Print Media Production test 1
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Sources of fibers for papermaking
wood, cotton, recycled paper, elephant poop, bamboo, banana, algae
How is paper weight measured?
in pounds, Lb
Pre-consumer vs. Post-consumer paper
pre-consumer: Any paper that has not been used by the general public, like leftover paper from the mill, trimmings from the printing process, and damaged paper.
Post-consumer: includes paper that has been printed, sold, used, and discarded by the consumer. Newspapers, cardboard boxes, copy paper, notebooks, etc
What is affected by the grain of the paper?
Grain effects folding, scoring, and tearing folds. and it tears easily parallel to the grain.
Linen paper
textured office or resume paper, looks like a linen criss cross pattern.
Laid paper
Lines on paper look laid next to each other, more organized.
Coated paper
glossy and a little shiny
Felt paper
soft and similar to fabric
Smooth paper
The surface feels uniform without bumps or irregularities. Threads are tightly woven, creating a sleek appearance.
The advantages and disadvantages of: Digital/On demand
Advantages:
-Economical for short runs (1-1000)
-Can change info during a print run for
-personalization from database (variable data)
Disadvantages:
-Limited paper types and weights
-Usually small press size
-Not economical for long runs
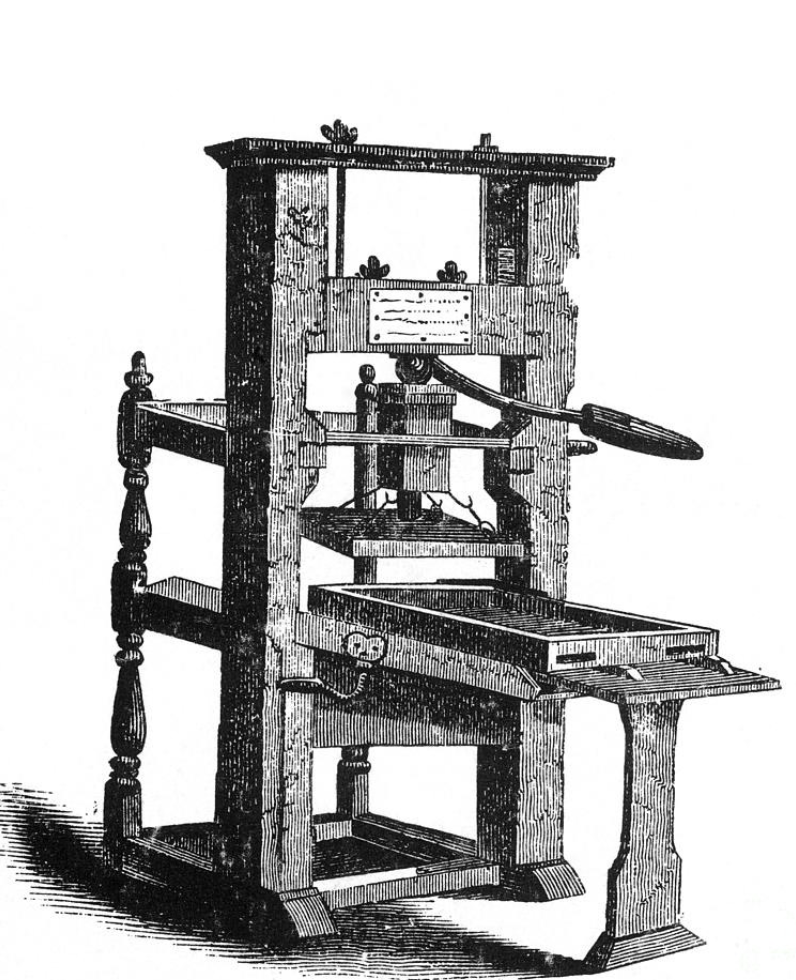
The advantages and disadvantages of :Letterpress
Advantages of letterpress:
-Capable of printing fine detail.
-Easily adjustable
-Can print on a wide range of material thickness
from cardboard to rice paper.
Disadvantages of letterpress:
-Can be more expensive than other printing methods.
-Considerably slower process than other printing
methods.
-Does not print smooth, flawless, large areas of ink
coverage.
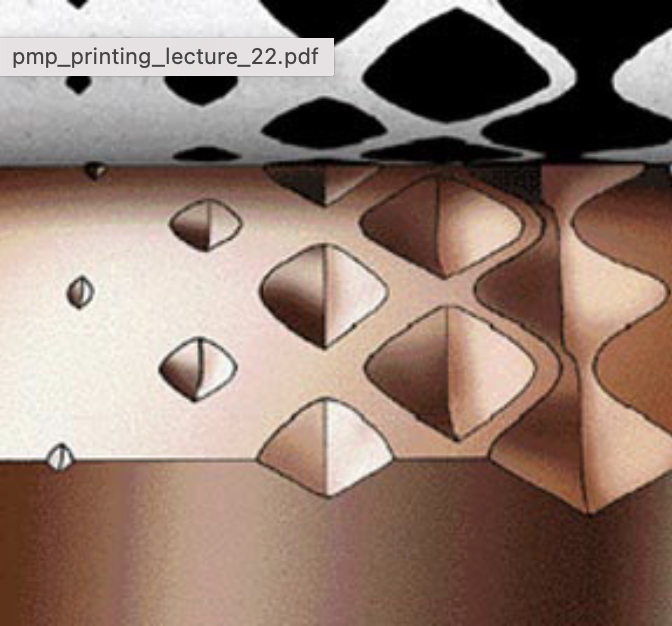
The advantages and disadvantages of :Gravure
Advantages of gravure printing:
• Prints very fine detail.
• Prints smooth, continuous tone.
• Prints at very high speed.
• Plates last for more than a million impressions.
• Can print on very thin/delicate papers.
• Can reproduce a wide dynamic range or colors.
Disadvantages of gravure printing
• Very expense.
• Takes a long time to make the copper plates or drums.
• Only economical for print runs of 800 thousand or more.

The advantages and disadvantages of : Offset lithography
Advantages of offset lithography:
-Can be economical for short or long print runs.
-Can register colors nearly perfectly.
-plates can be made quickly.
-Inexpensive reusable plates.
-Excellent color consistency.
-Can print very fine line screens.
-Can print on wide variety of textures.
Disadvantages of o!set lithography:
-Web-fed press limits paper weights to 40-100 text.
-Sheet-fed prints more slowly than web-fed.

The advantages and disadvantages of :Flexography
Advantages:
• Can print on almost any surface, metal,
plastic, textiles,and cardboard.
• Opaque inks.
• Thick coverage.
• Fast print speed (usually web).
Disadvantages:
• Short plate life, because of high friction.
• Can not print great details because of
course line screen (120 max).
• Ink spreads.

What is the most common type of commercial printing?
Commercial Offset Lithography is a commonly used printing technique in
which the inked image is transferred (or “offset”) from a plate to a rubber
blanket, then to the printing surface.

A sheet fed press vs. A web fed press
Sheet fed — Paper is fed from stacks of flat sheets
Web fed — paper is on a large roll and is drawn through the press
Texture simple.
A reversed raised surface is inked and pressed to the surface of the paper to reproduce an image.
Letterpress

prints in large quantities with beautiful tone an detail that don't change - money, museum prints, food, magazine.
Most common printing process in which the image to be printed is recessed into a plate,
and the printing ink fills the holes and is transferred to the paper.
Gravure
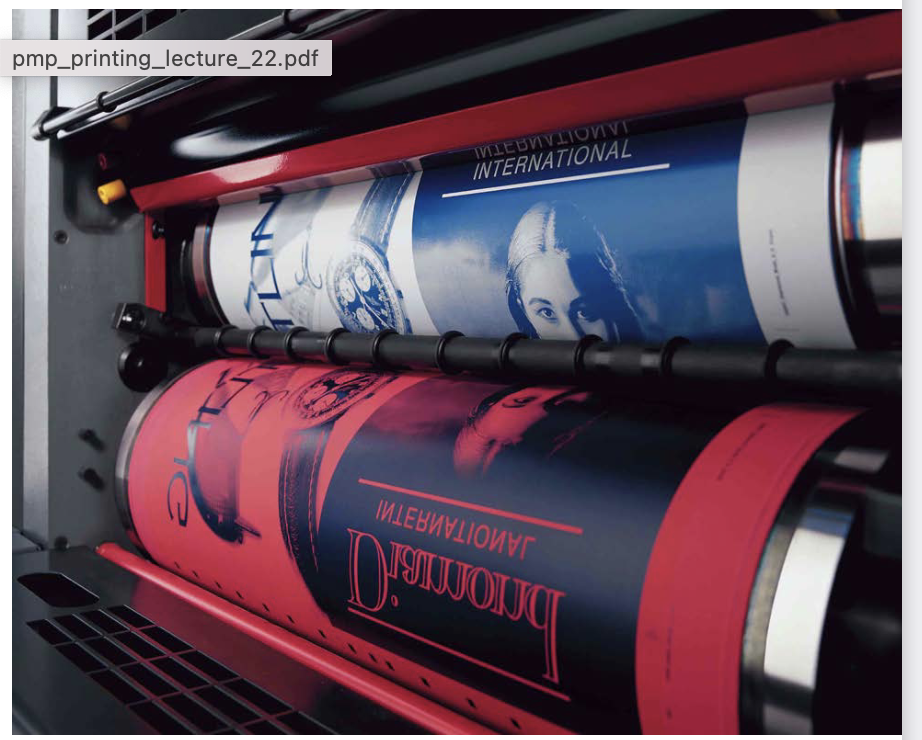

Most common printing technique world wide.
plate - rubber blanket - print
holds a different color ink on each blanket - cmyk
Offset lithography

printing that utilizes a flexible relief plate, inexspensive
ex- plastic bags, cardboard box
Flexography
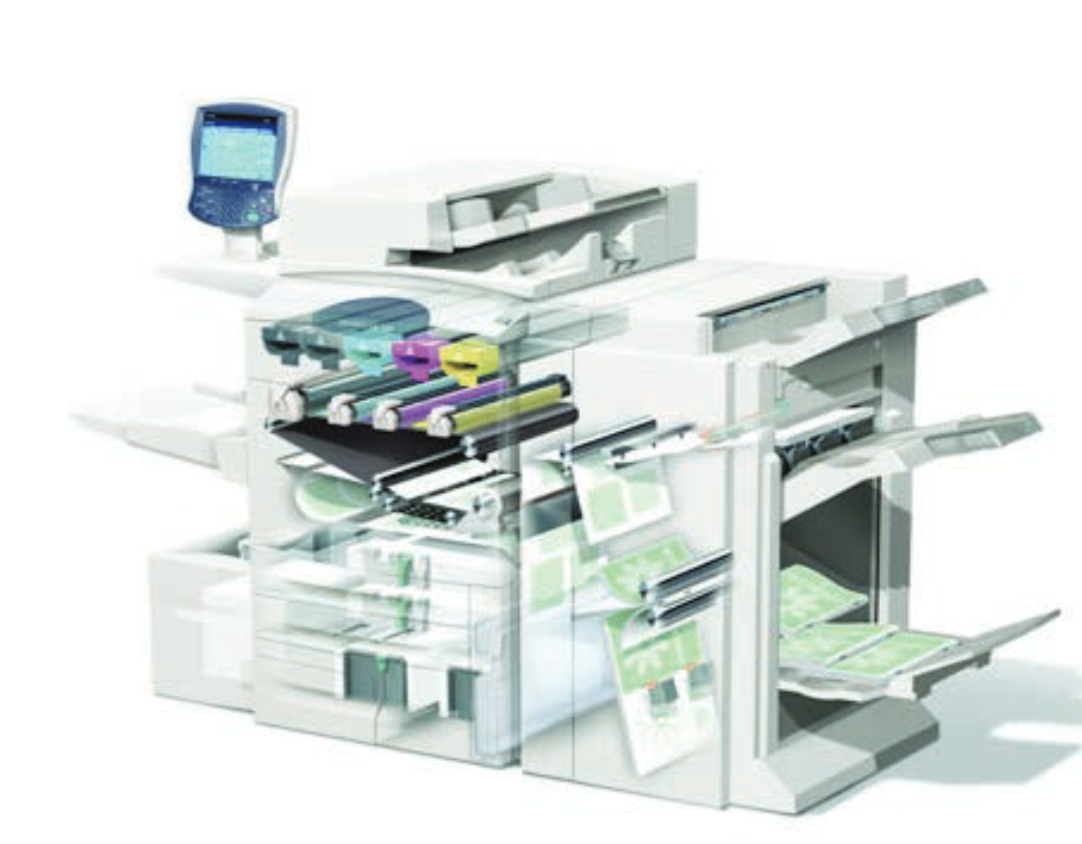

printing from a digital-based image directly to a variety of media without transferring the image to a plate. Commercial high-volume laser or inkjet printers.
ex- different names on email for college campus,
Digital/On demand
Additive vs. Subtractive colors
Additive Colors
• The primary additive colors are Red, Green, and Blue.
• Monitors show color in RGB.
• When all colors combine, you get white light.
Subtractive Colors
• The primary subtractive colors are Cyan, Magenta, and Yellow.
• Additive primaries are created by combining two of the subtractive primaries.
Ex. yellow and magenta make red.
Printing press colors are CMY(K=black)
• When all colors combine, you get black pigment.
Spot vs. Process color
There are two different color ink systems in commercial printing.
-Spot colors are special mix colors that are printed using one matched color of ink. This is how flat colors are printed.
• The Pantone Matching System is an example of
spot colors.
-Process colors are made up of the subtractive primaries
yellow, magenta, cyan with the addition of black CMYK
• Process colors are translucent and can be
overlaid to make many additional colors.
• This is how photographs and illustrations are
printed

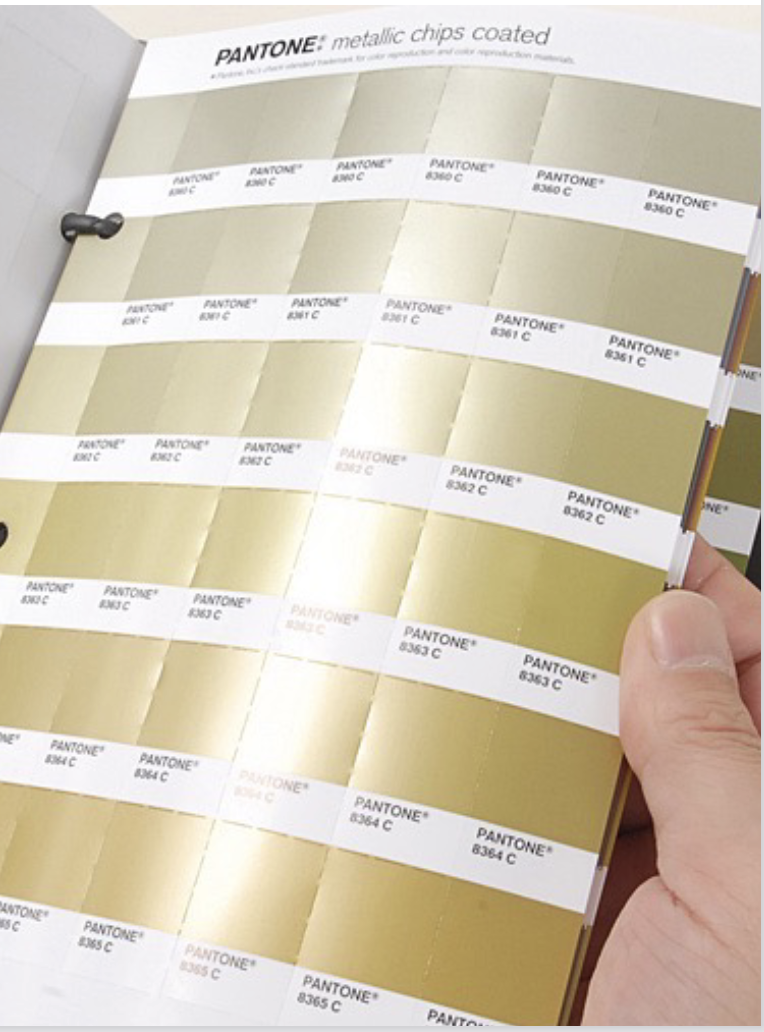
Pantone colors
A commercial printer mixes any combination of 18 base inks by using a
recipe which is generated by Pantone.
Ink swatch books or “chip books” have
multiple copies of the same colors
on tear out chips.
• Fan books have all color inks in one
category such as coated and uncoated.
• Pantone inks come in specialty colors
such as metallics, fluorescents, pastels.
Color viewing booths
Designers view press sheets under color viewing booths to make accurate
color corrections to printed work as the paper is being printed on a
commercial press.
How to measure light
Kelvin — The assigned numerical value of
color emitted by a light source.
Color temperatures are degrees Kelvin — ̊ K
Why is a folding dummy helpful?
Signatures can look complicated and be confusing at first. When in doubt,
make a miniature folding dummy for your benefit and to show the printer how
your piece is supposed to back up.

Parts of a layout
Live Area
• The part of the page that will print.
All information inside this area
prints.
Crop Marks
• Thin lines placed at the corners of
a layout to indicate where the
paper should be trimmed after
printing. They define the trim area
Slug Area
• The slug area is every part of a
press sheet that will be cut off of
the final print. This includes any
bleeding image content; all crop,
fold, and registration marks; and
any color bars
Bleed
• Any element that extends
beyond the trim area of the page
Folds - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
• Folds should be indicated with a
dashed line, You can draw these
with the pen tool in Illustrator or
InDesign.
the difference between work and turn and work and tumble
Work and Turn:
-left to right
-Most common method of
imposition
Work and Tumble:
-top to bottom
-Uses more paper waste,
because it uses two different
gripper edges.
Saddle stitch
staple through spine
Perfect binding
cover wraps around the spine and its glued
Case binding
hard cover, fabric usually on the inside of the first page, sewn spine
Spiral binding
1 loop in a continuous cycle, pages are uneven
wire-o
double loop wire, opens like a clam shell, cheaper than spiral
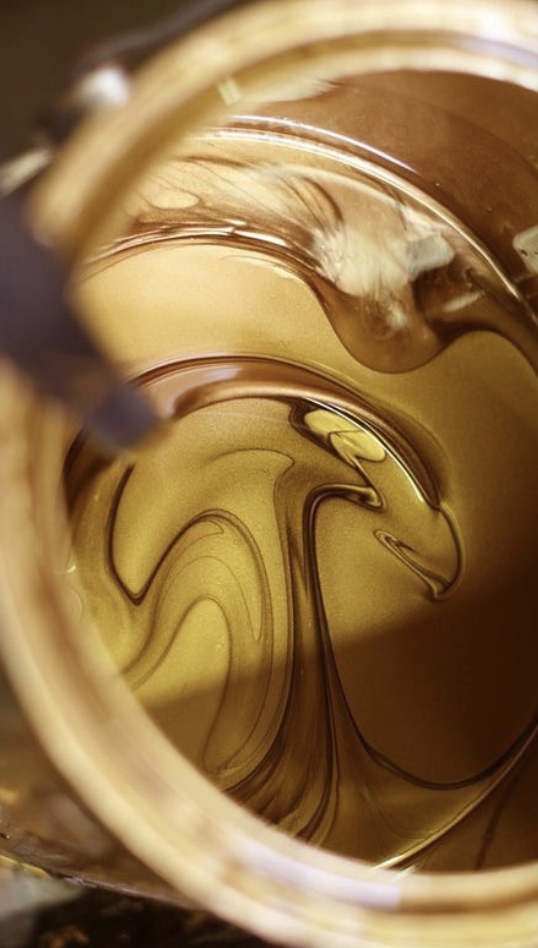

Metallic Ink
is an ink, containing metallic particles. Common metals used to Manufacture metallic ink include copper, aluminum, bronze or zinc

Ink effects vs. Press effects
Ink effect: varnish, Metallic, fluorescent inks, thermography
Press Effect: Emboss/Deboss, foil stamp, die cut, engraving
-anything that uses a machine or press.
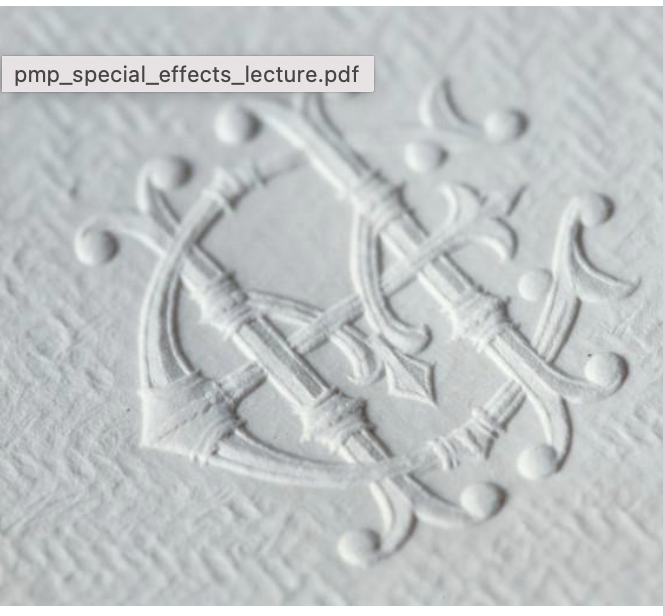
Emboss
is a method of pressing a raised plate onto paper or cardstock to create a three
dimensional design. Embossing results in a raised surface, with the design higher than the surrounding paper area.
Die-cut
refers to finishing process where sharp metal blades are shaped to
exact specifications using a die-line and pressed into the surface of the paper
either cutting out a shape or punching a hole in the surface
Foil stamp
is a process that involves a heated plate striking a metallic or pigmented foil, forcing it into the paper, making it permanently adhere to the surface.
-Shinier than metallic ink

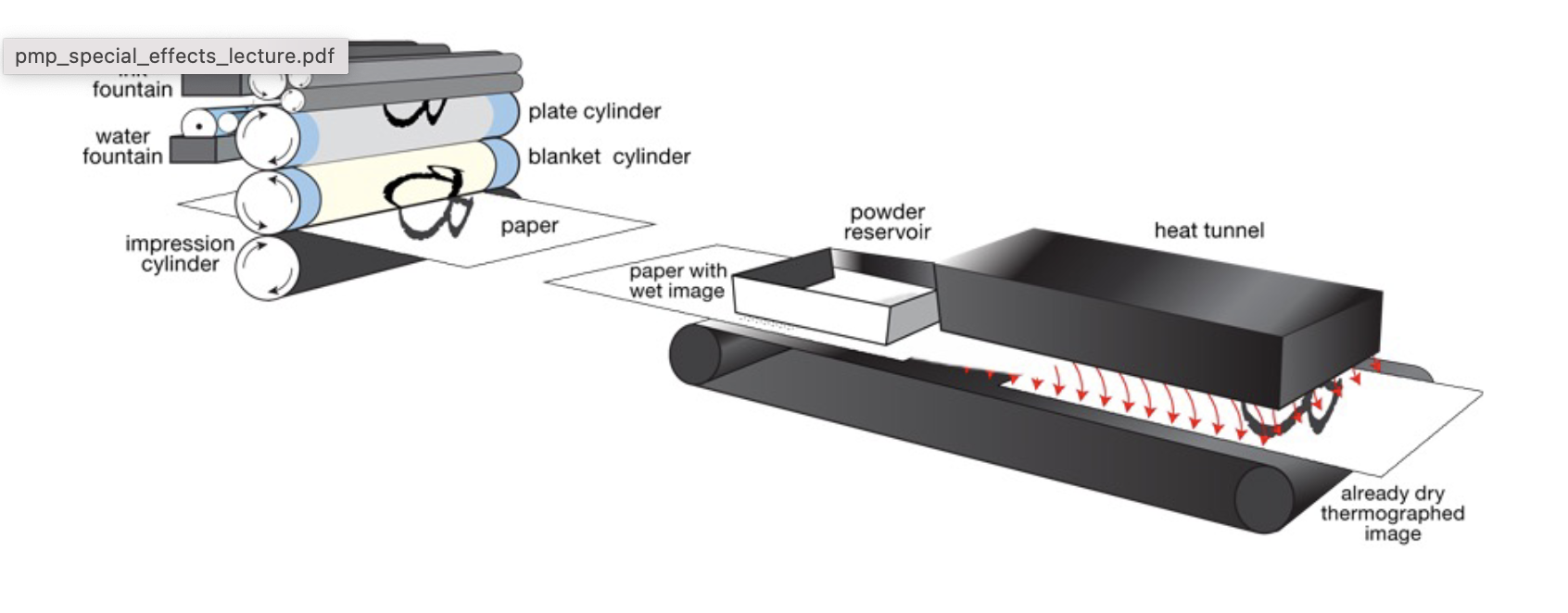
Thermography
a special powdered resin is added on top of the ink of
the printed document. After removing the excess powder the printed piece is
heated and the powder and ink mixture dries to form a raised effect on the paper.
