ITSS Exam 2 Review
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
What is IT Governance?
the responsibility of executives and the board of directors; consists of the leadership, organizational structures and processes that ensure that the enterprise's IT sustains and extends the enterprise's strategies and objectives.
What are the Components of IT Governance?
Strategy
Customer alignment
Compliance Requirements
What is the IT Governance term Strategy
• As the value of IT organizations grow in executing effective business strategies, the decisions of IT leadership create more and more of an impact on organizations.
•IT used to be “keep the lights on”
•IT now is a business accelerant
What is the IT Governance term Customer Alignment?
• The IT organization must develop its strategy based on the needs of the business
• Alignment with the business is critical when developing an effective IT governance strategy
What is the IT Governance term Compliance Requirements?
• Some things IT organizations can choose, others are required:
• Sarbanes Oxley (SOX) The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
• Payment Card Industry (PCI)
• General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
What terms can be used to enforce IT Governance?
• Personnel
• Documentation
• Oversight
•Incentivization
What is the enforced IT Governance term Personnel?
• When you build an organization, you can’t be all things to all people, and you can’t pay every position “top of the line” salaries.
• You need to decide where you want to invest your resources to execute on your strategy
• What is it you need your IT organization to be great at?
What is the enforced IT Governance term Documentation?
• Often called “policies and procedures”
• These are the rules of the road. The instruction manuals and the organizational requirements all employees need to align with.
• Avoid key personnel dependencies whenever possible with effective organizational documentation.
What is the enforced IT Governance term Oversight?
• Where do you want your management focusing their attention?
• What are you going to track?
• Uptime for software?
• Response time for incidents?
• Regulatory requirements?
What is the enforced IT Governance term Incentivization?
• How are you going to ensure the employees align with your goals and requirements?
• Bonuses?
• Penalties?
What is data?
Streams of raw facts
What is information?
Data shaped into meaningful form
What are the key terms of Data Elements and Components?
• Database –Group of related tables (files)
• Table (File) –Group of related rows (records)
• Row (Record) –Group of related columns (fields)
• Column (Field) –Group of characters, words, numbers, etc.
• Entity – Person, place, thing on which we store information
• Attribute (Metadata) – Each characteristic, or quality, describing the entity
What shows how Databases are used?
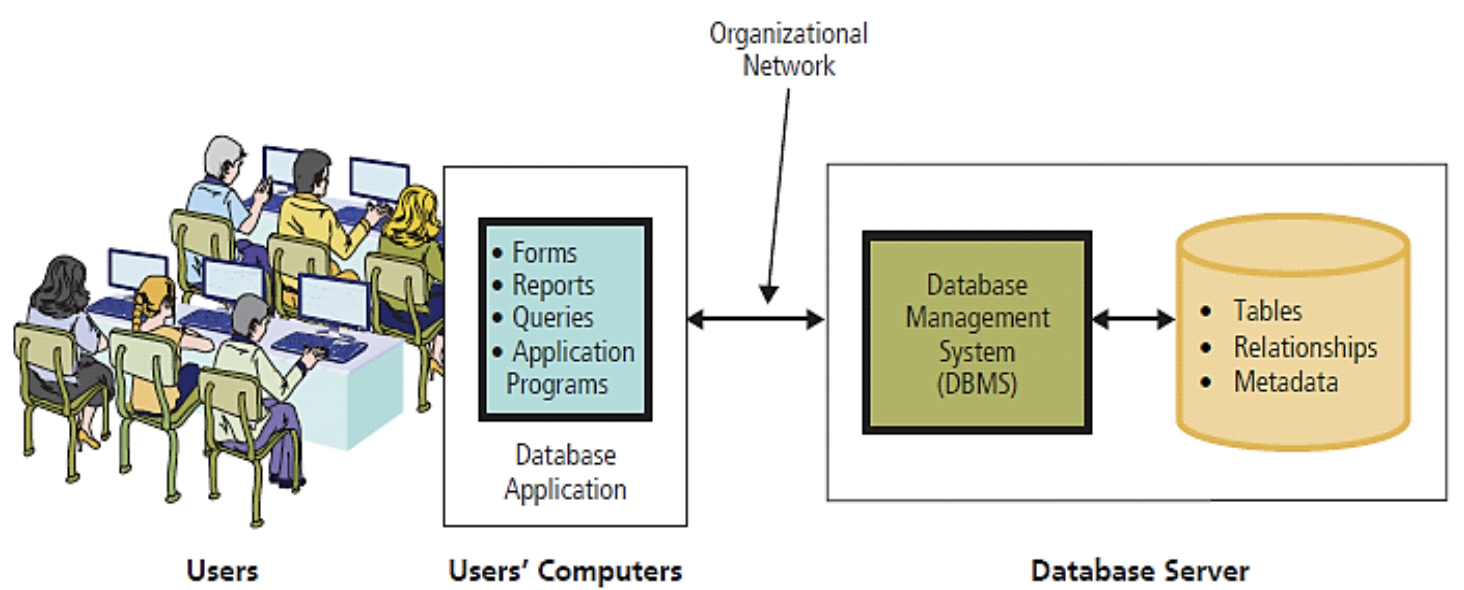
What is a Database Management System(DBMS)?
• Program to create, process, and administer a database
• Database serves many applications by centralizing data and controlling redundant data.
What connects to Relational DBMS representing data as two-dimensional tables?
• Key Field – Field used to uniquely identify each record (row)
• Primary Key – Field in table used for key fields
• Foreign Key – Primary key used in second table as look-up field to identify records from original table
What are the capabilites of DBMS?
• Data definition capability
• Data dictionary
• Querying and reporting
• Many DBMS have report generation capabilities for creating polished reports (Microsoft Access)
What shows Relationships Among Rows?
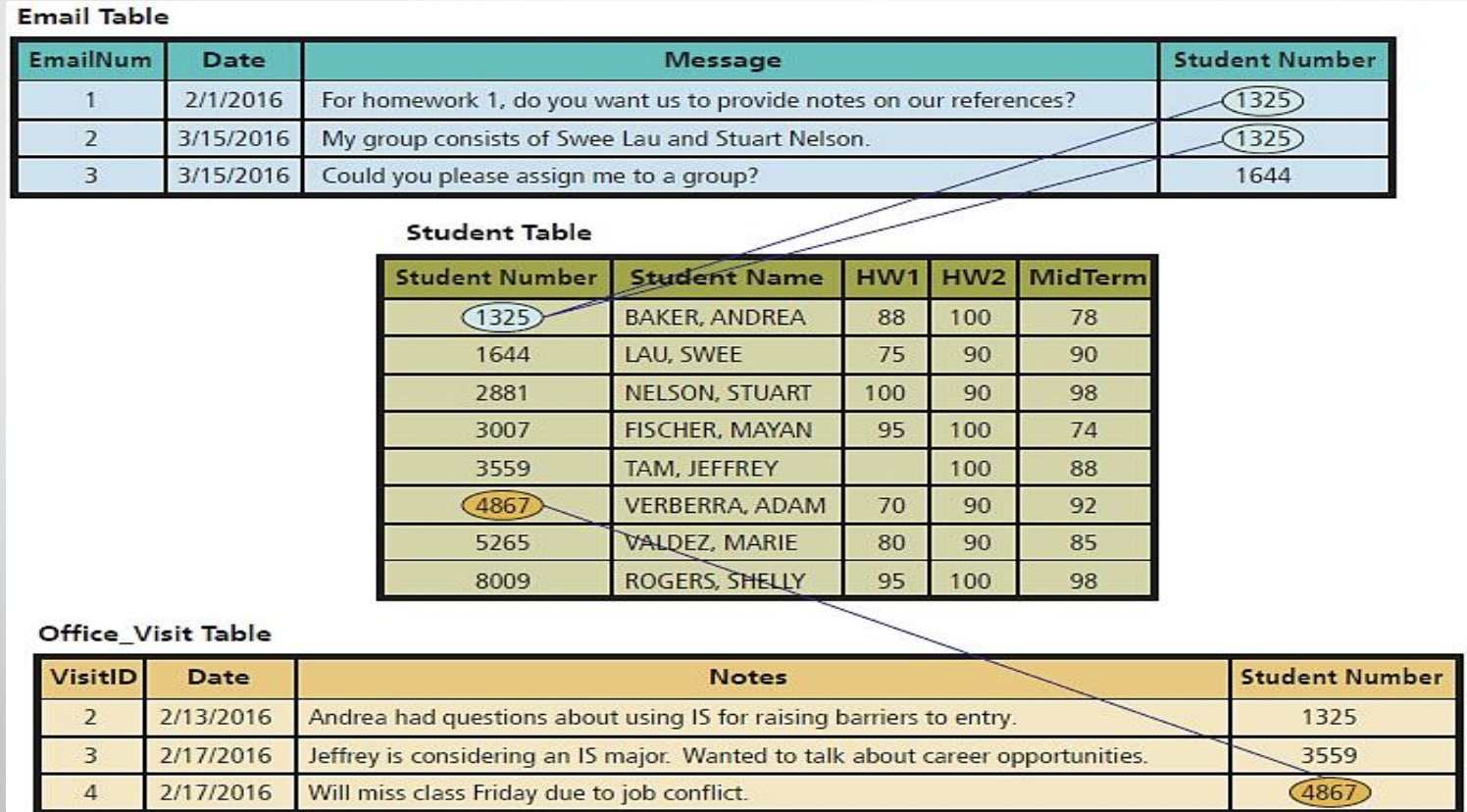
What is Normalization?
Streamlining complex groupings of data to minimize redundant data elements and awkward many-to-many relationships.
What is Referential Integrity?
Rules used by RDBMS to ensure relationships between tables remain consistent.
What shows the Entity-Relationship Diagram?
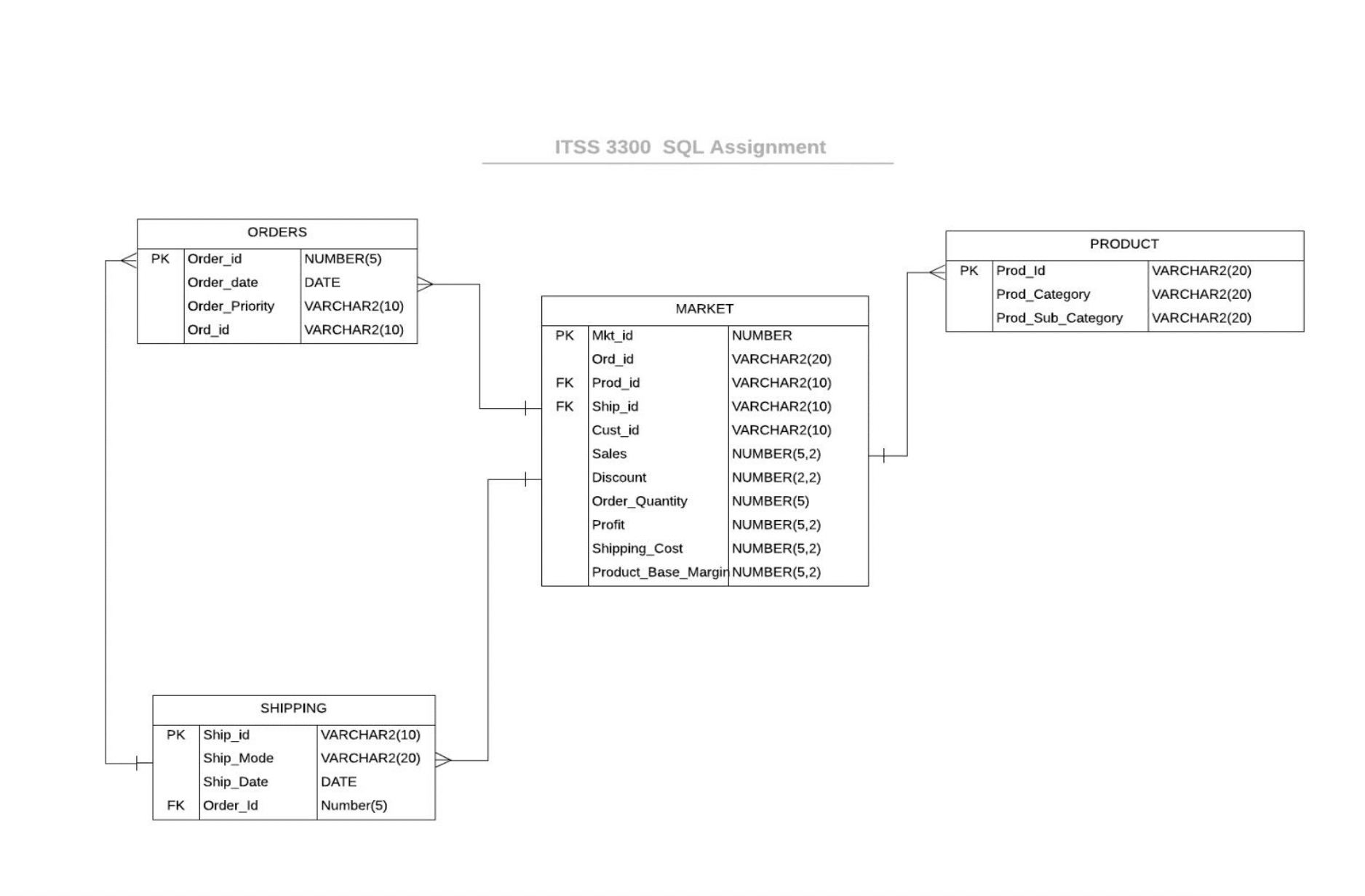
What are the Key SQL Script Commands?
• SELECT –What fields do you want to see?
• FROM – Source Tables for Fields
• WHERE – Operations and Conditions on Fields
• = (equals sign) – Establish Relationships (can also use JOIN)
• AND/OR – Combine Conditions
• ORDER BY – Sorting
• There are also various functions available
What is Big Data?
Massive sets of unstructured/semi-structured data from web traffic, social media, sensors, and so on.
• Can reveal more patterns, relationships and anomalies
• Requires new tools and technologies to manage and analyze
• Enables more robust Business Intelligence
What is the Data Warehouse?
– Stores current and historical data from many core operational transaction systems
– Consolidates and standardizes information for use across enterprise, but data cannot be altered
– Provides analysis and reporting tools
What is the Data mart?
– Subset of data warehouse
– Typically focus on single subject or line of business
What is the Hadoop?
Enables distributed parallel processing of big data across inexpensive computers.
What is In-memory computing?
• Used in big data analysis, requiring optimized hardware, reducing hours/days of processing to seconds
• Uses computers main memory (RAM) for data storage to avoid delays in retrieving data from disk storage
What is Analytic Platforms?
High-speed platforms using both relational and non-relational tools optimized for large datasets
What is the primary purpose of Business Intelligence?
Timely 2. Data-driven 3. Objective
What is the Decision Making Process?
• Identify and define the Problem
• What are the possible solutions?
• Determine the criteria to evaluate the alternatives
• Evaluation through Analysis
• Choose the alternative
• Communicate your findings
What are Strategic Decisions?
Typically Unstructured
◦ Involve higher-level issues concerned with the overall direction of the organization.
◦ These decisions define the organization’s overall goals and aspirations for the future.
What are Tactical Decisions?
Typically Semi-Structured
◦ Concern how the organization should achieve the goals and objectives set by its strategy.
◦ They are usually the responsibility of midlevel management
What are Operational Decisions?
Typically Structured
◦ Affect how the firm is run from day to day.
◦ They are the domain of operations managers, who are the closest to the customer.
What are the effective communications?
What happens if you FAIL TO EFFECTIVELY COMMUNICATE YOUR ANALYSIS AND RECOMMENDATIONS?
You failed to answer the business question.
What are the components of Business Intelligence efforts?
Business intelligence systems and platforms
◦ Infrastructure for collecting, storing, analyzing data produced by business
◦ Databases, data warehouses, data marts
Business analytics
◦ Tools and techniques for analyzing data
◦ OLAP, statistics, models, data mining
Business intelligence service providers
◦ Companies and contractors that create business intelligence and analytics purchased by firms
What are the Categories of Business Analytics?
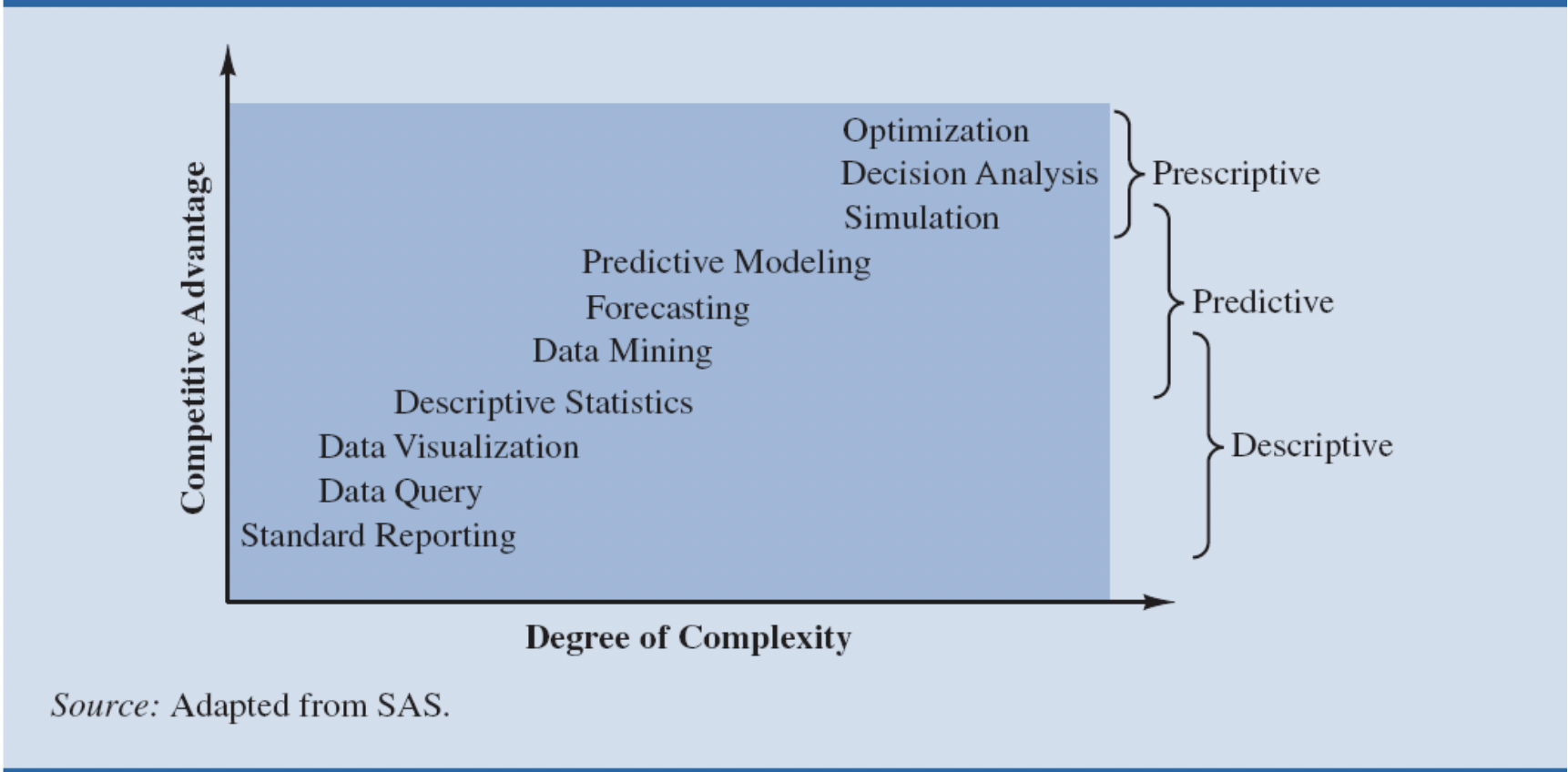
What is a Project?
a planned undertaking that has a beginning and end and that produces some definite result
• Used to develop an information system
• Requires knowledge of systems analysis and systems design tools and techniques
What is a Program?
Interrelated collection of projects
Holistic Approach
all of the ‘pieces’ must join together.
What must never be considered solely an IT Project?
Implementation Projects
What is Change Management?
• Required for successful system building
•New information systems have powerful behavioral and organizational impact
What is Implementation?
•All organizational activities working toward adoption, management, and routinization of an innovation
What is Role of End Users?
•With high levels of user involvement:
• System more likely to conform to requirements
•Users more likely to accept system
What is User-designer communication gap?
Users and information systems specialists
What is Management Support and Commitment?
• Effects positive perception by both users and technical staff
• Ensures sufficient funding and resources
•Helps enforce required organizational changes
Responsibility of Corporate strategic planning group
Firm’s strategic plan
Responsibility of Information systems steering committee
Reviews and approves plans for systems in all divisions
Responsibility of Project management group
Overseeing specific projects
Responsibility of Project Team
Individual systems project
What is Project Management?
Activities include planning work, assessing risk, estimating resources required, organizing the work, assigning tasks, controlling project execution, reporting progress, analyzing results
What is Triple Constraint?
– If you change one variable, you MUST change one or both of the remaining two.
• Scope – Includes Quality and Risk
• Time – Available timeframe until deadline
• Resources – Includes funding, human resources
What is Scope Management?
• Precisely define the deliverables, including the functions and capabilities to be included in the new system
• Verify that the identified capabilities are necessary and are important priorities for the project at hand
• Control the set of functions so it doesn’t grow inappropriately
What is Risk Management?
• Determine the potential areas of high risk for the project
• Develop strategies and plans of actions to reduce the identified risks
• Carry out the plans of action to monitor and control the project risks
What is Quality Management?
• Deliverable Fit for its intended purpose
• Robust, Reliable, Secure, Maintainable
Important Objectives for Projects
• To ensure that the project schedule accurately accommodates the work to be done
• To effectively use resources and techniques to accelerate the overall time to completion
What is Work Breakdown Structure?
Outline of all tasks, resources, and effort involved in the project. (Hint: do not list more detail than you can manage.)
What is Gantt Chart (and PERT)?
Graphic showing timeframes of tasks in a calendar view.
What is Critical Path?
The series of tasks, given their dependency relationship, that determines the total length (time) of project completion.
What is Early start time?
the earliest time that a task can begin due to predecessor durations
What is Late start time?
the latest time that a task can start to maintain the schedule
What is Slack Time?
the amount of time a task or leg of sequential tasks can be delayed without impacting the project schedule
What shows a Gantt Chart?
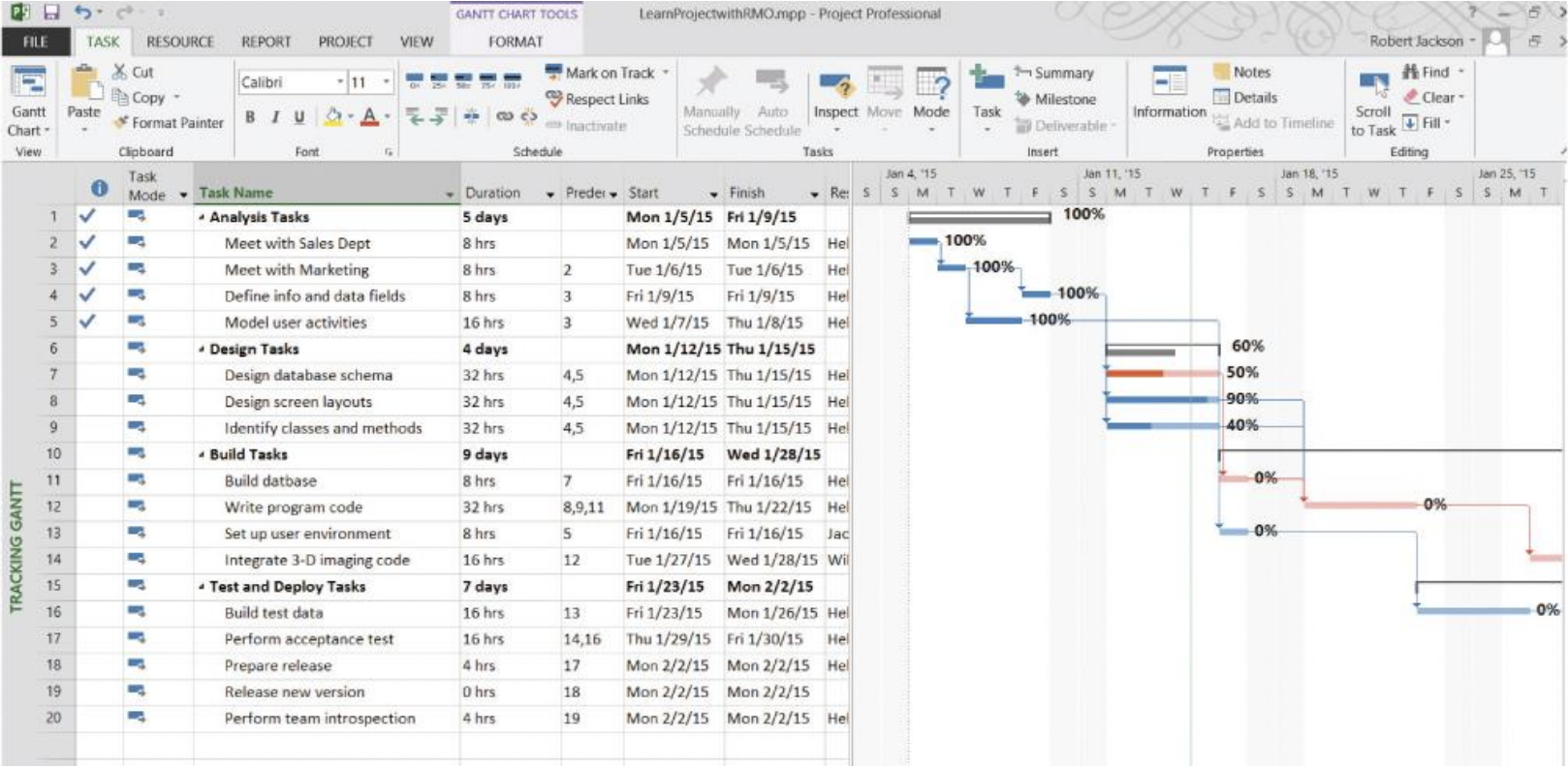
What shows objectives for Project Resources Management?
To accurately estimate the anticipated project costs
• To accurately predict the cash flow and timing of expenditures
• To confine actual project expenditures to those that are included within the plan
• To capture and record actual project expenditures correctly
• To ensure that the project team is staffed with the right number of people, at the right time with people who have adequate skills in the right mix
• To ensure that the working environment, including facilities, tools, and support, is conducive to accomplishing work
What is Budget Reporting?
-Over/Under Targets
What is Earned Value?
Accurately measure completed work to correctly assess the percentage completed. Typical measurements are Estimate to Complete and Estimate at Complete
What is Estimating?
Create initial estimates of effort required. Update as project progresses
What are Runaway Projects?
30–40 percent IT projects
• Exceed schedule, budget
• Fail to perform as specified
What are the types of system failure?
• Fail to capture essential business requirements
• Fail to provide organizational benefits
• Complicated, poorly organized user interface
• Inaccurate or inconsistent data
What indicates Poor Project Management?

How is Communications implemented in Project Management?
• Necessary information is gathered in a timely manner and is complete and accurate
• Project information is disseminated frequently and is an accurate representation of the project
• Members of the project team have current information
• Capture and record important project information in a central information repository
How is Change Management implemented in Project Management?
• Formal processes to ensure quality control and management buy-in
• Changes in business process, scope, budget, resources, timeframes, etc.
How is Stakeholder Management implemented in Project Management?
• Identify all the relevant stakeholders and understand their interest or role
• Understand and manage the expectations, involvement, and communication of stakeholders
What consists of Social Media Providers?
• Facebook, YouTube, LinkedIn, Twitter, Instagram, TikTok, and many others
• Attracting, targeting demographic groups.
• Popularity constantly changing
What are Users?
Individuals and Organizations.
What are Providers’ Functions?
• Develop and operate custom, proprietary, social networking application software.
• Procedures for creating content, managing user responses, removing obsolete or objectionable content, and extracting value from content.
What is Content Data?
data and responses to data contributed by users and sponsors.
What is Connection Data?
data about relationships.
What is Special Case: Internal Organizational Social Media?
• Using SharePoint for wikis, discussion board, photo sharing.
• Fine line between social media and collaboration tools
What is Sales and Marketing?
Customers craft their own relationship, able to search content, contribute reviews and commentary, ask questions, create user groups, etc.
What is Customer Service?
Relationships emerge from joint activity, customers have as much control as companies.
Product users freely help each other solve problems.
What is Manufacturing and Operations?
Business to Consumer communications.
Crowdsourcing
What is Human Resources?
Recruiting
Knowledge Management
What is Synthetic “Friends”?
Army of bots for company social media inflates follower count.
What is “click farms”?
Form of click fraud.
Large group of low-paid workers hired to click on paid advertising links for the click fraudster.
What indicates Problems from external sources?
Junk and crackpot contributions
Inappropriate content
Unfavorable reviews
How to Earn Money from Social Media?
Transform interactions with customers, employees, and partners into mutually satisfying relationships with them and their communities.
Advertising in Social Media is what?
• Pay-per-click
• Use increases value
• Conversion rate
What is Conversion Rate in social media?
-Frequency someone clicks on ad makes a purchase, “likes” a site, or takes some other action desired by advertiser.
What is Freemium in social media?
Offers users a basic service for free, and then charges a premium for upgrades or advanced features
What is Influence / Following (Blogs and Posts)?
• Focus on returning visitors
• Free ‘stuff’ and cash for promoting goods and services. ($$ for followers)
• Affiliate commissions, sponsored content, etc.
How you change change communication channels in social media?
• Employees can bypass managers and post ideas directly for CEO to read.
• Quickly identify internal experts to solve unforeseen problems
How you Develop and publicize social media policy?
• Delineate employees’ rights and responsibilities.
• Inappropriate use and/or content
• Index to 100 different policies at Social Media Today.
What is Corporate Risk in social media?
• Threats to information security, increased organizational liability, decreased employee productivity
• Seemingly innocuous comments inadvertently leak information used to secure access to organizational resources.
• Mutinous movements
What are Location Analytics?
Ability to gain business insight from the location (geographic) component of data
◦ Mobile phones
◦ Sensors, scanning devices
◦ Map data
What is Geographic information systems (GIS)?
◦ Ties location-related data to maps
◦ Example: For helping local governments calculate response times to disaster
What are the process for Loading a Data Warehouse?
EXTRACT
◦ Obtain data from operational, internal and external databases.
TRANSFORM
◦ Cleanse and translate data
◦ Normalize
LOAD
◦ Organize and relate data.
◦ Catalog data using metadata.
What is ESS: decision support for senior management?
Help executives focus on important performance information.
Data Sources
•Internal data from enterprise applications
•External data such as financial market databases
•Drill-down capabilities
What is Business Performance Management (BPM)?
Translates firm’s strategies (e.g., differentiation, low-cost producer, scope of operation) into operational targets
KPIs developed to measure progress toward targets
What is Balanced Scorecard Method?
Measures outcomes on multiple dimensions
•Financial
•Business process
•Customer
•Learning and growth
Key performance indicators (KPIs) measure each dimension