lec 2 - cell structure
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
what type of lipids make up the lipid bilayer
mostly phospholipids (75%)
glycolipids (5%)
cholesterol (20%)
plus small amounts of other lipids e.g. PIP2
what is the lipid bilayer permeable to:
non polar
uncharged
lipid soluble
impermeable to:
ions
large, charged molecules
water soluble
needs a channel or transporter proteins specific to solute
plasma membrane proteins
proteins needed for transport (channels, transporters), signalling (receptors), and connection (ECM/other cells)
integral - anchored to membrane and peripheral - on inside or outside of membrane, may attach to integral proteins or phsopholipids
fluid mosaic model
membrane is dynamic
lipids can move within their monolayer
proteins can move, be added, taken away
membrane components reflect function of the cell
passive transport
requires concentration/electrochemical gradient
lipid soluble/nonpolar/uncharged

facilitated transport
requires concentration gradient
water soluble/polar/charged
uses channel/pore or transport/carrier

active transport
moves against concentration gradient
requires ATP either directly or indirectly

bulk transport
large molecules or large volumes of small molecules
mediated by vesicles
cytoskeleton functions
helps maintain cell shape and structure
helps maintain internal organisation
essential for: cell division, cell movement, vesicle movement within cells
dynamic - changes to meet needs of cell
microfilament structure
actin
~7nm
two protofilaments twisted into a helix
assembled into large filaments, networks, 3D structures
microfilament function
movement - muscle contraction
cell junctions - adherens junctions
cell structure - cortical network
microvilli - increase surface area
microtubules structure
tubulin
~25nm diameter
interacts with motor proteins
organelle movement and vesicle trafficking
motility - cilia and flagella
microtubule function
organelle movement and vesicle trafficking
motility - cilia and flagella
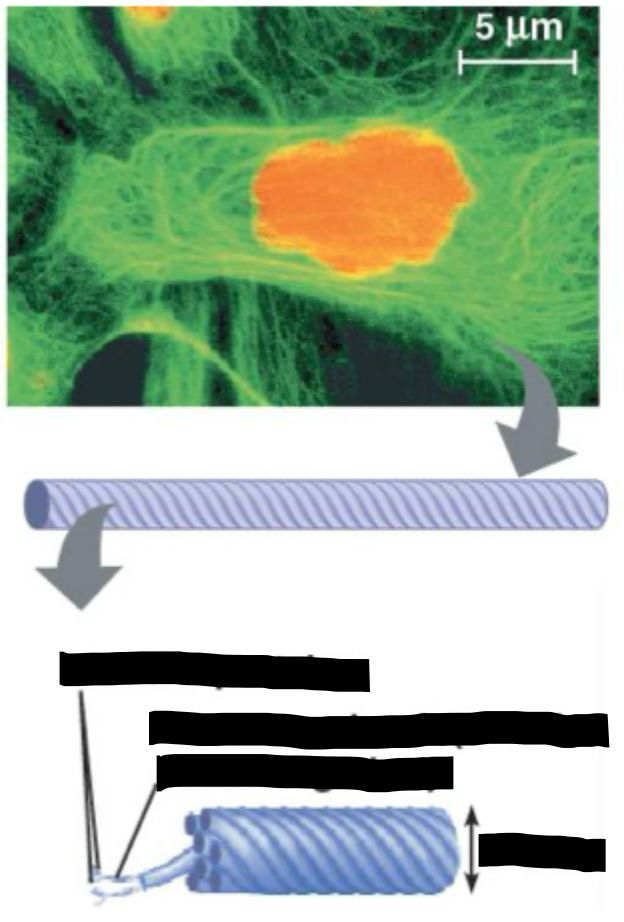
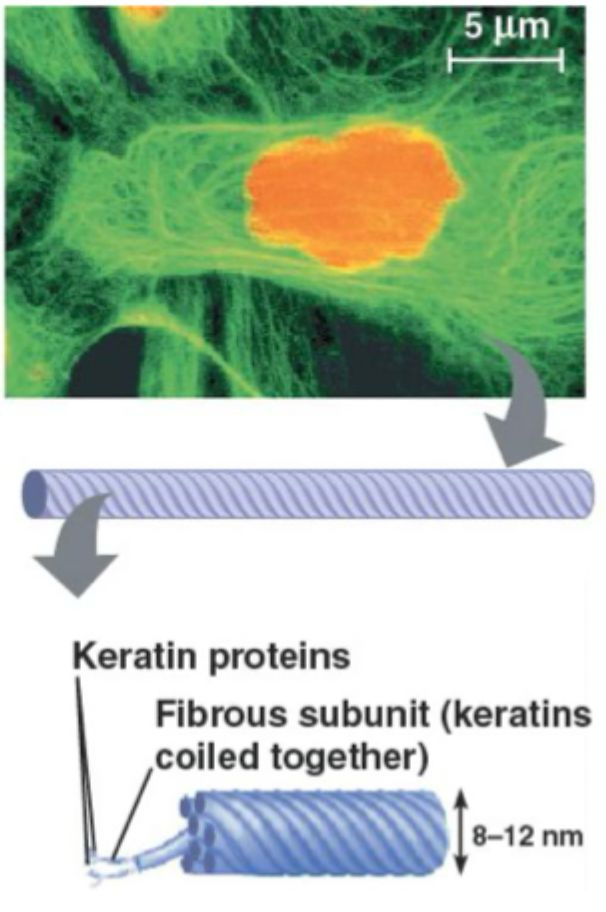
intermediate filaments structure
~10nm
50+ types made of various proteins
cytokeratins mist abundant in GI/renal epithelium
cytokeratin - support network within cell, cell junctions
intermediate filament function
support network within cell
cell junctions - desmosomes and hemidesmosomes - resist shearing forces
what are organelles
subcellular structures with specific functions
often membrane bound
form defined areas and environments within the cell
nucleus
usually one per cell
control centre of the cell
contains most of the cell's DNA - euchromatin and heterochromatin
contains nucleolus - makes rRNA and ribosomal subunits
surrounded by nuclear envelope - double membrane, continuous with ER
endomembrane system
interconnected system that includes:
endoplasmic reticulum
golgi apparatus
vesicles
endomembrane system function
modify, package and move proteins and lipids
smooth ER
lacks ribosomes on surface
synthesises lipids
metabolises carbohydrates
detoxification processes
stores calcium ions (used as a signal within the cell)
rough ER
covered in ribosomes on outer surface
role in protein synthesis - proteins enter lumen of rER, proteins are modified, folded and packaged into vesicles, transported to Golgi
Golgi apparatus/complex
series of membrane sacs and vesicles
vesicles from ER arrive at cis face
proteins modified, glycosylated, sorted into vesicles
vesicles leave from trans face
vesicles
membrane bound
move via motor proteins walking along microtubules
transport vesicles - move contents within cell
secretory vesicles - move contents out of cell
mitochondria
site of cellular respiration
double membrane structure
number per cell depends on energy demands
generate energy - consume glucose and oxygen, produce CO2, water and energy: ATP
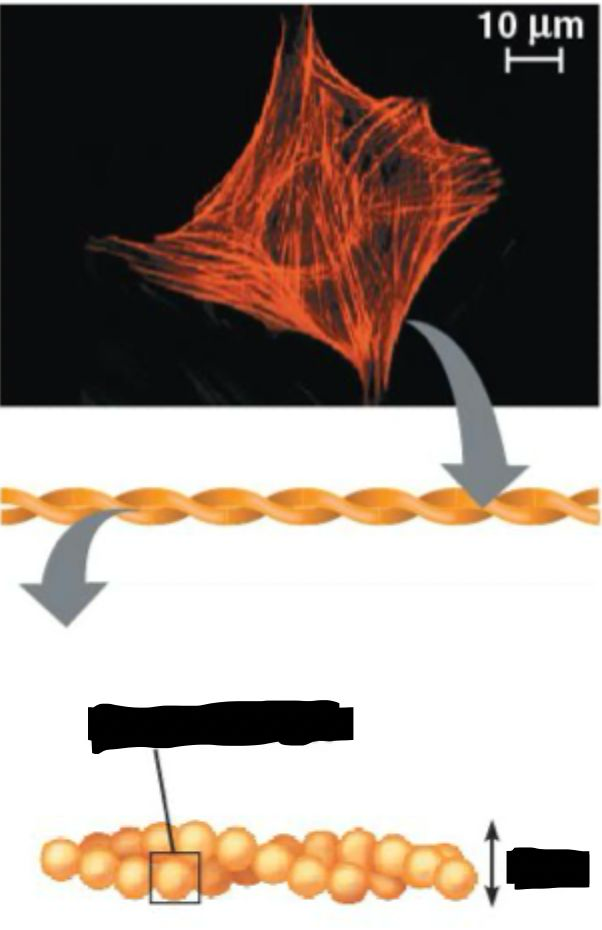
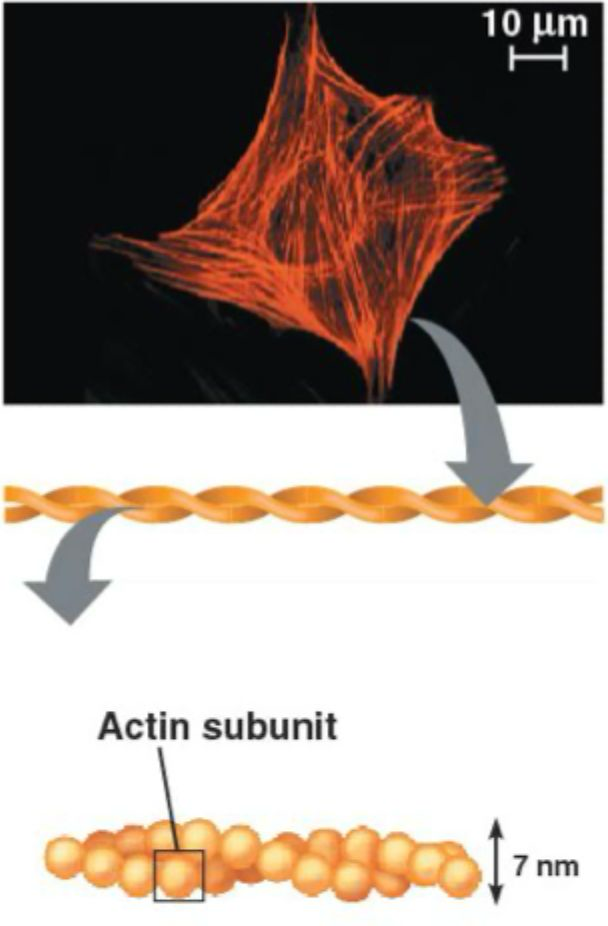
microfilament
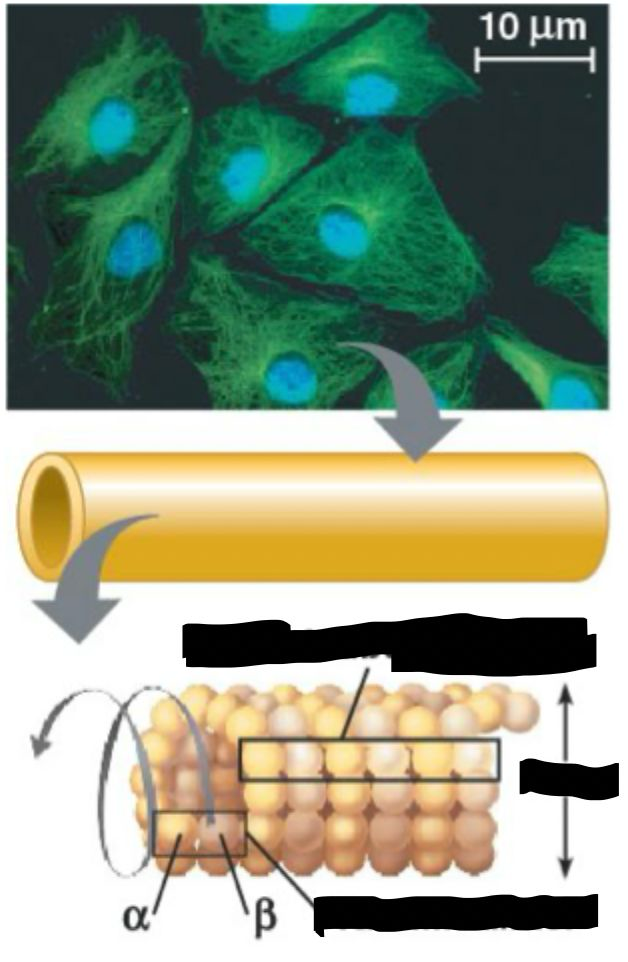
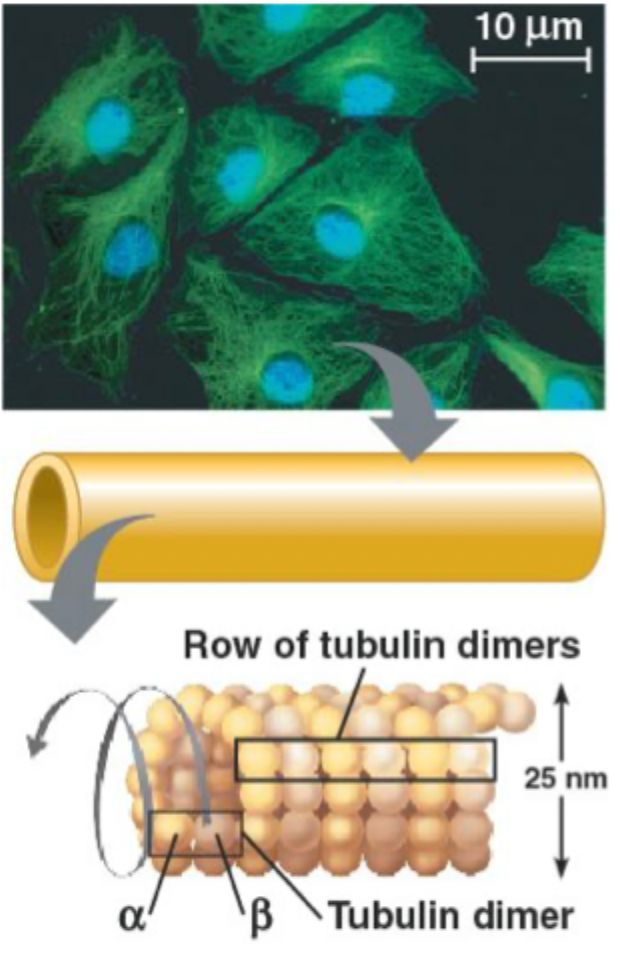
microtubules
intermediate filaments