Mass transports (organs and that)
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Define cells
The basic building blocks of all living organisms
Define tissue
A group of cells with a similar function and structure
Define organ
A group of tissues working together to perform a specific function
Define organ system
A group of organs workng together to perform a function
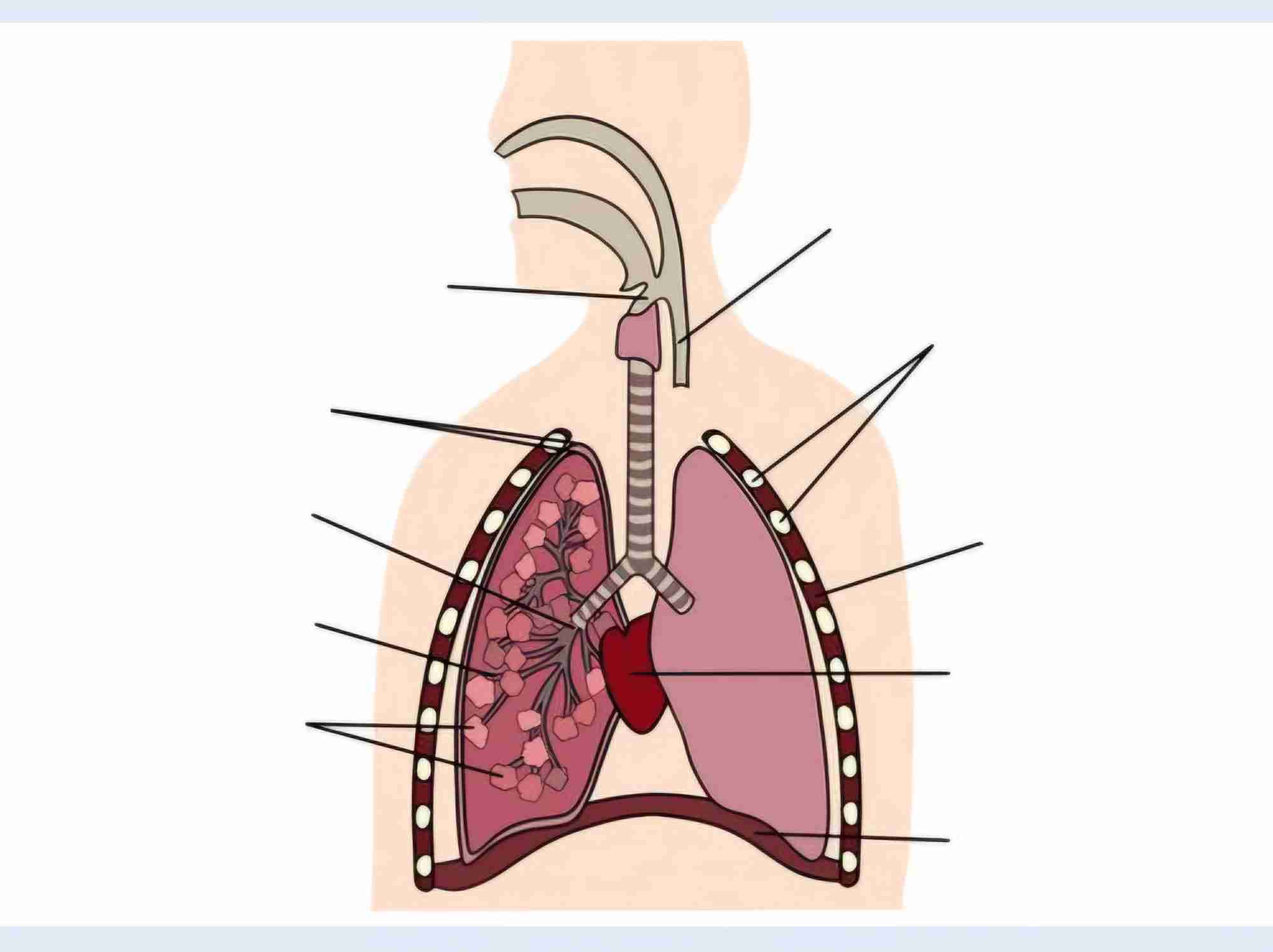
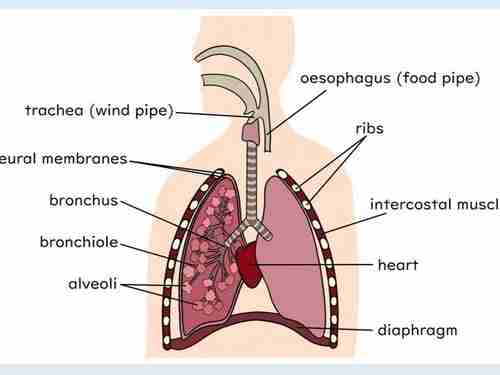
Name each structure
Describe inspiration
Intercostal muscles contract
Ribs move upwards and outwards
Diaphram flattens
Volume of the chest increases
Pressure inside the chest decreases
Air is drawn into the lungs
Describe expiration
Intercostal muscles relax
Ribs move downwards and in
Diaphram moves upwards
Volume of chest decreases
Pressure inside the chest increases
Air is forced outside of the lungs
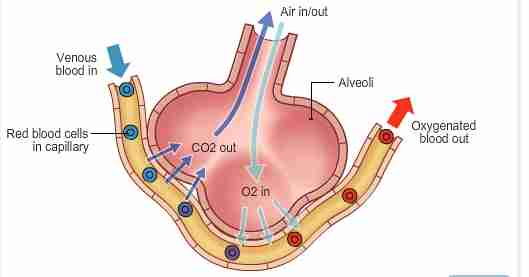
How are alveoli adapted for gas exchange?
Thin walls → shorter diffusion path
The air in and out allow for ventilation → creates a steep concentration gradient for CO2 and O2
Good blood supply → maintains concentration gradient for CO2 and O2
Large surface area → spherical and there are lots of them
Moist lining → allows gases to dissolve ad diffuse into the blood supply
What is the function of an artery?
Arteries carry oxygenated blood AWAY from the heart
How do the structures of arteries relate to their function?
Thick muscular wall
↳ Withstand and maintain high pressure
Narrow lumen
↳ Maintains high pressure needed to transport blood efficiently
Elastic fibres
↳ Allow the artery to stretch and recoil as the heart beats, helping it maintain a continuous blood flow
What do veins do?
Carry deoxygenated blood from the body to the heart
How does the structure of veins relate to its' function?
Thiner walls
↳ Blood pressure is lower in veins
Large lumen
↳ Wide lumen reduces friction since the pressure is much lower
Valves
↳ Prevent the backflow of blood
What do the capillaries do?
Exchanges oxygen and nutrients and carry away waste products (like CO2) between blood and tissues
How does the structure of capillaries relate to their function?
One cell thick walls
↳ Short diffusion distance
Small diameter
↳ Allows the capillaries to fit between cells and tissues
Permeable walls
↳ Allows substances to diffuse easily
What are the 4 main components of blood?
Plasma
White blood cells
Red blood cells
Platelets
What is the function of plasma?
Suspends blood cells and platelets → straw coloured
Transports substances
↳ oxygen, removes waste products such as carbon dioxide
What is the function of red blood cells?
To carry oxygen from the lungs to every cell in the rest of the body
What is the function of white blood cells?
To fight infection by pathogens and stop disease
What do platelets do?
Clots the blood
How do red blood cells carry oxygen to cells?
The oxygen moves in by diffusion into the red blood cells in the lungs.
They also have haemoglobin inside tem which binds with the oxygen so that it can be carried for respiration.
How are red blood cells adapted for their function?
Biconcave shape → larger surface area for rapid diffusion of oxygen
Contains haemoglobin → binds to oxygen to be used in respiration
No nucleus → contains more haemoglobin to carry more oxygen
Small → pass through capilaries
What are the 2 types of white blood cells?
Phagocytes
Lymphocytes
What is the function of phagocytes?
They engulf pathogens through phagocytosis to destroy them
What is the function of lymphocytes?
They produce antibodies that stick pathogens together
How is heart rate controlled?
By a group of cells in the right atrium which act as pacemakers