PHAR0002 - LA's & action potentials
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What are Local Anesthetics (LA's)?
Block conduction of action potentials by blocking sodium channels
What is the difference between LA's?
Amide or ester linkage
What are the two pathways for blocking Na+ channels?
Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic
What is the administration of LA's?
Topical, Infiltration, Peripheral nerve block, Central nerve block
What are synapses?
Allow for an action potential to move from one neuron to the next
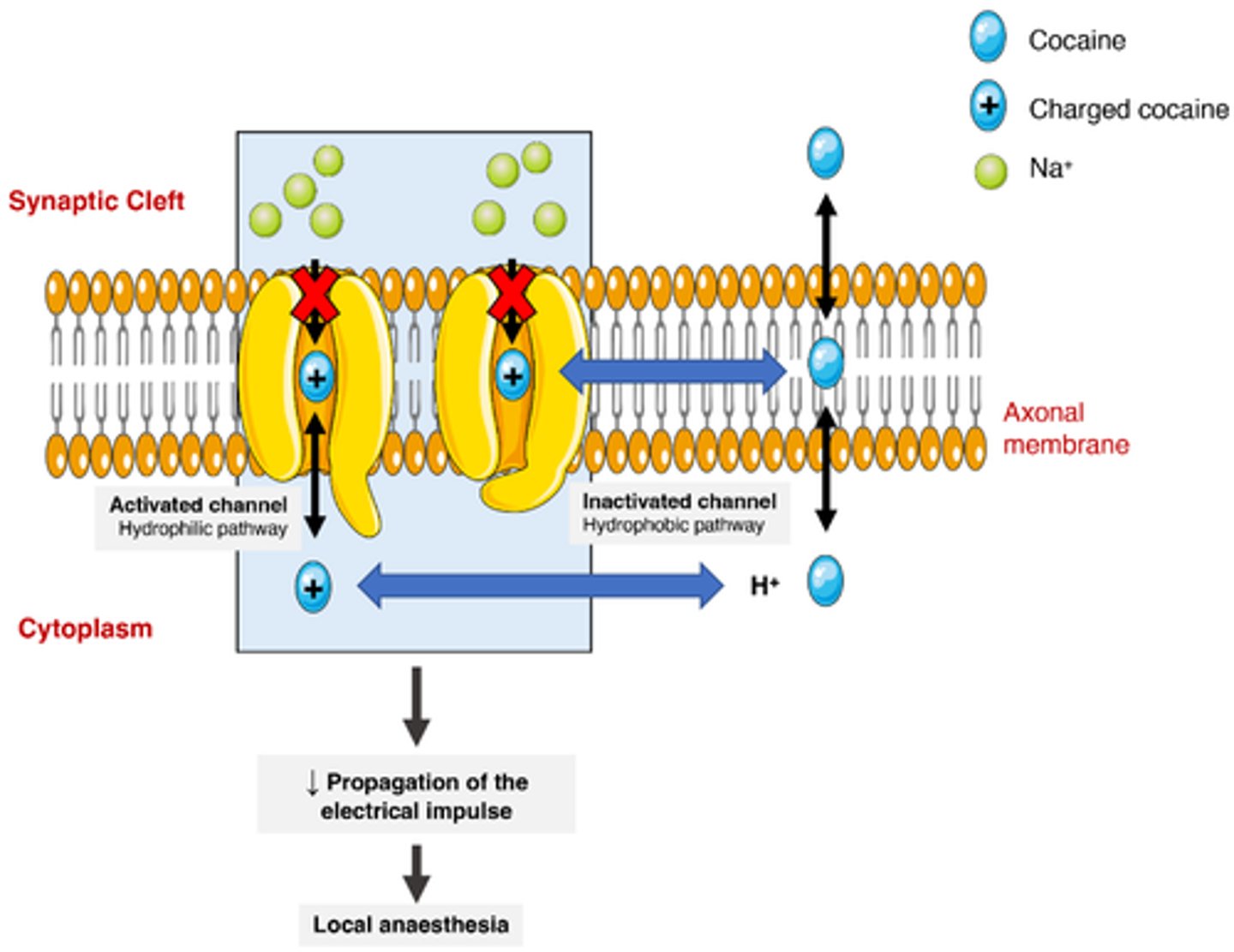
Describe the 2 pathways of LA
Hydrophilic : when Na channel is open LAs flow into channel from the inside of the membrane, blocking the flow of Na
Hydrophobic : when Na channel is closed LAs flow into channel from the middle of the membrane via diffusion, when channel is open LAs are already present to block flow
What are the two types of receptors that Acetylcholine can bind to?
Nicotinic or muscarinic receptors
What happens to Acetylcholine after it binds to the Nicotinic Ach receptor?
It is recycled & broken down to acetate & choline (AchE)
What happens to Acetate after it is broken down?
It is degraded
What is the carrier that Choline re-enters the pre-synaptic neuron?
Choline uptake carrier, secondary active transport with Na
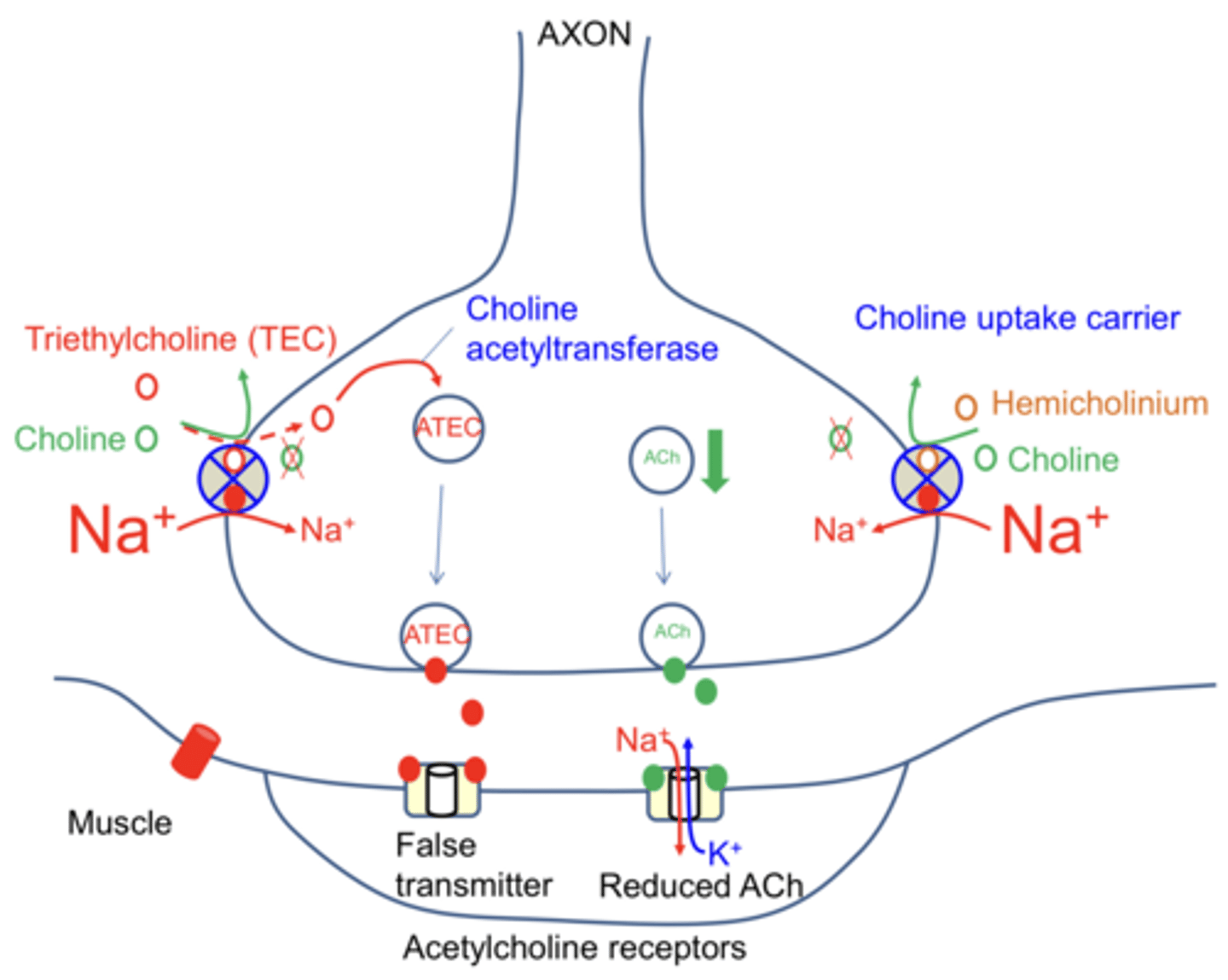
Name 2 drugs that affect NT synthesis in the presynaptic neuron
Hemicholinium and TEC (triethylcholine)
What is the result of Hemicholinium?
Physical block of choline uptake carrier causes reduced amount of Ach in each vesicle and a reduced amount of Ach in the synapse
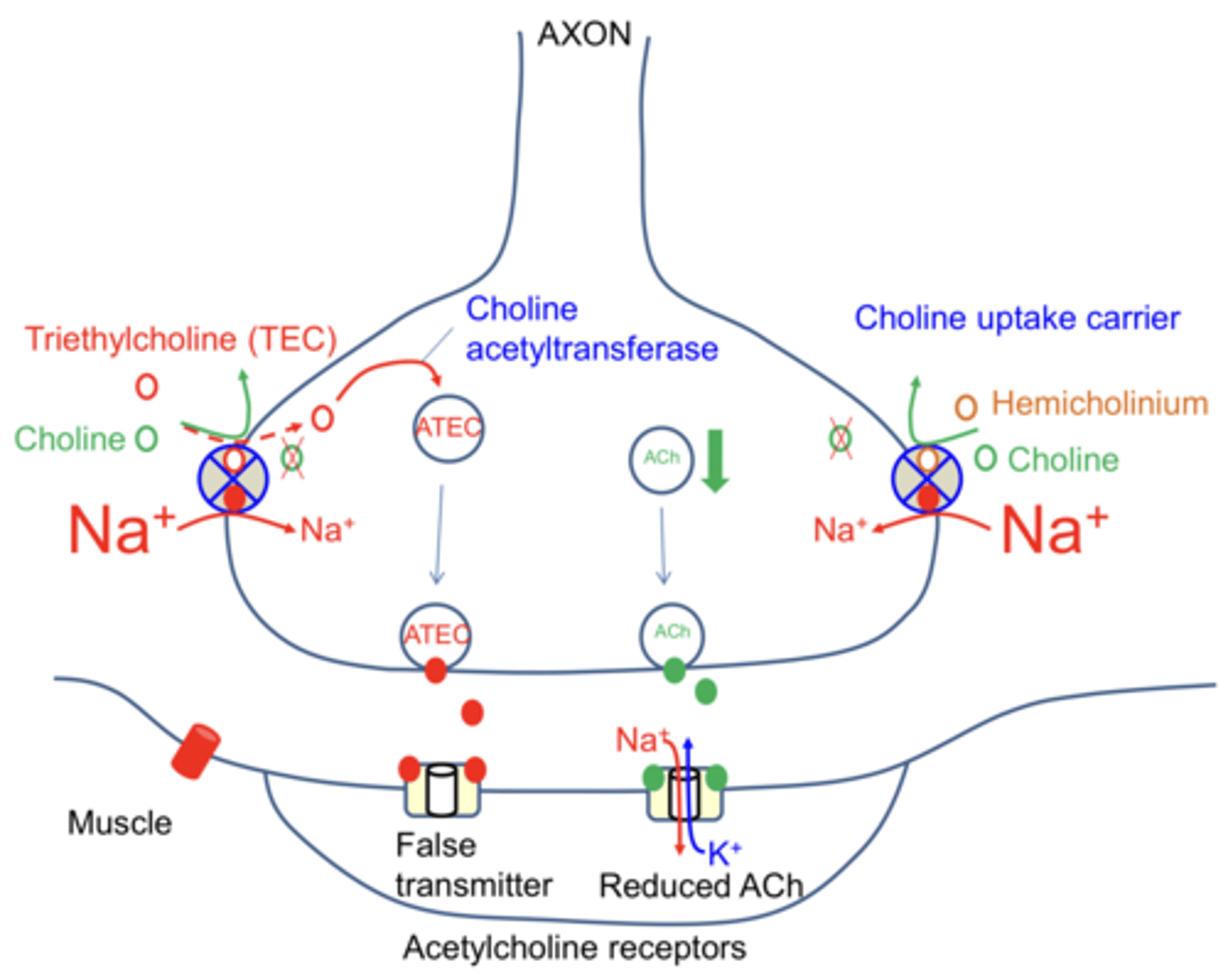
How does Triethylcholine (TEC) work?
Enters the pre-synaptic neuron in place of choline, causes ATEC to be in vesicle instead of Ach gets released into synapse causing false transmission (no depolarisation)
What are some inhibitors of NT release?
LA's, divalent cations (Mg, Cd, Mn), Toxins (botulinum toxin, TTX), antibiotics (streptomycin)
What are some potentiators of release?
K+ channel blockers (tetraethylammonium)
What are non-depolarising, competitive blockers?
Compete with Ach for receptor site, prevent flow of ions through channel, eg: gallamine, atracurium
What are depolarising, non-competitive blockers?
Initially compete for receptor site & don't block ion flow, then cause physical channel block or desensitisation, eg: suxamethonium
What is meant by postsynaptic (receptor site)?
The site on the postsynaptic neuron where neurotransmitters bind to initiate a response.