Wetlands Exam 1
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
What is the definition of a Wetland?
Water must be present at some point (inundation)
Soils inundated long enough to be anaerobic (hydride soil)
Biota adapted to saturated conditions (hydrophytic vegetation)
Hydroperiod?
is the balance between inflows and outflows of water; water budget
Hydrologic pathways
precipitation, surface runoff, groundwater, tides, river flow, evotranspiration
Hydrology Influences
species composition (diversity), primary productivity, organic accumulation, nutrient cycling
Hydrophyte
plant adapted to wet conditions
Halophyte
salt-tolerant plant
Hypoxia
waters (or soils) with dissolved oxygen less than 2mg/L
Anoxia
waters (or soils) with no dissolved oxygen
Soil is a combination of _______________________________
sand, silt, and clay aka soil matrix
Field capacity
water held by soil against gravity
Wilting point
level plants can not uptake water
Upland
ecosystems occur wherewater is far enough below the soil that only certain plants can thrive
Hydric soil
soils that formed under conditions of saturation, flooding, or ponding long enough during the growing season to develop anaerobic conditions in the upper part

A.
Litter

B.
Peat

C.
Muck

D.
Gleyed mineral soil
Organic soils %
More than 18% OC if more than 60% clay; 12-18% if less than 60% clay (%Corg = %OM/2)
Mineral soils %
Less than 20-35% organic content
Organic soil
contains plant remains at various levels of decomposition
Humification
the breakdown of organic materials in soils and composts leading to the formation of humus
humus
dark organic matter in soil that is formed by the decomposition of plant and animal matter
Saprists (muck)
more than 2/3 decomposed; less than 1/3 plant fibers identifiable
*Fibrists (peat)
less than 1/3 decomposed; more than 2/3 plant fibers identifiable
Hemists
(mucky peat OR peaty muck)
Folists:
caused by excess moisture
Redoximorphic features formed by
reduction, translocation, and/or oxidation of iron and manganese oxides

Oxidized rhizosphere

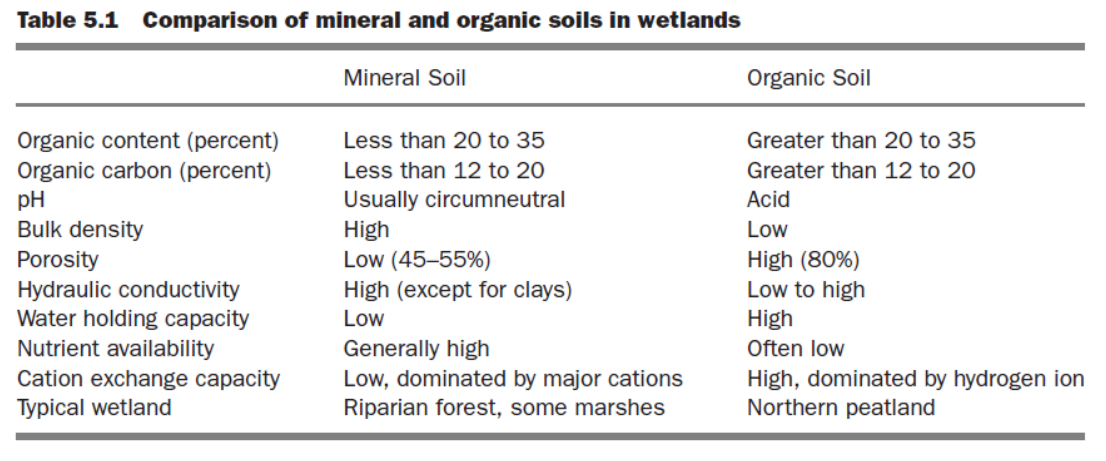
Biogeochemical cycling
transport and transformation of chemicals
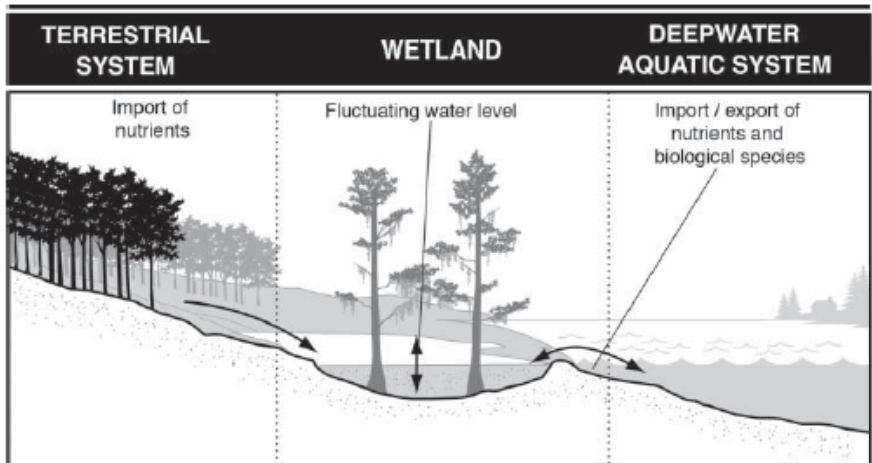
Terrestrial system Hydrology, Biochemical role, and Productivity?
Hydrology- Dry
Biochemical role- Source
Productivity- Low to Medium
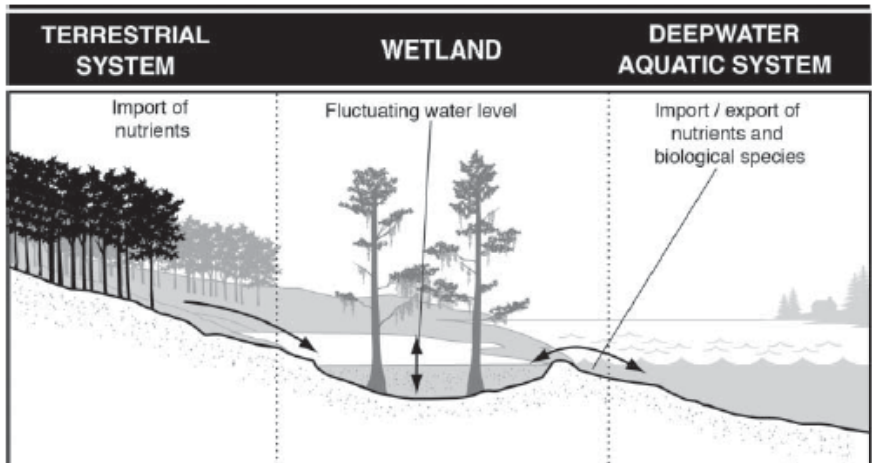
Wetland Hydrology, Biochemical role, and Productivity?
Hydrology- Intermittently to permanently flooded
Biochemical role- Source, sink, or transformer
Productivity- Generally High
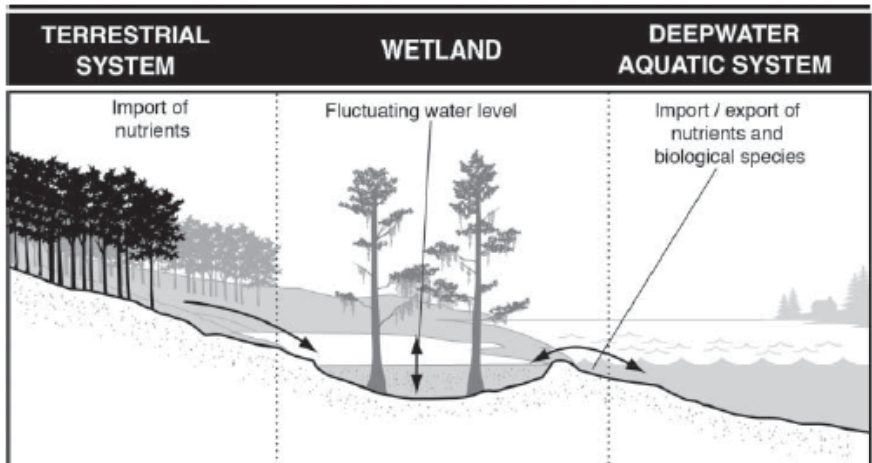
Deepwater aquatic system Hydrology, Biochemical role, and Productivity?
Hydrology- permanently flooded
Biochemical role- sink
Productivity- Generally low
Intrasystem
chemical cycling and transformations within the wetland
Intersystem
transport and exchange between adjacent systems
Oxidation reactions
is the loss of electrons
reduction reactions
is the gain of electrons
Reducing agents
are those that are oxidized
Oxidizing agents
are those that are reduced
Redox potential
Quantitative measure of the tendency of the soil to oxidize or reduce substances
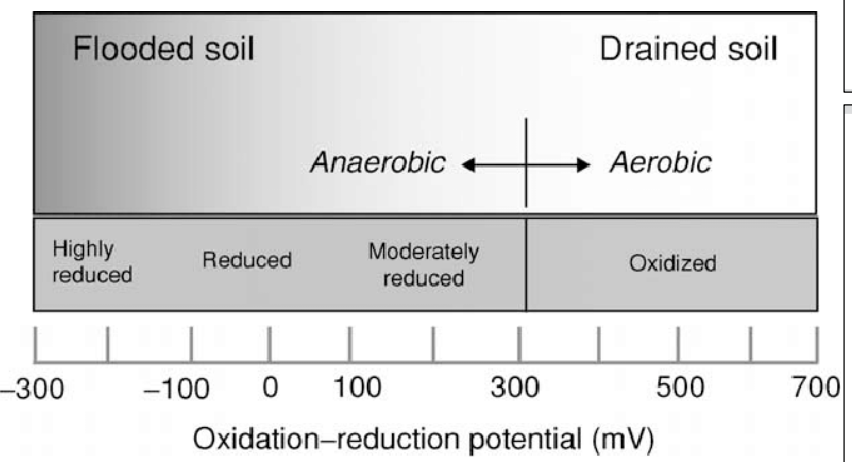
Oxidized states still occur in
Oxidized rhizosphere • Oxidized soil surface
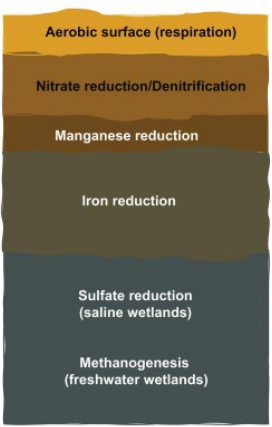
carbon cycle
Building block of life Oxidation states range from -4 to +4
carbon cycle in Wetlands
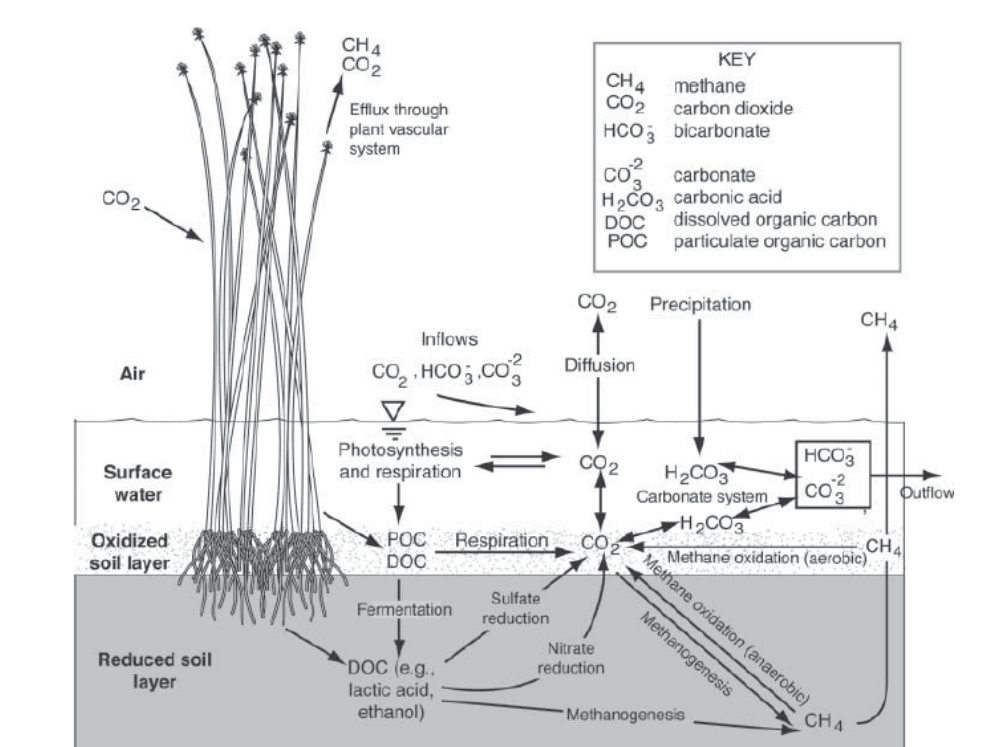
Key Reactions in Wetlands carbon cycle
Oxygenic photosynthesis ◦ Major pathway ◦ CO2 reduced to organic compound
Anoyxgenic photosynthesis ◦ CO2 reduced to organic compound but no O2 ◦ In bacteria
• Oxic respiration ◦ Oxygen is the biological oxidation of organic matter
• Anaerobic respiration ◦ Biological oxidation of organic matter ◦ No oxygen
• Fermentation ◦ Carbohydrates broken down to dissolved organic carbon ◦ Provides substrate for other microbes
• Methanogenesis ◦ Methanogens use CO2 for the production of methane gas (CH4) ◦ Released into atmosphere
Oxygenic photosynthesis
Major pathway ◦ CO2 reduced to organic compound
Anoyxgenic photosynthesis
CO2 reduced to organic compound but no O2 ◦ In bacteria
Oxic respiration
Oxygen is the biological oxidation of organic matter
Anaerobic respiration
Biological oxidation of organic matter ◦ No oxygen
Fermentation
Carbohydrates broken down to dissolved organic carbon ◦ Provides substrate for other microbes
Methanogenesis
Methanogens use CO2 for the production of methane gas (CH4) ◦ Released into atmosphere
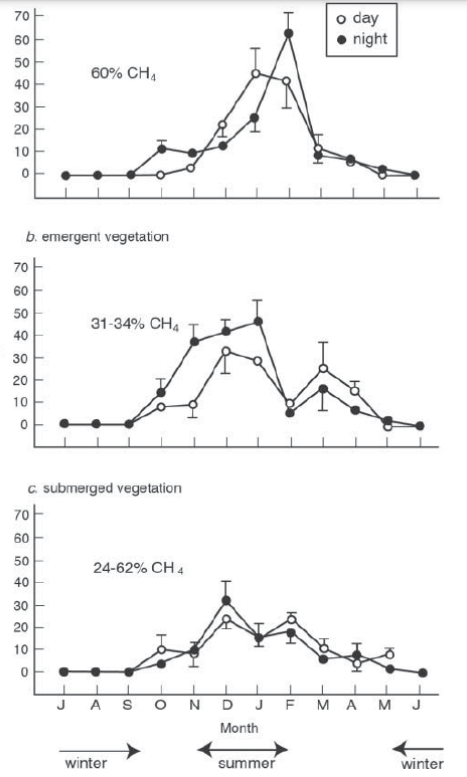
When is the wet season and when is the dry season?
Summer=wet
Winter=Dry
Nitrogen Cycle in Wetlands
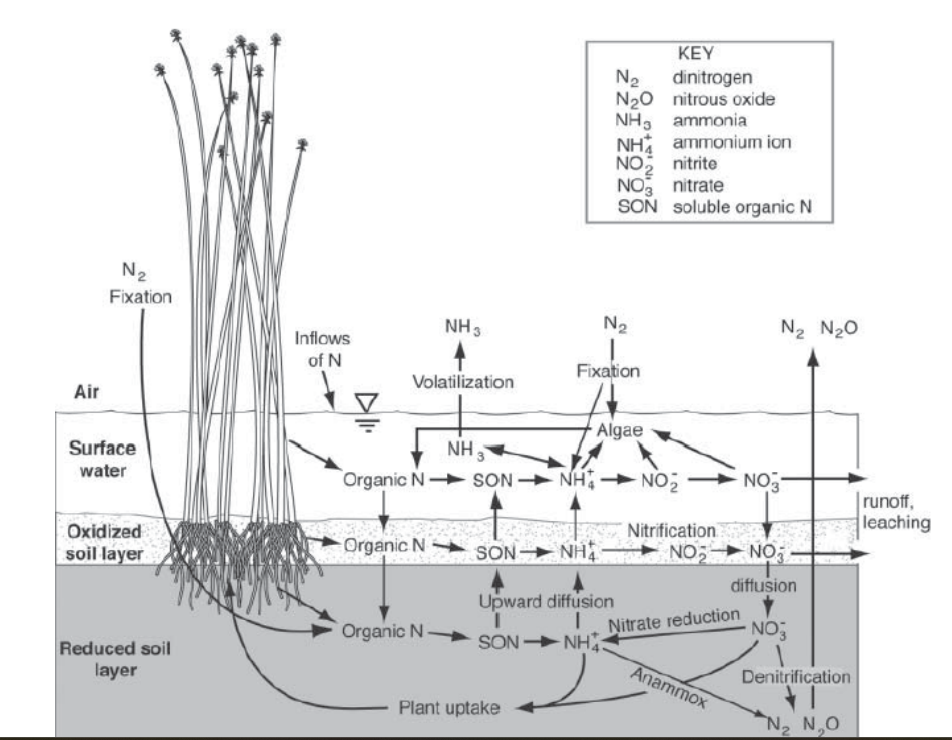
Key reactions in Nitrogen Cycle in wetlands?
Fixation ◦ N fixing bacteria ◦ Nitrogenase inhibited by oxygen
• Mineralization ◦ Conversion of organic nitrogen into ammonium ◦ Ammonification
Nitrification ◦ Conversion of ammonium to nitrite to nitrate ◦ Biologically accessible ◦ Aerobic process •
Denitrification ◦ Conversion of nitrate to nitrite to nitric oxide to nitrous oxide to dinitrogen
Fixation
N fixing bacteria ◦ Nitrogenase inhibited by oxygen
Mineralization
Conversion of organic nitrogen into ammonium ◦ Ammonification
Nitrification
Conversion of ammonium to nitrite to nitrate ◦ Biologically accessible ◦ Aerobic process
Denitrification
Conversion of nitrate to nitrite to nitric oxide to nitrous oxide to dinitrogen
Phosphorus Cycle in wetlands
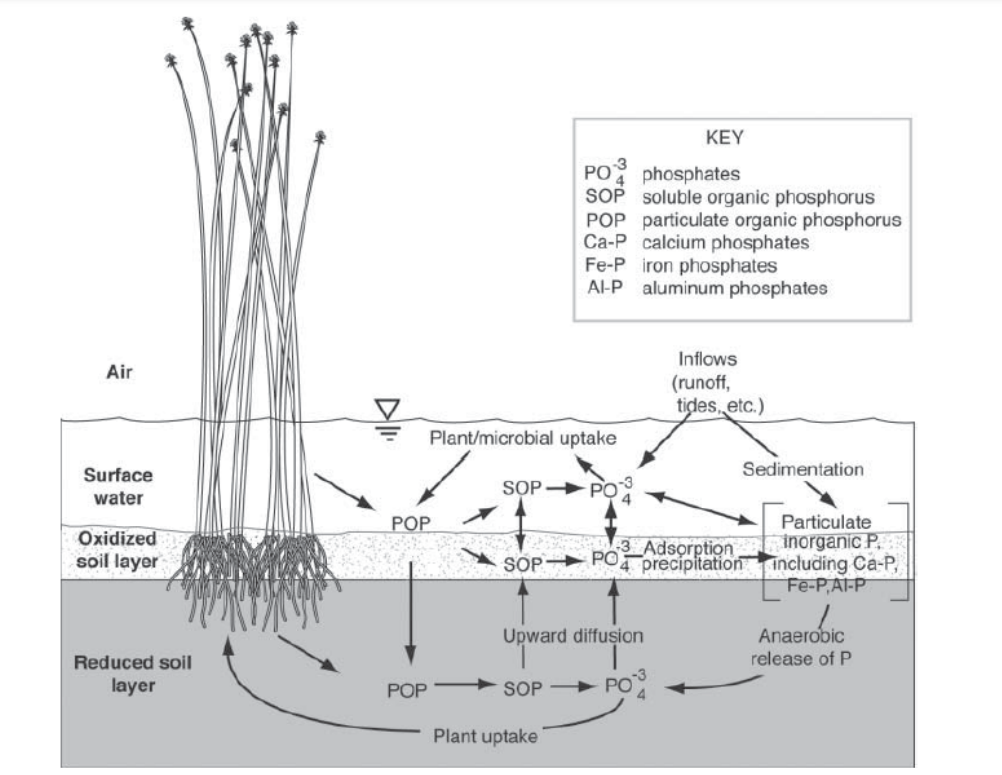
Key Reactions in Phosphorus Cycle in wetlands
Uptake
Sedimentation
Iron Transformation in wetlands
it is in reduced form –> ferrous
Manganese Transformation in wetlands
It is in reduced form –> manganous
Factors influencing nutrient budgets
Seasonality nutrient uptake •
Adjacent ecosystems •
Temporal and spatial variability •
Anthropogenic influence
Bog
A peat-accumulating wetland that has no significant inflows or outflows and supports acidophilic mosses, particularly Sphagnum
Fen
A peat-accumulating wetland that receives some drainage from surrounding mineral soil and usually supports marshlike vegetation
Marsh
A frequently or continually inundated wetland characterized by emergent herbaceous vegetation adapted to saturated soil conditions
Swamp
Wetland dominated by trees or shrubs
Five wetland indicator status categories
1) Upland (UPL)
2) Facultative Upland (FACU)
3) Facultative (FAC)
4) Facultative Wetland (FACW)
5) Obligate (OBL)
1) Upland (UPL)
Almost never occur in wetlands
2) Facultative Upland (FACU)
Usually occur in non-wetlands, but may occur in wetlands
3) Facultative (FAC)
Occur in wetlands and non-wetlands
4) Facultative Wetland (FACW)
Usually occur in wetlands, but may occur in nonwetlands
5) Obligate (OBL)
Almost always occur in wetlands
Submerged
= plants that conduct virtually all of their growth and reproductive activity under water
Free-floating
plants that most often grow with the leaves and other vegetative and reproductive organs floating on the water surface
Floating-leaved
plants that are rooted in sediment but also have leaves that float on the water surface
Emergent
herbaceous and woody plants that grow with their bases submerged and rooted in inundated sediment or seasonally saturated soil and their upper portions, including most of the vegetative and reproductive organs, growing above the water level
Hydrophytes
(plants adapted to wet conditions)
Aerenchyma tissue in roots and stem
helps with oxygen obsorbtion
Adventitious roots
helps with oxygen obsorbtion
Stem hypertrophy
makes bottom of trunks/stems thick (cypress) for added stability
Fluted trunks
thicker at truck for added stability
Shallow root systems/prop roots
providing a stable support system.
Lenticels
oxygen obsorbtion
Pneumatophores and cypress knees
oxygen obsorbtion
Physiological Adaptations
Pressurized gas flow
• Sulfide avoidance
• Anaerobic respiration
• Rhizospheric oxygenation
Decreased water uptake
• Salt excretion
• Altered nutrient absorption
Whole-Plant Strategies
Timing of seed production
Buoyant seeds and buoyant seedlings
Viviparous seedlings
• Persistent seed banks
• Resistant roots, tubers, and seeds
Succession
the process of directional change by which the species composition of a community changes over time
Proceeds through series of stages that remain relatively stable through (ecological) time
Pioneer species
the earliest species to arrive at a site
Climax community
The final seral stage in the process of succession
Wetland succession
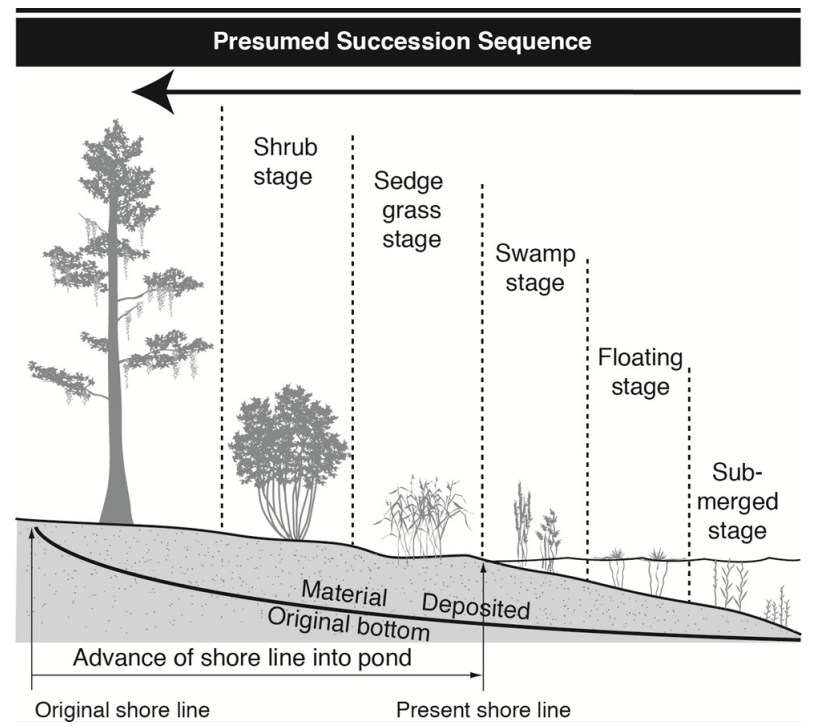
Autogenic succession
Vegetation in communities
• Community changes through time by the biota
• Changes are linear and directed toward a mature, stable climax ecosystem
Allogenic succession
Influenced by environmental factors
• Create wetlands to transition
Structural (or Morphological) Adaptations
Adventitious roots
Stem hypertrophy
Fluted trunks
Rapid vertical growth / growth dormancy
Shallow root systems/prop roots
Lenticels
Pneumatophores and cypress knees
Sulfur reactions in wetlands
Sulfur oxidation
Sulfate reduction
Sulfate absorption and leaching
Iron sulfide production
Hydrogen sulfide emissions
Sulfur cycle in wetlands
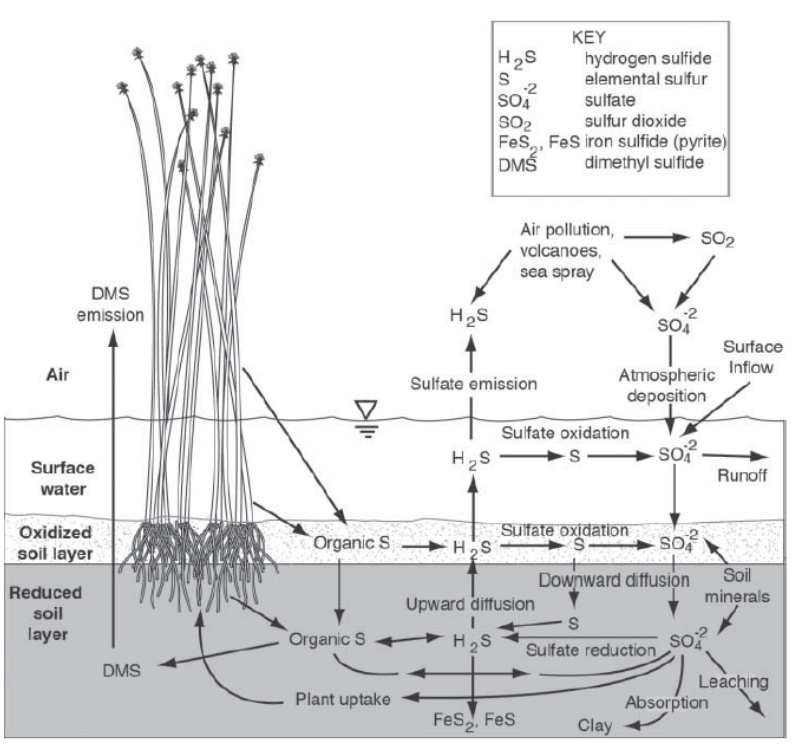
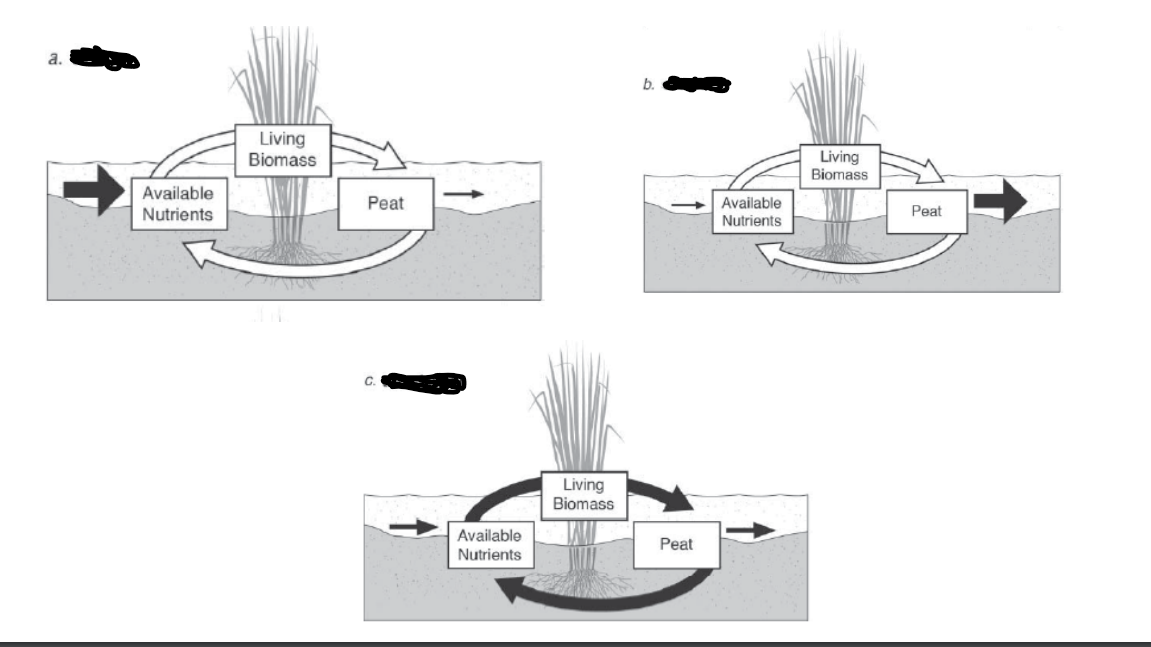
a.
sink
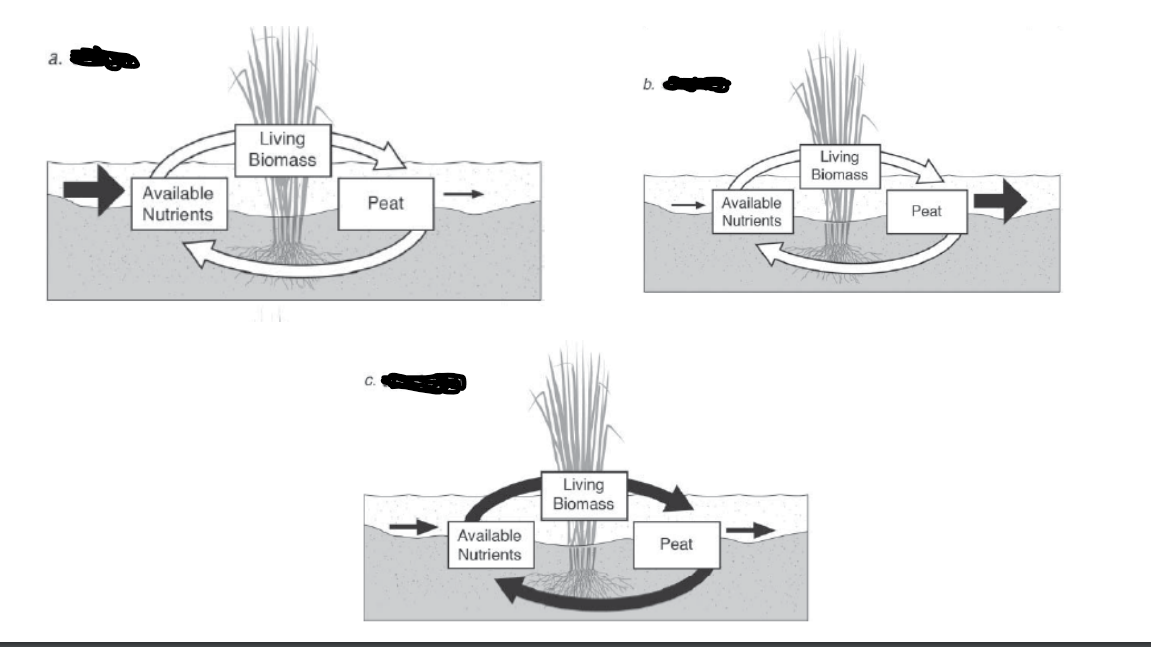
b.
source
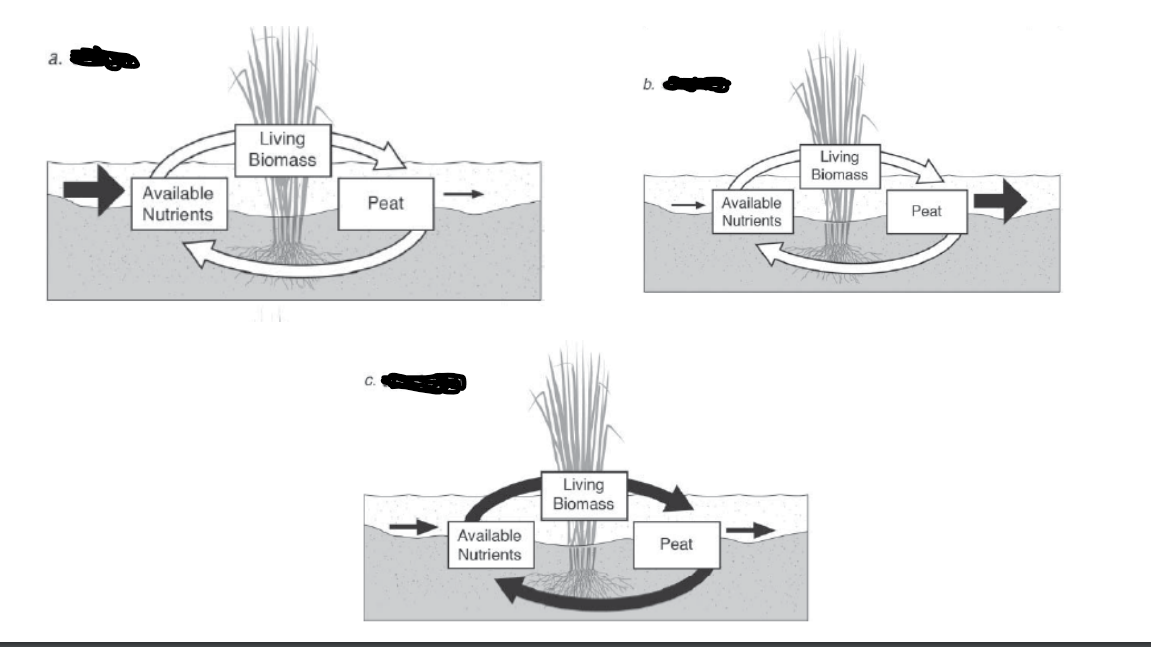
c.
transformer
What is probably the single most important determinant of the establishment and maintenance of specific types of wetlands and wetland processes?
Hydrology
Hydrology
water level, flow, frequency, etc.