3301 Exam 3
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
The onset of a given epidemic is indicated by a sharp rise in the number of cases reported daily over a brief interval. This indicates that the mode of transmission is:
A) a common source
B) host to host
C) insect vector
D) mechanical vector
A) common source
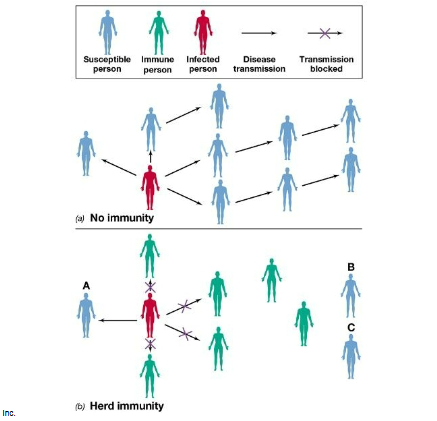
Which of the following is an example of herd immunity?
A) Brucellosis is no longer found in farm animals in the US
B) If 70% of the population is immunized against polio, the disease will be essentially absent from the population
C) Federal law requires that all cattle not immune to anthrax be destroyed
D) All farm animals used for food must be immunized against all the common agents of disease that infect humans
B) If 70% of the population is immunized against polio, the disease will be essentially absent from the population
Which of the following shows the correct relationship among the epidemiology terms listed?
A) prevalence > incidence > mortality
B) incidence > prevalence > mortality
C) mortality > morbidity > prevalence
D) mortality > incidence > prevalence
A) prevalence > incidence > mortality
Treponema pallidum is extremely sensitive to temperature changes and low moisture, thus it is transmitted:
A) by intimate person-to-person contact
B) by fomites
C) by vectors
D) through common sources such as food and water
A) by intimate person-to-person contact
Which stage of an acute infectious disease occurs between the time the organism begins to grow in the host and the appearance of disease symptoms?
A) acute period
B) decline period
C) infection
D) incubation period
D) incubation period
Influenza pandemics occur cyclically because:
A) less than 100% of the population is immunized
B) new strains emerge due to reassortment between bird, swine, and human variants
C) the vector is seasonal
D) there are environmental reservoirs that release the virus during particular seasons
B) new strains emerge due to reassortment between bird, swine, and human variants
Which group of organisms is difficult to control through immunization because of their rapid and unpredictable genetic mutations?
A) vector-borne organisms
B) RNA viruses
C) Archaea
D) DNA viruses
B) RNA viruses
Blood and lymph have the following in common EXCEPT:
A) nucleated cells
B) proteins
C) RBCs
D) none
C) RBCs
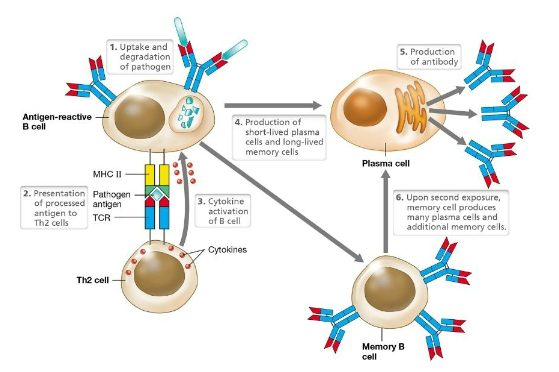
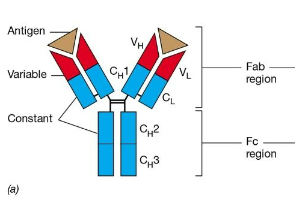
Immunoglobulins are produced by B cells and are also known as:
A) antibodies
B) antigens
C) bacteria
D) pathogens
A) antibodies
Which of the treatments listed below would be most effective for a patient with a genetic defect that causes severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID), a condition in which there is a severe deficiency in B and T lymphocytes?
A) intravenous antibiotics
B) bone marrow transplant
C) multiple immunizations
D) repeated doses of antisera
B) bone marrow transplant
Cells that can engulf foreign particles, and can ingest, kill, and digest most bacterial pathogens are called:
A) red blood cells
B) phagocytes
C) reticulocytes
D) resistant cells
B) phagocytes
Adaptive immunity occurs when:
A) death results from pathogen infection
B) the innate immune response is overly effective
C) a broad, rapid response is needed to a wide range of pathogens from the body regardless of the specific type of pathogen
D) the innate immune response fails to eliminate pathogens in the body and virulent infections persist after the initial innate defense response
D) the innate immune response fails to eliminate pathogens in the body and virulent infections persist after the initial innate defense response
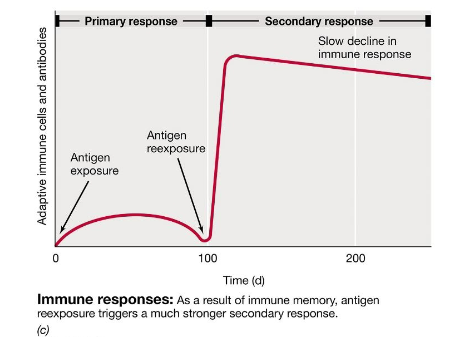
The rapid increase in adaptive immunity after a second antigen exposure is called:
A) immune memory
B) specificity
C) tolerance
D) immune memory, specificity, and tolerance
A) immune memory
Which of the following are molecular mediators of inflammation?
A) immunoglobulins
B) lipopolysaccharide
C) erythrocytes
D) both chemokines and cytokines
D) both chemokines and cytokines
Which of the following interact with toll-like receptors (TLRs)?
A) bacterial LPS
B) immunoglobulins
C) major histocompatibility complex proteins
D) none of these
A) bacterial LPS
The first cell type active in the innate immune response is usually a(n):
A) phagocyte
B) erythrocyte
C) fibroblast
D) antibody
A) phagocyte
_________ is the acquired inability to mount an adaptive immune response against self:
A) memory
B) specificity
C) tolerance
D) immunogenicity
C) tolerance
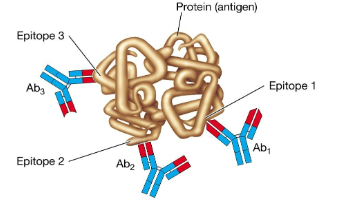
The part of the antigen recognized by the antibody or TCR is called the:
A) epitope
B) antigen-binding site
C) antigenic complex
D) light chain
A) epitope
Antigen-presenting cells present antigens to:
A) B lymphocytes
B) T lymphocytes
C) dendritic cells
D) neutrophils
B) T lymphocytes
Which of the following does NOT influence immunogenicity?
A) the routes of administration
B) foreign nature of immunogen to host
C) solubility
D) all of these influence immunogenicity
D) all of these influence immunogenicity
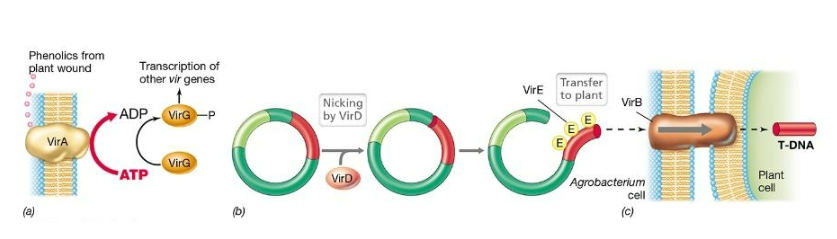
Which bacterium contains a large Ti plasmid and causes crown gall disease in plants?
A) Agrobacterium rhizogenes
B) Agrobacterium tumefaciens
C) Aliivibrio fischeri
D) Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens
B) Agrobacterium tumefaciens
What is the role of the vir genes on a Ti plasmid?
A) to cause crown gall disease (virulence)
B) to confer resistance to viral infection
C) to initiate replication of the plasmid
D) to allow T-DNA transfer
D) to allow T-DNA transfer
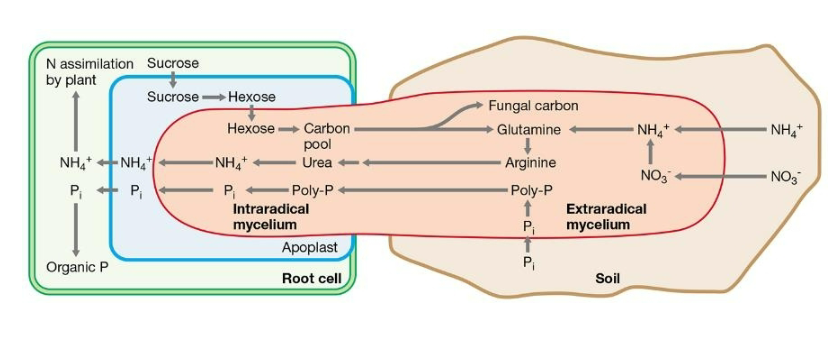
How do arbuscular mycorrhizae (AM) help plants obtain more nutrients from the soil?
A) By-products of AM metabolism serve as primary nutrient sources for the plants
B) The AM increase the total surface area to absorb more nutrients
C) The hyphae develop as specialized nodules that directly produce nutrients for the plant
D) Signaling molecules in the plant are passed to the AM to initiate electron flow, which is in turn used to create ATP
B) The AM increase the total surface area to absorb more nutrients
Which of the following is a common benefit of a microbe-plant symbiosis?
A) increased nutrient availability only
B) decreased pathogen colonization only
C) increased affinity for carbon dioxide
D) increased nutrient availability and decreased pathogen colonization
D) increased nutrient availability and decreased pathogen colonization
In mycorrhizal mutualisms between plant roots and fungi…
A) the plant supplies carbohydrates to the fungus and the fungus supplies phosphorus and nitrogen to the plant
B) the plant supplies water to the fungus and the fungus supplies essential amino acids to the plant
C) the plant protects the fungus from predation and the fungus supplies carbohydrates to the plant
D) the fungus infects the plant roots, stimulating plant growth through myc factors that act as growth hormones in the plant
A) the plant supplies carbohydrates to the fungus and the fungus supplies phosphorus and nitrogen to the plant
Clostridium difficile infections most often occur…
A) following antibiotic treatment
B) following a fecal transplant
C) following a dietary change
D) following the use of a new probiotic
A) following antibiotic treatment
Which of the following is a benefit of studying the human microbiome?
A) It may allow for the development of personalized medical treatments
B) It may allow for more finely targeted probiotics
C) It may allow for increased recognition of disease biomarkers
D) All of these answer choices are possible benefits
D) All of these answer choices are possible benefits
Normal microbiota helps to _______ colonization of pathogenic organisms…
A) promote
B) prevent
C) maintain
D) accelerate
B) prevent
Which of the following environmental and host factors influence the composition of the resident microbiota on the skin?
A) age
B) personal hygiene
C) weather
D) age, personal hygiene, and weather
D) age, personal hygiene, and weather
Gut microbiota is known to be linked with
A) obesity and inflammatory bowel syndrome
B) obesity, but not with inflammatory bowel syndrome
C) inflammatory bowel syndrome, but not with obesity
D) inflammatory bowl syndrome and Crohn’s disease only, but not with ulcerative colitis
A) obesity and inflammatory bowel syndrome
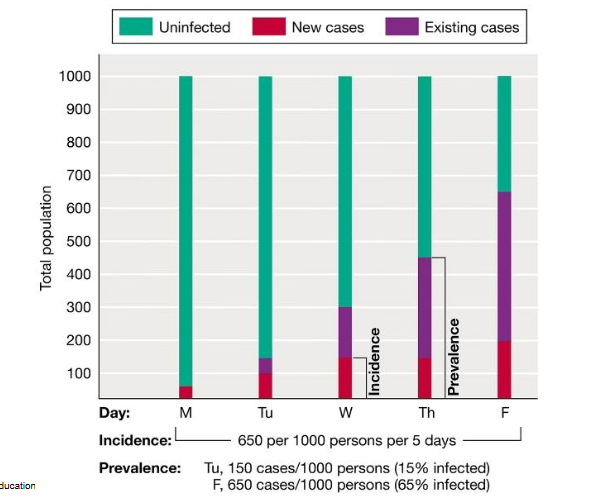
The prevalence of a disease is…
A) the total number of existing cases only
B) the total number of new cases only
C) the total number of both new and existing cases
D) the frequency of new cases relative to the existing cases
C) the total number of both new and existing cases
A disease that primarily infects an animal but is occasionally transmitted to humans is called a(n)…
A) emerging pathogen
B) emergence transmission
C) vector
D) zoonosis
D) zoonosis
Diseases can be transmitted…
A) by inanimate vehicles
B) by living vectors
C) person to person
D) by inanimate vectors
E) by a, b, and c
E) by a, b, and c
How do zoonotic diseases emerge?
A) the infectious agent is not propagated in an animal
B) the environment is not suitable for the propagation and transfer of the agent
C) a new susceptible host species is present
D) all of the above
C) a new susceptible host species is present
Which of the following can serve as a disease reservoir?
A) raccoons
B) silverware
C) soil
D) humans
E) only a, c, and d
E) only a, c, and d
The major cause of death in developing countries is infectious diseases, such as malaria. In developed countries the major causes are…
A) infectious diseases, such as cholera
B) non-infectious diseases, such as cancer
C) injuries
D) both a and c
B) non-infectious diseases, such as cancer
Which of these factors result(s) in the emergence of new pathogens?
A) human behavior
B) economic development
C) international travel
D) all of the above
D) all of the above
Which disease has been essentially eliminated as a result of rigorous vaccination and quarantining procedures?
A) bubonic plague
B) encephalitis
C) malaria
D) smallpox
D) smallpox
For individuals planning a trip to another country, such as Vietnam, which organization is the best source for information on which vaccines might be necessary?
A) Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
B) National Institutes of Health
C) National Safety Council
D) Tourist Travel Bureau
A) CDC
Why is it more difficult to eradicate a disease if the reservoir is a wild animal?
A) it involves destruction of wild animals, which can have a serious impact on biodiversity
B) wild animals are more difficult to immunize than domestic animals
C) chemicals used to eradicate the reservoir animals may adversely affect nonreservoir species
D) all of the above
D) all of the above
In the 2009 H1N1 swine flu pandemic, the influenza virus underwent a(n) _________, which made it especially deadly. Mortality of individuals _______ than 50 years of age was MOST common.
A) antigenic drift / older
B) antigenic drift / younger
C) reassortment / older
D) reassortment / younger
D) reassortment / younger
A disease outbreak that has a large number of cases diagnosed in a very short period of time is characteristic of…
A) a common source epidemic
B) a person-to-person epidemic
C) a pandemic
D) none of the above
A) a common source epidemic
Since 2007, the number of reported cholera cases has
significantly increased. The MOST common cause for outbreaks
of Vibrio cholerae is ________, although the 2010 outbreak in
Haiti was likely due to ________.
A) accidental transmission from another country / poor sanitation and
disposal of waste
B) accidental transmission of infected waste / infected
imported food
C) poor sanitation and disposal of waste / accidental
transmission from another country
D) poor sanitation and disposal of waste /
transmission of infected water via a hurricane
C) poor sanitation and disposal of waste / accidental transmission from another country
More than two-thirds of people infected with HIV in
the world live in the ________ region of Africa, and
the ________ are more commonly infected than
________.
A) Saharan / men / women
B) Saharan / women / men
C) sub-Saharan / men / women
D) sub-Saharan / women / men
D) sub-Saharan / women / men
Incidence and Disease Prevalence Diagram
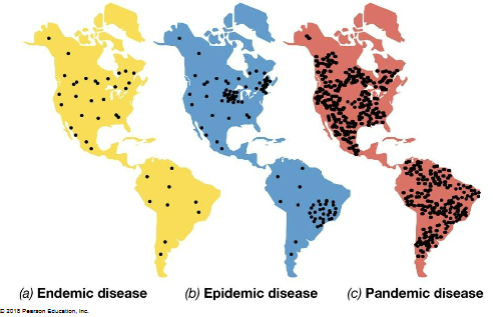
Endemic, epidemic, and pandemic diagram
Herd immunity diagram
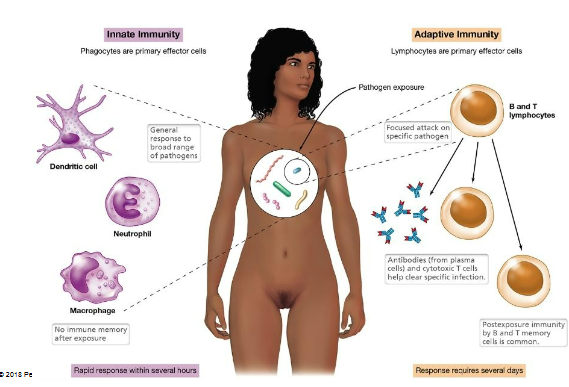
Immunity Diagram
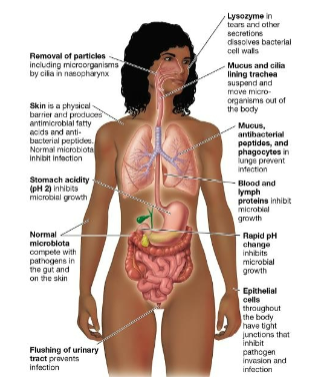
Barriers to infection diagram
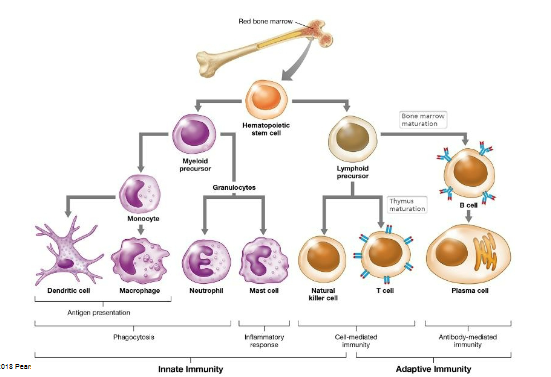
Lineage of immune response cells diagram
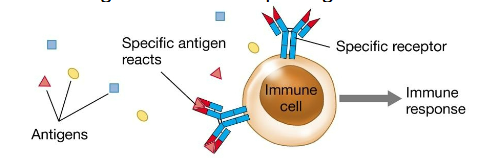
Specificity diagram
Graph of primary and secondary immune response strengths
Epitope diagram
B cell and T cell interaction
Immunoglobulin structure diagram
True or False: the two most common causes of laboratory accidents are ignorance and carelessness
TRUE
Healthcare-associated infections are also called…
A) opportunistic pathogenic infections
B) attenuated infections
C) virulent infections
D) nosocomial infections
D) nosocomial infections
Laboratories handling hazardous materials must practice ALL of the following EXCEPT…
A) restricting access to laboratory workers and essential support only.
B) periodically practicing mouth pipetting if mechanical pipetting devices are dysfunctional.
C) effective decontamination procedures.
D) vaccination of personnel working with hazardous infectious agents.
B) periodically practicing mouth pipetting if mechanical pipetting devices are dysfunctional
Which of the following has the highest level of containment and is where drug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis must be studied?
A) BSL-1
B) BSL-2
C) BSL-3
D) BSL-4
D) BSL-4
Which of the following healthcare procedures may unintentionally introduce microorganisms into the patient?
A) catheterization
B) surgery
C) spinal puncture
D) all of the above
D) all of the above
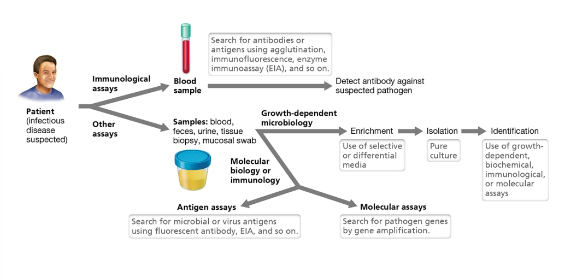
Laboratory identification of microbial pathogens diagram
The antimicrobial susceptibility of a bacterium can be determined by
A) the disk diffusion test.
B) the tube dilution technique.
C) determining the minimum inhibitory concentration.
D) all of the above.
D) all of the above
Antibiogram reports are useful for ALL of the following reasons EXCEPT to
A) monitor control of known pathogens.
B) track the emergence of a new pathogen.
C) identify antibiotic resistance.
D) determine the pathogen's origin.
D) determine the pathogen’s origin
Decisions on appropriate antimicrobial drug resistance must be made on a case-by-case basis for the following pathogens EXCEPT
A) those that are life-threatening.
B) those that require bacteriocidal rather than bacteriostatic drugs to prevent disease.
C) pathogens for which effective antimicrobial treatment exists based on current experience and practices.
D) pathogens for which antimicrobial resistance is common.
C) pathogens for which effective antimicrobial treatment exists based on current experience and practices
Media that can differentiate organisms based on colony appearance are
A) characteristic.
B) selective.
C) differential.
D) selective and differential
C) differential
Aseptic technique in obtaining clinical specimens is essential to ensure bacterial presence is due only to
A) normal flora.
B) infection.
C) contamination.
D) none of the above.
B) infection
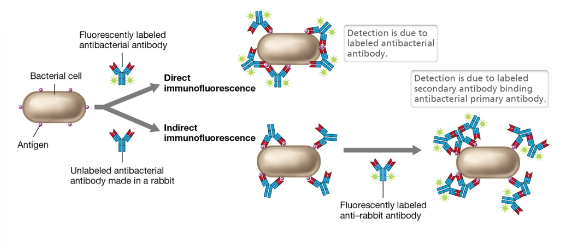
Direct and indirect immunofluorescence diagram
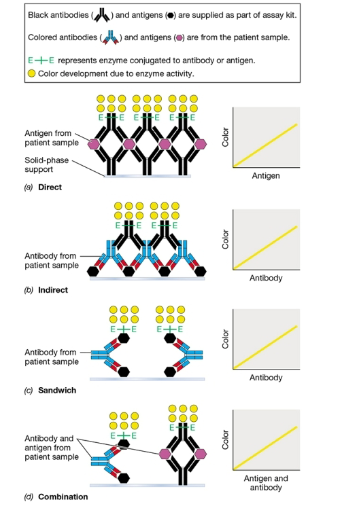
ELISA types diagram
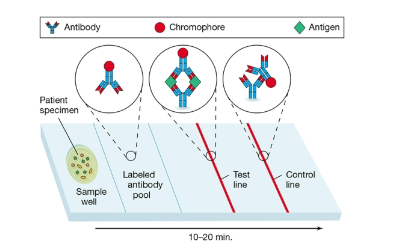
Rapid assay diagram
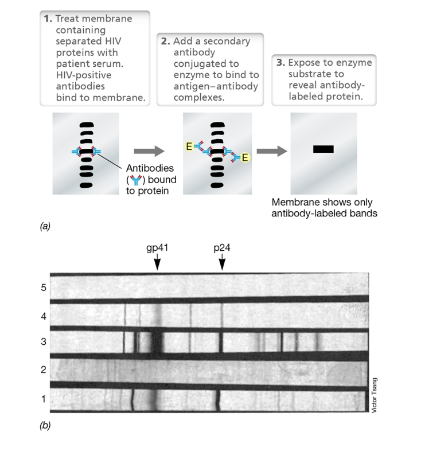
Western Blot diagram
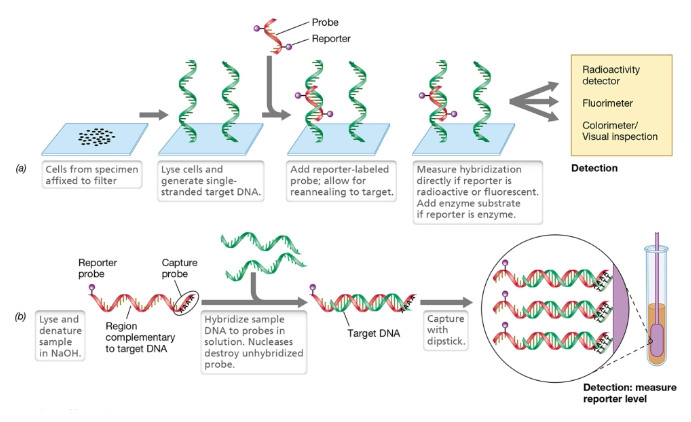
Nucleic acid probe diagram
True or False: If an individual is infected with a pathogen, the antibody titer to that pathogen will decrease.
FALSE
Advantages of nucleic acid over protein-based tools to detect pathogens include which of the following?
A) Nucleic acid probes are more specific than antibodies because they detect single nucleotide differences in DNA sequences.
B) Nucleic acids are more stable than proteins at high temperature and pH.
C) Nucleic acids are more resistant to organic solvents/chemicals than proteins.
D) Both a and b are correct.
D) Both a and b are correct
The presence of an antibody in a body is an indicator of
A) previous infection to a pathogen.
B) a recent immunization.
C) either a or b.
D) none of the above.
C) either a or b
Advantages of qPCR over traditional end-point PCR include
A) determining the amount of target DNA present in an original sample.
B) eliminating the need for agarose gel electrophoresis.
C) continuous monitoring.
D) all of the above.
D) all of the above
Which assay would MOST likely be used to determine whether a high antibody titer is due to Staphylococcus aureus infection?
A) agglutination
B) ELISA
C) qPCR
D) Western blot
D) Western blot
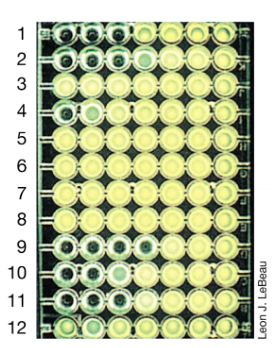
Antibiotic susceptibility testing (MIC) diagram
An inactivated toxin, such as that found in the tetanus vaccination, is called a(n)
A) anti-toxin.
B) toxoid.
C) toxin.
D) toxemia.
B) toxoid
The advantages of DNA vaccines include
A) no possibility of infection.
B) activation of T and B cells.
C) targeted immune response.
D) all of the above.
D) all of the above
There are vaccines for diseases caused by
A) bacteria.
B) viruses.
C) protozoa.
D) fungi.
E) a and b.
F)a, b, and c.
E) a and b
During the production of vaccines, which of the following is NOT a measure taken to reduce the risk that the vaccine will cause an infection or other adverse reactions?
A) converting exotoxins to toxoids
B) killing pathogens with heat
C) diluting pathogen concentrations so they are less virulent
D) killing pathogens with phenol
C) diluting pathogen concentration so they are less virulent
Which of the following are characteristics of attenuated viral vaccines?
A) They provide short-lived immune responses.
B) They are easy to store and maintain their potency for long periods of time.
C) They provide long-lasting T cell–mediated immunity.
D) They do not develop long-term memory responses.
C) They provide long-lasting T cell-mediated immunity
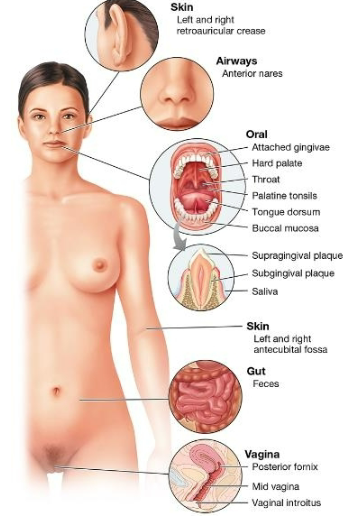
Areas of human (female) microbiome diagram
Human GI microbiome diagram
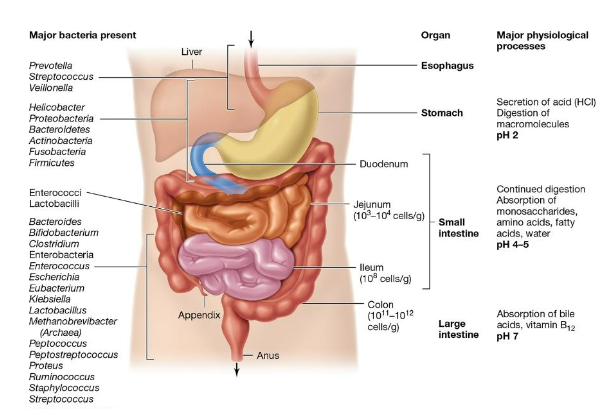
Skin bacteria diagram
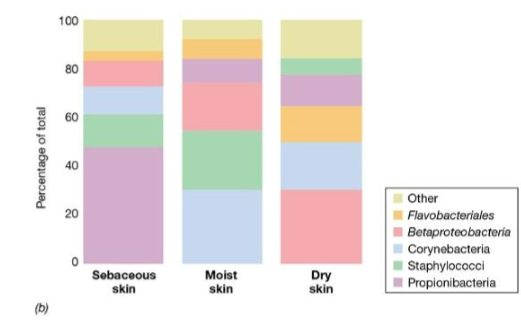
Gene diversity of gut microbiome in different patient populations
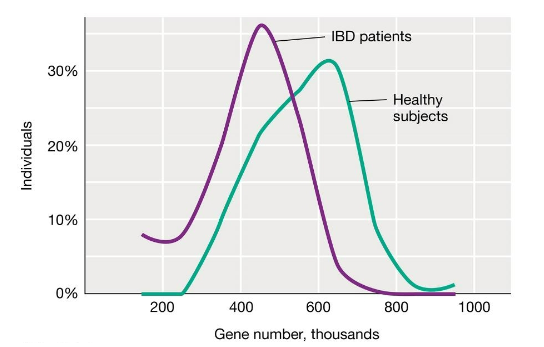
Connection between gut microbiota and obesity in mice diagram
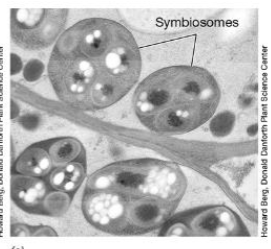
Symbiosomes diagram
Nutrient exchange in mycorrhizae diagram
Mechanism of gene transfer in crown gall disease of plants
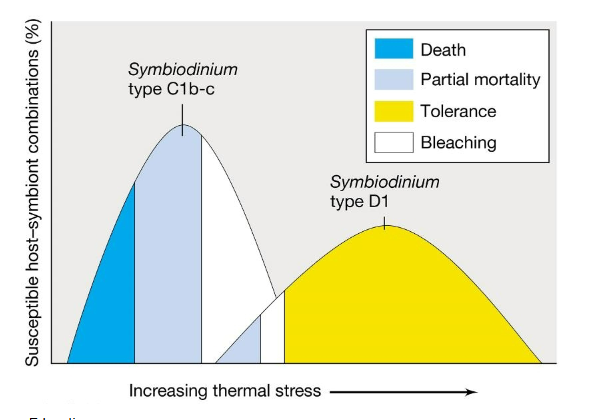
Stress tolerance of coral species diagram