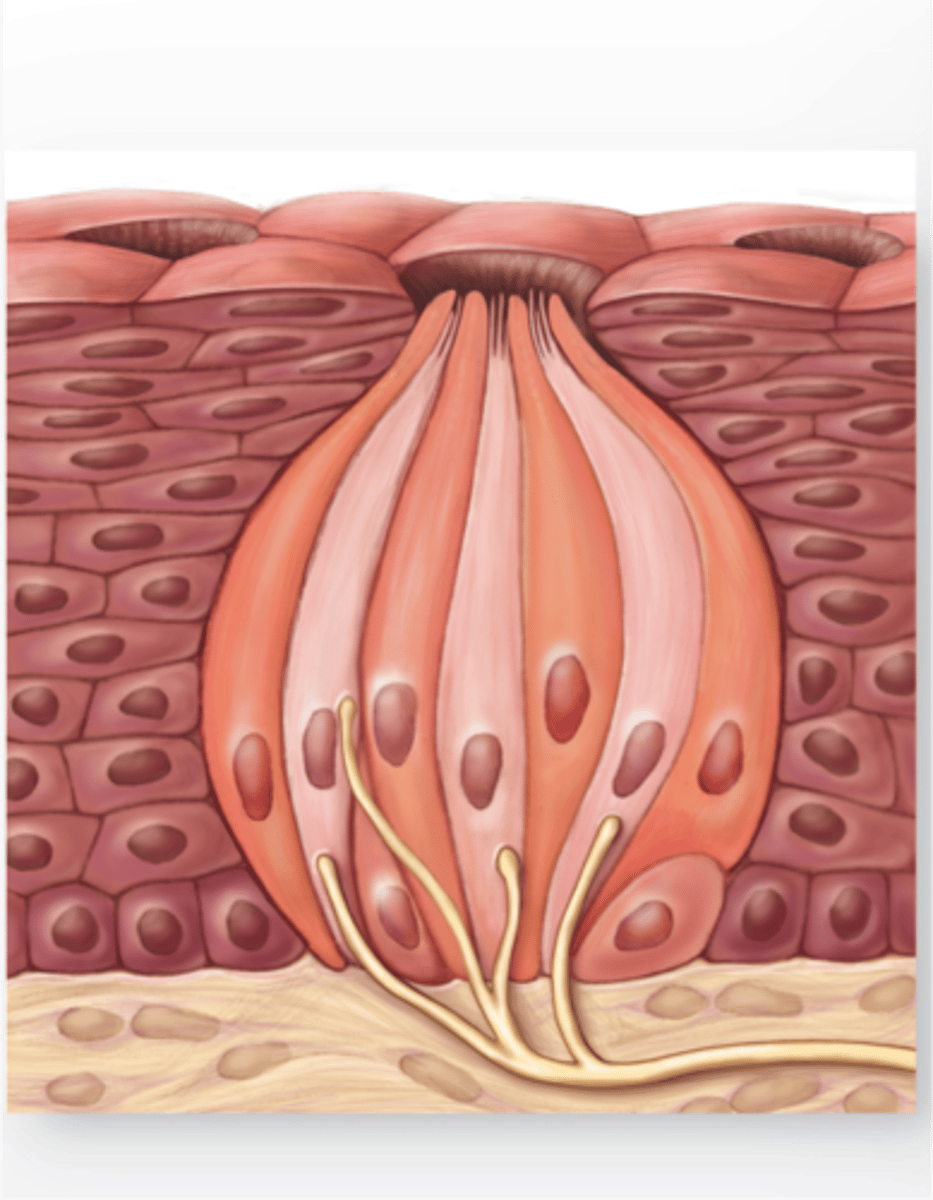
Chemoreceptor
Receptors that detect chemicals; involved in taste (taste bud) and smell (olfactory receptors)
Mechanoreceptors
Receptors that detect sound waves, touch and pressure, include: Sound waves → Hair cells (ear)
Touch → Meissner's corpuscles (skin)
Pressure → Pacinian corpuscles (skin)
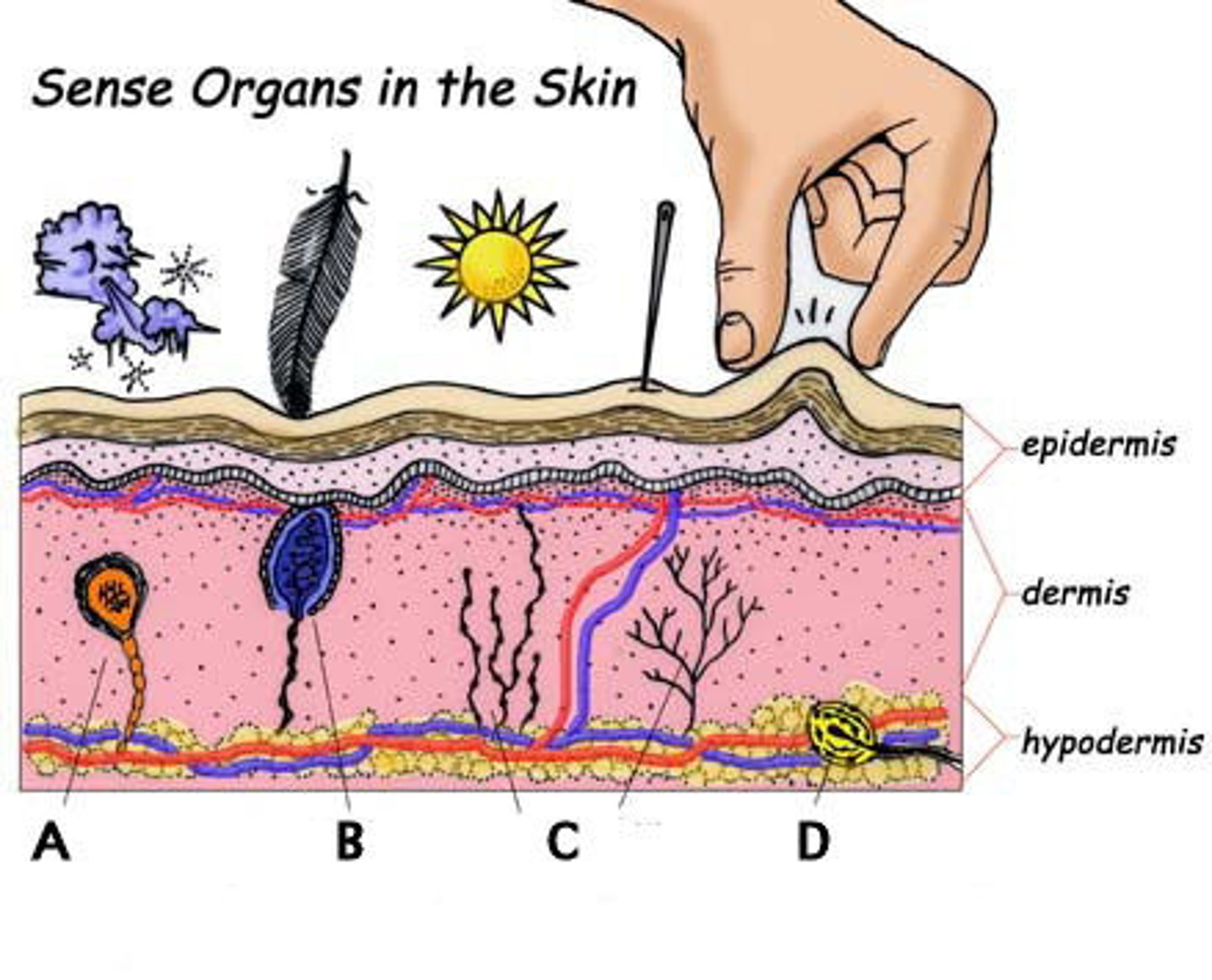
Pain Receptors
Receptors present in most tissues that respond to potentially damaging stimuli and send "threat" signals

Photoreceptors
Receptors that respond to light that are found in the retina (rods and cones)
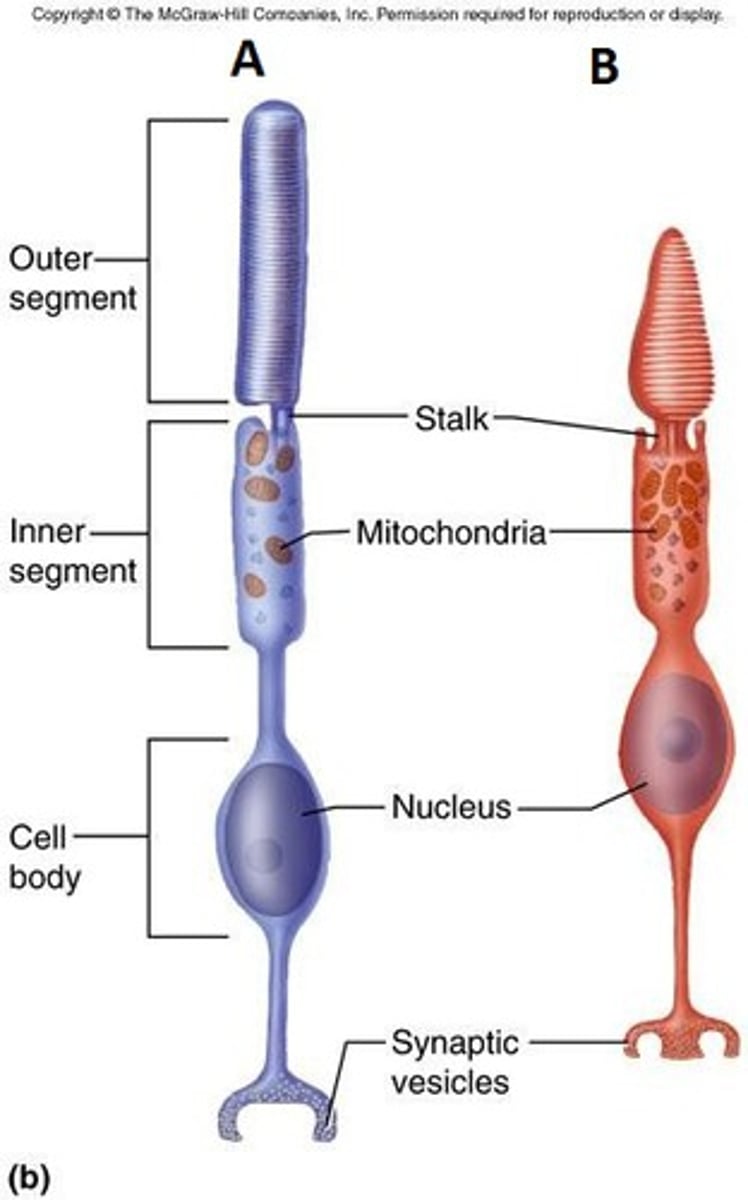
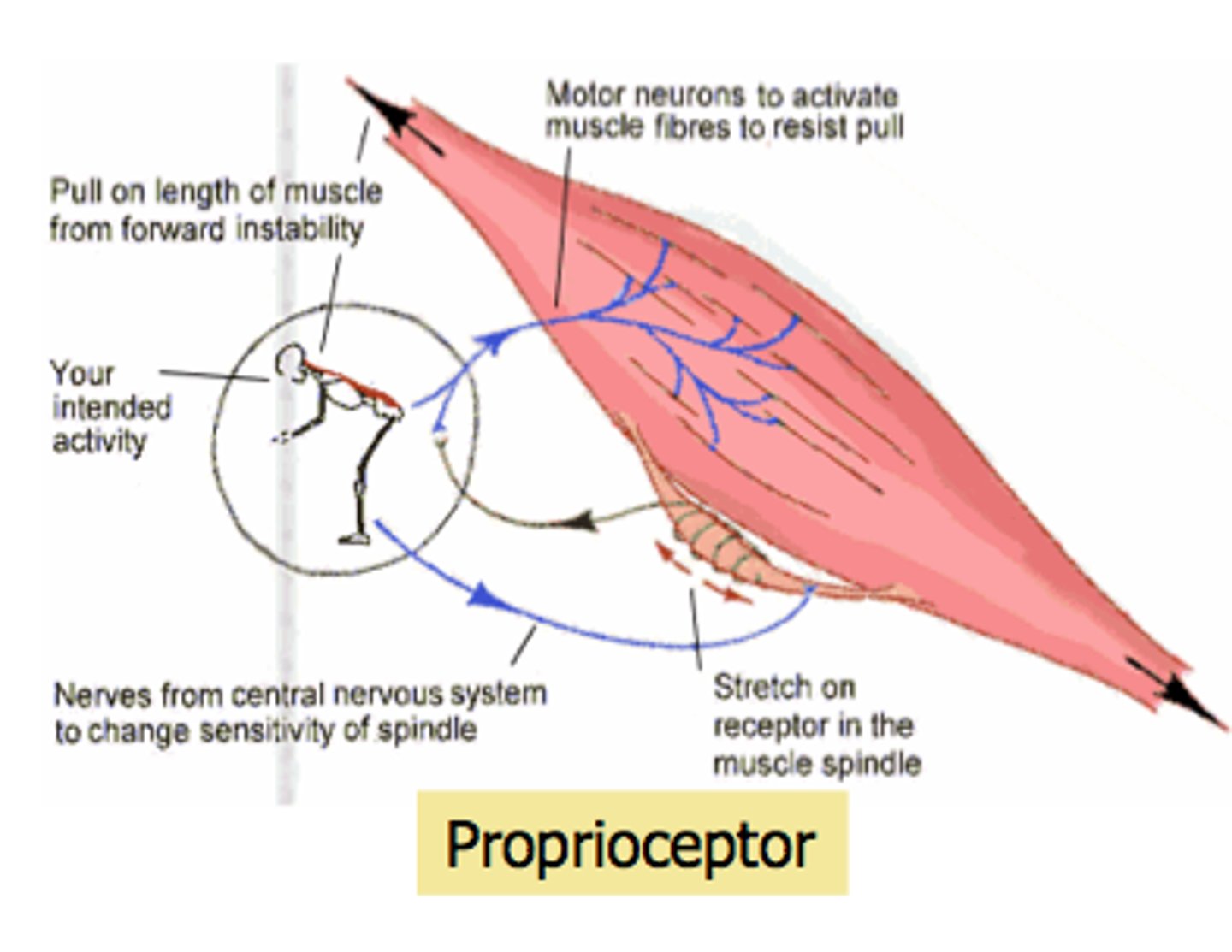
Proprioceptors
Receptors that detect stretch or tension and respond to position and movement
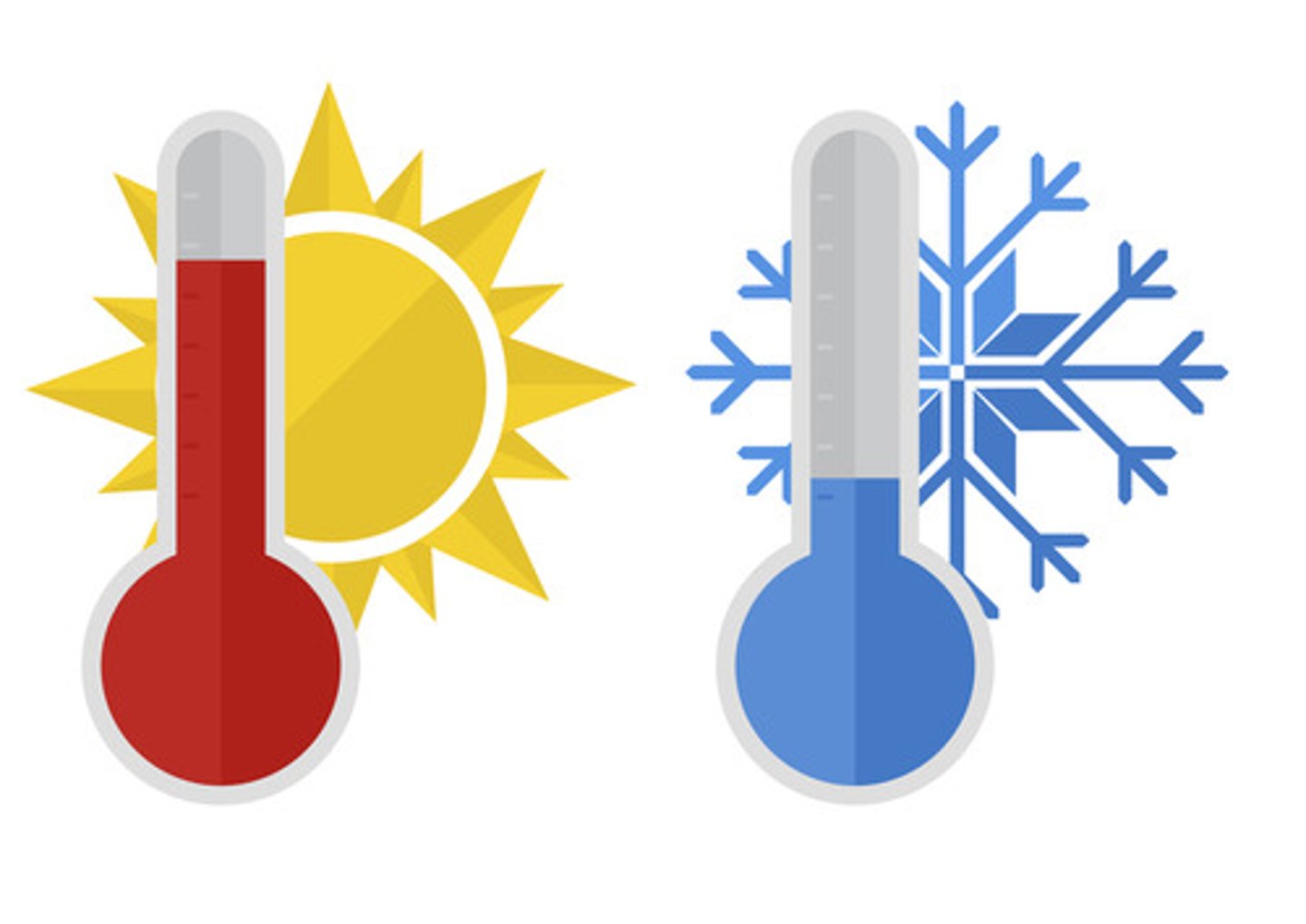
Thermoreceptors
Receptors that detect changes in temperature
Central Nervous System (CNS)
The part of the nervous system that consists of the brain and spinal cord
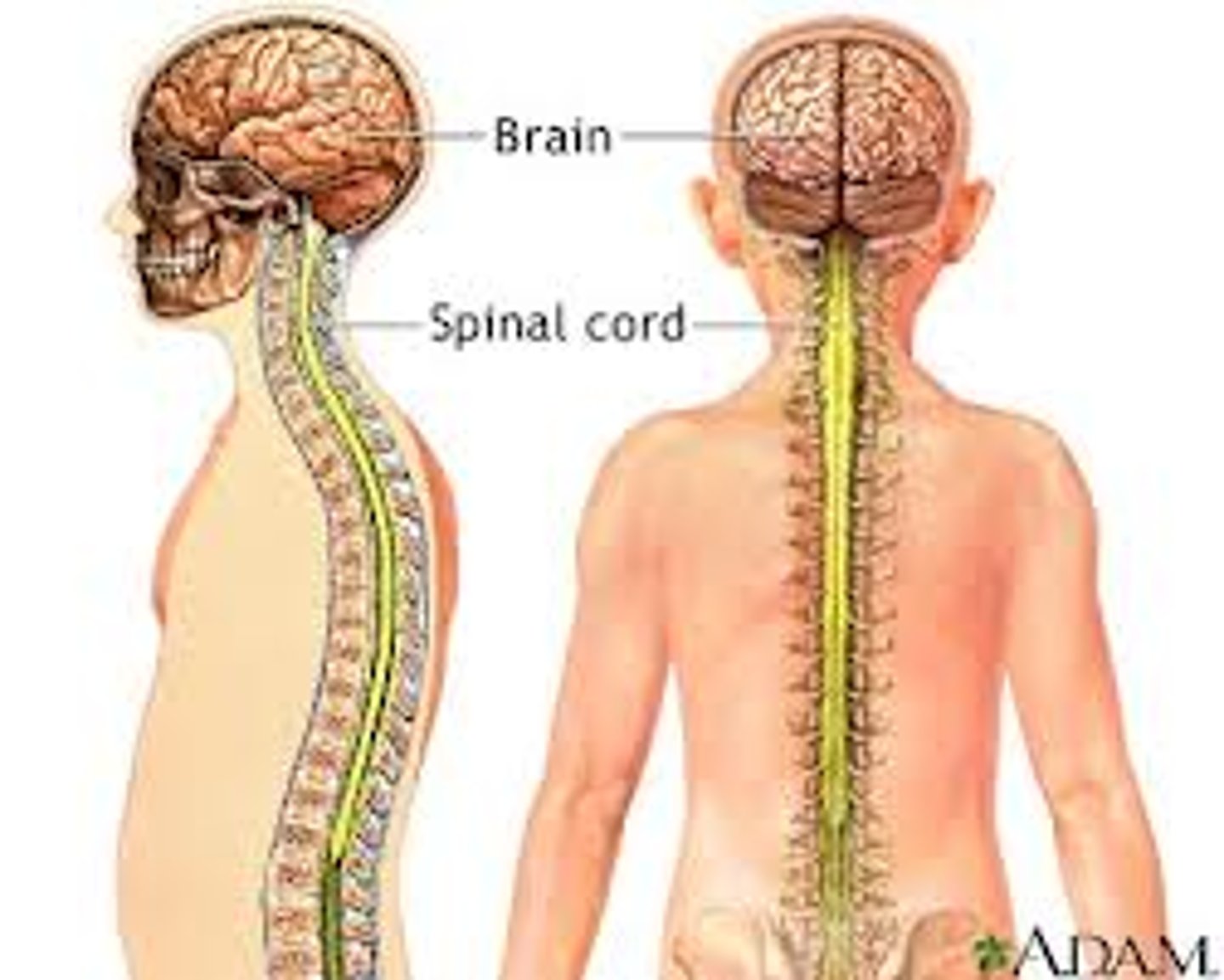
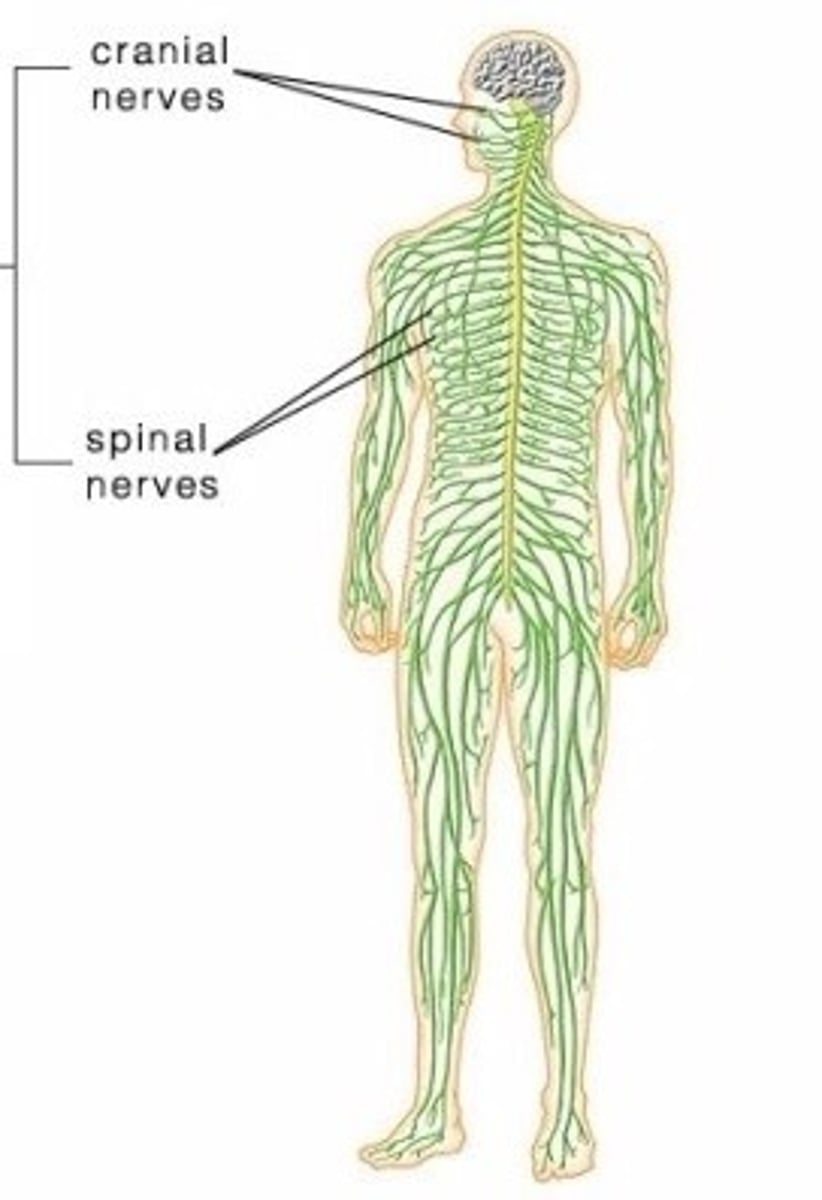
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
The part of the nervous system that includes the cranial and spinal nerves
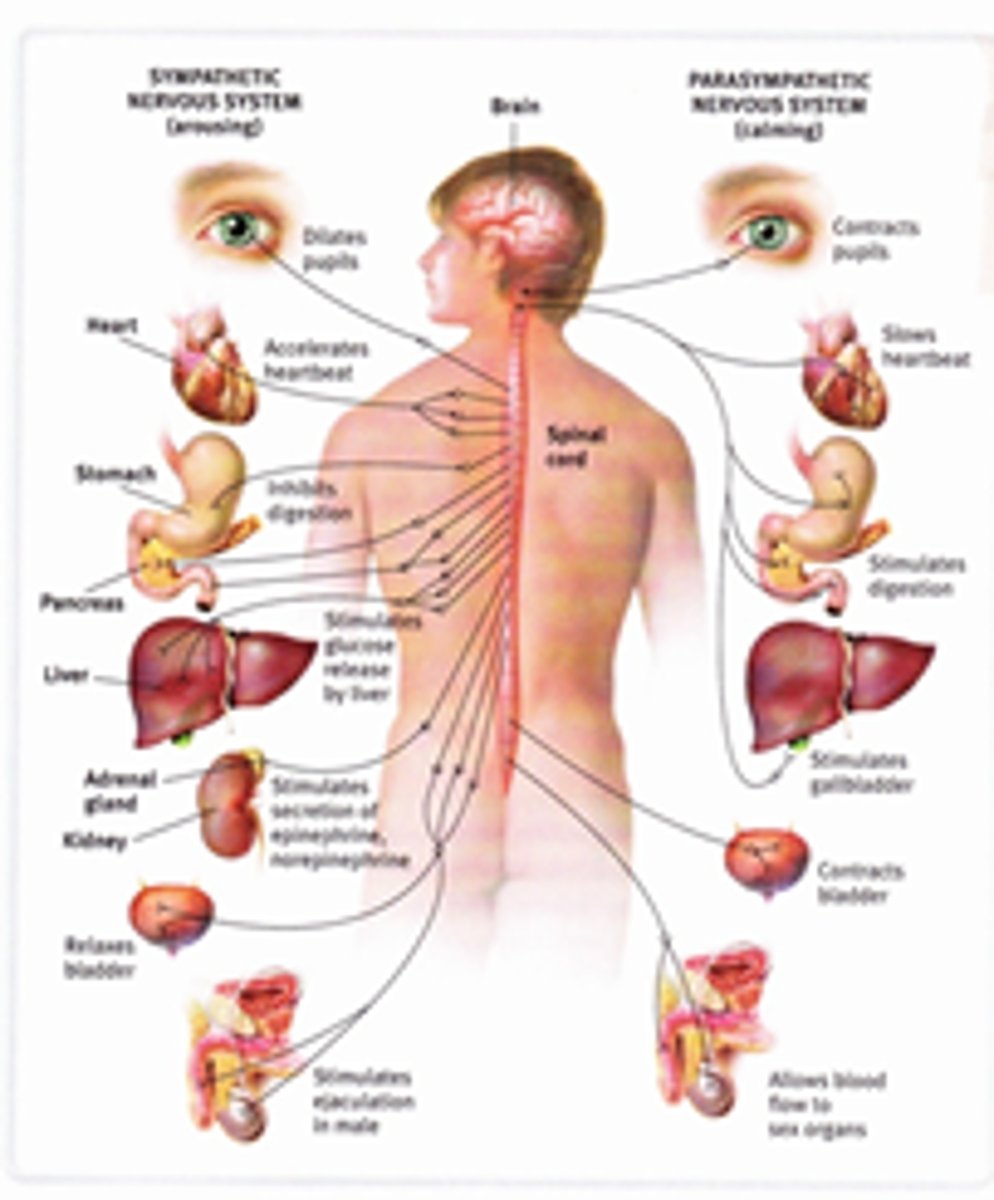
Autonomic Nervous System (Description)
The part of the peripheral nervous system responsible for controlling involuntary actions such as breathing, heartbeat, and digestive processes.
Somatic Nervous System (Description)
The part of the peripheral nervous system associated with controlling voluntary actions such as skeletal muscle contractions.
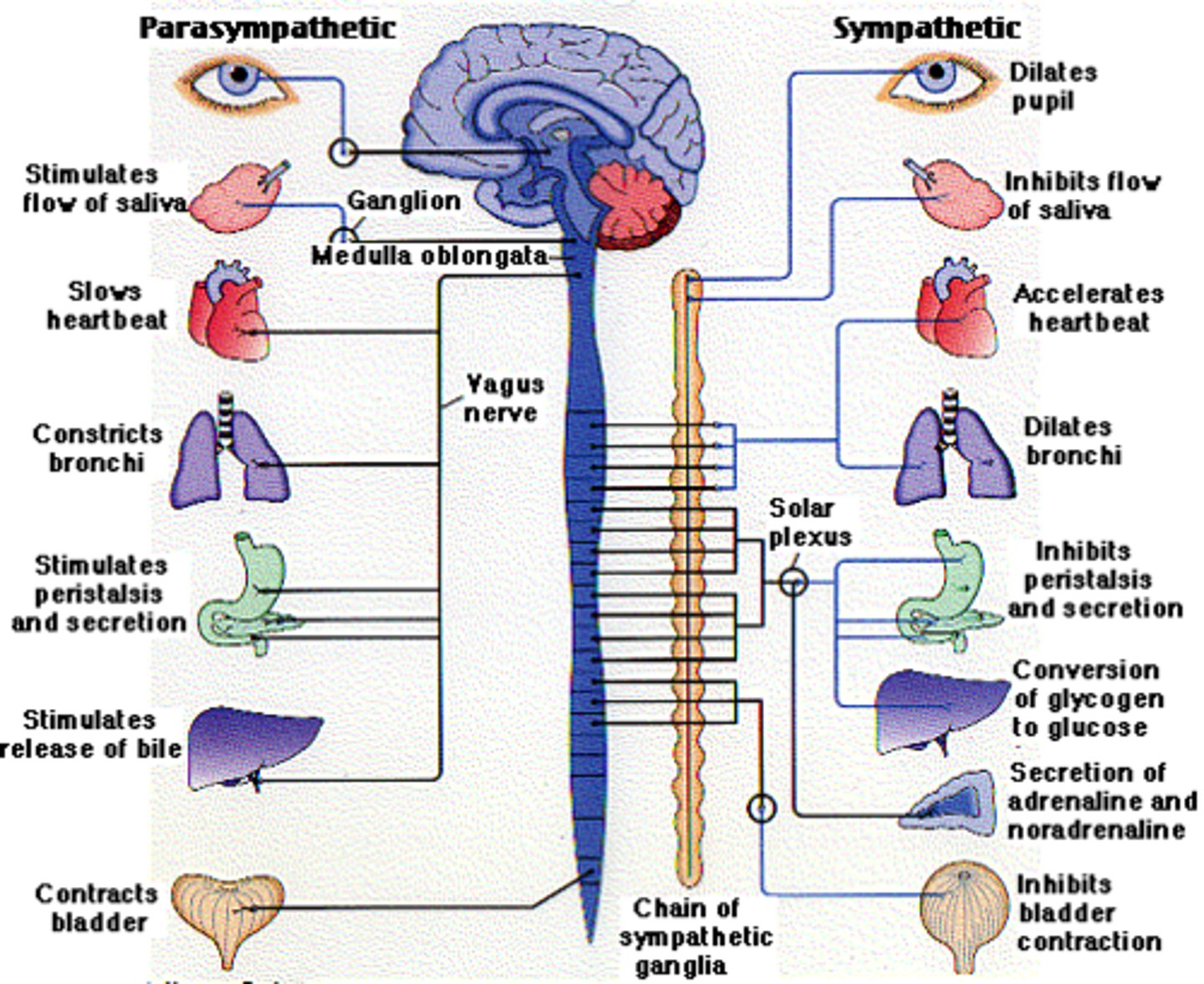
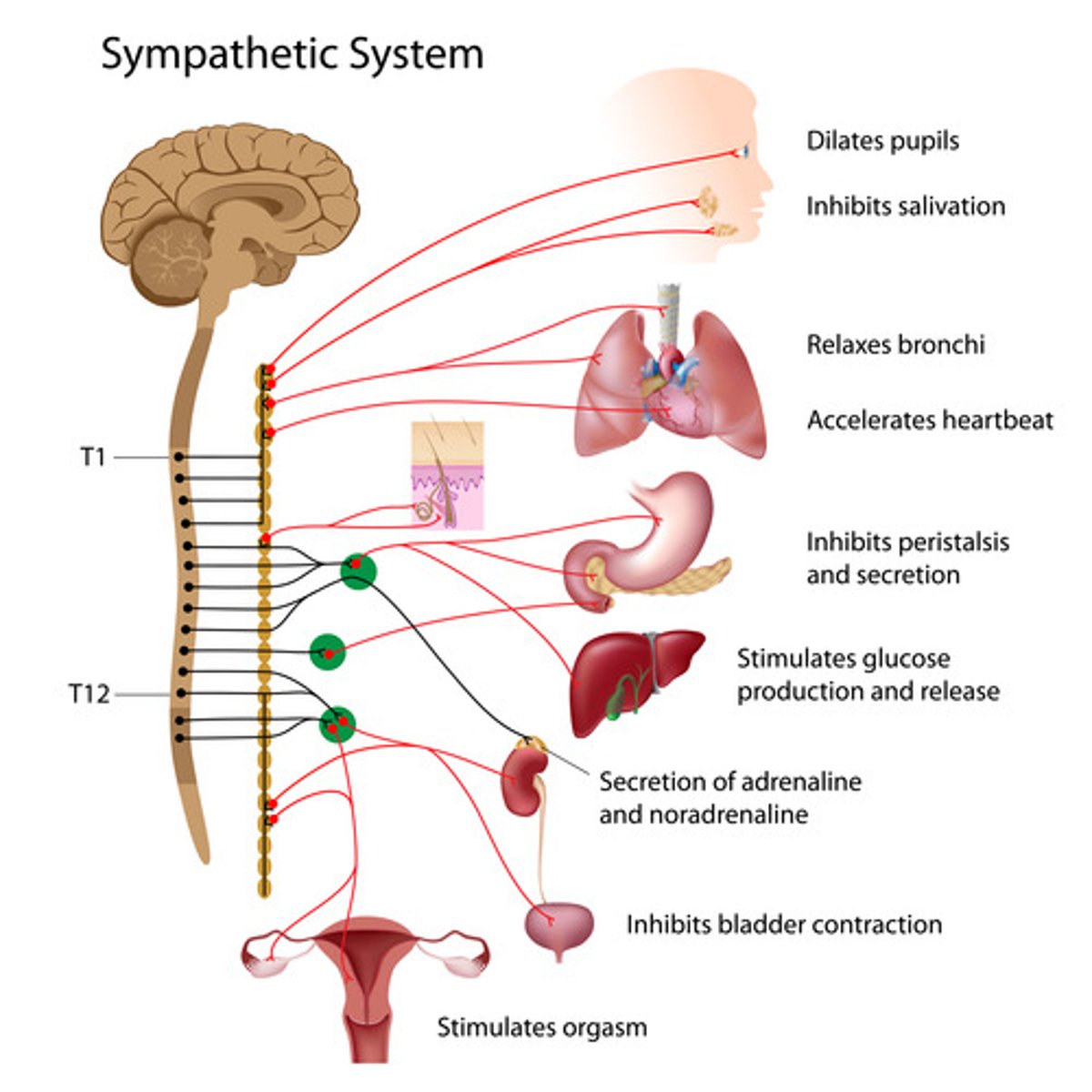
Sympathetic Nervous System
A division of the autonomic nervous system that increases heart rate and activates the fight or flight response; acts like a gas pedal
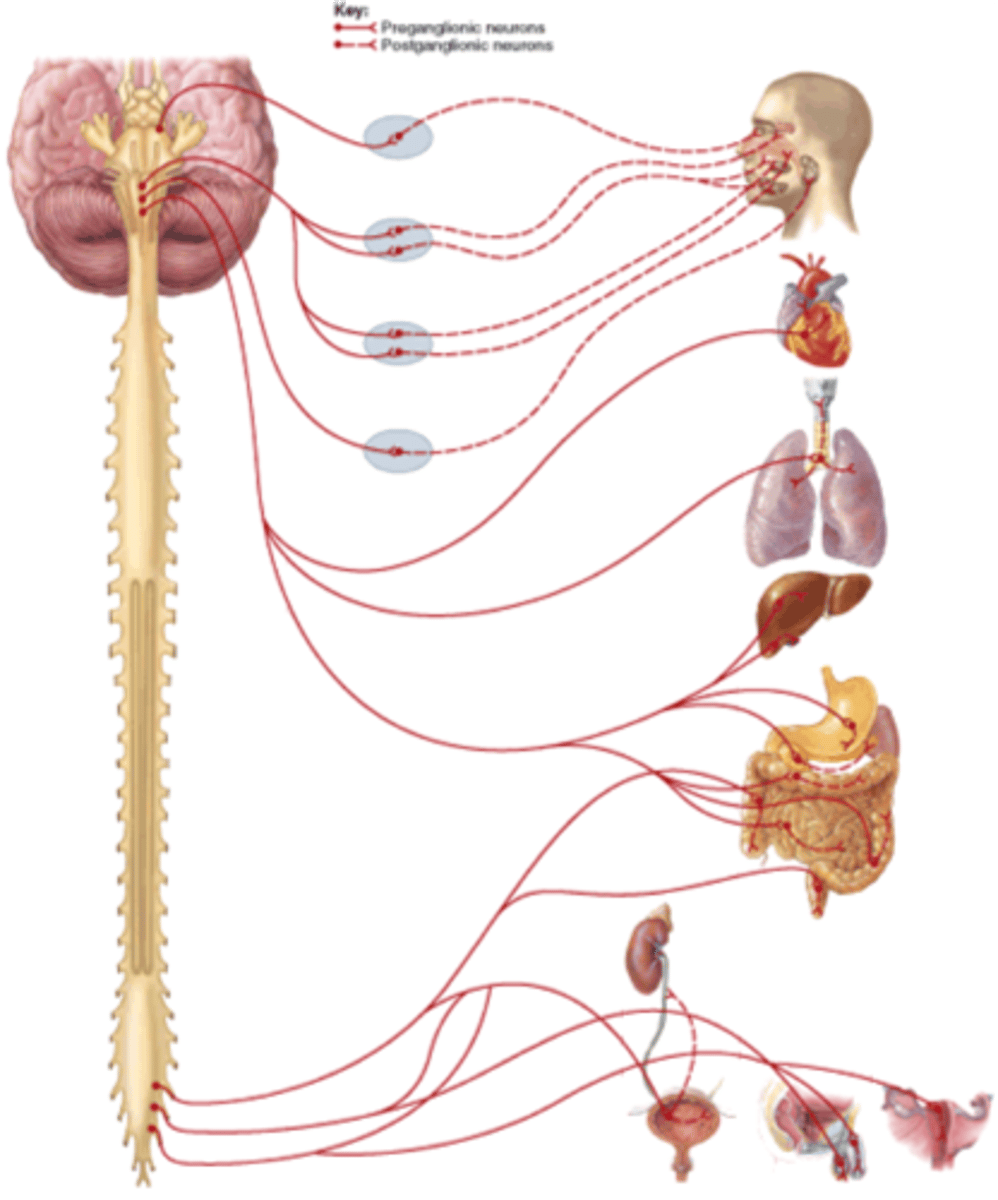
Parasympathetic Nervous System
A division of the autonomic nervous system that slows the heart rate and helps the body rest and digest; acts like a brake.
Nervous System (Functional Classification)
Classification that is based upon how information is processed; includes the sensory and motor divisions
Nervous System (Structural Classification)
Classification that is based upon where structures are located; includes the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system
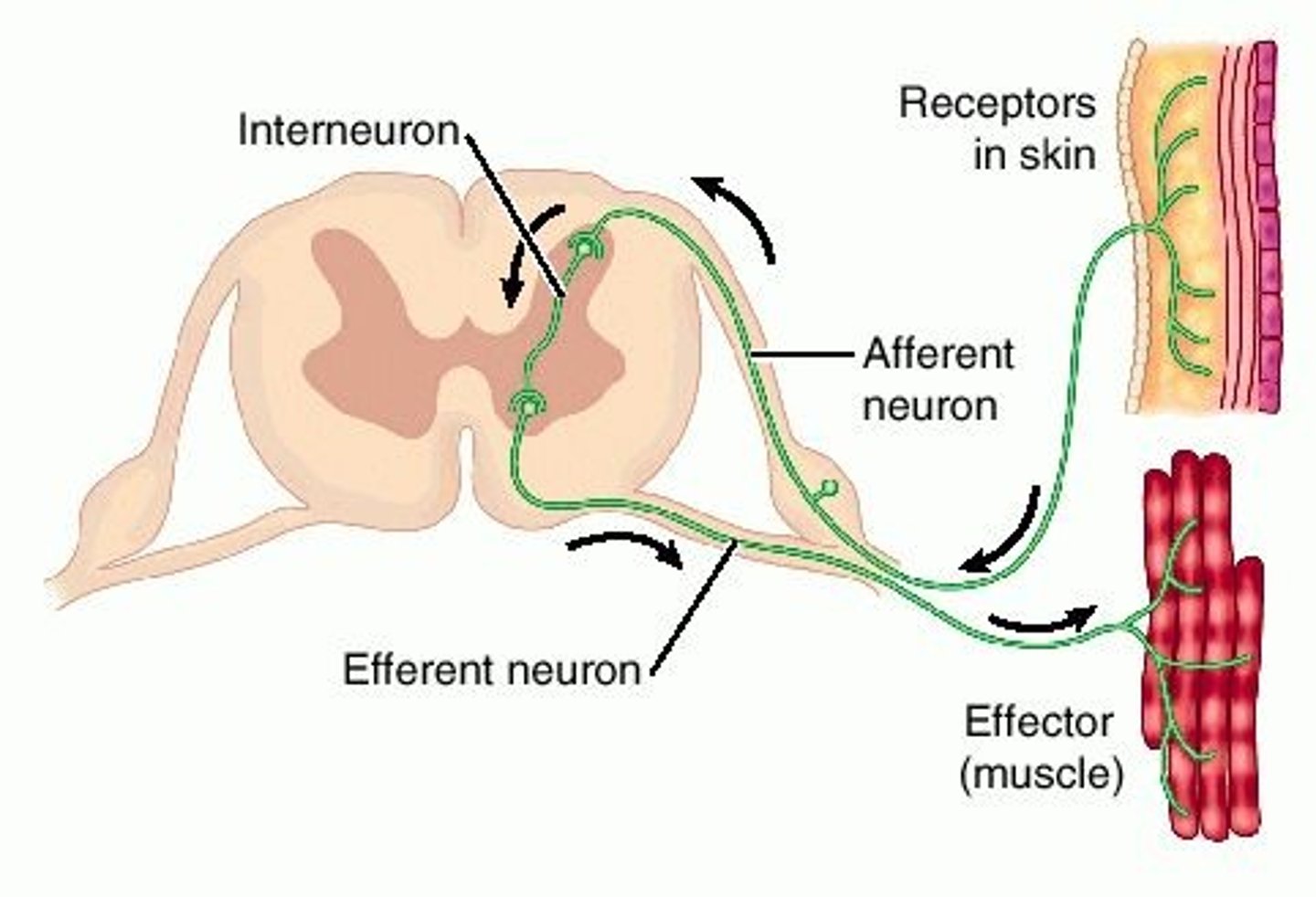
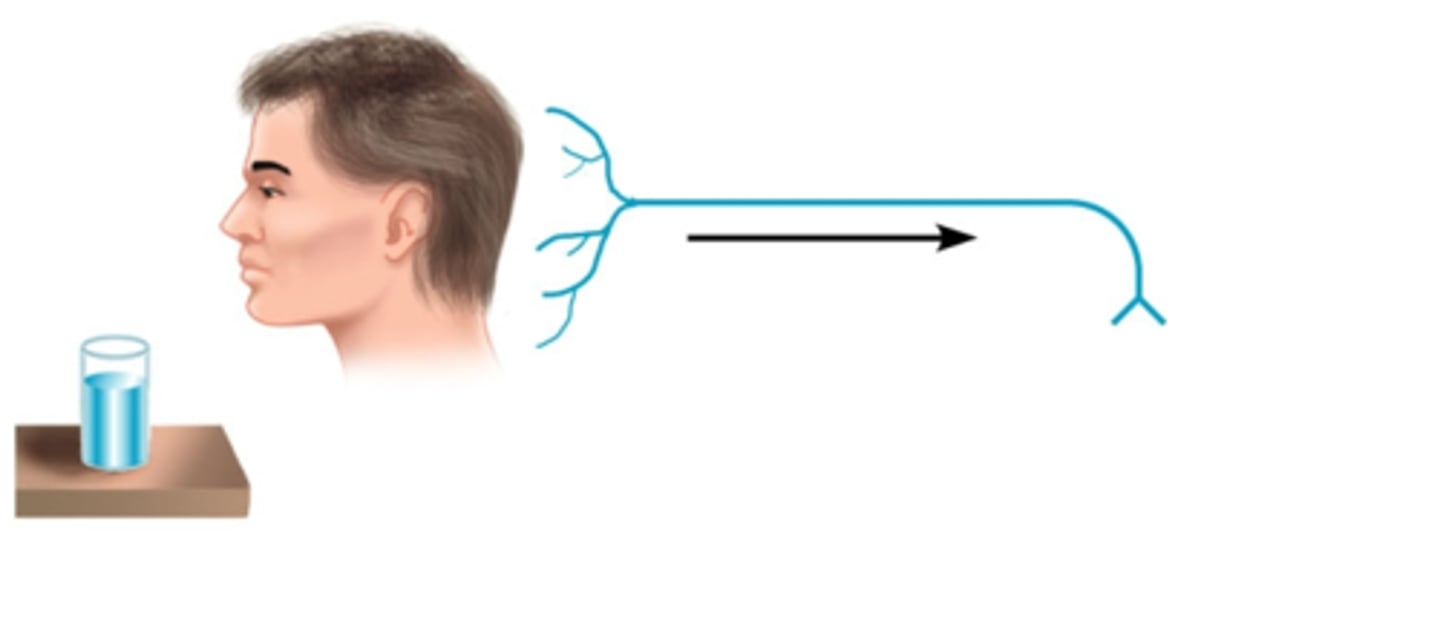
Sensory neuron (Afferent)
A neuron that carries information TO the CNS
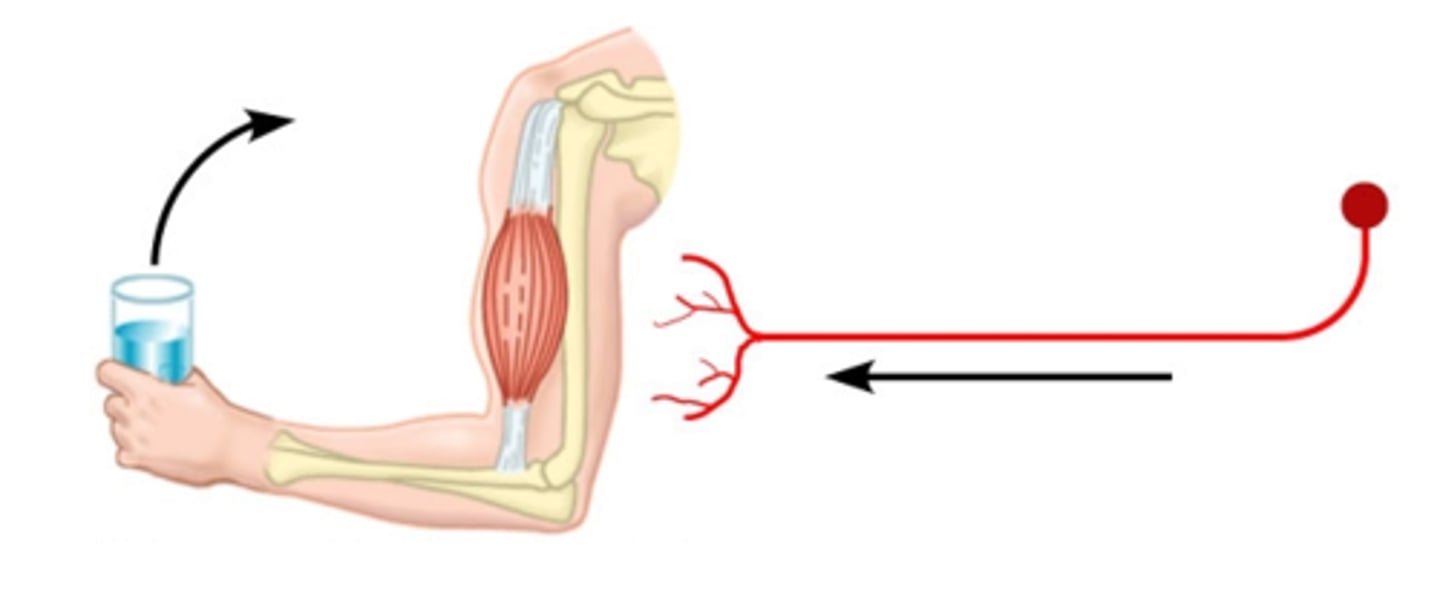
Motor neuron (Efferent)
A neuron that carries information FROM the CNS to an effector
Autonomic Nervous System (Divisions)
Sympathetic
Parasympathetic