1 - Clastic sediments and sedimentary rocks
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What % of rocks on Earth are sedimentary
75%
Features of continental crust
Andesitic/intermediate
20-30% Quartz
20-70% Feldspars
10-30% Mica
Features of Oceanic crust
Basaltic/Basic
0-50% Olivine
40-80% Pyroxenes
0-30% Plagioclase
Features of the upper mantle
Peridotite/ultrabasic
50-100% Olivine
0-50% Pyroxene
Describe the Goldich Weathering series
Olivine (least resistance to weathering)
Pyroxenes
Amphiboles
Biotite
Muscovite
K-Feldspar
Quartz (most resistance to weathering)
Types of physical weathering
Frost/freeze-thaw weathering
Exfoliation (heat-cool, peeling)
Action of plants
Types of chemical weathering
Hydrolysis
Hydration
Carbonation
Oxidation
Ion exchange
Chelation
Impact of chemical weathering
Water mediated formation of new minerals with different volumes
Factors controlling rate of weathering and regolith formation
High rainfall
High temperature
Topography
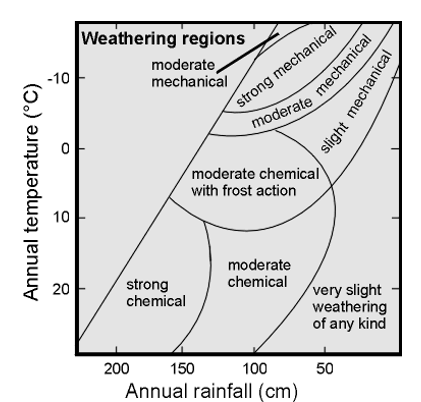
Where is the highest weathering rates
Tropics (hot + wet)
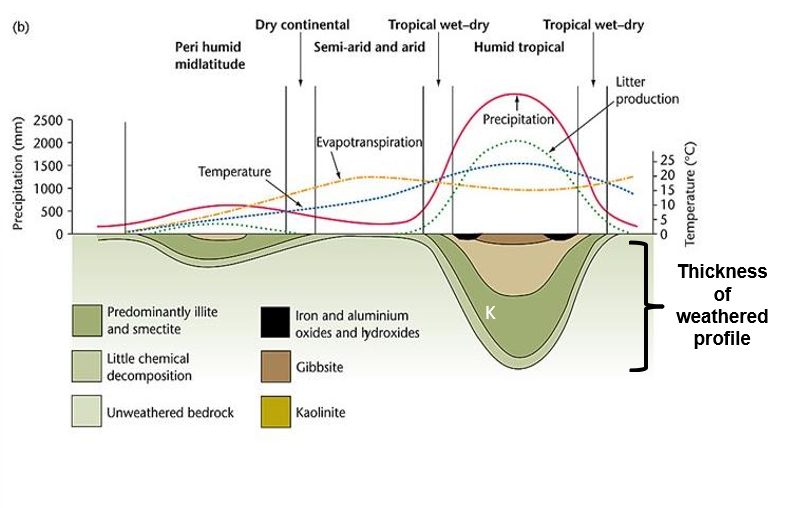
Clay negative feedback
Clay produced in weathering → impermeable material → prevents water reaching bedrock → limits weathering
Weathering and erosion
Generating regolith then removing the regolith
Facilitators of erosion
Gravity → hills, falls, landslides and runnoff
Main building blocks of andesites
Quartz
Feldspars
Mica
Features of Quartz
Inert
Hard (Moh’s 7)
Forms most common course grains or clasts
No cleavage
Weathering of feldspars and micas
Feldspars and micas are metastable → React readily with water and weak acids formed from hydrolysis → break down into clay (unlike quartz)
Features of clay
Sheet silicates with a single perfect cleavage
Soft (1-2.5)
Form a fine matrix/mud
Comprises shales and mudstones
Features of clastic sediments
Grains/clasts → visible to the naked eye → usually quartz
Clay → appears as a speckly mush
For sediments to form rock they must:
undergo diagenesis → cemented at high temperatures/pressures
For Carbon to be locked into the rock:
It must be buried in a sedimentary basin
Increasing distance and time leads to more texturally mature rocks:
Grainsize decreases
Grain angularity decreases
Grain sphericity increases
Grain sorting increases
Loss of feldspar, mica and lithic clasts in favour of quartz and clay matrix
Basic summary of diagenesis
Growth of crystals which precipitate out of water to form cement, holding the grains together